Intervention with citrus flavonoids reverses obesity, and improves metabolic syndrome and
|
|
|
- Amberly Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intervention with itrus flvonoids reverses oesity, nd improves metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis in oese Ldlr -/- mie Authors: Amy C. Burke 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3, Mris R. Morrow 1, Cynthi G. Swyez 1,3, Jne Y. Edwrds 1,3, Mri Drngov 4, Murry W. Huff 1,2,3,5 1 Moleulr Mediine, Rorts Reserh Institute, 2 Deprtments of Biohemistry nd 3 Mediine, 4 Imging Reserh Lortories, Rorts Reserh Institute, The University of Western Ontrio, 1151 Rihmond St N., London, Ontrio, Cnd N6A 5B7 5 Address Correspondene to: Murry W. Huff, Rorts Reserh Institute, Rm 4222 The University of Western Ontrio 1151 Rihmond St. N., London, Ontrio, Cnd, N6A 5B7 Phone: +1 (519) Fx: +1 (519) Emil: mhuff@uwo. Running title: Citrus flvonoids reverse oesity nd metoli dysfuntion. Arevitions: AUC, Are under the urve; BAT, rown dipose tissue; CE, holesteryl ester; ewat, Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 epididyml white dipose tissue; FC, free holesterol; HFHC, high ft, holesterol-ontining; HOMA-IR, homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistne; iwat, inguinl white dipose tissue; MiroCT, miro omputed tomogrphy; SMCs, smooth musle ells; SEM, stndrd error of the men; TC, totl holesterol 1
2 ABSTRACT Oesity nd its ssoited metoli dysfuntion nd rdiovsulr disese risk represent leding use of dult moridity world-wide. Currently ville phrmologil therpies for oesity hve hd limited suess in reversing existing oesity nd metoli dysregultion. Previous prevention studies demonstrted tht the itrus flvonoids, nringenin nd noiletin protet ginst oesity nd metoli dysfuntion in Ldlr -/- mie fed high-ft, holesterol-ontining (HFHC) diet. However, their effets in n intervention model re unknown. In this report, we show in Ldlr -/- mie with diet-indued oesity, itrus flvonoid supplementtion to HFHC diet reversed existing oesity, dipoyte size nd numer through enhned energy expenditure nd inresed hepti ftty id oxidtion. Clori intke ws unffeted nd no evidene of white dipose tissue rowning ws oserved. Reversl of diposity ws ompnied y improvements in hyperlipidemi, insulin sensitivity, hepti stetosis nd modest redution in lood monoytes. Together, this resulted in therosleroti lesions tht were unhnged in size ut hrterized y redued mrophge ontent, onsistent with more stle plque phenotype. These studies further suggest potentil therpeuti utility of itrus flvonoids, espeilly in the ontext of existing oesity, metoli dysfuntion nd rdiovsulr disese. Keywords: Oesity; Atheroslerosis; Stetoheptitis; Bet-oxidtion; Insulin Resistne; Hypolipidemi Drugs; Intervention; Flvonoid Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 2
3 INTRODUCTION Ft umultion, s result of n imlne etween energy input nd expenditure, leds to oesity, type 2 dietes, rdiovsulr disese nd hepti stetosis, whih olletively represent one of the leding uses of dult moridity nd mortlity world-wide (1-3). This suggests tht restortion of funtionl energy homeostsis is ritil for therpeuti intervention. Despite efforts to develop nti-oesity meditions tht urtil symptoms of metoli dysfuntion, drugs tht hve rehed mrket hve limited effiy for oesity (~5-8%) nd mny hve een withdrwn for negtive side effets (3-6). Currently ville therpeutis predominntly work y either reduing lori intke or loking food sorption (3). Additionlly, ptients often regin lost weight. The tretment strtegy with the most roust nd lsting improvements is gstri ypss surgery, whih hs shown up to ~25% weight loss t 12-yers together with 51% remission rte for type 2 dietes (7). Presently, gstri ypss surgery s n intervention for oesity nd metoli syndrome is limited to ptients with BMI 35kg/m 2 (8), exluding ptients with moderte oesity, lthough these ptients often present with inresed metoli dysfuntion nd rdiovsulr risk (9, 1). Therefore, there is urgent need for sfe nd effetive medil therpies for oesity nd its ssoited omplitions, inluding the metoli syndrome nd rdiovsulr disese. Epidemiologil studies show n inverse orreltion etween flvonoid ( lss of plnt-derived polyphenols) onsumption nd the development of type 2 dietes, metoli syndrome, nd theroslerosis (11, 12). Previous reserh in our l identified the itrus-derived flvonoids, nringenin Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 nd noiletin, s novel therpeutis for the prevention of metoli syndrome nd rdiovsulr disese (13-17). These flvonoids hve nti-inflmmtory properties, promote insulin sensitivity nd inhiit pob1 seretion from ultured heptoytes (16, 18-2). When extended to mouse model of oesity, metoli dysfuntion nd therogenesis, nmely the Ldlr -/- mouse fed high-ft, high holesterol (HFHC) diet, prevention studies reveled tht supplementtion of the HFHC diet with nringenin or noiletin ttenuted weight gin nd diposity, enhned insulin signling, lowered plsm lipids, prevented systemi inflmmtion nd hepti stetosis, resulting in slowed theroslerosis progression (13-17). While these studies highlight potentil therpeuti utility of the itrus flvonoids, it would e more linilly relevnt 3
4 to ssess the effiy of these ompounds in n intervention protool, where oesity, insulin resistne, hyperlipidemi nd theroslerosis hve een estlished prior to tretment. In the present study we show, in Ldlr -/- mie with pre-estlished diet-indued oesity, metoli dysregultion nd intermedite-stge theroslerosis, tht intervention y the ddition of either nringenin or noiletin to HFHC diet not only prevented ontinued oesity nd deteriortion in symptoms of the metoli syndrome, ut mrkedly redued dipose tissue mss, normlized gluose homeostsis, nd ttenuted oth hyperlipidemi nd hepti stetosis. Corretion of metoli prmeters ws ompnied y redution in irulting lood monoytes. Colletively, these metoli improvements did not resolve the size of orti sinus therosleroti lesions, ut plques in flvonoid-treted mie were hrterized y redued mrophge nd holesterol ontent, onsistent with lesion regression (21, 22). Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 4
5 MATERIALS AND METHODS Animls nd Diets Mle Ldlr -/- mie on C57BL/6 kground (Jkson Lortory, Br Hror, MA), were housed in pirs in stndrd ges t 23 C on 12 h light nd drk yle. The nimls were red for in ordne with the Cndin Guide for the Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls. All experimentl proedures were pproved y the Animl Cre Committee t the University of Western Ontrio (protool # AUP ). Mie 1-12 weeks of ge (n=1) were fed d liitum, purified rodent how diet (14% of lories from ft, Tekld Rodent Diet 864, Envigo, Mdison WI) for 24 weeks. Another group of mie (1-12 weeks of ge, n=12; 24/group) were fed high-ft, holesterol ontining (HFHC; 42% of lories from ft,.2% holesterol, Tekld TD9268, Envigo, Mdison WI) for 12 weeks (seline). A sugroup of these HFHC-fed mie (n=24) were srified t 12 weeks to provide seline dt for nlyses tht required srifie. The remining mie were divided mongst 4 different groups nd for the susequent 12 weeks: one group remined on the sme HFHC diet (n=24), one group remined on the HFHC supplemented with 3% nringenin (#N5893, Millipore-Sigm) (n=24), one group remined on the HFHC diet supplemented with.3% noiletin (# , R&S PhrmChem, Hngzhou City, Chin) (n=24) nd one group swithed to the stndrd rodent how (n=24). Food intke nd ody weights were mesured weekly. Clori intke ws lulted s weight of food eten (g) per dy multiplied y the lori ontent of eh diet (how 3. kl/g; HFHC 4.5 kl/g). We previously oserved tste version with nringenin nd noiletin, whih Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 ws mitigted y slowly inresing the flvonoid dose over the first week of intervention to prevent signifintly impt on food intke (dt not shown). Blood nd Tissue Colletion Mie were fsted for 6 hours t the strt of the light yle prior to lood tking or srifie. At srifie, nimls were nesthetized with Ketmine-Xylzine (1µg/g Ketmine hydrohloride, Bionihe Animl Helth Cnd In., Belleville, ON nd 1µg/g Xylzine, Byer Helthre, Animl Helth Division, Byer In., Toronto, ON). Blood ws olleted vi rdi punture in syringes ontining 8 µl of 7% N 2 - EDTA. Blood ws entrifuged t 12, rpm for 1 minutes t 4 C to seprte the plsm, whih ws stored 5
6 t -2 C for further use. Tissue dissetions were performed vi midline inision. To disset the hert for histologil nlysis, the left ventrile ws perfused with phosphte uffered sline (PBS) ontining heprin (1 units/ml) nd the right trium ws ut to drin the perfuste. The hert nd full-length ort were disseted together. Aorte were rinsed nd lened using disseting mirosope to remove ny dipose tissue. Aorte were snp frozen in liquid N 2 nd stored t -8 C for mrna nd lipid mesurements. The top hlf of the hert ws pled in Optimum Cutting Temperture (OCT) medium, frozen on dry ie nd stored t -8 C for histologil nlyses. A smll piee of epididyml nd inguinl white dipose tissue ws fixed in 4% prformldehyde nd prffin emedded for histologil nlyses. Liver, epididyml white dipose tissue (ewat), inguinl white dipose tissue (iwat), rown dipose tissue, qudrieps, gstronemii nd solei musles were removed, weighed nd snp frozen in liquid N 2 nd stored t -8 C. Metoli Cges From 1 to 4 weeks prior to ompletion of the intervention period, energy expenditure, respirtory exhnge rtio (RER), food onsumption nd loomotor tivity were ssessed using the Comprehensive Lortory Animl Monitoring System (CLAMS; Columus Instruments, Columus, OH). Mie were housed in metoli ges with free ess to food nd wter nd limtized for 48 hours. For the susequent 24 hours, every 1 minutes, dt on O 2 onsumption (VO 2 ; ml/h) nd CO 2 prodution (VCO 2 ; ml/h) were olleted. The RER ws derived from the rtio of VCO 2 to VO 2, nd energy expenditure ws determined s ( X RER) X VO 2 nd expressed s nlysis of ovrine (ANCOVA)-djusted energy Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 expenditure in kl/h. ANCOVA-djustments to energy expenditure were mde sed on ody weight, whih llowed for the determintion of differenes in energy expenditure, independent of group differenes in ody weight. The ANCOVA nlysis done for this work ws provided y the NIDDK Mouse Metoli Phenotyping Centers (MMPC, using their Energy Expenditure Anlysis pge ( nd supported y grnts DK76169 nd DK Amultory tivity ws mesured s infrred em reks in the X, Y, nd Z xis per hour. Aumulted food onsumption ws mesured in grms nd onverted to kl sed on diet omposition. MiroCT 6
7 Mie were first imged t 12 weeks (seline) on diet (n=8/group) nd regulrly following intervention (Week 14, 16, 18, 21, 23), s desried previously (13). Whole-ody omposition nlysis ws onduted y miro-ct imging using Lous Ultr miro-ct snner (GE Helthre) (23). Following 4 hour fst, mie were nesthetized with 1.5% isoflurne in O 2. The sn protool onsisted of n x-ry tue voltge of 8 kvp nd urrent of 55. ma. A lirting phntom, omprising ir nd wter, ws snned onurrently s lirtors tht enled the onversion of the reonstruted imge vlues into CT numers (Hounsfield Units (HU)). In sn time of 16 seonds, 1 views were quired in one ontinuous rottion. Imges were reonstruted to n isotropi voxel size of 15 µm 3. The nlysis ws onduted using MiroView softwre version 2.2 (GE Helthre). Totl dipose tissue volume ws lulted y seleting ll voxels with vlues within window of -225 to -6 HU nd then divided into suutneous nd viserl depots. Suutneous nd viserl dipose tissue depots were differentited using the musulr dominl wll, whih is redily identifile euse of its higher density (24). The suutneous nd viserl dipose depots were outlined mnully nd the volume of eh region ws lulted y MiroView s the numer of voxels flling within the threshold window multiplied y voxel volume (15 µm 3 ). Gluose Tolerne nd Insulin Tolerne Tests A gluose tolerne test ws performed following 6 hour fst y i.p. injetion with 15% gluose in.9% NCl (1g/kg ody weight) (15). Blood smples for gluose mesurements (Byer Contour Blood Gluose Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Monitoring System, Byer Helthre) were tken up to 12 minutes post-injetion. An insulin tolerne test ws onduted following 5 hour fst y i.p. injetion with insulin (.6 IU/kg ody weight; Novolin GE Toronto, Novo Nordsik, Cooksville, ON) (15). Blood smples for gluose mesurements were otined up to 6 minutes post-injetion. Gluose nd insulin tolerne were lulted s perent hnge in lood gluose from seline. Tissue Lipids 7
8 Lipids from liver, qudrieps, gstronemii nd solei, nd full-length orte disseted free of ft nd onnetive tissue, were extrted using the method of Folh et l. from smples stored t -8 C, s desried previously (14, 25). [Cholesteryl-1,2-3 H(N)]Cholesteryl olete (PerkinElmer, Guelph, Cnd: #NET746L) ws dded to ssess reovery. A omined 2 µg/ml triolein nd 2 µg/ml holesterol stndrd ws prepred in isopropnol nd liquoted for stndrd urves (-2µg). Smples nd stndrds were dried under N 2, nd 1% Triton X-1 solution in hloroform dded nd left t room temperture for 1 hour to soluilize. Smples nd stndrds were dried under N 2, followed y the ddition of deionized wter nd inution t 37 C for 15 minutes. Smples were nlyzed using enzymti regents for triglyeride (Rohe Dignostis: Triglyerides/glyerol lnked, # ), totl holesterol (WAKO Dignostis: Cholesterol E (CHOD-DAOS method) # ) nd free holesterol (WAKO Dignostis: Free holesterol (COD-DAOS) method # ). Cholesteryl ester ws determined s the differene etween totl holesterol nd free holesterol. Plsm Mesurements Plsm triglyeride (TG) nd totl holesterol (TC) were mesured on Cos Mir S utonlyzer (Rohe Dignostis, Lvl, Cnd) using lirtors nd ontrols from Rohe Dignostis (15). Enzymti regents for triglyeride (Rohe Dignostis: triglyerides/glyerol lnked # ) nd holesterol (Rohe Dignostis: Cholesterol CHOD-PAP # ) were used. Fresh-EDTA plsm (5 µl) ws seprted y fst protein liquid hromtogrphy (FPLC) using n AKTA purifier nd Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Superose 6 olumn (14). A onstnt flow rte of.4 ml/min ws used to ollet 5 µl frtions. An liquot of eh frtion ws used to mesure holesterol nd triglyerides enzymtilly in oth smples nd stndrds on mirotitre plte with dded enzymti regents (Triglyeride: Rohe Dignostis, triglyerides/glyerol lnked # nd totl holesterol: WAKO Dignostis, Rihmond, VA, Cholesterol E: (CHOD-DAOS method) # ). Blood gluose ws mesured in whole lood using the Byer Contour Blood Gluose Monitoring System (Byer Helthre, Etoioke, Cnd) (15). Plsm Insulin (ALPCO Dignostis, Slem, NH: mouse ultrsensitive ELISA #8-INSMSU-E1) ws determined 8
9 in EDTA-plsm smples, stored t -8 C, y mouse speifi ELISA. Homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistne (HOMA-IR) ws lulted using the following formul s previously desried for mie: HOMA-IR= 26 x fsting insulin level (ng/ml) x fsting gluose level (mg/dl)/45 (26). Liver Bet Oxidtion For hepti ftty id oxidtion, fresh liver (25 mg) ws homogenized in.1 M phosphte uffer, ph 7.2 ontining.25 M surose, 1mM EDTA, 1 mm dithiothreitol, nd 1 µl/ml of protese inhiitor (Sigm- Aldrih #P834). Homogentes were entrifuged t 1xg t 4 C for 1 minutes. 2 µl of superntnt ws inuted for 3 minutes t 37 C with onstnt shking in.1 M phosphte uffer, ph 7.2, ontining 15 mm KCl, 1 mm Hepes, 5 mm Tris mlonte, 1 mm MgCl 2, 1 mm rnitine, 5 mm ATP nd 2 µci of [9,1-3 H(N)]plmiti id (PerkinElmer: #NET431MC)/ 5 µm unleled plmiti id omplexed with.15 % ftty id-free BSA. Retions were stopped with 2 µl of.6 N perhlori id nd unreted ftty ids extrted with hexnes. 3 H 2 O in the queous phse ws mesured y liquid sintilltion ounting (15, 27). Gene Expression RNA ws isolted from liquots of liver, epididyml nd inguinl dipose tissue, rown dipose tissue nd whole orte using Trizol regent (Life Tehnologies, Mississug, Ontrio, Cnd). Reverse trnsription of 1 µg totl RNA ws performed using the High Cpity Reverse Trnsription kit (Applied Biosystems, ABI) to yield DNA. Speifi mrna undnes were mesured y quntittive rel-time PCR (qrt- Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 PCR) on n ABI ViiA 7 Sequene Detetion System (ABI) ording to the mnufturer s instrutions. In the epididyml, inguinl nd rown dipose tissue, mrna quntittion for Tnf, Cl2, Cl3, Emr1, Up1, Cide, Pdk4, Ppr, Lipe nd Pnpl2 ws determined. In liver, mrna quntittion for Cpt1, Pg1, Srepf1, Ppr, Aox1, Cl2, Cl3, nd Tnf ws determined. In the ort, mrna quntittion for Cl3, Il1, Cl2, Tnf, Emr1, Cr7, A1 nd Ag1 ws determined. 1 ng smples of DNA were ssyed in triplite in 1 µl retions using stndrd urve qrt-pcr protool to lulte speifi mrna onentrtions. Expression levels for eh gene were normlized to Gpdh expression in eh 9
10 tissue. With the exeption of Sref1, ll primer nd proe sets used were purhsed s TqMn Assys (ABI). The proe nd primer sequenes for Sref1 were designed from the known murine Sref1 lous to determine splie juntions. The intervening introni sequene ws removed nd primers nd proe were designed from the resultnt Srep1 exon1-exon2 sequene using Primer Express 2. softwre (ABI). Primers were otined from Sigm-Genosys nd the proes leled 5 with 6- roxyfluoresein (FAM) nd 3 with the quenher MGB were from ABI. TqMn ssy for mouse Sref1: Forwrd Primer: CAGGCCCGGGAAGTCACT; Reverse Primer: GACCACGGAGCCATGGATT; Proe: FAM- ATTTGAAGACATGCTCCA-MGB. Tissue Histology nd Immunohistohemistry Histologil nd morphometri nlyses were performed s desried previously (14, 17). Epididyml white dipose tissue ws fixed in 4% prformldehyde for 24 hours, proessed, emedded in prffin, nd setioned on Mirom HM335E mirotome (Thermo Fisher Sientifi) nd stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Frozen seril setions (7-1 per hert, 1 µm) of the orti sinus from herts frozen in OCT, inititing nterior to the origin of the orti vlves, were prepred using Lei CM 35S ryostt. For quntittion of lesion re in the orti sinus, setions were stined with oil red-o. Immunohistohemistry stining for mrophges y CD68 (BioRd, Mississug, Cnd: MCA 1957), smooth musle α-tin (Am, Toronto, Cnd: polylonl rit nti-smooth musle α-tin, 5694) nd tivted spse-3 (Am, rit nti-tive spse-3, 451), ws performed s desried previously (28). Slides were Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 fixed in etone nd loked in 2% ovine serum lumin (Sigm-Aldrih). After inution with primry ntiody, got iotinylted seondry ntiody ws used (Vetor Lortories, Burlington, ON). Slides were then inuted in peroxidse loking regent, followed y inution with the ABC regent (ABC Elite Stndrd Kit, Vetor Lortories). Slides were exposed to the DAB sustrte (Peroxidse sustrte kit, Vetor Lortories) followed y ounterstin in hemtoxylin (Sigm-Aldrih). Photomirogrphs were otined using n Olympus BX5 mirosope nd QImging Retig EXi FAST mer. Collgen firils were ssessed using irulr polrizing mirosopy s desried previously (28). Aorti sinus setions were stined with pirosirius red (Polysienes, Wrrington, PA) nd visulized using n Olympus 1
11 BX51 mirosope (Olympus Cnd, Rihmond Hill, Cnd) equipped with irulr polrizer/interferene filters, liquid rystl ompenstor, hrge-oupled devie video mer nd Ario imge-proessing softwre (Ario LC-Polsope, Cmridge Reserh nd Instrumenttion, In., Hopkinton, MA). Morphometri nlysis of lesion re, neroti ore re, CD68, smooth musle α-tin nd ollgen in lesions from mie from eh group ws performed on seril setions. The reltive re of the therosleroti plque positive for CD68, smooth musle α-tin or ollgen ws determined s the re of positive stining divided y the re of the respetive plque. Quntittion ws determined using ImgeJ 1.5 softwre (Ntionl Institutes of Helth) for CD68, smooth musle α-tin nd ollgen, or AxioVision softwre for lesion re nd neroti ore size. To determine the reltive tivtion of spse-3, the numer of ell nulei immunostined for tivted spse-3 ws expressed s perentge of the totl lesion re. To ensure tht stndrd region ws mesured in eh mouse, lesion nlyses egn t the origin of the orti vlves. All quntittions were performed independently y three people. Flow Cytometry Blood nd one mrrow ell nlyses were performed in seprte experiment in Ldlr -/- mie (n=8/group) using the sme indution nd intervention protool desried ove. Blood Leukoytes: Monoytes nd neutrophils were identified from whole lood. At srifie, lood ws olleted y rdi punture into EDTA lined tues nd immeditely pled on ie. For eh mouse smple, 1 µl of lood ws used. UltrComp ebeds (Affymetrix ebiosienes #1-2222, Cedrlne, Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Burlington, ON) were used s single positive ontrol, exept for the single positive ontrol for the Vitl Dye, where ArC Amine Retive Compenstion Bed Kit ws used (A1346, Life Tehnologies, Burlington, ON). Fluoresene Minus One (FMO) ontrols were performed on omined lood smples from ll mie, 1 µl eh. Viility ws ssessed using LIVE/DEAD Fixle Ded Cell Ner-IR Stin Kit (L1119, Invitrogen, Life Tehnologies, Burlington, ON) (Supplementry Tle S1) in ll smples fter inution for 25 min in the drk t room temperture. Cells were stined with oktil of ntiodies ginst CD45-eFluor 45 (Affymetrix ebiosienes, Cedrlne, Burlington, ON), Ly6-C/G-PerCP- Cy 5.5 (BD Biosienes, Cedrlne, Burlington, ON) nd CD115-APC (Affymetrix ebiosienes) on ie 11
12 for 2 minutes in the drk (Supplementry Tle S1), similr to previous studies (29). Red lood ells were lysed in 1X PhrmLyse (BD Biosienes) for 13 minutes t room temperture. The stined white lood ells were entrifuged, wshed, nd re-suspended in flow-uffer (Hnk s uffered slt solution (HBSS) +.1% BSA, w/v). Cells were fixed y the ddition of 4% prformldehyde. Monoytes were identified s CD45 hi CD115 hi nd further identified into Ly6-C hi nd Ly6-C lo ; neutrophils were identified s CD45 hi CD115 lo Ly6-C/G hi (Gr-1), similr to previous studies (Supplementry Figure S1A) (29). Hemtopoieti Stem Cell: Hemtopoieti stem nd progenitor ells from the one mrrow were nlyzed y flow ytometry. Bone mrrow ws hrvested from femurs nd tiis y flushing with HBSS +.1% BSA w/v through 7 µm ell striner. Spleen ws mined into smll piees, gently rued ginst 7 µm ell striner nd flushed with HBSS +.1% BSA w/v. The ell suspension ws entrifuged for 5 minutes t 5 g t 6 C, superntnt spirted nd the ells re-suspended in 1X PhrmLyse (BD Biosienes) for 3 minutes (spleen) or 5 minutes (one mrrow). RBC lysis ws stopped y the ddition of exess HBSS +.1% BSA. Cells were one gin entrifuged t 5 g for 5 min t 6 C nd the superntnt spirted. Cells were re-suspended in 1 ml HBSS +.1% BSA nd loked with norml got serum. Cells were one gin entrifuged t 5 g for 5 min t 6 C, nd the superntnt spirted. Bone mrrow ws re-suspended in 4 ml of HBSS +.1% BSA nd spleen ws re-suspended in 3 ml of HBSS +.1% BSA. For eh mouse lood smple, 15 µl of suspension ws used. UltrComp ebeds (Affymetrix ebiosienes #1-2222) were used s single positive ontrol, exept for the single positive ontrol for the Vitl Dye, where ArC Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Amine Retive Compenstion Bed Kit ws used (A1346, Life Tehnologies, Burlington, ON). FMO ontrols were done on omined smples from ll mie, 15 µl eh. Viility ws ssessed using LIVE/DEAD Fixle Ded Cell Ner-IR Stin Kit (L1119, Invitrogen, Life Tehnologies, Burlington, ON) (Supplementry Tle S1) in ll smples fter inution for 25 min in the drk t room temperture. Cells were stined with oktil of ntiodies ginst FITC Mouse Hemtopoieti Linege Coktil (CD3 (17A2), CD45R (B22)(RA3-6B2), CD11 (M1/7), TER-119, Ly-G6 (Gr-1) (RB6-8C5)) (Affymetrix ebiosienes), Brillint Violet 421 Anti-mouse CD117 (-Kit) (Biolegend, Cedrlne), Brillint Violet 65 nti-mouse Ly-6A/E (S-1) (Biolegend), Alex Fluor 7 Anti-mouse CD16/32 (Affymetrix 12
13 ebiosienes) nd PE Anti-mouse CD34 (Biolegend) on ie for 2 minutes in the drk (Supplementry Tle S1) similr to previous studies (29). The stined white lood ells were entrifuged, wshed, nd resuspended in flow-uffer (HBSS +.1% BSA, w/v). Cells were fixed y the ddition of 4% prformldehyde. Hemtopoieti stem nd progenitor ells were identified s Lin -, S-1 + nd kit + (LSK) while the hemtopoieti progenitor susets were seprted using ntiodies to CD16/32 (FγRII/III) nd CD34. CMPs were identified s lin -, S-1 -, kit +, CD34 hi, FγRII/III lo, GMPs s lin -, S-1 -, kit +, CD34 hi, FγRII/III hi, MEPs s lin -, S-1 -, kit +, CD34 lo, FγRII/III lo (Supplementry Figure S1B). Flow ytometry ws performed using n LSRII (for nlysis) running FACS DiV softwre. All flow ytometry dt were nlyzed using FlowJo softwre (Tree Str In.) Sttistil Anlysis Dt is presented s men ± SEM. Sttistil nlyses were performed using Sigm Plot version 14.. A One-wy ANOVA with post-ho Tukey s test ws used to test for differenes etween groups exept in the se of ody weight nd diposity mesured over time where 2-wy repeted mesures ANOVA with post-ho Tukey s test ws used. Signifine thresholds were P vlues less thn.5. Signifine differenes re indited y different lowerse letters. A Student s t-test ws used to test for differenes in ANCOVA-djusted energy expenditure. Signifint differenes (P<.5) re indited y n sterisk. Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
14 RESULTS Flvonoid Intervention Promotes Weight Loss nd Attenutes Adiposity. Previously, we determined tht ddition of either nringenin or noiletin to HFHC diet prevented the development of mny of the disorders of the metoli syndrome nd prevented theroslerosis (15-17). To determine the therpeuti utility of these flvonoids, we sought to ssess their effiy in n intervention model where these disorders were pre-estlished. Mie were initilly fed HFHC diet over 12 weeks to indue oesity, metoli syndrome nd intermedite therosleroti lesions, nd estlish disese seline to whih the effiy of intervention ws evluted (Figure 1A). Susequently, mie were divided mong 4 tretment groups for the susequent 12 weeks: one group remined on the HFHC diet, seond group reeived intervention with regulr mouse how, third group reeived intervention with the HFHC diet supplemented with 3% nringenin nd the fourth group reeived intervention with the HFHC diet supplemented with.3% noiletin (Figure 1A). All mie gined weight over the initil 12-week indution phse. Susequently, mie tht remined on the HFHC diet inresed their ody weight further 2% (Figure 1B). Mie tht reeived intervention with nringenin or noiletin, while lso remining on the sme HFHC diet, lost ~13% of the ody weight gined during the indution phse, loss similr to tht oserved in the how diet intervention group (Figure 1B). Chow intervention suppressed food intke during the first week, due to the rupt hnge in food texture, ut ws rpidly resolved (Figure 1C). Intervention with the ddition of nringenin or noiletin Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 to the HFHC diet did not signifintly redue lori intke throughout the 12 weeks of intervention, suggesting tht there ws no flvonoid effet on stiety or feeding ehvior (Figure 1C). Epididyml ft depots were inresed during indution with the HFHC diet (Figure 1D). Compred to seline, intervention with nringenin or noiletin redued epididyml ft y 29% nd 44%, respetively, similr to the ft loss in how-intervened mie (Figure 1D). By ontrst, in mie tht remined on the HFHC diet lone, epididyml ft mss inresed y 28%. The sme trends were oserved for inguinl dipose tissue (Supplementry Figure S2A). In seprte study, we onfirmed the intervention-indued dipose tissue redutions with the flvonoids y MiroCT (Figure 1E, Supplementry Figure S2B). 14
15 MiroCT showed tht viserl ft volume ws redued 38-53% nd suutneous ft volume ws redued 23-43% y flvonoid intervention (Figure 1E, Supplementry Figure S2B). Importntly, len tissue volume did not signifintly hnge during the 12 weeks of intervention (Figure 1F), inditing tht the intervention-indued weight loss ws driven y redution in diposity. Flvonoid Intervention Redued Adipose Tissue Inflmmtion. Previous prevention studies demonstrted tht nringenin ttenuted dipoyte hypertrophy nd dipose tissue inflmmtion in HFHC-fed Ldlr -/- mie (14). In the present study, ompred to mie tht remined on the HFHC-diet, intervention y either nringenin, noiletin or how indued shift in epididyml dipoyte re towrds smller dipoytes y 19%, 23% nd 3%, respetively (Figure 1G). Similrly, flvonoid-treted mie hd smller dipoytes in inguinl dipose tissue (Supplementry Figure S2A). We next mesured the mrna expression of inflmmtory genes in epididyml, inguinl nd rown dipose tissues. Consistently, intervention with nringenin or noiletin redued men mrna expressions of Tnf, Cl2, nd Cl3, similr to redutions oserved with how intervention. Although not sttistilly signifint, these redutions suggest shift to resolution of oesity-ssoited dipose tissue inflmmtion (Supplementry Figure S3A). To try nd understnd if the redution in diposity ws due to rowning or enhned lipolysis, the mrna expression of known mrkers of dipose tissue rowning nd lipolysis ws mesured. Tretment with noiletin, ut neither nringenin nor how, inresed the men Up1 mrna expressions in epididyml nd inguinl dipose tissue (not signifint). No intervention ltered Up1 Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 expression in rown dipose tissue (Supplementry Figure S3B). Neither intervention with nringenin, noiletin nor how, ffeted mrna expressions of other rowning mrkers Cide, Pdk4 nd Ppr, or the lipolysis ssoited genes, Lipe nd Pnpl2, in inguinl, epididyml or rown dipose tissue (Supplementry Figure S3B, C). This suggests tht the redution in diposity with eh intervention ws not likely medited diretly through rowning or enhned lipolysis within white dipose tissue. Histologil ssessment of rown dipose tissue reveled tht nringenin or noiletin intervention redued tissue lipid umultion similr to intervention with how (Supplementry Figure S3D). Flvonoid Intervention Inreses Energy Expenditure. 15
16 Previous prevention studies hve shown tht the ddition of either flvonoid to the HFHC diet inresed weight-normlized energy expenditure in mie (14, 16). Therefore, we ssessed whether flvonoid intervention would lso orret oesity-ssoited suppressed energy expenditure. Following HFHC diet indution, intervention with either nringenin or noiletin inresed ANCOVA-djusted energy expenditure in oth the light nd drk yles, ompred to mie tht ontinued on the HFHC diet lone, suggesting ompound-medited mehnism (Figure 2A). The RER, whih is inditive of metoli fuel soure, ws lso ltered y flvonoid intervention. Mie tht ontinued on the HFHC diet lone hd men RER in the light yle of.82, whih deresed to.75 in the drk yle, inditive of ft s the primry metoli fuel soure over 24hr (Figure 2B). Interestingly, intervention with either flvonoid to the HFHC diet mintined n RER ~.8 during the drk yle, when mie onsume the mjority of their dily lori intke (3). This indites shift to omintion of rohydrte nd ft utiliztion in the flvonoidtreted mie (Figure 2B). Intervention with the how diet inresed RER to.9, over 24 hours, inditing enhned oxidtion of rohydrtes. In mie intervened with either flvonoid, food onsumption inresed y 2.5 kl or ~.5 grms per dy, seletively in the drk yle (Figure 2C), nd without hnges in multory tivity (Figure 2D). This smll inrese in food intke ws not likely detetle when mesured every 3 dys in stndrd housing (Figure 1C). Together, this suggests tht flvonoid intervention enhned energy expenditure nd my indue mild strvtion response promoting greter food intke. Flvonoid Intervention Normlizes Insulin Sensitivity. Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 The ility of intervention with nringenin or noiletin to reverse estlished insulin resistne ws ssessed. After indution with the HFHC diet, Ldlr -/- mie developed elevted fsting plsm insulin nd mild hyperglyemi (Figure 3A, B). Intervention with how reversed hyperinsulinemi (-61%) nd modestly improved hyperglyemi (-15%). The ddition of either nringenin or noiletin to the HFHC diet reversed hyperinsulinemi t week 24 y 5% nd 54%, respetively, suggesting enhned insulin sensitivity, despite the onomitnt HFHC diet (Figure 3A). These signifint redutions in fsting insulin levels were ompnied y dereses in fsting gluose y intervention with nringenin (-13%, NS) nd noiletin (-35%) (Figure 3B). Temporlly, improvements in fsting gluose were oserved t 6 weeks of 16
17 flvonoid-intervention, nd were mintined up to 12 weeks (Figure 3C). Homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistne (HOMA-IR) lultions showed tht intervention with either flvonoid restored HOMA-IR to similr levels oserved in how-intervened mie (Figure 3D). To determine if normlized fsting insulin levels resulted in improved insulin or gluose tolerne, oth tolerne tests t seline, nd fter 12 weeks of intervention were performed (Figure 3E-J). At seline, ll groups hd similr insulin tolerne or lerne of gluose shown s hnge in lood gluose onentrtion over time (Figure 3E) nd % hnge in gluose over time (Figure 3F). Following intervention, the lower fsting gluose levels in flvonoid-treted mie were ompnied y lower insulin tolerne test re under the plsm gluose urve (AUC) (Figure 3G), ut there ws no hnge in the effiieny of gluose lerne over time (Figure 3H), suggesting tht improved insulin tolerne did not enhne gluose lerne. Intervention with how did not ffet insulin tolerne (Figure 3H). Similr gluose tolerne ws oserved in ll groups following 12 weeks of indution (Figure 3I). Intervention with the ddition of either nringenin or noiletin to HFHC or with how, improved gluose tolerne ompred to mie tht remined on the HFHC diet lone (Figure 3J). To understnd peripherl insulin sensitivity further, we ssessed musle triglyeride umultion in qudrieps nd gstronemii, whih is known to impir insulin signling (31) (Figure 3K, L). The umultion of triglyeride in oth the qudrieps nd gstronemius musles ws elevted t seline nd inresed further y ontinution on the HFHC diet (Figure 3K, L). In qudrieps, intervention with nringenin, noiletin or how reversed triglyeride umultion from seline (Figure 3K). In Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 gstronemii, intervention with either flvonoid or how deresed the men triglyeride levels from seline (trend), ut were signifintly lower ompred to triglyeride levels in HFHC-fed mie t 24 weeks (Figure 3L) Flvonoid Intervention Improves Ftty Liver. Ldlr -/- mie fed the HFHC indution diet umulted oth hepti triglyerides nd holesterol (Figure 4A-C). Compred to seline, liver triglyeride levels were reversed with intervention y either nringenin (-28%), noiletin (-4%) or how (-7%) (Figure 4A). Compred to the HFHC diet t 24 weeks, intervention with either flvonoid or how redued liver triglyeride y 58-82%. Compred to oth seline 17
18 nd HFHC t 24 weeks, liver holesteryl ester nd free holesterol were lower with intervention y either nringenin (-7%, -4%), noiletin (-6%, -33%) or how (-9%, -53%), respetively (Figure 4B,C). In prevention studies, we reported tht primry mehnism for flvonoid-indued redutions in liver lipids nd ssoited metoli normlities ws enhned Pg1- nd Cpt1-medited ftty id oxidtion nd ttenuted Srep1-indued ftty id synthesis (15, 16). In the present study, intervention with the ddition of either nringenin or noiletin to the HFHC diet reversed the HFHC diet indued suppression of hepti ftty id oxidtion, inresing it y 2-fold ompred to seline nd y 1.4-fold ompred to HFHC-fed mie t 24 weeks (Figure 4D,E). This ws ompnied y enhned liver mrna expressions of Cpt1 nd Pg1. Improvements in hepti lipids with flvonoid or how intervention were ssoited with redution in Sref1 mrna expression with nringenin (trend), noiletin nd how (Figure 4E), suggesting redued hepti de novo lipogenesis. Liver weight ws redued with flvonoid tretment nd there ws no effet on hepti Aox1 nd Ppr mrna expression, inditing tht the flvonoid effets were independent of peroxisome prolifertion or tivtion of PPAR, onsistent with our previous prevention studies (Figure 4F, Supplementry Figure S4A,B) (16). Hepti inflmmtion is lso exerted y high-ft feeding (14). Intervention with either flvonoid in ddition to HFHC ompletely normlized the mrna expression of hepti Cl2, Cl3, Tnf nd Il1, onsistent with dereses in hepti lipids nd improvements in hepti funtion (Supplementry Figure S4C-F). Flvonoid Intervention Improves Hyperlipidemi. Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Upon HFHC diet feeding, Ldlr -/- mie developed hyperholesterolemi nd hypertriglyeridemi (Figure 5A-G). Intervention with nringenin or noiletin supplementtion to the HFHC diet for 12 weeks redued plsm holesterol (>5%) nd triglyerides (>5%) (Figure 5A,B). Flvonoid-medited plsm lipid lowering ws onfined to VLDL nd LDL with no hnge in HDL holesterol levels (Figure 5C-H). Greter VLDL- nd LDL-holesterol redutions were oserved with how intervention (Figure 5F,G). Flvonoid Intervention Does Not Eliit Atherosleroti Lesion Contrtion. 18
19 Due to the signifint improvement in therosleroti risk ftors, we sought to determine the impt of flvonoid intervention on theroslerosis regression. Aorti sinus lesions were ssessed fter HFHC indution (seline) nd following flvonoid or how intervention (Figure 6A). While intervention with how did not indue regression of orti sinus lesions, their growth in size ws signifintly ttenuted. Intervention with either itrus flvonoid to the HFHC diet did not ffet lesion size; the re of sinus lesions ontinued to inrese t the sme rte s in mie fed the HFHC diet lone for 24 weeks (Figure 6A). Lipid mesurements in whole orte, disseted free from ft, reveled tht the ort of HFHC-fed mie ontinued to umulte free holesterol nd holesteryl ester (~4-fold) ompred to seline (Figure 6B). The ddition of either flvonoid t intervention slowed, ut did not hlt, the umultion of orti free or esterified holesterol (Figure 6B). Chow intervention prevented further inreses from seline in orti holesterol ontent. The orti mrna expression of the inflmmtory genes Cl3, Tnf nd Emr1 inresed from seline with ontinued HFHC, whih ws not offset y flvonoid intervention (Figure 6C). Aorti mrna of Il1 nd Cl2 were not different from seline in mie ontinued on HFHC or with flvonoid intervention. Chow intervention tended to hlt or reverse orti mrna expression of ll inflmmtory mrkers exmined (Figure 6C). Additionlly, intervention with either flvonoid did not inrese the expression of genes linked to regression nd how intervention tully deresed the mrna expression of Cr7, A1, nd Ag1 (Figure 6C). Flvonoid Intervention Redues Plque Mrophges. Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Although there ws no hnge in the plque size with flvonoid intervention, the derese in orti holesterol suggested tht lesion omposition my hve een fvorly ltered (Figure 6A,B). After 12 weeks indution, plques were omprised minly of mrophges (~66%) (Figure 7A,H). Lesion mrophge ontent ws redued with intervention y nringenin (-47%), noiletin (-5%) nd how (- 69%) (Figure 7A,H), onsistent with the onept tht depletion of mrophges is hrteristi of regressing plque (21). Although the perent of lesion re oupied y mrophges ws lso less in mie ontinuing on HFHC (-23%), the derese ws greter with flvonoid or how intervention (Figure 7A,H). Compred to lesions t seline, ontinution on the HFHC diet enlrged neroti ore re (from 6 to 19
20 14%), inresed the perent of poptoti ells (from.2 to 1.%), redued lesion smooth musle ells (SMCs) (from 3.5% to 1.8%) nd inresed lesion ollgen (from 2 to 35%) (Figure 7B-F, Supplementry Figure S5). Intervention with either nringenin, noiletin or how hlted the inrese in neroti ore size, inhiited the inrese in poptosis, ttenuted the derese in SMCs nd mintined the inrese in lesion ollgen (Figure 7B-F, Supplementry Figure S5). Colletively, these interventionindued hnges in lesion omposition re hrteristi of more stle lesions (Figure 7G). Flvonoid Intervention Prevents Enhned Monoytosis. Redued plque mrophge ontent is phenotypilly ssoited with theroslerosis regression (21, 32-34). Redued monoyte reruitment from the irultion hs een implited s mehnism ontriuting to regression (29). In this study, ontinution of the HFHC diet inresed the numer of irulting Ly6C hi monoytes (2-fold) (Figure 8A), the monoyte suset known to e the preursor of lesion M1 nd M2 mrophges (35). Intervention with how or noiletin ompletely prevented the inrese in Ly6C hi monoytes, while with nringenin intervention, there ws trend to ttenution of the HFHC-indued elevtion in Ly6C hi monoytes (Figure 8A). There ws no effet on irulting Ly6C lo monoytes or totl neutrophil levels with ontinution of the HFHC diet or with ny intervention (Figure 8B,D). To investigte this trend further, one mrrow progenitor popultions were mesured (Supplementry Figure S6). Intervention with how redued one mrrow hemtopoieti stem nd progenitor ell popultions, wheres the modest redutions with flvonoid intervention were not signifint (Supplementry Figure S6A,C). Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 A similr trend persisted when looking t one mrrow myeloid progenitor ells (Supplementry Figure S6B,C), ommon myeloid progenitor ells (Supplementry Figure S6D,G) nd grnuloyte mrophge progenitor ells (Supplementry Figure S6E,G). There ws no onsistent effet of ny tretment group on megkryoyte nd erythroyte progenitor ells (Supplementry Figure S6F,G). 2
21 DISCUSSION In the present study, we showed tht intervention with the itrus-derived flvonoids, nringenin or noiletin, when supplemented to HFHC diet, reversed diet-indued oesity, insulin resistne, improved hyperlipidemi nd hepti stetosis, nd fvorly ltered orti sinus therosleroti plque omposition. Flvonoid intervention enhned energy expenditure, despite promoting modest inrese in food onsumption during the tive time nd while mintining similr multory tivity. In the liver, ftty id oxidtion ws inresed s were Cpt1 nd Pg1 expressions, suggesting enhned ft moiliztion. In white dipose tissue, there were no onsistent effets on rowning genes in viserl or suutneous depots nd no enhnement of rowning genes in rown dipose tissue, suggesting non-rowning mehnism of enhned energy expenditure nd redued diposity. Although therosleroti lesion size ws unffeted, the improvements in metoli prmeters with flvonoid intervention orrelted with redution in irulting monoytes nd redued mrophge ontent in estlished therosleroti lesions, hrteristis onsistent with theroslerosis regression (22). Chnges in food onsumption n result from the effets of dietry omponents or drugs on ehvior, stiety or energy lne, whih in turn lter metoli regultion, inluding dipose tissue metolism (3). Consistent with previously reported prevention studies, ddition of flvonoids to the HFHC diet did not derese lori intke s mesured in stndrd ging (13-16). Studies from other lortories hve reported redued lori intke in high ft-fed mie with nringenin intervention, leding Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 to deresed ody weight nd diposity (36), n effet likely ttriuted to tste version to the ompound when dministered in the food. In the present study, tste version ws mitigted y strting intervention t low flvonoid dose, whih ws slowly inresed to the finl dose over the first week of intervention. Thus, food intke did not drop preipitously, whih would in itself use weight loss. In metoli ge studies, we unexpetedly identified smll (~.5 grms/dy) ut signifint inrese in lori onsumption during the drk yle in oth nringenin nd noiletin treted mie, t weeks 21-23, ner the end of the intervention. Despite this smll inrese, intervention with oth flvonoids indued weight loss, deresed diposity nd improved metoli indies, implying the moleulr mehnism for the flvonoid effets ws 21
22 not relted to suppressed food intke (3). The resons underlying the flvonoid-indued inrese in lori intke during the drk yle is not well understood, ut my e relted to mild strvtion response resulting from inresed energy expenditure. Pir-feeding experiments would help to onfirm nd further understnd this oservtion. Nringenin intervention hs previously een studied in ovretomised femle C57BL/6J mie to ssess its impt on post-menopusl metoli dysfuntion (36, 37). In how-fed ovretomised mie t norml ody weight, intervention y the ddition of nringenin to how prevented weight gin while promoting modest weight loss, redued diposity nd improved gluose homeostsis, ompnied y redution in lori intke (36). When the sme ovretomised mie were fed high-ft diet, intervention with the ddition of nringenin to the high-ft diet prevented further weight gin nd diposity, while inresing multory tivity, with no hnge in energy expenditure (37). In our mle Ldlr -/- mie fed high-ft diet, intervention with either flvonoid lso deresed ody weight nd diposity, ut ws due to n inrese in weight-normlized energy expenditure, with no hnge in multory tivity nd despite smll inrese in lori intke. Amultory tivity ws lower in treted post-menopusl mie ompred to our flvonoid-intervention Ldlr -/- mie, whih might e ttriuted to post-menopusl sropeni. It is possile tht the disrepny in tivity results ould e due to differenes in ge nd sex of the two models. The lk of effet of flvonoid intervention on tivity is onsistent with our previous prevention studies in high-ft fed Ldlr -/- mie treted with oth nringenin nd noiletin (15, 16). Experiments in ge-mthed Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 femle Ldlr -/- mie would help further understnd this oservtion. Hyperholesterolemi, hyperglyemi, oesity, nd more speifilly dipose tissue inflmmtion re ll independent risk ftors for leukoytosis, whih n ontriute to elerted theroslerosis (32, 38, 39). In the present study, intervention with either nringenin or noiletin redued therosleroti lesion mrophge ontent, onsistent with plque regression. Redued monoyte reruitment to therosleroti plques is hrteristi of theroslerosis regression (21, 34). While trffiking kinetis to determine the ontriution of monoyte reruitment to the redued lesion mrophge ontent were not performed, leukoyte levels in the irultion were quntitted. Intervention with nringenin or noiletin prevented ny 22
23 further inrese in irulting Ly6C hi monoytes, known to e the preursor of lesion mrophges (35). We lso showed tht intervention with how indued more notle, ut not signifint, redution from seline in lood Ly6C hi monoytes ompred to flvonoid intervention, ut this did not trnslte into redution in irulting totl monoytes. This how-lone intervention effet is onsistent with previous regression studies in high ft-fed Ldlr -/- mie (32), ut not studies in high ft-fed Ldlr -/- mie in whih the how intervention ws oupled to hepti Mttp deletion, whih resulted in more rpid regression nd lrge redution in irulting monoytes (33). It is possile tht interventions with dietry flvonoids plus HFHC or how-lone were not strong enough or long enough in durtion to hieve lrger signifint redutions in irulting monoytes (32, 33). In ddition, neither flvonoid nor how intervention ompletely orreted hyperholesterolemi therey restriting more roust redution in myelopoiesis (38). Furthermore, we used Ldlr -/- mie, whih develop more modest monoytosis ompred to Apoe -/- mie in response to high ft diet, whih would mke the effets of nringenin or noiletin intervention more sutle, espeilly onsidering the inomplete orretion of metoli dysfuntion (29). The mehnism(s) through whih either nringenin or noiletin regultes energy expenditure, lipid metolism nd insulin sensitivity re not ompletely understood. Previous in vitro studies demonstrted tht oth nringenin nd noiletin tivte insulin signling independent of the insulin reeptor or insulin reeptor sustrte (16, 4). Additionlly, in high-ft fed Ldlr -/- mie, oth nringenin nd noiletin upregulted Pg1- nd Cpt1-medited hepti ftty id oxidtion, independent of peroxisoml Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 prolifertion, nd suppressed Srep1-medited ftty id synthesis (15, 16). The upstrem mehnism(s) governing these effets hve remined somewht elusive. The hormone-like firolst growth ftor 21 eliits similr metoli improvements s nringenin when given exogenously to mie, ut nringenin prevented metoli dysfuntion nd oesity in high ft-fed Fgf21 -/- mie to the sme extent s in wild type mie (13). In short-term tretment of O/O mie, nringenin supplementtion to low ft diet reversed hyperlipidemi, ttenuted ody weight nd improved hepti stetosis nd insulin sensitivity, inditing tht the nringenin effet ws independent of leptin-defiieny (13). This suggests tht unlike other nturl ompounds, elstrol nd withferin A, nringenin does not work through enhning leptin sensitivity (41, 23
24 42). Alterntively, elstrol hs lso een shown to prevent weight gin nd improve metoli dysfuntion through tivtion of the het shok ftor 1-PGC1 xis in dipose tissue nd musle, ut not liver (43), more similr to, ut not identil to, the hepti effets of nringenin or noiletin. Reent studies reveled tht the ddition of nringenin plus pigenin ( relted flvonoid) to highft diet, prevented the exerted reound in ody weight in mie, when re-hllenged with high-ft diet following period of how-indued weight loss (44). Celstrol or leptin-sensitizing ntgonist did not mitigte weight reound. Flvonoid tretment repled the persistent high ft diet-indued loss of miroiome-derived flvonoid vilility, resulting in inresed energy expenditure nd upregultion of Up1 expression in rown dipose tissue (44). In prevention models, we hve shown tht nringenin modestly inreses Up1 expression in inguinl white dipose tissue (13), ut in the present study we sw no effet with either nringenin or noiletin on inguinl or rown dipose tissue Up1 expression. Additionlly, we reported no hnge with noiletin tretment on non-shivering thermogenesis, however experiments were not onduted t thermoneutrlity (16). This suggests tht flvonoid-medited enhned rowning my not e the mehnism through whih itrus flvonoids exert their nti-oesity effets. It is possile tht the rowning effet of flvonoids in the weight yling mouse model ws pigenin speifi. Noiletin, ut not nringenin, hs een shown to enhne the mplitude of irdin rhythms, speifilly in oese mie (45). In our previous studies, we hve not oserved ny differenes in the effets of either nringenin or noiletin tretment side from poteny. Noiletin is ~1-times more potent thn nringenin, Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 whih is refleted in its lower effetive dose (.3% vs 3% of diet) (15, 16). It is possile tht nringenin my lso enhne lok sensitivity nd tht differenes in dosing nd dministrtion my e responsile for the disrepny in results etween nringenin nd noiletin (15, 45). In the present study, we tested one protool of indution nd intervention times, 12 weeks indution with HFHC diet followed y 12 weeks intervention with either itrus flvonoid supplemented to the HFHC diet. These timelines were hosen sed on theroslerosis regression models in the literture nd re similr to other dietry flvonoid-intervention timelines (21, 36, 37). Twelve weeks of HFHC indution 24
25 ws suffiient time to indue moderte oesity, signifint hyperlipidemi, moderte insulin resistne, hepti stetosis nd intermedite theroslerosis. Twelve weeks intervention ws suffiient to ompletely improve oesity nd insulin resistne, ut moderte hyperlipidemi nd hepti stetosis persisted, resulting in improvements in lesion morphology ut no regression of plque size. This rises the intriguing possiility tht longer durtion of flvonoid intervention would result in greter resolution of these disorders. It would e of interest to test different intervention durtions nd potentilly longer indution periods to test the limits of flvonoid intervention on the resolution of diet-indued oesity, metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis. A numer of humn studies using purified itrus flvonoids hve demonstrted improvements in plsm lipids, gluose metolism nd oesity (reviewed in (11)). However, results were modest nd inonsistenies etween studies, nd onsiderle inter-ptient vrition were oserved. Biovilility of flvonoids is low, espeilly in humns, metolism of flvonoids differs etween sujets, nd differenes in the enteri miroflor my e responsile for onsiderle inter-individul vriility in sorption nd phrmokineti prmeters (11). Lrger ontrolled humn studies re required to ssess dose, iovilility, effiy nd sfety for therpeuti development. In summry, we hve shown tht intervention y the ddition of either of the itrus flvonoids, nringenin or noiletin, to high-ft diet in oese mie, reverses weight gin nd diposity similr to intervention with how, without reduing food intke. Mie treted with nringenin or noiletin onsume Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 more lories, ut expend more energy without inresed multory tivity. Flvonoid-treted mie regin insulin sensitivity nd reverse hyperinsulinemi ompletely. Plsm lipids re deresed nd hepti ftty id oxidtion is inresed resulting in redued hepti lipids. Colletively these improvements in therogeni risk ftors did not result in lesion ontrtion ut improved lesion morphology, most notly redued lesion mrophge ontent, onsistent with erly stges of theroslerosis regression. These studies highlight the potentil therpeuti utility of either nringenin or noiletin, espeilly in the ontext of existing oesity nd metoli dysfuntion. 25
26 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work ws supported y grnts from the Cndin Institutes of Helth Reserh (MOP-12645) nd the Hert nd Stroke Foundtion of Cnd (G ) to MWH. ACB ws supported y Cndin Dietes Assoition Dotorl Reserh Grnt (DS AB). The uthors would like to thnk Kristin Chdwik (London Regionl Flow Cytometry Fility) nd Cory Fink (Rorts Reserh Institute) for ssistne in designing flow ytometry stining pnels nd tehnil ssistne, Juli St. John for tehnil ssistne in flow ytometry experiments, Roert Gros (Rorts Reserh Institute) for use of metoli ges, nd Dr. Joseph Umoh nd Joy Dunmore-Buyze for miro- CT imging of mie. Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
27 REFERENCES 1. Hmilton, M. T., D. G. Hmilton, nd T. W. Zderi. 27. Role of low energy expenditure nd sitting in oesity, metoli syndrome, type 2 dietes, nd rdiovsulr disese. Dietes. 56: Olshnsky, S. J., D. J. Pssro, R. C. Hershow, J. Lyden, B. A. Crnes, J. Brody, L. Hyflik, R. N. Butler, D. B. Allison, nd D. S. Ludwig. 25. A potentil deline in life expetny in the United Sttes in the 21st entury. N. Engl. J. Med. 352: Sltiel, A. R New therpeuti pprohes for the tretment of oesity. Si. Trnsl. Med. 8: 323rv Rodgers, R. J., M. H. Tshop, nd J. P. Wilding Anti-oesity drugs: pst, present nd future. Dis. Model Meh. 5: Heymsfield, S. B., nd T. A. Wdden Mehnisms, Pthophysiology, nd Mngement of Oesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 376: Kher, R., M. H. Murd, A. K. Chndr, P. S. Duli, Z. Wng, L. J. Prokop, R. Loom, M. Cmilleri, nd S. Singh Assoition of Phrmologil Tretments for Oesity With Weight Loss nd Adverse Events: A Systemti Review nd Met-nlysis. JAMA. 315: Adms, T. D., L. E. Dvidson, S. E. Litwin, J. Kim, R. L. Kolotkin, M. N. Nnjee, J. M. Gutierrez, S. J. Frogley, A. R. Iele, E. A. Brinton, P. N. Hopkins, R. MKinly, S. C. Simper, nd S. C. Hunt Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Weight nd Metoli Outomes 12 Yers fter Gstri Bypss. N. Engl. J. Med. 377: Nguyen, N. T., nd J. E. Vrel Britri surgery for oesity nd metoli disorders: stte of the rt. Nt. Rev. Gstroenterol. Heptol. 14: Ekel, R. H., S. M. Grundy, nd P. Z. Zimmet. 25. The metoli syndrome. Lnet. 365: Wilson, P. W., R. B. D'Agostino, L. Sullivn, H. Prise, nd W. B. Knnel. 22. Overweight nd oesity s determinnts of rdiovsulr risk: the Frminghm experiene. Arh. Intern Med. 162:
28 11. Mulvihill, E. E., A. C. Burke, nd M. W. Huff Citrus Flvonoids s Regultors of Lipoprotein Metolism nd Atheroslerosis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 36: Amiot, M. J., C. Riv, nd A. Vinet Effets of dietry polyphenols on metoli syndrome fetures in humns: systemti review. Oes. Rev. 17: Assini, J. M., E. E. Mulvihill, A. C. Burke, B. G. Sutherlnd, D. E. Telford, S. S. Chhoker, C. G. Swyez, M. Drngov, A. C. Adms, A. Khritonenkov, C. L. Pin, nd M. W. Huff Nringenin prevents oesity, hepti stetosis, nd gluose intolerne in mle mie independent of firolst growth ftor 21. Endorinology. 156: Assini, J. M., E. E. Mulvihill, B. G. Sutherlnd, D. E. Telford, C. G. Swyez, S. L. Felder, S. Chhoker, J. Y. Edwrds, R. Gros, nd M. W. Huff Nringenin prevents holesterol-indued systemi inflmmtion, metoli dysregultion, nd theroslerosis in Ldlr-/- mie. J. Lipid Res. 54: Mulvihill, E. E., E. M. Allister, B. G. Sutherlnd, D. E. Telford, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, J. M. Mrkle, R. A. Hegele, nd M. W. Huff. 29. Nringenin prevents dyslipidemi, polipoprotein B overprodution, nd hyperinsulinemi in LDL reeptor-null mie with diet-indued insulin resistne. Dietes. 58: Mulvihill, E. E., J. M. Assini, J. K. Lee, E. M. Allister, B. G. Sutherlnd, J. B. Koppes, C. G. Swyez, J. Y. Edwrds, D. E. Telford, A. Chronneu, P. St-Pierre, A. Mrette, nd M. W. Huff Noiletin ttenutes VLDL overprodution, dyslipidemi, nd theroslerosis in mie with diet-indued Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 insulin resistne. Dietes. 6: Mulvihill, E. E., J. M. Assini, B. G. Sutherlnd, A. S. DiMtti, M. Khmi, J. B. Koppes, C. G. Swyez, S. C. Whitmn, nd M. W. Huff. 21. Nringenin dereses progression of theroslerosis y improving dyslipidemi in high-ft-fed low-density lipoprotein reeptor-null mie. Arteriosler. Throm. Vs. Biol. 3: Borrdile, N. M., L. E. de Dreu, nd M. W. Huff. 23. Inhiition of net HepG2 ell polipoprotein B seretion y the itrus flvonoid nringenin involves tivtion of phosphtidylinositol 3-kinse, independent of insulin reeptor sustrte-1 phosphoryltion. Dietes. 52:
29 19. Whitmn, S. C., E. M. Kurowsk, J. A. Mnthey, nd A. Dugherty. 25. Noiletin, itrus flvonoid isolted from tngerines, seletively inhiits lss A svenger reeptor-medited metolism of etylted LDL y mouse mrophges. Atheroslerosis. 178: Lin, N., T. Sto, Y. Tkym, Y. Mimki, Y. Sshid, M. Yno, nd A. Ito. 23. Novel ntiinflmmtory tions of noiletin, itrus polymethoxy flvonoid, on humn synovil firolsts nd mouse mrophges. Biohem. Phrmol. 65: Burke, A. C., nd M. W. Huff Regression of theroslerosis: lessons lerned from genetilly modified mouse models. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 29: Bsu, D., Y. Hu, L. A. Huggins, A. E. Mullik, M. J. Grhm, T. Wieteh, S. Brnhrt, A. Mogul, K. Pfeiffer, A. Zirlik, E. A. Fisher, K. E. Bornfeldt, F. Willeke, nd I. J. Golderg Novel Reversile Model of Atheroslerosis nd Regression Using Oligonuleotide Regultion of the LDL Reeptor. Cir. Res. 122: Grnton, P. V., C. J. Norley, J. Umoh, E. A. Turley, B. C. Frier, E. G. Nole, nd D. W. Holdsworth. 21. Rpid in vivo whole ody omposition of rts using one em muct. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 19: Luu, Y. K., S. Lulinsky, E. Ozivii, E. Cpill, J. E. Pessin, C. T. Ruin, nd S. Judex. 29. In vivo quntifition of suutneous nd viserl diposity y miro-omputed tomogrphy in smll niml model. Med. Eng. Phys. 31: Downloded from y guest, on August 19, Folh, J., M. Lees, nd G. H. Slone Stnley A simple method for the isoltion nd purifition of totl lipides from niml tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226: Murkmi, N., T. Ohtsuo, Y. Knsui, K. Goto, H. Noguhi, Y. Hg, Y. Nkeppu, K. Mtsumur, nd T. Kitzono Mie heterozygous for the xnthine oxidoredutse gene filitte lipid umultion in dipoytes. Arteriosler. Throm. Vs. Biol. 34: Huss, J. M., I. P. Torr, B. Stels, V. Giguere, nd D. P. Kelly. 24. Estrogen-relted reeptor lph direts peroxisome prolifertor-tivted reeptor lph signling in the trnsriptionl ontrol of energy metolism in rdi nd skeletl musle. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24:
30 28. Boji, L. A., A. C. Burke, S. S. Chhoker, D. E. Telford, B. G. Sutherlnd, J. Y. Edwrds, C. G. Swyez, R. G. Tiron, H. Yin, J. G. Pikering, nd M. W. Huff Peroxisome prolifertor-tivted reeptor delt gonist GW1516 ttenutes diet-indued orti inflmmtion, insulin resistne, nd theroslerosis in low-density lipoprotein reeptor knokout mie. Arteriosler. Throm. Vs. Biol. 34: Murphy, A. J., M. Akhtri, S. Tolni, T. Pgler, N. Bijl, C. L. Kuo, M. Wng, M. Snson, S. Armowiz, C. Welh, A. E. Bohem, J. A. Kuivenhoven, L. Yvn-Chrvet, nd A. R. Tll ApoE regultes hemtopoieti stem ell prolifertion, monoytosis, nd monoyte umultion in therosleroti lesions in mie. J. Clin. Invest. 121: Ellott, K. L., G. J. Morton, S. C. Woods, P. Tso, nd M. W. Shwrtz. 21. Assessment of feeding ehvior in lortory mie. Cell Met. 12: Kim, J. K., J. J. Fillmore, M. J. Sunshine, B. Alreht, T. Higshimori, D. W. Kim, Z. X. Liu, T. J. Soos, G. W. Cline, W. R. O'Brien, D. R. Littmn, nd G. I. Shulmn. 24. PKC-thet knokout mie re proteted from ft-indued insulin resistne. J. Clin. Invest. 114: Ngreddy, P. R., A. J. Murphy, R. A. Stirzker, Y. Hu, S. Yu, R. G. Miller, B. Rmkhelwon, E. Distel, M. Westerterp, L. S. Hung, A. M. Shmidt, T. J. Orhrd, E. A. Fisher, A. R. Tll, nd I. J. Golderg Hyperglyemi promotes myelopoiesis nd impirs the resolution of theroslerosis. Cell Met. 17: Downloded from y guest, on August 19, Distel, E., T. J. Brrett, K. Chung, N. M. Girgis, S. Prthth, C. C. Essu, A. J. Murphy, K. J. Moore, nd E. A. Fisher mir33 inhiition overomes deleterious effets of dietes mellitus on theroslerosis plque regression in mie. Cir. Res. 115: Potteux, S., E. L. Gutier, S. B. Huthison, N. vn Rooijen, D. J. Rder, M. J. Thoms, M. G. Sori-Thoms, nd G. J. Rndolph Suppressed monoyte reruitment drives mrophge removl from therosleroti plques of Apoe-/- mie during disese regression. J. Clin. Invest. 121:
31 35. Rhmn, K., Y. Vengrenyuk, S. A. Rmsey, N. R. Vil, N. M. Girgis, J. Liu, V. Gusrov, J. Gromd, A. Weinstok, K. J. Moore, P. Loke, nd E. A. Fisher Inflmmtory Ly6Chi monoytes nd their onversion to M2 mrophges drive theroslerosis regression. J. Clin. Invest. 127: Ke, J. Y., K. L. Kliewer, E. M. Hmd, R. M. Cole, K. A. Powell, R. R. Andridge, S. R. Strk, L. D. Yee, nd M. A. Belury The flvonoid, nringenin, dereses dipose tissue mss nd ttenutes ovrietomy-ssoited metoli disturnes in mie. Nutr. Met. 12: Ke, J. Y., R. M. Cole, E. M. Hmd, Y. H. Hsio, B. M. Cotten, K. A. Powell, nd M. A. Belury Citrus flvonoid, nringenin, inreses loomotor tivity nd redues diylglyerol umultion in skeletl musle of oese ovrietomized mie. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 6: Tolni, S., T. A. Pgler, A. J. Murphy, A. E. Bohem, S. Armowiz, C. Welh, P. R. Ngreddy, S. Hollern, G. K. Hovingh, J. A. Kuivenhoven, nd A. R. Tll Hyperholesterolemi nd redued HDL-C promote hemtopoieti stem ell prolifertion nd monoytosis: studies in mie nd FH hildren. Atheroslerosis. 229: Ngreddy, P. R., M. Krkmn, S. L. Msters, R. A. Stirzker, D. J. Gormn, R. W. Grnt, D. Drgoljevi, E. S. Hong, A. Adel-Ltif, S. S. Smyth, S. H. Choi, J. Korner, K. E. Bornfeldt, E. A. Fisher, V. D. Dixit, A. R. Tll, I. J. Golderg, nd A. J. Murphy Adipose tissue mrophges promote myelopoiesis nd monoytosis in oesity. Cell Met. 19: Allister, E. M., E. E. Mulvihill, P. H. Brrett, J. Y. Edwrds, L. P. Crter, nd M. W. Huff. 28. Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Inhiition of pob seretion from HepG2 ells y insulin is mplified y nringenin, independent of the insulin reeptor. J. Lipid Res. 49: Lee, J., J. Liu, X. Feng, M. A. Slzr Hernndez, P. Muk, D. Ii, J. W. Choi, nd U. Ozn Withferin A is leptin sensitizer with strong ntidieti properties in mie. Nt. Med. 22: Liu, J., J. Lee, M. A. Slzr Hernndez, R. Mzitshek, nd U. Ozn Tretment of oesity with elstrol. Cell. 161:
32 43. M, X., L. Xu, A. T. Aleroello, O. Gvrilov, A. Bgttin, M. Skrulis, J. Liu, T. Finkel, nd E. Mueller Celstrol Protets ginst Oesity nd Metoli Dysfuntion through Ativtion of HSF1-PGC1lph Trnsriptionl Axis. Cell Met. 22: Thiss, C. A., S. Itv, D. Rothshild, M. Meijer, M. Levy, C. Moresi, L. Dohnlov, S. Brvermn, S. Rozin, S. Mlitsky, M. Dori-Bhsh, Y. Kupermn, I. Biton, A. Gertler, A. Hrmelin, H. Shpiro, Z. Hlpern, A. Ahroni, E. Segl, nd E. Elinv Persistent miroiome ltertions modulte the rte of post-dieting weight regin. Nture. 54: He, B., K. Nohr, N. Prk, Y. S. Prk, B. Guillory, Z. Zho, J. M. Gri, N. Koike, C. C. Lee, J. S. Tkhshi, S. H. Yoo, nd Z. Chen The Smll Moleule Noiletin Trgets the Moleulr Osilltor to Enhne Cirdin Rhythms nd Protet ginst Metoli Syndrome. Cell Met. 23: Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
33 FIGURES A Noiletin Nringenin Ldlr -/- Chow 12 Chow 24 HFHC à HFHC HFHC HFHC B Body Weight (g) E Viserl Ft Volume (m 3 ) G Reltive Frequeny (%) Weeks Chow Weeks d de e C Kl/mouse/dy 18 N.S Suutneous Ft Volume (m 3 ) Adipoyte Are (µm 2 ) Adipoyte Are (µm 2 ) Weeks Weeks d d de e D Epididyml Ft/BW F Len Tissue Volume (m 3 ) 12 Weeks (Bseline) Bseline à Chow Weeks 24 Weeks N.S 24 Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Figure 1. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Promotes Weight Loss nd Dereses Adiposity. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. A; Struture of nringenin nd noiletin, nd study design. B; Body weight mesured weekly following intervention fter indution (n=6-1/group). C; 33
34 Clori intke mesured weekly during intervention (n=6-1/group). D; Adiposity ssessed s epididyml ft pd weight/totl ody weight (n=6-1/group). E; Viserl nd suutneous ft volume ssessed y Miro-CT (n=6/group). F; Len tissue volume ssessed y Miro-CT (n=6/group). G; Frequeny distriution of dipoyte re in mie t the end of intervention (n=6/group). Inset shows men dipoyte re. Representtive imges of epididyml white dipose tissue stined with H&E. Sle r is 1 µm. Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y two-wy ANOVA with postho Tukey test (B,C,E,F) nd one-wy ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (D,G) (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
35 A ANCOVA-Adjusted Energy Expenditure (kl/h) B RER C Aumulted Food Intke (kl) D Ativity Counts/hr : : : 11: 7: 11: Light 11: 15: 19: Drk Time (24 Hrs) Light 11: 15: 19: 23: 3: 7: Drk Time (24 Hrs) Light Light 15: 19: 15: 19: 23: 3: 7: Drk Time (24 Hrs) Drk Time (24 Hrs) 23: 3: 7: 23: 3: 7: ANCOVA-Adjusted Men Energy Expenditure (kl/h) Men RER Food Intke (kl/dy) Men Ativity Counts/hr Light Drk Light * * * Drk * * * N.S Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Figure 2. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Inreses Energy Expenditure. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. Between weeks 8-12 of intervention, mie were ssessed in metoli ges. A; ANCOVA-djusted energy expenditure (kl/h) over 24 hours nd men ANCOVA-djusted energy expenditure in oth the drk nd light periods (n=6-8/group). B; Respirtory exhnge rtio (RER) over 24 hours nd men RER in oth the drk nd light periods (n=6-8/group). C; Aumulted food intke over 24 hours nd totl food eten during 24 hours (n=6-8/group). D; Amultory tivity over 24 hours nd men multory tivity per hour (n=6-8/group). Dt represent the men±sem. Different 35
36 letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. * indites sttistil signifint y Student s t-test (P<.5). Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
37 A Plsm Insulin (ng/ml) E G I Blood Gluose (mmol/l) Blood Gluose (mmol/l) Blood Gluose (mmol/l) K Triglyerides (mg/g tissue) Bseline ITT - Bseline Time (min) AUC Time (min) Qudrieps TG ITT - Tretment GTT - Bseline Bseline AUC Time (min) % Chnge in Gluose % Chnge in Gluose Blood Gluose (mmol/l) Time (min) Time (min) GTT - Tretment N.S AUC B Blood Gluose (mmol/l) L Triglyerides (mg/g tissue) Bseline Gstronemius TG F N.S H J C Blood Gluose (mmol/l) Bseline Weeks ITT - Bseline ITT - Tretment AUC AUC AUC Time (min) D HOMA-IR N.S N.S Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Figure 3. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Restores Gluose Homeostsis. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. A; Fsting (6 h) plsm insulin levels (n=17-2/group). B; Fsting (6 h) lood gluose (n=1-32/group). C; Fsting (6 h) lood gluose in the sme mie t seline nd 6 weeks 37
38 nd 12 weeks of intervention (n=11/group). D; Homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistne (HOMA-IR) (n=7-12/group). E,F; Insulin tolerne test t seline shown s lood gluose onentrtions (n=4-6/group) (E) nd % hnge in gluose from time= (n=6-9/group) (F). G,H; Insulin tolerne test t 12 weeks intervention shown s lood gluose onentrtions (n=5-6/group) (G) nd % hnge in gluose from time= (n=22-24/group) (H). I; Gluose tolerne test t seline (n=6-9/group). J; Gluose tolerne test t 12 weeks intervention (n=1-11/group). K,L; Musle triglyeride ontent in qudrieps (n=8/group) (K) nd gstronemii nd solei (n=7-8/group) (L). Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
39 A Triglyerides (mg/g tissue) C Free Cholesterol (mg/g tissue) E Gene of Interest/Gpdh (Fold Chnge of Bseline) F Liver Weight (g) B D Cpt1 Pg1 Sref1 d Bseline Bseline Bseline Cholesteryl Ester (mg/g tissue) Plmitte Oxidized (pmol/min/mg tissue) (Fold Chnge) Bseline Bseline Bseline Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Figure 4. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Inreses Hepti Ftty Aid Oxidtion nd Redues Liver Stetosis. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. A; Hepti triglyerides (n=7-8/group). B; Hepti holesteryl ester (n=7-8/group). C; Hepti free holesterol (n=7-8/group). D; Ex vivo hepti ftty id oxidtion (n=7-1/group). E; Hepti gene expression (n=12/group). F; Liver weight (n=22/group). Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). 39
40 A Plsm Triglyerides (mmol/l) C Plsm Triglyerides (μg/ml) E Plsm Cholesterol (μg/ml) G AUC Frtion d B D AUC 4 AUC Frtion LDL-C d Bseline Bseline Bseline Bseline Plsm Cholesterol (mmol/l) F H AUC Bseline d Bseline Bseline VLDL-TG VLDL-C 15 HDL-C N.S. d e d Bseline Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 Figure 5. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Lowers Plsm Lipids from Bseline. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. Mie were fsted for 6 hours prior to srifie. Plsm ws sujeted to fst protein liquid hromtogrphy (FPLC) nd lipids were mesured in eh frtion y enzymti ssy. A; Plsm triglyerides (n=19-24/group). B; Plsm holesterol (n=21-24/group). C; Plsm triglyeride FPLC tring (n=6-7/group). D; Plsm VLDL triglyeride AUC lultions (n=6-7/group). E; Plsm holesterol FPLC tring (n=6-7/group) F; Plsm VLDL holesterol AUC lultions (n=6-7/group). 4
41 G; Plsm LDL holesterol AUC lultions (n=6-7/group). H; Plsm HDL holesterol AUC lultions (n=6-7/group. Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. Downloded from y guest, on August 19,
42 Figure 6 Lesion Are (um2 X 16) Bseline 1.5 B Cl Tnf Emr TC Il1 FC Bseline CE N.S Cl2.5 Cr7 1 4 N.S A1 Ag1 Figure 6. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids does not Attenute Lesion Size ut Slows Aorti Cholesterol Aumultion. Ldlr-/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. Aorte were disseted nd the orti sinus setioned nd nlyzed histologilly. A; Representtive setions of the orti sinus stined with oil red-o nd hemtoxylin nd lesion re quntittion (n=12-21/group). Sle r is 5µm. B; Totl holesterol, holesteryl ester nd free holesterol in whole orte (n=6-8/group). C; Gene expression in whole orte (n=6-8/group). Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. 42 Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 r e 24 ow lin +N No + Ch HC se C C F à H H B H HF HF à à C Gene of Interset/Gpdh (Fold Chnge of Bseline) Aorti Cholesterol (mg/g tissue) A
43 A % Lesion Mrophges (CD68+) % Lesion Collgen (PSR) CD d Bseline % Neroti Lesion Are Men Collgen Firil Retrdtion (nm) Bseline Figure 7. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Improves Lesion Morphology. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. Aorte were disseted nd the orti sinus setioned nd nlyzed histologilly. A; Perent of lesion re oupied y CD68+ mrophges (n=14-22/group). B; Perent of % Ativted Cspse-3 Are E F G H Bseline B Bseline C Plque Component (%) N.S Bseline D Bseline % Lesion SMC (SMC α-tin+) Mrophges Collgen Smooth Musle Cells Bseline Bseline Neroti Core Unknown Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 lesion re oupied y the neroti ore (n=14-17). C; Perent of lesion positive for tivted pse-3 (n=9-2/group). D; Perent of lesion re oupied y smooth musle ells (SMC α-tin) (n=12-23/group). E; Perent of lesion re oupied y ollgen (pirosirius red) (n=12-19/group). F; Collgen orgniztion mesured s men ollgen firil retrdtion (n=12-19/group). G; Lesion omposition for eh dietry group. H; Representtive histologil setions of the orti sinus stined with CD68 (mrophges) nd ounterstined with hemtoxylin. Sle r is 5µm. Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. 43
44 A Ly6C hi Monoytes (%CD45+ Cells) CD115 APC Bseline Ly6C lo Monoytes (%CD45+ Cells) B Figure 8. Intervention with Citrus Flvonoids Prevents Further Elevtion in Blood Monoytes. Ldlr -/- mie were fed HFHC diet for 12 weeks. Susequently the sme mie were treted with flvonoids dded to the HFHC diet for n dditionl 12 weeks. Peripherl lood mononuler ells (PBMCs) were isolted nd stined for monoyte nd neutrophil mrkers. A; Perent PBMCs tht were Ly6C hi N.S Bseline monoytes (n=9-1/group). B; Perent of PBMCs tht were Ly6C lo monoytes (n=9-1/group). C; Perent of PBMCs tht were oth Ly6C hi nd Ly6C lo monoytes. D; Perent of PBMCs tht were neutrophils. E; Representtive flow ytometri pseudoolor plots show monoytes nd neutrophil popultions from eh dietry group. Dt represent the men±sem. Different letters re sttistilly C Totl Monoytes (%CD45+ Cells) Ly-6G/Ly-6C PerCP-Cy D Totl Neutrophils (CD45 +, CD115 -, Gr-1 + ) (% of CD45+ Cells) E Bseline CD45: CD45: CD45: CD45: CD45: monoytes monoytes monoytes monoytes monoytes neutrophils -1 3 neutrophils -1 3 neutrophils neutrophils neutrophils N.S Bseline N.S Bseline Downloded from y guest, on August 19, 218 different y ANOVA with post-ho Tukey test (P<.5). N.S. indites no signifint differene. 44
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Effect of Diets Containing Sucrose vs. D-tagatose in Hypercholesterolemic Mice
 nture pulishing group ARTICLES Effet of Diets Contining Surose vs. D-tgtose in Hyperholesterolemi Mie S r B. Poli e 1, J. C l y Hr r is 2, Roert A. Lodder 1, 2 nd Lis A. Cssis 1 Effets of funtionl sweeteners
nture pulishing group ARTICLES Effet of Diets Contining Surose vs. D-tgtose in Hyperholesterolemi Mie S r B. Poli e 1, J. C l y Hr r is 2, Roert A. Lodder 1, 2 nd Lis A. Cssis 1 Effets of funtionl sweeteners
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Hydrodynamic Delivery of mil10 Gene Protects Mice From High-fat Diet-induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure S1
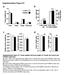 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Effect of age and moderate food restriction on insulin sensitivity in Wistar rats: role of adiposity
 131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Supplemental epilactose prevents metabolic disorders through uncoupling protein-1 induction in the skeletal muscle of mice fed high-fat diets
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Transplantation of PC1/3-Expressing α-cells Improves Glucose Handling and Cold Tolerance in Leptin-resistant Mice
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
Beta-Glucan-Rich Extract from
 Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine Volume 2013, Artile ID 185259, 10 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/185259 Reserh Artile Bet-Glun-Rih Extrt from Pleurotus sjor-ju (Fr.) Singer Prevents
Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine Volume 2013, Artile ID 185259, 10 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/185259 Reserh Artile Bet-Glun-Rih Extrt from Pleurotus sjor-ju (Fr.) Singer Prevents
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
CB1 antagonism exerts specific molecular effects on visceral and subcutaneous fat and reverses liver steatosis in diet-induced obese mice.
 CB1 ntgonism exerts speifi moleulr effets on viserl nd suutneous ft nd reverses liver stetosis in diet-indued oese mie. Tony Jourdn, Louiz Djouti, Lurent Demizieux, Joseph Gresti, Bruno Vergès, Psl Degre
CB1 ntgonism exerts speifi moleulr effets on viserl nd suutneous ft nd reverses liver stetosis in diet-indued oese mie. Tony Jourdn, Louiz Djouti, Lurent Demizieux, Joseph Gresti, Bruno Vergès, Psl Degre
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Food Research & Development, CJ Cheiljedang Corporation, Seoul , Korea; s: (H.-J.K.); (B.S.M.
 Int. J. Mol. Si. 214, 15, 17778-17789; doi:1.339/ijms15117778 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms The Benefiil Effets of Comined Grpe Pome nd Omij
Int. J. Mol. Si. 214, 15, 17778-17789; doi:1.339/ijms15117778 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms The Benefiil Effets of Comined Grpe Pome nd Omij
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD controls fat mass development by altering the browning process and gut microbiota
 Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Department of Animal Resource and Science, Dankook University, Cheonan, Choongnam, , Republic of Korea
 British Journl of Nutrition (1), 115, 57575 The Authors 1 doi:1.117/s711515857 Ltoillus idophilus modultes inflmmtory tivity y regulting the TLR nd NF-κB expression in porine peripherl lood mononuler ells
British Journl of Nutrition (1), 115, 57575 The Authors 1 doi:1.117/s711515857 Ltoillus idophilus modultes inflmmtory tivity y regulting the TLR nd NF-κB expression in porine peripherl lood mononuler ells
Supplementary information to accompany the manuscript entitled:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET
 EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Epiphyseal growth plate growth hormone receptor signaling is decreased in chronic kidney disease related growth retardation
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
Ob/ob mice are leptin deficient and become hyperphagic,
 ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
Anti-diabetic effect of Cyclo-His-Pro (CHP)-enriched yeast hydrolysate in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
 Vol. 12(35), pp. 5473-5479, 28 August, 213 DOI: 1.5897/AJB12.1556 ISSN 1684-5315 213 Ademi Journls http://www.demijournls.org/ajb Afrin Journl of Biotehnology Full Length Reserh Pper Anti-dieti effet of
Vol. 12(35), pp. 5473-5479, 28 August, 213 DOI: 1.5897/AJB12.1556 ISSN 1684-5315 213 Ademi Journls http://www.demijournls.org/ajb Afrin Journl of Biotehnology Full Length Reserh Pper Anti-dieti effet of
Effect of Prebiotics Inulin and Mannan on Lipid Profile and Intestinal Micro Flora of Hypercholesterolemic Rats
 J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Si., 6(8)22-31, 216 216, TextRod Pulition ISSN: 29-4274 Journl of Applied Environmentl nd Biologil Sienes www.textrod.om Effet of Preiotis Inulin nd Mnnn on Lipid Profile nd Intestinl
J. Appl. Environ. Biol. Si., 6(8)22-31, 216 216, TextRod Pulition ISSN: 29-4274 Journl of Applied Environmentl nd Biologil Sienes www.textrod.om Effet of Preiotis Inulin nd Mnnn on Lipid Profile nd Intestinl
F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Breast Cancer to mir-143-based Therapeutics by Targeting Tumor Glycolysis
 Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids () 5, e57; doi:.8/mtn..7 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Brest Cner to -Bsed Therpeutis
Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids () 5, e57; doi:.8/mtn..7 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring the Response of Brest Cner to -Bsed Therpeutis
White adipose tissue overproduces the lipid-mobilizing factor zinc a2-glycoprotein in chronic kidney disease
 si reserh http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 13 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology White dipose tissue overprodues the lipid-moilizing ftor zin -glyoprotein in hroni kidney disese Croline C. Pelletier 1,,3,5,
si reserh http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 13 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology White dipose tissue overprodues the lipid-moilizing ftor zin -glyoprotein in hroni kidney disese Croline C. Pelletier 1,,3,5,
BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A
 BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Vriose veins re hrterized by. 1. tortuous nd irregulr diltions in superfiil veins due to inompetent vlves 2. being used by prolonged bk pressure
BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Vriose veins re hrterized by. 1. tortuous nd irregulr diltions in superfiil veins due to inompetent vlves 2. being used by prolonged bk pressure
Effects of Plant Sphingolipids on Inflammatory Stress in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells
 Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 2017 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety doi : 10.5650/jos.ess17171 J. Oleo Si. 66, (12) 1337-1342 (2017) NOTE Effets of Plnt Sphingolipids on Inflmmtory Stress in Differentited Co-2
Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 2017 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety doi : 10.5650/jos.ess17171 J. Oleo Si. 66, (12) 1337-1342 (2017) NOTE Effets of Plnt Sphingolipids on Inflmmtory Stress in Differentited Co-2
Irisin biomarker, TSH, Trygleceriads and High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid diesase patients
 Interntionl Journl of ChemTeh Reserh CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.2, pp 674-678, 2017 Irisin biomrker, TSH, Trygleerids nd High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid
Interntionl Journl of ChemTeh Reserh CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.2, pp 674-678, 2017 Irisin biomrker, TSH, Trygleerids nd High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid
Combined AGE inhibition and ACEi decreases the progression of established diabetic nephropathy in B6 db/db mice
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology originl rtile Comined AGE inhiition nd ACEi dereses the progression of estlished dieti nephropthy in B6 d/d mie F Zheng 1,2, Y-j
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology originl rtile Comined AGE inhiition nd ACEi dereses the progression of estlished dieti nephropthy in B6 d/d mie F Zheng 1,2, Y-j
Mesozeaxanthin protects the liver and reduces cardio-metabolic risk factors in an insulin resistant rodent model
 FOOD & NUTRITION RESEARCH, 217 VOL. 61, 135336 https://doi.org/1.18/16546628.217.135336 ARTICLE Mesozexnthin protets the liver nd redues rdio-metoli risk ftors in n insulin resistnt rodent model Kzim Shin,
FOOD & NUTRITION RESEARCH, 217 VOL. 61, 135336 https://doi.org/1.18/16546628.217.135336 ARTICLE Mesozexnthin protets the liver nd redues rdio-metoli risk ftors in n insulin resistnt rodent model Kzim Shin,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
ARTICLE. Keywords Lipotoxicity. MicroRNA. Pancreatic beta cells. Stearic acid
 Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Targeting TSLP With shrna Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Decreases Epithelial CCL17 in a Murine Model of Asthma
 Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
Alternative rapamycin treatment regimens mitigate the impact of rapamycin on glucose homeostasis and the immune system.
 Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Research Article Decaffeinated Green Coffee Bean Extract Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine, Artile ID 718379, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/718379 eserh Artile Deffeinted Green Coffee Ben Extrt Attenutes Diet-Indued
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Evidene-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Mediine, Artile ID 718379, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/718379 eserh Artile Deffeinted Green Coffee Ben Extrt Attenutes Diet-Indued
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Raina Devi Ramnath, Jia Sun, and Madhav Bhatia. Department of Pharmacology, National University of Singapore, Singapore
 -3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
-3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
LIPIDOMICS OF BLOOD AND ORGANS OF RATS FED DIETS SUPPLEMENTED WITH DIFFERENT EDIBLE OILS
 Animl Reserh Interntionl (215) 12(2): 2189 222 2189 LIPIDOMICS OF BLOOD AND ORGANS OF RATS FED DIETS SUPPLEMENTED WITH DIFFERENT EDIBLE OILS 1 UGBAJA, Regin Ngozi, 2 AFOLABI, Olusegun Kyode, 1 ONUNKWOR,
Animl Reserh Interntionl (215) 12(2): 2189 222 2189 LIPIDOMICS OF BLOOD AND ORGANS OF RATS FED DIETS SUPPLEMENTED WITH DIFFERENT EDIBLE OILS 1 UGBAJA, Regin Ngozi, 2 AFOLABI, Olusegun Kyode, 1 ONUNKWOR,
a SpringerOpen Journal
 Kumr et l. SpringerPlus 213, 2:639 SpringerOpen Journl RESEARCH Open Aess Enhned glyemi ontrol, pnres protetive, ntioxidnt nd heptoprotetive effets y umelliferon-α-d-gluopyrnosyl-(2 I 1 II )-α-dgluopyrnoside
Kumr et l. SpringerPlus 213, 2:639 SpringerOpen Journl RESEARCH Open Aess Enhned glyemi ontrol, pnres protetive, ntioxidnt nd heptoprotetive effets y umelliferon-α-d-gluopyrnosyl-(2 I 1 II )-α-dgluopyrnoside
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Differential expression of cyclin G2, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C and peripheral myelin protein 22 genes during adipogenesis..
 The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
GLP-1 oestrogen attenuates hyperphagia and protects from beta cell failure in diabetes-prone New Zealand obese (NZO) mice
 Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Soy protein isolates prevent loss of bone quantity associated with obesity in rats through regulation of insulin signaling in osteoblasts
 The FASE Journl Reserh ommunition Soy protein isoltes prevent loss of one quntity ssoited with oesity in rts through regultion of insulin signling in osteolsts JinRn hen,,,, Jin Zhng,,, Oxn P. Lzrenko,,
The FASE Journl Reserh ommunition Soy protein isoltes prevent loss of one quntity ssoited with oesity in rts through regultion of insulin signling in osteolsts JinRn hen,,,, Jin Zhng,,, Oxn P. Lzrenko,,
MiR-29a Assists in Preventing the Activation of Human Stellate Cells and Promotes Recovery From Liver Fibrosis in Mice
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
Systemic Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Reverses Hypoalgesia and Improves Mobility in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
One-year Treatment of Morpholino Antisense Oligomer Improves Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle Functions in Dystrophic mdx Mice
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy One-yer Tretment of Morpholino Antisense Oligomer Improves Skeletl nd Crdi Musle Funtions in Dystrophi mdx Mie Bo Wu 1, Bin Xio 2,3, Cryn Cloer 1,
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy One-yer Tretment of Morpholino Antisense Oligomer Improves Skeletl nd Crdi Musle Funtions in Dystrophi mdx Mie Bo Wu 1, Bin Xio 2,3, Cryn Cloer 1,
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
The Body Vitamin B 1 Levels of Rats Fed a Diet Containing the Minimum Requirement of Vitamin B 1 Is Reduced by Exercise
 J Nutr Si Vitminol, 59, 87 92, 213 The Body Vitmin B 1 Levels of Rts Fed Diet Contining the Minimum Requirement of Vitmin B 1 Is Redued y Exerise Ktsumi Shit nd Tsutomu Fukuwtri Deprtment of Food Siene
J Nutr Si Vitminol, 59, 87 92, 213 The Body Vitmin B 1 Levels of Rts Fed Diet Contining the Minimum Requirement of Vitmin B 1 Is Redued y Exerise Ktsumi Shit nd Tsutomu Fukuwtri Deprtment of Food Siene
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Garcinia cambogia Extract Ameliorates Visceral Adiposity in C57BL/6J Mice Fed on a High-Fat Diet
 Biosi. Biotehnol. Biohem., 72 (7), 1772 1780, 2008 Grini mogi Extrt Ameliortes Viserl Adiposity in C57BL/6J Mie Fed on High-Ft Diet Keun-Young KIM, Hye Nm LEE, Yun Jung KIM, nd Tesun PARK y Deprtment of
Biosi. Biotehnol. Biohem., 72 (7), 1772 1780, 2008 Grini mogi Extrt Ameliortes Viserl Adiposity in C57BL/6J Mie Fed on High-Ft Diet Keun-Young KIM, Hye Nm LEE, Yun Jung KIM, nd Tesun PARK y Deprtment of
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (2014), 111, 445 451 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s0007114513002584 PUFA rtio is involved in regulting lipid metolism nd inflmmtion in pigs Yehui Dun 1,2, Fengn Li 1 *, Lili
British Journl of Nutrition (2014), 111, 445 451 q The Authors 2013 doi:10.1017/s0007114513002584 PUFA rtio is involved in regulting lipid metolism nd inflmmtion in pigs Yehui Dun 1,2, Fengn Li 1 *, Lili
Naringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflammation, metabolic dysregulation and atherosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice.
 Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT LEVELS OF OLIVE OIL IN RATION SUPPLEMENTATION ON SOME BIOCHEMICAL AND PRODUCTIVE TRAITS IN BROILERS
 I.J.S.N., VOL.9 (1) 2018: 137-142 ISSN 2229 6441 TH T O IRNT LVLS O OLIV OIL IN RTION SUPPLMNTTION ON SOM IOHMIL N PROUTIV TRITS IN ROILRS huh Smir Hdi, s wzy l- khlisy ep. of Veterinry Puli Helth/ollege
I.J.S.N., VOL.9 (1) 2018: 137-142 ISSN 2229 6441 TH T O IRNT LVLS O OLIV OIL IN RTION SUPPLMNTTION ON SOM IOHMIL N PROUTIV TRITS IN ROILRS huh Smir Hdi, s wzy l- khlisy ep. of Veterinry Puli Helth/ollege
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
