G-TRACE: rapid Gal4-based cell lineage analysis in Drosophila
|
|
|
- Eileen Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 nature methods G-TRACE: rapid Gal4-based cell lineage analysis in Drosophila Cory J Evans, John M Olson, Kathy T Ngo, Eunha Kim, Noemi E Lee, Edward Kuoy, Alexander N Patananan, Daniel Sitz, PhuongThao Tran, Minh-Tu Do, Kevin Yackle, Albert Cespedes, Volker Hartenstein, Gerald B Call & Utpal Banerjee Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Figure 4 Supplementary Figure 5 Supplementary Figure 6 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Table 2 Supplementary Table 3 Supplementary Table 4 Supplementary Table 5 Supplementary Data Full schematic depicting the G-TRACE analysis system. The G-TRACE analysis system recapitulates real-time expression patterns and reveals prior expression via lineage tracing. A survey of G-TRACE patterns in the late larval brain. G-TRACE analysis of late larval lymph glands. Temporal analysis of G-TRACE patterns with several Gal4 drivers. The efficiency of Gal4-based lineage marking G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval brain. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval eye-antenna imaginal disc. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval wing imaginal disc. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval lymph gland. Primer sequences for amplification of the Ubip63E promoter G-TRACE expression patterns in four tissues
2 Supplementary Figure 1 A) The Drosophila G-TRACE analysis system Gal4-expressing line G-TRACE test stock UAS RFP Enhancer gal4 UAS FLP STOP Ubi p63 FRT FRT negfp B) Gal4 - ACTIVE Gal4 - POST -ACTIVE Enhancer gal4 Enhancer gal4 UAS RFP UAS RFP UAS FLP UAS FLP STOP Ubi p63 FRT FRT negfp Ubi p63 FRT negfp Ubi p63 FRT negfp
3 Supplementary Figure 1. Full schematic depicting the G-TRACE analysis system. A) Individual Gal4- expressing lines are crossed to the G-TRACE analysis test stock, which has the genotype UAS-RedStinger UAS-FLP Ubi-p63FRT>STOPFRT>nEGFP. B) Cells expressing Gal4 activate the expression of RFP and FLP recombinase, which in turn mediates the excision of the FRT-flanked STOP cassette. Subsequently, negfp is expressed from the Ubi-p63E promoter and is heritably maintained in all daughter cells, even cells in which Gal4 expression is subsequently downregulated ( POST-ACTIVE ). The circles at the bottom of the figure represent cells that appear red or yellow (left), when Gal4 activates RFP expression followed by EGFP expression, or green (right), when Gal4 expression has been downregulated such that cell only express the lineage-tracing marker EGFP.
4 Supplementary Figure 2 enhancer trap reporter G-TRACE real-time expression G-TRACE lineage-traced expression + MERGE posterior A B C anterior compartment compartment hh-lacz βgal hh-gal4 RFP RFP EGFP DNA MERGE D E F anterior compartment posterior compartment ptc-lacz βgal ptc-gal4 RFP RFP EGFP DNA MERGE G H I dpp-lacz βgal dpp-gal4 RFP RFP EGFP DNA MERGE Supplementary Figure 2. The G-TRACE analysis system recapitulates real-time expression patterns and reveals prior expression via lineage tracing. Comparison of lacz expression patterns with G-TRACE expression patterns for three well-characterized genes in the late third instar wing imaginal disc. hh-lacz expression (A, βgal) and hh-gal4 expression (B, RFP) are restricted to the posterior (P) wing compartment. Lineage-traced EGFP expression (C) is also restricted to the P compartment indicating that hh-gal4 expression is limited to P compartment cells throughout wing development; Scale bar: 50 microns. ptc-lacz (D, βgal) and ptc-gal4 (E, RFP) are expressed similarly in a stripe of cells in the anterior (A) compartment along the A/P boundary. By contrast, lineage tracing (F, EGFP) reveals that the entire A compartment either expressed ptc-gal4 at one point or that all A compartment cells are derived from precursors, such as those at the A/P boundary, that expressed ptc-gal4; Scale bar: 50 microns. dpp-lacz (G, βgal) and dpp-gal4 (H, RFP) are, like ptc (compare to D and E), expressed in a stripe of A compartment cells at the A/P boundary. Despite the similarity in expression of realtime RFP patterns, the lineage-traced pattern for dpp-gal4 (I, EGFP) is markedly different from that of ptc-gal4 (compare to F), indicating that these Gal4 lines are differentially regulated during the course of wing disc development; Scale bar: 50 microns.
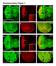
5 Supplementary Figure 3 whole 3IL brain hemisphere - RFP, current hemisphere - EGFP, lineage hemisphere - MERGE OK107-gal4 A B C D E F G H gcm-gal4 ptc-gal4 NP0189 NP0114 I J K L M N O P Q R S T dome-gal4 upd-gal4 U V W X Y Z AA BB
6 Supplementary Figure 3. A survey of G-TRACE patterns in the late larval brain. Low-magnification images (whole third-instar larval brain, first column) of several known and unknown Gal4-expressing lines showing real-time (RFP) and lineage-traced (EGFP) patterns throughout the late third instar brain (blue, DNA). Close-up images of single brain hemispheres detailing G-TRACE real-time (RFP, current, second column) and lineage-traced (EGFP, lineage, third column) expression patterns (MERGE, fourth column). A-D) OK107-gal4 expression is restricted to the mushroom body at this stage (B) but exhibits extensive lineage tracing in the optic lobe (C, D). E-H) Gal4-ET NP0114 expression is also highly restricted to the mushroom body (F) but traces only subset of cell clusters in the optic lobe (G, H). I-L) Like OK107-gal4 and NP0114, real-time expression of Gal4-ET NP0189 is highly restricted to the mushroom body (J), but traces significantly more cell clusters (K, L) than NP0114. M-P) gcm-gal4 exhibits real-time RFP expression in both a subset of mushroom body as well as the optic lobe (N), however most of the lineage-tracing is restricted to the optic lobe (O, P). Another observed pattern was one in which both the real-time and lineage-traced expression patterns were found to be restricted primarily to the optic lobes. Gal4-expressing lines that exhibit such a pattern include ptc-gal4 (Q-T), dome-gal4 (U-X), and upd-gal4 (Y-B'). While variable in extent, most Gal4-expressing lines examined were found to trace brain surface glia. Scale bars in Column 1 are 100 microns. Scale bars in Column 4 are 50 microns.
7 Supplementary Figure 4 A Late 3IL Late embryo cortical zone medullary zone differentiating cells progenitor cells PSC cells PSC pericardial nephrocytes dorsal vessel cardioblasts lymph gland - RFP, current lymph gland - EGFP, lineage B C D lymph gland - MERGE + DNA Cg-gal4 MZ MZ MZ dome-gal4 E F G MZ MZ MZ H I J Antp-gal4 PSC K L M Dot-gal4 PSC
8 Supplementary Figure 4. G-TRACE analysis of late larval lymph glands. A) Schematic depicting lymph gland structure in late embryos and late larvae; only one half is depicted. The lymph gland primordium flanks dorsal vessel cardioblast and is anterior to pericardial cells that will develop into nephrocytes. The posterior signaling center (PSC) is already specified by this stage. In late 3IL, the lymph gland has grown and the medullary and cortical zones have formed. The medullary zone consists of blood progenitor cells where as the cortical zone contains differentiating hemocytes. Real-time and lineage-traced expression of Cg-gal4 (B-D) is restricted to the cortical zone and absent from the medullary zone (MZ). Many RFP-negative, EGFP-positive cells can be observed in the cortical zone in C. Real-time expression of dome-gal4 (E-G) is restricted to the medullary zone, but lineage-traces both the medullary and cortical zones. Real-time and lineage-traced expression of Antp-gal4 (H-J) is restricted to the PSC. A few RFPnegative, EGFP-positive cells can be observed (J, arrows). Real-time expression of Dot-gal4 (K-M) is restricted to the PSC (K, arrow), but lineage-traces cells throughout the lymph gland. Scale bars are 50 microns.
9 Supplementary Figure 5 Late Third Instar Earlier Developmental Stages RFP, current RFP, current EGFP, lineage DNA RFP, current RFP, current EGFP, lineage DNA A B C early 3IL D gcm-gal4 gcm-gal4 E F G early 3IL H NP0224 NP0224 I J K emb L Dot-gal4 LG PSC Dot-gal4 Supplementary Figure 5. Temporal analysis of G-TRACE patterns with several Gal4 drivers. G-TRACE on gcmgal4 (A-D; inset: single optical section), NP0224 (E-H), and Dot-gal4 (I-L) lines at early and late developmental stages, as indicated. LG, lymph gland. PSC, posterior signaling center. 3IL, third instar larvae; emb, embryo. Scale: (C-D, 25 µm; K-L, 10 µm; Others, 50 µm).
10 Supplementary Figure 6 Ubi-gal4 RFP + DNA EGFP + DNA RFP + EGFP + DNA RFP + EGFP Ubi-gal4 RFP + DNA EGFP + DNA RFP + EGFP + DNA RFP + EGFP RFP + EGFP + DNA Late 3IL RFP Late emb DV hand-gal4 hand-gal4 Supplementary Figure 6. The efficiency of Gal4-based lineage marking. G-TRACE analysis using Ubiquitin-gal4 (Ubi-gal4) essentially marks all cells, although some cells exhibit differences in level of expression. In the wing hinge regions (A-D) virtually all cells express EGFP however a few cells near the lateral edges have low or undetectable levels of RFP expression. Similarly, nearly all cells express EGFP in the wing pouch (E-H) although cells of the dorsal/ventral boundary exhibit low-level expression, suggesting that the Ubi-p63E promoter is less active in these cell types. This interpretation is consistent with the pattern of RFP expression (E), which is also low in the dorsal/ventral boundary. Based upon numerous examples like these, it appears that FLP-out and EGFP expression can occur in all cells, with the major limiting factor being the strength of the Gal4 line being used. For example, the hand gene is expressed throughout the cardiogenic mesoderm from which the lymph gland is derived. Furthermore, the hand-gal4 reporter line has been shown to recapitulate this pattern and be active in all such cells including the developing lymph gland. Using hand-gal4 with G-TRACE, however, often generates sectors of untraced cells in the lymph gland (I, arrowhead). Furthermore, these negative sectors are reproducibly located in the periphery of the primary lobes, indicating that precursors of these cells likely have lower levels of Gal4 activity relative to precursors of cells position medially. Indeed, examination of late embryo and first instar larvae (not shown) demonstrated that, although expressed throughout the lymph gland, cells located laterally, away from the midline, exhibited markedly lower level RFP expression (J, arrows). Dotted lines outline lymph gland cells and dorsal vessel cardioblasts (DV) visible in a single optical section. 3IL, third instar larvae; emb, embryo.
11 Supplementary Table 1. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval brain Expression None Ubiquitous Central Brain Optic Lobe Glia Comment Stock ID NP Identifier RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP NP0112 CB RFP in MB?; minor EGFP in CB NP0114 CB RFP strong in MB NP0131 possible minor CB RFP NP0138 low sample number NP0158 minor RFP expression in CB NP0168 possible minor OL RFP NP NP NP NP NP NP0224 highly specific EGFP in laminar placode NP0239 low OL RFP, low CB EGFP NP0244 low expession levels NP0269 CB RFP/EGFP in MB? and elsewhere NP NP NP NP0346 CB RFP strong in MB NP0652 low RFP in CB/OL, low EGFP in CB NP NP0675 CB RFP strong in MB NP NP0699 possible OL EGFP NP0708 RFP/EGFP in MB NP NP0727 possible OL EGFP NP NP0829 RFP strong in CB, weaker in OL along furrow NP NP NP NP NP NP NP0949 CB RFP strong in MB Other Gal4 lines BL 8699 Hemese BL 1767 how[24b] BL 8860 Bx[MS1096] BL BL 6902 Dot BL 3750 c355 * BL 7011 Collagen BL 8641 daughterless * gcm BL 6773 Grunge hand hedgehog BL 854 OK107 PG14 dome PG33 PG50 Peroxidasin BL 2017 patched[559.1] serpent-hemo Ubx upd[e132] LEGEND Lines not scored:103557, , , , BL 2721, Antp-gal4, BL 7031, BL 1553, BL 3039 No expression RFP expression EGFP expression sporadic *
12 Supplementary Table 2. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval eye-antenna imaginal disc Expression None Ubiquitous Eye Specific Ant. Specific PMF MF AMF PPM Ant. Ant. Comment RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP RFP RFP RFP RFP EGFP Stock ID NP Identifier EGFP EGFP EGFP EGFP NP0112 * increased clone density in ventral antenna NP0131 minor RFP at edges of eye/ant peripodial/disc? NP0138 Ant. EGFP in A-1 and A-2 * NP0158 Ant. RFP/EGFP specific to A-1, A-2; minor, variable EGFP in eye NP0168 * NP NP NP0188 * NP0189 * NP0211 appears RFP downregulated PMF NP0219 * NP0224 variable, RFP in small clusters NP0239 * RFP in small cell clusters throughout NP0244 RFP/EGFP in clusters at A1 ring of antenna NP0269 increased clone density in ventral antenna; * * * * variable expression NP0293 possible EGFP in anterior antenna * NP NP NP0346 few sporadic EGFP clones * NP NP0662 near ventral(?) opitc stalk NP NP0680 * NP NP NP0723 ventral EGFP in antenna, RFP unclear NP NP0729 specific expression in A1; eye glia express EGFP NP0829 * variable, RFP in small clusters, primarily in antenna NP0837 * variable, RFP in small clusters NP0864 * variable, RFP in small clusters, peripodial? NP0870 RFP expression high in antenna and eye glia NP0873 variable, RFP in small clusters, primarily in antenna NP0882 variable, RFP in small clusters NP0883 * * NP0898 RFP high in dorsal antenna; variable RFP in small clusters NP0902 RFP/EGFP expressed in three clusters in the A2 region NP0911 * NP0949 * Other Gal4 lines BL RFP expression PMF? BL 8699 Hemese BL 1767 how[24b] BL 7031 G115 BL 8860 Bx[MS1096] * * BL BL 6902 Dot RFP/EGFP in the ventral side of the antenna disc BL 3750 c355 * BL 7011 Collagen RFP/EGFP cluster in A3 BL 8641 daughterless * BL 6773 Grunge hand Majority of clones posterior to the furrow PG142 cut (?) RFP marks AR/A1 in antenna PG14 dome PG33 svr (?) PG50 N (?) BL 3039 pannier[md237] Restricted to anterior-most antenna and Bolwig's nerve Peroxidasin RFP/EGFP in hemocytes BL 2017 patched[559.1] Verticle stripe at A/P boundary marked in antenna serpent-hemo RFP/EGFP in circulating hemocytes Ubx RFP is expressed in dorsal margin of eye; anterior-most region in antenna upd[e132] RFP is expressed near the optic stalk; EGFP is expressed in ventral region of eye/antenna LEGEND Lines not scored: , Antp-gal4, BL 1553, gcm-gal4, BL 854 No expression RFP expression EGFP expression sporadic * Ant. Antenna PMF posterior to the morphogenetic furrow MF morphogenetic furrow AMF anterior to the morphogenetic furrow PPM peripodial membrane
13 Supplementary Table 3. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval wing imaginal disc Expression None Ubiquitous Compartment Pouch Hinge/Notum PPM Comment Stock ID NP Identifier RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP NP0112 * minor RFP in pouch, possible proneural clusters NP0114 minor, variable NP NP0138 * minor, variable NP0158 * * NP0168 * expressd in trachea NP NP NP0188 * variable Pouch RFP expression in small clusters NP0189 * minor RFP in pouch, possible proneural clusters NP0211 higer RFP in pouch?, unclear NP0219 may have low RFP in hinge/notum NP NP NP0244 EGFP in tracheal NP0269 * * NP0293 * RFP/EGFP in trachea NP NP NP0346 possible trachea EGFP, few PPM clones NP0652 minor RFP in pouch, possible proneural clusters NP0662 RFP/EGFP in trachea NP NP0680 * minor RFP in pouch, possible proneural clusters NP0699 RFP expression primarily in pouch along A/P boundary NP NP0723 expressd in trachea NP0727 * minor, variable RFP NP0729 RFP specific to hinge regions NP0829 * * increased EGFP clone density at anterior compartment edge? NP0837 * * minor, variable RFP NP0864 * * minor, variable RFP NP NP0873 * minor, variable RFP throughout, strong RFP cluster in notum NP0882 * minor, variable RFP throughout NP0883 * * * minor, variable RFP throughout NP NP0911 * NP0949 * Other Gal4 lines BL BL 8699 Hemese BL 1767 how[24b] BL 7031 G115 BL 8860 Bx[MS1096] BL BL 6902 Dot BL 3750 c355 * BL 7011 Collagen BL 8641 daughterless * BL 1553 Dpp RFP expressed at A/P boundary. EGFP expressed in anterior compartment. BL 6773 Grunge hand hedgehog Posterior compartment PG142 RFP/EGFP restricted to notum; expressed in trachea. PG14 dome Low sample PG33 RFP/EGFP in trachea PG50 BL 3039 pannier[md237] Peroxidasin RFP/EGFP in hemocytes BL 2017 patched[559.1] RFP expressed in A/P boundary. EGFP expressed in anterior compartment. serpent-hemo serpent Ubx RFP expressed in trachea upd[e132] LEGEND Lines not scored: , Antp-gal4, gcm-gal4, BL 854 No expression RFP expression EGFP expression sporadic * PPM peripodial membrane
14 Supplementary Table 4. G-TRACE expression patterns in the late larval lymph gland Expression None Ubiquitous Primary Secondary Tertiary DV PC SS Comment Stock ID NP Identifier RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP RFP EGFP NP0112 minor, variable NP NP NP0138 * minor, variable NP NP NP NP NP0188 variable in lymph gland lobes NP0189 RFP in seven-up subset NP NP0219 minor expression in primary lobe/cortical zone? NP NP NP0244 expression in stringy stuff and ring gland NP NP NP0346 possibly in circulating hemocytes NP NP NP0675 * NP NP0699 possible SS expression NP NP0727 * * * NP NP NP0837 minor, variable NP0864 minor, variable NP0870 RFP mostly in primary, minor in tertiary; mature cells? NP0873 * NP0882 * minor, variable NP NP0898 RFP pattern unclear; inconsistent NP NP NP0949 EGFP also in ring gland Other Gal4 lines BL BL 8699 Hemese RFP/EGFP expression may be in cortical zone Antp Expressed in PSC BL 1767 how[24b] BL 7031 G115 BL 8860 Bx[MS1096] BL BL 6902 Dot RFP expressed in the PSC BL 3750 c355 * BL 7011 Collagen RFP/EGFP in cortical zone BL 8641 daughterless * RFP low in hemocytes relative to DV, etc. BL 6773 Grunge hand hedgehog RFP is in pericardial cells? PG142 RFP/EGFP restricted to mature hemocytes PG14 dome RFP expressed in medullary zone PG33 PG50 BL 3039 pannier[md237] RFP/EGFP restricted to mature hemocytes Peroxidasin RFP/EGFP restricted to mature hemocytes BL 2017 patched[559.1] serpent-hemo serpent Possible EGFP in primary lobe expression Ubx RFP/EGFP possibly in pericardial cells upd[e132] LEGEND No expression Lines not scored: , , , BL 1553, gcm-gal4, BL 854 RFP expression EGFP expression sporadic * DV dorsal vessel PC pericardial cells SS stringy stuff, a long, thin cellular structure associated with secondary and tertiary lobes
15 Supplementary Table 5 Primers sequences for amplification of the Ubi p63e promoter Forward 5 GAG AAT TCT GTC CGT ATC CTT TAG GC 3 Reverse 5 GAG GTA CCT TGG ATT ATT CTG CGG GA 3
16 Supplementary Data G-TRACE expression patterns in four tissues Gal4 line brain eye-antenna wing lymph gland
17
18
19
20
21
22 Antp c355
23 collagen daughterless Dpp Gcm Grunge hand hedgehog
24 Hemese OK107 PG142 PG14 PG33 PG50 pannier
25 Peroxidasin ptc srp Srp-Hemo Ubx upd
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal
 glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6
 Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 Genotype Abbreviation Expression patterns Ubi-Gal4 Ubi Ubiquitous dome-gal4;elav-gal80 dome MZ Progenitor-specific
Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 Genotype Abbreviation Expression patterns Ubi-Gal4 Ubi Ubiquitous dome-gal4;elav-gal80 dome MZ Progenitor-specific
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Table 3. 3 UTR primer sequences. Primer sequences used to amplify and clone the 3 UTR of each indicated gene are listed.
 Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc.
 Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
(a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Supplementary Figure 1 (a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from Sema3d +/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ and Sema3d -/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ embryos.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Supplementary Figure 1 (a-r) Whole mount X-gal staining on a developmental time-course of hearts from Sema3d +/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ and Sema3d -/- ;Ephb4 LacZ/+ embryos.
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Targeted expression of teashirt induces ectopic eyes in Drosophila
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 15508 15512, December 1998 Genetics Targeted expression of teashirt induces ectopic eyes in Drosophila DUOJIA PAN AND GERALD M. RUBIN* Department of Molecular and
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 15508 15512, December 1998 Genetics Targeted expression of teashirt induces ectopic eyes in Drosophila DUOJIA PAN AND GERALD M. RUBIN* Department of Molecular and
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
Compartmental organization of the Drosophila genital imaginal discs
 Development 124, 205-218 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV8366 205 Compartmental organization of the Drosophila genital imaginal discs Elizabeth H. Chen 1 and Bruce
Development 124, 205-218 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV8366 205 Compartmental organization of the Drosophila genital imaginal discs Elizabeth H. Chen 1 and Bruce
Università degli Studi di Torino. Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC)
 Università degli Studi di Torino Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC) Francesca Messa Forkhead family CBP?? Ub Ub CBP Ub Ac Ac
Università degli Studi di Torino Ruolo del fattore trascrizionale FoxO-3 nei progenitori CD34+ Ph positivi nella leucemia mieloide cronica (LMC) Francesca Messa Forkhead family CBP?? Ub Ub CBP Ub Ac Ac
A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines
 Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Developmental Biology
 Developmental iology 356 (2011) 553 565 ontents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental iology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Multipotent neural stem cells generate glial
Developmental iology 356 (2011) 553 565 ontents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental iology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Multipotent neural stem cells generate glial
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3836
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Sulcus Classification Rating Protocol: Anterior Temporobasal Sulci (SCRaP:aTB)
 Sulcus Classification Rating Protocol: Anterior Temporobasal Sulci (SCRaP:aTB) 2012 Reckess, Dunn, Bauer & Leonard Address correspondence to: Gila Z. Reckess, Ph.D. reckessg@gmail.com Anterior Temporobasal
Sulcus Classification Rating Protocol: Anterior Temporobasal Sulci (SCRaP:aTB) 2012 Reckess, Dunn, Bauer & Leonard Address correspondence to: Gila Z. Reckess, Ph.D. reckessg@gmail.com Anterior Temporobasal
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Midterm 1. Number of students Score. Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98
 Midterm 1 14 12 Number of students 10 8 6 4 2 0 35-40 41-45 Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98 46-50 51-55 56-60 61-65 66-70 71-75 Score 76-80 81-85 86-90 91-95 96-100 Write your name and student ID# on
Midterm 1 14 12 Number of students 10 8 6 4 2 0 35-40 41-45 Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98 46-50 51-55 56-60 61-65 66-70 71-75 Score 76-80 81-85 86-90 91-95 96-100 Write your name and student ID# on
Viktorin, G. and Riebli, N. and Popkova, A. and Giangrande, A. and Reichert, H.
 Institutional Repository of the University of Basel University Library Schoenbeinstrasse 18-20 CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland http://edoc.unibas.ch/ Year: 2011 Multipotent neural stem cells generate glial
Institutional Repository of the University of Basel University Library Schoenbeinstrasse 18-20 CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland http://edoc.unibas.ch/ Year: 2011 Multipotent neural stem cells generate glial
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 327 (2009) 288 300 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology The HLH protein Extramacrochaetae is required
Developmental Biology 327 (2009) 288 300 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology The HLH protein Extramacrochaetae is required
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
A smart acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive. live cell mrna imaging by the target-triggered intracellular self-assembly
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Negative regulation of atonal in proneural cluster formation of Drosophila R8 photoreceptors
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 5055 5060, April 1999 Developmental Biology Negative regulation of atonal in proneural cluster formation of Drosophila R8 photoreceptors CHIEN-KUO CHEN AND CHENG-TING
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 96, pp. 5055 5060, April 1999 Developmental Biology Negative regulation of atonal in proneural cluster formation of Drosophila R8 photoreceptors CHIEN-KUO CHEN AND CHENG-TING
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the Drosophila eye: the roles of Hedgehog, Decapentaplegic and the Raf pathway
 Development 126, 5795-5808 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV5368 5795 Progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the Drosophila eye: the roles of Hedgehog, Decapentaplegic
Development 126, 5795-5808 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV5368 5795 Progression of the morphogenetic furrow in the Drosophila eye: the roles of Hedgehog, Decapentaplegic
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5
 Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5 "#$ ABSTRACT Modifier screens in Drosophila have proven to be a powerful tool for uncovering gene interaction and elucidating molecular pathways.
Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5 "#$ ABSTRACT Modifier screens in Drosophila have proven to be a powerful tool for uncovering gene interaction and elucidating molecular pathways.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most
 Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration
 Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplemental Information. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal. Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based. Model of Parkinson's Disease
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
SUPPLEMENTARY RESULTS
 SUPPLEMENTARY RESULTS Supplementary Table 1. hfpr1- Flpln-CHO hfpr2-flpln-cho pec 50 E max (%) Log( /K A) Log( /K A) N pec 50 E max (%) Log( /K A) Log( /K A) n ERK1/2 phosphorylation fmlp 9.0±0.6 80±7
SUPPLEMENTARY RESULTS Supplementary Table 1. hfpr1- Flpln-CHO hfpr2-flpln-cho pec 50 E max (%) Log( /K A) Log( /K A) N pec 50 E max (%) Log( /K A) Log( /K A) n ERK1/2 phosphorylation fmlp 9.0±0.6 80±7
Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report. a a*
 2009 63 6 379 384 Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report a b a a a* a b 380 63 6 Chest x ray and computed tomography (CT). A, Chest x ray on admission
2009 63 6 379 384 Malignant Amelanotic Melanoma of the Pleura without Primary Skin Lesion: An Autopsy Case Report a b a a a* a b 380 63 6 Chest x ray and computed tomography (CT). A, Chest x ray on admission
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
Dampening the Signals Transduced through Hedgehog via MicroRNA mir-7 Facilitates Notch-Induced Tumourigenesis
 Dampening the Signals Transduced through Hedgehog via MicroRNA mir-7 Facilitates Notch-Induced Tumourigenesis Vanina G. Da Ros, Irene Gutierrez-Perez, Dolors Ferres-Marco, Maria Dominguez* Instituto de
Dampening the Signals Transduced through Hedgehog via MicroRNA mir-7 Facilitates Notch-Induced Tumourigenesis Vanina G. Da Ros, Irene Gutierrez-Perez, Dolors Ferres-Marco, Maria Dominguez* Instituto de
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at
 Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila
 Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila Anica M. Wandler, Karen Guillemin* Institute of Molecular
Transgenic Expression of the Helicobacter pylori Virulence Factor CagA Promotes Apoptosis or Tumorigenesis through JNK Activation in Drosophila Anica M. Wandler, Karen Guillemin* Institute of Molecular
ErbB4 migrazione II parte
 ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
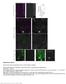 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Single-Molecule Analysis of Gene Expression Using Two-Color RNA- Labeling in Live Yeast
 Supplemental Figures, Tables and Results Single-Molecule Analysis of Gene Expression Using Two-Color RNA- Labeling in Live Yeast Sami Hocine 1, Pascal Raymond 2, Daniel Zenklusen 2, Jeffrey A. Chao 1 &
Supplemental Figures, Tables and Results Single-Molecule Analysis of Gene Expression Using Two-Color RNA- Labeling in Live Yeast Sami Hocine 1, Pascal Raymond 2, Daniel Zenklusen 2, Jeffrey A. Chao 1 &
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Notch regulates wingless expression and is not required for reception of the
 Development 121, 2813-2824 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2813 Notch regulates wingless expression and is not required for reception of the paracrine wingless signal
Development 121, 2813-2824 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2813 Notch regulates wingless expression and is not required for reception of the paracrine wingless signal
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
2/2/2011. Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE 1 C Supplemental Figure 1. pproach for removal of snorns from Rpl13a gene. () Wild type Rpl13a exonintron structure is shown, with exo in black and intronic snorns in red rectangles.
SUPPLEMENTL FIGURE 1 C Supplemental Figure 1. pproach for removal of snorns from Rpl13a gene. () Wild type Rpl13a exonintron structure is shown, with exo in black and intronic snorns in red rectangles.
Supplemental Information. Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier. to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Figures
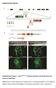 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information included with Nature MS 2008-02-01484B by Colantonio et al., entitled The dynein regulatory complex is required for ciliary motility and otolith biogenesis in the inner ear. This
Supplementary Information included with Nature MS 2008-02-01484B by Colantonio et al., entitled The dynein regulatory complex is required for ciliary motility and otolith biogenesis in the inner ear. This
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
CD31 5'-AGA GAC GGT CTT GTC GCA GT-3' 5 ' -TAC TGG GCT TCG AGA GCA GT-3'
 Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes
 Di Salvio et al. 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes vulnerability to MPTP Michela Di Salvio, Luca Giovanni Di Giovannantonio, Dario
Di Salvio et al. 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Otx2 controls neuron subtype identity in ventral tegmental area and antagonizes vulnerability to MPTP Michela Di Salvio, Luca Giovanni Di Giovannantonio, Dario
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells
 Nature Methods Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells Matthew J Kennedy, Robert M Hughes, Leslie A Peteya, Joel W Schwartz, Michael D Ehlers & Chandra L Tucker Supplementary
Nature Methods Rapid blue-light mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells Matthew J Kennedy, Robert M Hughes, Leslie A Peteya, Joel W Schwartz, Michael D Ehlers & Chandra L Tucker Supplementary
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation
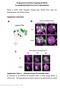 Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
