Education vs Selling:
|
|
|
- Noel Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Understanding the 5 Primary Kinetic Chains for Clinical Assessment and Application By Dr. Alan Smith, DC Sponsored by Foot Levelers Education vs Selling: Elevate your cash practice through certainty by understanding fascial diaphragms and kinetic chains! 1
2 Inefficient Healthcare In the USA, $3.2 trillion per year is spent on healthcare (2015) This equates to $9,900 per person per year 17.8% of the US economy is devoted to healthcare spending Healthcare spending is exorbitant, but quality of life remains poor US Healthcare System Among 11 high-income countries evaluated by the Commonwealth Fund, the US healthcare system ranked worst (Newsweek, 2014) Study ranked care process, access, administrative efficiency, equity and health care outcomes US scored especially poor in equality of coverage 44% of low-income Americans have trouble accessing healthcare, compared to 7% in the UK 2
3 Medical Errors 10% of deaths attributed to medical error Medical institutions spent an estimated $28 billion due to medical errors (2008) More recently, it s estimated that the true cost of medical errors is $850 billion (2014) People in pain do drastic things to alleviate suffering Opiate addiction is on the rise and the effects are devastating Addictions are so problematic there is discussion of mitigating hazards (overdose, HIV infection, etc.) by opening safe injection sites in which drug users are able to legally inject while being supervised 3
4 4
5 Keys to a Successful Cash-Based Practice: Are You Insurance Dependent Versus Insurance Enhanced? Reimbursement problems????? Changing plans Are Traditional Practice Models Outdated? Prepaid plans Gym membership mentality What will a patient need in 3 months??? Escrow accounts - legality 5
6 What s Your Patient Visit Average? 35 National Average 62+ Axiom Wellness 50+ Keys to a Successful Cash-Based Practice: You must LOVE your practice to succeed Educate your patients Keep learning and growing 6
7 Why I Have a Cash-Based Practice: DO UNTO OTHERS AS YOU WOULD HAVE THEM DO UNTO YOU The Golden Rule 7
8 Why You Should Have a Cash-Based Practice: The pie is big enough for everyone to thrive Competition is unnecessary Subluxation-centered practice versus Subluxation-focused From Philosophical to Bio-Mechanical 8
9 Chiropractic The Five Axioms 1. Chiropractic 2. Exercise 3. Positive Mental Attitude 4. Nutrition 5. Sleep Subluxation Type equation here. Everyone is a Crooked Man Orthotics + Simple Structure-based Rehab + Chiropractic = TRUE SUCCESS 9
10 Maggs Law of Tissue Tolerance When the loading of a tissue exceeds the capacity of that tissue, compensatory physiological changes occur. Fascia. What is it? A biological fabric that surrounds every structure in the body and invests most of them 10
11 The Elementary View of Fascia Superficial - just below the skin Deep - surrounds muscles and bones Visceral - envelopes organs within their cavities Fascia: The body suit The fascia is a single 3 dimensional interdependent structure covering and linking muscles, tendons and visceral organs together throughout the entire body. 11
12 The 8 Transverse Diaphragms Plantar fascia Knee diaphragm Pelvic diaphragm Respiratory diaphragm Thoracic outlet Suboccipital triangle Tentorium cerebella Diaphragm sella The Transverse Diaphragms of the Spine A membrane or flexible layer that separates one space from another Occurs in the four spiral transition zones 12
13 Cranio-cervical Junction (CCJ) Articulation between the occiput, atlas, and axis Extensive mobility - head balances on the cervical spine Site of the tonic neck reflexes, which influences postural muscular tone throughout the trunk Disturbed function creates hypertonus of the postural muscles, disturbances of equilibrium and locomotor deficits Cranio-cervical Junction Suboccipital triangle Tentorium cerebella Diaphragm sella 13
14 Cervicothoracic Junction Articulation between cervical and thoracic spine Most mobile part of the spinal column is joined to the relatively rigid thoracic spine Anatomically, it is referred as the thoracic inlet and clinically, as the thoracic outlet Cervicothoracic Junction Thoracic outlet Anterior cervical fascia Subclavius muscles Costocoracoid ligaments Costoclavicular ligaments 14
15 Thoracolumbar Junction Abrupt change in function from rotation to flexion Respiratory diaphragm Lumbosacral Junction Forms base of axial skeleton therefore necessity for stabilization Movement of legs is directly translates through this junction Pelvic Diaphragm/Pelvic Floor 15
16 Five Primary Kinetic Chains Intrinsic Deep Longitudinal Lateral Posterior Spinal Anterior Spinal Five Primary Kinetic Chains Built on the principal actions that apply to all locomotion and movement Interdependent relationship that relies on the other to create balanced, efficient, reciprocal movement. One side of the body is active in one chain while the other side of the body is active in another 16
17 Five Primary Kinetic Chains Contralateral Synergists: Posterior Spiral / Deep Longitudinal Lateral / Anterior Spiral Functional Opposites: Deep Longitudinal / Lateral Lateral / Lateral Posterior Spiral / Anterior Spiral Intrinsic 17
18 Intrinsic DIAPHRAGM TRANSVERSE ABDOMINIS MULTIFIDUS PELVIC FLOOR Intrinsic Kinetic Chain Sets foundation for movement and locomotion Interdependent with the nervous system Principal action = 18
19 Deep Longitudinal abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 19
20 Lateral Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps 20
21 Posterior Spiral Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 21
22 Master Fascial Spring The Thoracolumbar Fascia The rotary action of the core cylinder allows for an efficient coiling and uncoiling of stored elastic energy. The top of the cylinder is capped with thoracic diaphragm; the bottom with the pelvic diaphragm. This connects the contralateral balance to hip and shoulder with the direct influence of breathe. Anterior Spiral 22
23 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces PUTTING IT ALL TOGETHER 23
24 The Gait Cycle The gait cycle starts with the Deep Longitudinal, shock absorption. The kinetic wave of energy is absorbed and translated into the axis of the spine. The Lateral completes the dynamic platform for the power generating Spirals. The Posterior Spiral coils fascial spring tension. That energy is then translated through the Anterior Spiral into forward motion and next absorption phase of the Deep Longitudinal. Deep Longitudinal The Deep Longitudinal Kinetic Chain is an energy absorption system. The strike phase of the gait absorbs kinetic energy from gravity and the subsequent swing phase of the Anterior Spiral Kinetic Chain. Ground engagement starts with the heel strike. The kinetic energy wave moves up to and through the axis of the spine. The energy of group engagement is absorbed through the Deep Longitudinal, and the response of the structure is ground force reaction. The Lateral Kinetic Chain responds to shock absorption with push into the earth. 24
25 Lateral Lateral Kinetic Chain takes the kinetic energy of ground engagement and translates it into ground force reaction. The stance phase of the gate is a transition between energy absorption of the Deep Longitudinal and the energy generation of the Posterior Spiral. Dynamic stability is the interdependent relationship between mobility and stability. Walking is a series of transitioning weight from one leg to the other while making forward progress. The midline stabilization of the stance phase orientates the spiral energy to the axis of the spine. The Lateral Kinetic Chain is paired with the contra-lateral opposite, anterior Spiral. The lateral completes the dynamic platform for forward movement. The feet are rich in pressure receptors that direct ground force reaction. The integrated activation of the mechanoreceptors in the joints of the feet are vital for kinetic chain sequencing. Walking gait integration starts at the feet and moves upwardly joint by joint. Posterior Utilizes the dynamic platform of the previous three kinetic chains. The work production of the Posterior Spiral activates the fascial matrix to store elastic energy. A fascial spring is how energy is stored for location. Elastic energy is stored in the tissues by two mechanisms. One is the compression occurring as the tissues are coining into a tight spring. The second mode of storing elastic energy is through the lengthening, or stretching of fascia or connective tissue. The Posterior Spiral has four major fascial springs ~ the thoracolumbar fascia, the iliotibial band, the Achilles tendon, and the plantar aponeurosis. These facial springs work together synergistically to create efficient movement so that the muscles do not have to work as hard. 25
26 Anterior The Anterior Spiral completes the gait cycle. Elastic energy up to this point has been stored in the tissues, and now the body is poised to do something with that energy. The Anterior Spiral redirects the elastic energy of the Posterior Spiral into the swing phase of the gait. This forward motion then becomes the next shock absorption of the Deep Longitudinal, thus completing the gait cycle. Anterior Spiral is the release of elastic energy into the complementary movement. Clinical Gems 26
27 Everyone is Crooked Man Journey and Applications Fulford Rolf Arthro stim/ Impulse IQ Vibracussor Oscillation/Vibration plates Rolfing, IASTM Cold Laser Nutraceuticals 27
28 Journey and Application Rollers Balls Canes Sticks Additional Pre/Post Adjustment Assessments Eyes Open/Eyes Closed Walking Postural Assessment 28
29 Here is a simple movement you can do to feel coiling and translation into the complementary opposite. Stand in a split stance Rotate the torso to the front leg side Notice the pelvis rotating to the back-leg side Contralateral rotation of shoulders to legs Head forward, eyes level to horizon Notice cervical spine in opposite rotation to thoracic This is coiled and poised to translate stored elastic energy into the complementary opposite Release the stored elastic energy to arrive in the opposite split stance This simple movement drill demonstrates the spiral counter spiral of the axial skeleton. This is an essential function that coils elastic energy into the connective tissue structures during gait. Plantar Fasciitis Direct plantar aponeurosis 29
30 Plantar Fasciitis Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps 30
31 Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus Everyone is Crooked Man 31
32 Shin Splits Direct Tibialis Anterior Shin Splints 32
33 abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces 33
34 Everyone is Crooked Man Inversion Sprain Direct Peroneus Longus 34
35 Inversion Sprain abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 35
36 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces Everyone is Crooked Man 36
37 Eversion Sprain Direct Tibialis Posterior Eversion Sprain 37
38 Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 38
39 Everyone is Crooked Man Foot Drop Direct Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus 39
40 Foot Drop Active Chain Assessment abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 40
41 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces Foot Drop Passive/Entrapment Assessment 41
42 Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 42
43 Everyone is Crooked Man Knee Pain Passive Chain Assessment 43
44 Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 44
45 Knee Pain Active Chain Assessment abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 45
46 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces Everyone is Crooked Man 46
47 Pelvic Dysfunction Passive Chain Assessment -- CORE Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps 47
48 Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus Pelvic Dysfunction Active Chain Assessment 48
49 abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces 49
50 Pelvic Dysfunction Breathe Intrinsic DIAPHRAGM TRANSVERSE ABDOMINIS MULTIFIDUS PELVIC FLOOR 50
51 Everyone is Crooked Man Lower Crossed Syndrome Tight/Facilitatd Rectus Femoris Vastus intermedialis Erector Spinae Quadratus Lumborum TFL/Hip Flexors Piriformis Tight BUT Weak Gastrocnemius Soleus Hamstrings Weak/Inhibited Core: Abdominals Gulteal Muscles Vastus Latealis Vastus Medialis Tibialis Anterior Tibialis Posterior Peroneus Longus 51
52 Lower Crossed Syndrome Active Chain Assessment abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 52
53 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces Lower Crossed Syndrome Passive Chain Assessment -- CORE 53
54 Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 54
55 Everyone is Crooked Man Upper Crossed Syndrome Tight/Facilitatd Pectoralis Musculature Upper Trapezius Erector Spinae Splenius Musculature Levator Scapulae Piriformis Weak/Inhibited Neck Flexors Rhomboids Serratus Anterior Lower Trap Tight BUT Weak Suboccipitals 55
56 Upper Crossed Syndrome Active Chain Assessment abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus 56
57 Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces Upper Crossed Syndrome Passive Chain Assessment -- CORE 57
58 Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus 58
59 Everyone is Crooked Man Upper Rib/Wrist Active Chain Assessment 59
60 abductor pollicis extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis middle deltoid Deep Longitudinal pectoralis serratus anterior upper trapezius ERECTOR SPINAE THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA SACROILIAC JOINT SACROTUBEROUS LIGAMENT iliotibial band gluteus medius adductor magnus rectus femoris BICEPS FEMORIS PERONEUS LONGUS TIBIALIS ANTERIOR extensor hallucis longus Anterior Spiral dorsal interossei extensor carpi radialis longus brachialis splenius capitis pectoralis major serratus anterior EXTERNAL OBLIQUE SCM INTERNAL OBLIQUE RECTUS ABDOMINIS iliacus ADDUCTOR LONGUS biceps femoris peroneus longus tibialis anterior extensor halluces 60
61 TMJ Passive Chain Assessment -- CORE Lateral thoracolumbar fascia QUADRATUS LUMBORUM thoracolumbar fascia quadratus lumborum upper trapezius middle trapezius latissimus dorsi ADDUCTOR MAGNUS GLUTEUS MEDIUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps 61
62 Posterior Spiral Lumbricals extensor carpi ulnaris triceps posterior deltoid SCM LATISSIMUS DORSI THORACOLUMBAR FASCIA splenius capitis SACROILIAC JOINT GLUTEUS MEDIUS GLUTEUS MAXIMUS iliotibial band vastus lateralis tibialis posterior peroneus longus soleus achilles tendon plantar aponeurosis flexor halluces longus Everyone is Crooked Man Orthotics + Simple Structure-based Rehab + Chiropractic = TRUE SUCCESS 62
63 Chiropractic Success Requires You to Work Backwards 1. How much do you need / want to earn? 2. How long do spend with each patient? Once you know these answers, you then can determine the amount you need to charge. $$$$ $$$$ The Five Axioms 1. Chiropractic 2. Exercise 3. Positive Mental Attitude 4. Nutrition 5. Sleep Subluxation Type equation here. 63
64 F E A R Acronym False Evidence Appearing Real 64
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
STRETCHING. Benefits of stretching
 STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS
 A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
A P P E N D I X O N E OVERVIEW OF THE SIX FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAYS THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY HIGHWAY LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 PHOTO A1.1A AND B STRETCHING THE ANTERIOR FLEXIBILITY
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Anatomy Module Study Guide
 Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley,
 Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS
 PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Role Of The Fitness Professional. Causes of Fitness Related Injuries. The Assessments. Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach 2/9/2016
 Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST
 ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
4/28/2017. Treatment Targets for MFDTM. Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes. Trigger Points. Travel and Simons
 Treatment Targets for MFDTM Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes Trigger Points Travel and Simons 1 Trigger Points Lower levels of oxygen, nutrients, blood perfusion Increased levels of
Treatment Targets for MFDTM Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes Trigger Points Travel and Simons 1 Trigger Points Lower levels of oxygen, nutrients, blood perfusion Increased levels of
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat
 How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Flexibility Training Concepts
 Flexibility Training Concepts The normal extensibility of all soft tissues that allow the full range of motion of a joint. Flexibility The combination of flexibility and the nervous system's ability to
Flexibility Training Concepts The normal extensibility of all soft tissues that allow the full range of motion of a joint. Flexibility The combination of flexibility and the nervous system's ability to
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Primary Movements. Which one? Rational - OHS. Assessment. Rational - OHS 1/1/2013. Two Primary Movement Assessment: Dynamic Assessment (other)
 Primary Movements Practical Application for Athletic Trainers Two Primary Movement Assessment: NASM-CES Overhead Squat Single-leg Squat Dynamic Assessment (other) Single-leg Step Off Functional Movement
Primary Movements Practical Application for Athletic Trainers Two Primary Movement Assessment: NASM-CES Overhead Squat Single-leg Squat Dynamic Assessment (other) Single-leg Step Off Functional Movement
An athlete s ability to handle their own
 Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional
 THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
THROWING A CROSS PUNCH body movement analysis GENERAL DESCRIPTION This paper will analyze the holistic dynamic body movement of a professional boxer s cross punch. I mentioned professional boxer because
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs
 Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
Myoskeletal Alignment for Low Back, Hip, and Leg Pain DVDs Use these handy time markers to locate the specific treatment techniques on the Level 4 Dynamic Body 6 DVD set as demonstrated by Erik Dalton
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body
 Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
Stretching Exercises for the Lower Body Leg Muscles The leg has many muscles that allow us to walk, jump, run, and move. The main muscle groups are: Remember to: Warm-up your muscles first before stretching
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
The Massage Routine. Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position. Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes
 The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
Lower Crossed Syndrome
 Lower Crossed Syndrome Sang mi Yun October 23 rd 2017 Costa Mesa 2016 Abstract Lower-Crossed Syndrome (LCS) is also referred to as distal or pelvic crossed syndrome. In LCS, tightness of the thoracolumbar
Lower Crossed Syndrome Sang mi Yun October 23 rd 2017 Costa Mesa 2016 Abstract Lower-Crossed Syndrome (LCS) is also referred to as distal or pelvic crossed syndrome. In LCS, tightness of the thoracolumbar
External Obliques Abdominal muscles that attaches at the lower ribs, pelvis, and abdominal fascia.
 The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint
 Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INDEX
 abdominal muscles anatomy, 21 23 breathing and, 26, 30 exercises, 64 67 external oblique, 21, 23, 64 importance of strong, 63 internal oblique, 22, 23, 64 rectus abdominis, 22, 23, 64 stretching, 68 69
abdominal muscles anatomy, 21 23 breathing and, 26, 30 exercises, 64 67 external oblique, 21, 23, 64 importance of strong, 63 internal oblique, 22, 23, 64 rectus abdominis, 22, 23, 64 stretching, 68 69
Overuse Injuries. Overuse injury defined. Overuse Injuries
 Overuse Injuries Lisa DeStefano, DO Associate Professor and Chair Department of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University Overuse injury defined Overuse
Overuse Injuries Lisa DeStefano, DO Associate Professor and Chair Department of Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine College of Osteopathic Medicine Michigan State University Overuse injury defined Overuse
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP
 2015 한국보바스소아학술대회 THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP KYOUNG SOOK PARK INSTRUCTOR THE BOBATH CONCEPT The NDT/Bobath Concept offers a forward looking interdisciplinary problem solving approach
2015 한국보바스소아학술대회 THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP KYOUNG SOOK PARK INSTRUCTOR THE BOBATH CONCEPT The NDT/Bobath Concept offers a forward looking interdisciplinary problem solving approach
INTRODUCTION. Objectives
 Objectives Functional Anatomy for Fitness Professionals focuses on functional anatomy, with an emphasis on weight training. Through the emphasis on biomechanics, neurology, and muscle physiology, participants
Objectives Functional Anatomy for Fitness Professionals focuses on functional anatomy, with an emphasis on weight training. Through the emphasis on biomechanics, neurology, and muscle physiology, participants
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Connecting the Core. Rationale. Physiology. Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS. Athletes have been inundated with terminology
 Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk
 The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015 There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Health Level 3 A/600/9051 Mock Paper March 1 st 2015 August 31 st 2015 There are 40 questions within this paper. To achieve a pass you will need to score 28 out
Lowe w r e r B ody Resistance Training
 Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
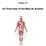 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
9/4/10. James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO. Why is posture important to you, the chiropractic physician?
 James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO The posture of homo sapiens is a complex biomechanical continuum, which involves the function of muscles, ligaments, fascia, nerves, osseous structures, neuromuscular control,
James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO The posture of homo sapiens is a complex biomechanical continuum, which involves the function of muscles, ligaments, fascia, nerves, osseous structures, neuromuscular control,
Muscle Energy Technique
 PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
PRACTICE SESSION: Muscle Energy Technique BE AN ARTIST and work out the best way for you to use the Muscle Energy Technique (MET). This technique works best when muscles are shortened. If you try MET on
OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST
 OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST Sajid A. Surve, DO Associate Professor, UNTHSC-TCOM Co-Director, UNT Texas Center for Performing Arts Health http://tcpah.unt.edu Occupation History for the Performer Pertinent
OMT FOR THE PERFORMING ARTIST Sajid A. Surve, DO Associate Professor, UNTHSC-TCOM Co-Director, UNT Texas Center for Performing Arts Health http://tcpah.unt.edu Occupation History for the Performer Pertinent
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
The Time Constrained Athlete:
 The Time Constrained Athlete: Developing a 15 Minute Rehabilitation Program Josh Stone, MA, ATC, NASM-CPT, CES, PES Sports Medicine Program Manager National Academy of Sports Medicine Agenda 1. Introduction
The Time Constrained Athlete: Developing a 15 Minute Rehabilitation Program Josh Stone, MA, ATC, NASM-CPT, CES, PES Sports Medicine Program Manager National Academy of Sports Medicine Agenda 1. Introduction
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
National Fitness Leadership Alliance
 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base 2015 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base These competencies are intended as
National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base 2015 National Fitness Leadership Alliance Exercise Theory Prerequisite Knowledge Base These competencies are intended as
Training Philosophy. There are numerous views on core conditioning.
 Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
