Connection of the lower limb (juncturae ossium extremitatis inferioris)
|
|
|
- Marjorie Black
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Connection of the lower limb (juncturae ossium extremitatis inferioris) Connection of the pelvic girdle (juncturae ossium cinguli extremitatis inferioris) 1. Sacroiliac joint (articulatio sacroiliaca) (simple joint) Articular surfaces: auricular surface of the pelvic bone (facies auricularis ossis coxae) and auricular surface of the sacral bone (facies auricularis ossis sacri) Articular capsule: tight and attached to the margins of the articular surfaces Additional features: anterior, interosseous and posterior sacroiliac ligaments (ligamenta sacroiliaca anteriora, interossea and posteriora). Type of joint: articular surfaces are uneven, amphiarthrosis (almost immobile joint), children articular surfaces nearly flat adults uneven. 2. Pubic symphysis (symhysis pubica) Articular surfaces: symphyseal surfaces of left and right pubic bone (facies symphyseales ossis pubis dextra et sinistra), cartilaggineous discus (females 4,5cm, males 5cm). Additional features: interpubic disc (discus interpubicus) from fibrous tissue, superior and inferior pubic ligaments, inferior also arcuate pubic ligament is stronger (ligamentum pubicum superius et inferius, inferius also ligamentum arcuatum pubis). Type of joint: almost immobile joint. 3. Obturator membrane (membrana obturatoria) (syndesmosis) stiff membrane, attachment of the muscles (mm. obturatorii) 4. Ligaments in the pelvic region (syndesmoses) iliolumbar ligament (ligamentum iliolumbale), sacrospinal ligament (ligamentum sacrospinale), sacrotuberal ligament (ligamentum sacrotuberale), faciforme process (processus falciformis), sacrospinal ligament (ligamentum sacrospinale). Greater sciatic foramen (foramen ischiadicum majus) Lesser sciatic foramen (foramen ischiadicum minus) Pelvic bone (pelvis) Terminal line (linea terminalis): (promontorium arcuate line (linea arcuata) iliopubic eminence (eminentia iliopubica) cranial margin of symphysis). Greater pelvis (pelvis major) cranially from terminal line (abdominal organs) Lesser pelvis (pelvis minor) caudally from terminal line (genital and urinary system) Superior pelvic aperture (apertura pelvis superior) - inlet Inferior pelvic aperture (apertura pelvis inferior) - outlet Female pelvis has four planes: 1. Superior pelvic aperture, pelvic inlet (apertura pelvis superior, aditus pelvis) Transverse diameter (diameter transversa) 13cm Diagonal conjugate (conjugata diagonalis): measurable in female per vaginam, between caudal margin of the symphysis and ventral surface of the promontorium 12,5 13cm. 2. Width of pelvis (amplitudo pelvis) rounded shape, Oblique diameter (diameter obliqua): 12,5cm. 3. Narrow part of the pelvis (angustia pelvis): 11,5cm
2 4. pelvic outlet (apertura pelvis inferior) exitus pelvis rhomboid shape Direct diameter (diameter recta): between inferior margin of symphysis and apex of coccygeal bone 11-11,5cm. Saggital axis (length of newborn head 11cm) of the newborn head insert to the different diameters in different planes during delivering: 1. pelvic inlet: in transverse diameter 2. amplitude: twisting (oblique diameter) 3. angustia: in direct diameter 4. pelvic outlet: in direct diameter 5. Diagonal conjugate (conjugata diagonalis): measurable in female per vaginam, between caudal margin of the symphysis and ventral surface of the promontorium 12,5 13cm. External diameters of pelvis: Bispinal diameter (distantia bispinalis): superior anterior iliac spine of both sides (spina iliaca anterior superior) 26cm Bicristalis diameter (distantia bicristalis): the most lateral points on iliac crest 29cm. Bitrochanteric diameter (distatia bitrochanterica): between grater trochanters 31cm. Bituberal diameter (distantia bituberalis): between ischial tuberosities 12cm. External conjugate (conjugata externa): spinous process of L5 and superior margin of pubic symphysis (syphysis pubica) 20cm (minimally 18cm). Gender differences The female pelvis is larger and broader than the male pelvis which is taller, narrower, and more compact. Ala ossis illi is in male more in sagittal plane in females more in frontal plane. The iliac crests are higher and more pronounced in males, making the male false pelvis deeper and more narrow than in females. Inschial tuberosities are in females more distant than in males. Symphysis is higher in males and the angle between the inferior pubic rami is acute (70 degrees) in men, but obtuse ( degrees) in women. Accordingly, the angle is called subpubic angle in men and pubic arch in women. Additionally, the bones forming the angle/arch are more concave in females but straight in males. The female inlet is larger and oval in shape, while the male sacral promontory projects further (i.e. the male inlet is more heart-shaped). The male sacrum is long, narrow, more straight, and has a pronounced sacral promontory. The female sacrum is shorter, wider, more curved posteriorly, and has a less pronounced promontory. Greater sciatic notch is broader in females, in males is narrow. Superior ramus of pubic bone is in females longer. Obturator foramen is in females triangular and in males oval.
3 Connections of the free part of the lower limb (juncturae ossium extremitatis inferioris liberae) 1. Hip joint (articulatio coxae) Articular surfaces: lunate articular surface in acetabulum (facies lunata), acatabular pillow (pulvinar acetabuli) and head of the femur (caput femoris). Articular capsule: attached to the margins of acetabulum on the femur reaches anteriorly to the intertrochanteric line (linea intertrochanterica) and posteriorly mediall away from the trochanteric fossa (fossa trochanterica) that is outside of capsule. Additional features: acetabular lip (labrum acetabulare), transverse acetabular ligament (ligamentum transversum acetabulare), iliofemoral ligament (ligamentum iliofemorale), pubofemoral ligament (ligamentum pubofemorale), ischiofemoral ligament (ligamentum ischiofemorale), orbicular zone (zona orbicularis) formed by pubofemoral and ischiofemoral ligaments, ligament of the head of the femur (ligamentum capitis femoris), iliopectine bursa (bursa iliopectinea). Type of joint: ball and socket (sheroidal) but with limited movements - enarthrosis, movements are possible to all directions (three degrees of freedom of movements). 2. Knee joint (articulatio genus) compound joint Articular surfaces: a) medial femoral condyle (condylus femoris medialis) and medial articular surface on the proximal end of the tibia (facies articularis medialis) b) lateral femoral condyle (condylus femoris lateralis) and lateral articular surface on the proximal end of the tibia (facies articularis lateralis) c) articular surface of the patella (facies articularis patellae) and patellar surface of femur (facies patellaris femoris) Articular capsule: is solid and spacious and is attached 1-1,5cm from margins of articular surfaces. Synovial membrane is placed on the cruciate ligaments (ligamenta cruciata) and anteriorly from them protrudes towards to the patella as (plica synovialis patellae). Caudally from patella is inserted between the fibrous and synovial membrane (corpus adiposum genus). Infrapatellar synovial plica (plica synovialis infrapatellaris), (plicae alares). Additional features: medial menisc (meniscus medialis)(attach to the area intercondylaris anterior et posterior) - semicircular fuses with joint capsule and through with medial collateral ligament is less movable than lateral menisc (meniscus lateralis) almost circular (attach to the lateral intercondylar tubercle), tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle, patellar ligament (ligamentum patellae), medial and lateral patellar retinaculum (retinaculum patellae mediale et laterale), collateral tibial and fibular ligaments (ligamentum collaterale tibiale et fibulare), oblique popliteal ligament (ligamentum popliteum obliqum), anterior and posterior ruciate ligaments (ligamenta cruciata anterior et posterior), suprapatellar, praepatellar and subcutaneous praepatellar borsae (bursa suprapatellaris, praepatellaris, praepatellaris subsutanea), Type of joint: compound joint, hinge joint (monoaxial), flexio, extension, in small flexion slight external and internal rotation is possible. 3. Connections of the shin bones (juncturae tibiofibulares) A. Tibiofibular articulation (articulatio tibiofibularis) Articular surfaces : articular surfaces of the head of the fibula (facies articularis capitis fibulae) and articular fibular surface of the tibia (facies articularis fibularis tibiae). Articular capsule: is short and stiff, and attached to the margins of articular surfaces. Additional features: ligament of the head of the fibula (ligamentum capitis fibulae).
4 Type of joint: plane joint, small movements anteriorrlly and posteriorlly. B. Interosseous membrane of the shin bones (membrane interossea cruris) Stiff membrane attached to the interosseous margins of the tibia and fibula, attachments of some muscles and course of nerves and vessels. C. Tibiofibular syndesmosis (syndesmosis tibiofibularis) (syndesmosis!!) Distal end of the fibula is inserted in fibular notch (incisura fibularis tibiae) it is not joint!!!! Connection by strong ligaments anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments (ligamentum tibiofibulare anterius et posterius). Movements: small movements but in case of tearing of ligaments it is not possible to. Joints of the foot (articulationes pedis) A. Talocrural joint (articulatio talocruralis) : Articular surfaces : inferior articular surface of tibia (facies articularis inferior tibiae), articular surface of medial malleolus (facies articularis malleoli medialis), articular surface of lateral melleolus (facies articularis melleoli lateralis) and talar trochlea (trochlea tali). Articular capsule: is attached to the articular margins, anterior and posterior part is lax and on side is reinforced by strong ligaments. Additional features: Medial collateral ligament, deltoid ligament (ligamentum collaterale mediale, ligamentum deltoideum) has four parts: tibionavicular part (pars tibionavicularis) to navicular bone, anterior tibiotalr part (pars tibiotalaris anterior) to anterior part of talus, tibiocalcanear part (pars tibiocalcanea) to sustentaculum tali and posterior tibiotalar part (pars tibiotalaris posterior) to posterior part os talus. Lateral part has three ligaments: anterior talofibular ligament (ligamentum talofibulare anterius) to collum tali, calcaneofibular ligament (ligamentum calcaneofibulare) between lateral melleolus and lateral surface of the calcaneus, posterior talofibular ligament (ligamentum talofibulare posterius) between lateral malleolar fossa (fossa melleoli lateralis) and posterior talar process (processus posterior tali). Type of the joint: trochlear joint, hinge joint, plantar and dorsal flexion, trochlea tali is narrower proximally slight side to side movements are possible. B. Intertarsal joints (articulations intertarsales) Subtalar joint (articulatio subtalaris) Articular surfaces: posterior calcanear surface of talus and posterior talar surface of calcaneus (facies articularis calcanea posterior tali et facies articularis talaris posterior calcanei). Articular capsule: short and attached to the articular margins. Additional features: lateral and medial talocalcanear ligaments (ligamentum talocalcaneum laterale et mediale), interosseous talocalcaneal ligament (ligamentum talocalcaneum interosseum). Talocalcaneonavicular joint (articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis) (compound joint) Articular surfaces: anterior and medial calcanear surface of talus and anterior and medial talar surface of calcaneus (facies articularis calcanea anterior et media tali et facies articularis talaris anterior et media calcanei) and head of talus (caput tali) with navicular bone (os naviculare).
5 Articular capsule: is very thin and common for all parts attach to the margins of articular surfaces. Additional feature: Plantarly: plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (ligamentum calcaneonaviculare plantare). Dorsaly: dorsal calcaneonavicular ligament (ligamentum calcaneonaviculare dorsale) part of the bifurcate ligamentum (ligamentum bifurcatum), talonavicular ligament (ligamentum talonaviculare), interosseou talocalcanear ligament (ligamentum talocalcaneare interosseum), Both joints represent mechanical unit with possible movements according to the axis that goes through tarsal sinus (sinus tarsi), pronatio and supinatio (internal and external rotation). Calcaneocuboid joint (articulatio calcaneocuboidea) Articular surfaces: cuboid articular surface of calcaneus (facies articularis cuboidea) and proximal articular surface of cuboid bone. Articular capsule: thin and attached to the articular margins. Additional features: plantar calcaneocuboid ligament (ligamentum calcaneocuboideum plantare) long plantar ligament (ligamentum plantare longum), calcaneocuboid ligament (ligamentum calcaneocuboideum) is second part of bifurcate ligament (ligamentum bifurcatum). Type of joint: saddle joint but movements are limited by other joints subtalar joint, axis of movements is in sinus tarsi. Chopart s articulation (joint), transverse tarsal joint (articulatio tarsi transversa): joint fissure between head of talus (caput tali) and nevicular bone (os naviculare) and between calcaneus and coboid bone (os cuboideum). Opening of this fissure in case of exarticulation is by cutting the bifurcate ligament. Cuneonavicular joint (articulatio cuneonavicularis) Articular surfaces: distal articular surface of navicular bone (os naviculare) and proximal articular surfaces of cuneiform bones (ossa cuneiformia). Additional features: plantar and dorsal cuneonavicular ligaments (ligamenta cuneonavicularia plantaria et dorsalia), articular fissure is connected with articular fissure of intermatatarsal joints, common articular capsule if enforced by dorsal, plantar and interosseous intercuneiform ligaments (ligamenta intercuneiformia dorsalia, plantaria et interossea). Cuneocuboid joint (articulatio cuneocuboidea) Articular surfaces: articular surface on medial side of cuboid bone and lateral articular surface of lateral cuneiform bone. Additional features: dorsal, plantar and interosseous cuneocuboid ligaments (ligamenta cuneocuboidea- dorsale, plantare, interosseum). Intermetatarsal joint (articulatio intermetatarsalis) C. Tarsomatatarsal joints (articulationes tarsomatatarsales) (Lisfranck s joint) Articular surfaces: three parts a) Medial cuneiform bone with base of I. metatarsal bone b) Intermediate and lateral cuneiform bone with II. and III. metatarsal bones c) Cuboid bone with IV. and V. metatarsal bones
6 Articular capsule: thin and attached to the articular margins. Additional feature: dorsal, plantar and interosseous tarsomatatarsal ligaments (ligamenta tarsomatatarsalia dorsalia, plantaria et interossea). Movements: slight movements during loading of platar arch. Lisfranck s joint: place to axarticulation of toe. D. Metatarsophalangeal joints (articulationes metatarsophalangeales) Articular surfaces: heads of metatarsal bones and bases of proximal phalanges. Articular capsule: is attached to margins of the articular surfaces. Additional features: fibrous cartilages increase articular fossa laminae fibrocartilagines plantares, deep transverse metatarsal ligament (ligamentum metatarsale transversum profundum), collateral ligaments (ligamenta collateralia), sesamoid bones (ossa sesamoidea) in first metacarpophalangeal joint. Type of joint: ball and socket, flexion, extension, abduction and adduction movements restricted by collateral ligaments. E. Interphalangeal joints (articulationes interphalangeae pedis) Articular surfaces: trochlea phalangis of the proximal phalanx, basis of distal phalanx. Articular capsule: is attached to margins of the articular surfaces. Additional features: fibrous cartilages increase articular fossae laminae fibrocartilagineae plantares. Articular capsules are reinforced by the strong collateral ligaments (ligg. collateralia), tendons of extensors. Type of joint: hinge joint (articulatio trochlearis), movements flexion and extension. Arches of the foot The bones of the foot do not lie in a horizontal plane. Instead, they form longitudinal and transverse arches relative to the ground, which absorb and distribute downward forces from the body during standing and moving on different surfaces. Longitudinal arch Medially: talus, navicular bone, cuneiform bones, I. III. metatarsal bones Laterally: calcaneus, cuboid bone, IV- and V. metatarsal bones. Medial arch is over the lateral arch Transverse arch Ossa cuneiformia Arches are kept by ligaments and muscles. Function: protection of soft parts of planta pedis before press (long standing), weight bearing points are tuber calcanei, heads I. and V. metatarsal bones. Flat foot pes planus.
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
Skeleton of lower extremity Ossa membri inferioris
 Skeleton of lower extremity Ossa membri inferioris Skeleton of lower extremity consists of lower extremity girdle (cingulum membri inferioris) created by pelvis bone (os coxae) and bones of free lower
Skeleton of lower extremity Ossa membri inferioris Skeleton of lower extremity consists of lower extremity girdle (cingulum membri inferioris) created by pelvis bone (os coxae) and bones of free lower
Skeleton of the lower limb
 Skeleton of the lower limb (ossa membri inferioris) RNDr. Michaela Račanská, Ph.D. Lecture 3 DENTISTRY Autumn 2016 Skeleton of the lower limb support the weight of the body and transfers that support to
Skeleton of the lower limb (ossa membri inferioris) RNDr. Michaela Račanská, Ph.D. Lecture 3 DENTISTRY Autumn 2016 Skeleton of the lower limb support the weight of the body and transfers that support to
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
 BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. 1 SCCC BIO130 Lab 7 Appendicular Skeleton & Articulations
 The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
SPECIAL ARTHROLOGY Connections of the upper limb
 SPECIAL ARTHROLOGY Connections of the upper limb (juncturae ossium membri superioris) RNDr. Michaela Račanská, Ph.D. Lecture 8 DENTISTRY Autumn 2016 Connections of the shoulder girdle: scapula + clavicle
SPECIAL ARTHROLOGY Connections of the upper limb (juncturae ossium membri superioris) RNDr. Michaela Račanská, Ph.D. Lecture 8 DENTISTRY Autumn 2016 Connections of the shoulder girdle: scapula + clavicle
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The topic of the lesson Bones of the lower limb Course 1 st Number
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The topic of the lesson Bones of the lower limb Course 1 st Number
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
The Lower Limb. Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD.
 The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
* Articular system II
 Articular system II Hyaline Fibrous Elastic - Has an intercellular matrix rich in hyaluronic acid and mucopolysaccharides, which are natural lubricants - Forms the articular cartilage in most joints -
Articular system II Hyaline Fibrous Elastic - Has an intercellular matrix rich in hyaluronic acid and mucopolysaccharides, which are natural lubricants - Forms the articular cartilage in most joints -
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
 C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
PELVIS & SACRUM Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Learning Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the bony structures of the pelvis. Describe in detail
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives
 Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47993 1 Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis Donna Browne Based on The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed
OpenStax-CNX module: m47993 1 Skeletal System Module 13: The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis Donna Browne Based on The Pelvic Girdle and Pelvis by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Located more distal and anterior together with Trapezoid, anterior to scaphoid Trapezium rarely to be fractured.
 The hand The hand consists of the 3 groups: Proximal part: carpals bones (8) Middle part: metacarpal bones (5) Distal part: fingers or phalanges bones (3 for each finger except for the thumb just 2 bones).
The hand The hand consists of the 3 groups: Proximal part: carpals bones (8) Middle part: metacarpal bones (5) Distal part: fingers or phalanges bones (3 for each finger except for the thumb just 2 bones).
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Appendicular Skeleton. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum.
 The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
The os coxae The os coxae or hip bone consists of three flat bones, ilium, ischium and pubis, which fuse together to form the acetabulum. The ilium extends from the acetabulum upwards forming the lateral
DORSAL MUSCLES OF THE HINDLIMB (ca)
 Fascia thoracolumbalis Fascia glutea Fascia lata Lamina superficialis Lamina profunda Fascia cruris DORSAL MUSCLES OF THE HINDLIMB (ca) M. gluteus superficialis o Origin: sacrum and first caudal vertebrae,
Fascia thoracolumbalis Fascia glutea Fascia lata Lamina superficialis Lamina profunda Fascia cruris DORSAL MUSCLES OF THE HINDLIMB (ca) M. gluteus superficialis o Origin: sacrum and first caudal vertebrae,
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
8.2: Fibrous Joints. There are three (3) types of fibrous joints (synarthroses): Syndesmosis Suture Gomphosis. Interosseus membrane of leg.
 8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Exercise 11. The Appendicular Skeleton
 Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Lecture 10. JOINTS of the FOOT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 10 JOINTS of the FOOT. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 20.02.2018 The joints of the foot are numerous. They are classified: A. Intertarsals B. Tarso metatarsals C. Intermetatarsals D. Metatarsophalangeal
Lecture 10 JOINTS of the FOOT. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 20.02.2018 The joints of the foot are numerous. They are classified: A. Intertarsals B. Tarso metatarsals C. Intermetatarsals D. Metatarsophalangeal
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES:
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
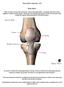 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
