Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
|
|
|
- Jeffry McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing Luo 1, Lourdes G Oroz 1, Frneso Srvilli 3, Dougls F Eston 4, Riner Duden 5, Chir J O Kne 2 & Dvid C Ruinsztein 1 Huntington disese is one of nine inherited neurodegenertive disorders used y polyglutmine trt expnsion. Expnded polyglutmine proteins umulte normlly in intrellulr ggregtes. Here we show tht mmmlin trget of rpmyin (mtor) is sequestered in polyglutmine ggregtes in ell models, trnsgeni mie nd humn rins. Sequestrtion of mtor impirs its kinse tivity nd indues utophgy, key lerne pthwy for mutnt huntingtin frgments. This protets ginst polyglutmine toxiity, s the speifi mtor inhiitor rpmyin ttenutes huntingtin umultion nd ell deth in ell models of Huntington disese, nd inhiition of utophgy hs the onverse effets. Furthermore, rpmyin protets ginst neurodegenertion in fly model of Huntington disese, nd the rpmyin nlog CCI-779 improved performne on four different ehviorl tsks nd deresed ggregte formtion in mouse model of Huntington disese. Our dt provide proof-ofpriniple for the potentil of induing utophgy to tret Huntington disese. Huntington disese is n utosoml dominnt neurodegenertive ondition used y (CAG) n expnsion muttion (n > 35), whih is trnslted into n normlly long polyglutmine trt t the N terminus of huntingtin. There is no effetive tretment for Huntington disese. Huntington disese nd relted diseses ssoited with polyglutmine expnsions (spinoereellr txi types 1, 2, 3, 6, 7 nd 17; spinoulr musulr trophy nd denttorurl-pllidoluysin trophy) re proly used y gin-of-funtion mehnisms. The mutnt proteins using these diseses umulte in intrneuronl ggregtes (lso lled inlusions) 1. Some propose tht ggregtes re deleterious, ut others rgue tht ggregtes re protetive, whih ounts for the prtil disordne etween the presene of ggregtes in neuronl sutypes nd the speifi rin regions ffeted in Huntington disese 2 4. No protetive mehnisms for ggregtes hve een reported. Polyglutmine-expnded proteins intert with vrious trgets, inluding severl trnsription ftors or oftors, leding to dysregultion of ertin trnsriptionl pthwys. Polyglutmine diseses my e trnsriptionopthies, ut the trnsriptionl pthwys ffeted my differ in speifi diseses 5 7. Mutnt huntingtin is leved to form N-terminl frgments omprising the first residues ontining the polyglutmine repets, whih re elieved to e the toxi speies found in ggregtes 1. Aordingly, the pthogenesis of Huntington disese is frequently modeled with exon 1 frgments, whih use toxiity nd ggregte in ell models nd in vivo. The turnover of mutnt huntingtin frgments nd other ggregteprone proteins is impired y inhiitors of the utophgy-lysosome pthwy in ell lines 8,9. To test whether indution of utophgy proteted ginst the toxiity of mutnt huntingtin, we previously treted ells with rpmyin, speifi inhiitor of mtor 10. mtor is kinse tht regultes importnt ellulr proesses 10 (Supplementry Fig. 1 online), nd its tivity inhiits utophgy in ells from yest to humn 10. Tretment with rpmyin for 15 h, strting 9 h fter trnsfetion with mutnt huntingtin exon 1, redued ggregte formtion nd ell deth, onsistent with the indution of utophgy. But ells hd mny more ggregtes 33 h fter trnsfetion thn 9 h fter trnsfetion with the sme onstruts, nd tretment with rpmyin for 15 h strting t 33 h fter trnsfetion did not derese ggregtion or ell deth. Thus, we onluded tht the ility of rpmyin to inhiit mtor tivity might e impired fter prolonged huntingtin expression or inresed ggregte formtion 8. Therefore, erly tretment with rpmyin my ttenute Huntington disese in vivo, s rpmyin (nd its nlogs) re lipophili, show good lood-rin rrier penetrtion nd re designed for long-term use in humns Deprtment of Medil Genetis, Cmridge Institute for Medil Reserh, Wellome/MRC Building, Addenrooke s Hospitl, Hills Rod, Cmridge CB2 2XY, UK. 2 Deprtment of Genetis, Cmridge University, Cmridge CB2 3EH, UK. 3 Division of Neuropthology, Institute of Neurology, University College London, London, UK. 4 Cner Reserh U.K., Geneti Epidemiology Unit, Deprtment of Puli Helth, University of Cmridge, Cmridge, UK. 5 Deprtment of Clinil Biohemistry, Cmridge Institute for Medil Reserh, Wellome/MRC Building, Addenrooke s Hospitl, Hills Rod, Cmridge, CB2 2XY, UK. 6 These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to D.C.R. (dr1000@us.m..uk). Pulished online 16 My 2004; doi: /ng1362 NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
2 RESULTS mtor is sequestered into huntingtin ggregtes We speulted tht the ility of rpmyin to inhiit mtor tivity might eome impired fter prolonged huntingtin expression if ggregtes sequester nd intivte mtor. mtor ws diffusely distriuted in untrnsfeted ells, in ells expressing wild-type protein (Gln 23 ; Fig. 1) nd in ells expressing mutnt protein (Gln 74 ) without ggregtes ut ololized with oth ytoplsmi nd nuler ggregtes in >98% of mutnt ells with ggregtes (Fig. 1 nd Supplementry Fig. 2 online). This degree of mtor ololiztion is muh greter thn oserved with most other proteins previously nlyzed 15. We never oserved mtor ggregtion in the sene of huntingtin ggregtes (dt not shown). Sequestrtion of mtor ws not n rteft of protein overexpression or ggregtion, s we found no ololiztion of ertin upstrem mtor regultors or unrelted proteins (Akt, Pdk1, Pten) with mutnt huntingtin ggregtes (dt not shown). mtor ws lso sequestered in huntingtin ggregtes in rins of trnsgeni mie expressing N-terminl mutnt huntingtin frgments 16 (Fig. 1) nd of individuls with Huntington disese (Fig. 1), ut not in rins of ontrols. Western lots of whole-ell lystes showed tht sustntil mount of mtor (normlly 289-kD protein) ws present in the form of n normlly slowly migrting, high-moleulr-mss produt in the stking gel (hrteristi of ggregtes) in mutnt ut not wild-type ells (Fig. 1d,e). The presene of mutnt huntingtin in the stking gel is frequently onsidered to e inditive of its insoluility 17. We lso deteted this high-moleulr-mss produt in the stking gel using ntiodies to phosphorylted mtor (Fig. 1e) nd to green fluoresent protein (GFP) direted to the huntingtin trnsgene (Fig. 1e). Sustntil mounts of endogenous mtor in the mutnt lines were sequestered into the insolule frtion (Fig. 1d). We lotted lystes from these ell lines with numerous ntiodies (>20), inluding ntiodies to hsp70, hdj1, CBP nd other proteins tht ololize with ggregtes, nd never oserved suh s ovious umultion of these proteins in the stking gels (dt not shown). Therefore, this intertion might e very tight. We onfirmed the intertion etween mutnt huntingtin nd mtor y oimmunopreipittion of mtor with mutnt huntingtin exon 1 from PC12 nd COS-7 ells, mostly s high-moleulr-mss ggregtes in the stk (Fig. 1f). The differene in the moility of these high-moleulr-mss immunopreipittes in PC12 nd COS-7 ells my reflet greter heterogeneity in ggregtes in the trnsiently trnsfeted ells versus the stle induile ells. This is not generi feture of mutnt huntingtin, s similr immunopreipittions did not pull down d f e g Figure 1 mtor is sequestered in mutnt huntingtin ggregtes in ell models, trnsgeni mie nd humn rin. () COS-7 ells expressing EGFP-tgged wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin exon 1 (green) for 48 h stined for endogenous mtor (red) show mtor in mutnt ggregtes. () Douleleling immunohistohemistry of huntingtin (EM48; green) nd mtor (red) in rin tissue of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16. () Immunohistohemistry of rin tissue from individuls with grde III Huntington disese or unffeted ontrols using ntiody to mtor. (d) Western lot of lystes from stle induile PC12 ells 48 h fter expression of wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin showing mtor in the stking gel (mtor insolule) in ells expressing mutnt huntingtin. (e) High-moleulr-mss ggregtes of mtor in oth PC12 (i) nd COS-7 (ii) ells expressing mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin. Blots of ell lystes from PC12 ells were proed with ntiodies to phosphorylted mtor (Ser2448; p-mtor; iii) nd to GFP (iv); oth showed insolule mteril in the stk. (f) Cell lystes from stle induile PC12 ells nd trnsiently trnsfeted COS-7 ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin for 48 h were immunopreipitted using ntiody to GFP nd immunolotted with ntiody to mtor. Unindued PC12 ells with mutnt huntingtin (UI) nd untrnsfeted COS-7 ells (UT) were ontrols. (g) Brin lystes from mie expressing mutnt huntingtin (Tg) 16 or ontrol (Cont) littermtes were immunopreipitted with ntiody to mtor nd immunodeteted with n ntiody reognizing the polyglutmine trt (IC2). Htt, huntingtin. 586 VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE 2004 NATURE GENETICS
3 proteins suh s S6 kinse-1 (S6K1) nd eif-4e inding protein (4E- BP1; dt not shown). This intertion requires expnded polyglutmines, s wild-type huntingtin did not ssoite with mtor. The mutnt huntingtin frgment from rin lystes of trnsgeni mie lso immunopreipitted with ntiody to mtor (Fig. 1g). Sequestrtion of mtor to ggregtes ws ssoited with redued mounts of solule mtor (reltive to tuulin) in stle induile ell lines expressing mutnt versus wild-type huntingtin (Figs. 1d nd 2) nd in rin lystes of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 (Fig. 2) versus ontrol littermtes. mtor sequestrtion would impir nuleoytoplsmi shuttling of mtor, whih is ruil for its tivity 18. Polyglutmine expnsion impirs mtor kinse tivity mtor phosphoryltes 4E-BP1 nd riosoml protein S6K1 (ref. 19), importnt regultors of p-dependent nd terminl oligopyrimidine trt (TOP)-dependent trnsltion, respetively. 4E-BP1 ws diffusely distriuted in wild-type ells (Fig. 2) ut ololized with ggregtes in 30% of mutnt ells with ggregtes (Fig. 2) nd ws seen in nuler inlusions of rins of individuls with Huntington disese (Fig. 2d). 4E-BP1 ws not immunopreipitted y mutnt huntingtin, nd so these intertions my e wek or trnsient. Unfortuntely, we ould not test whether S6K1 ws lolized to ggregtes euse the S6K1 ntiody gve no speifi immunoytohemil stining ove kground in wild-type ells, with either immunofluoresene or ABC detetion methods. We first ssessed mtor tivity under ontrolled onditions in PC12 stle induile ell lines, whih experiened no enhned ell deth or mitohondril dysfuntion for t lest 3 d fter indution of expression of the mutted trnsgene (lthough inresed toxiity ws pprent 6 d fter indution 20 ). 48 h fter indution of expression of the trnsgene, when we rried out the following experiments, there ws no evidene of endoplsmi retiulum stress in wild-type or mutnt lines, s judged y BiP levels on western lots (dt not shown). mtor kinse tivity n e inferred from levels of phosphoryltion of S6K1 nd 4E-BP1 (ref. 10). We found redued endogenous phosphorylted versus totl S6K1 (Fig. 2e) nd 4E-BP1 (Fig. 2f) in mutnt ell lines reltive to wild-type ell lines. The ility of mtor to phosphorylte trnsiently trnsfeted FLAG-tgged 4E-BP1 (ref. 21) ws lso impired in mutnt ells reltive to wild-type ells (Fig. 2g). The polyglutmine expnsion did not lter levels of phosphorylted Akt, suggesting tht there is no generi kinse inhiition (dt not shown). Figure 2 Redued levels of solule mtor nd impired mtor-dependent phosphoryltion of its sustrtes S6K1 nd 4E-BP1 in Huntington disese. () Redued levels of solule mtor (s funtion of tuulin) in stle induile PC12 ells expressing mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin ompred with those expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) huntingtin (four independent experiments; P < ; unpired t-test). () Redued levels of solule mtor in rin lystes from mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 (M1, M2; n = 9) ompred with ge-mthed wild-type littermtes (C1, C2; n = 9; P < 0.001, unpired t-test). () COS-7 ells trnsiently trnsfeted with wildtype (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin (green) leled for endogenous 4E-BP1 (red). (d) Immunohistohemistry of rin tissue from individuls with grde III Huntington disese showed 4E-BP1 in intrnuler inlusions. No 4E- BP1-stined inlusions were seen in ontrols (dt not shown). (e) Western lot of ell lystes from stle induile PC12 ells trnsfeted with wildtype (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin shows tht ells expressing mutnt huntingtin hd 31% (± 4.3% s.e.) less phosphorylted S6K1 (top) reltive to totl S6K1 (ottom) thn ells expressing wild-type huntingtin. (f) Similrly, ells expressing mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin hd 30% (± 4.5% s.d.) less phosphorylted 4E-BP1 (top) reltive to totl 4E-BP1 (ottom) thn ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) huntingtin. Expression of wild-type nd mutnt huntingtin ws indued for 48 h (e,f). (g) Cells expressing mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin lso hd lower levels of phosphorylted forms of trnsiently trnsfeted FLAG-tgged 4E- BP1 thn ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) huntingtin. The multiple nds in 4E-BP1 (f,g) re due to its different phosphorylted speies. d e f g NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
4 We next tested whether phosphoryltion of the riosoml protein S6, the trget of tivted, phosphorylted S6K1, ws speifilly redued in ells with ggregtes, y immunofluoresene 21. We found tht 26% (± 2.6% s.e.) of mutnt ells with ggregtes did not show stining for phosphorylted S6, ompred with 8.5% (± 1.2% s.e.) nd 3.8% (± 0.5% s.e.) of wild-type ells nd mutnt ells without ggregtes, respetively (Fig. 3). We oserved similr trends using huntingtin exon 1 onstruts with 25 (Gln 25 ) or 103 (Gln 103 ) glutmine repets (Supplementry Fig. 3 online) nd in rins of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin versus ontrol mie, where ells with ggregtes hd less stining for phosphorylted S6 thn ells without ggregtes (Fig. 3). In mouse rins, 60% of ells with ggregtes hd mrkedly less immunoretivity to phosphorylted S6, wheres rins of ontrol mie hd no ovious redutions (<2% of ells). Polyglutmine expnsion impirs mtor-dependent trnsltion Phosphoryltion of S6 y S6K1 positively regultes the initition of trnsltion of mrnas ontining 5 TOPs, suh s riosoml proteins nd trnsltion elongtion ftors. We used vlidted luiferse reporter ssy to mesure mtor-dependent TOP trnsltion 18,22 in the presene or sene of rpmyin in order to ssess the mount of funtionl ellulr mtor tht n e inhiited. Rpmyin signifintly redued TOP-dependent (+TOP) luiferse expression in wild-type (Gln 23 ) PC12 ells fter serum stimultion y 18% (Fig. 3), similr to results of previous studies with this ssy in norml ells 18,22. This effet is modest euse mtor only prtilly ontrols this proess 18. Rpmyin hd no suh inhiitory effet in mutnt (Gln 74 ) ells. As expeted, rpmyin did not inhiit luiferse tivity in wild-type ells trnsfeted with n otherwise identil ontrol-luiferse onstrut without the TOP sequene ( TOP; Fig. 3). These dt suggest tht rpmyin nnot redue mtor tivity in mutnt ells euse it is lredy impired, onsistent with the rw luiferse dt with the +TOP onstruts showing lower vlues in mutnt ells in the sene of rpmyin thn in wild-type ells (Supplementry Fig. 4 online). The inrese in TOP-independent trnsltion in the mutnt lines (Fig. 3) is omptile with dt from previous ssys 18,22, in whih it ws ttriuted to ompetition etween different lsses of mrna for the ellulr trnsltion mhinery 18. But the key issue is the TOP-dependent trnsltion. We onfirmed the TOP-dependent effets (Fig. 3) in COS-7 ells trnsiently trnsfeted with wild-type or mutnt huntingtin long with e g d f Figure 3 Impired phosphoryltion of riosoml protein S6 nd dysregultion of TOP-dependent trnsltion. () COS-7 ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin (green) were leled for S6 phosphorylted t Ser235 nd Ser236 (red). Perentges of ells expressing wild-type or mutnt huntingtin tht did (+gg) or did not ( gg) ontin ggregtes were sored for negtive stining for phosphorylted S6 (p-s6). () Brin setions from ontrol (WT) nd mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 (HD) were stined for phosphorylted S6 (red) nd with ntiody to huntingtin (EM48; green). (,d) Impired mtor-dependent TOP trnsltion in ells expressing mutnt huntingtin. () PC12 ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin were trnsfeted with luiferse onstruts ontining 5 untrnslted sequene with 22 (+) or without ( ) TOP sequene long with β-gl. Eh r represents the differene etween the luiferse tivities in the presene versus the sene of rpmyin. Dt shown re from one representtive experiment (of three) done in sextuplite (error rs represent s.e.; rw dt re given in Supplementry Fig. 4 online). (d) COS-7 ells were otrnsfeted with wild-type or mutnt huntingtin, nontypil TOP or ontrol luiferse vetor 18 nd β-gl. The experiment ws done nd nlyzed s in (rw dt re given in Supplementry Fig. 4 online) (e g) Relevne of mtor sequestrtion to other polyglutmine expnsion diseses (e) COS-7 ells expressing Xpress-tgged txin-1 with 92 polyglutmine repets (Q92) for 48 h were douly leled with ntiodies to Xpress (green) nd to mtor (red). (f) mtor immunohistohemistry in rins of individuls with denttorurlpllidoluysin trophy (DRPLA) nd spinoereellr txi types 2, 3 nd 7 (SCA2, SCA3 nd SCA7). (g) Stining for phosphorylted S6 (red) in COS-7 ells trnsiently trnsfeted with mutnt (txin Q92; green) or wild-type (txin Q2) txin-1 onstruts. Results were signifint nd similr to those in. Arrows in,, e nd g show ells ontining ggregtes. 588 VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE 2004 NATURE GENETICS
5 nother set of luiferse reporter onstruts with nontypil TOP sequene, whose trnsltion is lso normlly inhiited y rpmyin tretment 18 (Fig. 3d). Cells trnsfeted with wild-type huntingtin showed rpmyin-dependent redution (23%) in luiferse tivity tht ws similr to tht previously desried 18, ut we oserved no suh effet in ells trnsfeted with mutnt huntingtin, whih ehved like ells expressing nonfuntionl mtor mutnts 18. Agin, we noted tht the rw luiferse dt (Fig. 3d) with the +TOP onstruts showed lower vlues in mutnt ells in the sene of rpmyin thn in wild-type ells (Supplementry Fig. 4 online). These dt suggest tht mutnt huntingtin uses trnsltionl dysregultion y impiring mtor signling to its downstrem effetors. Deresed mtor tivity in other polyglutmine diseses The huntingtin exon 1 onstruts tht we used previously formed mostly ytoplsmi ggregtes (90% of ggregtes in mutnt Gln 74 ells nd 98% of ggregtes in mutnt Gln 103 ells). But mtor ws lso sequestered y intrnuler txin-1 ggregtes (Fig. 3e), ggregtes formed y isolted polyglutmine strethes fused to GFP (Gln 81 ; Supplementry Fig. 5 online) nd ggregtes in rins of individuls with spinoereellr txi types 2, 3 nd 7 nd denttorurl-pllidoluysin trophy (Fig. 3f). We lso oserved less stining of phosphorylted S6 stining in ggregte-ontining COS-7 ells expressing txin-1 (Fig. 3g) nd mutnt Gln 81 huntingtin (Supplementry Fig. 5 online), suggesting tht mtor sequestrtion nd inhiition might e polyglutmine-dependent irrespetive of lotion. Polyglutmine expnsion indues utophgy mtor inhiition indues utophgy, whih hs een previously reported in rins of individuls with Huntington disese, in trnsgeni mie expressing mutnt huntingtin frgments nd in ell model of Huntington disese, using morphologil riteri 23,24. It hs een diffiult to differentite utophgosomes from other vesiles in the sene of speifi utophgosome mrkers. This issue is simplified y the identifition of LC3-II, form of mirotuule-ssoited protein-1 light hin-3 (MAP-LC3) ssoited with mmmlin utophgosomes 25. Levels of LC3-II (reltive to tin), whih orrelte with utophgosome numer 25, were higher in mutnt (Gln 74 ) thn in wild-type (Gln 23 ) ell lines (Fig. 4). Although this effet ws sutle, it ws onsistent nd reproduile in four independent experiments. Furthermore, levels of LC3-II inresed fter expression of mutnt huntingtin ws indued in stle PC12 ells (dt not shown), wheres no differene ws seen upon indution of expression of wild-type huntingtin. Autophgi tivity lso orreltes with the numer of LC3-stined vesiles 25, whih inresed fter serum strvtion or tretment with rpmyin (known to stimulte utophgy) nd in ggregte-ontining ells expressing mutnt Gln 74 or Gln 103 huntingtin ut not in ells expressing wild-type Gln 23 or Gln 25 huntingtin (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 6 online). The smll size of PC12 ells mde visuliztion of LC3-stined vesiles indistint oth in ontrol ells nd in ells treted with rpmyin. The ssoition of mtor with polyglutmine ggregtes nd the impirment of mtor signling re not due to ell deth. We oserved these phenomen in mutnt PC12 ells t times where ell deth ws negligile 20, nd ell deth ws not ovious in the mie expressing mutnt huntingtin tht we studied 16. In ddition, we oserved sequestrtion of mtor to mutnt huntingtin ggregtes in ssoition with deresed S6 phosphoryltion nd inresed utophgy in ggregteontining ells with nonpoptoti nuler morphologies nd in ells treted with the pn-spse inhiitor z-vad-fmk (Supplementry Figs. 7 9 online). Inresing mtor tivity enhnes polyglutmine toxiity Our hypothesis tht inhiition of mtor protets ells with polyglutmine expnsion predits tht tivtion of mtor would enhne ggregtion nd toxiity of mutnt huntingtin. This nnot e investigted in wild-type ells y overexpressing Figure 4 Polyglutmine expnsion indues utophgy. () LC3-II levels, whih losely orrelte with utophgi tivity, were higher in mutnt lines (expressing Gln 74 huntingtin; Q74; lnes 3 nd 4) thn in wild-type lines (expressing Gln 23 huntingtin; Q23; lnes 1 nd 2). Atin ws used s loding ontrol. Dt re shown for two independent lonl lines expressing mutnt or wild-type huntingtin. Quntifition of the nd intensity is shown in the right pnel. () Immunofluoresene nlysis of COS-7 ells expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ; Q23) or mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin with ntiody to LC3 showed more utophgi vuoles in ells expressing mutnt huntingtin tht hd ggregtes (rrow). COS-7 ells without the primry ntiody (negtive) nd COS-7 ells without ny tretment (untreted) stined for LC3 re lso shown. The numers of EGFP-positive ells expressing wild-type or mutnt huntingtin with (+gg) nd without ( gg) ggregtes tht hd higher numers of utophgi vuoles (>15 20 vesiles per ell) is shown in the grph. COS-7 ells grown in strvtion medium (strvtion) or treted with rpmyin (Rp) for 4 h to indue utophgy hd more utophgi vuoles (rrows). NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
6 mtor, euse mtor overexpression in flies results in phenotypes similr to those used y mtor defiieny 26. Overexpression of the smll G protein rhe, whih gretly enhnes mtor signling 27, however, mrkedly inresed oth ggregte formtion nd ell deth used y mutnt huntingtin (Fig. 5 nd Supplementry Fig. 10 online). Rpmyin redues neurodegenertion in fly model We first tested the therpeuti potentil of rpmyin in vivo using fruit flies expressing the first 171 residues of huntingtin with 120 glutmines (Gln 120 ) in photoreeptors 28. The fly s ompound eye omprises mny ommtidi, eh ontining eight photoreeptor neurons with light-gthering prts lled rhdomeres, seven of whih n e visulized using the pseudopupil tehnique 29. The numer of visile rhdomeres in eh ommtidium dereses over time in flies expressing mutnt Gln 120 huntingtin ut not in trnsgeni flies expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ) huntingtin 28. Flies expressing mutnt huntingtin tht were treted with rpmyin (whih ws previously shown to effetively inhiit TOR funtion in flies 30 ) experiened mrkedly slower neurodegenertion thn those treted with the rrier dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO; used s ontrol; Fig. 5, nd Supplementry Fig. 11 online). CCI-779 relieves symptoms in mouse model Rpmyin hs poor wter soluility nd stility in queous solution. The rpmyin ester CCI-779 (ref. 31) hs more fvorle phrmeutil properties, indues only mild side effets in humns nd is undergoing evlution in phse 2 nd phse 3 linil trils for tretment of ner 32. We onfirmed tht CCI-779 enhned lerne of mutnt huntingtin exon 1 frgments in ell model (Supplementry Fig. 12 online) nd then used it to tret mie expressing mutnt huntingtin. We used Ross/Borhelt mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 insted of the more ommonly used R6/2 model 33 for the following resons. First, rpmyin my e most potent when used efore disese onset 8. R6/2 mie develop pthologil signs t 3.5 weeks (ref. 34). Beuse we intended to strt our tril fter wening the mie (round 4 weeks), the lter onset in the Ross/Borhelt model mde it more suitle. Seond, the Ross/Borhelt trnsgene driven y the mouse prion protein promoter hs lmost exlusively neuronl expression 16. R6/2 mie develop inlusions in mny peripherl tissues nd hve musle trophy 35 ; it is not ler how these peripherl pthologies ffet performne on motor-dependent tsks, suh s rotrod tests, tht re routinely used to ssess tretment responses. If the tretment ompounds improve musle (or other peripherl) pthologies in the R6/2 mie ut do not ross the lood-rin rrier or t in neurons, these tests ould yield misleding positive results. We identified four tsks or phenotypes tht relily disriminte etween the Ross/ Borhelt mie nd their wild-type littermtes: rotrod test, grip strength test, wire Figure 5 mtor tivity regultes polyglutmine toxiity in ells nd flies. () Ativtion of mtor tivity with rhe inreses ggregtion nd toxiity of mutnt (Gln 74 ; Q74) huntingtin. COS-7 ells were otrnsfeted with mmmlin expression vetor enoding rhe (or empty vetor ontrol) nd mutnt huntingtin for 48 h t 3:1 mss rtio (rhe or empty vetor to huntingtin) to ensure tht lmost ll ells expressing huntingtin lso expressed rhe. The perentges of EGFP-positive ells with ggregtes or poptoti nuler morphology (s desried previously 15 ) were mrkedly higher when rhe ws overexpressed. Control ells express mutnt huntingtin (green) without rhe. The middle pnels show imges ptured t the sme omprtively low gin to distinguish ggregtes from solule EGFP. The left pnels show the sme fields t similr higher gin to indite the totl numer of EGFP-positive ells (this shows tht the effet seen in the middle pnels is not due to loss of ells). Nuler stining with DAPI (lue) is shown in the right pnels. ***P < Error rs represent s.e. for representtive triplite experiment. (,) Tretment with rpmyin resues huntingtinindued degenertion in flies 2 d fter elosion. Photogrphs of ommtidi of flies expressing mutnt (Gln 120 ; Q120) huntingtin 28 treted with DMSO or rpmyin from the lrvl stge into dulthood. More rhdomeres re visile in the ommtidi of flies treted with rpmyin. This effet is signifint (P < ; Mnn-Whitney U test). At 2 d fter elosion, there is no redution in the numer of visile rhdomeres in wild-type untreted flies (dt not shown). 590 VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE 2004 NATURE GENETICS
7 mneuver test nd tremors 36. Ross/Borhelt mie treted with CCI- 779 performed signifintly etter on eh of these tsks thn their Ross/Borhelt littermtes treted with pleo (Fig. 6 nd Supplementry Fig. 13 online). Although weight loss is ssoited with disese in Ross/Borhelt mie, weight is not meningful mesure of response to tretment with rpmyin or CCI-779, euse CCI-779 redues weight gin in wild-type mie (Fig. 7), omptile with previous oservtions in rodents 37. These effets my e more severe in mie up to 5 months of ge when they re normlly gining weight, s weight loss is not prominent omplition of tretment with rpmyin or CCI-779 in dult humns 38. Brin weight ws redued in Ross/Borhelt mie treted with CCI-779 ompred with Ross/Borhelt mie treted with pleo (Fig. 7), ut rin weight orreted for ody weight ws not redued y this tretment nd tended to e higher in the group treted with CCI-779 (Fig. 7). There were fewer ggregtes in the stritum of mie treted with CCI-779 tht in tht of mie treted with pleo. Furthermore, the ggregtes of mie treted with CCI-779 were smller nd more diffiult to see thn those of mie treted with pleo (Fig. 8). The differene in ggregte density indued y CCI-779 is proly greter thn it ppers, s the overll rin mss (nd therefore volume) of mie treted with CCI-779 ws signifintly lower thn tht of ontrol mie treted with pleo. These hnges re omptile with the ide tht CCI-779 impirs mtor tivity nd indues utophgy. We onfirmed tht CCI-779 redued mtor signling in the rins of treted mie, using n ntiody speifi for phosphorylted S6, s desried previously 14,21 (Fig. 8). DISCUSSION Our dt show tht mutnt huntingtin interts with mtor, whih it sequesters in inlusions, leding to deresed mtor tivity. In ells with mutnt huntingtin ggregtes, mtor tivity ws not further redued y rpmyin tretment. This my explin why rpmyin did not effiiently redue huntingtin ggregte levels (y utophgy of mutnt huntingtin frgments) in popultions in whih 30% of ells ontined ggregtes ut did redue ggregtes in popultions in whih 10% of ells ontined ggregtes 8. The lower tivity of mtor in mutnt ells is proly due to its tight sequestrtion in ggregtes, leding to redued solule mtor. mtor my e sequestered y ggregtes tht re lrge nd visile or smller nd not visile y light mirosopy, s mtor ssoites with huntingtin tht enters stking or resolving gels. Beuse there ws more totl (solule plus ggregted) mtor in mutnt ells thn in wild-type ells (Fig. 1d) nd we oserved deresed mtor funtion in Figure 6 CCI-779 improves ehvior nd motor performne in mouse model of Huntington disese 16. Open rs, mie treted with pleo; filled rs, mie treted with CCI-779. ( ) Behviorl tests in mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 fter tretment t 16 weeks (CCI-779, n = 14; pleo, n = 14), 18 weeks (CCI-779, n = 10; pleo, n = 9), 20 weeks (CCI-779, n = 9; pleo, n = 7) nd 22 weeks (CCI-779, n = 5; pleo, n = 6) of ge. Sores re explined in Methods. Dt for ll time points re given in Supplementry Figure 13 online. () Tremors. Overll effet from ll treted time points: P = , odds rtio (OR) = 0.21, 95% onfidene intervl (95%.i.) = weeks, P = 0.01; 18 weeks, P = 0.08; 20 weeks, P = 0.14; 22 weeks, P = () Wire mneuver. Overll effet from ll treted time points: P = 0.02, OR = 0.51, 95%.i. = weeks, P = 0.29; 18 weeks, P = 0.40; 20 weeks, P = 0.003; 22 weeks, P = () Grip strength. Overll effet from ll treted time points: P < OR = 12.73, 95%.i. = weeks, P = ; 18 weeks, P = ; 20 weeks, P = ; 22 weeks, P = (d) Aelerting rotrod tests in mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 fter tretment t 4 weeks, (CCI-779, n = 16; pleo, n = 17), 14 weeks (CCI-779, n = 11; pleo, n = 10), 16 weeks (CCI-779, n = 14; pleo, n = 14) nd 18 weeks (CCI-779, n = 10; pleo, n = 9) of ge. Overll effet from ll treted time points: P = weeks, P = 0.227; 14 weeks, P = 0.012; 16 weeks, P = ; 18 weeks, P = CCI-779 hd no disernle effets on the performne of nontrnsgeni mie on ny of these ehviorl tests (dt not shown). There ws no differene in the mle:femle rtios of the groups treted with pleo or with CCI-779. d NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
8 mutnt ells, the ggregted mtor is proly intivted. This is onsistent with nuler-ytoplsmi shuttling eing required for mtor tivity 18 nd is suffiient to explin the deresed tivity in ells with polyglutmine expnsion. The greter totl mounts of mtor re onsistent with the predited slower turnover of ggregted versus solule protein. The overll effet of ggregtes my e toxi 1, ut inlusions proly modulte numerous pthwys, some toxi nd some tht redue polyglutmine toxiity. Impired mtor signling tht indues utophgy provides the first moleulr sis for protetive pthwy indued y polyglutmine ggregtes. This my ontriute to the typil lte onset of Huntington disese nd help ount for the mny surviving ells with ggregtes in rins of individuls with Huntington disese 4,39. Despite the indution of utophgy, ggregtes will umulte if their prodution exeeds their lerne. Although ggregtes visile y light mirosopy re proly too lrge to e lered y utophgosomes (typilly up to 1.5 µm in dimeter), miroggregtes nd solule huntingtin re omptile in size with these vesiles 40. Chronilly impired mtor tivity my lso explin neuronl shrinkge, whih ontriutes to muh of the rin trophy seen in Huntington disese 1. The mtor trget S6K1, whih hs redued phosphoryltion nd tivity in ells with mutnt huntingtin, is key regultor of ell volume 10. Our dt suggest tht mtor inhiition y mutnt polyglutmine expnsions lso ffets trnsltion regulted y S6K1 nd 4E-BP1 (ref. 43). Beuse the dependene of gene trnsltion on mtor tivity depends on the sequene nd struture of the 5 untrnslted region, this effet will vry from gene to gene 41. This effet might theoretilly ontriute to some of the memory defets in Huntington disese nd to the defets in long-term potentition seen in mouse models of polyglutmine disese 42 44, euse long-term potentition requires mtor-dependent protein synthesis t synpses 45. But we re not wre of memory or ognitive prolems developing in humns using rpmyin or its nlogs in the long term. Our trils with rpmyin nd CCI-779 in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese suggest tht the therpeuti potentil of mtor inhiition deserves serious onsidertion. Rpmyin seems to e more protetive thn other ompounds tested in flies (e.g., SAHA 46 ). Mie treted with rpmyin experiene improvements in four different phenotypes ttriutle to neurologil dysfuntion. We did not oserve signifint improvement in lifespn (Supplementry Fig. 14 online), ut lifespn mesurements were onfounded y severl ftors. First, our liense to rry out experiments on mie requires tht we euthnize mie when their disese exeeds defined, modertely severe, humne end points. Beuse 50% of mie in eh group required euthnsi nd euse the mie tht died spontneously frequently died without wrning, ovious reson or orreltion to pprent disese severity 16, the deth dt we otined ws not s preise s it would hve een if ll mie were llowed to die nturlly. This irumstne preluded detetion of smll effets on lifespn. Seond, Ross/Borhelt mie hve more vrile lifespns thn R6/2 mie 47. Third, the use of deth in the Ross/Borhelt mie is unknown nd my e more dependent on weight loss thn ny true Huntington disese relted neurologil pthology. Rpmyin mrkedly redues weight gin in oth trnsgeni mie nd nontrnsgeni littermtes, whih my ounterlne the effets of reduing mutnt huntingtin levels in the trnsgeni mie. Beuse weight loss is not ommon omplition of rpmyin therpy in dult humns, however, this effet my differ etween dult humns nd developing mie. Aordingly, we do not elieve tht the sene of definite effet on lifespn redues the potentil therpeuti vlue of rpmyin or CCI-779. Other reserhers lso do not use lifespn s n inditor in therpeuti trils in mie, whih they euthnize t humne end points 48. Theoretilly, the rpmyin or CCI-779 strtegy hs some dvntges over pprohes tht im to ttenute Huntington disese y Figure 7 CCI-779 redues weight gin in mie. () Weights of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin (Tg) nd nontrnsgeni (NT) littermtes treted with CCI-779 or with pleo. () Brin weights of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin treted with CCI-779 (lk rs) or with pleo (white rs) nd nontrnsgeni untreted littermtes (gry rs) t 8 weeks (CCI-779, n = 3; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 7; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.023), 12 weeks (CCI-779, n = 2; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 5; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.90) nd 16 weeks (CCI-779, n = 2; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 2; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.22) of ge. () Rtio of rin weight to ody weight of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin treted with CCI-779 (lk rs) or with pleo (white rs) nd nontrnsgeni untreted littermtes (gry rs) t 8 weeks (CCI-779, n = 3; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 7; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.06), 12 weeks (CCI-779, n = 2; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 5; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.38) nd 16 weeks (CCI-779, n = 2; pleo, n = 3; nontrnsgeni, n = 2; CCI-779 versus pleo, P = 0.56) of ge. 592 VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE 2004 NATURE GENETICS
9 ting on downstrem trgets suh s poptosis, retive oxygen speies or trnsriptionl dysregultion (reviewed in ref. 1). Polyglutmine expnsion my indue deleterious hnges in mny prllel nd distint pthwys. Therefore, it my e more effetive to tret Huntington disese y reduing levels of the toxi mutnt protein rther thn y resuing eh pthwy tht is pertured (prtiulrly s mny of these my e unknown). This pproh is simplified y the ft tht hemizygous loss of funtion of huntingtin does not use overt deleterious effets in humns or mie (reviewed in ref. 1). Although rpmyin or CCI-779 my lose effiy fter ggregte pthology is well developed, this does not prelude its use to tret Huntington disese. The medin ge t onset of Huntington disese is t lest 40 yers, nd lmost ll ses hve fmily histories. Beuse polyglutmine expnsion sttus n e ssessed efore symptoms pper, one possile tretment strtegy would e to dely disese onset with therpy initited t the erliest fesile ge. If disese onset ould e delyed eyond norml life expetny, then one would effetively ure mny ses. Beuse CCI-779 nd rpmyin re designed for long-term use in humns, they deserve serious onsidertion; the enefits of delying onset of Huntington disese would outweigh the side effets of these drugs. In ddition to Huntington disese, we elieve tht tretment with rpmyin or CCI-779 might e effetive for other neurodegenertive diseses, s rpmyin enhnes the lerne of ytosoli model ggregte-prone proteins with either polyglutmine or polylnine expnsions s well s vrious forms of α-synulein ssoited with Prkinson disese nd synule- inopthies in ell models 8,9. METHODS Mmmlin ell ulture nd trnsfetion. We grew Afrin green monkey kidney ells (COS-7) in Duleo s modified Egle medium (Sigm) supplemented with 10% fetl ovine serum, 100 U ml 1 of peniillin/streptomyin, 2 mm L-glutmine nd 1 mm sodium pyruvte t 37 C in 5% ron dioxide. We mintined the PC12 stle ells with 75 µg ml 1 of hygromyin in stndrd medium onsisting of high-gluose Duleo s modified Egle medium (Sigm) with 100 U ml 1 of peniillin/streptomyin, 2 mm L-glutmine (Invitrogen), 10% het-intivted horse serum (Invitrogen), 5% Tet-pproved fetl ovine serum (Clonteh) nd 100 µg ml 1 of G418 (Invitrogen) t 37 C in 10% ron dioxide. We seeded ells per well in six-well pltes nd indued them with 1 µg ml 1 of doxyyline (Sigm). We rried out trnsient trnsfetion using LipofetAMINE regent (Invitrogen) using the mnufturer s protool. CCI-779 ws provided y Wyeth Phrmeutils. For tissue ulture experiments, we prepred stok solution of 1M in ethnol on the dy of experiment nd diluted it in the pproprite medium. We onfirmed ll dt reported in this pper in the stle induile PC12 ells in two independent sets of wild-type (Gln 23 ) nd mutnt (Gln 74 ) lonl lines. Western-lot nlysis. We rried out western-lot nlysis using stndrd tehniques with ECL or ECL Plus detetion kit (Amershm). Primry ntiodies inluded ntiodies to GFP (Clonteh), mtor, phosphorylted mtor (Ser2448), S6K1, phosphorylted S6K1 (Thr389; 1A5), 4E-BP1 nd phosphorylted 4E-BP1 (Thr37) from Cell Signling Tehnology; ntiody to huntingtin (EM48, Chemion); nd ntiody to tuulin (Sigm). We used rins from nine mie expressing mutnt huntingtin (N-terminl 171 mino ids Figure 8 CCI-779 redues mtor tivity nd ggregte lod in mie expressing mutnt huntingtin. () CCI-779 redues ggregte lod in mie expressing mutnt huntingtin. Peroxidse immunohistohemistry of rins of mie expressing mutnt huntingtin t 16 weeks of ge. Mie treted with CCI-779 hd fewer ggregtes per unit re in the stritum thn mie treted with pleo. Overll ell stining in the tissues of mie treted with CCI-779 ws weker thn in those treted with pleo nd in nontrnsgeni untreted littermtes (dt not shown). Aggregtes, when visile, were smller in mie treted with CCI-779 thn in those treted with pleo, s pprent in the higher mgnifition imges of single ells with ggregte (ottom pnels). Six oronl setions per mouse were nlyzed; these orresponded to the regm ± 1 mm. We ounted ggregtes in five different high-power fields (60 ojetive) per slide on eh side of the rin, smpling fields from the dorsl to the ventrl prt of the stritum just underneth the externl psule. The strit of mie treted with CCI-779 hd 70% fewer ggregtes thn the strit of mie treted with pleo (P = , two-tiled t- test). () CCI-779 loks mtor signling in vivo. Immunohistohemistry of mie with Huntington disese t 16 weeks of ge with ntiody to phosphorylted S6, in the ortil re nd stritum. Levels of phosphorylted S6 were lower in mie treted with CCI-779 thn in those treted with pleo. NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
10 with 82 glutmine repets) 16 nd ge-mthed wild-type littermte ontrols. We dded 2.5 volume of uffer B (50 mm Tris (ph 7.5), 10% glyerol, 5 mm mgnesium ette, 0.2 mm EDTA, 0.5 mm dithiothreitol nd protese inhiitor) to slied rin tissue nd homogenized it t 4 C. We entrifuged the homogente t 12,000 r.p.m. t 4 C. We removed the superntnt nd used it for western lotting. For immunopreipittion, we lysed ells in RIPA uffer (1 phosphte-uffered sline, 1% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxyholte nd 0.1% SDS) nd immunopreipitted them using relevnt ntiodies. We rried out densitometry nlysis using Sion Imge Bet 4.02 softwre. Assy of exogenous 4E-BP1 phosphoryltion. We trnsiently trnsfeted PC12 ells stly expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ) or mutnt (Gln 74 ) huntingtin with FLAG-tgged 4E-BP1 for 72 h nd simultneously indued the trnsgene. We mintined the ells in norml growth medium for 48 h nd then trnsferred them to strvtion medium for 24 h. At this time point >99% of the mutnt PC12 ells formed insolule mutnt ggregtes 20. We then stimulted mtor tivity with 10% fetl ovine serum for 1 h nd proessed the ells for immunopreipittion. We immunopreipitted ells with ntiody to FLAG nd immunolotted them with oth ntiody to 4E-BP1 (Thr36/37) nd ntiody to FLAG. Immunoytohemistry nd immunohistohemistry. We rried out immunoytohemistry in COS-7 ells fixed with 4% prformldehyde (Sigm). For histohemil nlysis, we used free-floting rin setions from mie expressing mutnt huntingtin 16 nd ontrol mie nd prffin-emedded rin slies from humns with grde III Huntington disese nd unffeted humns, spnning the udte nd putmen regions. Primry ntiodies inluded ntiodies to mtor, phosphorylted mtor (Ser2448), 4E-BP1, phosphorylted S6 (Ser235/236; Cell Signling Tehnologies), LC3 (gift from T. Yoshimori, Ntionl Institute of Genetis, Jpn), huntingtin nd uiquitin (oth from Chemion). We rried out immunohistohemil nlysis y stndrd fluoresene methods or peroxidse leling using the Vetstin Avidin: Biotinylted enzyme Complex (ABC) kit. We nlyzed relevnt negtive ontrols without the primry ntiodies longside ll experiments. Luiferse ssy. We trnsfeted PC12 ells stly expressing wild-type (Gln 23 ) or mutnt (Gln 74 ) huntingtin with luiferse onstrut tht ontined 5 untrnslted region from the eef2 gene with or without the TOP sequene long with β-gltosidse (β-gl; to ontrol trnsfetion effiieny) 22. We mintined trnsfeted ells in serum-free medium with doxyyline for 36 h nd then stimulted the ells with 15% serum with or without rpmyin for 3 h. We then lysed ells nd rried out luiferse ssys ording to stndrd protool. We otrnsfeted COS-7 ells with wild-type or mutnt huntingtin nd with the ontrol or TOP luiferse onstruts long with β-gl for 48 h nd rried out experiments s desried ove. In ddition to the lssil TOP onstrut, we lso used onstrut with nonlssil TOP sequene tht is sensitive to rpmyin nd n pproprite ontrol onstrut 18. As oth ontrol nd TOP luiferse onstruts hve the sme promoters nd trnsfetion is ontrolled for with β-gl onstrut, the rpmyin-sensitive redution in luiferse tivity tht is speifi to the TOP onstrut is onsidered n indition of the dependeny of the trnsltion of the TOP onstrut of mtor regultion 18,22. We rried out experiments in sextuplite nd repeted them severl times. Tretment of flies with rpmyin. We otined Drosophil melnogster yw;gmr-q120 line from G. Jkson (University of Cliforni Los Angeles, USA) nd rossed it to w[1118] stok isogenized for the X hromosome nd two mjor utosomes, whih hs een hrterized for numer of ehviors nd used s the geneti kground for the Europen Drosophil Deletion Kit (DrosDel Consortium). The rossed flies were llowed to mte on norml food for 2 3 d nd then trnsferred to food ontining 1 µm rpmyin (Sigm) or DMSO. After elosion, we pled the flies on food ontining 1 µm rpmyin or DMSO. We trnsferred the flies to newly prepred food every dy. Pseudopupil nlysis of flies. We removed the heds of dult mle flies nd then mounted them onto mirosope slides using nil polish. We rried out pseudopupil nlysis with n optil mirosope using 60 ojetive with the oserver linded to the identity of the slides. We evluted 75 ommtidi for eh group ( 15 ommtidi from five individuls). Eh experiment ws done twie. The frequeny of ommtidi with different numers of visile rhdomeres ws sed on ll visile photoreeptor neurons, irrespetive of their shpe or rightness. We rised the flies t 25 C with 12-h light:12-h drk yle in 70% humidity. Mie nd ehviorl tests. All studies nd proedures were done under the jurisdition of pproprite Home Offie Projet nd Personl niml lienses nd with lol ethil ommittee pprovl. We genotyped HD-N171-N82Q mie 16 expressing the first 171 mino ids of humn huntingtin under the expression of mouse PrP promoter t 3 weeks of ge y PCR (primer sequenes re ville on request). We prepred CCI-779 in ethnol s stok solution t 50 mg ml 1 on the dy of experiment nd diluted it to 2 mg ml 1 in 0.15 M NCl, 5% Tween 20 nd 5% PEG 400 immeditely efore injetion. We ompred trnsgeni mie with nontrnsgeni littermtes. We oded mie with lphnumeri identities tht provided no lues to their genotype or tretment sttus, nd treted nd untreted mie were not housed in seprte ges. Thus, oservers were lind to their tretment nd geneti sttus during testing. There were no signifint differenes in test performnes in the mie ssigned to the tretment nd pleo groups t 4 weeks nd no differenes in the sex rtios in the groups. We weighed mie three times per week nd then injeted them intrperitonelly with 1% v/w solution of CCI-779 (20 mg per kg ody weight) or pleo (equivlent solution without CCI-779). We did three injetions every week from the ges of 4 16 weeks, nd then did this every other week until they rehed 21 weeks of ge. We monitored mie dily. We ssessed motor performne t 4, 14, 16 nd 18 weeks of ge with rotrod pprtus (Aelerting Model, Ugo Bsile, Biologil Reserh Apprtus); our liense limited rotrod ssessments to four testing time points. The mie were given three trining sessions per dy for two onseutive dys to dpt to the pprtus. On the third dy, the mie were given six seprte trils. On the trining nd testing dys, we set the speed of the rotrod to inrese from 4 r.p.m. to 40 r.p.m. in 250 s; we kept the mie on the rotrod for no more thn 300 s. We did not injet mie during the weeks tht they were tested on the rotrod to void ny onfounding effets of the injetions. Grip strength, wire mneuver nd tremor monitoring re prt of the SHIRPA ttery of ehviorl tests 36. We ssessed performne on these tests in mie t 4, 14, 16, 18, 20 nd 22 weeks of ge. To ssess grip strength, mie were llowed to hold metl grid with their forelims, lifted y the til so tht the hindlims were not in ontt with the grid nd gently pulled kwrds y the til until they ould no longer hold the grid. Grip strength ws sored s follows: 0, none; 1, slight grip, semi-effetive; 2, moderte grip, effetive; 3, tive grip, effetive. For tremors, the mie were pled on grid in ler Perspex ylinder for 5 min. We reorded tremors for the lst 2 min nd sored the mie s follows: 0, none; 1, mild; 2, mrked. For the wire mneuver, mie were held ove horizontl wire y the til nd lowered to llow the forelims to grip the wire. The mie were held in extension, rotted round to the horizontl nd relesed. We sored them s follows: 0, tive grip with hind legs; 1, diffiulty grsping with hind legs; 2, unle to grsp with hind legs; 3, unle to lift hind legs, flls within 10 s; 4, flls immeditely. Sttistis. We determined signifine levels for omprisons etween groups using t-tests, repeted-mesures or ftoril ANOVA, s pproprite, for prmetri dt nd using Mnn-Whitney U tests for nonprmetri dt, using the STATVIEW softwre, version 4.53 (Aus Conepts). For mouse ehviorl dt tht were nonprmetri nd nlyzed t multiple time points (tremors, grip strength nd wire mneuver), we used the following strtegy to provide mesure of the signifine of the pooled dt ross ll the treted time points. We ompred sores etween the treted nd ontrol groups using logisti regression pproh. We ssessed the effet size in terms of the odds rtio per unit hnge in sore. To llow for the ft tht the sme mie were oserved repetedly, we ssessed signifine levels y simultion. To do this, the tretment groups were rndomly permuted mong the mie 10,000 times, nd the signifine level ws determined s the proportion of simultions for whih the Z sore for the tretment effet from the logisti regression exeeded the oserved vlue. We otined 95% onfidene limits for the odds rtio y using the roust vrine pproh. We did ll lultions in Stt, version 7.0 (SttCorp). We nlyzed nonprmetri mouse dt t individul time points y Mnn-Whitney nd rotrod y repeted-mesures ANOVA. 594 VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE 2004 NATURE GENETICS
11 Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Genetis wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk Wyeth Phrmeutils for the gift of CCI-779; G. Jkson for the fly model of Huntington disese; E. J. L. Mller nd J. Chen for ontrol nd TOP luiferse vetors; N. Khn for rin smples from humns with Huntington disese nd ontrols; A. Toin for Gln 25 nd Gln 103 onstruts; H. Zoghi for the txin onstruts; W. J. Strittmtter for Gln 19 nd Gln 81 onstruts; K. L. Gun for rhe nd FLAG-4E-BP1 onstruts; T. Yoshimori for the ntiody to LC3; A. Aevedo nd E. Terrenoire for help with mouse rin smples; R. Pdinjt for help with pseudopupil illumintion; nd M. Borow, D. Clyton nd J. D. Cooper for helpful suggestions. We knowledge funding from the Commonwelth Sholrship Commission for Ph.D. sholrship (B.R.), the Wellome Trust for Senior Clinil Reserh Fellowship (D.C.R.), Senior Fellowship in Bsi Biomedil Siene (R.D.), Prize Studentship (Z.B.), The Cmridge Overses Trust (Z.B.), The Biotehnology nd Biologil Sienes Reserh Counil for Creer Development Awrd (C.J.O.) nd Medil Reserh Counil progrmme grnt to D.C.R nd S. Brown. COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The uthors delre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. Reeived 16 Jnury; epted 16 April 2004 Pulished online t 1. Ruinsztein, D.C. Lessons from niml models of Huntington s disese. Trends Genet. 18, (2002). 2. Dvies, S.W. et l. Formtion of neuronl intrnuler inlusions underlies the neurologil dysfuntion in mie trnsgeni for the HD muttion. Cell 90, (1997). 3. Sudou, F., Finkeiner, S., Devys, D. & Greenerg, M.E. Huntingtin ts in the nuleus to indue poptosis ut deth does not orrelte with the formtion of intrnuler inlusions. Cell 95, (1998). 4. Gutekunst, C.A. et l. Nuler nd neuropil ggregtes in Huntington s disese: reltionship to neuropthology. J. Neurosi. 19, (1999). 5. Dunh, A.W. et l. Sp1 nd TAFII130 trnsriptionl tivity disrupted in erly Huntington s disese. Siene 296, (2002). 6. L Spd, A.R. & Tylor, J.P. Polyglutmines pled into ontext. Neuron 38, (2003). 7. Chi, Y., Wu, L., Griffin, J.D. & Pulson, H.L. The role of protein omposition in speifying nuler inlusion formtion in polyglutmine disese. J. Biol. Chem. 276, (2001). 8. Rvikumr, B., Duden, R. & Ruinsztein, D.C. Aggregte-prone proteins with polyglutmine nd polylnine expnsions re degrded y utophgy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, (2002). 9. We, J.L., Rvikumr, B., Atkins, J., Skepper, J.N. & Ruinsztein, D.C. α-synulein is degrded y oth utophgy nd the protesome. J. Biol. Chem. 278, (2003). 10. Shmelzle, T. & Hll, M.N. TOR, entrl ontroller of ell growth. Cell 103, (2000). 11 Hung, S., Bjornsti, M.A. & Houghton, P.J. Rpmyins: mehnism of tion nd ellulr resistne. Cner. Biol. Ther. 2, (2003). 12. Serkov, N. et l. Sirolimus, ut not the struturlly relted RAD (everolimus), enhnes the negtive effets of ylosporine on mitohondril metolism in the rt rin. Br. J. Phrmol. 133, (2001). 13. Supko, J.G. & Mlspeis, L. Dose-dependent phrmokinetis of rpmyin-28-n-ndimethylglyinte in the mouse. Cner Chemother. Phrmol. 33, (1994). 14. Kwon, C.-H., Zhu, X., Zhng, J. & Bker, S.J. mtor is required for hypertrophy of Pten-defiient neuronl som in vivo. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 100, (2003). 15. Wyttenh, A. et l. Effets of het shok, het shok protein 40 (HDJ-2), nd protesome inhiition on protein ggregtion in ellulr models of Huntington s disese. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 97, (2000). 16. Shilling, G. et l. Intrnuler inlusions nd neuriti ggregtes in trnsgeni mie expressing mutnt N-terminl frgment of huntingtin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, (1999). 17. Welter, S. et l. Aumultion of mutnt huntingtin frgments in ggresome-like inlusion odies s result of insuffiient protein degrdtion. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, (2001). 18. Kim, J.E. & Chen, J. Cytoplsmi-nuler shuttling of FKBP12-rpmyin-ssoited protein is involved in rpmyin-sensitive signling nd trnsltion initition. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 97, (2000). 19. Fingr, D.C., Slm, S., Tsou, C., Hrlow, E. & Blenis, J. Mmmlin ell size is ontrolled y mtor nd its downstrem trgets S6K1 nd 4EBP1/eIF4E. Genes Dev. 16, (2002). 20. Wyttenh, A. et l. Polyglutmine expnsions use deresed CRE-medited trnsription nd erly gene expression hnges prior to ell deth in n induile ell model of Huntington s disese. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, (2001). 21. Kim, D.H. et l. GetL, positive regultor of the rpmyin-sensitive pthwy required for the nutrient-sensitive intertion etween rptor nd mtor. Mol. Cell 11, (2003). 22. Shw, M.S. et l. p70(s6k) ontrols seletive mrna trnsltion during ooyte mturtion nd erly emryogenesis in Xenopus levis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, (1999). 23. Kegel, K.B. et l. Huntingtin expression stimultes endosoml-lysosoml tivity, endosome tuultion, nd utophgy. J. Neurosi. 20, (2000). 24. Spp, E. et l. Huntingtin loliztion in rins of norml nd Huntington s disese ptients. Ann. Neurol. 42, (1997). 25. Key, Y. et l. LC3, mmmlin homologue of yest Apg8p, is lolized in utophgosome memrnes fter proessing. EMBO J. 19, (2000). 26. Hennig, K.M. & Neufeld, T.P. Inhiition of ellulr growth nd prolifertion y dtor overexpression in Drosophil. Genesis 34, (2002). 27. Mnning, B.D. & Cntley, L.C. Rhe fills GAP etween TSC nd TOR. Trends Biohem. Si. 28, (2003). 28. Jkson, G.R. et l. Polyglutmine-expnded humn huntingtin trnsgenes indue degenertion of Drosophil photoreeptor neurons. Neuron 21, (1998). 29. Frneshini, N. & Kirshfeld, K. Pseudopupil phenomen in the ompound eye of drosophil. Kyernetik 9, (1971). 30. Zhng, H., Stllok, J.P., Ng, J.C., Reinhrd, C. & Neufeld, T.P. Regultion of ellulr growth y the Drosophil trget of rpmyin dtor. Genes Dev. 14, (2000). 31. Hung, S. & Houghton, P.J. Mehnisms of resistne to rpmyins. Drug Resist. Updte 4, (2001). 32. Elit, L. CCI-779 Wyeth. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 3, (2002). 33. Mngirini L. et l. Exon 1 of the HD gene with n expnded CAG repet is suffiient to use progressive neurologil phenotype in trnsgeni mie.cell 87, (1996). 34. Lione, L.A. et l. Seletive disrimintion lerning impirments in mie expressing the humn Huntington s disese muttion J. Neurosi. 19, (1999). 35. Sthsivm, K. et l. Formtion of polyglutmine inlusions in non-cns tissue. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, (1999). 36. Rogers, D.C. et l. Behviorl nd funtionl nlysis of mouse phenotype: SHIRPA, proposed protool for omprehensive phenotype ssessment. Mmm. Genome 8, (1997). 37. Wlpoth, B.H. et l. Prevention of neointiml prolifertion y immunosuppression in syntheti vsulr grfts. Eur. J. Crdiothor. Surg. 19, (2001). 38. British Medil Assoition nd Royl Phrmeutil Soiety of Gret Britin. British Ntionl Formulry 4 (2003). 39. Kuemmerle, S. et l. Huntington ggregtes my not predit neuronl deth in Huntington s disese. Ann. Neurol. 46, (1999). 40. Mizushim, N., Ohsumi, Y. & Yoshimori, T. Autophgosome formtion in Mmmlin ells. Cell Strut. Funt. 27, (2002). 41. Gingrs, A.C., Rught, B. & Sonenerg, N. Control of trnsltion y the trget of rpmyin proteins. Prog. Mol. Suell. Biol. 27, (2001). 42. Usdin, M.T., Shelourne, P.F., Myers, R.M. & Mdison, D.V. Impired synpti plstiity in mie rrying the Huntington s disese muttion. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, (1999). 43. Murphy, K.P. et l. Anorml synpti plstiity nd impired sptil ognition in mie trnsgeni for exon 1 of the humn Huntington s disese muttion. J. Neurosi. 20, (2000). 44. Yoo, S.Y. et l. SCA7 knokin mie model humn SCA7 nd revel grdul umultion of mutnt txin-7 in neurons nd normlities in short-term plstiity. Neuron 37, (2003). 45. Tng, S.J. et l. A rpmyin-sensitive signling pthwy ontriutes to long-term synpti plstiity in the hippompus. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 99, (2002). 46. Steffn, J.S. et l. Histone deetylse inhiitors rrest polyglutmine-dependent neurodegenertion in Drosophil. Nture 413, (2001). 47. Ferrnte, R.J. et l. Therpeuti effets of oenzyme Q10 nd rememide in trnsgeni mouse models of Huntington s Disese. J. Neurosi. 22, (2002). 48. Hokly, E. et l. Sueroylnilide hydroxmi id, histone deetylse inhiitor, meliortes motor defiits in mouse model of Huntington s disese. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 100, (2003). NATURE GENETICS VOLUME 36 NUMBER 6 JUNE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Stimulation of the insulin/mtor pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
 Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Systemic Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Reverses Hypoalgesia and Improves Mobility in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therapeutic for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
 Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
ANGPTL binding ANGPTL binding ANGPTL4 GST ANGPTL5 ANGPTL6 ANGPTL7. A5+LILRB2 Fc. A5+Tie-2 Fc 10,000 7,500. Tie-2 Fc LILRB2 Fc. 5,000 K d = 5.
 doi:1.138/nture1195 ; Inhiitory reeptors ind ANGPTLs nd support < lood stem ells nd leukemi development Junke Zheng 1,2, Msto Umikw 1,3, Chngho Cui 1, Jiyun Li 1, Xioli Chen 1, Chozheng Zhng 1, HongDinh
doi:1.138/nture1195 ; Inhiitory reeptors ind ANGPTLs nd support < lood stem ells nd leukemi development Junke Zheng 1,2, Msto Umikw 1,3, Chngho Cui 1, Jiyun Li 1, Xioli Chen 1, Chozheng Zhng 1, HongDinh
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling
 LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Role of HCP5-miR-139-RUNX1 Feedback Loop in Regulating Malignant Behavior of Glioma Cells
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
Differential expression of cyclin G2, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C and peripheral myelin protein 22 genes during adipogenesis..
 The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
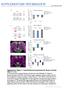 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
Epiphyseal growth plate growth hormone receptor signaling is decreased in chronic kidney disease related growth retardation
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
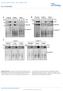 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
... Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. immunology letters to nature
 Supplementry informtion is ville in Nture s World-Wide We site (http:// www.nture.om) or s pper opy from the London editoril offie of Nture. Aknowledgements Supported in prt y grnts from the NIH (A.A.,
Supplementry informtion is ville in Nture s World-Wide We site (http:// www.nture.om) or s pper opy from the London editoril offie of Nture. Aknowledgements Supported in prt y grnts from the NIH (A.A.,
