Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
|
|
|
- Lesley Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8 Purpose and parts of the muscular system, tendons, ligaments, etc. Circulatory System...13 Purpose and parts of the circulatory system, heart, veins, capillaries, arteries, blood, etc. Digestive System...19 Purpose and parts of the digestive system, mechanical and chemical digestion, teeth, etc. Respiratory System...24 Purpose and parts of the respiratory system, respiration, smoking, etc. Excretory System...28 Purpose and parts of the excretory system, urinary tract, ways of removing wastes, etc. Nervous System...31 Purpose and parts of the nervous system, neurons, brain, nerves, the five senses, etc. Endocrine System...35 Purpose and parts of the endocrine system, metabolism, glands, hormones, etc. Diagram of...36 Diagram of Heart...37 Diagram of Digestive System...37 Diagram of Respiratory System...38 Diagram of Urinary System...39 Answer Keys...40 ii
3 Introduction to the Teacher Introduction to the Teacher It is important for students to periodically review the information they have previously learned. Jumpstarters help students do just that while also preparing them for the day s lesson by focusing on the topic of study. The short warm-up activities in this book provide activities that help students review what they have learned. Each page contains five warm-ups (one for each day of the school week). Suggestions for using warm-up activities: Copy and cut apart one page each week. Give students one warm-up activity each day at the beginning of class. Give each student a copy of the entire page to keep in their binders to complete as assigned. Make transparencies of individual warms-ups and complete activities as a group. Put copies of warm-ups in a learning center for students to complete on their own when they have a few extra minutes. Use warm-ups as homework assignments. Use warm-ups as questions in a review game. Keep some warm-ups on hand to use when the class has a few extra minutes before dismissal. 1
4 Body Organization Body Organization Body Organization 1 Match each of these cell parts with their jobs. 1. nucleus a. jelly-like material around the outside of the nucleus 2. nuclear membrane b. controls movement of material in and out of the cell 3. cytoplasm c. controls the activities of the cell 4. cell membrane d. surrounds the nucleus to keep the parts inside Body Organization 2 Label this diagram of a cell. Use the terms listed below. nucleus vacuole cytoplasm nuclear membrane cell membrane Body Organization 3 Tell if each is a tissue, organ, or system. Write T, O, or S. 1. heart 2. respiratory 3. bone 4. skeletal 5. muscle 6. kidney 7. brain 8. nerve 9. digestive 10. pancreas Body Organization 4 Which body system 1. Carries blood throughout the body? 2. Disposes of waste material? 3. Gives structure and form to the body? 4. Provides the body with oxygen? Body Organization 5 Which body system 1. Moves the body parts? 2. Sends signals to control all the other systems? 3. Uses chemicals (hormones) to help control other systems? 4. Breaks down foods to nourish the body? 2
5 1 List three organs that are protected by the skeletal system Fill in the blanks. 1. Red bone is where red and white blood cells are made. 2. cells are stored in yellow bone marrow. 3. The skeletal system works with the system to move the parts of the body. 3 Unscramble these four parts of the skeletal system. 1. snebo 2. glaectira 3. mgstliaen 4. itsnoj 5 Write Yes or No to indicate if each of these is a job of the skeletal system. 1. shapes and supports the body 2. transmits messages to all parts of the body 3. protects organs 4. works with the muscular system to move parts of the body 5. helps rid the body of wastes 6. warehouses fat cells, calcium, and other minerals 4 1. How is the skeletal system like a factory? 2. How is the skeletal system like a storehouse? 3
6 6 Write T for true or F for false. 1. Bones are made of minerals, protein, water, and living matter. 2. The protein found in bones gives them their flexibility. 3. The periosteum is in the center of the bone. 4. Haversian canals are tiny tunnels in the bone for nerves and blood vessels. 5. Spongy bone is called compact bone. 7 Draw lines to match the basic shapes of bones with the purpose of each. 1. flat bones (ribs) a. support weight 2. long bones (leg) b. to allow small movements 3. short bones (wrist) c. for protection 8 Write the common name for each of these bones. 1. mandible 2. scapula 3. cranium 4. sternum 5. tibia 9 Write the common name for each of these bones. 1. phalanges 2. pelvis 3. patella 4. humerus 5. vertebrae 10 List three places cartilage is found in the body
7 11 1. Why is it important for ligaments to be stretchy? Which kind of joint helps protect organs inside the body? 2. Why is it important to have cartilage around the ends of bones? 2. Which kinds of joints help the body move? 13 Match each of these joints with the type that it is a. ball-and-socket joint b. hinge joint c. pivot joint d. fixed joint e. gliding joint 14 What bone am I? (Use scientific names.) 1. bony cage that protects the lungs 2. inner arm below the elbow 3. large, fixed bone that protects the brain 4. bones of the wrist 15 What bone am I? (Use scientific names.) 1. large, inner leg bone below the knee 2. bones of the foot between the heel and the toe 3. upper arm bone between the shoulder and the elbow 4. bone to which the ribs are connected 5
8 16 Identify the type of fracture described below. greenstick fracture Why is it so important to have a proper diet during your growing years? 2. What is ossification? simple fracture 18 Number these four steps of ossification in the order they happen. a. calcium compounds stay in the cells b. bone cells absorb calcium compound fracture c. calcium is changed to calcium compounds d. calcium compounds harden and become bone 1. Which type of fracture is when the bone is completely broken and the skin is broken too? 19 Calculate the approximate weight of your bones using this formula: Your weight times 35 divided by Which type of fracture is a break in the bone that does not go all the way through the bone? 20 Write T for true or F for false. 3. Which type of fracture is where the bone has broken all the way through, but the skin is not broken? 1. Bones have blood vessels and nerves in them. 2. Babies skeletal systems are mostly cartilage. 3. Calcium is an important mineral for bone strength. 4. The center of the bone is the hardest part. 6
9 21 Fill in the missing vowels of these regions of the spinal column 1. c r v c l 2. c c c y g l 3. t h r c c 4. l m b r 5. s c r l 22 Circle the bone that is connected to the one listed. 1. femur: scapula patella 2. ulna: radius clavicle 3. tibia: fibula coccyx 4. rib: phalanges sternum 23 Write T for true or F for false. 1. The humerus is below the ulna. 2. The tibia is connected to the patella. 3. The coccyx is at the very bottom of the spinal column. 4. The clavicle is part of the leg. 5. The mandible is below the sternum. 24 Label these bones in the skeletal system on the diagram on page Number these bones in order from the top (#1) of the body to the bottom (#8). cranium ribs femur vertebrae pelvis mandible humerus patella phalanges metatarsals femur ribs carpals metatarsals cranium radius clavicle tibia 7
10 1 1. and 3 Write T for true or F for false. are the two kinds of protein in a muscle cell. 2. They past each other, and that makes a muscle cell work. 1. Groups of muscle fibers are wrapped together inside a special covering. 2. Muscles are not living tissue. 3. Muscles have nerve tissue in them. 4. Muscles need oxygen and nutrients. 2 Males are about 40% muscle, and females are about 35% muscle. 1. If a boy weighs 110 pounds, about how much of his weight is from muscles? 2. If a girl weighs 80 pounds, about how much of her weight is from muscles? 4 Unscramble the three main parts of the muscular system. 1. ucsmels 2. stneond 3. lmsitgnae 80 5 Circle the correct answer. 1. There are more than muscles in your body Groups of muscle tissue are organs. True False 3. is the basic unit of a muscle. protein muscle cell 8
11 6 Explain the difference between a voluntary muscle and an involuntary muscle. Give an example of each kind. 7 Draw lines to match these three types of muscles to their scientific names. 1. skeletal muscles a. visceral muscles 2. smooth muscles b. cardiac muscles 3. heart muscles c. striated muscles 8 Write V for voluntary muscles or I for involuntary muscles. 1. heart muscles 2. jaw muscles 3. leg muscles 4. arm muscles 5. finger muscles 6. small intestine muscles 7. blood vessel muscles 8. foot muscles Can you name one muscle that can be both? 9 Write S for skeletal, or striated, muscle; V for visceral, or smooth, muscle; or C for cardiac muscle. 1. heart muscle 2. arm muscle 3. muscles that line the digestive tract 4. leg muscle 5. muscles that line the blood vessels 10 Write T for true or F for false. 1. When a muscle contracts, it gets longer. 2. After a muscle contracts, it relaxes. 3. Most muscles work in pairs. 4. Smooth muscles can stay contracted for long periods of time. 9
12 11 Fill in the blanks with these words: contract, overstretched, oxygen, exercise, strain, cramp 1. If you don t warm up before you exercise, your muscle might involuntarily, causing a. 2. When you, or work your muscles, they need extra food and. 3. If a muscle gets, it causes an injury called a. 12 Number these steps in order to explain how your arm moves. a. The biceps contracts, which raises the arm, and the triceps relaxes. b. The brain sends a message to move your arm. c. The message travels through nerves connected to single muscle fibers. d. The biceps relaxes, straightening the arm, and the triceps contracts. 13 Write Yes or No to indicate if each of these is a type of movement controlled by smooth muscles. 1. moving blood through blood vessels 2. opening and closing eyelids 3. pushing food through the digestive tract 4. widening the pupils in the eyes 14 What muscle am I? Clue one: I am the most important muscle involved in breathing. Clue two: I am a sheet of thin, flat muscle. Clue three: If I get irritated, I cause the hiccups What does weight-lifting do for your muscles? 2. How does aerobic exercise help the cardiac muscle? 10
13 16 Write T for true or F for false. 1. Your pulse is the feeling of your blood moving through your blood vessels. 2. The average heart rate is around 150 beats per minute. 3. The beating of your heart is a voluntary muscle movement. 4. You can usually feel your pulse in your neck and wrist. 17 Fill in each blank with either the word bone or the word muscle. 1. Ligaments connect to. 2. Tendons attach to. 18 Fill in each blank with the correct muscle type. 1. A(n) muscle causes a joint to bend when it contracts. 2. A(n) muscle causes a joint to straighten when it contracts. 19 Place the correct letter on each blank. a. tendonitis b. insertion c. sprain d. origin 1. is the end of the muscle that does not move. 2. is the end of the muscle that can move. 3. is a swelling of the tendons. 4. A is a ligament, muscle, or tendon that has been stretched too far. 20 Write each of these muscle names next to the area of the body where it is found. pectoral masseter soleus deltoid quadriceps intercostals triceps gluteus maximus tibialis Arm & Hand: Leg & Foot: Head & Trunk: 11
14 Answer Keys Answer Keys Body Organization 1 (page 2) 1. c 2. d 3. a 4. b Body Organization 2 (page 2) nucleus nuclear membrane Body Organization 3 (page 2) 1. O 2. S 3. T 4. S 5. T 6. O 7. O 8. T 9. S 10. O Body Organization 4 (page 2) 1. circulatory 2. excretory 3. skeletal 4. respiratory Body Organization 5 (page 2) 1. muscular 2. nervous 3. endocrine 4. digestive 1 (page 3) brain, heart, lungs (Other answers are possible.) 2 (page 3) 1. marrow 2. Fat 3. muscular 3 (page 3) 1. bones 2. cartilage 3. ligaments 4. joints 4 (page 3) 1. Red and white blood cells are manufactured in the red bone marrow. 2. Fat cells, calcium, and other minerals are stored in the yellow bone marrow. 5 (page 3) 1. Yes 2. No 3. Yes 4. Yes 5. No 6. Yes 6 (page 4) 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F 7 (page 4) 1. c 2. a 3. b vacuole cytoplasm cell membrane 8 (page 4) 1. jawbone 2. shoulder blade 3. skull 4. breastbone 5. shinbone/lower leg bone 9 (page 4) 1. finger/toe bones 2. hip bones 3. kneecap 4. upper arm bone 5. backbone 10 (page 4) 1. nose 2. ears 3. ends of bones 11 (page 5) 1. Ligaments need to be stretchy so that they will not tear as they work with muscles to move the body. 2. Cartilage absorbs the shocks when two bones meet. 12 (page 5) 1. Fixed joints (such as the skull) 2. Ball-and-socket joints, hinged joints, pivot joints, gliding joints 13 (page 5) 1. d 2. b 3. e 4. a 5. c 14 (page 5) 1. rib cage 2. ulna 3. cranium 4. carpals 15 (page 5) 1. femur 2. metatarsals 3. humerus 4. sternum 16 (page 6) 1. compound fracture 2. greenstick fracture 3. simple fracture 17 (page 6) 1. You need a proper diet to get the nutrients your body needs to grow correctly. Your bones especially need calcium and other minerals to grow. 2. Ossification is the process where the cartilage changes into bone. 18 (page 6) a. 3 b. 1 c. 2 d (page 6) Answers will vary. 20 (page 6) 1. T 2. T 3. T 4. F 40
15 Answer Keys 21 (page 7) 1. cervical 2. coccygeal 3. thoracic 4. lumbar 5. sacral 22 (page 7) 1. patella 2. radius 3. fibula 4. sternum 23 (page 7) 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F 5. F 24 (page 7) phalanges mandible humerus vertebrae metatarsals 25 (page 7) 1 cranium 2 clavicle 3 ribs 4 radius 5 carpals 6 femur 7 tibia 8 metatarsals 1 (page 8) 1. actin, myosin 2. slide 2 (page 8) lbs lbs. 3 (page 8) 1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T 4 (page 8) 1. muscles 2. tendons 3. ligaments 5 (page 8) True 3. muscle cell 6 (page 9) Voluntary muscles you consciously decide to move. Example: biceps/arm muscle cranium ribs femur patella pelvis 41 Involuntary muscles are those that move automatically. Example: heart muscle 7 (page 9) 1. c 2. a 3. b 8 (page 9) 1. I 2. V 3. V 4. V 5. V 6. I 7. I 8. V Diaphragm; You can breathe voluntarily, but you also breathe involuntarily. 9 (page 9) 1. C 2. S 3. V 4. S 5. V 10 (page 9) 1. F 2. T 3. T 4. T 11 (page 10) 1. contract, cramp 2. exercise, oxygen 3. overstretched, sprain 12 (page 10) a. 3 b. 1 c. 2 d (page 10) 1. Yes 2. No 3. Yes 4. Yes 14 (page 10) The diaphragm 15 (page 10) 1. It shapes and defines them. 2. It makes the heart bigger, stronger, and more efficient by making it pump harder and faster. 16 (page 11) 1. T 2. F 3. F 4. T 17 (page 11) 1. bone, bone 2. muscle, bone 18 (page 11) 1. flexor 2. extensor 19 (page 11) 1. d 2. b 3. a 4. c 20 (page 11) Arm & Hand: pectoral, triceps, deltoid Leg & Foot: quadriceps, soleus, tibialis Head & Trunk: masseter, intercostals, gluteus maximus
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
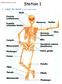 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Human Body. Bones, Joints and Muscles
 Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems
 Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project
 Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Team Members: System:
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is to prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is to prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Section Chapter 36. The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems. Go to Section:
 Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
Section 35-1 Chapter 36 The Skeletal, Muscular and Integumentary Systems Section Outline Section 36-1 36 1 The Skeletal System A. The Skeleton B. Structure of Bones C. Development of Bones D. Types of
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
The Musculoskeletal system
 Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017
 IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male
 http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Musculoskeletal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma
 Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
What is the skeletal system?
 .^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
.^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY
 THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
October. Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives
 October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
Bones are made up of bone cells and tissues Hard, dense and smooth outer materials, which are made of calcium, give bones there shape and strength.
 1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise. Unit Accreditation Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
The Muscular System. The Muscular System: Moving your Body
 The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
Body Organization and Structure
 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Contents. Copyrighted material. May not be reproduced without permission from the publisher.
 Contents I. BODY SUPPLY SYSTEMS................................. 2 Digestive System...................................... 3 Excretory System..................................... 6 Respiratory System....................................
Contents I. BODY SUPPLY SYSTEMS................................. 2 Digestive System...................................... 3 Excretory System..................................... 6 Respiratory System....................................
S.A.F.E. Elements of Technique. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and STRENGTH ALIGNMENT FLEXIBILITY ENDURANCE
 Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 33
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
What type of tissue is this
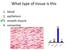 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY
 UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018
 Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
