Leptin as a Potential Regulator of FGF21
|
|
|
- Darcy Haynes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Paper 2016 The Author(s) Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: March 17, 17, Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1218 Accepted: February 10, /16/ $39.50/0 This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND) ( Usage and distribution for commercial purposes as well as any distribution of modified material requires written permission. Leptin as a Potential Regulator of FGF21 Mohamed Asrih a Christelle Veyrat-Durebex b Anne-Laure Poher b Jacqueline Lyautey b Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud b François R. Jornayvaz a a Service of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, b Laboratory of Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine Specialties, Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland Key Words FGF21 Leptin Insulin resistance Obesity Abstract Background/Aims: Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), a potent metabolic regulator, has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in animal models of insulin resistance. Several studies have focused on identifying mediators of FGF21 effects. However, the identification of factors involved in FGF21 regulation is far from complete. As leptin is a potent metabolic modulator as well, we aimed at characterizing whether leptin may regulate FGF21. Methods: We investigated a potential regulation of FGF21 by leptin in vivo in Wistar rats and in vitro using human derived hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. This model was chosen as the liver is considered the main FGF21 expression site. Results: We found that leptin injections increased plasma FGF21 levels in adult Wistar rats. This was confirmed in vitro, as leptin increased FGF21 expression in HepG2 cells. We also showed that the leptin effect on FGF21 expression was mediated by STAT3 activation in HepG2 cells. Conclusion: New findings regarding a leptin- STAT3-FGF21 axis were provided in this study, although investigating the exact mechanisms linking leptin and FGF21 are still needed. These results are of great interest in the context of identifying potential new clinical approaches to treat metabolic diseases associated with insulin resistance, such as obesity and type 2 diabetes The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel Introduction Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a potent metabolic regulator, predominantly expressed in the liver and white adipose tissue, but also in skeletal muscle and pancreas [1, 2]. Pharmacological doses of FGF21 have been shown to exert notable anti-diabetic effects. In particular, FGF21 improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, and reduces plasma and hepatic triglycerides in ob/ob, db/db, and wild-type mice fed a high-fat diet [3-6]. It also protects against high glucose induced cellular damage in endothelial cells, thus potentially promoting vascular health in diabetes [7]. Several studies focused on the identification M. Asrih and C. Veyrat-Durebex contributed equally. François Jornayvaz, MD Service of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Lausanne University Hospital, Mont-Paisible 18, 1011 Lausanne, (Switzerland) Tel , Fax , Francois.Jornayvaz@chuv.ch
2 1219 of potential FGF21 mediators [8-10]. Among these mediators, adiponectin was shown to mediate part of FGF21 effects [8, 9]. Recent evidence also suggests that other factors, such as dual specificity phosphatase 4 or uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) may mediate FGF21 actions [11, 12]. With regard to the regulation of FGF21 expression, very limited information is available as yet [13]. Interestingly, FGF21 expression was shown to be under the control of the stress responsive transcription factor, Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3 (STAT3) [14], which is also known to mediate leptin effects [15]. Subsequently, other studies demonstrated that FGF21 is modulated by key metabolic transcription factors such as PPARα and PPARγ [16-18] which are also induced by leptin [19]. Leptin is also known to promote metabolic health by notably increasing fat oxidation in muscle cells [20] and decreasing inflammation [21]. In the present study, we first investigated whether leptin may regulate FGF21 expression in vivo in Wistar rats. Since FGF21 is predominantly produced by the liver [22], potential leptin effects on FGF21 were also investigated in vitro, in human derived hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells, a cell line known to produce FGF21 although at very low concentrations under basal conditions [23]. This allowed us to investigate the potential signaling pathways involved in the regulation of FGF21 by leptin. Materials and Methods Animals All procedures were performed in accordance with and approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Animal Care in Geneva and Cantonal Veterinary Office. Four month-old male Wistar rats were obtained from Charles River (L Arbresle, France). They were housed under controlled temperature (22 C) and lighting (lights on: 7 AM to 7 PM) with free access to water and food (standard diet, laboratory diet RM3, SDS, Essex, UK). To test the effect of leptin on FGF21 secretion, a cohort of rats was euthanized 30 minutes after a single intraperitoneal injection of human recombinant leptin (2 mg/kg) (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ) or vehicle (saline). This leptin dose was chosen because previous experiments were performed in similar conditions with reliable results. Notably, this dose of leptin was able to decrease food intake in Wistar rats, confirming a response to leptin, which was not the case with lower doses of leptin [24]. Blood and tissues were sampled and stored at 80 C for further analysis. Plasma measurements A commercial ELISA kit was used for the measurement of plasma FGF21 (R&D systems Europe Ltd, Oxon, UK). Cell culture Human derived hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (Gibco, Life Technologies, Zug, Switzerland) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Sigma-Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland), 1% (v/v) penicillin streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich,) at 37 C with 5% CO 2. Equivalent numbers of HepG2 cells starved in DMEM basal serumfree media were treated with 200 ng/ml recombinant leptin (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK), PBS (control group), and/or a STAT3 inhibitor (10 µmol/l) (Stattic, Sigma-Aldrich) for 1 h. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Total RNA from HepG2 cells was extracted using a single-step extraction with Trizol reagent (Sigma- Aldrich). RNA integrity was assessed by electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel and concentration was determined by spectrophotometry. A quantity of 1 µg of total RNA was used for RT, using a commercial kit (Takara Bio Europe, St Germain-en-Laye, France). For quantitative PCR, amplification of genes was performed from 50 ng cdna using the SYBR green PCR Master Mix (Roche, Rotkreuz, France) and a StepOne Real-Time PCR system (Life Technologies), as previously described [25]. Oligonucleotides were used at 300 nmol/l and results were normalized to the expression levels of housekeeping genes (Table 1).
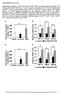
3 1220 Table 1. Sequences of oligonucleotides used Western blot HepG2 cells lysates were prepared in RIPA buffer (150 mmol/l NaCl, 1% (v/v) Triton X-100, 0.1% (w/v) SDS, 0.5% (w/v) Na deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris-HCl) with phosphatase and protease inhibitors (Halt protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail, Pierce, Lausanne, Switzerland) as previously described [26]. Samples were resolved on a 4 12% Bis-Tris gel and transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Thereafter, proteins were detected using the following antibodies: anti-pstat3 (1:2000, Cell signaling, Allschwil, Switzerland), anti-stat3 (1:2000, Cell signaling), anti-pparα (1:2000, Cell signaling) and tubulin (1:4000, Sigma-Aldrich). The bands were visualized by chemiluminescence (Supersignal West Dura substrate, Pierce) on a detection system (GE Healthcare Europe GmbH, Glattbrugg, Switzerland). Densitometric analysis of chemiluminescent signals captured on camera was performed using the Image J software (National Institutes of Health). Statistical analyses Results are expressed as Mean ± SEM. Statistical calculations were carried out with GraphPad Prism 6 (GraphPad Prism, La Jolla, CA). Statistical significance was established at p<0.05 and determined by unpaired Student s t-test or one-way ANOVA. Results Leptin increases plasma FGF21 levels in rats To study the link between leptin and FGF21, adult male Wistar rats were challenged with an intraperitoneal leptin injection (2 mg/kg). Plasma FGF21 levels were then evaluated 30 minutes later. Leptin treatment significantly increased plasma FGF21 levels compared to the injection of vehicle (saline), confirming a stimulatory effect of leptin on FGF21 release in this model (Fig. 1). The mrna expression of Fgf21 was thereafter evaluated in different tissues. The liver was the tissue predominantly expressing Fgf21, compared to brown (BAT) and inguinal white (WATi) adipose tissue (Fig. 2). However, under our experimental conditions (i.e. 30 minutes after injection), leptin was unable to increase Fgf21 mrna levels in the liver or in the other tissues (Fig. 2). This suggests a potential time-dependant effect, or an effect of leptin on FGF21 release rather than expression. Leptin induces Fgf21 expression in HepG2 cells To strengthen our in vivo results, we used an in vitro model, focusing on the liver, which is considered the main site of FGF21 production. HepG2 cells were therefore chosen and treated for 1 h with leptin (200 ng/ml). Leptin treatment enhanced Fgf21 expression under these experimental conditions (Fig. 3A). Interestingly, an almost significant (p=0.07) stimulation of the mrna expression of Socs3, a direct target of STAT3, was observed (Fig. 3A). As leptin is known to promote activation of STAT3 [27], we assessed whether the leptininduced increase in Fgf21 expression could be mediated by the STAT3 signaling pathway.
4 1221 Fig. 1. Leptin increases plasma FGF21 levels in Wistar rats. Plasma FGF21 levels in control (saline) or leptin-treated (2 mg/kg, i.p.) Wistar rats. Mean + SEM. *p<0.05 using Student s t-test. Fig. 2. Acute leptin treatment does not affect Fgf21 mrna levels in the liver, brown adipose tissue (BAT), or inguinal white adipose tissue (WATi) of Wistar rats. mrna expression of Fgf21 in control (saline) or leptin-treated (2 mg/kg, i.p.) Wistar rats. Mean + SEM. Fig. 3. Leptin regulation of FGF21 in HepG2 cells. A) mrna expression of Fgf21 and Socs3 in untreated (Control) or leptin-treated (Leptin, 200 ng/ml) HepG2 cells. B) Quantification and representative Western blots of phosphorylated STAT3 (pstat3) and STAT3 in the presence (Leptin + Stattic, 1 h) or absence (Leptin) of the STAT3 inhibitor, Stattic, compared to untreated cells (C). C) mrna expression of Fgf21 in untreated (C) or leptintreated HepG2 cells in the presence, or the absence of Stattic. Mean + SEM of n=4 experiments for qpcr using Student s t-test or one-way ANO- VA. *p<0.05 leptin versus control, #p<0.05 leptin versus control, p<0.05 leptin + stattic versus leptin. To this end, HepG2 cells were treated with leptin (200 ng/ml) in the presence, or in the absence, of a STAT3 inhibitor (Stattic, 10 µmol/l, 1 h). As expected, leptin increased STAT3 phosphorylation whereas the presence of the STAT3 inhibitor in the medium resulted in a significant inhibition of phosphorylation (Fig. 3B). Importantly, the presence of the
5 1222 Fig. 4. Effect of leptin on PPARα in HepG2 cells. A) mrna expression of Pparα; B) Quantification and representative Western blots of PPARα and Tubulin in untreated (Control) or leptin-treated (Leptin) HepG2 cells. Mean + SEM of n=4 experiments for qpcr. *p<0.05 using Student s t-test. inhibitor also prevented the leptin-induced Fgf21 expression (Fig. 3C), confirming that the effect of leptin on FGF21 is mediated by STAT3 activation. As PPARα is also known to regulate Fgf21 gene expression [28], we then tested whether leptin could stimulate Fgf21 expression through the PPARα pathway. We observed that 1 h of leptin treatment increased Pparα mrna expression in HepG2 cells (Fig. 4A). However, as determined using Western blotting, PPARα protein levels tended to be increased by leptin (Fig. 4B), but this was not significant (p=0.1). These results could potentially suggest a post-transcriptional regulation of PPARα by leptin, which will require further investigations in future studies. Alternatively, it is conceivable that 1 h of leptin treatment was not long enough to observe any significant difference in protein synthesis. Discussion FGF21, a potent metabolic regulator, has been shown to improve glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as to reduce body weight and adipose tissue mass [3-6, 29-31]. These favorable effects seem to be mainly mediated by white adipose tissue, since lack of FGF receptor 1 (FGFR1) in this tissue abolishes the metabolic actions of FGF21 [32, 33]. FGF21 has also been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis in high-fat fed mice [4]. On the opposite, mice lacking Fgf21 develop hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin resistance when fed a high-fat ketogenic diet [23]. Several studies focused on the identification of FGF21 mediators [8-10]. Although adiponectin was described as one of the main mediators of FGF21 action, recent evidence suggests that other factors may be involved as well [11, 12]. Nevertheless, limited information is available regarding the regulation of Fgf21 expression itself. Here, we report that leptin is a potential new regulator of FGF21. Indeed, we observed that leptin administration acutely increased plasma FGF21 plasma levels in Wistar rats. This likely resulted from a release of FGF21 from the liver, as suggested by the literature [3], although we could not find any difference in Fgf21 expression in the liver or other tissues. However, skeletal muscle has also been suggested as a site of FGF21 production [34, 35] and could have revealed increased Fgf21 expression after leptin administration. However, we did not sample any skeletal muscle in our rats. Nonetheless, it is also possible that timing of tissue harvesting (30 minutes in our in vivo experimental conditions) might have accounted for our findings, suggesting that a faster or slower regulation by leptin on tissue Fgf21 expression might occur. The rapid effect of leptin on FGF21 levels however suggests an effect on secretion. Notably, leptin is known to rapidly (within minutes) and directly inhibit insulin secretion by the pancreas [36]. FGF21 is also rapidly (within 15 minutes) expressed by the pancreas after acute pancreatic injury [37]. Therefore, it could be hypothesized that leptin
6 1223 might stimulate rapid pancreatic FGF21 expression and release. Unfortunately, we did not sample the pancreas of our leptin-treated rats. Altogether, these considerations therefore warrant further in vivo research. Nevertheless, our in vitro results obtained in HepG2 cells clearly show an effect of leptin on Fgf21 expression. Moreover, we show that this leptin effect is mediated by STAT3 activation, as not only STAT3 phosphorylation, but also Fgf21 expression, were prevented in the presence of a STAT3 inhibitor. These findings therefore provide a potential signaling pathway by which leptin regulates FGF21. A possible involvement of PPARα activation remains to be elucidated in future studies, but is likely to play a role in the crosstalk between leptin and FGF21. As in vitro studies do not take into account potential interactions between tissues, for example between liver and white adipose tissue, further studies are required in vivo to better clarify the potential regulation of FGF21 by leptin. The role of FGF21 as a mediator of leptin action may be of significant relevance in various metabolic regulation processes. As an example, impaired leptin signaling in the liver, known to promote hepatic steatosis [38], may be due to impaired hepatic Fgf21 expression. Nevertheless, the peripheral effect of leptin is a subject of debate. Notably, mice with specific leptin receptor deletion in the liver do not recapitulate the metabolic phenotype of db/db mice. Indeed, metabolic effects of leptin and notably its weight-reducing effects are more likely to be the results of the central leptin action on the brain [39]. However, obesity is a leptin resistance state [40]. Moreover, FGF21 levels are also increased in obesity, which also suggest a resistant state [41, 42]. Therefore, it could be speculated that co-administration of leptin and FGF21 could reveal a synergistic effect in obesity to overcome this state of hormonal resistance. This may also be true in other situations of hormone resistance, notably insulin resistance, encountered not only in obesity, but also in conditions associated with the metabolic syndrome, such as type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [43]. These considerations warrant further in vivo studies. Altogether, our results provide new findings regarding a leptin-stat3-fgf21 axis that may lead to beneficial metabolic effects. These findings warrant further in vivo work to assess whether leptin-induced FGF21 could improve diseases associated with insulin resistance such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acknowledgments This work was supported by the Helmut Horten Foundation, the Novartis Foundation for medical-biological research, the Leenaards Foundation and the Raymond Berger Foundation to FR Jornayvaz and by a grant from the Swiss National Science Foundation (Bern, Switzerland), FNRS: 31003A_ and _160290/1 to F. Rohner-Jeanrenaud. Disclosure Statement The authors have nothing to disclose. References 1 Murata Y, Konishi M, Itoh N: FGF21 as an Endocrine Regulator in Lipid Metabolism: From Molecular Evolution to Physiology and Pathophysiology. J Nutr Metab 2011;2011: Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N: Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000;1492: Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers JS, Owens RA, Gromada J, Brozinick JT, Hawkins ED, Wroblewski VJ, Li DS, Mehrbod F, Jaskunas SR, Shanafelt AB: FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest 2005;115: Camporez JP, Jornayvaz FR, Petersen MC, Pesta D, Guigni BA, Serr J, Zhang D, Kahn M, Samuel VT, Jurczak MJ, Shulman GI: Cellular mechanisms by which FGF21 improves insulin sensitivity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013;154:
7 Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A: Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 2008;149: Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen M, Sivits G, Vonderfecht S, Hecht R, Li YS, Lindberg RA, Chen JL, Jung DY, Zhang Z, Ko HJ, Kim JK, Veniant MM: Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 2009;58: Wang XM, Song SS, Xiao H, Gao P, Li XJ, Si LY: Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against high glucose induced cellular damage and dysfunction of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase in endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 2014;34: Holland WL, Adams AC, Brozinick JT, Bui HH, Miyauchi Y, Kusminski CM, Bauer SM, Wade M, Singhal E, Cheng CC, Volk K, Kuo MS, Gordillo R, Kharitonenkov A, Scherer PE: An FGF21-adiponectin-ceramide axis controls energy expenditure and insulin action in mice. Cell Metab 2013;17: Lin Z, Tian H, Lam KS, Lin S, Hoo RC, Konishi M, Itoh N, Wang Y, Bornstein SR, Xu A, Li X: Adiponectin mediates the metabolic effects of FGF21 on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Metab 2013;17: Veniant MM, Hale C, Helmering J, Chen MM, Stanislaus S, Busby J, Vonderfecht S, Xu J, Lloyd DJ: FGF21 promotes metabolic homeostasis via white adipose and leptin in mice. PLoS One 2012;7:e Muise ES, Souza S, Chi A, Tan Y, Zhao X, Liu F, Dallas-Yang Q, Wu M, Sarr T, Zhu L, Guo H, Li Z, Li W, Hu W, Jiang G, Paweletz CP, Hendrickson RC, Thompson JR, Mu J, Berger JP, Mehmet H: Downstream signaling pathways in mouse adipose tissues following acute in vivo administration of fibroblast growth factor 21. PLoS One 2013;8:e Markan KR, Naber MC, Ameka MK, Anderegg MD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA, Mohammadi M, Potthoff MJ: Circulating FGF21 is liver derived and enhances glucose uptake during refeeding and overfeeding. Diabetes 2014;63: Lundasen T, Hunt MC, Nilsson LM, Sanyal S, Angelin B, Alexson SE, Rudling M: PPARalpha is a key regulator of hepatic FGF21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007;360: Yang C, Lu W, Lin T, You P, Ye M, Huang Y, Jiang X, Wang C, Wang F, Lee MH, Yeung SC, Johnson RL, Wei C, Tsai RY, Frazier ML, McKeehan WL, Luo Y: Activation of Liver FGF21 in hepatocarcinogenesis and during hepatic stress. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13: Luo W, Bodary PF, Shen Y, Wickenheiser KJ, Ohman MK, Guo C, Bahrou KL, Myers MG, Jr., Eitzman DT: Leptin receptor-induced STAT3-independent signaling pathways are protective against atherosclerosis in a murine model of obesity and hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2011;214: Muise ES, Azzolina B, Kuo DW, El-Sherbeini M, Tan Y, Yuan X, Mu J, Thompson JR, Berger JP, Wong KK: Adipose fibroblast growth factor 21 is up-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and altered metabolic states. Mol Pharmacol 2008;74: Mraz M, Bartlova M, Lacinova Z, Michalsky D, Kasalicky M, Haluzikova D, Matoulek M, Dostalova I, Humenanska V, Haluzik M: Serum concentrations and tissue expression of a novel endocrine regulator fibroblast growth factor-21 in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009;71: Galman C, Lundasen T, Kharitonenkov A, Bina HA, Eriksson M, Hafstrom I, Dahlin M, Amark P, Angelin B, Rudling M: The circulating metabolic regulator FGF21 is induced by prolonged fasting and PPARalpha activation in man. Cell Metab 2008;8: Qian H, Hausman GJ, Compton MM, Azain MJ, Hartzell DL, Baile CA: Leptin regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, tumor necrosis factor, and uncoupling protein-2 expression in adipose tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998;246: Nozhenko Y, Rodriguez AM, Palou A: Leptin rapidly induces the expression of metabolic and myokine genes in C2C12 muscle cells to regulate nutrient partition and oxidation. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015;35: Landgraf MA, Silva RC, Correa-Costa M, Hiyane MI, Carvalho MH, Landgraf RG, Camara NO: Leptin downregulates LPS-induced lung injury: role of corticosterone and insulin. Cell Physiol Biochem 2014;33: Diaz-Delfin J, Hondares E, Iglesias R, Giralt M, Caelles C, Villarroya F: TNF-alpha represses beta-klotho expression and impairs FGF21 action in adipose cells: involvement of JNK1 in the FGF21 pathway. Endocrinology 2012;153:
8 Camporez JP, Asrih M, Zhang D, Kahn M, Samuel VT, Jurczak MJ, Jornayvaz FR: Hepatic insulin resistance and increased hepatic glucose production in mice lacking Fgf21. J Endocrinol 2015;226: Veyrat-Durebex C, Poher AL, Caillon A, Somm E, Vallet P, Charnay Y, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F: Improved leptin sensitivity as a potential candidate responsible for the spontaneous food restriction of the Lou/C rat. PLoS One 2013;8:e Asrih M, Altirriba J, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F, Jornayvaz FR: Ketogenic Diet Impairs FGF21 Signaling and Promotes Differential Inflammatory Responses in the Liver and White Adipose Tissue. PLoS One 2015;10:e Asrih M, Montessuit C, Philippe J, Jornayvaz FR: Free Fatty Acids Impair FGF21 Action in HepG2 Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015;37: Jiang L, Li Z, Rui L: Leptin stimulates both JAK2-dependent and JAK2-independent signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 2008;283: Vernia S, Cavanagh-Kyros J, Garcia-Haro L, Sabio G, Barrett T, Jung DY, Kim JK, Xu J, Shulha HP, Garber M, Gao G, Davis RJ: The PPARalpha-FGF21 hormone axis contributes to metabolic regulation by the hepatic JNK signaling pathway. Cell Metab 2014;20: Arner P, Pettersson A, Mitchell PJ, Dunbar JD, Kharitonenkov A, Ryden M: FGF21 attenuates lipolysis in human adipocytes - a possible link to improved insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett 2008;582: Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E: Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab 2007;5: Wente W, Efanov AM, Brenner M, Kharitonenkov A, Koster A, Sandusky GE, Sewing S, Treinies I, Zitzer H, Gromada J: Fibroblast growth factor-21 improves pancreatic beta-cell function and survival by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Diabetes 2006;55: Adams AC, Yang C, Coskun T, Cheng CC, Gimeno RE, Luo Y, Kharitonenkov A: The breadth of FGF21's metabolic actions are governed by FGFR1 in adipose tissue. Mol Metab 2012;2: Woo YC, Xu A, Wang Y, Lam KS: Fibroblast growth factor 21 as an emerging metabolic regulator: clinical perspectives. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013;78: Hojman P, Pedersen M, Nielsen AR, Krogh-Madsen R, Yfanti C, Akerstrom T, Nielsen S, Pedersen BK: Fibroblast growth factor-21 is induced in human skeletal muscles by hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes 2009;58: Lindegaard B, Hvid T, Grondahl T, Frosig C, Gerstoft J, Hojman P, Pedersen BK: Expression of fibroblast growth factor-21 in muscle is associated with lipodystrophy, insulin resistance and lipid disturbances in patients with HIV. PLoS One 2013;8:e Kulkarni RN, Wang ZL, Wang RM, Hurley JD, Smith DM, Ghatei MA, Withers DJ, Gardiner JV, Bailey CJ, Bloom SR: Leptin rapidly suppresses insulin release from insulinoma cells, rat and human islets and, in vivo, in mice. J Clin Invest 1997;100: Johnson CL, Weston JY, Chadi SA, Fazio EN, Huff MW, Kharitonenkov A, Koester A, Pin CL: Fibroblast growth factor 21 reduces the severity of cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2009;137: Huynh FK, Neumann UH, Wang Y, Rodrigues B, Kieffer TJ, Covey SD: A role for hepatic leptin signaling in lipid metabolism via altered very low density lipoprotein composition and liver lipase activity in mice. Hepatology 2013;57: Cohen P, Zhao C, Cai X, Montez JM, Rohani SC, Feinstein P, Mombaerts P, Friedman JM: Selective deletion of leptin receptor in neurons leads to obesity. J Clin Invest 2001;108: Myers MG, Jr., Leibel RL, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW: Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2010;21: Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS, Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, Badman MK, Martinez-Chantar ML, Maratos-Flier E: Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2010;139: Fisher FM, Chui PC, Antonellis PJ, Bina HA, Kharitonenkov A, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E: Obesity is a fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21)-resistant state. Diabetes 2010;59: Asrih M, Jornayvaz FR: Metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Is insulin resistance the link? Mol Cell Endocrinol 2015;418:55-65.
Free Fatty Acids Impair FGF21 Action in HepG2 Cells
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 13, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1767 Accepted: September 29,
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 13, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1767 Accepted: September 29,
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice
 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami ABSTRACT
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Increases Hepatic FGF21 Production and Decreases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Independently of Insulin in db/db Mice Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami ABSTRACT
Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21
 Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21 Dionysios V Chartoumpekis, 1* Ioannis G Habeos, 1* Panos G Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E Kyriazopoulou,
Brown Adipose Tissue Responds to Cold and Adrenergic Stimulation by Induction of FGF21 Dionysios V Chartoumpekis, 1* Ioannis G Habeos, 1* Panos G Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E Kyriazopoulou,
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Molecular Medicine. Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic
 Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic stimulation by induction of FGF21 Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1, Ioannis G. Habeos, 1, Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E.
Brown adipose tissue responds to cold and adrenergic stimulation by induction of FGF21 Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, 1, Ioannis G. Habeos, 1, Panos G. Ziros, 1 Agathoklis I. Psyrogiannis, 1 Venetsana E.
The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to energy balance in dairy cows
 Xu et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:271 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0585-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to
Xu et al. BMC Veterinary Research (2015) 11:271 DOI 10.1186/s12917-015-0585-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The relationship between Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 and characteristic parameters related to
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes
 People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Induced in Human Skeletal Muscles by Hyperinsulinemia
 BRIEF REPORT Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Induced in Human Skeletal Muscles by Hyperinsulinemia Pernille Hojman, Maria Pedersen, Anders Rinnov Nielsen, Rikke Krogh-Madsen, Christina Yfanti, Thorbjørn
BRIEF REPORT Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Induced in Human Skeletal Muscles by Hyperinsulinemia Pernille Hojman, Maria Pedersen, Anders Rinnov Nielsen, Rikke Krogh-Madsen, Christina Yfanti, Thorbjørn
Identification of Binding Partners of Fibroblast Gro wth Factor221 in Cell Membrane of 3T32L1 Cells
 ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2008 7 24 (7) :667 673 3T32L1 FGF221 1), 1),, 3 (, 150030) (fibroblast growth factor,fgf)221 1, 2.,FGF221.,, 3T32L1, FGF221,
ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2008 7 24 (7) :667 673 3T32L1 FGF221 1), 1),, 3 (, 150030) (fibroblast growth factor,fgf)221 1, 2.,FGF221.,, 3T32L1, FGF221,
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist. Research Summary:
 Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Diabetes Care 32: , 2009
 Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Elevated in Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Type 2 Diabetes and Correlates With Muscle and Hepatic
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Is Elevated in Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Type 2 Diabetes and Correlates With Muscle and Hepatic
The Effects of LY , an FGF21 Analog, in Obese Human Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
 Article The Effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 Analog, in Obese Human Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Gregory Gaich, 1 Jenny Y. Chien, 1 Haoda Fu, 1 Leonard C. Glass, 1 Mark A. Deeg, 1 William L. Holland, 2
Article The Effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 Analog, in Obese Human Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Gregory Gaich, 1 Jenny Y. Chien, 1 Haoda Fu, 1 Leonard C. Glass, 1 Mark A. Deeg, 1 William L. Holland, 2
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a member of the. Distinct Changes in Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Different Subtypes of Diabetes
 JCEM ONLINE Brief Report Endocrine Research Distinct Changes in Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Different Subtypes of Diabetes Yang Xiao, Aimin Xu, Lawrence S. C. Law, Cheng Chen, Hui Li, Xia
JCEM ONLINE Brief Report Endocrine Research Distinct Changes in Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Different Subtypes of Diabetes Yang Xiao, Aimin Xu, Lawrence S. C. Law, Cheng Chen, Hui Li, Xia
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Introduction. Physiol. Res. 60: , Received December 6, 2010 Accepted April 7, 2011 On-line August 1, 2011
 Physiol. Res. 60: 757-767, 2011 Increased Circulating and Epicardial Adipose Tissue mrna Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 After Cardiac Surgery: Possible Role in Postoperative Inflammatory Response
Physiol. Res. 60: 757-767, 2011 Increased Circulating and Epicardial Adipose Tissue mrna Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 After Cardiac Surgery: Possible Role in Postoperative Inflammatory Response
Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects
 28 ORIGINAL Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects Qing-Ri Jin 1, Yukiko Bando 2, Katsuyuki Miyawaki 1, Yosuke Shikama 2, Chisato Kosugi
28 ORIGINAL Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects Qing-Ri Jin 1, Yukiko Bando 2, Katsuyuki Miyawaki 1, Yosuke Shikama 2, Chisato Kosugi
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Controls Glycemia via Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Flux and Insulin Sensitivity
 DIABETES-INSULIN-GLUCAGON-GASTROINTESTINAL Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Controls Glycemia via Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Flux and Insulin Sensitivity Eric D. Berglund, Candice Y. Li, Holly A. Bina, Sara
DIABETES-INSULIN-GLUCAGON-GASTROINTESTINAL Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Controls Glycemia via Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Flux and Insulin Sensitivity Eric D. Berglund, Candice Y. Li, Holly A. Bina, Sara
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression and Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet
 A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami Abstract Background: Fibroblast growth
A Tryptophan Hydroxylase Inhibitor Decreases Hepatic FGF21 Expression Circulating FGF21 in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet Katsunori Nonogaki, Takao Kaji, Mari Murakami Abstract Background: Fibroblast growth
FGF21 mediates the lipid metabolism response to amino acid starvation
 FGF21 mediates the lipid metabolism response to amino acid starvation Ana Luísa De Sousa-Coelho, *, Joana Relat, *, Elayne Hondares,, Albert Pérez-Martí, *, Francesc Ribas,, Francesc Villarroya,, Pedro
FGF21 mediates the lipid metabolism response to amino acid starvation Ana Luísa De Sousa-Coelho, *, Joana Relat, *, Elayne Hondares,, Albert Pérez-Martí, *, Francesc Ribas,, Francesc Villarroya,, Pedro
High Glucose Represses b-klotho Expression and Impairs Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Action in Mouse Pancreatic Islets
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Glucose Represses b-klotho Expression and Impairs Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Action in Mouse Pancreatic Islets Involvement of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor g Signaling
ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Glucose Represses b-klotho Expression and Impairs Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Action in Mouse Pancreatic Islets Involvement of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor g Signaling
Significant gender difference in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in Danish children and adolescents
 Bisgaard et al. International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology 2014, 2014:7 RESEARCH Open Access Significant gender difference in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in Danish children and adolescents
Bisgaard et al. International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology 2014, 2014:7 RESEARCH Open Access Significant gender difference in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in Danish children and adolescents
Original Article Decreased levels of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 in Chinese patients with coronary artery disease
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9625-9630 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0035246 Original Article Decreased levels of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 in Chinese patients with coronary artery disease
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9625-9630 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0035246 Original Article Decreased levels of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 in Chinese patients with coronary artery disease
Plasma Concentrations of Fibroblast Growth Factors 21 and 19 in Patients with Cushing's Syndrome
 Physiol. Res. 59: 415-422, 2010 Plasma Concentrations of Fibroblast Growth Factors 21 and 19 in Patients with Cushing's Syndrome V. ĎUROVCOVÁ 1, J. MAREK 1, V. HÁNA 1, M. MATOULEK 1, V. ZIKÁN 1, D. HALUZÍKOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 59: 415-422, 2010 Plasma Concentrations of Fibroblast Growth Factors 21 and 19 in Patients with Cushing's Syndrome V. ĎUROVCOVÁ 1, J. MAREK 1, V. HÁNA 1, M. MATOULEK 1, V. ZIKÁN 1, D. HALUZÍKOVÁ
FGF21 Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance
 Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance The ICDM 213 & 5 th AASD Scientific Meeting Seoul, Korea, Nov 8, 213 Aimin Xu Dept of Medicine & Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacy The University
Resistance in Adipose Tissues as a Cause of Insulin Resistance The ICDM 213 & 5 th AASD Scientific Meeting Seoul, Korea, Nov 8, 213 Aimin Xu Dept of Medicine & Dept of Pharmacology and Pharmacy The University
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11):
 902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
Supplemental Information. Intermittent Fasting Promotes. White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity. by Shaping the Gut Microbiota
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota Guolin Li, Cen Xie, Siyu Lu, Robert G. Nichols,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota Guolin Li, Cen Xie, Siyu Lu, Robert G. Nichols,
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice
 Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO. Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu ABSTRACT
 Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Supplementary Information. Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis.
 Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
Diabetes Care 36: , 2013
 Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts the Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes in Caucasians THOMAS BOBBERT, MD 1 FRANZISKA SCHWARZ 1 ANTJE
Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Predicts the Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes in Caucasians THOMAS BOBBERT, MD 1 FRANZISKA SCHWARZ 1 ANTJE
Obesity is a complex disease involving a number of
 ORIGINAL Endocrine ARTICLE Research Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF-21) and Its Relation to Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Children: A Longitudinal Analysis Thomas Reinehr,
ORIGINAL Endocrine ARTICLE Research Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF-21) and Its Relation to Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Children: A Longitudinal Analysis Thomas Reinehr,
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Pak. J. Biotechnol. Vol 15 (3) (2018) ISSN Print: ISSN Online:
 Pak. J. Biotechnol. Vol 15 (3) 855-864 (2018) ISSN Print: 1812-1837 www.pjbt.org ISSN Online: 2312-7791 Review THE STERATEGIC ROLE OF FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR-21IN OBESITY Mir Hassan Khoso 1, Meng Fanrui
Pak. J. Biotechnol. Vol 15 (3) 855-864 (2018) ISSN Print: 1812-1837 www.pjbt.org ISSN Online: 2312-7791 Review THE STERATEGIC ROLE OF FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR-21IN OBESITY Mir Hassan Khoso 1, Meng Fanrui
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Effect of Immune Challenge on Different Genotypes: How Sick Do They Get?
 Introduction Effect of Immune Challenge on Different Genotypes: How Sick Do They Get? M.T. Leininger, C.P. Portocarrero, C.A. Bidwell, M.E. Spurlock, J.N. Nielsen, and K.L. Houseknecht Department of Animal
Introduction Effect of Immune Challenge on Different Genotypes: How Sick Do They Get? M.T. Leininger, C.P. Portocarrero, C.A. Bidwell, M.E. Spurlock, J.N. Nielsen, and K.L. Houseknecht Department of Animal
FGF21 Reverses Hepatic Steatosis, Increases Energy Expenditure and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-induced Obese Mice
 Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 7, 2008 FGF21 Reverses Hepatic Steatosis, Increases Energy Expenditure and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-induced Obese Mice Jing Xu (Ph.D.)
Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 7, 2008 FGF21 Reverses Hepatic Steatosis, Increases Energy Expenditure and Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-induced Obese Mice Jing Xu (Ph.D.)
FOR REVIEW. BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission. Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: BMB
 BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
Pelagia Research Library
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2014, 5(3): 32-36 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Study of the effect of ethanolic extract of Solanum xanthocarpum schrad &
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Der Pharmacia Sinica, 2014, 5(3): 32-36 ISSN: 0976-8688 CODEN (USA): PSHIBD Study of the effect of ethanolic extract of Solanum xanthocarpum schrad &
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Activités scientifiques
 Prof. Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud Activités scientifiques I. A role for adipose tissue de novo lipogenesis in glucose homeostasis during catch-up growth: A Randle cycle favoring fat storage Catch-up growth
Prof. Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud Activités scientifiques I. A role for adipose tissue de novo lipogenesis in glucose homeostasis during catch-up growth: A Randle cycle favoring fat storage Catch-up growth
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat
 A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Transcriptional Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Expression
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:105-111 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.2.105 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Transcriptional Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Expression Kwi-Hyun
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2014;29:105-111 http://dx.doi.org/10.3803/enm.2014.29.2.105 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 Transcriptional Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Expression Kwi-Hyun
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans
 Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 5, 2008 Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans Xinmei Zhang 1,2 *
Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 5, 2008 Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans Xinmei Zhang 1,2 *
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism
 Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Charalambous et al. 10.1073/pnas.1406119111 SI Experimental Procedures Serum and Tissue Biochemistry. Enzymatic assay kits were used for determination of plasma FFAs (Roche), TAGs
Supporting Information Charalambous et al. 10.1073/pnas.1406119111 SI Experimental Procedures Serum and Tissue Biochemistry. Enzymatic assay kits were used for determination of plasma FFAs (Roche), TAGs
Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and New-Onset Metabolic Syndrome: KoGES-ARIRANG Study
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2018 Mar;59(2):287-293 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and New-Onset Metabolic Syndrome: KoGES-ARIRANG Study Jung Ran Choi 1, Jang-Young
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2018 Mar;59(2):287-293 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and New-Onset Metabolic Syndrome: KoGES-ARIRANG Study Jung Ran Choi 1, Jang-Young
The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family is composed
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Serum FGF1 Levels Are Increased in Obesity and Are Independently Associated With the Metabolic Syndrome in Humans Xinmei Zhang, 1, Dennis C.Y. Yeung, 1, Michal Karpisek, 3 David Stejskal,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Serum FGF1 Levels Are Increased in Obesity and Are Independently Associated With the Metabolic Syndrome in Humans Xinmei Zhang, 1, Dennis C.Y. Yeung, 1, Michal Karpisek, 3 David Stejskal,
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes Prof. Marc Y. Donath
 Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
Inflammation & Type 2 Diabetes 1, MD Chief Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism University Hospital Basel Petersgraben 4 CH-431 Basel, Switzerland MDonath@uhbs.ch Innate immunity as a sensor of metabolic
The Circulating Metabolic Regulator FGF21 Is Induced by Prolonged Fasting and PPARa Activation in Man
 Short Article The Circulating Metabolic Regulator FGF21 Is Induced by Prolonged Fasting and PPARa Activation in Man Cecilia Gälman, 1,5 Tomas Lundåsen, 1,5 Alexei Kharitonenkov, 3 Holly A. Bina, 3 Mats
Short Article The Circulating Metabolic Regulator FGF21 Is Induced by Prolonged Fasting and PPARa Activation in Man Cecilia Gälman, 1,5 Tomas Lundåsen, 1,5 Alexei Kharitonenkov, 3 Holly A. Bina, 3 Mats
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]
![TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1] TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]](/thumbs/89/99233308.jpg) ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
Kenneth, King-yip CHENG (Assistant Professor)
 Kenneth, King-yip CHENG (Assistant Professor) QUALIFICATIONS: 2003 2009 BSc (Hons) Biochemistry, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology PhD, Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong
Kenneth, King-yip CHENG (Assistant Professor) QUALIFICATIONS: 2003 2009 BSc (Hons) Biochemistry, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology PhD, Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong
University of California, San Diego La Jolla CA 92093
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
mir-577 inhibits pancreatic β-cell function and survival by targeting fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) in pediatric diabetes
 mir-577 inhibits pancreatic β-cell function and survival by targeting fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) in pediatric diabetes X.Y. Chen 2, G.M. Li 1, Q. Dong 1,2 and H. Peng 1,3 1 Pediatric Department,
mir-577 inhibits pancreatic β-cell function and survival by targeting fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF-21) in pediatric diabetes X.Y. Chen 2, G.M. Li 1, Q. Dong 1,2 and H. Peng 1,3 1 Pediatric Department,
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents
 Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Regulates PPARg Activity and the Antidiabetic Actions of Thiazolidinediones
 Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Regulates PPARg Activity and the Antidiabetic Actions of Thiazolidinediones Paul A. Dutchak, 1 Takeshi Katafuchi, 2 Angie L. Bookout, 2,3 Jang Hyun Choi, 5 Ruth T. Yu, 6 David
Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Regulates PPARg Activity and the Antidiabetic Actions of Thiazolidinediones Paul A. Dutchak, 1 Takeshi Katafuchi, 2 Angie L. Bookout, 2,3 Jang Hyun Choi, 5 Ruth T. Yu, 6 David
University of Groningen. Adipose tissue Nies, Vera
 University of Groningen Adipose tissue Nies, Vera IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below.
University of Groningen Adipose tissue Nies, Vera IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below.
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Data. (continued)
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Gating strategy for Figure 1. Splenocytes were gated for dimension and for positivity to the different markers representing different cell populations. (A) B cells,
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Gating strategy for Figure 1. Splenocytes were gated for dimension and for positivity to the different markers representing different cell populations. (A) B cells,
Daniel Cuevas-Ramos* and Carlos A. Aguilar-Salinas Modulation of energy balance by fibroblast growth factor 21
 Horm Mol Biol Clin Invest 2016; aop Daniel Cuevas-Ramos* and Carlos A. Aguilar-Salinas Modulation of energy balance by fibroblast growth factor 21 DOI 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0023 Received April 13, 2016; accepted
Horm Mol Biol Clin Invest 2016; aop Daniel Cuevas-Ramos* and Carlos A. Aguilar-Salinas Modulation of energy balance by fibroblast growth factor 21 DOI 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0023 Received April 13, 2016; accepted
Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3 Huating Li, 1,2 Zhanguo Gao, 3 Jin Zhang, 3 Xin Ye, 3 Aimin Xu, 4,5
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Butyrate Stimulates Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Liver by Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase 3 Huating Li, 1,2 Zhanguo Gao, 3 Jin Zhang, 3 Xin Ye, 3 Aimin Xu, 4,5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. By: Jose Vega. Copyright May 2016, Jose Vega and Koni Stone
 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease By: Jose Vega Copyright May 2016, Jose Vega and Koni Stone Millions of people worldwide are diagnosed with diabetes, as it is one of the most common diseases
Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease By: Jose Vega Copyright May 2016, Jose Vega and Koni Stone Millions of people worldwide are diagnosed with diabetes, as it is one of the most common diseases
Understanding the Physiology of FGF21
 ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides Navigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev.
ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides Navigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
IL METABOLISMO EPATICO DEI CARBOIDRATI IN FISIOLOGIA E PATOLOGIA
 UNIGASTRO Il fegato come centrale metabolica e i fattori di danno oltre ai virus epatitici IL METABOLISMO EPATICO DEI CARBOIDRATI IN FISIOLOGIA E PATOLOGIA Dr Elisabetta Bugianesi Divisione di Gastro-Epatologia
UNIGASTRO Il fegato come centrale metabolica e i fattori di danno oltre ai virus epatitici IL METABOLISMO EPATICO DEI CARBOIDRATI IN FISIOLOGIA E PATOLOGIA Dr Elisabetta Bugianesi Divisione di Gastro-Epatologia
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Fat and HIV persistence, role of fat metabolism and inflammation
 NIDDK Workshop Obesity and Fat Metabolism in HIV infected individuals Rockville, MD May 22-23, 2018 Centro de Investigación Biomédica En Red Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición Fat and HIV persistence,
NIDDK Workshop Obesity and Fat Metabolism in HIV infected individuals Rockville, MD May 22-23, 2018 Centro de Investigación Biomédica En Red Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición Fat and HIV persistence,
Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5
 Dec 8, 2015 Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5 1 Functional Food & Nutrition Division, National Institute of Agricultural Science, 2 Seoul Women s Univ, 3 Eulji
Dec 8, 2015 Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5 1 Functional Food & Nutrition Division, National Institute of Agricultural Science, 2 Seoul Women s Univ, 3 Eulji
Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the. Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Expanded View Figures
 Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Supplemental Information. FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating. Antibody Act on the Nervous System. to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
