Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B
|
|
|
- Dennis Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy & Physiology, 10e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: A) D B) A C) C D) B 1) Thoracic cavity. Global LO: G3
2 2) Cranial cavity. Global LO: G3 3) Abdominal cavity. Global LO: G3 4) Vertebral cavity. Global LO: G3 Answers: 1) C 2) B 3) A 4) D
3 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following descriptions to the most appropriate letter on the diagram: A) E B) A C) B D) D E) C 5) Information about body temperature is sent through afferent pathways to the brain. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 6) Free nerve endings in the skin detect changes in skin temperature (getting colder). Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 7) Appropriate response information is sent through efferent pathways. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3
4 8) A change in the temperature of the external environment (getting colder). Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 9) Skeletal muscles respond with shivering reflex which provides heat to return the body's temperature to a homeostatic balance or "ideal" value. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 Answers: 5) E 6) C 7) D 8) B 9) A
5 Match the following systems to their functions: A) Muscular B) Skeletal C) Integumentary D) Nervous 10) Provides the force to move bones about their joints., HAPS5 11) Responds to environmental changes by transmitting electrical impulses., HAPS5 12) Provides a ridged framework to support the body and stores minerals., HAPS5 13) Prevents water loss, entry of germs into the body and synthesizes vitamin D., HAPS5 Answers: 10) A 11) D 12) B 13) C
6 Match the following systems to their functions: A) Lymphatic B) Endocrine C) Immune D) Cardiovascular 14) Controls the body with chemical molecules called hormones., HAPS5 15) Delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues., HAPS5 16) Produces antibodies that attach to foreign substances., HAPS5 17) Removes and filters excess fluid from tissues., HAPS5 Answers: 14) B 15) D 16) C 17) A
7 Match the following examples of feedback mechanisms: A) Negative feedback B) Positive feedback 18) Used for changes in blood glucose levels. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 19) Used for changes in blood pressure. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 20) Used for blood clotting. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 21) Used for childbirth. Learning Outcome: 1.7, 1.8 Global LO: G2, G3, HAPS3 Answers: 18) A 19) A 20) B 21) B
8 Match the following systems and organs: A) Respiratory B) Endocrine C) Digestive D) Urinary E) Cardiovascular 22) Arteries, veins, heart., HAPS5 23) Trachea, bronchi, alveoli., HAPS5 24) Adrenal glands, pancreas, pituitary., HAPS5 25) Esophagus, large intestine, rectum., HAPS5 26) Kidneys, bladder, ureters., HAPS5 Answers: 22) E 23) A 24) B 25) C 26) D
9 Match the following cavities and organs: A) Abdominopelvic B) Cranial C) Thoracic 27) Stomach. 28) Heart. 29) Uterus. 30) Brain. 31) Lungs. Answers: 27) A 28) C 29) A 30) B 31) C
10 Match the following regional terms and common terms: A) Brachial B) Gluteal C) Thoracic D) Patellar E) Cephalic 32) Arm. 33) Buttock. 34) Head. 35) Knee (anterior aspect). 36) Chest. Answers: 32) A 33) B 34) E 35) D 36) C
11 Match the regional/directional terms and examples: A) Proximal B) Anterior C) Distal D) Medial E) Lateral 37) The bridge of the nose is to the left eye. 38) The upper arm is to the forearm. 39) The lungs are to the heart. 40) The fingers are to the wrist. 41) The stomach is to the spine. Answers: 37) D 38) A 39) E 40) C 41) B
12 1.2 True/False Questions 1) Positive feedback mechanisms tend to enhance the original stimulus so that the response is accelerated. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 2) Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) imaging is most useful in discovering obstructed blood supplies in organs and tissues. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: 1.8 Global LO: G9 HAPS LO: HAPS6, HAPS7 3) The elbow is proximal to the shoulder. Answer: FALSE 4) The part of the serous membrane that lines the peritoneal cavity wall is called visceral peritoneum. Answer: FALSE 5) A major function of serous membranes is to decrease friction. Answer: TRUE
13 6) The right hypochondriac region contains the majority of the stomach. Answer: FALSE 7) Lungs carry out an excretory function. Answer: TRUE 8) Embryology concerns the structural changes that occur in an individual from conception through old age. Answer: FALSE Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1 9) A tissue consists of groups of similar cells that have a common function. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: ) It is important for any organism to maintain its boundaries, so that its internal environment remains distinct from the external environment surrounding it. Answer: TRUE Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: 1.5
14 11) Without some sort of negative feedback mechanism, it would be impossible to keep our body chemistry in balance. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 12) Responsiveness or irritability is the ability to sense changes in the environment and then respond to them. Answer: TRUE Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) The epigastric region is superior to the umbilical region. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: 1.13
15 1.3 Multiple Choice Questions 1) Histology would be best defined as a study of. A) tissues B) the gross structures of the body C) cell chemistry D) cells Answer: A Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1 2) The study of large body structures, visible to the naked eye, such as the heart is called anatomy. A) microscopic B) gross C) systemic D) developmental Answer: B Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1 3) Generally what is the result of the negative feedback process? A) to keep the body's blood sugar level high B) to control body movement C) to regulate excretion via the kidneys D) to maintain homeostasis Answer: D Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 4) The coxal joint is most likely found in region of the body. A) hip B) hand C) foot D) groin Answer: A
16 5) A structure that is composed of two or more tissue types that work together to perform specific functions for the body is a(n). A) complex tissue B) organ C) complex cell D) organ system Answer: B Learning Outcome: 1.3, HAPS2 6) A good example of a positive feedback mechanism would be. A) enhancement of labor contractions B) body temperature regulation C) blood calcium level regulation D) regulating glucose levels in the blood Answer: A Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 7) Which of the following organs or structures would be found in the left iliac region? A) liver B) appendix C) intestines D) stomach Answer: C Learning Outcome: ) The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane. A) lining the abdominal cavity B) covering the heart C) covering individual lungs D) lining the thoracic cavity Answer: D
17 9) Which one of the following systems responds fastest to environmental stimuli? A) immune B) lymphatic C) muscular D) nervous Answer: D, HAPS5 10) Choose the anatomical topic and definition that is not correctly matched. A) Cytology: study of the structures in a particular region. B) Microscopic anatomy: study of structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. C) Embryology: study of the changes in an individual from conception to birth. D) Gross anatomy: study of structures visible to the eye. Answer: A Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: ) Homeostasis is the condition in which the body maintains. A) a dynamic state within an unlimited range, depending on circumstances B) a relatively stable internal environment, within limits C) the lowest possible energy usage D) a static state with no deviation from preset points Answer: B Learning Outcome: 1.7, HAPS3 12) In which body cavities are the lungs located? A) pleural, dorsal, and abdominal B) pleural, ventral, and thoracic C) pericardial, ventral, and thoracic D) mediastinal, thoracic, and ventral Answer: B
18 13) Place the following in correct sequence from simplest to most complex: 1. molecules 2. atoms 3. tissues 4. cells 5. organs A) B) C) D) Answer: B Learning Outcome: 1.3, HAPS2 14) Which of the following imaging devices would best localize a tumor in a person's brain? A) PET B) DSA C) MRI D) X ray Answer: C Learning Outcome: Global LO: G9 HAPS LO: HAPS6, HAPS7 15) Which of these is not part of the dorsal cavity? A) spinal cord B) cranial cavity C) thoracic cavity D) vertebral cavity Answer: C 16) In which quadrant of the abdominopelvic cavity is the stomach located? A) left upper quadrant B) right upper quadrant C) right lower quadrant D) left lower quadrant Answer: A
19 Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following statements is the most correct regarding homeostatic imbalance? A) It is considered the cause of most diseases. B) Positive feedback mechanisms are overwhelmed. C) Negative feedback mechanisms are functioning normally. D) The internal environment is becoming more stable. Answer: A Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 18) The term pollex refers to the. A) fingers B) thumb C) great toe D) calf Answer: B 19) The dorsal body cavity is the site of which of the following? A) liver B) brain C) intestines D) lungs Answer: B 20) Select the most correct statement. A) Organ systems can be composed of cells or tissues, but not both. B) The immune system is closely associated with the lymphatic system. C) Organ systems operate independently of each other to maintain life. D) The endocrine system is not a true structural organ system. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 1.3
20 , HAPS2 21) One of the functional characteristics of life is excitability or responsiveness. This refers to. A) the necessity for all organisms to reproduce B) sensing changes in the environment and then reacting or responding to them C) indigestible food residues stimulating the excretory system D) the nervous system causing all living things to sometimes experience anger Answer: B Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following are survival needs of the body? A) nutrients, water, growth, and reproduction B) nutrients, water, atmospheric pressure, and oxygen C) nutrients, water, movement, and reproduction D) water, atmospheric pressure, growth, and movement Answer: B Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) What is a vertical section through the body, dividing it into left and right, called? A) frontal B) transverse C) regional D) sagittal Answer: D 24) What is a vertical section through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior regions called? A) median B) sagittal C) frontal D) transverse Answer: C
21 25) The body cavities that protect the nervous system are located in the cavity. A) ventral B) cranial C) dorsal D) vertebral E) thoracic Answer: C 26) Which of the following describes the operation of the heart and blood vessels? A) systemic anatomy B) cardiovascular anatomy C) cardiovascular physiology D) systemic physiology Answer: C Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: ) It is wise to study anatomy alongside with physiology because. A) it makes for more efficient use of students' and teachers' time B) physiology is only explainable in terms of the underlying anatomy C) anatomy and physiology are practically the same thing D) to understand anatomy requires complete understanding of physiology Answer: B Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 28) The study of anatomy and physiology assumes and describes a healthy body. Select the description below that does NOT explain why this approach is useful. A) Study of a healthy body is less intimidating and more familiar new students. B) A healthy body provides a common standard to compare to. C) A healthy body establishes what "normal" is. D) Study of a healthy body provides a foundation for a more complete understanding of all human bodies.
22 Answer: A Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.2 Bloom's Level: 6 Evaluation 29) One of the descriptions below is from the perspective of anatomical study, the rest are from a physiological perspective. Select the description below that comes from an anatomical perspective. A) The extremely thin tissue (simple squamous epithelium) of the lungs allows for the quick diffusion of respiratory gases into and out of the body. B) The direction of blood flow through the heart is directed by one way valves. C) The cell-to-cell connections between heart (cardiac) muscle cells are strong. They hold the tissue together for a life time of forceful contractions. D) The innermost lining of the lungs is composed primarily of a thin tissue called simple squamous epithelium. Answer: D Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1, HAPS2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 30) One of the descriptions below is from the perspective of physiological study, the rest are from an anatomical perspective. Select the description below that comes from physiological perspective. A) The pancreas lies deep to the stomach within the abdominal cavity. B) The skull is formed by 22 facial and cranial bones. C) The contraction of smooth muscle in blood vessels (vasoconstriction) can reduce the flow of blood through the vessel. D) The chambers of the heart and blood vessels leading to and from the heart are separated by valves composed of fibrous connective tissue. Answer: C Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1, HAPS2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 31) Which of the following is the best explanation for why cells are considered the smallest units of living things. A) Cells are the simplest structure to fit all of the characteristic necessary to be considered alive. B) Cells have the ability to reproduce identical copies of themselves in a process called mitosis. C) Cells are highly ordered and complex. D) Cells cannot be seen with the naked eye and are considered microscopic. Answer: A, 1.3 Learning Outcome: 1.3, 1.5
23 Global LO: G2, HAPS2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 32) Prevention of water loss is a necessary function for life that would best fit in the category of. A) metabolism B) responsiveness C) maintaining boundaries D) excretion Answer: C Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: 1.5 Global LO: G2, HAPS2 33) Anabolic reactions are chemical reactions of the body that build things, make them bigger or more complex. Catabolic reactions break things down making them smaller or less complex. If the rate of anabolic reaction in the body is much faster than the rate of catabolic reactions which of the following necessary life function will be accomplished? A) digestion B) responsiveness C) growth D) movement Answer: C Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: 1.5 Global LO: G2, HAPS2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 34) Anatomical position is important because. A) it allows a common point of reference for body position to help communicate anatomical relationships B) it provides the greatest circulation to the extremities C) it allows diagrams within textbooks to display a greater surface area of the body with one simple diagram D) it is the position most comfortable to hospital patients Answer: A Learning Outcome: 1.10a, HAPS6 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 35) Positive feedback differs from negative feedback because. A) positive feedback is critical to health while negative feedback serves only to alert us to potential health threats
24 B) positive feedback is generally beneficial while negative feedback is typically harmful C) positive feedback tends to enhance the triggering stimulus while negative feedback tends to return the body to a homeostatic balance or "ideal" level D) positive feedback provides moment-to-moment wellbeing while negative feedback causes a cascade effect Answer: C Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 36) When a baby suckles at its mother's breast the stimulus at the breast is sent to the mother's brain (a region called the hypothalamus). The brain responds by releasing hormones to stimulate the production and the ejection of milk from the breast. This helps the newborn to receive nourishment and encourages more suckling. This example is best described as a. A) negative feedback B) necessary life function C) loss of homeostasis D) positive feedback Answer: D Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 37) Some of the nerve endings in the skin are sensitive to changes in temperature. They are part of a negative feedback mechanism regulating body temperature. These nerve endings represent a(n) in the negative feedback mechanism. A) receptor B) control center C) homeostatic balance or "ideal" value D) effector Answer: A Learning Outcome: 1.8, HAPS3 38) You are asked to take a person's heart rate at the popliteal pulse point. You will look for this pulse. A) on the palmar side of the hand B) in the distal end of the lower leg C) on the posterior side of the knee D) at the posterior side of the wrist Answer: C
25 , HAPS6 39) You are told to take an axillary temperature on a small child. You will place the thermometer. A) in the armpit B) in the rectum C) under the tongue D) on the forehead Answer: A, HAPS6 40) You are asked to draw blood from the median cubital vein. You will search for this vein in the. A) lateral side of the foot B) proximal arm C) anterior side of the elbow D) hand Answer: C, HAPS6 41) The thoracic cavity contains the. It is found to the vertebral cavity. A) stomach and liver: superficial B) heart and lungs: anterior C) digestive viscera: inferior D) kidneys and spleen: deep Answer: B Global LO: G2
26 1.4 Short Answer Questions 1) Similar cells that have a common function are called. Answer: tissues Learning Outcome: 1.3 2) What does the "principle of complementarity of structures and function" mean? Answer: What a structure can do depends on its specific form, or "structure determines function." Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.2 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 3) The term that describes the back of the elbow is. Answer: olecranal 4) The term that describes the neck region is. Answer: cervical 5) The heart is to the lungs. Answer: medial 6) is explained by chemical and physical principles and is concerned with the function of specific organs or organic systems. Answer: Physiology Section: 1.1 Learning Outcome: 1.1
27 7) What is a dynamic equilibrium of your internal environment termed? Answer: homeostasis Learning Outcome: 1.8 HAPS LO: HAPS3 8) Which cavity contains the bladder, some reproductive organs, and the rectum? Answer: pelvic 9) What is the serous membrane that covers the intestines called? Answer: visceral peritoneum 10) What broad term covers all chemical reactions that occur within the body cells? Answer: metabolism Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) What is the function of the serous membranes? Answer: They act to reduce friction and allow the organs to slide across cavity walls. 12) Can lungs carry out excretory functions? Explain your answer. Answer: Yes, carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste the lungs excrete., 1.3 HAPS LO: HAPS5
28 13) The ability to sense changes in the environment and respond to them is called. Answer: responsiveness or excitability Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) Why must a normal body temperature be maintained in order for chemical reactions to be continued at life-sustaining rates? Answer: If body temperature is too low, chemical reactions slow and eventually stop. If body temperature is too high, chemical reactions speed up and body proteins lose their normal shape, resulting in loss of function. Section: 1.3 Learning Outcome: ) What is the pathway between the receptor and the control center in the reflex pathway called? Answer: afferent pathway Learning Outcome: ) What type of homeostatic feedback reflex is the withdrawal reflex? Answer: negative Learning Outcome: ) Why are the abdominopelvic cavity organs the most vulnerable to blunt deceleration in an automobile accident with seat belts? Answer: The walls of the abdominal cavity are formed only by trunk muscles and are not reinforced by bone. The pelvic organs receive a somewhat greater degree of protection from the bony pelvis. Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis
29 18) What is the action of all of the negative feedback mechanisms of the body? Answer: They prevent sudden severe changes within the body. Learning Outcome: ) Which feedback mechanism causes the variable to deviate further and further from its original value or range? Answer: positive feedback Learning Outcome: ) What can happen when the usual negative feedback mechanisms are overwhelmed and destructive positive feedback mechanisms take over? Answer: Homeostatic imbalances increase our risk for illness and produce the changes we associate with aging. Learning Outcome: 1.8 Global LO: G2 HAPS LO: HAPS4 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 21) Which body system would be most affected by a lower than normal atmospheric pressure? Answer: respiratory system Global LO: G2 HAPS LO: HAPS4 Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 22) Describe the overlap in function between the cardiovascular system and respiratory system. In other words, describe how they work together. Answer: The blood is provided a consistent supply of oxygen from the lungs while the circulatory system delivers carbon dioxide which will be removed from the body by the respiratory system., HAPS5 Bloom's Level: 5 Synthesis 23) Describe the overlap in function between the muscular system and skeletal system. In other words, describe how they work together. Answer: The skeleton provides the ridged frame work (levers) for muscles to attach to. Muscles
30 provide the force to move the bones about the joints., HAPS5 Bloom's Level: 5 Synthesis 24) The integumentary system helps to maintain a boundary between the internal and external environment. Give an example of something that is prevented entry to the body and an example of something prevented from escaping the body by the integumentary system. Answer: The integument prevents entry of pathogens (germs, viruses, bacteria) OR harmful chemicals. The integumentary system prevents water (body fluid) loss., HAPS5 Bloom's Level: 5 Synthesis 25) Describe the opposing ways that the muscular system and integumentary system act as effectors in the regulation of body temperature. Answer: The integument cools the body through sweat while the muscular system warms the body by shivering., HAPS5 Bloom's Level: 5 Synthesis
31 1.5 Clinical Questions 1) A small family was traveling in its van and had a minor accident. The children in the back seats were wearing lap belts, but still sustained numerous bruises about the abdomen, and had some internal organ injuries. Why is this area more vulnerable to damage than others? Answer: The abdominal organs are the least protected in the body because they are not surrounded by a bony covering such as the ribs, pelvis, or cranium. Bloom's Level: 4 Analysis 2) Steve was injured in a football accident. X-ray examination showed a fracture underlying his left brachial deformity. What part of his body was injured? Answer: His left upper arm 3) The nurse charted: "Patient has an open wound located on lateral aspect of leg." Describe where the wound is located. Answer: The wound is located on the outer side of the leg, the peroneal or fibular area.
Chapter 1. Figure 1.1. Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. Answer: C. 2) Cranial cavity. Answer: A
 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Chapter 1. Figure 1.1. Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. Answer: C. 2) Cranial cavity. Answer: A
 Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Chapter 1 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following
Figure 1.2. Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5) Umbilical region. Answer: C. 6) Right hypochondriac. Answer: B
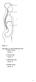 Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following cavities: 1) Thoracic cavity. 2) Cranial cavity. 3) Abdominal cavity. 4) Vertebral cavity. 1 Figure 1.2 Using Figure 1.2, match the following regions: 5)
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13
 CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
CHAPTER 1: THE HUMAN BODY A & P 8/20/13 ANATOMY The study of the Structure and Shapes of the body and their relationships to one another. Gross Anatomy: The study of large easily observable structures
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
Ch 1.1 An Overview of Anatomy and Physiology The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology Study of how the body and its parts work or function
The Human Body: An Orientation
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts Physiology
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
The HUMAN BODY. Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY
 The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
The HUMAN BODY Concepts of ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY 1 1 ANATOMY The scientific study of structures and the relationship of structures to each other. FORM Other terms include shape, structure, and appearance.
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed.
 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (Chapter 1) Notes for these slides can be printed. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth, and the hottest on record, with temperatures
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Anatomy & Physiology. Next >> COURSE 1 MODULE 1
 Anatomy & Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology course introduces the structure and function of the human body. You will read about the cells, tissues and membranes that make up our bodies and how our
Anatomy & Physiology The Anatomy and Physiology course introduces the structure and function of the human body. You will read about the cells, tissues and membranes that make up our bodies and how our
Systemic The study of anatomy by body systems
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
NOSE GOES. What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent?
 1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
The Human Body: An Orientation Activity Booklet Name: Per: #: Label the following diagram with the levels of structural organization and the examples of each: 1 Identify the following body systems and
1. Define Anatomy and Physiology-
 Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
8/27/2017. The Human Body: An Orientation. Homeostasis BODY SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER TO MAINTIN HOMEOSTASIS. Chapter 1 Part B
 Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
 Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms
 1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
1 Lesson 1.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Use the terms listed below to fill in the sentence blanks. abdominal cavity cavity nasal cavity posterior (dorsal) body abdominopelvic cavity cranial cavity
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I: INTRO & FEEDBACK LOOPS What is anatomy and physiology? Anatomy Describes the structures of the body: what they are made of, where they are located associated
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
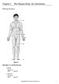 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Anatomy Physiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Then think about these: Check your Packet- three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last?
 Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
Chapter 1 Check your Packet- Then think about these: 1. If a doctor gives your three pills and tells you to take one pill every half hour, how long will they last? 2. Mrs. Smith has 5 children. Half of
