Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8
|
|
|
- Willis Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then you will be graded on only the first 50 of these, regardless of whether the extra questions are answered correctly. Choose any 50 questions on the basis of your knowledge of the material. A good strategy is to first attempt to answer all 60 questions, but spend no more than 1 minute on any one. Then choose the 50 with which you are most confident, and then, and only then, transcribe your answers to the answer sheet. Be careful to record your answers on the appropriate number of the answer sheet. Completely blacken the letter of your choice. Completely strike out the number and all letters of the questions you choose not to answer. Turn in only your answer sheet. You may keep the questions. e.g. to indicate response "B", do this: 12) A C D E ; don't circle B e.g. to omit a question, do this: 12) A B C D E ; don't just leave it blank 1) Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding the biceps brachii muscle. A) the long head originates from the coracoid process B) it inserts on the radial tuberosity C) its innervation is by the musculocutaneous nerve D) the long head is lateral to the short head E) its function is brachial and antebrachial flexion 2) Identify the INCORRECT description of muscle function. A) levator costarum costal elevation B) infraspinatus medial brachial rotation C) iliacus femoral flexion D) peroneus brevis eversion E) latissimus dorsi brachial extension 3) Which of the following muscles is NOT a flexor? A) transversospinalis B) scaleneus posterior C) short head of biceps femoris D) flexor pollicis longus E) iliopsoas 4) What is circumscribed by the omohyoid, posterior belly of the digastric, and sternocleidomastoid? A) quadrangular space B) deltopectoral triangle C) submandibular triangle D) posterior triangle of the neck E) carotid triangle 5) Which of the following muscles does NOT originate from the pelvis? A) gluteus medius B) adductor magnus C) rectus abdominis D) semimembranosus E) short head of the biceps femoris 6) Identify the correct statement regarding the respiratory diaphragm. A) it is innervated by the phrenic nerve B) the psoas major muscles pass through it via the arcuate ligaments (lateral retinacula) C) it inserts on the costal margin D) its function is exhalation E) the descending aorta passes through it via the caval hiatus
2 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 2 of 8 7) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and compartment or group. A) rectus abdominis rectus sheath B) subscapularis rotator cuff C) plantaris plantar pes D) peroneus longus lateral crural E) soleus sural 8) Which of the following statements about the extensor digitorum communis muscle is INCORRECT? A) its innervation is the radial nerve B) its insertion is the extensor expansion C) its origin is the medial humeral epicondyle D) one of its antagonists is the flexor digitorum superficialis E) it is located in the superficial layer of the posterior antebrachial compartment 9) Which of the following is a symptom of long thoracic nerve deficit? A) drop hand B) claw hand C) ptosis D) ape hand E) winged scapula 10) Innervation of the teres minor muscle is by which of the following? A) musculocutaneous nerve B) lateral pectoral nerve C) axillary nerve D) long thoracic nerve E) thoracodorsal nerve 11) Which of the following does NOT insert on the humerus? A) biceps brachii B) supraspinatus C) deltoideus D) coracobrachialis E) latissimus dorsi 12) What is the insertion of the pectoralis minor? A) fovea capitis B) greater tubercle C) coracoid process D) deltoid tuberosity E) costae ) Which of the following pairs of muscles have the same innervation? A) gluteus maximus and iliacus B) triceps and supinator C) flexor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi ulnaris D) tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior E) flexor digitorum longus and flexor digitorum profundus 14) Identify the INCORRECT statement. A) the subscapular nerve is transmitted through the quadrangular space B) the cephalic vein is transmitted through the deltopectoral triangle C) the tendons of deep posterior crural muscles are transmitted through the tarsal tunnel D) the piriformis muscle is transmitted through the greater sciatic foramen E) the femoral artery is transmitted through the adductor hiatus
3 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 3 of 8 15) Which of the following is a thenar muscle? A) flexor pollicis longus B) extensor pollicis longus C) extensor pollicis brevis D) abductor pollicis brevis E) adductor pollicis 16) Which of the following have a common (shared) origin? A) pectoralis major and pectoralis minor B) biceps brachii and brachialis C) iliacus and gluteus maximus D) medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius E) flexor carpi ulnaris and palmaris longus 17) What is the innervation of the anterior crural muscles? A) femoral nerve B) sciatic nerve C) tibial nerve D) common peroneal nerve E) deep peroneal nerve 18) The inguinal canal perforates which of the following? A) aponeuroses of abdominal oblique muscles B) the respiratory diaphragm C) the obturator membrane D) the urogenital diaphragm E) the adductor magnus muscle 19) What is the principle action of the triceps? A) brachial extension B) brachial adduction C) antebrachial extension D) antebrachial supination E) none of the above 20) Which of the following is an appendicular muscle? A) erector spinae B) rhomboideus major C) splenius capitis D) quadratus lumborum E) serratus posterior superior 21) Which of the following is a hypaxial muscle? A) transversospinalis B) rectus abdominis C) obturator internus D) subclavius E) quadratus femoris 22) Which of the following does NOT originate from costae? A) scalene muscles B) serratus anterior C) intercostal muscles D) trapezius E) pectoralis major
4 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 4 of 8 23) Which of the following is a medial brachial rotator? A) piriformis B) teres major C) teres minor D) supraspinatus E) infraspinatus 24) Identify the INCORRECT insertion. A) gracilis adductor tubercle B) biceps femoris fibular head C) plantaris calcaneal tuberosity D) gluteus maximus gluteal tuberosity (in part) E) gastrocnemius calcaneal tuberosity 25) Identify the correct association of muscle and group or compartment. A) brachioradialis superficial anterior antebrachial B) longissimus erector spinae C) peroneus tertius lateral femoral D) sartorius medial femoral E) tensor fasciae latae anterior femoral 26) Identify the INCORRECT relationship. A) the ischial tuberosity is deep to the gluteus maximus B) the flexor carpi radialis is lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris C) the transversus abdominis is deep to the internal abdominal obliquus D) the gluteus medius is superficial to the gluteus minimus E) the adductor magnus is anterior to the adductor longus 27) Which of the following is the principle antagonist of the tensor fasciae latae muscle? A) gastrocnemius B) quadriceps C) popliteus D) gluteus minimus E) iliopsoas 28) Muscles of the medial compartment of the femur are innervated by which of the following nerves? A) obturator B) femoral C) tibial D) phrenic E) common peroneal 29) From what do all of the lateral femoral rotator muscles originate? A) femur B) sacrum C) the true pelvis D) the false pelvis E) intertrochanteric crest 30) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its innervation. A) superior obliquus trochlear nerve B) trapezius spinal accessory nerve C) buccinator mandibular nerve D) genioglossus hypoglossal nerve E) arytenoideus recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
5 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 5 of 8 31) What terms describe the actions performed by a person sitting down from a standing position? A) flexion of the femur, extension of the crus B) extension of the of femur, flexion of the crus C) flexion of both the femur and crus D) extension of both the femur and crus E) none of the above 32) What is the insertion of the internal abdominal oblique? A) lower costae B) transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae C) iliac crest D) linea alba E) inguinal ligament 33) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its insertion. A) infraspinatus greater tubercle B) biceps femoris fibular head C) semimembranosus linea aspera D) quadriceps patella E) peroneus brevis tuberosity of metatarsal V 34) Identify the INCORRECTLY stated relationship. A) the biceps brachii is anterior to the brachialis B) the adductor magnus is anterior to the semimembranosus C) the multifidus is superficial to the short rotatores D) the subscapularis is superficial to the serratus anterior where they overlap E) the flexor hallucis longus muscle is medial to the flexor digitorum longus muscle 35) Identify the INCORRECTLY stated relationship. A) the palmaris longus is anterior to the flexor digitorum superficialis B) the sternocleidomastoid is superficial to the platysma C) abductor hallucis is medial to abductor digiti minimi D) the tendon of the plantaris is deep to the medial head of the gastrocnemius E) gluteus medius is deep to gluteus maximus where they overlap 36) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its insertion. A) subclavius first costa B) flexor carpi ulnaris pisiform C) tibialis anterior first metatarsal and cuneiform D) iliacus lesser trochanter E) gastrocnemius calcaneal tuberosity 37) Which of the following muscles does NOT traverse the knee? A) sartorius B) semitendinosus C) popliteus D) soleus E) gastrocnemius 38) Which of the following muscles either originates from or inserts on the femur? A) semitendinosus B) gracilis C) sartorius D) rectus femoris E) iliopsoas
6 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 6 of 8 39) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and function. A) pubococcygeus continence B) extensor carpi ulnaris carpal adduction C) flexor carpi ulnaris carpal adduction D) tibialis anterior dorsiflexion E) palmar interossei digital flexion and adduction 40) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle or group and innervation. A) iliocostalis thoracodorsal nerve B) tensor fasciae latae superior gluteal nerve C) peroneus longus superficial peroneal nerve D) triceps radial nerve E) hypothenar ulnar nerve 41) Muscles of the anterior brachium are innervated by which of the following nerves? A) lateral pectoral B) suprascapular C) musculocutaneous D) median E) radial 42) Which of the following muscles is innervated by two different nerves? A) pectoralis minor B) biceps femoris C) flexor digitorum superficialis D) masseter E) sternocleidomastoid 43) Identify the pair of synergistic muscles. A) pectineus adductor brevis B) serratus posterior superior serratus posterior inferior C) latissimus dorsi erector spinae D) teres major teres minor E) temporalis digastric 44) What is the innervation of the levator palpebrae superioris? A) facial nerve B) ophthalmic nerve C) oculomotor nerve D) trochlear nerve E) abducens nerve 45) Which of the following muscles does NOT insert on the radius? A) pronator quadratus B) supinator C) biceps brachii D) triceps E) brachioradialis 46) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and function. A) sternocleidomastoid cranial/cervical rotation B) rectus abdominis abdominal flexion C) tibialis anterior hallucal extension D) puborectalis continence E) lateral pterygoideus mandibular protraction
7 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 7 of 8 47) Identify the INCORRECT association of passage and structure(s) that pass through it. A) deltopectoral triangle cephalic vein B) intertubercular sulcus tendon of long head of biceps brachii C) lesser sciatic foramen piriformis D) bifurcation of tendons of tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis tendons of flexor digitorum profundus E) tarsal tunnel tendon of tibialis posterior 48) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and function. A) gastrocnemius plantarflexion B) lateral obliquus ocular abduction C) peroneus longus inversion D) quadriceps crural extension E) quadratus femoris lateral femoral rotation 49) Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding the adductor longus muscle. A) it inserts on the linea aspera B) it inserts on the adductor tubercle C) it is innervated by the obturator nerve D) its primary antagonists are the gluteus medius and minimus E) it is directly anterior to the adductor magnus 50) Identify the INCORRECT association of passage and structure(s) that pass through it. A) carpal tunnel tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis B) quadrangular space axillary nerve C) carpal tunnel tendons of flexor digitorum profundus D) pelvic diaphragm vagina E) adductor hiatus femoral artery 51) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and function. A) gluteus maximus femoral extension B) pectoralis major brachial flexion C) pectoralis minor brachial flexion D) semimembranosus crural flexion (in part) E) semimembranosus femoral extension (in part) 52) Which of the following passes between the anterior and middle scalene muscles? A) phrenic nerve B) carotid sheath C) subclavian vein D) roots of the brachial plexus E) internal jugular vein 53) Which of the following muscles is an abductor? A) styloglossus B) levator costarum C) digastric D) rhomboideus minor E) sternocleidomastoid 54) Identify the pair of synergistic muscles. A) serratus anterior trapezius B) orbicularis oculi orbicularis oris C) latissimus dorsi pectoralis major D) serratus posterior superior serratus posterior inferior E) rectus femoris biceps femoris
8 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 8 of 8 55) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its origin. A) brachioradialis lateral humeral epicondyle B) stylohyoideus styloid process C) omohyoideus superior margin of scapula D) supraspinatus supraspinous fossa E) temporalis temporal fossa and line 56) Which of the following pairs of muscles have the same innervation? A) flexor carpi radialis and flexor carpi ulnaris B) respiratory diaphragm and innermost intercostal C) coracobrachialis and serratus anterior D) iliacus and sartorius E) latissimus dorsi and trapezius 57) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its insertion. A) occipitalis galea aponeurotica B) palmaris longus palmar aponeurosis C) respiratory diaphragm central tendon D) plantaris plantar aponeurosis E) biceps brachii bicipital aponeurosis (in part) 58) Identify the INCORRECT association of muscle and its origin. A) long head of triceps infraglenoid tubercle B) biceps femoris ischial tuberosity C) quadratus lumborum iliac crest D) obturator externus obturator membrane E) trapezius scapular spine 59) Which of the following muscles is innervated by the median nerve? A) palmar interosseous B) brachialis C) brachioradialis D) adductor pollicis E) opponens pollicis 60) Identify the INCORRECT statement. A) lumbricals originate from the tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus B) the pectoralis major inserts on the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii C) the quadratus plantae inserts on the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus D) the gluteus maximus inserts on the iliotibial tract (in part) E) the gemelli muscles insert on the tendon of the obturator internus
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
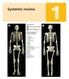 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Appendix. Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance
 Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Muscular System. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
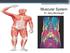 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp ) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a
 The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Chapter 10. The Muscular System. AP1-Lecture Goodwin College. Introduction. In this chapter we will cover: 4/27/2015
 Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
3D Digital Human Information Modeling
 3D Digital Human Information Modeling SC24 WG9 & Web3D Meetings January 21-24, 2019 Myeong Won Lee (U. of Suwon) and Seung-Pyo Lee (Seoul National U.) Topics for 3D Digital Human Information Model A whole
3D Digital Human Information Modeling SC24 WG9 & Web3D Meetings January 21-24, 2019 Myeong Won Lee (U. of Suwon) and Seung-Pyo Lee (Seoul National U.) Topics for 3D Digital Human Information Model A whole
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla
 Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Part One Anatomy Practice MeQ's
 Part One natomy Practice MeQ's 1. Regarding the flexor retinaculum, which of the following statements is FLS?: o It is crossed by palmaris longus, the palmar branch of the median nerve, and the superficial
Part One natomy Practice MeQ's 1. Regarding the flexor retinaculum, which of the following statements is FLS?: o It is crossed by palmaris longus, the palmar branch of the median nerve, and the superficial
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
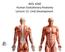 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Skeletal Muscular system Objectives Know muscle Group or compartment Location Function Origin and insertion Innervation Synergists and antagonists
 Skeletal Muscular system Objectives Know muscle Group or compartment Location Function Origin and insertion Innervation Synergists and antagonists Skeletal Muscular system voluntary movements of body through
Skeletal Muscular system Objectives Know muscle Group or compartment Location Function Origin and insertion Innervation Synergists and antagonists Skeletal Muscular system voluntary movements of body through
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016
 LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association
 C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration-
 This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
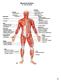 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
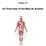 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
