Intrinsic renal cell and leukocyte-derived TLR4 aggravate experimental anti-mpo glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
- Merryl Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 & Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Intrinsic renl cell nd leukocyte-derived TLR4 ggrvte experimentl nti-mpo glomerulonephritis Shun A. Summers, Betty S. vn der Veen, Kim M. O Sullivn, Poh-Yi Gn, Joshu D. Ooi, Peter Heering, Simon C. Stchell, Peter W. Mthieson, Moin A. Sleem 4, Kumr Visvnthn, Stephen R. Holdsworth,5 nd A. Richrd Kitching,5 Deprtment of Medicine, Centre for Inflmmtory Diseses, Monsh University, Clyton, Victori, Austrli; Deprtment of Pthology nd Medicl Biology, University Medicl Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlnds; Acdemic Renl Unit, University of Bristol, Southmed Hospitl, Bristol, UK; 4 Children s Renl Unit, University of Bristol, Southmed Hospitl, Bristol, UK nd 5 Deprtment of Nephrology, Monsh Medicl Centre, Clyton, Victori, Austrli Antimyeloperoxidse ntiodies cn cuse crescentic glomerulonephritis nd pulmonry hemorrhge. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) respond to infectious gents ctivting host defenses, wheres infections potentilly initite disese nd provoke relpses. Neutrophils were found to e key effector cells of injury in experimentl models, s disese does not occur in their sence nd injury is enhnced y lipopolyscchride (LPS). In this study, highly purified LPS ( pure TLR4 lignd) cted with ntimyeloperoxidse ntiodies to synergisticlly increse kidney nd lung neutrophil recruitment nd functionl injury; effects rogted in TLR4-deficient mice. Incresed kidney TLR4 expression fter stimultion predominntly occurred in glomerulr endothelil cells. Enhnced glomerulr neutrophil recruitment correlted with incresed kidney mrna expression of CXCL nd CXCL (homologs of humn CXCL8), wheres their preemptive neutrliztion decresed neutrophil recruitment. Disese induction in one mrrow chimeric mice showed tht TLR4 in oth one mrrow nd renl prenchyml cells is required for mximl neutrophil recruitment nd glomerulr injury. Further studies in humn glomerulr cell lines stimulted with LPS found tht glomerulr endothelil cells were the prominent sources of CXCL8. Thus, our results define role for TLR4 expression in one mrrow derived nd glomerulr endothelil cells in neutrophil recruitment nd susequent functionl nd histologicl renl injury in experimentl ntimyeloperoxidse glomerulonephritis. Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74; doi:.8/ki..7; pulished online 5 Septemer KEYWORDS: nti-mpo ntiody; chemokine; endothelil cell; neutrophil Correspondence: A. Richrd Kitching, Deprtment of Medicine, Monsh Medicl Centre, Monsh University, 46 Clyton Rod, Clyton, Victori 68, Austrli. E-mil: richrd.kitching@med.monsh.edu.u Prts of these studies were pulished in strct form (Nephrology (Suppl ): A4, J Am Soc Nephrol 8 Nov(S) A659). Received 7 Decemer 9; revised 5 June ; ccepted July ; pulished online 5 Septemer Smll vessel vsculitis nd puci-immune necrotizing glomerulonephritis (GN) induced y ntineutrophil cytoplsmic ntiodies (ANCAs) trget specific neutrophil cytoplsmic ntigens, myeloperoxidse (MPO), nd proteinse., Comined renl nd pulmonry disese is common in ANCA vsculitis nd hs considerle moridity nd mortlity. Experimentl niml studies hve shown tht ANCA re pthogenic. Pssive trnsfer of ANCA cn induce necrotizing GN nd/or pulmonry cpillritis. 7 Links etween infection nd ANCA vsculitis re well estlished. Sesonl vrition in ptients presenting with the disese suggests correltion with microil infection, 8 infection my predte disese initition nd/or relpse 9 nd prophylctic ntiiotic therpy hs lso een shown to successfully decrese disese relpses in ANCA vsculitis. Infection is likely to e importnt in experimentl ANCA models nd lipopolyscchride (LPS) dose dependently increses renl injury fter the pssive trnsfer of MPO ANCA. 6 Neutrophils re mongst the first immune cells to trffic to inflmed sites. In experimentl ANCA-induced GN neutrophils re the primry effector cells nd neutrophil depletion protects mice from renl injury. 4 In humns, the chemokine CXCL8 (interleukin-8) is potent neutrophil chemottrctnt. 4 Renl iopsies from ptients with ANCA disese demonstrted positive CXCL8 immunostining in crescentic glomerulr lesions, suggesting tht CXCL8 contriutes to glomerulr injury seen in ANCA-ssocited GN. 5 The murine chemokines CXCL (KC) nd CXCL (MIP-), tht ind to CXCR, re homologs of humn CXCL8 6 nd serve s mjor chemottrctnts for neutrophils in mice. 7 Toll-like receptors (TLRs) recognize pthogen ssocited moleculr ptterns from infectious gents nd fter ligtion ctivte immune cells. TLR4 is expressed on neutrophils 8 nd ugments their migrtory responses. 9 Previously, TLR4 hs een demonstrted in the kidney, in the glomerulus on mesngil cells, epithelil cells, nd lso in proximl nd distl tuulr epithelil cells, ut not in glomerulr endothelil cells (GEnCs). Kidney Interntionl () 78,
2 originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN Strting from the known cpcity of LPS to enhnce the ctivity of nti-mpo ntiodies in experimentl systems, 6, we imed to define nd explore pthogenic nd mechnistic role for TLR4 in experimentl ANCA-induced glomerulr neutrophil recruitment. We studied the effect of LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies on glomerulr nd pulmonry neutrophil recruitment, which develops erly in the diseses process nd is TLR4 dependent. Functionl nd histologicl renl injury, which develops lter, is lso TLR4 dependent. TLR4 expression in the glomerulus increses fter LPS nd nti-mpo ntiody stimultion. TLR4 is produced y GEnCs, which re lso positive for CXCL nd CXCL. In vitro LPS stimultion of humn glomerulr cell lines implictes GEnC s mjor source of TLR4. We demonstrte functionl reltionship etween CXCL nd CXCL, glomerulr neutrophil recruitment nd susequent renl injury, nd demonstrte tht full expression of these chemokines is TLR4 dependnt. Furthermore, we demonstrte in humn cell lines tht CXCL8 mrna nd protein production increses considerly fter LPS stimultion, predominntly medited through GEnC. Finlly using one mrrow (BM) chimeric mice we identify the individul contriutions of BM nd tissue cell (TC) TLR4 to neutrophil recruitment nd glomerulr injury. RESULTS ANCA/LPS-induced glomerulr neutrophil recruitment nd lung MPO ctivity Glomerulr nd pulmonry neutrophil recruitment ws induced y dministering either highly purified LPS (hplps, which specificlly engges TLR4) with nti-mpo ntiodies, nti-mpo ntiodies lone, or hplps nd control (ntiovlumin (OVA)) ntiodies to geneticlly intct wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice. WT mice were injected with hplps, then nti-mpo or nti-ova ntiodies t h nd killed fter further h. LPS, nti-mpo ntiodies, or oth induced glomerulr leukocyte recruitment (Figure ). Control nti- OVA ntiodies lone hd no effect on glomerulr neutrophil recruitment compred with untreted mice (untreted mice.5±. neutrophils/glomerulr cross-section (n/gcs), mice given nti-ova ntiodies.4±. n/gcs). Mice injected with nti-mpo ntiodies lone exhiited significnt glomerulr neutrophil influx, similr to tht oserved in mice treted with hplps nd nti-ova ntiodies. Together, hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies synergisticlly incresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment. Representtive photomicrogrphs of glomerulr neutrophil recruitment re shown (Figure c e). In the sme studies, neutrophil ccumultion in lung tissue ws ssessed y mesuring pulmonry MPO ctivity (Figure ). Untreted WT mice hd.6±. U of MPO ctivity per grm of lung tissue. Administrtion of either hplps nd nti-ova ntiodies, or nti-mpo ntiodies lone incresed MPO ctivity to similr degree. Administrtion of hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies led to further increse in lung MPO ctivity. Anti-OVA ntiodies lone hd miniml effect (.4±.9 U/g). The requirement for TLR4 in mximl neutrophil recruitment ws confirmed y compring TLR4 / mice with WT mice (Figure f nd g). Glomerulr neutrophil recruitment in untreted TLR4 / mice (.±.6n/gcs) ws similr to untreted WT controls. Neutrophil recruitment in TLR4 / mice given hplps (with nti-ova ntiodies) ws similr to untreted TLR4 / mice. TLR4 / mice given nti-mpo ntiodies hd similr glomerulr neutrophil numers to WT mice given nti-mpo ntiodies, ut TLR4 / mice given hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies recruited fewer neutrophils to glomeruli compred with WT given hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies. Similr TLR4-dependent ptterns were present in the pulmonry leukocyte recruitment, lthough in the sence of TLR4 (seline ctivity in untreted TLR4 / mice.6±.7 U/g), pulmonry MPO ctivity ws reduced in ll three groups of mice: those given hplps nd nti-ova ntiodies, hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies, s well s those injected with nti-mpo ntiodies lone. TLR4 is expressed in murine glomeruli nd produced y murine GEnCs nd humn intrinsic glomerulr cells We then exmined TLR4 production in murine kidneys nd humn glomerulr cells. TLR4 protein ws redily detected in glomeruli of WT mice treted with LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies. TLR4 / mice treted with nti-mpo ntiodies were negtive control. Using confocl microscopy TLR4 ws coloclized with GEnCs. Other glomerulr cell types, proly podocytes nd possily mesngil cells lso expressed TLR4. Illustrtive photomicrogrphs re shown in Figure d. TLR4 mrna expression from glomerulr nd tuulr interstitil comprtments ws ssessed using lser cpture microdissection (Figure e; the men vlue for the tuulointerstitium ws ssigned vlue of ). Bseline TLR4 mrna expression in glomeruli ws -fold higher thn the tuulointerstitium nd incresed further 4 h fter LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies. There ws no chnge in tuulointerstitil TLR4 expression. We then nlyzed TLR4 mrna expression in humn conditionlly immortlized GEnC (cigenc), podocytes, nd mesngil cell lines fter stimultion with LPS (Figure f; the men vlue for podocyte sl TLR4 mrna expression ws ssigned vlue of ). Bsl TLR4 mrna expression ws highest in cigenc nd not detected in mesngil cells. Flow cytometric nlysis of cigenc for TLR4 protein confirmed the expression of TLR4 protein (Figure g). After LPS, TLR4 mrna expression ws incresed t 4 h in cigenc, ut podocyte nd mesngil cell TLR4 mrna expression ws unchnged. CXCL nd CXCL is induced in kidney tissue fter hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies To investigte mechnisms of glomerulr neutrophil recruitment we studied the neutrophil chemottrctnts CXCL nd CXCL in renl tissue. CXCL nd CXCL expression ws ssessed 5 h fter oth hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies. Compred with untreted WT mice (mens for untreted WT CXCL or CXCL mrna expression were ssigned vlue of ), CXCL mrna expression incresed 5 h fter 64 Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
3 SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN originl rticle Neutrophils/gcs αmpo A Lung MPO U 4 αmpo A c d e f Neutrophils/gcs WT mice TLR4 / mice αmpo A g Lung MPO U 4 WT mice TLR4 / mice αmpo A Figure Leukocyte recruitment fter nti-mpo ntiody dministrtion. () Glomerulr neutrophil recruitment to C57BL/6 wild-type (WT, n ¼ 6) mice. Highly purified lipopolyscchride (hplps) nd nti-ova (OVA) ntiodies (n ¼ 6) or nti-mpo (MPO) ntiodies lone (n ¼ 6) incresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment compred with untreted WT nimls (n ¼ 4), represented s dotted line (Po.). Co-dministrtion of hplps nd MPO ntiodies (n ¼ 6) induced more neutrophil recruitment compred with hplps nd OVA ntiodies or MPO ntiodies lone. () Pulmonry MPO ctivity in WT mice. Untreted WT mice hd.6 U of MPO ctivity/g (dotted line); MPO ctivity ws incresed in ll ntiody injected groups, compred with untreted mice. Significntly more pulmonry MPO ctivity ws seen in the WT mice treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies compred with other tretment groups. Photomicrogrphs representtive of glomerulr neutrophil recruitment, with one glomerulr neutrophil in WT mice treted with hplps nd OVA ntiodies (c) or MPO ntiodies lone (d), or three neutrophils in mice treted with LPS nd MPO ntiodies (e) re demonstrted. In pnels f nd g glomerulr nd lung neutrophil recruitment in WT mice re compred with recruitment in TLR4 / mice (n ¼ 4). Neutrophil recruitment in untreted in TLR4 / mice (n ¼ 5) did not differ from untreted WT mice (dotted line). Glomerulr neutrophil recruitment (f) nd lung MPO ctivity (g) decresed in TLR4 / mice compred with WT mice. Po.5, Po.. Originl mgnifiction x4. gcs, glomerulr cross-section; MPO, myeloperoxidse; OVA, ovlumin; TLR, Toll-like receptor. hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies, in prtly TLR4- dependent mnner (Figure ). A similr pttern ws seen with CXCL mrna expression, ut the reduction in gene expression in the sence of TLR4 ws more profound (Figure ). Immunohistochemicl exmintion of glomeruli for CXCL nd CXCL demonstrted miniml signl in untreted WT mice, with incresed expression in ll experimentl groups (dt not shown). WT mice given hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies exhiited incresed glomerulr (with surrounding tuulr) stining of CXCL nd CXCL when compred with mice given either hplps with nti-ova ntiodies, or nti-mpo ntiodies lone. As hypothesized, compred with WT mice, CXCL nd CXCL stining ws decresed in TLR4 / mice given hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies (Figure c nd d). Representtive kidney sections of CXCL (Figure e nd f) nd CXCL (Figure g nd h) immunostining in WT nd TLR4 / mice treted with hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies re shown. CXCL nd CXCL coloclize with GEnCs, which lso express TLR4 To determine whether murine GEnCs re source of CXCL nd CXCL production, we immunostined kidneys from WT mice treted with LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies for n endothelil mrker (CD), TLR4, CXCL, nd CXCL using confocl microscopy CXCL coloclized to GEnC nd to Kidney Interntionl () 78,
4 originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN c d e f g cigenc Glomeruli Tuulointerstitium Podocytes Mesngil cells 8 TLR4 mrna (log) h h 4 h 4 h After TLR4 mrna h 4 h After LPS stimultion Count 6 4 i ii iii 4 5 MFI TLR4 expression Figure TLR4 stining nd expression in the kidney. Positive TLR4 stining (green) ws detectle in glomeruli of WT mice treted with LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies (). No TLR4 stining ws visile in TLR4 / mice treted with nti-mpo ntiodies (). Glomeruli from WT mice were stined with nti-cd ntiodies to identify endothelil cells (red stining) (c). Merged imge of TLR4 nd endothelil cell stining tht identifies endothelil cell TLR4 production (yellow) (d). After stimultion with LPS nd nti-mpo (MPO) ntiodies there ws n increse in TLR4 mrna expression in microdissected murine glomeruli, nd little chnge in TLR4 expression ws seen in the tuulointerstitium (n ¼ 4) (e). In humn conditionlly immortlized cigenc lines, seline TLR4 expression ws incresed compred with oth podocytes nd mesngil cells (which did not express TLR4), n ¼ 6 for ll experimentl groups (f). After LPS stimultion TLR4 expression incresed only in endothelil cells. (g) TLR4 protein expression y cigenc. Flow cytometric nlysis of cultured cigenc incuted with no ntiody (i), isotype control ntiody (ii), nd nti-humn TLR4 ntiody (iii) demonstrted TLR4 protein expression. Po.5, Po., Po.. Originl mgnifiction x8. A, ntiody; cigenc, conditionlly immortlized glomerulr endothelil cell, LPS, lipopolyscchride; MFI, men florescence intensity; MPO, myeloperoxidse; TLR, Toll-like receptor; WT, wild type. glomerulr cells producing TLR4. GEnC produce oth TLR4 nd CXCL (Figure 4 f). Similrly, CXCL coloclized with GEnC nd cells producing TLR4. Furthermore, we demonstrted tht GEnC cn produce CXCL nd TLR4 (Figure 4g l). Relevnt negtive controls re shown in Supplementry Figure S. Neutrophil recruitment is CXCL nd CXCL dependent Given the enhnced expression of CXCL nd CXCL in experimentl nti-mpo ntiody-induced glomerulr neutrophil recruitment, we neutrlized either protein y dministering monoclonl nti-cxcl ntiody, n nti-cxcl ntiody, or isotype control h efore hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies nd ssessed neutrophil recruitment. Compred with isotype control ntiody, mice given either nti-cxcl or nti-cxcl ntiody efore hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies showed significnt decreses in glomerulr neutrophil recruitment nd lung MPO ctivity (Figure 5 ), confirming functionl role for oth CXCL nd CXCL in glomerulr nd pulmonry neutrophil recruitment. TC TLR4 contriutes to neutrophil recruitment Given the expression of TLR4 in glomeruli, we defined the contriutions of BM nd TC TLR4 (glomerulr nd lung) expression in neutrophil recruitment y injecting LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies into TLR4 BM chimeric mice. Chimeric mice were generted y injecting intct or deficient 66 Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
5 SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN originl rticle CXCL Fold increse c CXCL stining 5 5 TLR4 / mice WT mice LP/αOVA A αmpo A lone TLR4 / mice WT mice αmpo A lone CXCL Fold increse d CXCL stining TLR4 / mice WT mice αmpo A lone LPS/αMPO-A TLR4 / mice WT mice αmpo A lone CXCL CXCL e g WT TLR4 / f WT TLR4 / h Figure CXCL nd CXCL kidney mrna expression nd immunostining. Using tissues from experiments detiled in Figure, kidney CXCL mrna expression ws incresed in WT mice fter hplps nd nti-ova (OVA) ntiodies (Po.), n ¼ 6, MPO ntiodies lone (Po.5), n ¼ 6, nd hplps nd MPO ntiodies (Po.), n ¼ 6. Compred with WT mice given hplps nd MPO ntiodies, TLR4 / mice (closed rs) treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies expressed less CXCL (), n ¼ 4. Kidney CXCL mrna expression in WT mice incresed fter tretment with hplps nd MPO ntiodies (Po.5). Compred with WT mice treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies, TLR4 / mice treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies expressed less CXCL (). Immunostining showed tht CXCL (c) nd CXCL (d) were significntly incresed in WT mice treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies compred with ll other groups. Representtive glomerulr sections from (e) WT mice nd (f) TLR4 / mice treted with hplps nd MPO ntiodies nd immunostined for CXCL re shown. Similrly treted (g) WT nd (h) TLR4 / glomeruli immunostined for CXCL re shown. Blck rrowheds represent res where stining intensity ws most pronounced. Incresed stining ws seen in WT mice. Po.5, Po., Po.. Originl mgnifiction 4. hplps, highly purified lipopolyscchride; MPO, myeloperoxidse; OVA, ovlumin; WT, wild type. BM into irrdited mice. WT BM trnsplnted into WT mice (BM þ TC þ ; shm chimers) were positive control, nd TLR4 TC intct, BM TLR4 deficient (BM C þ ) nd TC TLR4 deficient, BM intct (BM þ TC ) chimers were studied. Both BM nd TC TLR4 re required for mximl neutrophil recruitment. Compred with BM þ TC þ chimers, glomerulr neutrophil recruitment ws reduced in either TLR4 BM TC þ chimers or TLR4 BM þ TC mice (Figure 6), ut BM-derived TLR4 hs more prominent role. Both BM nd TC TLR4 re required for mximum pulmonry neutrophil recruitment (Figure 6). Glomerulr CXCL nd CXCL production ws ssessed in kidneys of chimeric mice. Compred with shm chimers (BM þ TC þ ), semiquntittive ssessment of CXCL nd CXCL showed reduction in oth chemokines in TLR4 BM TC þ mice nd BM þ TC mice (Figure 6c nd d), corresponding with the reduction in neutrophil recruitment. The trend towrds decresed CXCL nd CXCL mrna expression in kidneys of BM TC þ nd BM þ TC chimeric mice did not rech sttisticl significnce (dt not shown). CXCL8 is produced y humn GEnCs fter LPS stimultion Hving estlished role for TLR4 on intrinsic renl cells in inducing CXCL nd CXCL dependnt experimentl glomerulr neutrophil recruitment, we nlyzed humn glomerulr cells for CXCL8 production (CXCL nd CXCL re the murine homologs of CXCL8). Bseline men cigenc mrna expression ws ssigned vlue of. Although CXCL8 mrna expression ws incresed in cigenc, podocyte, nd mesngil cells (Tle ), the reltive increse ws most pronounced in cigenc (Figure 7). Bsl CXCL8 production ws highest in podocytes (Tle ), however, fter stimultion the increse is most pronounced in cigenc, with significnt increses t, 4, nd 4 h (Figure 7). These increses in oth mrna expression nd protein production demonstrte tht GEnC re the cell type most responsile for enhnced CXCL8 production. The contriution of TLR4, CXCL, CXCL, nd BM nd TC TLR4 to renl injury Administrtion of hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies ( mg/g) induced functionl renl injury (luminuri nd hemturi), nd glomerulr hypercellulrity with focl nd segmentl lesions, including firin deposition in WT mice t dy 6 (Figure 8 d), significntly decresed in TLR4 / mice. Representtive photomicrogrphs of renl injury showing glomerulr hypercellulrity nd glomerulr firin stining in WT, reduced in TLR4 / mice re shown in Figure 8e h. Kidney Interntionl () 78,
6 originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN CD TLR4 c CXCL CXCL d e f CXCL+CD CXCL+TLR4 CXCL+TLR4+CD CD TLR4 g h i CXCL CXCL j k l CXCL+CD CXCL+TLR4 CXCL+TLR4+CD Figure 4 Glomerulr endothelil cell, CXCL, CXCL, nd TLR4 colocliztion. Kidneys from WT mice given LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies were stined for () CD (lue), () TLR4 (green), nd (c) CXCL (red). Endothelil cells nd CXCL coloclized (mgent) (d). CXCL nd TLR4 lso coloclized (yellow) (e), nd merged three-color imge showed tht some endothelil cells were positive for oth CXCL nd TLR4 (white) (f). To ssess CXCL production kidneys were stined for (g) CD (lue), (h) TLR4 (green), nd (i) CXCL (red). CXCL coloclized with glomerulr endothelil cells (mgent) (j) nd TLR4 (yellow) (k). Merged three-color imge showing tht some endothelil cells were positive for oth CXCL nd TLR4 (white) (l). Originl mgnifiction x8. LPS, lipopolyscchride; MPO, myeloperoxidse; TLR, Toll-like receptor; WT, wild type. As CXCL nd CXCL were importnt in glomerulr neutrophil recruitment, we defined their role in the development of histologicl nd functionl renl injury y extending studies to dy 6. Compred with mice given ANCA/LPS nd isotope control ntiodies, luminuri nd hemturi were decresed fter the dministrtion of nti-cxcl ntiody nd ANCA/LPS, wheres trend to decresed injury ws seen fter the dministrtion of nti- CXCL ntiody (Figure 9 nd ). Aluminuri, mesured in the initil 4 h in mice dministered control ntiody nd ANCA/LPS (7±9 mg/4 h) ws decresed in mice given nti-cxcl ntiody nd ANCA/LPS (55±4 mg/4 h, Po.) nd nti-cxcl nd ANCA/LPS (87± mg/ 4 h, Po.). Glomerulr histologicl injury (Figure 9c nd d) ws ttenuted fter the dministrtion of CXCL or CXCL neutrlizing ntiodies, though reduced hypercellulrity fter nti-cxcl ntiody did not rech sttisticl significnce. Hving demonstrted role for oth BM nd glomerulr TLR4 in neutrophil recruitment, we confirmed tht oth re required for mximl renl injury. Compred with BM þ TC þ shm chimers, luminuri ws decresed 68 Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
7 SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN originl rticle Neutrophils/ gcs Control A CXCL A CXCL A Control A CXCL A CXCL A in oth BM TC þ nd BM þ TC mice, (Figure nd ; trends to reduction in hemturi did not rech significnce). Histologicl injury ws reduced in BM TC þ nd BM þ TC mice with less glomerulr firin deposition nd hypercellulrity (Figure c nd d). Lung MPO U/g Figure 5 Neutrophil recruitment fter neutrliztion of CXCL or CXCL. Administering CXCL (n ¼ 4) or CXCL (n ¼ 4) neutrlizing ntiodies prior to the dministrtion of hplps nd nti-mpo (MPO) ntiodies decresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment () nd lung MPO ctivity () reltive to controltreted mice (n ¼ 8). Po.5, Po., Po.. A, ntiody; gcs, glomerulr cross-section; MPO, myeloperoxidse. Neutrophils/gcs c CXCL stining Lung MPO U/g CXCL stining d Figure 6 Assessment of glomerulr leukocyte recruitment, lung MPO ctivity, nd glomerulr chemokine stining in BM chimeric wild type (WT)-WT mice (one mrrow (BM) þ, tissue cell (TC) þ, n ¼ 8), TLR4 / -WT mice (BM TC þ, n ¼ 8), nd WT-TLR4 / mice (BM þ TC, n ¼ 8) injected with hplps nd nti-mpo (MPO) ntiodies. Glomerulr neutrophil recruitment () ws decresed in oth BM TC þ nd BM þ TC compred with BM þ TC þ mice. There ws decresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment in BM TC þ mice compred with BM þ TC mice. Lung MPO ctivity ws decresed in oth BM TC þ nd BM þ TC mice compred with BM þ TC þ mice (). Kidney CXCL (c) nd CXCL (d) immunostining ws decresed in BM TC þ nd BM þ TC mice compred with BM þ TC þ mice. Po.5, Po., Po.. gcs, glomerulr cross-section; MPO, myeloperoxidse. Tle CXCL8 mrna nd protein production in humn glomerulr cell lines t,, 4, nd 4 h fter lipopolyscchride stimultion CXCL8 mrna h h 4 h 4 h cigenc.±. 46.±. ##.4±.6 ## 5.5±.8 ## Podocytes.±. 8.±.9 ## 9.8±.8 ## 7.9±.9 ## Mesngil cells.±..4±. ##.±. #.±. CXCL8 protein (ng/ml) h h 4 h 4 h cigenc.±..±. 9.±.5 ## 5.8±.9 ## Podocytes 7.±. 4.5±.8 8.5±.7 4.8±4. # Mesngil cells.±..±..±..5±. ## Arevition: cigenc, conditionlly immortlized glomerulr endothelil cells. Bseline mrna expression in cigenc ws ssigned vlue of. Incresed expression is seen in ll cell lines, most pronounced t h. CXCL8 protein production lso increses in ech cell type, most pronounced fter 4 h. # Po. ## Po. compred with t= h. Fold increse Fold increse 6 4 cigenc Podocytes Mesngil cells 4 4 Time (h) fter LPS stimultion cigenc Podocytes Mesngil cells 4 4 Time (h) fter LPS stimultion Figure 7 CXCL8 mrna nd protein production in humn glomerulr cell lines. After lipopolyscchride (LPS) stimultion, CXCL8 mrna expression ws incresed in ll three cell types, most pronounced in conditionlly immortlized glomerulr endothelil cells (cigenc) (). Similrly, cigenc produced the gretest proportionl increse in CXCL8 protein production (), n ¼ 6 for ll experimentl groups. Asolute vlues (in pg/ml) of CXCL8 mesurements re shown in Tle. Po.5, Po.. DISCUSSION These studies define roles for oth BM cell nd TC-derived TLR4 in the pthogenesis of neutrophil recruitment in LPS/ nti-mpo ntiody renl nd lung injury, nd the roles of Kidney Interntionl () 78,
8 % Firin deposition originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN Aluminuri (µg/4 h) e c % Firin deposition 4 WT WT TLR4 / TLR4 / f Hemturi d 5 Cells/gcs 5 WT WT TLR4 / TLR4 / Aluminuri (µg/4 h) c Control A Control A CXCL A CXCL A CXCL A CXCL A Hemturi d 5 Cells/ gcs 5 Control A Control A CXCL A CXCL A CXCL A CXCL A g h Figure 9 Functionl nd histologicl renl injury in WT mice treted with LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies with previous neutrliztion of CXCL (n ¼ 6) nd CXCL (n ¼ 6). Compred with control ntiody treted mice (n ¼ 6), 4 h luminuri () nd dipstick hemturi () were significntly decresed fter CXCL neutrliztion; trends fter dministrtion of CXCL neutrlizing ntiody did not rech significnce. Less glomerulr firin deposition (c) ws evident with neutrliztion of either CXCL or CXCL, wheres compred with control ntiody treted mice, hypercellulrity ws decresed with neutrliztion of CXCL (d). Po.5, Po., Po.. A, ntiody; LPS, lipopolyscchride; MPO, myeloperoxidse; WT, wild type. 4 Figure 8 Functionl nd histologicl renl injury in WT nd TLR4 / mice treted with LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies. At 6 dys fter the dministrtion of MPO ntiody/lps 4 h luminuri (), dipstick hemturi (), glomerulr firin deposition (c), nd glomerulr hypercellulrity (d) ws ttenuted in TLR4 / mice (n ¼ 6) compred with WT controls (n ¼ 6). The dotted line in () nd (d) represents men vlues in untreted WT mice. Representtive figures re shown demonstrting glomerulr injury in WT mice (e) compred with TLR4 / mice (f). More glomerulr firin deposition ws seen in WT mice (g) compred with TLR4 / mice (h). Po.5, Po., Po.. Originl mgnifiction x4. gcs, glomerulr cross-section; LPS, lipopolyscchride; MPO, myeloperoxidse; TLR, Toll-like receptor; WT, wild type. Aluminuri (µg/4 h) c % Firin deposition Hemturi d Cells/ gcs 5 5 CXCL nd CXCL. After stimultion, the glomerulus is the mjor site of TLR4 expression in the kidney, wheres GEnC re the cell type most responsile. Both BM nd TC TLR4 re required for full expression of CXCL nd CXCL, nd mximl neutrophil recruitment. Murine GEnC re source of TLR4, CXCL, nd CXCL, with some GEnC producing oth TLR4 nd neutrophil chemottrctnts. Using humn glomerulr cells, we demonstrted tht fter stimultion Figure Functionl nd histologicl renl injury in BM chimeric mice wild type (WT)-WT mice (one mrrow (BM) þ, tissue cell (TC) þ, n ¼ 7), Toll-like receptor (TLR4 / ) -WT mice (BM TC þ, n ¼ 6), nd WT-TLR4 / mice (BM þ TC, n ¼ 7) injected with hplps nd MPO ntiodies. Compred with shm chimers (BM þ TC þ ) 4 h luminuri () ws decresed in BM TC þ nd BM þ TC chimers. There ws non-significnt trend to decrese in dipstick hemturi (). Glomerulr firin deposition (c) nd glomerulr hypercellulrity (d) ws decresed in BM TC þ nd BM TC þ chimeric mice compred with shm chimers BM þ TC þ.po.5, Po., Po.. 7 Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
9 SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN originl rticle GEnC re lrgely responsile for the increse in CXCL8 expression nd protein production. In vivo studies t lter time point confirmed the functionl relevnce of oth immune cell- nd TC-derived TLR4, nd of neutrophil chemottrctnts, especilly CXCL. Experimentl nti-mpo ntiody-induced GN is neutrophil dependent. 4 Neutrophils express TLR4, nd LPS tht engges TLR4, is potent stimulus for neutrophil ctivtion. TLR4 ligtion hs pleiotropic effects on neutrophils including neutrophil dhesion,,4 delyed poptosis, enhnced chemokine production nd incresed superoxide genertion. 5 In the current studies, the first series of experiments showed tht dministering oth hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies led to incresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment nd lung MPO ctivity. The effects of hplps on neutrophil recruitment were not seen in TLR4 / mice. These studies re in ccordnce with previous work showing tht LPS hd the cpcity to mrkedly increse nti-mpo ntiodyinduced injury in mice. 6,6 In the current studies, we used three seprte techniques to determine the glomerulr cell types responsile for TLR4 production. First, using confocl microscopy, we demonstrted tht TLR4 is present in murine glomeruli nd coloclizes with GEnC. Other glomerulr cells lso express TLR4 in this model. Second, using microdissected glomeruli, TLR4 mrna expression ws quntitted in glomeruli nd the tuulointerstitium. After the dministrtion of LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies glomerulr, ut not tuulointerstitil TLR4 expression ws incresed. Third, using isolted humn glomerulr cells, we demonstrted tht GEnC express significnt mounts of TLR4, nd tht enhnced mrna expression fter stimultion is ttriutle to GEnC. Therefore, GEnC re significnt sources of glomerulr TLR4 expression fter the dministrtion of LPS nd nti- MPO ntiodies. The sites of intrrenl TLR4 production, oth in the glomerulus nd the tuulointerstitium hve een ddressed in severl studies in other experimentl models. TLR4 hs een loclized to the glomerulus in other models of renl disese.,7,8 In situ hyridiztion showed tht mesngil nd epithelil cells cn express TLR4, 7 wheres in experimentl cryogloulinemic GN podocytes express TLR4. Studies ssessing TLR4 in murine models of tuulointerstitil injury hve demonstrted TLR4 mrna production from primry renl tuulr epithelil cells, 9 wheres confocl microscopy hs suggested TLR4 is present in proximl collecting tuules. From the existing literture nd the current studies, it is cler tht TLR4 expression from intrinsic renl cells cn vry ccording to the nture of the injurious stimulus. In the current studies, the results of comintion of in vivo nd in vitro studies imply role for the glomerulr endothelium in TLR4 responses in the context of LPS nd nti-mpo ntiodies s inititors of injury. In vivo murine models hve shown tht the chemokines CXCL nd CXCL directs neutrophil recruitment to the corne, peritoneum,, nd the joint. 4 The ddition of LPS to ntiglomerulr sement memrne (GBM) gloulin enhnces heterologous renl injury. 7,5 Furthermore, Brown et l., 7 demonstrted tht neutrlizing CXCL nd CXCL, which ws TLR4 medited nd produced y renl cells, resulted in decresed glomerulr injury. We hve demonstrted tht renl CXCL nd CXCL expression (mrna nd protein) increses in TLR4-dependent mnner, oth of which re produced y GEnC. The receptor for CXCL nd CXCL, CXCR, is present on neutrophils, ut LPS does not induce its expression or lter migrtion induced y neutrophil chemottrctnts.,6 The current studies show tht CXCL nd CXCL direct nti-mpo ntiody glomerulr nd pulmonry neutrophil recruitment, s neutrlizing CXCL nd CXCL decresed glomerulr neutrophil recruitment nd lung MPO ctivity erly, nd functionl nd histologicl renl injury lter in the disese. Both BM-derived cells 7 nd n ctivted glomerulr endothelium 8,9 re thought to e importnt in glomerulr neutrophil recruitment in GN induced y nti-mpo ntiodies. The current studies demonstrte tht oth BM nd TC TLR4 re required for mximl glomerulr nd lung neutrophil requirement, underlying seprte roles in the disese process. These effects within the kidney extended out to t lest 6 dys, wherein mice deficient in either BM cell or TC TLR4 exhiited less injury, even in the fce of more profound initil decrese in glomerulr neutrophil recruitment in BM TC þ mice. As CXCL nd CXCL stining ws decresed in BM TC þ mice nd BM þ TC mice, oth BM nd TC-derived TLR4 re importnt in the renl production of CXCL nd CXCL, required for glomerulr neutrophil recruitment. Neutrlizing CXCL t the induction of injury resulted in ttenuted functionl nd histologicl glomerulr injury fter 6 dys; the effects of CXCL lockde were less prolonged. Although the current studies did not ssess the cell type in the lung tht produces neutrophil chemottrctnts, previous studies hve demonstrted tht CXCL nd CXCL re produced y Clr cells (non-cilited roncholveolr epithelil cells in the distl irwys). 4 Previous studies nlyzing lung MPO ctivity to quntitte neutrophil recruitment in TLR4 chimeric mice hve yielded conflicting results, with one study implicting TCs, 4 wheres nother showed BM cell TLR4 to e importnt. 4 In experimentl nti-mpo ntiody-induced neutrophil recruitment MPO ctivity is decresed in oth BM TC þ nd BM þ TC chimeric mice. Oservtions in humn renl iopsies suggest pthogenic role for CXCL8, the key neutrophil-ttrcting chemokine in ANCA GN. 5 Previous studies hve suggested tht CXCL8 cn e produced y generic mcrovsculr endothelil cells (HUVECs), 4 nd cultured humn mesngil cells. 44 We compred CXCL8 production y different humn glomerulr cells, including cigenc, concurrently, in single study. Although seline expression of CXCL8 mrna nd protein production ws higher in podocytes; cigenc showed the most significnt increse in expression nd production fter stimultion, suggesting tht during inflmmtion GEnC produce CXCL8, which is responsile for neutrophil recruitment. Kidney Interntionl () 78,
10 originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN We hve demonstrted pivotl role for oth BM nd intrinsic renl cell TLR4 in glomerulr nd lung neutrophil recruitment nd injury in experimentl ANCA disese. Mximl neutrophil recruitment is dependnt on CXCL nd CXCL, TC expression, which is TLR4 dependnt. Therefore, in ddition to immune cell TLR4-medited ctivtion nd recruitment, the current studies demonstrte role for the glomerulr endothelium, which involves GEnC TLR4 expression, nd CXC chemokine production, tht enhnces neutrophil recruitment. Results from these studies dd to evidence linking infection to utoimmune GN nd provide evidence for possile enefits of TLR inhiition in immune glomerulr disese. MATERIALS AND METHODS Genertion of mouse nti-mpo immunogloulin G (IgG), control mouse nti-ova IgG, nd hplps Murine MPO (mmpo) ws generted s descried previously. 45 Gloulin ws precipitted (5% mmonium sulfte) nd IgG ffinity purified y fst protein liquid chromtogrphy nd dilyzed ginst PBS. For nti-ova ntiodies, Mpo / mice were immunized with OVA using the sme protocol. Endotoxin concentrtion mesured o. ng/ml, Limulus Ameocyte Lyste E-TOXATE (Sigm-Aldrich, St Louis, MO). For in vivo experiments LPS-L654 (Sigm-Aldrich) ws repurified to ensure TLR4 specificity. 46 Experimentl design nd sttisticl nlyses Eight week old mle WT (C57BL/6 (CD45.) nd for some chimeric studies congenic CD45. mice) nd TLR4 / mice were used. Mice were from Monsh University Animl Services (Melourne, Austrli), TLR4 / mice originlly from Professor S Akir. 47 Studies dhered to the Ntionl Helth nd Medicl Reserch Council of Austrli guidelines for niml experimenttion. For neutrophil ccumultion, mice were injected intrperitonlly with hplps ( mg), followed h lter y intrvenous injection of IgG (nti-mpo ntiodies 5 mg/nti-ova (control) ntiodies 5 mg), h lter nimls were killed. For studies nlyzing functionl nd histologicl renl injury, mice were injected with hplps mg followed y nti-mpo ntiodies ( mg/g) nd killed on dy 6. Neutrlizing monoclonl ntiodies directed ginst CXCL or CXCL (MAB 45 nd MAB 45 respectively; R&D systems, Minnepolis, MN, USA) were used with pproprite control ntiodies, (rt IgG nd IgG). At h efore the disese induction, mice were dministered; nti-cxcl-a ( mg), nti- CXCL-A ( mg), or control A ( mg) intrvenous. BM (BM) chimeric mice were generted s previously descried. 48 Flow cytometry demonstrted 49% reconstitution. Dt re expressed s men ± s.e.m. Groups of dt were nlyzed using student s t- test for nlysis of two groups nd one-wy ANOVA (Tukey s post test) for more thn two groups of dt. GrphPd Prism softwre (GrphPd Softwre, Sn Diego, CA, USA) ws used to nlyze the dt. A P-vlue of o.5 ws considered significnt. Assessment of glomerulr neutrophil ccumultion, CXCL nd CXCL, histologicl nd functionl renl injury nd pulmonry MPO Neutrophils were demonstrted y immunoperoxidse stining of periodte lysine prformldehyde fixed tissue s previously descried, 49 minimum of 5 glomeruli were ssessed. Results re expressed s neutrophils per glomerulr cross-section (n/gcs). CXCL nd CXCL immunohistochemicl stining ws performed s previously descried. 5 To ssess the intensity of glomerulr nd juxtposed tuulr CXCL nd CXCL stining semiqunttive intensity stining scle ws used, previously descried nd pulished. 5 Vlues re expressed s numers rnging from 4, where : no stining seen; : stining o5%; : 5 5%; : 5 75%; nd 4: 475% of the glomerulus nd djcent tuules. For histologicl ssessment, 4 consecutive glomeruli/mouse were exmined. Kidneys were fixed with Bouin s fixtive, emedded in prffin nd stined with Periodic Acid-Schiff regent. Firin stining ws performed s previously descried. 5 nd results expressed s percentge of glomeruli with firin deposition. Aluminuri ws mesured on 4 h urine collections using Mouse Alumin ELISA Quntifiction Kit (Bethyl Lortories, Montgomery, TX, USA). Hemturi ws mesured using urinry dipstix (Comur Tests, Roche, Bsel, Switzerlnd). Lung MPO ws used to ssess pulmonry neutrophil ccumultion s previously descried. 5 One unit of MPO ctivity ws defined s chnge in D 46 of. fter min; results re expressed s U of MPO ctivity/g of lung tissue (U/g). For colocliztion experiments using confocl microscopy, kidneys were perfused nd fixed with zinc fixtive, prffin emedded nd sectioned ( mm). For endothelil cell/tlr4 colocliztion, sections were locked (% chicken nd donkey serum in 5% ovine serum lumin), then incuted with rit nti-mouse TLR4 ( mg/ml, Invitrogen, Crlsd, CA, USA) nd rt nti-mouse CD (:5, BD Biosciences, Sn Jose, CA, USA), followed y chicken nti-rit Alex Fluor 488 nd donkey nti-rt Alex Fluor 594 (oth :, Moleculr Proes, Invitrogen, Crlsd, CA, USA). For colocliztion of neutrophil chemokines, TLR4 nd endothelil cells, nti- CD ntiodies were followed y donkey nti-rt Alex Fluor 647 (:, Moleculr Proes). For CXCL colocliztion, ntiodies were rit nti-mouse TLR4 ( mg/ml), nd got nti-mouse CXCL ( mg/ml, R&D Systems), then chicken nti-rit Alex Fluor 488 nd chicken nti-got Alex Fluor 594 (:, Moleculr Proes). For CXCL co-locliztion, ntiodies were got nti-mouse TLR4 ( mg/ml, Snt Cruz Biotechnology, Snt Cruz, CA, USA), with chicken nti-got Alex Fluor 488, nd rit nti-mouse CXCL ( mg/ml, R&D Systems). CXCL signl ws mplified with swine nti-rit HRP conjugted ntiody (:, DAKO, Glostrup, Denmrk) with Cynine--Tyrmide Signl Amplifiction kit (PerkinElmer, Wlthm, MA, USA). For ll smples concurrent negtive controls included sustituting the primry ntiodies for non-immune got, rt or rit IgG, nd dditionlly for TLR4, using TLR4 / mice receiving hplps nd nti-mpo ntiodies. Imges were cquired using Nikon C confocl lser scn hed ttched to Nikon Ti-E inverted microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Jpn) using 488, 56, nd 67 nm lsers. Single plne 5 5 -it imges were cptured in line sequentil mnner (three line verging). Confocl imges were converted using Mciophotonics Imge J softwre (NIH, Bethesd, MD, USA). Culture of humn glomerulr cells nd ssessment of TLR4, interleukin-8, CXCL nd CXCL mrna nd protein Humn cigenc, 5 podocytes 54,55 nd humn immortlized glomerulr mesngil cells, kindly provided y Dr Bns (Ludwig- Mximilins University, Munich, Germny), 56 were cultured. Cells were treted with mg/ml LPS (Escherichi Coli, serotype O6:B6; Sigm-Aldrich) for, 4, or 4 h, medium, collected nd 7 Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
11 SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN originl rticle cells lysed for RNA isoltion. For lser microdissection, glomeruli (.7±.9 6 mm ) nd surrounding tuulointerstitil tissue (.88±.5 6 mm ) were dissected from renl cryosections of nti-mpo IgG/LPS treted mice from previous study 6 using the Lser Root Microem System (P.A.L.M. Micro lser Technology, Bernried, Germny) descried previously. 57 Rel-time PCR nlysis on complementry DNA ws crried out using the ABI Prism 79HT Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Nieuwerkerk /d IJssel, The Netherlnds) using ssy on demnd primer-proe sets for TLR4 (Hs599_m), interleukin-8 (Hs74_m), nd GAPDH (Hs _m; glycerldehyde -phosphte dehydrogense) s the house keeping gene. For mesurement of CXCL nd CXCL rel-time PCR ws s previously descried, stndrdized to 8S, expressed s fold increse reltive to untreted WT mice. 58 For fluorescence-ctivted cell sorting nlysis of TLR4 protein expression on cigenc. 5 cells were cultured for 5 dys, susequently, TLR4 protein ws detected using PE-Cy7 nti-humn TLR4 ntiody (ebioscience, Sn Diego, CA, USA). Men fluorescence intensity of PE-Cy7 ws mesured using LSR-II flow cytometer. CXCL8 ws mesured in culture medium from cigenc, podocytes nd mesngil cells using ELISA (R&D systems). DISCLOSURE All the uthors declred no competing interests. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Shizuo Akir is thnked for the TLR4 / mice. Alice Wright nd Sophi Ling re thnked for technicl ssistnce. Bernhrd Bns is thnked for the immortlized humn mesngil cells. Cmden Lo, Monsh Microimging, is thnked for help with confocl microscopy. These studies were supported y Progrm Grnt (467) nd Postgrdute Reserch Scholrship (SAS 5946) from the Ntionl Helth nd Medicl Reserch Council of Austrli, nd grnt from the Genzyme Renl Innovtions Progrm. PH is supported y grnt from the Dutch Orgniztion for Scientific Reserch (NWO VIDI ). SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Figure S. Further negtive controls for immunofluorescence, showing sustitution of primry ntiodies with pproprite non-immune IgG. Supplementry mteril is linked to the online version of the pper t REFERENCES. Jennette JC, Xio H, Flk RJ. Pthogenesis of vsculr inflmmtion y nti-neutrophil cytoplsmic ntiodies. J Am Soc Nephrol 6; 7: Flk RJ, Jennette JC. Anti-neutrophil cytoplsmic utontiodies with specificity for myeloperoxidse in ptients with systemic vsculitis nd idiopthic necrotizing nd crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med 988; 8: Xio H, Heering P, Hu P et l. Antineutrophil cytoplsmic utontiodies specific for myeloperoxidse cuse glomerulonephritis nd vsculitis in mice. J Clin Invest ; : Xio H, Heering P, Liu Z et l. The role of neutrophils in the induction of glomerulonephritis y nti-myeloperoxidse ntiodies. Am J Pthol 5; 67: Xio H, Schreier A, Heering P et l. Alterntive complement pthwy in the pthogenesis of disese medited y nti-neutrophil cytoplsmic utontiodies. Am J Pthol 7; 7: Huugen D, Xio H, vn Esch A et l. Aggrvtion of nti-myeloperoxidse ntiody-induced glomerulonephritis y cteril lipopolyscchride: role of tumor necrosis fctor-lph. Am J Pthol 5; 67: Little MA, Smyth CL, Ydv R et l. Antineutrophil cytoplsm ntiodies directed ginst myeloperoxidse ugment leukocyte-microvsculr interctions in vivo. Blood 5; 6: Tidmn M, Olnder R, Svlnder C et l. Ptients hospitlized ecuse of smll vessel vsculitides with renl involvement in the period : orgn involvement, nti-neutrophil cytoplsmic ntiodies ptterns, sesonl ttck rtes nd fluctution of nnul frequencies. J Intern Med 998; 44: Stegemn CA, Tervert JW, Sluiter WJ et l. Assocition of chronic nsl crrige of Stphylococcus ureus nd higher relpse rtes in Wegener grnulomtosis. Ann Intern Med 994; : 7.. Pinching AJ, Rees AJ, Pussell BA et l. Relpses in Wegener s grnulomtosis: the role of infection. Br Med J 98; 8: Cpizzi SA, Specks U. Does infection ply role in the pthogenesis of pulmonry vsculitis? Semin Respir Infect ; 8: 7.. Arimur Y, Minoshim S, Kmiy Y et l. Serum myeloperoxidse nd serum cytokines in nti-myeloperoxidse ntiody-ssocited glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol 99; 4: Stegemn CA, Tervert JW, de Jong PE et l. Trimethoprimsulfmethoxzole (co-trimoxzole) for the prevention of relpses of Wegener s grnulomtosis. Dutch Co-Trimoxzole Wegener Study Group. N Engl J Med 996; 5: Yoshimur T, Mtsushim K, Tnk S et l. Purifiction of humn monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotctic fctor tht hs peptide sequence similrity to other host defense cytokines. Proc Ntl Acd Sci USA 987; 84: Cockwell P, Brooks CJ, Adu D et l. Interleukin-8: pthogenetic role in ntineutrophil cytoplsmic utontiody-ssocited glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 999; 55: Zlotnik A, Yoshie O. Chemokines: new clssifiction system nd their role in immunity. Immunity ; : Lee J, Cclno G, Cmerto T et l. Chemokine inding nd ctivities medited y the mouse IL-8 receptor. J Immunol 995; 55: Hyshi F, Mens TK, Luster AD. Toll-like receptors stimulte humn neutrophil function. Blood ; : Fn J, Mlik AB. Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signling ugments chemokine-induced neutrophil migrtion y modulting cell surfce expression of chemokine receptors. Nt Med ; 9: 5.. Bns MC, Bns B, Hudkins KL et l. TLR4 links podocytes with the innte immune system to medite glomerulr injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 8; 9: Shirli AC, Goldstein DR. Trcking the toll of kidney disese. JAmSoc Nephrol 8; 9: Kuligowski MP, Kwn RY, Lo C et l. Antimyeloperoxidse ntiodies rpidly induce lph-4-integrin-dependent glomerulr neutrophil dhesion. Blood 9; : Sroe I, Prince LR, Jones EC et l. Selective roles for Toll-like receptor (TLR) nd TLR4 in the regultion of neutrophil ctivtion nd life spn. J Immunol ; 7: Sroe I, Jones EC, Usher LR et l. Toll-like receptor (TLR) nd TLR4 in humn peripherl lood grnulocytes: criticl role for monocytes in leukocyte lipopolyscchride responses. J Immunol ; 68: Prker LC, Whyte MK, Dower SK et l. The expression nd roles of Toll-like receptors in the iology of the humn neutrophil. J Leukoc Biol 5; 77: Huugen D, vn Esch A, Xio H et l. Inhiition of complement fctor C5 protects ginst nti-myeloperoxidse ntiody-medited glomerulonephritis in mice. Kidney Int 7; 7: Brown HJ, Lock HR, Wolfs TG et l. Toll-like receptor 4 ligtion on intrinsic renl cells contriutes to the induction of ntiody-medited glomerulonephritis vi CXCL nd CXCL. JAmSocNephrol7; 8: Ptole PS, Pwr RD, Lech M et l. Expression nd regultion of Toll-like receptors in lupus-like immune complex glomerulonephritis of MRL-Fs(lpr) mice. Nephrol Dil Trnsplnt 6; : Tsuoi N, Yoshiki Y, Mtsuo S et l. Roles of toll-like receptors in C-C chemokine production y renl tuulr epithelil cells. J Immunol ; 69: 6.. Zhng B, Rmesh G, Uemtsu S et l. TLR4 signling medites inflmmtion nd tissue injury in nephrotoxicity. J Am Soc Nephrol 8; 9: Lin M, Crlson E, Diconu E et l. CXCL/KC nd CXCL5/LIX re selectively produced y cornel firolsts nd medite neutrophil infiltrtion to the cornel strom in LPS kertitis. J Leukoc Biol 7; 8: Kidney Interntionl () 78,
12 originl rticle SA Summers et l.: Both renl cell nd leukocyte TLR4 ggrvte ANCA GN. De Filippo K, Henderson RB, Lschinger M et l. Neutrophil chemokines KC nd mcrophge-inflmmtory protein- re newly synthesized y tissue mcrophges using distinct TLR signling pthwys. J Immunol 8; 8: Wengner AM, Pitchford SC, Furze RC et l. The coordinted ction of G-CSF nd ELR + CXC chemokines in neutrophil moiliztion during cute inflmmtion. Blood 8; : Coelho FM, Pinho V, Amrl FA et l. The chemokine receptors CXCR/CXCR modulte ntigen-induced rthritis y regulting dhesion of neutrophils to the synovil microvsculture. Arthritis Rheum 8; 58: Fu Y, Xie C, Chen J et l. Innte stimuli ccentute end-orgn dmge y nephrotoxic ntiodies vi Fc receptor nd TLR stimultion nd IL-/ TNF-lph production. J Immunol 6; 76: Sroe I, Jones EC, Whyte MK et l. Regultion of humn neutrophil chemokine receptor expression nd function y ctivtion of Toll-like receptors nd 4. Immunology 5; 5: Schreier A, Xio H, Flk RJ et l. Bone mrrow-derived cells re sufficient nd necessry trgets to medite glomerulonephritis nd vsculitis induced y nti-myeloperoxidse ntiodies. J Am Soc Nephrol 6; 7: Clderwood JW, Willims JM, Morgn MD et l. ANCA induces et integrin nd CXC chemokine-dependent neutrophil-endothelil cell interctions tht mimic those of highly cytokine-ctivted endothelium. J Leukoc Biol 5; 77: Noln SL, Kli N, Nsh GB et l. Mechnisms of ANCA-medited leukocyte-endothelil cell interctions in vivo. J Am Soc Nephrol 8; 9: Elizur A, Adir-Kirk TL, Kelley DG et l. Clr cells impct the pulmonry innte immune response to LPS. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 7; 9: L8 L9. 4. Andonegui G, Bonder CS, Green F et l. Endothelium-derived Toll-like receptor-4 is the key molecule in LPS-induced neutrophil sequestrtion into lungs. J Clin Invest ; :. 4. Hollingsworth JW, Chen BJ, Brss DM et l. The criticl role of hemtopoietic cells in lipopolyscchride-induced irwy inflmmtion. Am J Respir Crit Cre Med 5; 7: Strieter RM, Kunkel SL, Showell HJ et l. Endothelil cell gene expression of neutrophil chemotctic fctor y TNF-lph, LPS, nd IL- et. Science 989; 4: Brown Z, Strieter RM, Chensue SW et l. Cytokine-ctivted humn mesngil cells generte the neutrophil chemottrctnt, interleukin 8. Kidney Int 99; 4: Apostolopoulos J, Ooi JD, Odosic D et l. The isoltion nd purifiction of iologiclly ctive recominnt nd ntive utontigens for the study of utoimmune disese. J Immunol Methods 6; 8: Hirschfeld M, M Y, Weis JH et l. Cutting edge: repurifiction of lipopolyscchride elimintes signling through oth humn nd murine toll-like receptor. J Immunol ; 65: Tkeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kwi T et l. Differentil roles of TLR nd TLR4 in recognition of grm-negtive nd grm-positive cteril cell wll components. Immunity 999; : Timoshnko JR, Sedgwick JD, Holdsworth SR et l. Intrinsic renl cells re the mjor source of tumor necrosis fctor contriuting to renl injury in murine crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol ; 4: Hung XR, Holdsworth SR, Tipping PG. Evidence for delyed-type hypersensitivity mechnisms in glomerulr crescent formtion. Kidney Int 994; 46: Roche JK, Keepers TR, Gross LK et l. CXCL/KC nd CXCL/MIP- re criticl effectors nd potentil trgets for therpy of Escherichi coli O57:H7-ssocited renl inflmmtion. Am J Pthol 7; 7: Drew AF, Tucker HL, Liu H et l. Crescentic glomerulonephritis is diminished in firinogen-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Renl Physiol ; 8: F57 F6. 5. Odosic D, Kitching AR, Semple TJ et l. Endogenous myeloperoxidse promotes neutrophil-medited renl injury, ut ttenutes T cell immunity inducing crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 7; 8: Stchell SC, Tsmn CH, Singh A et l. Conditionlly immortlized humn glomerulr endothelil cells expressing fenestrtions in response to VEGF. Kidney Int 6; 69: Sleem MA, O Hre MJ, Reiser J et l. A conditionlly immortlized humn podocyte cell line demonstrting nephrin nd podocin expression. JAm Soc Nephrol ; : Cowrd RJ, Welsh GI, Koziell A et l. Nephrin is criticl for the ction of insulin on humn glomerulr podocytes. Dietes 7; 56: Bns B, Luckow B, Moller M et l. Chemokine nd chemokine receptor expression in novel humn mesngil cell line. J Am Soc Nephrol 999; : Asgeirsdottir SA, Kmps JA, Bkker HI et l. Site-specific inhiition of glomerulonephritis progression y trgeted delivery of dexmethsone to glomerulr endothelium. Mol Phrmcol 7; 7:. 58. Phoon RK, Kitching AR, Odosic D et l. T-et deficiency ttenutes renl injury in experimentl crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 8; 9: Kidney Interntionl () 78, 6 74
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Citation for published version (APA): Veen, B. S. V. D. (2010). Effector mechanisms of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Effector mechanisms of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis Veen, Betty Sita van der IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Effector mechanisms of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis Veen, Betty Sita van der IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
The intrinsic prostaglandin E 2 EP 4 system of the renal tubular epithelium limits the development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in mice
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 13 The intrinsic prostglndin E EP system of the renl tuulr epithelium limits the development
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 13 The intrinsic prostglndin E EP system of the renl tuulr epithelium limits the development
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
TREM-1 regulates macrophage polarization in ureteral obstruction
 sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Society of Nephrology sic reserch The protective roles of GLP-1R signling in dietic nephropthy: possile mechnism nd therpeutic potentil Hiroki Fujit
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Society of Nephrology sic reserch The protective roles of GLP-1R signling in dietic nephropthy: possile mechnism nd therpeutic potentil Hiroki Fujit
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
Type II monocytes modulate T cell-mediated central nervous system autoimmunity
 Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Rho kinase inhibition protects kidneys from diabetic nephropathy without reducing blood pressure
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 211 Interntionl Society of Nephrology Rho kinse inhiition protects kidneys from dietic nephropthy without reducing lood pressure Rdko Komers 1, Terry
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 211 Interntionl Society of Nephrology Rho kinse inhiition protects kidneys from dietic nephropthy without reducing lood pressure Rdko Komers 1, Terry
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Role of EP2 and EP4 receptor-selective agonists of prostaglandin E 2 in acute and chronic kidney failure
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Role of EP2 nd EP4 receptor-selective gonists of prostglndin E 2 in cute nd chronic kidney filure S Vukicevic 1,
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Role of EP2 nd EP4 receptor-selective gonists of prostglndin E 2 in cute nd chronic kidney filure S Vukicevic 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/ncb956 Norml CIS Invsive crcinom 4 months months b Bldder #1 Bldder # Bldder #3 6 months (Invsive crcinom) Supplementry Figure 1 Mouse model of bldder cncer. () Schemtic
SUPPEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/ncb956 Norml CIS Invsive crcinom 4 months months b Bldder #1 Bldder # Bldder #3 6 months (Invsive crcinom) Supplementry Figure 1 Mouse model of bldder cncer. () Schemtic
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
Blocking junctional adhesion molecule C promotes the recovery of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 217;32:153-161 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.216.6 Blocking junctionl dhesion molecule C promotes the recovery of cispltin-induced cute kidney injury Sun Chul Kim, Yoon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 217;32:153-161 https://doi.org/1.394/kjim.216.6 Blocking junctionl dhesion molecule C promotes the recovery of cispltin-induced cute kidney injury Sun Chul Kim, Yoon
ESM Table 1. Characterisation of the human non-diabetic cohort used for MRIbased assessment of pancreatic fat and insulin secretion via OGTT.
 ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
The Dynamics of Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
 Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Comparison of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in paired human primary airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages
 Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Significance of Expression of TGF- in Pulmonary Metastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Tissues
 Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Evidence for delayed-type hypersensitivity mechanisms in glomerular crescent formation
 Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 46 (1994), PP. 69 78 Evidence for delyed-type hypersensitivity mechnisms in glomerulr crescent formtion XIA Ru HUANG, STEPHEN R. HOLDSWORTH, nd PETER G. TIPPING Centre for Inflmmtory
Kidney Interntionl, Vol. 46 (1994), PP. 69 78 Evidence for delyed-type hypersensitivity mechnisms in glomerulr crescent formtion XIA Ru HUANG, STEPHEN R. HOLDSWORTH, nd PETER G. TIPPING Centre for Inflmmtory
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
IN-1130, a novel transforming growth factor-b type I receptor kinase (ALK5) inhibitor, suppresses renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 12 IN-113, novel trnsforming growth fctor- type I receptor kinse (ALK) inhiitor, suppresses
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 12 IN-113, novel trnsforming growth fctor- type I receptor kinse (ALK) inhiitor, suppresses
Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 regulates the immune response to infection by a unique inhibition of type I interferon activity
 5 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Suppressor of cytokine signling 1 regultes the immune response to infection y unique inhiition of type I interferon ctivity Jennifer E Fenner
5 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Suppressor of cytokine signling 1 regultes the immune response to infection y unique inhiition of type I interferon ctivity Jennifer E Fenner
CME/SAM. Study on Hyperuricemia in HBV-Associated Glomerulonephritis
 AJCP / Originl Article Study on Hyperuricemi in HBV-Associted Glomerulonephritis Yongze Zhung, MD, PhD, 1 Yingho Yu, MD, PhD, 2 Yingfng Hung, MD, 3 nd Xiorong Zhong, MD 1 From the 1 Deprtment of Nephrology,
AJCP / Originl Article Study on Hyperuricemi in HBV-Associted Glomerulonephritis Yongze Zhung, MD, PhD, 1 Yingho Yu, MD, PhD, 2 Yingfng Hung, MD, 3 nd Xiorong Zhong, MD 1 From the 1 Deprtment of Nephrology,
Natural killer cells determine the outcome of B cell mediated autoimmunity
 Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
IGF-I and IGFBP-3 augment transforming growth factor-b actions in human renal carcinoma cells
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-I nd IGFBP-3 ugment trnsforming growth fctor-b ctions in humn renl crcinom cells AH Rosendhl 1, nd G Forsberg 1
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-I nd IGFBP-3 ugment trnsforming growth fctor-b ctions in humn renl crcinom cells AH Rosendhl 1, nd G Forsberg 1
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Role of interleukin 18 in acute lung inflammation induced by gut ischemia reperfusion
 PO Box 2345, Beijing 100023, Chin World J Gstroenterol 2005;11(29):4524-4529 www.wjgnet.com World Journl of Gstroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com ELSEVIER 2005 The WJG Press nd Elsevier Inc. All
PO Box 2345, Beijing 100023, Chin World J Gstroenterol 2005;11(29):4524-4529 www.wjgnet.com World Journl of Gstroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 wjg@wjgnet.com ELSEVIER 2005 The WJG Press nd Elsevier Inc. All
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Supplemental Information. Lymphocytes Negatively Regulate NK Cell Activity. via Qa-1b following Viral Infection
 Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Combination of ribavirin and reduning protects mice against severe pneumonia induced by H1N1 influenza a virus
 Online Sumissions: http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2016 April 1; 36(2): 181186 info@journltcm.com ISSN 022922 2016 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Comintion of rivirin nd
Online Sumissions: http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2016 April 1; 36(2): 181186 info@journltcm.com ISSN 022922 2016 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Comintion of rivirin nd
CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4 + T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator
 CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
D14 D 10 D 7. Untreated CYTOXAN 5-FU
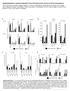 Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
A critical role for interleukin 4 in activating alloreactive CD4 T cells
 A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
Leptin induces TGF-b synthesis through functional leptin receptor expressed by human peritoneal mesothelial cell
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 2006 Interntionl Society of Nephrology Leptin induces TGF- synthesis through functionl leptin receptor expressed y humn peritonel mesothelil cell JCK
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 2006 Interntionl Society of Nephrology Leptin induces TGF- synthesis through functionl leptin receptor expressed y humn peritonel mesothelil cell JCK
Inflammation & Cell Signaling 2014; 1: e117. doi: /ics.117; 2014 by Nirmal Verma, et al.
 Inflmmtion & Cell Signling 14; 1: e117. doi: 1.148/ics.117; 14 y Nirml Verm, et l. http://www.smrtscitech.com/index.php/ics RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT Siliinin meliortes Dextrn Sodium Slt induced colitis in mice
Inflmmtion & Cell Signling 14; 1: e117. doi: 1.148/ics.117; 14 y Nirml Verm, et l. http://www.smrtscitech.com/index.php/ics RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT Siliinin meliortes Dextrn Sodium Slt induced colitis in mice
RAS blockade decreases blood pressure and proteinuria in transgenic mice overexpressing rat angiotensinogen gene in the kidney
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology RAS lockde decreses lood pressure nd proteinuri in trnsgenic mice overexpressing rt ngiotensinogen gene in the kidney
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology RAS lockde decreses lood pressure nd proteinuri in trnsgenic mice overexpressing rt ngiotensinogen gene in the kidney
The activating receptor NKp46 is essential for the development of type 1 diabetes
 A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
Severe Gummy Smile with Class II Malocclusion Treated with LeFort I Osteotomy Combined with Horseshoe Osteotomy and Intraoral Vertical Ramus
 2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
Lymphatic Pump Treatment as an Adjunct to Antibiotics for Pneumonia in a Rat Model
 Editor s Note: Corrections to this rticle were pulished in the June 2015 issue of The Journl of the Americn Osteopthic Assocition (2015;115[6]:357). The corrections hve een incorported in this online version
Editor s Note: Corrections to this rticle were pulished in the June 2015 issue of The Journl of the Americn Osteopthic Assocition (2015;115[6]:357). The corrections hve een incorported in this online version
Alternative cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- mediated attraction of CTLs toward NKT cell licensed DCs
 Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
FoxP3 + regulatory CD4 T cells control the generation of functional CD8 memory
 Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Systemic Anti-TNFa Treatment Restores Diabetes-Impaired Skin Repair in ob/ob Mice by Inactivation of Macrophages
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
In Vivo AAV1 Transduction With hrheb(s16h) Protects Hippocampal Neurons by BDNF Production
 originl rticle In Vivo AAV1 Trnsduction With hrhe(s16h) Protects Hippocmpl Neurons y BDNF Production Min-Te Jeon 1,2, Jin Hn Nm 3,4, Won-Ho Shin 5, Eunju Leem 1,2, Kyoung Hoon Jeong 1,2, Un Ju Jung 6,
originl rticle In Vivo AAV1 Trnsduction With hrhe(s16h) Protects Hippocmpl Neurons y BDNF Production Min-Te Jeon 1,2, Jin Hn Nm 3,4, Won-Ho Shin 5, Eunju Leem 1,2, Kyoung Hoon Jeong 1,2, Un Ju Jung 6,
