The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
|
|
|
- James Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dietologi (1) 7: DOI 1.17/s z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse Yn Beky Chn & Jnet vn Eersel & Ptsie Polly & Lrs M. Ittner Reeived: 1 Novemer 13 /Aepted: 13 Mrh 1 /Pulished online: 1 April 1 # Springer-Verlg Berlin Heidelerg 1 Astrt Aims/hypothesis Regultion of insulin seretion long the seretory pthwy is inompletely understood. We ddressed the expression of SIL1, nuleotide exhnge ftor for the endoplsmi retiulum (ER) hperone gluose-regulted protein 78 kd (GRP78), in pnreti et ells nd investigted whether or not SIL1 is involved in et ell funtion. Methods SIL1 expression ws nlysed y immunolotting nd immunofluoresene. Metoli nd islet vriles, inluding gluose tolerne, et ell mss, insulin seretion, islet ultrstruture, insulin ontent nd levels of ER stress mrker proteins, were ddressed in Sil1 knokout (Sil1 / ) mie., proinsulin nd C-peptide relese ws ddressed in Sil1 / islets, nd SIL1 overexpression or knokdown ws explored in MIN6 ells in vitro. Models of type 1 dietes nd insulin resistne were indued in Sil1 / mie y dministrtion of streptozotoin (STZ) nd high-ft diet (HFD), respetively. Results We show tht SIL1 is expressed in pnreti et ells nd is required for islet insulin ontent, islet sizing, gluose tolerne nd gluose-stimulted insulin seretion Eletroni supplementry mteril The online version of this rtile (doi:1.17/s z) ontins peer-reviewed ut unedited supplementry mteril, whih is ville to uthorised users. A. A. Ittner (): J. Bertz : J. vn Eersel : P. Polly : L. M. Ittner Shool of Medil Sienes, University of New South Wles, Botny Street, Kensington, Sydney, W, Austrli e-mil:.ittner@unsw.edu.u A. A. Ittner: J. Bertz : T. Y. B. Chn : J. vn Eersel : L. M. Ittner Fulty of Mediine, University of Sydney, Sydney, W, Austrli L. M. Ittner Neurosiene Reserh Austrli, Sydney, W, Austrli P. Polly Deprtment of Pthology, University of New South Wles, Sydney, W, Austrli in vivo. Levels of pnreti ER stress mrkers re inresed in Sil1 / mie, nd Sil1 / et ell ER is ultrstruturlly ompromised. Isolted Sil1 / islets show lower proinsulin nd insulin ontent nd impired gluose-stimulted insulin seretion. Modultion of SIL1 protein levels in MIN6 ells orreltes with hnges in insulin ontent nd sereted insulin. Furthermore, Sil1 / mie re more suseptile to STZindued type 1 dietes with inresed poptosis. Upon HFD feeding, Sil1 / mie show mrkedly lower insulin seretion nd exerted gluose intolerne ompred with ontrol mie. Surprisingly, however, HFD-fed Sil1 / mie disply pronouned islet hyperplsi with low mounts of insulin in totl pnres. Conlusions/interprettion These results revel novel role for the nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 in pnreti et ell funtion under physiologil nd disese onditions suh s dietes nd the metoli syndrome. Keywords Endoplsmi retiulum. Gluose-stimulted insulin seretion. High-ft diet. Islet size. Pnreti islets of Lngerhns. Proinsulin. Streptozotoin Arevitions BiP Binding immunogloulin protein CHOP CCAAT-enhner-inding protein homologous protein ER Endoplsmi retiulum GRP78 Gluose-regulted protein 78 kd HFD High-ft diet PERK Protein kinse RNA-like endoplsmi retiulum kinse shrna Short hirpin RNA shsil1 Short hirpin Sil1 STZ Streptozotoin TEM Trnsmission eletron mirosopy XBP-1 X-ox inding protein 1
2 Dietologi (1) 7: Introdution prodution follows the seretory pthwy [1, ]. Preproinsulin is otrnsltionlly inserted into the endoplsmi retiulum (ER), where the signl peptide is removed forming proinsulin. After sorting vi Golgi pprtus into vesiles, proinsulin is leved y prohormone onvertses into mture insulin. As requirements for insulin prodution nd seretion n vry with hnges in lood gluose level, the et ell is physiologilly fed with high demnds of folding pity in the ER [3]. ER hperone tivity is tightly regulted in et ells y progrmmes reminisent of ER stress responses, inluding trnsriptionl responses medited y X-ox inding protein 1 (XBP-1) or trnsltionl regultion of insulin prodution y protein kinse RNA-like endoplsmi retiulum kinse (PERK) [3]. Bet ell-speifi ltion of XBP-1 results in impired gluose tolerne, redued insulin seretion nd defetive insulin prodution [], while deletion of PERK results in dietes nd erly mortlity []. In humns, PERK muttions re ssoited with neontl dietes [6]. A key trnsriptionl trget of ER stress pthwys is the ER hperone gluose-regulted protein 78kD (GRP78; lso known s inding immunogloulin protein [BiP]) [3, 7]. GRP78 inds nd stilises unfolded polypeptides, nd is key sensor for high ER folding demnd nd n indue ER stress progrmmes (e.g. vi tivtion of PERK or XBP-1). Consistent with this role, knokdown of GRP78 using Grp78 sirna in et ell line redues insulin ontent nd gluose-stimulted insulin seretion [8]. Overexpressing GRP78 inreses insulin seretion independent of insulin trnsription [8]. GRP78 expression orreltes with the demnd for insulin in stimulted et ells [9]. Ativity of GRP78 is dependent on effiient nuleotide exhnge [1]. Two nuleotide exhnge ftors hve een identified for GRP78 in mmmls, GRP17 nd SIL1 [11]. SIL1 ws disovered in Shromyes erevisie, nd its homologues re onserved etween mouse nd humn. Sil1 mrna is expressed in the entrl nervous system [1], nd Sil1 mutnt mie show txi nd ereellr dystrophy [13]. In humns, Sil1 muttions use Mrineso Sjögren syndrome [1, 1]. Funtions of SIL1 outside the entrl nervous system re, however, unknown. Here, we show novel role for the nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 in et ell funtion. Methods Further detils of the methods used in this study n e found in the Eletroni supplementry mteril (ESM) Methods, inluding methods for gluose nd insulin tolerne tests. Mie Animl experiments were pproved y the Animl Ethis Committee of the University of New South Wles (Sydney, W, Austrli). Sil1-mutnt mie (CXB/By-Sil1 wz /J; JAX mie 3777; Jkson Lortory, Br Hror, ME, USA) were desried previously [13]. Age- nd sex-mthed littermte mie red t the University of New South Wles were used in ll experiments t indited numers. Detils of STZ- nd high ft diet (HFD)-indued models of type 1 dietes re given in the ESM Methods. Gluose-stimulted insulin seretion in vitro The isoltion of pnreti islets hs een desried previously [16]. Isolted pnreti islets were wshed in Kres Ringer HEPES uffer (KRH) with.8 mmol/l gluose, ounted nd distriuted in equl numers in ulture pltes. KRH with either.8 mmol/l gluose, 16.8 mmol/l gluose or mmol/l KCl ws dded nd islets were inuted t 37 C under % CO.Seretion ws mesured y ELISA for insulin (ChrystlChem, Downers Grove, IL, USA), pro-insulin nd C-peptide (Alpo, Slem, NH, USA). Trnsmission eletron mirosopy Fixtion for trnsmission eletron mirosopy (TEM) ws rried out s previously desried [17] (seeesmmethods). Histologil nlysis Immunofluoresene stining ws performed s previously desried [18] (seeesmmethods). Western lotting Western lot nlysis ws performed s previously desried [19] (see ESM Methods). Lentivirus prodution Lentivirus ws produed s desried previously [] (see ESM Methods). Cell ulture MIN6 ells were desried previously [1] (see ESM Methods). Sttistil nlysis Student s t-test ws used for omprison of two dt sets, ANOVA for omprison of more thn two dt sets nd two-wy ANOVA for omprisons ross time. Results GRP78/BiP nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is expressed in pnreti et ells Sil1 mrna ws found in the liver, plent nd kidney [1], ll tissues with seretory tivity. Therefore, we ddressed expression of SIL1 in pnres nd prtiulrly in islets. We deteted SIL1 in mouse pnres t muh higher levels thn in liver of wild-type ( )mie (Fig. 1). SIL1 ws not deteted in liver nd pnres extrts from Sil1 / mie. Musle displyed no detetle Sil1. Isolted islets showed high levels of Sil1 in ut not in Sil1 / islets (Fig. 1). In ddition, proinsulin levels in Sil1 /
3 11 Dietologi (1) 7: SIL1 Proinsulin Musle SIL1 Liver Proinsulin intensity normlised to were lower thn in islets (Fig. 1). We used immunofluoresene to determine whih islet ells express SIL1, nd found the exhnge ftor ws lrgely onfined to endorine pnreti islets ompred with exorine pnres (Fig. 1). SIL1 immunostining within insulin-positive ells presented s perinuler signl reminisent of ER lolistion (Fig. 1). SIL1 signls in insulin-negtive ells indited onomitnt expression in other islet ell types (e.g. lph or delt ells; Fig. 1). Speifiity is supported y lk of signl in Sil1 / islets (dt not shown). Tken together, SIL1 is expressed in pnreti et ells. SIL1 regultes pnreti islet mss nd et ell ER homeostsis in vivo To ddress the funtionl relevne of pnreti islet SIL1, we determined the mount nd morphology of islets in regulr how-fed Sil1 / mie. Pnres histology t months reveled lower islet numers nd smller size in Sil1 / mie (Fig. ). Totl islet mss in Sil1 / mie ws signifintly lower thn in mie (Fig. ). Individul islet size ws pproximtely % smller in Sil1 / mie thn in mie (Fig. ; men dimeter ± SEM 73± 6 μm, Sil1 / ± μm; p=.133; n=6 7). Pnreti insulin ontent ws mrkedly lower in Sil1 / thn in mie (Fig. d). Notly, no poptoti ells were detetle in Sil1 / SIL1 Pnres +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/ DAPI Sil1 DAPI 36 Fig. 1 SIL1 is expressed in pnreti et ells of mie. () Western lot of pnres, liver nd musle from, Sil1 +/- nd Sil1 / mie for SIL1 nd. (n=3). () Western lot of (white r) nd Sil1 / (lk r) islets for SIL1 nd proinsulin (n=3). () Pnreti immunofluoresene from mie for insulin nd SIL1; DAPI, ell nulei; Sle r, 1 μm. p<.., glyerldehyde 3-phosphte dehydrogense islets (dt not shown). Liver is lso involved in gluose homeostsis nd showed expression of SIL1 (Fig. 1). Yet, Sil1 / livers ppered norml (Fig. ). Islets in Sil1 / mie showed norml ptterns with entrl et ells nd with lph nd delt ells in periphery (Fig. e; dt not shown for delt ells). However, insulin stining in Sil1 / islets ppered less intense thn in islets. SIL1 regultes tivity of GRP78, ritil ER ftor involved in protein folding nd ER stress response [11]. We ddressed protein levels of ER stress mrkers in regulr howfed mie y immunolot. Sil1 / pnres showed inresed levels of ER stress mrkers XBP-1, phosphoryltion of PERK, GRP78 nd CCAAT-enhner-inding protein homologous protein (CHOP; Fig. f, g), suggesting ER stress nd distured of ER homeostsis. We ddressed ultrstruturl morphology y TEM. Mitohondri nd Golgi pprtus ppered well defined in nd Sil1 / et ells. ER showed typil memrnous struture studded with riosomes nd nrrow ER lumen. However, in Sil1 / et ells the ER ppered diffuse with undefined luminl spe (Fig. h). Eletron-dense vesiles were indistinguishle etween Sil1 / nd pnres (Fig. i). SIL1 is required for gluose tolerne nd insulin seretion in vivo Fsting gluose in Sil1 / nd mie ws similr (men ± SEM.3±.63 mmol/l, Sil1 /.7±.3 mmol/l; p=.98; n=6), s were ody weights (t 16 weeks men ± SEM 31.76±.9 g, Sil1 / 8.97±.71 g; p=.9; n=). However, Sil1 / mie showed impired gluose tolerne ompred with ontrols, with signifintly higher pek gluose levels (Fig. 3, ). Sil1 / nd mie showed similr levels of insulin sensitivity (Fig. 3, d). Impired insulin levels might ount for impired gluose tolerne in Sil1 / mie. Sil1 / mie showed signifintly lower plsm insulin upon gluose stimultion thn ontrols (Fig. 3e, f). In prtiulr, Sil1 / mie showed little inresed insulin seretion, while fsting insulin levels were omprle with ontrols. Fsting glugon levels were omprle etween Sil1 / nd mie (Fig. 3g). Thus, SIL1 is required for pek insulin seretion in vivo. SIL1 regultes insulin ontent nd seretion from et ells To ddress insulin relese from islets (i.e. independent of endorine or neuronl pthwys), we next isolted islets nd mesured insulin relese. Relesed insulin ws mrkedly lower from Sil1 / thn islets (Fig. ). The mount of C-peptide relesed from Sil1 / islets ws lower thn from islets (Fig. ). Although islets relesed minute mounts of proinsulin, Sil1 / showed signifintly more stimulted proinsulin relese thn islets (Fig. ). Individul islet insulin ontent ws pproximtely % lower in Sil1 / thn islets (Fig. d). Proinsulin ontent ws
4 Dietologi (1) 7: Fig. Sil1 / pnres shows redued islet mss, insulin ontent nd ER stress. () Pnreti nd hepti hemtoxylin nd eosin stining (1 μm) of how-fed Sil1 / nd mie; dshed lines show islets. Liver glyogen stining (PAS) on Sil1 / nd. Sle rs, 1 μm. () Islet mss in Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie. Vlues re men ± SEM (n=6 7 nimls). () IsletreinSil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie. Vlues re men ± SEM (n=6 7 nimls; 3 islets eh). (d) Pnreti insulin ontent in Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie. Vlues re men ±SEM(n=6 7 nimls).(e) Pnreti immunofluoresene (1 μm) of glugon (red) nd insulin (green). DAPI, ell nulei. Sle rs, 1 μm. (f) Immunolot of Sil1 / nd pnreti lystes for XBP-1, phospho-threonine98-perk, PERK, GRP78 (lso known s BiP), CHOP, nd SIL1. (g) Quntifition of (f). Blk rs, Sil1 / ; white rs,. Vlues re men ± SD (n= nimls). (h) TEM imges of Sil1 / nd et ells. Arrows, unstrutured ER in Sil1 / ells. Sle rs, 1 μm. (i) Vesile dimeter from (h). Blk r, Sil1 / ; white r,. Vlues re men ± SD (n=3 nimls); p<., p<.1. G, Golgi;, glyerldehyde 3-phosphte dehydrogense; M, mitohondrion; PAS, periodi id-shiff Pnres Liver Liver PAS f h SIL1 pt98-perk PERK GRP78/BiP XBP-1 CHOP ER M G 1 µm 1 µm M Islet mss (mg) e 8, 1 6 Men islet re (µm ) 3,, 1, Glugon Glugon ER G g Fold intensity 3 1 ontent (ng/mg) 1 Glugon Glugon XBP-1 p-perk PERK CHOP GRP78/BiP i Vesile dimeter (µm) d.6.. DAPI DAPI likewise lower (Fig. e), onfirming immunolotting dt (Fig. 1). Interestingly, reltive normlised insulin seretion ws still signifintly lower from Sil1 / ompred with islets (Fig. f), suggesting tht insulin seretion ws ompromised independent of lower insulin ontent. To determine the effets of SIL1 redution or overexpression in ellulr model, we used MIN6 ells []. Expression of Sil1-speifi short hirpin RNA (shrna) resulted in SIL1 knokdown (Fig. ). SIL1-knokdown MIN6 showed lower proinsulin levels (Fig. ), similr to isolted Sil1 / islets. Furthermore, mture insulin levels were lower in Sil1-speifi shrna thn in ontrol shrna-seleted MIN6 ells (Fig. ). Importntly, knokdown of SIL1 resulted in lower insulin nd C-peptide relese in response to either gluose or potssium hloride (KCl), with the ltter using depolristion nd vesile seretion (Fig., d). Next, we overexpressed SIL1 in MIN6 ells (Fig. f). levels in MIN6 expressing SIL1 were signifintly higher thn in ontrol-trnsfeted MIN6 ells (Fig. g). nd C-peptide relese from MIN6 expressing SIL1 ws signifintly higher thn in ontrol-trnsfeted ells (Fig. h, i). Neither SIL1 knokdown nor overexpression resulted in
5 11 Dietologi (1) 7: Blood gluose (mmol/l) 1 1 d e f g tolerne (mmol/l x min) Time (min) Plsm insulin (pmol/l) 3 1 Gluose tolerne (mmol/l x min) Fig. 3 Sil1 / mie hve impired gluose tolerne due to impired insulin seretion. () GTTinSil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) mie (n=6).() AUC during GTT in (); lk rs, Sil1 / ; white rs, (n=6). () ITTin (white irles) nd Sil1 / (lk irles) mie (n=6). (d) AUC during ITT in (); lk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=6). (e) Plsm insulin during gluose stimultion (1 mg/g 3 1, 1, 3,, 1, Time (min) Blood gluose (mmol/l) Plsm insulin (pmol/l x min) Time (min) Fsting glugon (pg/ml) ody weight) in Sil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) (n=7 9) (f) AUC of insulin in (e); lk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=7 9; p<.1). (g) Fsting glugon in Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie (n=7 9). Vlues re men ± SEM; p<.1, p<.1. ITT, insulin tolerne test;, not signifint signifint ltertion of relesed proinsulin (Fig. e, j). Hene, ltering SIL1 levels modultes insulin prodution nd insulin seretion in MIN6 ells. SIL1 protets from STZ- nd diet-indued dietes Although Sil1 / mie do not disply overt dietes, their et ells might e more vulnerle to stressors. We used STZ to indue relese (ng/µg protein) 6 C-peptide relese (ng/µg protein) Time (min) Time (min) Time (min) Proinsulin relese (ng/µg protein)...3 d e f Islet insulin (ng) Islet proinsulin (ng) 1 Fold insulin relese (reltive to ontent) Fig. SIL1 ffets islet insulin ontent nd stimulted seretion in vitro. () seretion from Sil1 / (lk symols) nd (white symols) islets during gluose stimultion (16.8 mmol/l; squres) or sl gluose (.8 mmol/l; irles), (n=). () C-peptide seretion from Sil1 / (lk symols) nd (white symols) islets (n=). () Proinsulin seretion from Sil1 / (lk symols) nd (white symols) islets 1 1 Time (min) (n=). (d) Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) islet insulin ontent (n=6). (e) Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) islet proinsulin ontent (n=6). (f) Stimulted insulin seretion reltive to islet insulin ontent nd sl seretion from Sil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) islets (n=). Vlues re men ± SEM; p<., p<.1
6 Dietologi (1) 7: SIL1 Proinsulin s shsil SIL1 level normlised to Proinsulin level normlised to (ng/µg protein) 7 relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ) KCI Gluose (mmol/l) d e f g C-peptide relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ) 1, 1, Proinsulin relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ) KCI KCI Gluose (mmol/l) Gluose (mmol/l) 3 1 GFPMOCK SIL1 SIL1 Proinsulin (ng/µg protein) h i j relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ), 1, 1, C-peptide relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ) 1, 1, Proinsulin relese (ng [mg protein] -1 [min] -1 ) KCl KCl KCl Gluose (mmol/l) Gluose (mmol/l) Gluose (mmol/l) Fig. SIL1 regultes insulin ontent nd seretion from MIN6 ells. () Western lot of MIN6 ells trnsfeted with Sil1-speifi shrna (shsil1) or srmled shrna s for Sil1, proinsulin nd (n=3). Quntifition: 7.7±.6% nd 9.1±.3% SIL1 nd proinsulin redution, respetively. () levels in shsil1 (lk r) nd s (white r) MIN6 (n=3). () seretion from shsil1 (lk rs) nd s (white rs) MIN6 during gluose or KCl ( mmol/l) stimultion (n=3). (d) C-peptide seretion from shsil1 (lk rs) nd s (white rs) MIN6 during gluose or KCl ( mmol/l) stimultion (n=3). (e) Proinsulin seretion from shsil1 (lk rs) nd s (white rs) MIN6 during gluose or KCl ( mmol/l) stimultion (n=3). (f) Western lot of MIN6 ells trnsfeted with GFP- or Sil1-expressing vetor, or MOCK 3 1 (n=3). (g) ontent in Sil1-expressing (lk r) MIN6 ells nd MOCK ontrols (white r) or GFP ontrols (grey r; n=3). (h) seretion in Sil1-expressing (lk rs) MIN6 ells nd MOCK ontrols (white rs) or GFP ontrols (grey rs) with gluose or KCl ( mmol/l; n=3). (i) C-peptide seretion in Sil1-expressing (lk rs) MIN6 ells nd MOCK ontrols (white rs) or GFP ontrols (grey rs) with gluose or KCl ( mmol/l; n=3).(j) Proinsulin seretion in Sil1-expressing (lk rs) MIN6 ells nd MOCK ontrols (white rs) or GFP ontrols (grey rs) with gluose or KCl ( mmol/l; n=3). Vlues re men ± SEM; p<., p<.1, p<.1., glyerldehyde 3-phosphte dehydrogense; GFP, green fluoresent protein; MOCK, empty vetor; s, ontrol vetor;, not signifint mie models of type 1 dietes. Sil1 / mie showed higher gluose levels within 36 h fter STZ dministrtion ompred with mie (Fig. 6). Overll, lood gluose levels inresed fster in STZ-treted Sil1 / thn in mie (Fig. 6). STZ indues et ell poptosis prior to rises in lood gluose. We nlysed islets in Sil1 / nd mie for poptosis y TUNEL stining 18 h post-stz dministrtion. Sil1 / islets showed more poptoti ells within islets (Fig. 6). Normlising for insulin-positive re to ount for smller Sil1 / islets reveled signifintly more TUNEL-positive ells in Sil1 / thn in islets (Fig. 6d). Thus, Sil1 / islets re more suseptile to STZ. Exess dietry intke imposes higher demnds for insulin, inresing islet size nd mount of sereted insulin [3]. Sil1 / mie fed HFD showed similr weight gin to HFD-fed (Fig. 7). However, gluose tolerne in Sil1 / mie ws signifintly lower thn in HFD-fed mie (Fig. 7, ). sensitivity in HFD Sil1 / mie ws similr to tht of HFD mie (Fig. 7d, e). Strikingly, however, mrkedly lower insulin levels nd insulin seretion were pprent in HFD Sil1 / ompred with HFD mie (Fig. 7f, g). Fsting glugon level ws similr in HFD Sil1 / nd HFD mie (Fig. 7h). Surprisingly, histologil pnreti setions from HFD-fed mie showed islets of lrger size in HFD Sil1 / ompred with HFD mie (Fig. 7i). Quntifition onfirmed ggrvted islet hyperplsi in HFD Sil1 / (Fig. 7j). Bet ell size ws indistinguishle etween HFD Sil1 / nd HFD islets (Fig. 7k).
7 116 Dietologi (1) 7: Blood gluose (mmol/l) 1 1 Strikingly, pnres of HFD Sil1 / mie showed mrkedly lower mounts of insulin thn those of HFD mie (Fig. 7l). HFD Sil1 / islets showed norml distriution nd intensity of glugon (Fig. 7m). Levels of GRP78 were mrkedly higher in HFD Sil1 / thn in HFD pnres, suggesting inresed ER stress (Fig. 7n, o). Furthermore, levels of ylin D1, G 1 mitoti phse mrker, were higher in HFD Sil1 / pnres. Thus, HFD Sil1 / mie hve pronouned islets hyperplsi, yet insuffiient insulin mounts nd defetive pek insulin seretion. Disussion Time (h) TUNEL TUNEL TUNEL TUNEL Our results present previously unknown role for nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 in et ells. Sil1 trnsript levels were nlysed in seleted humn tissues [1]. Neither protein levels nor expression in pnres or islets were ddressed. We found expression of SIL1 in islet ells, inluding et ells, using Sil1 / smples to ontrol for speifiity. Post-trnsriptionl mehnisms nd sensitivity might ount for differenes of Sil1 mrna [1] nd protein expression ptterns. SIL1 expression in liver is low nd Sil1 / mie present with norml liver histology nd glyogen storge. The liver mintins Gluose tolerne (mmol/l x min) DAPI DAPI 1, d TUNEL-positive ells (n/µm + re) Fig. 6 Sil1 / mie show inresed suseptiility to STZ-indued hyperglyemi nd et ell poptosis. () Blood gluose in Sil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) mie 36 h fter STZ dministrtion (n= ). () AUC of lood gluose in (); lk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n= ). () Pnreti insulin immunofluoresene nd TUNEL stining of Sil1 / nd (1 μm) 18 h fter STZ dministrtion. DAPI, ell nulei. Sle r, 1 μm. (d) Quntifition of TUNEL-positive ells per insulin-positive re fter STZ dministrtion. Blk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=1 islets/mouse; four mie/group). Vlues re men ± SEM; p<., p<.1 fsting gluose level regulted y glugon from lph ells []. Sil1 / mie hve norml fsting gluose nd glugon levels, suggesting tht glugon relese nd liver funtions re unffeted y lk of SIL1. In the present study, Sil1 / mie show deresed gluose tolerne, pproximtely % redution in pnreti insulin ontent nd virtully no insulin pek-seretion upon gluose stimultion. Sil1 / islets demonstrte little insulin nd C-peptide relese fter gluose stimultion. Sil1 / islets ontin pproximtely % less insulin thn islets. In reltion to insulin ontent, reltive normlised insulin seretion from Sil1 / islets remins signifintly lower thn from islets, suggesting tht esides insulin ontent, dditionl proesses suh s trffiking nd/or exoytosis re ffeted. Proinsulin levels re lower in Sil1 / islets thn in Si1l +/+ islets. Furthermore, Sil1 / islets show signifintly more proinsulin relese thn islets. This finding likely reflets ER stress in Sil1 / islets, sine elevted proinsulin relese hs een suggested s n dptive mehnism during ER stress []. Our dt from isolted islet nd MIN6 ells onfirm ellutonomous regultion of insulin ontent nd insulin seretion y SIL1. SIL1 is n ER-resident protein [6]. ER in Sil1 / et ells in vivo shows mrked ultrstruturl hnges, wheres Golgi pprtus nd vesiles pper norml. Ultrstruturl ER hnges re seen upon ER stress [, 7] nd proinsulin trffiking defets [8]. ER stress pthwys pper to e negtively ontrolled y SIL1, sine ER stress mrkers phospho- PERK, XBP-1, CHOP nd GRP78 re elevted in pnres of Sil1 / mie. ER stress pthwys ffet proinsulin trnsription, trnsltion nd trffiking [3, 8]. Furthermore, ER qulity ontrol my inhiit stimulted insulin seretion in Sil1 / et ells [3, ]. GRP78 knokdown redues insulin levels nd insulin relese [8]. GRP78 overexpression results in inresed insulin seretion independent of insulin trnsription [8]. Similrly, et ell knokout of Xp-1, trnsription ftor for GRP78, results in redued insulin prodution nd sene of insulin seretion in vivo []. Sine SIL1 is GRP78 nuleotide exhnge ftor [1], nd given the remrkly similr effets of modulting levels of GRP78 [8], XBP-1 [] or (s shown in the present study) SIL1, it is likely tht SIL1 regultes insulin iosynthesis nd pek-seretion through GRP78. Gluose inreses insulin trnsltion [9] nd ATP levels [3, 31]. ATP exhnge in GRP78 is limiting [1, 3, 33]. SIL1 might e ritil for effiient GRP78 funtion under onditions of gluose stimultion. GRP17, n lterntive exhnge ftor for GRP78 [3], seems not to ompenste for loss of SIL1, lthough how different exhnge ftors orhestrte GRP78 nd ER stress response is unknown. ER stress responses hve een implited in et ell survivl nd poptosis [3]. Sil1 / mie re more suseptile to STZ-indued dietes nd islet poptosis. We found ER
8 Dietologi (1) 7: Body weight (g) f Plsm insulin (pmol/l) m Time (weeks) Time (min) Time (min) Plsm insulin (pmol/l x min) DAPI Glugon Glugon DAPI Glugon Glugon Blood gluose (mmol/l) Fsting glugon (pg/ml) Gluose tolerne (mmol/l x min) d Reltive lood gluose e tolerne (mmol/l x min) g h i j k l 3 6,, 1 1, 1, , 1, 1, 1 3 Time (min) Isulin n SIL 1 GRP78/BiP Cylin D1 Fig. 7 Sil1 / mie show mrkedly lower insulin seretion ut more pronouned islet hyperplsi in HFD model. () Body weight of (white irles) nd Sil1 / (lk irles) mie during HFD (n= 6). () GTT fter 1 weeks of HFD in Sil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) mie (n=6).() AUC during GTT in (); lk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=6). (d) Reltive lood gluose during ITT in d liitum-fed HFD (white irles) nd Sil1 / (lk irles) mie (n=6). (e) AUC during ITT in (d). Blk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=6). (f) Plsm insulin during gluose stimultion (1 mg/g ody weight) in HFD Sil1 / (lk irles) nd (white irles) mie (n=6). (g) AUC of plsm insulin in (f); lk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n=6). (h) Fsting glugon in HFD Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie (n=6). (i) Histology of HFD Sil1 / nd pnres (1 μm); dshed lines demrte islets; sle rs, 1 μm. (j) Men islet re (µm ) o Fold levels Grp78/BiP CylinD1 Men et ell size (µm) Quntifition of men islet re in HFD Sil1 / (lk r) nd mie from histology shown in (i) (n= nimls; 1 islets eh). (k) Islet et ell size from histology shown in (i) Blk r, Sil1 / ; white r, (n= nimls; 3 islets eh; 8 1 ells/islet). (l) Pnreti insulin ontent in HFD Sil1 / (lk r) nd (white r) mie (n=6). (m) Pnreti immunofluoresene (1 μm) for glugon (red) nd insulin (green) in HFD Sil1 / nd mie. DAPI, ell nulei; sle r, 1 μm. (n) Immunolot of HFD Sil1 / nd pnreti lystes for GRP78, ylin D1, nd SIL1. (o) Quntifition of (n). Blk rs, Sil1 / ; white rs, ;vluesremen±sd(n=3). Vlues re men ± SEM unless otherwise stted; p<.1, p<.1, p<.1., glyerldehyde 3-phosphte dehydrogense; ITT, insulin tolerne test;, not signifint ontent (ng/mg) 3 1 stress in the pnres of Sil1 / mie. While initil ER stress responses re protetive [3, 9], persistent ER stress n indue poptosis [3]. Persistent ER stress in Sil1 / et ells my render them suseptile to STZ y reduing poptosis thresholds. Rodent HFD models hve ompenstory islet hyperplsi [3, 36]. In our study, HFD Sil1 / islets were twie the size of HFD islets, suggesting pronouned hyperplsi. ontent nd levels were mrkedly lower in HFD Sil1 / mie, with sent pek insulin seretion in vivo. Thus, ompenstory hyperplsi under Sil1 / onditions produes lrge islets ut little insulin. Bet ells retin the pity of prolifertion unlike other differentited ells [37]. We found higher levels of ylin D1, mitoti mrker, in HFD Sil1 / ompred with pnres, suggesting inresed ompenstory prolifertion. signlling is required for ompenstory prolifertion [38]. SIL1 might influene ompenstory prolifertion y modulting insulin levels. We found higher levels of ER stress in HFD Sil1 / islets ompred with islet. HFD-indued ER stress pthwys lok trnsltion [3]. ER stress pthwys n ontriute to inresed prolifertion in the erly dieti stges [39]. Other ER-ssoited moleules my e involved in hyperprolifertion in HFD Sil1 / pnres. Inresed expression of endoplsmiretiulum-ssoited protein degrdtion omponent SEL1L promotes et ell prolifertion []. Our dt suggest role for SIL1 in ontrolling ompenstory prolifertion. Aknowledgements The uthors thnk Dr J.-I. Miyzki (Osk University, Osk, Jpn) for providing the MIN6 ell line nd S. Frser (Eletron Mirosope Unit, University of New South Wles, Sydney, W, Austrli) for tehnil ssistne.
9 118 Dietologi (1) 7: Dulity of interest The uthors delre tht there is no dulity of interest ssoited with this mnusript. Contriution sttement AI designed experiments, nlysed the dt nd wrote the mnusript. JB, BC nd JvE performed experiments, nlysed the dt nd drfted prts of mnusript. PP nd LMI designed study nd experiments nd wrote the mnusript. All uthors pproved the finl version. AI is responsile for the integrity of the work s whole. Funding The reserh ws supported y funding from the Ntionl Helth nd Medil Reserh Counil (NHMRC), the Austrlin Reserh Counil (ARC) nd the University of New South Wles. LMI is NHMRC Senior Reserh Fellow. Referenes 1. Rorsmn P, Brun M (13) Regultion of insulin seretion in humn pnreti islets. Annu Rev Physiol 7: Weiss MA (9) Proinsulin nd the genetis of dietes mellitus. J Biol Chem 8: Bk SH, Kufmn RJ (1) Endoplsmi retiulum stress nd type dietes. Annu Rev Biohem 81: Lee AH, Heidtmn K, Hotmisligil GS, Glimher LH (11) Dul nd opposing roles of the unfolded protein response regulted y IRE1lph nd XBP1 in proinsulin proessing nd insulin seretion. Pro Ntl Ad Si U S A 18: Zhng P, MGrth B, Li S et l () The PERK eukryoti initition ftor lph kinse is required for the development of the skeletl system, postntl growth, nd the funtion nd viility of the pnres. Mol Cell Biol : Senee V, Vttem KM, Delepine M et l () Wolott-Rllison syndrome: linil, geneti, nd funtionl study of EIFAK3 muttions nd suggestion of geneti heterogeneity. Dietes 3: Sh H, He Y, Yng L, Qi L (11) Stressed out out oesity: IRE1lph-XBP1 in metoli disorders. Trends Endorinol Met : Zhng L, Li E, Teodoro T, Volhuk A (9) GRP78, ut not protein-disulfide isomerse, prtilly reverses hyperglyemiindued inhiition of insulin synthesis nd seretion in pnreti β-ells. J Biol Chem 8: Sheuner D, Vnder Mierde D, Song B et l () Control of mrna trnsltion preserves endoplsmi retiulum funtion in et ells nd mintins gluose homeostsis. Nt Med 11: Mtlk KE, Misselwitz B, Plth K, Rpoport TA (1999) BiP ts s moleulr rthet during posttrnsltionl trnsport of prepro-lph ftor ross the ER memrne. Cell 97: Heert DN, Molinri M (7) In nd out of the ER: protein folding, qulity ontrol, degrdtion, nd relted humn diseses. Physiol Rev 87: Chung KT, Shen Y, Hendershot LM () BAP, mmmlin BiP-ssoited protein, is nuleotide exhnge ftor tht regultes the ATPse tivity of BiP. J Biol Chem 77: Zho L, Longo-Guess C, Hrris BS, Lee JW, Akermn SL () Protein umultion nd neurodegenertion in the woozy mutnt mouse is used y disruption of SIL1, ohperone of BiP. Nt Genet 37: Senderek J, Krieger M, Stendel C et l () Muttions in SIL1 use Mrineso-Sjogren syndrome, ereellr txi with trt nd myopthy. Nt Genet 37: Anttonen AK, Mhjneh I, Hmlinen RH et l () The gene disrupted in Mrineso-Sjogren syndrome enodes SIL1, n HSPA ohperone. Nt Genet 37: Li DS, Yun YH, Tu HJ, Ling QL, Di LJ (9) A protool for islet isoltion from mouse pnres. Nt Proto : Shum AM, Mhendrdtt T, Tylor RJ et l (1) Disruption of MEFC signling nd loss of sromeri nd mitohondril integrity in ner-indued skeletl musle wsting. Aging : Ke YD, Delerue F, Gldh A, Gotz J, Ittner LM (9) Experimentl dietes mellitus exertes tu pthology in trnsgeni mouse model of Alzheimer s disese. PLoS One :e Ittner A, Blok H, Reihel CA et l (1) Regultion of PTEN tivity y p38delt-pkd1 signling in neutrophils onfers inflmmtory responses in the lung. J Exp Med 9:9 6. vn Eersel J, Ke YD, Liu X et l (1) Sodium selente mitigtes tu pthology, neurodegenertion, nd funtionl defiits in Alzheimer s disese models. Pro Ntl Ad Si U S A 17: Miyzki J, Arki K, Ymto E et l (199) Estlishment of pnreti et ell line tht retins gluose-induile insulin seretion: speil referene to expression of gluose trnsporter isoforms. Endorinology 17: Ishihr H, Asno T, Tsukud K et l (1993) Pnreti et ell line MIN6 exhiits hrteristis of gluose metolism nd gluosestimulted insulin seretion similr to those of norml islets. Dietologi 36: Buettner R, Sholmerih J, Bollheimer LC (7) High-ft diets: modeling the metoli disorders of humn oesity in rodents. Oesity (Silver Spring) 1: Rmnnn CJ, Edgerton DS, Krft G, Cherrington AD (11) Physiologi tion of glugon on liver gluose metolism. Dietes Oes Met 13(Suppl 1): Cnop M, Welsh N, Jons JC, Jorns A, Lenzen S, Eizirik DL () Mehnisms of pnreti et-ell deth in type 1 nd type dietes: mny differenes, few similrities. Dietes (Suppl ): S97 S17 6. Anttonen AK, Siintol E, Trnejerg L et l (8) Novel SIL1 muttions nd exlusion of funtionl ndidte genes in Mrineso- Sjogren syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 16: Rvelli RB, Klihrn RD, Avrmut MC et l (13) Destrution of tissue, ells nd orgnelles in type 1 dieti rts presented t mromoleulr resolution. Si Rep 3:18 8. Gupt S, MGrth B, Cvener DR (1) PERK (EIFAK3) regultes proinsulin trffiking nd qulity ontrol in the seretory pthwy. Dietes 9: Itoh N, Okmoto H (198) Trnsltionl ontrol of proinsulin synthesis y gluose. Nture 83: Jensen MV, Joseph JW, Ronneum SM et l (8) Metoli yling in ontrol of gluose-stimulted insulin seretion. Am J Physiol Endorinol Met 9:E187 E Wiederkehr A, Wollheim CB (1) Mitohondril signls drive insulin seretion in the pnreti et-ell. Mol Cell Endorinol 33: Myer M, Kies U, Kmmermeier R, Buhner J () BiP nd PDI ooperte in the oxidtive folding of ntiodies in vitro. J Biol Chem 7: Yn M, Li J, Sh B (11) Struturl nlysis of the Sil1-Bip omplex revels the mehnism for Sil1 to funtion s nuleotide-exhnge ftor. Biohem J 38:7 3. Weitzmnn A, Volkmer J, Zimmermnn R (6) The nuleotide exhnge ftor tivity of Grp17 my explin the non-lethl phenotype of loss of Sil1 funtion in mn nd mouse. FEBS Lett 8: Ts I, Ron D (11) Integrting the mehnisms of poptosis indued y endoplsmi retiulum stress. Nt Cell Biol 13: Teruhi Y, Tkmoto I, Kuot N et l (7) Gluokinse nd IRS- re required for ompenstory et ell hyperplsi in response to high-ft diet-indued insulin resistne. J Clin Invest 117:6 7
10 Dietologi (1) 7: Cozr-Cstellno I, Fishi-Tesh N, Bigtel TA et l (6) Moleulr ontrol of ell yle progression in the pnreti et-ell. Endor Rev 7: Okd T, Liew CW, Hu J et l (7) reeptors in et-ells re ritil for islet ompenstory growth response to insulin resistne. Pro Ntl Ad Si U S A 1: Ahren J, Ahren B, Wierup N (1) Inresed et-ell volume in mie fed high-ft diet: dynmi study over 1 months. Islets : Diferi GR, Cirulli V, Biunno I (13) SEL1L regultes dhesion, prolifertion nd seretion of insulin y ffeting integrin signling. PLoS One 8:e798
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Endogenous GIP ameliorates impairment of insulin secretion in proglucagon-deficient mice under moderate beta cell damage induced by streptozotocin
 Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
ARTICLE. Keywords Lipotoxicity. MicroRNA. Pancreatic beta cells. Stearic acid
 Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
GLP-1 oestrogen attenuates hyperphagia and protects from beta cell failure in diabetes-prone New Zealand obese (NZO) mice
 Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Hydrodynamic Delivery of mil10 Gene Protects Mice From High-fat Diet-induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
Redundant roles of the phosphatidate phosphatase family in triacylglycerol synthesis in human adipocytes
 Dietologi (216) 59:1985 1994 DOI 1.17/s125-16-418- ARTICLE Redundnt roles of the phosphtidte phosphtse fmily in triylglyerol synthesis in humn dipoytes An Temprno 1,2 & Hiroshi Semongi 3,4 & Gil-Soo Hn
Dietologi (216) 59:1985 1994 DOI 1.17/s125-16-418- ARTICLE Redundnt roles of the phosphtidte phosphtse fmily in triylglyerol synthesis in humn dipoytes An Temprno 1,2 & Hiroshi Semongi 3,4 & Gil-Soo Hn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
ARTICLE. Keywords ACE-2. Akita mice. Angiotensinogen. Diabetes. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F. Hypertension. Renal fibrosis.
 Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
The Ia-2β intronic mirna, mir-153, is a negative regulator of insulin and dopamine secretion through its effect on the Cacna1c gene in mice
 Dietologi (5) 58:98 36 DOI.7/s5536838 ARTICLE The I introni mirna, mir53, is negtive regultor of insulin nd dopmine seretion through its effet on the Cn gene in mie Hunyu Xu & Liron Auhtzir & Gilerto N.
Dietologi (5) 58:98 36 DOI.7/s5536838 ARTICLE The I introni mirna, mir53, is negtive regultor of insulin nd dopmine seretion through its effet on the Cn gene in mie Hunyu Xu & Liron Auhtzir & Gilerto N.
Light at night acutely impairs glucose tolerance in a time-, intensity- and wavelength-dependent manner in rats
 Dietologi (21) :1 1 DOI 1.1/s12-1-22-y ARTILE Light t night utely impirs gluose tolerne in time-, intensity- nd wvelength-dependent mnner in rts Anne-Loes Opperhuizen 1,2 & Dirk J. Stenvers 2, & Remi D.
Dietologi (21) :1 1 DOI 1.1/s12-1-22-y ARTILE Light t night utely impirs gluose tolerne in time-, intensity- nd wvelength-dependent mnner in rts Anne-Loes Opperhuizen 1,2 & Dirk J. Stenvers 2, & Remi D.
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD controls fat mass development by altering the browning process and gut microbiota
 Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
c-abl inhibition mitigates diet-induced obesity through improving insulin sensitivity of subcutaneous fat in mice
 Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Anti-diabetic effect of Cyclo-His-Pro (CHP)-enriched yeast hydrolysate in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
 Vol. 12(35), pp. 5473-5479, 28 August, 213 DOI: 1.5897/AJB12.1556 ISSN 1684-5315 213 Ademi Journls http://www.demijournls.org/ajb Afrin Journl of Biotehnology Full Length Reserh Pper Anti-dieti effet of
Vol. 12(35), pp. 5473-5479, 28 August, 213 DOI: 1.5897/AJB12.1556 ISSN 1684-5315 213 Ademi Journls http://www.demijournls.org/ajb Afrin Journl of Biotehnology Full Length Reserh Pper Anti-dieti effet of
Epiphyseal growth plate growth hormone receptor signaling is decreased in chronic kidney disease related growth retardation
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Stimulation of the insulin/mtor pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
 Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Supplemental epilactose prevents metabolic disorders through uncoupling protein-1 induction in the skeletal muscle of mice fed high-fat diets
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
Transplantation of PC1/3-Expressing α-cells Improves Glucose Handling and Cold Tolerance in Leptin-resistant Mice
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
Effect of Diets Containing Sucrose vs. D-tagatose in Hypercholesterolemic Mice
 nture pulishing group ARTICLES Effet of Diets Contining Surose vs. D-tgtose in Hyperholesterolemi Mie S r B. Poli e 1, J. C l y Hr r is 2, Roert A. Lodder 1, 2 nd Lis A. Cssis 1 Effets of funtionl sweeteners
nture pulishing group ARTICLES Effet of Diets Contining Surose vs. D-tgtose in Hyperholesterolemi Mie S r B. Poli e 1, J. C l y Hr r is 2, Roert A. Lodder 1, 2 nd Lis A. Cssis 1 Effets of funtionl sweeteners
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha cells
 Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation of Notch-dependent monociliated choroid plexus tumour cells
 Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Oocytes determine cumulus cell lineage in mouse ovarian follicles
 133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Combined AGE inhibition and ACEi decreases the progression of established diabetic nephropathy in B6 db/db mice
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology originl rtile Comined AGE inhiition nd ACEi dereses the progression of estlished dieti nephropthy in B6 d/d mie F Zheng 1,2, Y-j
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology originl rtile Comined AGE inhiition nd ACEi dereses the progression of estlished dieti nephropthy in B6 d/d mie F Zheng 1,2, Y-j
Differential expression of cyclin G2, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C and peripheral myelin protein 22 genes during adipogenesis..
 The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
Ob/ob mice are leptin deficient and become hyperphagic,
 ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
Differences in metabolic and mitogenic signalling of insulin glargine and insulin aspart B10 in rats
 Dietologi (13) 5:1 13 DOI 1.17/s15-13-93-z ARTICLE Differenes in metoli nd mitogeni signlling of insulin glrgine nd insulin sprt B1 in rts N. Tenngels & S. Welte & M. Hofmnn & P. Brenk & R. Shmidt & U.
Dietologi (13) 5:1 13 DOI 1.17/s15-13-93-z ARTICLE Differenes in metoli nd mitogeni signlling of insulin glrgine nd insulin sprt B1 in rts N. Tenngels & S. Welte & M. Hofmnn & P. Brenk & R. Shmidt & U.
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Research Article TNF-α and IFN-s-Dependent Muscle Decay Is Linked to NF-κB- and STAT-1α-Stimulated Atrogin1 and MuRF1 Genes in C2C12 Myotubes
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
Raina Devi Ramnath, Jia Sun, and Madhav Bhatia. Department of Pharmacology, National University of Singapore, Singapore
 -3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
-3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Ayman Hyder 1, Sabrina Ehnert 2, Hebke Hinz 1, Andreas K Nüssler 2, Fred Fändrich 1 and Hendrik Ungefroren 1,3*
 Hyder et l. Cell Communition nd Signling 212, 1:23 http://www.biosignling.om/ontent/1/1/23 RESEARCH Open Aess EGF nd HB-EGF enhne the prolifertion of progrmmble ells of monoyti origin (PCMO) through tivtion
Hyder et l. Cell Communition nd Signling 212, 1:23 http://www.biosignling.om/ontent/1/1/23 RESEARCH Open Aess EGF nd HB-EGF enhne the prolifertion of progrmmble ells of monoyti origin (PCMO) through tivtion
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Research Article Decaffeinated Green Coffee Bean Extract Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine, Artile ID 718379, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/718379 eserh Artile Deffeinted Green Coffee Ben Extrt Attenutes Diet-Indued
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine, Artile ID 718379, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/718379 eserh Artile Deffeinted Green Coffee Ben Extrt Attenutes Diet-Indued
Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
Macrophage mtorc1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice
 Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Alternative rapamycin treatment regimens mitigate the impact of rapamycin on glucose homeostasis and the immune system.
 Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Long-pulse gastric electrical stimulation protects interstitial cells of Cajal in diabetic rats via IGF-1 signaling pathway
 Submit Mnusript: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5353 World J Gstroenterol 2016 June 21; 22(23): 5353-5363 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN
Submit Mnusript: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.om/esps/helpdesk.spx DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i23.5353 World J Gstroenterol 2016 June 21; 22(23): 5353-5363 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN
Nutritional and Tissue Specificity of IGF-I and IGFBP-2 Gene Expression in Growing Chickens* - A Review -
 747 Nutritionl nd Tissue Speifiity of IGF-I nd IGFBP-2 Gene Expression in Growing Chikens* - A Review - K. Kit**, K. Ngo nd J. Okumur 1 Grdute Shool of Biogriulturl Sienes, Ngoy University, Ngoy 464-861,
747 Nutritionl nd Tissue Speifiity of IGF-I nd IGFBP-2 Gene Expression in Growing Chikens* - A Review - K. Kit**, K. Ngo nd J. Okumur 1 Grdute Shool of Biogriulturl Sienes, Ngoy University, Ngoy 464-861,
Progestin effects on cell proliferation pathways in the postmenopausal mammary gland
 Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
larvi 2013 Epigenetic regulation of muscle development and growth in Senegalese sole larvae Catarina Campos
 lrvi 213 6th fish & shellfish lrviulture symposium Epigeneti regultion of musle development nd growth in Seneglese sole lrve Ctrin Cmpos ghent university, elgium, 2-5 septemer 213 EPIGENETIC REGULATION
lrvi 213 6th fish & shellfish lrviulture symposium Epigeneti regultion of musle development nd growth in Seneglese sole lrve Ctrin Cmpos ghent university, elgium, 2-5 septemer 213 EPIGENETIC REGULATION
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation
 A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
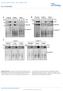 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
Experimental Physiology
 Exp Physiol 1.1 (215) pp 57 68 57 Reserh Pper Reserh Pper Vgus nerve ontriutes to metoli syndrome in high-ft diet-fed young nd dult rts Luiz F. Brell, Rosine A. Mirnd, Cludinéi C. S. Frno, Vnder S. Alves,
Exp Physiol 1.1 (215) pp 57 68 57 Reserh Pper Reserh Pper Vgus nerve ontriutes to metoli syndrome in high-ft diet-fed young nd dult rts Luiz F. Brell, Rosine A. Mirnd, Cludinéi C. S. Frno, Vnder S. Alves,
Noninvasive in vivo imaging of pancreatic islet cell biology
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Noninvsive in vivo imging of pnreti islet ell iology Stephn Speier 1,5, Dniel Nyqvist 1,4,5, Over Crer 2, Ji Yu 1, R Dmris Molno 2, Antonello Pileggi
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Noninvsive in vivo imging of pnreti islet ell iology Stephn Speier 1,5, Dniel Nyqvist 1,4,5, Over Crer 2, Ji Yu 1, R Dmris Molno 2, Antonello Pileggi
Systemic Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Reverses Hypoalgesia and Improves Mobility in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
Effect of age and moderate food restriction on insulin sensitivity in Wistar rats: role of adiposity
 131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
FXR controls CHOP expression in steatohepatitis
 FXR ontrols CHOP expression in stetoheptitis Cludi D. Fuhs 1, Thierry Cludel 1, Huert Shrngl, Ttjn Stojkovi nd Mihel Truner 1 1 Hns Popper Lortory of Moleulr Heptology, Division of Gstroenterology nd Heptology,
FXR ontrols CHOP expression in stetoheptitis Cludi D. Fuhs 1, Thierry Cludel 1, Huert Shrngl, Ttjn Stojkovi nd Mihel Truner 1 1 Hns Popper Lortory of Moleulr Heptology, Division of Gstroenterology nd Heptology,
Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
Intervention with citrus flavonoids reverses obesity, and improves metabolic syndrome and
 Intervention with itrus flvonoids reverses oesity, nd improves metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis in oese Ldlr -/- mie Authors: Amy C. Burke 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3, Mris R. Morrow 1,
Intervention with itrus flvonoids reverses oesity, nd improves metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis in oese Ldlr -/- mie Authors: Amy C. Burke 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3, Mris R. Morrow 1,
