SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma -
|
|
|
- Charla Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIRT6 histone deacetylase functions as a potential oncogene in human melanoma - Garcia-Peterson et al Supplementary Figure S:Tissue microarray (TMA) staining and organization. A) Diagram of the TMA indicating location and tissue type of each core. B) Whole image of the SIRT6- stained slide with hematoxylin counterstaining. ME004c indicates the catalog number from US Biomax, Inc that was used for the study.
2 Supplementary Figure S2: Multiple SIRT6-targeting shrna constructs were analyzed for SIRT6 knockdown. (A) A375 melanoma cells were transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 using manufacturer s protocol (using 4 μg of DNA and 0 μl of Lipofectamine reagent per well in six well plate) with nonsense (NS) and five SIRT6-targeting shrna for 48 h, and cells were analyzed 48 h later. Cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blotting for SIRT6 protein as in Materials and Methods. Equal loading was confirmed by reprobing the blot for β- tubulin. Further, the two best constructs were chosen to determine which had the best knockdown via lentiviral transduction. (B) A375 cells were transduced with nonsense (NS) and the two best SIRT6 knockdown constructs from A, -73 and -76, for 48 h and collected 48 h later. Cell lysates were subjected to western blot and RT-qPCR to confirm SIRT6 knockdown. β- tubulin and GAPDH were used as controls, respectively.
3 Supplementary Table S: Quantification of SIRT6 staining and description of samples. Type Sex Age Organ Pathology Stage TNM Position Nuclear SIRT6 Mean Cytoplasmic SIRT6 Mean Whole Cell SIRT6 Mean Malignant M Adrenal 42 gland Pheochromocytoma (tissue marker) Benign F 2 Skin Intradermal nevus of right leg J Benign M 38 Skin Compound nevus of right face I Benign M 25 Skin Compound nevus of left leg I Benign F 29 Skin Compound nevus of left shoulder I Benign F 30 Skin Intradermal nevus of left rump I Benign M 20 Skin Compound nevus of left shoulder J Benign M 39 Skin Intradermal nevus of head J Benign F 34 Skin Sebaceous nevus of head (skin tissue) J Benign F 23 Skin Compound nevus of right lumbar part I Benign F 2 Skin Junctional nevus of neck I Benign M 50 Skin Compound nevus of upper arm J Benign M 8 Skin Sebaceous nevus of left frontal region (skin tissue) J Benign M 6 mo Skin Intradermal nevus of face I Benign M Skin Intradermal nevus of left thigh J Benign M 42 Skin Intradermal nevus of face J Benign M 73 Skin Compound nevus of left heel J Benign F 0 Skin Junctional nevus of right foot I Benign M 55 Skin Compound nevus of back J Malignant M 7 Skin Malignant melanoma of right rump II T4N0M0 A Malignant F 38 Vulva Malignant melanoma I E Malignant M 60 Skin Malignant melanoma of right rump III T4NM0 A Malignant F 4 Skin Malignant melanoma of scalp II T4N0M0 C Malignant F 32 Skin Malignant melanoma of right lumbar part (fibrofatty tissue) II T4N0M0 A Malignant M 79 Skin Malignant melanoma of left face I TN0M0 B Malignant F 38 Rectum Malignant melanoma I E Malignant M 55 Skin Malignant melanoma of left sole II T4N0M0 A Malignant M 64 Rectum Malignant melanoma II E Malignant F 46 Skin Malignant melanoma of right thumb II T4N0M0 D Malignant M 55 Stomach Malignant melanoma I F Malignant M 6 Skin Malignant melanoma of left armpit IV T4bN0M A Malignant M 3 Skin Malignant melanoma of scalp II T4N0M0 D Malignant M 65 Skin Malignant melanoma of scalp II T4N0M0 D Malignant F 44 Vulva Malignant melanoma I E Malignant M 4 Skin Malignant melanoma of left leg II T3N0M0 B Malignant M 49 Skin Malignant melanoma of left arm II T4N0M0 C Malignant F 72 Rectum Malignant melanoma I F Malignant M 55 Stomach Malignant melanoma I F Malignant F 52 Rectum Malignant melanoma I E Malignant F 47 Skin Malignant melanoma of left upper arm II T4N0M0 D Malignant M 5 Skin Malignant melanoma of back II T4N0M0 A Malignant F 84 Rectum Malignant melanoma of crissum I E Malignant F 67 Rectum Malignant melanoma I E Malignant F 42 Skin Malignant melanoma of right thigh II T4N0M0 B Malignant M 75 Rectum Malignant melanoma II F Malignant F 72 Vulva Malignant melanoma I D Malignant melanoma of left shoulder Malignant M 50 Skin (fibrous tissue and blood vessel) II T4N0M0 B Malignant F 83 Skin Malignant melanoma of right little finger I T2N0M0 C Malignant M 6 Skin Malignant melanoma of right groin III T4N2M0 B Malignant M 25 Skin Malignant melanoma of left sole I T2N0M0 A Malignant F 66 Rectum Malignant melanoma I F Malignant M 42 Skin Malignant melanoma of left heel IV T3N2M C Malignant M 80 Skin Malignant melanoma of right sole II T4N0M0 A Malignant M 37 Skin Malignant melanoma of right upper arm II T4N0M0 B Malignant M 72 Skin Malignant melanoma of left sole IB T2aN0M0 A Malignant M 52 Skin Malignant melanoma of left abdominal wall II T4N0M0 B Malignant M 50 Esophagus Malignant melanoma II F Malignant M 73 Intestine Malignant melanoma I G
4 Continued from previous page Malignant M 4 Skin Malignant melanoma of left forearm II T4N0M0 C Malignant M 7 Skin Malignant melanoma of right groin II T4N0M0 C Malignant F 54 Rectum Malignant melanoma of anal tube II F Malignant M 66 Rectum Malignant melanoma I F Malignant M 45 Skin Malignant melanoma of crissum II T4N0M0 D Malignant M 66 Skin Malignant melanoma of right thigh II T4N0M0 C Malignant F 59 Skin Malignant melanoma with necrosis of anus II T4N0M0 B Malignant M 5 Skin Malignant melanoma of left armpit II T4N0M0 C Malignant M 5 Skin Malignant melanoma of left upper arm III T4NM0 C Malignant F 46 Skin Malignant melanoma of thigh II T4N0M0 A Malignant F 62 Vulva Malignant melanoma I E Malignant F 45 Skin Malignant melanoma of left thigh I T2N0M0 D Malignant F 57 Vulva Malignant melanoma I D Malignant F 72 Skin Malignant melanoma of right cheek II T4N0M0 D Malignant M 40 Skin Malignant melanoma of right chest wall II T4N0M0 B Malignant F 44 Rectum Malignant melanoma I E Malignant M 7 Intestine Malignant melanoma I F Malignant F 45 Vulva Malignant melanoma I E Malignant M 64 Esophagus Malignant melanoma I F Malignant F 59 Skin Malignant melanoma of right rump I TN0M0 B Malignant melanoma of left parotid Malignant F 70 Oral cavity gland I G Malignant M 49 Skin Malignant melanoma of left foot III T4NM0 D Malignant M 56 Skin Malignant melanoma of abdominal wall II T4N0M0 C node groin H node Malignant malignant melanoma from right armpit G node left groin G node right groin (fibrous tissue and blood vessel) I node thigh H node Malignant malignant melanoma from right armpit H node Malignan tmalignant melanoma from left sole H node left groin H node right groin H node right groin H node right heel G node right groin G node neck I node left ear H node left thump G node right groin G node left groin G node right leg H node left Lower gum G node left groin H "-" indicates fields where data was not available or not provided. Samples without a staining intensity were eliminated because of either lack of sufficient melanocytes or poor section quality for tissue segmentation.
5 Supplementary Table S2: Details of shrna vectors used Vector ID Clone ID Sequence Control Vector (shns) N/A CCGGCAACAAGATGAAGAGCACCAACTCGAGTTGGTGCT CTTCATCTTGTTGTTTTT TRCN (shsirt6-73) NM_ sc CCGGTGGAAGAATGTGCCAAGTGTACTCGAGTACACTTG GCACATTCTTCCATTTTTG TRCN (shsirt6-74) NM_ sc CCGGGCAGTCTTCCAGTGTGGTGTTCTCGAGAACACCAC ACTGGAAGACTGCTTTTTG TRCN (shsirt6-75) NM_ sc CCGGGCTGGGTACATCGCTGCAGATCTCGAGATCTGCAG CGATGTACCCAGCTTTTTG TRCN (shsirt6-76) NM_ sc CCGGCACCCGGATCAACGGCTCTATCTCGAGATAGAGCC GTTGATCCGGGTGTTTTTG TRCN (shsirt6-77) NM_ sc CCGGCACGGGAACATGTTTGTGGAACTCGAGTTCCACAA ACATGTTCCCGTGTTTTTG
6 Supplementary Table S3: Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR validation. Gene Amplicon Primer Length Tm Primer Bank Primer Sequence (5' - > 3') size (bp) orientation (bp) ( C) ID SIRT6 94 F CCCACGGAGTCTGGACCAT c R CTCTGCCAGTTTGTCCCTG 9 60 AKT 96 F AGCGACGTGGCTATTGTGAAG c R GCCATCATTCTTGAGGAGGAAGT ATG0 80 F ATAAGATGCGACTGCTACAGGG c3 R CAATGCTCAGCCATGATGTGAT 22 6 ATG2 53 F TAGAGCGAACACGAACCATCC c2 R CACTGCCAAAACACTCATAGAGA ATG3 25 F GATGGCGGATGGGTAGATACA c3 R TCTTCACATAGTGCTGAGCAATC ATG7 4 F ATGATCCCTGTAACTTAGCCCA c3 R CACGGAAGCAAACAACTTCAAC 22 6 BAK 92 F CATCAACCGACGCTATGACTC c3 R GTCAGGCCATGCTGGTAGAC BCL2L 79 F GACTGAATCGGAGATGGAGACC c2 R GCAGTTCAAACTCGTCGCCT CLN3 24 F CGCCCACGACATCCTTAGC c R AGCAGCCGTAGAGACAGAGTT 2 63 CTSB 59 F AGAGTTATGTTTACCGAGGACCT c3 R GATGCAGATCCGGTCAGAGA 20 6 CTSS 3 F TGACAACGGCTTTCCAGTACA c2 R GGCAGCACGATATTTTGAGTCAT 23 6 DRAM2 36 F CTGTGCTTACCTTTGGTATGGG c R GCACTTACTCCACACCAGATAAC 23 6 GAA 29 F TGCCCTCGCAGTATATCACAG c3 R GAGACCCGTAGAGGTTCGC 9 62 HSP90AA 87 F GCTTGACCAATGACTGGGAAG c3 R AGCTCCTCACAGTTATCCATGA IRGM 89 F GCCATGAATGTTGAGAAAGCCT c R GTCCTGGACACTATCTTCAGAGT 23 6 NPC 89 F GTCCAGCGCAGGTGTTTTC c R GCCGAACATCACAACAGAGAC 2 6 SQSTM 6 F AAGCCGGGTGGGAATGTTG c3 R CCTGAACAGTTATCCGACTCCAT 23 6 TNFα 9 F GAGGCCAAGCCCTGGTATG c2 R CGGGCCGATTGATCTCAGC 9 63 GAPDH 0 F CTGGGCTACACTGAGCACC c3 R AAGTGGTCGTTGAGGGCAATG 2 63
7 Supplementary Table S4: Human Autophagy PCR Array genes modulated upon SIRT6 knockdown in A375 melanoma cells. Gene Gene Description Autophagy Machinery Components Fold Change AKT V-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2 AMBRA Autophagy/beclin- regulator Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation APP Amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis ATG0 ATG0 autophagy related 0 homolog Responsible for Protein Transport 2.03 ATG2 ATG2 autophagy related 2 homolog Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Co-Regulators of -2 Autophagy and Apoptosis ATG6L ATG6 autophagy related 6-like Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for.0 Protein Transport ATG6L2 ATG6 autophagy related 6-like 2 Responsible for Protein Transport -.59 ATG3 ATG3 autophagy related 3 homolog Involved in Protein Ubiquitination, Responsible for Protein -2 Transport ATG4A ATG4 autophagy related 4 homolog A Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Targeting to Membrane / Vacuole, Responsible for Protein Transport, Gene with Protease Activity ATG4B ATG4 autophagy related 4 homolog B Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Targeting to Membrane / Vacuole, Responsible for Protein Transport, Gene with Protease Activity ATG4C ATG4 autophagy related 4 homolog C Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for - Protein Targeting to Membrane / Vacuole, Responsible for Protein Transport, Gene with Protease Activity ATG4D ATG4 autophagy related 4 homolog D Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for - Protein Targeting to Membrane / Vacuole, Responsible for Protein Transport, Gene with Protease Activity ATG5 ATG5 autophagy related 5 homolog Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis ATG7 ATG7 autophagy related 7 homolog Responsible for Protein Transport, Involved in Protein -2 Ubiquitination ATG9A ATG9 autophagy related 9 homolog A Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Transport ATG9B ATG9 autophagy related 9 homolog B Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation -.26 BAD BCL2-associated agonist of cell death Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis BAK BCL2-antagonist/killer Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2.0 BAX BCL2-associated X protein Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle BCL2 B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.58 BCL2L BCL2-like Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2 BECN Beclin, autophagy related Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis, Involved in - Autophagic Vacuole Formation BID BH3 interacting domain death agonist Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.58 BNIP3 BCL2/adenovirus EB 9kDa interacting protein 3 Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.58 CASP3 Caspase 3, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis CASP8 Caspase 8, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis - CDKNB Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor B (p27, Kip) Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle -.6 CDKN2A Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (melanoma, Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle - p6, inhibits CDK4) CLN3 Ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 3 Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2 CTSB Cathepsin B Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2.0 CTSD Cathepsin D Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals -.0 CTSS Cathepsin S Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals -4 CXCR4 Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis DAPK Death-associated protein kinase Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis DRAM DNA-damage regulated autophagy modulator Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis, Gene Linking Autophagosome to Lysosome DRAM2 DNA-damage regulated autophagy modulator 2 Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals -2 EIF2AK3 Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-alpha Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis, Autophagy.0 kinase 3 Induction by Intracellular Pathogens EIF4G Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma, Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals ESR Estrogen receptor Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals FADD Fas (TNFRSF6)-associated via death domain Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.59 FAS Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6) Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis - GAA Glucosidase, alpha; acid Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals 2.0 GABARAP GABA(A) receptor-associated protein Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Transport, Gene Linking Autophagosome to Lysosome
8 Continued from previous page GABARAPL GABA(A) receptor-associated protein like Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Transport GABARAPL2 GABA(A) receptor-associated protein-like 2 Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation, Responsible for Protein Transport -.57 HDAC Histone deacetylase Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis HDAC6 Histone deacetylase 6 Involved in Protein Ubiquitination HGS Hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals kinase substrate HSP90AA Heat shock protein 90kDa alpha (cytosolic), Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy class A member HSPA8 Heat shock 70kDa protein 8 Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy - HTT Huntingtin Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis IFNG Interferon, gamma Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle, Autophagy Induction by Intracellular Pathogens IGF Insulin-like growth factor (somatomedin C) Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis INS Insulin Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis IRGM Immunity-related GTPase family, M Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation LAMP Lysosomal-associated membrane protein Gene Linking Autophagosome to Lysosome, Autophagy.0 Induction by Intracellular Pathogens MAPLC3A Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation alpha MAPLC3B Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation.02 beta MAPK4 Mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals - MAPK8 Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis - MTOR Mechanistic target of rapamycin Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis (serine/threonine kinase) NFKB Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.26 enhancer in B-cells NPC Niemann-Pick disease, type C Gene Linking Autophagosome to Lysosome -2 PIK3C3 Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, class 3 Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals PIK3CG Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, catalytic, gamma Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.04 polypeptide PIK3R4 Phosphoinositide-3-kinase, regulatory subunit 4 Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals PRKAA Protein kinase, AMP-activated, alpha catalytic Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis subunit PTEN Phosphatase and tensin homolog Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle RAB24 RAB24, member RAS oncogene family Responsible for Protein Transport RB Retinoblastoma Co-Regulators of Autophagy and the Cell Cycle RGS9 Regulator of G-protein signaling 9 Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation RPS6KB Ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70kDa, Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals - polypeptide SNCA Synuclein, alpha (non A4 component of amyloid Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis.28 precursor) SQSTM Sequestosome Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -2 TGFB Transforming growth factor, beta Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle TGM2 Transglutaminase 2 (C polypeptide, proteinglutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis TMEM74 Transmembrane protein 74 Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals -.59 TNF Tumor necrosis factor Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis TNFSF0 Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, Co-Regulators of Autophagy and Apoptosis -.03 member 0 TP53 Tumor protein p53 Co-Regulators of Autophagy, Apoptosis and the Cell Cycle ULK Unc-5-like kinase (C. elegans) Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation ULK2 Unc-5-like kinase 2 (C. elegans) Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals UVRAG UV radiation resistance associated gene Autophagy in Response to Other Intracellular Signals WIPI WD repeat domain, phosphoinositide interacting Involved in Autophagic Vacuole Formation
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy se
 A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
A particular set of insults induces apoptosis (part 1), which, if inhibited, can switch to autophagy. At least in some cellular settings, autophagy serves as a defence mechanism that prevents or retards
Table 1. Clinicopathological features of melanoma samples (shown in Fig. 2) exhibiting higher XYZ mrna levels.
 Sheikh MS et al., Privileged communication. Probe: N T N T N T N T N T N T Table 1. Clinicopathological features of melanoma samples (shown in Fig. 2) exhibiting higher mrna levels. Patient No. Age (yrs)
Sheikh MS et al., Privileged communication. Probe: N T N T N T N T N T N T Table 1. Clinicopathological features of melanoma samples (shown in Fig. 2) exhibiting higher mrna levels. Patient No. Age (yrs)
Knockdown of Malic Enzyme 2 Suppresses Lung Tumor Growth, Induces Differentiation and Impacts PI3K/AKT Signaling
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Knockdown of Malic Enzyme 2 Suppresses Lung Tumor Growth, Induces Differentiation and Impacts PI3K/AKT Signaling Jian-Guo Ren 1, Pankaj Seth 1, Clary B. Clish 2, Pawel K. Lorkiewicz
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Knockdown of Malic Enzyme 2 Suppresses Lung Tumor Growth, Induces Differentiation and Impacts PI3K/AKT Signaling Jian-Guo Ren 1, Pankaj Seth 1, Clary B. Clish 2, Pawel K. Lorkiewicz
Effect of Hydroxychloroquine and Characterization of Autophagy in a Mouse Model of Endometriosis
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Cell Biology, Microbiology, and Molecular Biology Faculty Publications Cell Biology, Microbiology, and Molecular Biology 1-14-2016 Effect of Hydroxychloroquine
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Cell Biology, Microbiology, and Molecular Biology Faculty Publications Cell Biology, Microbiology, and Molecular Biology 1-14-2016 Effect of Hydroxychloroquine
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. b-galactosidase staining of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Hippocampal sections from new-born Pten+/+ and PtenFV/FV pups were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and were imaged at (a) low and (b) high
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
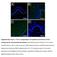 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Case Study - Informatics
 bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
bd@jubilantbiosys.com Case Study - Informatics www.jubilantbiosys.com Validating as a Prognostic marker and Therapeutic Target for Multiple Cancers Introduction Human genome projects and high throughput
Samali A Figure S1.
 Deegan S, Saveljeva S, Logue SE, Pakos-Zebrucka K, Gupta S, Vandenabeele P, Bertrand MJ,Samali A. (2014) Deficiency in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway reveals the toxic potential of autophagy under
Deegan S, Saveljeva S, Logue SE, Pakos-Zebrucka K, Gupta S, Vandenabeele P, Bertrand MJ,Samali A. (2014) Deficiency in the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway reveals the toxic potential of autophagy under
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury
 Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods Assessment of clinical characteristics of the single-agent anti-pd-1 cohort Clinical data were retrospectively collected from patient record, including age,
Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods Assessment of clinical characteristics of the single-agent anti-pd-1 cohort Clinical data were retrospectively collected from patient record, including age,
Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion
 Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Applied Biosystems models 7500 (Fast block), 7900HT (Fast block), StepOnePlus, ViiA 7 (Fast block)
 RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
Supplementary Information
 Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo, Induces Apoptosis in a T-Cell Leukemia Cell Line, Jurkat E6-1
 Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3224-3257; doi:10.3390/md11093224 Article OPEN ACCESS marine drugs ISSN 1660-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo,
Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3224-3257; doi:10.3390/md11093224 Article OPEN ACCESS marine drugs ISSN 1660-3397 www.mdpi.com/journal/marinedrugs Epigonal Conditioned Media from Bonnethead Shark, Sphyrna tiburo,
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells.
 Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
Figure 1 Figure 1: Effects of cisplatin on survival of lung cancer cells. To determine the IC 50 concentration of cisplatin, cells were treated with various concentrations of cisplatin and cell survival
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: /690105
 q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1086/690105 Appendix from R. M. Cox et al., Hormonally Mediated Increases in Sex-Biased Gene Expression Accompany the Breakdown of Between-
q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1086/690105 Appendix from R. M. Cox et al., Hormonally Mediated Increases in Sex-Biased Gene Expression Accompany the Breakdown of Between-
Cell Death & Renewal (part 2)
 17 Cell Death & Renewal (part 2) Programmed Cell Death A major signaling pathway that promotes cell survival is initiated by the enzyme PI 3-kinase, which phosphorylates PIP2 to form PIP3, which activates
17 Cell Death & Renewal (part 2) Programmed Cell Death A major signaling pathway that promotes cell survival is initiated by the enzyme PI 3-kinase, which phosphorylates PIP2 to form PIP3, which activates
Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions
 Supplementary data Table S1. Primary and Secondary antibody sources Devi et al, TXNIP in mitophagy A. Primary Antibodies Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions 1. TXNIP mouse MBL KO205-2 1:2000 (WB)
Supplementary data Table S1. Primary and Secondary antibody sources Devi et al, TXNIP in mitophagy A. Primary Antibodies Name Animal source Vendor Cat # Dilutions 1. TXNIP mouse MBL KO205-2 1:2000 (WB)
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Thanks to: Signal Transduction. BCB 570 "Signal Transduction" 4/8/08. Drena Dobbs, ISU 1. An Aging Biologist s. One Biologist s Perspective
 BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Tumor suppressor Spred2 interaction with LC3 promotes autophagosome maturation and induces autophagy-dependent cell death Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors
 Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Wang et al LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. IHC and proliferation analysis of pten-deficient mammary tumors A. Induced expression of estrogen receptor α (ERα) in AME vs PDA
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 28, 2014 Signal Transduction Pathway Smorgasbord Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Outline 1.
Lapatinib and Sorafenib Kill GBM Tumor Cells in a Greater than Additive Manner
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2013 Lapatinib and Sorafenib Kill GBM Tumor Cells in a Greater than Additive Manner Seyedmehrad Tavallai Virginia
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2013 Lapatinib and Sorafenib Kill GBM Tumor Cells in a Greater than Additive Manner Seyedmehrad Tavallai Virginia
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Chapter 2 Autophagy in Cancer Cells vs. Cancer Tissues: Two Different Stories
 Chapter 2 Autophagy in Cancer Cells vs. Cancer Tissues: Two Different Stories Chi Zhang, Tao Sheng, Sha Cao, Samira Issa-Boube, Tongyu Tang, Xiwen Zhu, Ning Dong, Wei Du, and Ying Xu Abstract Autophagy
Chapter 2 Autophagy in Cancer Cells vs. Cancer Tissues: Two Different Stories Chi Zhang, Tao Sheng, Sha Cao, Samira Issa-Boube, Tongyu Tang, Xiwen Zhu, Ning Dong, Wei Du, and Ying Xu Abstract Autophagy
Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy
 Pivotal Role of the Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy Keishi Fujiwara, Shigeru Daido, Akitsugu Yamamoto, Ryuji Kobayash, Tomohisa Yokoyama, Hiroshi Aok, Eiji Iwado,
Pivotal Role of the Cyclin-dependent Kinase Inhibitor p21 WAF1/CIP1 in Apoptosis and Autophagy Keishi Fujiwara, Shigeru Daido, Akitsugu Yamamoto, Ryuji Kobayash, Tomohisa Yokoyama, Hiroshi Aok, Eiji Iwado,
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20177 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Kester, Maria Sophia van (Marloes) Title: Molecular aspects of cutaneous T-cell
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20177 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Kester, Maria Sophia van (Marloes) Title: Molecular aspects of cutaneous T-cell
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
 Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Validated Mouse Quantitative RT-PCR Genes Gene Gene Bank Accession Number Name
 5HT1a NM_008308.4 Serotonin Receptor 1a 5HT1b NM_010482.1 Serotonin Receptor 1b 5HT2a NM_172812.2 Serotonin Receptor 2a ACO-2 NM_080633.2 Aconitase 2 Adora2A NM_009630.02 Adenosine A2a Receptor Aif1 (IbaI)
5HT1a NM_008308.4 Serotonin Receptor 1a 5HT1b NM_010482.1 Serotonin Receptor 1b 5HT2a NM_172812.2 Serotonin Receptor 2a ACO-2 NM_080633.2 Aconitase 2 Adora2A NM_009630.02 Adenosine A2a Receptor Aif1 (IbaI)
PI3K / AKT / mtor. Signalling Pathway in Cancer. PI3K / AKT / mtor Related Antibodies from CovalAb
 NEWSLETTER Version 1 From Research to Discovery PI3K / AKT / mtor Signalling Pathway in Cancer PI3K / AKT / mtor Related Antibodies from CovalAb www.covalab.com CovalAb - 11 avenue Albert Einstein 69100
NEWSLETTER Version 1 From Research to Discovery PI3K / AKT / mtor Signalling Pathway in Cancer PI3K / AKT / mtor Related Antibodies from CovalAb www.covalab.com CovalAb - 11 avenue Albert Einstein 69100
Pro-apoptotic signalling through Toll-like receptor 3 involves TRIF-dependent
 Pro-apoptotic signalling through Toll-like receptor 3 involves TRIF-dependent activation of caspase-8 and is under the control of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in melanoma cells Arnim Weber, Zofia Kirejczyk,
Pro-apoptotic signalling through Toll-like receptor 3 involves TRIF-dependent activation of caspase-8 and is under the control of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in melanoma cells Arnim Weber, Zofia Kirejczyk,
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Effect of Acid and Pepsin on LPR-Sensitive Mucins In Vitro
 Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Appendix Table of Contents. 1. Appendix Figure legends S1-S13 and Appendix Table S1 and S2. 2. Appendix Figures S1-S13
 Appendix Table of Contents. Appendix Figure legends S-S3 and Appendix Table S and S. Appendix Figures S-S3 . Appendix Figure legends S-S3 and Appendix Table S and S Appendix Figure S. Western blot analysis
Appendix Table of Contents. Appendix Figure legends S-S3 and Appendix Table S and S. Appendix Figures S-S3 . Appendix Figure legends S-S3 and Appendix Table S and S Appendix Figure S. Western blot analysis
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval
 Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES
 Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Figure 1
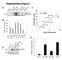 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
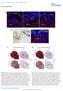 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Role for autophagy in cellular response to influenza virus infection
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Role for autophagy in cellular response to influenza virus infection AHY Law, DCW Lee, TYY Leon, ASY Lau * K e y M e s s a g e s 1. A differential induction
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Role for autophagy in cellular response to influenza virus infection AHY Law, DCW Lee, TYY Leon, ASY Lau * K e y M e s s a g e s 1. A differential induction
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Cancer. Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions.
 Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 #19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
LPS LPS P6 - + Supplementary Fig. 1.
 P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
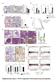 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of therapeutic strategies
 Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
EFFECTORS IMPLICATED IN THE AC1 INHIBITORY EFFECT ON CELL PROLIFERATION IN PANCREATIC CANCER CELLS
 EFFECTORS IMPLICATED IN THE AC1 INHIBITORY EFFECT ON CELL PROLIFERATION IN PANCREATIC CANCER CELLS VIDYA MEDEPALLI ADVISOR: Maria Eugenia Sabbatini, PhD PHI KAPPA PHI RESEARCH CONFERENCE MARCH 18 TH, 2016
EFFECTORS IMPLICATED IN THE AC1 INHIBITORY EFFECT ON CELL PROLIFERATION IN PANCREATIC CANCER CELLS VIDYA MEDEPALLI ADVISOR: Maria Eugenia Sabbatini, PhD PHI KAPPA PHI RESEARCH CONFERENCE MARCH 18 TH, 2016
Supplementary Information. Table of contents
 Supplementary Information Table of contents Fig. S1. Inhibition of specific upstream kinases affects the activity of the analyzed readouts Fig. S2. Down-regulation of INCENP gene induces the formation
Supplementary Information Table of contents Fig. S1. Inhibition of specific upstream kinases affects the activity of the analyzed readouts Fig. S2. Down-regulation of INCENP gene induces the formation
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
FOXO3 Regulates Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Sickle Cell Anemia. Yankai Zhang, Jacy R. Crosby, Eric Boerwinkle, Vivien A. Sheehan
 FOXO3 Regulates Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Sickle Cell Anemia Yankai Zhang, Jacy R. Crosby, Eric Boerwinkle, Vivien A. Sheehan Sickle Cell Anemia Steinberg MH. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1021-1030. Akinsheye
FOXO3 Regulates Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Sickle Cell Anemia Yankai Zhang, Jacy R. Crosby, Eric Boerwinkle, Vivien A. Sheehan Sickle Cell Anemia Steinberg MH. N Engl J Med 1999;340:1021-1030. Akinsheye
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression
 ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream signals in in vitro Symbol Gene ID RefSeqID Clone ID
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric
 Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch
 SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch. A. RNA and B. protein extracts from TNF treated and untreated human chondrocytes (hch) were analyzed via qpcr (left) and immunoblot analyses (right) for
SD-1 SD-1: Cathepsin B levels in TNF treated hch. A. RNA and B. protein extracts from TNF treated and untreated human chondrocytes (hch) were analyzed via qpcr (left) and immunoblot analyses (right) for
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Protein Arrays High Throughput Protein Quantification from Total Cell Lysates
 Protein Arrays High Throughput Protein Quantification from Total Cell Lysates Dr. Markus Ehrat Mr. Markus Tobler Zeptosens A Division of Bayer (Schweiz) AG Benkenstr. 254 CH-4108 Witterswil Switzerland
Protein Arrays High Throughput Protein Quantification from Total Cell Lysates Dr. Markus Ehrat Mr. Markus Tobler Zeptosens A Division of Bayer (Schweiz) AG Benkenstr. 254 CH-4108 Witterswil Switzerland
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit
 AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
