Chapter 3. Your Wonderful Body
|
|
|
- Blaise Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Your Wonderful Body
2 Warm Up- Day 1 Ê Emma is conducting an experiment on whether or not whitening toothpaste works better than non-whitening toothpaste. She obtains two fake teeth and brushes one with whitening toothpaste and one with the plain toothpaste. After 2 weeks, she compares her results. Ê Identify the independent variable. Ê Identify the dependent variable. Ê What are some controlled variables Emma should consider. Ê Is there a control group? If so, what is it?
3 Lesson 1.1- A Systematic Study Ê The body is broken down into three main groups Ê Head/Neck Ê Trunk- contains most of the vital organs. Ê Appendages- arms and legs.
4 Levels of Organization Ê Cells- the smallest units of living things. Ê Tissues- groups of similar types of cells, working together. Ê Organ- a group of tissues arranged to perform a specific function. Ê Body System- a group of organs that work together to perform a job for the body.
5 Body Systems Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê Ê System- transports nutrients, wastes, respiratory gases, and other minerals System- provides oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide from it. System- breaks down and absorbs nutrients. System- concentrates and removes liquid wastes. System- transports lymph, protects body against infection. System- covers and protects the body System- supports the body and provides attachment for muscles. Protects vital organs. System- moves body parts System- controls body functions and activities. System- controls certain internal body functions. System- forms reproductive cells.
6 Warm Up- Day 2 Ê Which part of the body contains the heart and other vital organs? Ê Name the levels of organization in the body. Ê What is an appendage?
7 Lesson 3.2A- Cardiovascular System Ê Cardiovascular System- includes your heart, blood, and blood vessels. Ê This system may also be called the circulatory system.
8 Blood Ê Blood is made up of four parts: Ê Plasma- straw-colored liquid that blood cells are suspended in. Ê Red Blood Cells- transport oxygen. Ê Hemoglobin- a special protein found in red blood cells that helps transport oxygen. Ê White Blood Cells- protect the body from disease. Ê Platelets- help with clotting.
9 What does the blood carry? Ê Oxygen from the respiratory system. Ê Nutrients from the digestive system. Ê Hormones from the endocrine system. Ê Antibodies and white blood cells from the immune system. Ê Water and wastes from the urinary system.
10 The Heart Ê Your blood moves through a series of blood vessels in your body by the pumping action of the heart. Ê Arteries- large blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. Ê Arteries branch into smaller vessels called arterioles. Ê Arterioles branch into even smaller vessels called capillaries, which come into close contact with your body s cells. Ê Oxygen, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between blood in the capillaries and your body s cells through a process called diffusion.
11 The Heart Ê Capillaries merge together to form venules, which carry blood from the capillary network to the veins. Ê Veins- large blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart. Ê The heart is divided into a right and left side, each containing two chambers. Ê Atrium- the upper chamber. Ê Ventricle- the lower chamber. Ê The two halves of the heart are separated by a wall called the septum.
12 Blood Flow Ê Blood enters your heart through a large vein called the vena cava and flows into the right atrium. The blood is pushed through to the right ventricle, then to the pulmonary arteries, transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs. In the lungs, the hemoglobin molecules release CO2 and pick up O2 and return oxygenated blood to the heart via the pulmonary veins. The oxygenated blood travels to the left atrium, and on to the left ventricle and is pumped into the aorta- the body s largest artery- which pumps it out to the rest of the body.
13 Types of Circulation Ê Pulmonary Circulation- transports blood back and forth between the lungs and the heart, through the pulmonary arteries and the pulmonary veins. Ê Systemic Circulation- the flow of blood between the heart and all of the body except the lungs. Ê Coronary Circulation- provides large amounts of oxygen and nutrients to the heart tissues through coronary arteries, which branch off the aorta and return through the atrium via the cardiac vein.
14 Warm Up- Day 3 Ê What are the 4 components of blood? Ê How does blood get from the capillaries to the cells? Ê Name three things that the blood carries. Ê What distinguishes an artery from a vein?
15 Lesson 3.2B- The Respiratory System Ê Main Function: to exchange oxygen from the air with carbon dioxide from the blood. Ê Air Flow Ê Nasal cavity- lined by a mucous membrane, which creates a sticky mucous that helps trap dust and foreign substances. Ê Pharynx- throat Ê Larynx- voice box Ê Trachea- windpipe Ê Bronchi- two pipes that split off the trachea and allow air to enter the lungs.
16 The Lungs Ê Located in the thoracic cavity, are your right and left lungs. Ê The right lung has three lobes, and the left lung has two lobes. Ê The lungs are enclosed in a thin, double-layered membrane, called the pleura. Ê Your lungs contain about 300 million tiny air sacs, that look like tiny bunches of grapes, called alveoli. Alveoli allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between your blood and the air. Ê Diaphragm- a dome-shaped muscle situated below the lungs. It expands and contracts to help you to breathe. Ê The diaphragm is controlled by the phrenic nerve.
17 Warm Up- Day 4 Ê Give the anatomical name for the voice box. Ê Give the anatomical name for the throat. Ê Give the anatomical name for the windpipe
18 Lesson 3.2C- The Digestive System Ê Function: to break down the food you eat, allow it to be absorbed by the body and used as a source of energy. Ê Digestion happens in two ways: Ê Mechanical Digestion: breaks down food through physical forces such as chewing and churning. Ê Chemical digestion: uses chemical reactions to break down the food.
19 The Path of Food Ê The path food following through the digestive system is called the alimentary canal. Ê Mouth- chews the food and mixes it with saliva. Ê Saliva contains enzymes- molecules designed to speed up chemical reactions- that break down starch from food into sugar. Ê Teeth- critical for digestion. Ê Crown- the visible, top-portion of the tooth. Covered by enamel- the hardest substance in the body. Ê Root- the part of the tooth that is not covered by enamel. Ê Dentin- hard, bone-like tissue which forms the tooth. Surrounded by cementum, which holds the tooth in place. Ê Pulp- inside the dentin. Contains the tooth s nerves and blood vessels and provides nutrients to the dentin. Ê Periodental Membrane- connects the cementum to the jawbone.
20
21 The Path of Food Ê Epiglottis- covers the trachea (windpipe) to keep food from entering. Ê Esophagus- long, muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Ê Peristalsis- the involuntary contraction of muscles in the esophagus that pushes the food toward the stomach. Ê Stomach- muscular organ that functions as the mixing chamber. Combines food with digestive juices and enzymes that help to break down food further.
22 The Path of Food Ê Small Intestine- where most of the chemical and mechanical digestion occurs. About 3 m (10 ft) long with three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Ê Villi- hair like tubes along the inside walls of the intestines. Aid in absorption of nutrients. Nutrients enter the bloodstream through capillaries that surround villi and are transported by the blood to the rest of the body. Ê Large Intestine/Colon- long tube (1.5m) that absorbs most of the water and nutrients. Remains are excreted out the colon as feces.
23 Digestive System
24 Digestive Helpers Ê Liver- the body s largest internal organ. Produces bile, which is mixed with food in the small intestine to help digest fat. Bile is stored in the gallbladder. The liver also helps to filter out toxins and store glucose. Ê Pancreas- produces pancreatic juices that contain enzymes that help digest carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in the small intestines.
25 The Excretory/Urinary System Ê Function: excretes wastes from your body. Includes the lungs, liver, colon, and sweat glands. Ê Urinary System- a special part of the excretory system that removes liquid wastes. Includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Ê Kidneys- bean shaped organs that contain a system of very small tubes that filter waste from the body. Ê Ureters- small tunes that connect kidneys to the bladder. Ê Bladder- stores liquid waste (called urine) until it is eliminated from the urethra.
26 Warm Up- Day 5 Ê What is peristalsis? Ê List the path that food takes through the alimentary canal from when it is taken into the body until it is eliminated as feces.
27 Lesson 3.2D- The Lymphatic System Ê Function: to circulate body fluids and protect your body from disease. Ê Lymph- a liquid supplied by the cardiovascular system that surrounds every cell in your body. Helps maintain water balance and keeps cells clean. Ê Moves one-way through a series of lymph capillaries and larger lymphatic vessels until it reaches the lymph nodes- large bundles of lymphatic tissue that clean lymph of debris and microorganisms before sending it back into the blood.
28 The Lymphatic System Ê Lymphatic Tissues Ê Peyer s Patches- groups of lymph nodes in the ileum of the small intestine. Ê Tonsils and Adenoids- prevent pathogens from entering your body through your throat. Ê Pathogens- disease causing organisms. Ê Spleen- the largest lymphatic organ. Filters out and disposes of dead cells and microbes in the blood and serves as storage for extra blood. The spleen also houses lots of white blood cells.
29
30 The Immune System Ê Function: to fight invading microorganisms. Ê Includes Ê Skin- prevents harmful microorganisms from entering the body. Ê Mucous Membranes- line body passageways that open to the outside and use mucus to trap invaders. Ê Body Secretions- tears and sweat contain enzymes, called lysozymes, that destroys bacterial cells. Ê Thymus- located behind your breastbone, between your lungs. The site where lymphocytes grow and mature.
31 White Blood Cells Ê When a pathogen is detected in the body, several types of white blood cells jump into action. Ê Neutrophils- non-specific WBCs that are the first responders. Ê Macrophages- big eaters - second responders. Ê Lymphocytes- include B cells, helper T cells, and killer T cells. Ê B cells produce antibodies, which bind to pathogens and inactivate them and mark them for destruction. Ê Some B cells form memory B cells, which remain in the body from a future attack from the same pathogen. Ê Killer T Cells- destroy infected cells.
32 Immunity Ê Immunity- any ability of the body to resist invasion by being exposed to a pathogen or by vaccine. Ê Vaccines- a substance that causes the body to produce memory cells and antibodies against a pathogen but does not actually cause the disease. Ê Types of Immunity Ê Innate- the first line of defense against microbial cells. General, non-specific response. Ê Acquired- the immunity provided by memory B cells. Specific response to the invading cell.
33 Warm Up- Day 6 Ê What is the function of an antibody? Ê What is a phagocyte? Ê Explain the difference between the two main types of immunity.
34 Lesson 3.3A- Integumentary System and Skeletal System Ê Integumentary Systemconsists of the skin, hair, and nails that cover and protect your body.
35 Layers of the Skin Ê Skin- uses special sensory receptors to detect pressure and pain. Your skin also slows the loss of water from your body. Ê Epidermis- the top layer of skin, the outer layer of which is made of dead cells. The inner layers consist of living cells. The cells of the epidermis contain pigment that gives the skin its color- the most important of which is melanin. Ê Dermis- the second layer of skin which contains a network of blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves. Sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles are also found within the dermis. Muscle fibers are woven throughout the dermis too. Ê Subcutaneous Layer (Hypodermis)- located beneath the dermis. Contains adipose tissue and the major blood vessels of the skin. This layer aids in insulation. The subcutaneous layer also connects the skin to the muscles that lie below it.
36 The Skin
37 Skeletal System Ê Function: supports your body and gives it shape, protects vital structures, stores calcium, and provides a location for the formation of new red blood cells, which are produced in the bone marrow- the soft, fatty tissue in the porous center of a long bone. Ê An adult skeleton has 206 bones.
38 Skeletal System Ê Bones are classified into 4 categories: Ê Long Bones- these bones are longer than they are wide and have enlarged ends. Includes the humerous, femur, and phalanges. Ê Short Bones- roughly cube shaped. Most are found in wrist and ankles. Ê Flat Bones- often used to protect vital organs, such as the ribs. Ê Irregular Bone- such as the vertebrae found in your spine.
39 Types of Bones
40 Skeletal System Ê The skeleton is divided into two parts: Ê Axial Skeleton- includes the 80 bones of the head, spine and ribs. Ê Includes the cranium, maxillae, mandible, sinuses, vertebral column, sacrum, coccyx, ribs and sternum. Ê Appendicular Skeleton- includes the 126 bones found in the appendages, and the bones that connect the appendages to the axial skeleton. Ê Includes clavicles, scapulas, and pelvis.
41 Skeletal System Ê Joint- the place where two or more bones meet. Ê Immovable Joints- do not allow connecting bones to move. Ê Example: bones of the cranium Ê Movable Joints- allow the bones to move easily. The ends of these bones are covered with a smooth tissue called cartilage. Ê Several Types: hinge joints, ball and socket joints, pivot joints.
42 Skeletal System Ê Ligaments- strong, tough tissues that connect bones to other bones at moveable joint.
43 Skeletal System Ê Fracture- a break or crack in a bone. Ê Simple Fracture- a crack or break that does not cause the bone to pierce the skin s surface. Ê Compound Fracture- the bone breaks through the skin s surface.
44 Warm Up- Day 7 Ê What is the brown pigment that gives skin its color? Ê Name the two divisions of the skeletal system and what is included in each? Ê What is the top/outer layer of skin called?
45 Lesson 3.3B- Muscular and Nervous Systems Ê The muscular system is composed of over 600 muscles, responsible for producing the movements of your body. Ê Muscles work in pairs. When one muscle in the pair contracts to pull a body part toward it, the other muscle relaxes. Ê Each end of a skeletal muscle is attached to a different body part. Ê Origin- a relatively immovable part (like a bone) where a muscle is anchored. Ê Insertion- a movable part of the body (such as another bone or skin) where muscle attaches. Ê The insertion is always pulled toward the origin.
46 The Muscular System Ê Two Types of Muscles Ê Voluntary- muscles that you can move whenever you wish. Ê Example: muscles in your arms, fingers, legs, etc. Ê Involuntary- muscles that are vital to your body and work without you thinking about them. Ê Example: muscles in the heart that help with pumping blood or those in the intestines that aid in digestion.
47 The Nervous System Ê Function: to coordinate the activities of your body. Ê The nervous system is divided into two parts: Ê Central Nervous System (CNS)- includes the brain and the spinal cord. Ê Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)- composed of the nerves, called neurons, and nerve tissue, called ganglia. Ê Nerves (aka: Neurons)- bundles of fibers that connect the central nervous system with the rest of the body. Neurons transmit information throughout your body as electrochemical messages, called impulses.
48 The Central Nervous System Ê Brain- includes the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Ê Cerebrum- the largest part of the brain, which controls conscious thought and reasoning. Ê The cerebrum is divided into two halves, called hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the right half of the body and the right hemisphere controls the left half of the body. Ê Cerebellum- sits at the back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It is responsible for balance and coordination. Ê Brain Stem- connects the brain to the spinal cord. It is responsible for the body s autonomic activities.
49 The Central Nervous System Ê Spinal Cord- located inside the vertebral column. Transmits impulses from the brain to the peripheral nervous system. The spinal cord also controls simple reflexes.
50 Peripheral Nervous System Ê Types of Nerve Cells Ê Sensory Neurons- transmit information to the brain and the spinal cord. Ê Motor Neurons- transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles and other organs.
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM
 CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
CELLS/TISSUE/ORGANS/ORGAN SYSTEM CELLS ARE THE BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE TISSUES ARE MADE OF CELLS ORGANS ARE MADE OF TISSUES ORGAN SYSTEMS ARE MADE OF ORGANS THESE WORK TOGETHER TO HELP TO PROVIDE
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
RESPIRATION- Life function. Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male
 http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
http://www.spongelab.com/register/index.cfm Build A Body Virtual Tour Questions Male The Digestive System 1. How is the digestive system described? Esophagus 2. The esophagus leads from the to the. 3.
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
Chapter 20 UNIFYING CONCEPTS OF ANIMAL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION I. Life is based on many structural levels Levels of animal structure: Atoms and molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism: May
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL Phone: (630) Fax: (630)
 319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
Summary of Human Systems
 Summary of Human Systems Background Information Levels of Organization/: atom, molecule, organelles, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Tissue Types: epithelial, nervous, connective, muscle Homeostasis:
Summary of Human Systems Background Information Levels of Organization/: atom, molecule, organelles, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism Tissue Types: epithelial, nervous, connective, muscle Homeostasis:
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test
 The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test Please read the following directions. This test comprises ten (10) questions of which you will choose and answer only five (5) questions. If
The Living Environment Units 18, 19, and 20 Human Body Test Please read the following directions. This test comprises ten (10) questions of which you will choose and answer only five (5) questions. If
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Travel Brochure of the Body System
 Travel Brochure of the Body System By: Hector Capo, Mater Gardens Middle School, Miami Lakes, FL Name: Your team at the (create a name for your ad agency) has been hired as a travel consultant to design
Travel Brochure of the Body System By: Hector Capo, Mater Gardens Middle School, Miami Lakes, FL Name: Your team at the (create a name for your ad agency) has been hired as a travel consultant to design
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL
 1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN BODY ANSWER KEY
 PRE-VISIT CLASSROOM ACTIVITY - MEET THE HUMAN BODY Use the guided reading activity and matching worksheet as an in-class activity to introduce your students to the basic functions of the body systems and
PRE-VISIT CLASSROOM ACTIVITY - MEET THE HUMAN BODY Use the guided reading activity and matching worksheet as an in-class activity to introduce your students to the basic functions of the body systems and
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Karen Storey. Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer.
 Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
The Human Body. The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course.
 The Human Body The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course. Circulatory - Immune Respiratory - Digestive Musculoskeletal - Nervous Urinary - Endocrine THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.0
The Human Body The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course. Circulatory - Immune Respiratory - Digestive Musculoskeletal - Nervous Urinary - Endocrine THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.0
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
8 th Grade Science. Directed Reading Packet. The Human Body. Name: Teacher: Period:
 Wh 8 th Grade Science Directed Reading Packet The Human Body Name: Teacher: Period: Chapter 1, Section 1: Introduction to the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Human Cells 1. Explain how cells
Wh 8 th Grade Science Directed Reading Packet The Human Body Name: Teacher: Period: Chapter 1, Section 1: Introduction to the Human Body Organization of the Human Body Human Cells 1. Explain how cells
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below.
 SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
SECTION 45-1 REVIEW THE HUMAN BODY PLAN VOCABULARY REVIEW Describe the functions of the tissues listed below. 1. nervous tissue 2. muscular tissue 3. skeletal muscle 4. epithelial tissue 5. connective
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique. Systems Shuffle. By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side
 Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
Review of 10 major human body systems using a puzzle technique Systems Shuffle By: Heidi Hisrich of The Dork Side Teaching students about the different human body systems is one of my favorite things to
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
A Single Neuron from the Brain
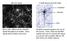 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
