The corrected Figure S1J is shown below. The text changes are as follows, with additions in bold and deletions in bracketed italics:
|
|
|
- Darleen James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Correction H3K4me3 readth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency érénice A. enayoun, Elizabeth A. Pollina, Duygu Ucar, Salah Mahmoudi, Kalpana Karra, Edith D. Wong, Keerthana Devarajan, Aaron C. Daugherty, Anshul. Kundaje, Elena Mancini, enjamin C. Hitz, Rakhi Gupta, Thomas A. Rando, Julie C. aker, Michael P. Snyder, J. Michael Cherry, and Anne runet* *Correspondence: (Cell 158, , July 31, 214) Our paper reported that broad H3K4me3 domains in a given cell type are associated with genes that are important for the identity/function of that cell type and that they are associated with increased transcriptional consistency, but not increased expression. It has come to our attention that we made a programming error in the code used to generate Figure S1J. When the code is corrected, the top 5% broadest H3K4me3 domains display a statistically significant increased expression compared to the rest of the distribution (see corrected Figure S1J below). In addition, if one uses the rank-based Spearman correlation instead of the Pearson correlation we had used, H3K4me3 breadth exhibits a positive correlation with gene expression. Thus, the correct conclusion is that broad H3K4me3 domains are, on average, more expressed than non-broad H3K4me3 domains. This error does not affect our conclusions that H3K4me3 breadth is associated with cell identity and transcriptional consistency. However, we acknowledge that the increased transcriptional consistency of genes marked by broad H3K4me3 domains could be due to their increased average expression, as normalized transcriptional variability and average expression have been observed to be anti-correlated. The corrected Figure S1J is shown below. The text changes are as follows, with additions in bold and deletions in bracketed italics: Summary: Indeed, genes marked by the broadest H3K4me3 domains exhibit enhanced transcriptional consistency and [rather than] increased transcriptional levels. Page 674, second paragraph of Results: H3K4me3 breadth quantiles did not linearly correlate with mrna levels (Figures 1D and 1E, Pearson correlation). However, H3K4me3 breadth showed positive rank correlation with mrna levels (R , Spearman correlation). In addition, the top 5% broadest H3K4me3 domains were more highly expressed on average compared to the rest of the distribution (Figure S1J) [even when comparing the most extreme example to the rest of the distribution (Figure S1J)]. Thus, broad H3K4me3 domains are present in many cell types across taxa but cannot be explained as simple readouts of promoter complexity [or high expression levels]. Figure 1 title: readth Is an Evolutionarily Conserved Feature [that Is Not Predictive of Expression Levels] After we identified this programming error, we had the entire manuscript and lines of code independently scrutinized. This process identified the following inadvertent errors that do not affect our conclusions but that we would like to correct. In Figures 1E and S6A, there was an incorrect attribution of datasets (C2C12 myotubes for myoblasts and H1 hesc population for single cells). The corrected Figures 1E and S6A are shown below. The conclusions are not changed. In Figures 7D, 7E, 7G, and S7L, the statistical analyses were done using two different tests (one-sided one-sample and one-sided two-sample Wilcoxon tests), but only one set of p values was reported in the original panels, and the corresponding statistical tests were not appropriately described. Results from both tests are shown in updated Figures 7D, 7E, 7G, and S7L. Upper p values (7D, 7G), black lines (7E, S7L): one-sided two-sample Wilcoxon tests for increased variability between genes with maintained versus changed H3K4me3 breath. Lower p values (7D, 7G), gray lines (7E, S7L): one-sided one-sample Wilcoxon tests for increased variability between genes with changed H3K4me3 breadth versus the expectation of no change in variability. The overall conclusions are not changed. Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc. 1281
2 We sincerely regret these errors and apologize for any inconvenience they may have caused. We would also like to thank Wei Li and Kaifu Chen from the aylor College of Medicine for alerting us to the discrepancy between the Pearson and Spearman correlation results and for helping us to identify the error in Figure S1J. A Distribution of H3K4me3 ChIP-seq peaks in Distribution of H3K4me3 ChIP-seq peaks in C2C12 myotubes Number of ChIP-seq peaks (Density of distribution) chr kb chr11 63,755, 63,76, 63,765, 86 chr9 11,25, 11,255, 2 OTU1 1,635, 1,64, 1,645, ZIC2 KLF H3K4me3 breadth (kb) C H3K4me3 signal around transcription start sites Number of ChIP-seq peaks (Density of distribution) chr17 34,255, H3K4me3 breadth (kb) Metazoans Metaphytes Fungi Mammals Human Mouse D. melanogaster C. elegans A. thaliana S. cerevisiae HeLa-S3 C2C12 myotubes S2 cells Embryos Leaves Cells chr7 1 1 kb chr7 134,515, 134,525, 1 Zfp747 74,51, 74,52, Mef2a 34,265, rd2 H3K4me3 domain breadth -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb -5kb +5kb D H3K4me3 breadth and mrna levels () mrna levels (FPKM) % broad H3K4me3 domains Cell population R ~ Single cells 1-7 R ~ E H3K4me3 breadth and mrna levels (C2C12 myoblasts) mrna levels (FPKM) % broad H3K4me3 domains Cell population Single cells R ~ R ~ Figure 1. H3K4me3 readth Is an Evolutionarily Conserved Feature 1282 Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc.
3 A C D E F G H Figure 7. Experimental Perturbation of H3K4me3 readth Results in Changes to Transcriptional Consistency Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc. 1283
4 chr16 1M 5M M 5M M M M 5M M M 1M 5M M M A Skewness of breadth distribution H. sapiens (99) Skewed distribution.4 Symmetric distribution M. musculus (74) E MACS2 HOMER QuEST CCAT Liver one marrow Myotubes HOMER.947 QuEST C Read density and breadth () 95th percentile Read density per bp of MACS peak (tag per bp) H3K4me3 breadth quantile Spearman rank correlation of H3K4me3 breadth CCAT SICER chr17 chr15 chr18 5M M chr19 5M M M 5M D Read density per bp of MACS peak (tag per bp) chr2 M 5M M Read density and breadth (C2C12 myotubes) 95th percentile M 5M chr21 chr M chrx 5M H3K4me3 breadth quantile F Genomic localization in 1M 15M chry 5M chr1 1M 15M 2M M 5M chr2 Top 5% broadest H3K4me3 domains 1M 15M 2M M 5M 1M chr3 15M M 5M 1M 15M 5M 1M 15M chr4 chr all pairs correlated with p < 2.2E-38 chr14 1M 5M M 1M 15M M 5M 1M chr6 chr13 5M 1M 5M M 15M chr12 M 1M 5M M 1M 5M 1M 5M M 1M 5M chr8 chr11 chr7 G H3K4me3 breadth and gene length H -95% broad H3K4me3 domains I Associated gene length (kb) H3K4me3 breadth and TSS usage from PolII-ChIP Number of PolII peaks % broad H3K4me3 domains A GM HeLa-S HepG2 1 C2C12 myotubes K S2 cells Number of TSSs J H3K4me3 breadth and TSS usage from RNA-seq 5 ends -95% broad H3K4me3 domains H3K4me3 breadth and mrna levels Median normalized mrna levels (A.U.) H9 hescs A GM % broad H3K4me3 domains H9 hescs A549 GM HeLa-S3 1 chr1 3 6 chr9 HepG K562 1 C. el Embryos S2 cells E E E E-1 1.6E E-7 4.2E E E E-1 6.4E-7 1.2E-12 HeLa-S3 HepG2 K562 C2C12 C. el Embryos S2 cells NPCs Figure S1. road H3K4me3 Stretches Are Present in Different Cell Types and Organisms but Are Independent of Signal Intensity, Promoter Architecture, Gene Length, and Genomic Location, Related to Figure Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc.
5 A Scaled log1(p value) for low transcriptional variability H3K4me3 breadth and transcriptional variability (single cells) LNCaP MCF 7 HCT 116 C2C12 myoblasts MEFs H3K4me3 domain breadth quantile (%) Intensity quantile (%) Transcriptional variability (cell populations, continued from Fig. 6C) -95% broad H3K4me3 domains C Transcriptional variability (cell populations) Scaled and normalized expression variance between replicates(a.u.) E-97 HUVECs 2.E E E E E E 51 MEFs C2C12 Myoblasts C2C12 Myotubes CH12 Kc167 A. thaliana leaves Scaled and normalized expression variance between replicates(a.u.) E 9 8.9E 23-95% broad H3K4me3 domains after exclusion of bivalent/poised genes Top 5% broadest H3K4me3 domains after exclusion of bivalent/poised genes D Transcriptional variability (cell populations) E H3K4me3 breadth and transcriptional consistency (cell populations, nascent RNA) Nornalized mean scaled variance of genes in sample set (A.U.) Signal-matched H3K4me3 promoters (N=1, samples) 1.1E 49 9.E 126 Scaled log1(p value) for low transcriptional variability IMR C.elegans embryos H3K4me3 domain breadth quantile (%) Intensity quantile (%) Figure S6. H3K4me3 readth Is Associated with Increased Transcriptional Consistency, Related to Figure 6 Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc. 1285
6 A C D E F G H I J K L Figure S7. Effect of H3K4me3 Regulators on H3K4me3 readth and Transcriptional Consistency, Related to Figure Cell 163, , November 19, 215 ª215 Elsevier Inc.
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
H3K4me3 Breadth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency
 H3K4me3 Breadth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency Bérénice A. Benayoun, 1,2,7 Elizabeth A. Pollina, 1,3,7 Duygu Ucar, 1,6,7 Salah Mahmoudi, 1 Kalpana Karra, 1 Edith D. Wong, 1
H3K4me3 Breadth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency Bérénice A. Benayoun, 1,2,7 Elizabeth A. Pollina, 1,3,7 Duygu Ucar, 1,6,7 Salah Mahmoudi, 1 Kalpana Karra, 1 Edith D. Wong, 1
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants
 Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants Gosia Trynka 1-4 *, Cynthia Sandor 1-4 *, Buhm Han 1-4, Han Xu 5, Barbara E Stranger 1,4#, X Shirley Liu 5, and Soumya
Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants Gosia Trynka 1-4 *, Cynthia Sandor 1-4 *, Buhm Han 1-4, Han Xu 5, Barbara E Stranger 1,4#, X Shirley Liu 5, and Soumya
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data
 Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome
 Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq
 Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics 2017 University of Cambridge Overview Peak-calling: identify enriched (signal) regions in ChIP-seq or ATAC-seq
Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics 2017 University of Cambridge Overview Peak-calling: identify enriched (signal) regions in ChIP-seq or ATAC-seq
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression deviation of the genes mapped to gene-wise recurrent mutations in the TCGA breast cancer cohort (top) and the TCGA lung cancer cohort (bottom). For each gene (each pair
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression deviation of the genes mapped to gene-wise recurrent mutations in the TCGA breast cancer cohort (top) and the TCGA lung cancer cohort (bottom). For each gene (each pair
Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos 3, Hui Yang 1, and Guillermo Garcia-Manero 1
 Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1 33,312. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2 # 44,325 # 44,055. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2.
 a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
Inference of Isoforms from Short Sequence Reads
 Inference of Isoforms from Short Sequence Reads Tao Jiang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, Riverside Tsinghua University Joint work with Jianxing Feng and Wei Li
Inference of Isoforms from Short Sequence Reads Tao Jiang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, Riverside Tsinghua University Joint work with Jianxing Feng and Wei Li
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development
 Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Chip Seq Peak Calling in Galaxy
 Chip Seq Peak Calling in Galaxy Chris Seward PowerPoint by Pei-Chen Peng Chip-Seq Peak Calling in Galaxy Chris Seward 2018 1 Introduction This goals of the lab are as follows: 1. Gain experience using
Chip Seq Peak Calling in Galaxy Chris Seward PowerPoint by Pei-Chen Peng Chip-Seq Peak Calling in Galaxy Chris Seward 2018 1 Introduction This goals of the lab are as follows: 1. Gain experience using
The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis
 The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis Chongzhi Zang zang@virginia.edu http://zanglab.com PHS5705: Public Health Genomics March 20, 2017 1 Outline Epigenome: basics review ChIP-seq overview
The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis Chongzhi Zang zang@virginia.edu http://zanglab.com PHS5705: Public Health Genomics March 20, 2017 1 Outline Epigenome: basics review ChIP-seq overview
Computational Modeling of mirna Biogenesis
 Computational Modeling of mirna Biogenesis Brian Caffrey and Annalisa Marsico Abstract Over the past few years it has been observed, thanks in no small part to high-throughput methods, that a large proportion
Computational Modeling of mirna Biogenesis Brian Caffrey and Annalisa Marsico Abstract Over the past few years it has been observed, thanks in no small part to high-throughput methods, that a large proportion
Lung Met 1 Lung Met 2 Lung Met Lung Met H3K4me1. Lung Met H3K27ac Primary H3K4me1
 a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and
 Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
MODULE 4: SPLICING. Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing
 Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis. Lei Zhou
 High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis Lei Zhou (leizhou@ufl.edu) High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis 1. Representation of HTS data. 2. Visualization of HTS data. 3. Discovering genomic
High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis Lei Zhou (leizhou@ufl.edu) High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis 1. Representation of HTS data. 2. Visualization of HTS data. 3. Discovering genomic
Package NarrowPeaks. August 3, Version Date Type Package
 Package NarrowPeaks August 3, 2013 Version 1.5.0 Date 2013-02-13 Type Package Title Analysis of Variation in ChIP-seq using Functional PCA Statistics Author Pedro Madrigal , with contributions
Package NarrowPeaks August 3, 2013 Version 1.5.0 Date 2013-02-13 Type Package Title Analysis of Variation in ChIP-seq using Functional PCA Statistics Author Pedro Madrigal , with contributions
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data. Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016
 Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
mirna-guided regulation at the molecular level
 molecular level Hervé Seitz IGH du CNRS, Montpellier, France March 3, 2016 microrna target prediction . microrna target prediction mirna: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN 3 NNNNNN the seed microrna target
molecular level Hervé Seitz IGH du CNRS, Montpellier, France March 3, 2016 microrna target prediction . microrna target prediction mirna: target: 2 7 5 N NNNNNNNNNNNNNN 3 NNNNNN the seed microrna target
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD,
 Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Histone Modifications Are Associated with Transcript Isoform Diversity in Normal and Cancer Cells
 Histone Modifications Are Associated with Transcript Isoform Diversity in Normal and Cancer Cells Ondrej Podlaha 1, Subhajyoti De 2,3,4, Mithat Gonen 5, Franziska Michor 1 * 1 Department of Biostatistics
Histone Modifications Are Associated with Transcript Isoform Diversity in Normal and Cancer Cells Ondrej Podlaha 1, Subhajyoti De 2,3,4, Mithat Gonen 5, Franziska Michor 1 * 1 Department of Biostatistics
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq. John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory
 Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
Figure S1, Beyer et al.
 Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
REVIEWERS' COMMENTS: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Editorial Note: this manuscript has been previously reviewed at another journal that is not operating a transparent peer review scheme. This document only contains reviewer comments and rebuttal letters
Editorial Note: this manuscript has been previously reviewed at another journal that is not operating a transparent peer review scheme. This document only contains reviewer comments and rebuttal letters
Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder Labs August 30, 2012
 Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf. Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016
 Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
ChIP-seq analysis. J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand
 ChIP-seq analysis J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand Tuesday : quick introduction to ChIP-seq and peak-calling (Presentation + Practical session)
ChIP-seq analysis J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand Tuesday : quick introduction to ChIP-seq and peak-calling (Presentation + Practical session)
Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data
 Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data Haipeng Xing, Yifan Mo, Will Liao, Michael Q. Zhang Clayton Davis and Geoffrey
Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data Haipeng Xing, Yifan Mo, Will Liao, Michael Q. Zhang Clayton Davis and Geoffrey
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Inferring Biological Meaning from Cap Analysis Gene Expression Data
 Inferring Biological Meaning from Cap Analysis Gene Expression Data HRYSOULA PAPADAKIS 1. Introduction This project is inspired by the recent development of the Cap analysis gene expression (CAGE) method,
Inferring Biological Meaning from Cap Analysis Gene Expression Data HRYSOULA PAPADAKIS 1. Introduction This project is inspired by the recent development of the Cap analysis gene expression (CAGE) method,
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING. R. Piazza (MD, PhD) Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca
 NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING R. Piazza (MD, PhD) Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca SANGER SEQUENCING 5 3 3 5 + Capillary Electrophoresis DNA NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING SOLEXA-ILLUMINA
NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING R. Piazza (MD, PhD) Dept. of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca SANGER SEQUENCING 5 3 3 5 + Capillary Electrophoresis DNA NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING SOLEXA-ILLUMINA
EXTENDED DATA FORMATTING GUIDE
 EXTENDED DATA FORMATTING GUIDE Nature paper but are included online within the full-text HTML and at the end of the online PDF. Nature separate panel (for example, see Extended Data Figure 2, panel d)
EXTENDED DATA FORMATTING GUIDE Nature paper but are included online within the full-text HTML and at the end of the online PDF. Nature separate panel (for example, see Extended Data Figure 2, panel d)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information for Ho et al., modencode and ENCODE resources for analysis of metazoan chromatin organization Supplementary Content Supplementary Methods ---------------------------------------------------------
Supplementary Information for Ho et al., modencode and ENCODE resources for analysis of metazoan chromatin organization Supplementary Content Supplementary Methods ---------------------------------------------------------
Reconstruction of enhancer-target networks in 935 samples of human primary cells, tissues and cell lines
 Reconstruction of enhancer-target networks in 935 samples of human primary cells, tissues and cell lines Qin Cao, Christine Anyansi,2, Xihao Hu, Liangliang Xu 3, Lei Xiong 4, Wenshu Tang 3, Myth T.S. Mok
Reconstruction of enhancer-target networks in 935 samples of human primary cells, tissues and cell lines Qin Cao, Christine Anyansi,2, Xihao Hu, Liangliang Xu 3, Lei Xiong 4, Wenshu Tang 3, Myth T.S. Mok
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well
 Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution
 The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution Galit Lev-Maor 1[, Amir Goren 1[, Noa Sela 1[, Eddo Kim 1, Hadas Keren 1, Adi Doron-Faigenboim 2, Shelly Leibman-Barak 3, Tal Pupko 2,
The Alternative Choice of Constitutive Exons throughout Evolution Galit Lev-Maor 1[, Amir Goren 1[, Noa Sela 1[, Eddo Kim 1, Hadas Keren 1, Adi Doron-Faigenboim 2, Shelly Leibman-Barak 3, Tal Pupko 2,
Yingying Wei George Wu Hongkai Ji
 Stat Biosci (2013) 5:156 178 DOI 10.1007/s12561-012-9066-5 Global Mapping of Transcription Factor Binding Sites by Sequencing Chromatin Surrogates: a Perspective on Experimental Design, Data Analysis,
Stat Biosci (2013) 5:156 178 DOI 10.1007/s12561-012-9066-5 Global Mapping of Transcription Factor Binding Sites by Sequencing Chromatin Surrogates: a Perspective on Experimental Design, Data Analysis,
Cross species analysis of genomics data. Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets
 02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
Supplemental Materials
 Supplemental Materials Sequence Features and Chromatin Structure around the Genomic Regions Bound by 119 Human Transcription Factors Running title: Analysis of Sites of 119 TFs in the Human Genome Jie
Supplemental Materials Sequence Features and Chromatin Structure around the Genomic Regions Bound by 119 Human Transcription Factors Running title: Analysis of Sites of 119 TFs in the Human Genome Jie
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Immediate late genes decode ERK signal duration Florian Uhlitz et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV. cquired samples from HEK9ΔRF:ER cells. Microarrays - Untreated I +U6-5 6 7
Molecular Systems iology Immediate late genes decode ERK signal duration Florian Uhlitz et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV. cquired samples from HEK9ΔRF:ER cells. Microarrays - Untreated I +U6-5 6 7
Integrated analysis of sequencing data
 Integrated analysis of sequencing data How to combine *-seq data M. Defrance, M. Thomas-Chollier, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, J. van Helden *ChIP-seq, RNA-seq, MeDIP-seq, Transcription factor binding ChIP-seq
Integrated analysis of sequencing data How to combine *-seq data M. Defrance, M. Thomas-Chollier, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, J. van Helden *ChIP-seq, RNA-seq, MeDIP-seq, Transcription factor binding ChIP-seq
TITLE: The Role Of Alternative Splicing In Breast Cancer Progression
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0598 TITLE: The Role Of Alternative Splicing In Breast Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Klemens J. Hertel, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0598 TITLE: The Role Of Alternative Splicing In Breast Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Klemens J. Hertel, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells
 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
Intragenic Enhancers Act as Alternative Promoters
 Article Monika S. Kowalczyk,,6 Jim R. Hughes,,6 David Garrick,,7 Magnus D. Lynch,,7 Jacqueline A. Sharpe, Jacqueline A. Sloane-Stanley, Simon J. McGowan, 2 Marco De Gobbi, Mona Hosseini, 3 Douglas Vernimmen,
Article Monika S. Kowalczyk,,6 Jim R. Hughes,,6 David Garrick,,7 Magnus D. Lynch,,7 Jacqueline A. Sharpe, Jacqueline A. Sloane-Stanley, Simon J. McGowan, 2 Marco De Gobbi, Mona Hosseini, 3 Douglas Vernimmen,
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data
 Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data Supplementary Note 1: SCnorm does not require spike-ins, since we find that the performance of spike-ins in scrna-seq is often compromised,
Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data Supplementary Note 1: SCnorm does not require spike-ins, since we find that the performance of spike-ins in scrna-seq is often compromised,
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis. Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford
 Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19357 Figure 1a Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔSL Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔL E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19357 Figure 1a Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔSL Chd8 +/+ Chd8 +/ΔL E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E10.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole brain E14.5_Whole
REACTIN: Regulatory activity inference of transcription factors underlying human diseases with application to breast cancer
 Zhu et al. BMC Genomics 2013, 14:504 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access REACTIN: Regulatory activity inference of transcription factors underlying human diseases with application to breast cancer Mingzhu
Zhu et al. BMC Genomics 2013, 14:504 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access REACTIN: Regulatory activity inference of transcription factors underlying human diseases with application to breast cancer Mingzhu
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: f-i
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: Comparisons of the biological replicates of ChIP-seq, Input and Bisulfite-seq. (a) Density plot of MeCP2 ChIP-seq genome coverage (calculated using tiled 15 bp windows) shows high
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1: Comparisons of the biological replicates of ChIP-seq, Input and Bisulfite-seq. (a) Density plot of MeCP2 ChIP-seq genome coverage (calculated using tiled 15 bp windows) shows high
Recruitment of HBO1 Histone Acetylase and Blocks
 Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
Molecular Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information JNK1 Phosphorylation of Cdt1 Inhibits Recruitment of HO1 Histone cetylase and locks Replication Licensing in Response to Stress enoit Miotto and Kevin
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supporting Information
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
Constitutive AP-1 Activity and EBV Infection Induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin. Lymphomas and Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders:
 Constitutive AP-1 Activity and EBV Infection Induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin Lymphomas and Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Implications for Targeted Therapy Running title: AP-1 Activity and EBV
Constitutive AP-1 Activity and EBV Infection Induce PD-L1 in Hodgkin Lymphomas and Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders: Implications for Targeted Therapy Running title: AP-1 Activity and EBV
Additional file: Cell cycle, oncogenic and tumor suppressor pathways regulate numerous long and macro non-protein coding RNAs
 Additional file: Cell cycle, oncogenic and tumor suppressor pathways regulate numerous long and macro non-protein coding RNAs February 6, 2014 Jö rg Hackermü ller 1,2,,, Kristin Reiche 1,2,,, Christian
Additional file: Cell cycle, oncogenic and tumor suppressor pathways regulate numerous long and macro non-protein coding RNAs February 6, 2014 Jö rg Hackermü ller 1,2,,, Kristin Reiche 1,2,,, Christian
Supplemental Information. Genomic Characterization of Murine. Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription. Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells
 Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Alternative splicing. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6
 Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11243 Supplementary Table of Contents I. Supplementary Methods II. III. IV. Supplementary References Supplementary Figures Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Number of uniquely
doi:10.1038/nature11243 Supplementary Table of Contents I. Supplementary Methods II. III. IV. Supplementary References Supplementary Figures Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Number of uniquely
The Emergence of Alternative 39 and 59 Splice Site Exons from Constitutive Exons
 The Emergence of Alternative 39 and 59 Splice Site Exons from Constitutive Exons Eli Koren, Galit Lev-Maor, Gil Ast * Department of Human Molecular Genetics, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University,
The Emergence of Alternative 39 and 59 Splice Site Exons from Constitutive Exons Eli Koren, Galit Lev-Maor, Gil Ast * Department of Human Molecular Genetics, Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures.8 57 essential gene density 2 1.5 LTR insert frequency diversity DEL.5 DUP.5 INV.5 TRA 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Locations and minor
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures.8 57 essential gene density 2 1.5 LTR insert frequency diversity DEL.5 DUP.5 INV.5 TRA 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Locations and minor
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Sudin Bhattacharya Institute for Integrative Toxicology
 Beyond the AHRE: the Role of Epigenomics in Gene Regulation by the AHR (or, Varied Applications of Computational Modeling in Toxicology and Ingredient Safety) Sudin Bhattacharya Institute for Integrative
Beyond the AHRE: the Role of Epigenomics in Gene Regulation by the AHR (or, Varied Applications of Computational Modeling in Toxicology and Ingredient Safety) Sudin Bhattacharya Institute for Integrative
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data
 Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003
 NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
NEUROBLASTOMA DATA -- TWO GROUPS -- QUANTITATIVE MEASURES 38 15:37 Saturday, January 25, 2003 Obs GROUP I DOPA LNDOPA 1 neurblst 1 48.000 1.68124 2 neurblst 1 133.000 2.12385 3 neurblst 1 34.000 1.53148
Exploring DNA methylation changes in promoter, intragenic, and intergenic regions as early and late events in breast cancer formation
 Rauscher et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:816 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1777-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Exploring DNA methylation changes in promoter, intragenic, and intergenic regions as early and late events
Rauscher et al. BMC Cancer (2015) 15:816 DOI 10.1186/s12885-015-1777-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Exploring DNA methylation changes in promoter, intragenic, and intergenic regions as early and late events
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 1 7 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4460-x Table S1 Human paired-end RNA-Seq data sets from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database Experiment
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 1 7 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4460-x Table S1 Human paired-end RNA-Seq data sets from the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database Experiment
Large-Scale Discovery of Enhancers from Human Heart Tissue
 Large-Scale Discovery of Enhancers from Human Heart Tissue Dalit May, Matthew J. Blow, Tommy Kaplan, David J. McCulley, Brian C. Jensen, Jennifer A. Akiyama, Amy Holt, Ingrid Plajzer-Frick, Malak Shoukry,
Large-Scale Discovery of Enhancers from Human Heart Tissue Dalit May, Matthew J. Blow, Tommy Kaplan, David J. McCulley, Brian C. Jensen, Jennifer A. Akiyama, Amy Holt, Ingrid Plajzer-Frick, Malak Shoukry,
STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN
 Statistics 1 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN These are subjects that are frequently confused. Both subjects often evoke student anxiety and avoidance. To further complicate matters, both areas appear have
Statistics 1 STATISTICS AND RESEARCH DESIGN These are subjects that are frequently confused. Both subjects often evoke student anxiety and avoidance. To further complicate matters, both areas appear have
The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs6983267 at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling Sari Tuupanen 1, Mikko Turunen 2, Rainer Lehtonen 1, Outi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs6983267 at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling Sari Tuupanen 1, Mikko Turunen 2, Rainer Lehtonen 1, Outi
Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection
 Author's response to reviews Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection Authors: Jestinah M Mahachie John
Author's response to reviews Title: A robustness study of parametric and non-parametric tests in Model-Based Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction for epistasis detection Authors: Jestinah M Mahachie John
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
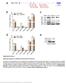 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION. Ana M. Martinez
 NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION Ana M. Martinez Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs can Up-Regulate Translation. Shoba Vasudevan, Yingchun Tong, Joan A. Steitz AU-rich
NOVEL FUNCTION OF mirnas IN REGULATING GENE EXPRESSION Ana M. Martinez Switching from Repression to Activation: MicroRNAs can Up-Regulate Translation. Shoba Vasudevan, Yingchun Tong, Joan A. Steitz AU-rich
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities
 Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
