Rice in vivo RNA structurome reveals RNA secondary structure conservation and divergence in plants
|
|
|
- Evan Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rice in vivo RN structurome reveals RN secondary structure conservation and divergence in plants Hongjing Deng 1,2,,5, Jitender heema 3, Hang Zhang 2, Hugh Woolfenden 2, Matthew Norris 2, Zhenshan Liu 2, Qi Liu 2, Xiaofei Yang 2, Minglei Yang 2, Xian Deng 1, Xiaofeng ao 1,5, Yiliang Ding 2,5 1 State Key Laboratory of Plant enomics and National enter for Plant ene Research, S enter for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences, Institute of enetics and Developmental Biology, hinese cademy of Sciences. Beijing 111, hina 2 Department of ell and Developmental Biology, John Innes entre, Norwich Research Park, Norwich NR 7H, nited Kingdom 3 Department of omputational and Systems Biology, John Innes entre, Norwich Research Park, Norwich NR 7H, nited Kingdom ollege of Life Sciences, niversity of hinese cademy of Sciences, 19, Beijing, hina 5 S-JI entre of Excellence for Plant and Microbial Science (EPMS), John Innes entre, Norwich NR 7H, nited Kingdom orresponding author: X.. (xfcao@genetics.ac.cn) or Y.D. (yiliang.ding@jic.ac.uk). Running title: RN secondary structurome in rice 1
2 15 min DMS - % ddt dd dd dd () () () () Lane
3 Supplemental Figure 1 Preliminary experiment for optimizing concentration of DMS treatment. The fragment from nt to 1 33 nt of 18S rrn was analyzed. Lanes 1-5:,.75, 1.5, 2.5, % (v/v) DMS concentration, respectively, for 15 min at 28 ; lanes 6 to 9: /// sequencing lanes. The red and blue stars show the obviously modified and in concentration course, respectively.
4 B DMS S Reactivity DMS - + P =.6 P = 5.57E S Lane P =.89 P < 2.2E Relative DMS reactivity el reactivity Nucleotide position Reactivity Nucleotide position Lane Relative DMS reactivity el reactivity
5 Supplemental Figure 2 High agreement between Structure-seq and conventional gel-based RN secondary structure probing. () Left: gel-based probing. Right: the comparison of Structure-seq (purple bars) and gel-based probing (orange line) from nt to 1 3 nt of 18S rrn. (B) Left: gel-based probing. Right: the comparison of Structure-seq (purple bars) and gel-based probing (orange line) from 156 nt to 253 nt of 25S rrn. Lane 1 and 2, without and with 2.5% DMS treatment; lane 3 to 6, /// sequencing lanes. The positions of each well-visible and are coloured by red and blue stars, respectively. P and P values were shown in the corresponding region.
6 B F1 score Sensitivity P = PPV 75 1 D PPV F1 score Sensitivity P = P = PPV 75 1 P = PPV 75 1
7 Supplemental Figure 3 High correlation of PPV with sensitivity and F1 score. ()-(B) orrelation of PPV with sensitivity () and F1 score (B) in rice. Both P values are less than 2.2E-16. ()-(D) orrelation of PPV with sensitivity () and F1 score (D) in rabidopsis. Both P values are less than 2.2E-16.
8 ini index DMS reactivity DMS reactivity DMS reactivity DMS reactivity DMS reactivity. P = 2.118E- P < 2.2E B 5 TR DS... DS 3 TR Position Position Spliced events nspliced events end of 5 exon 5 end of 3 exon Position 5 splice site 3 splice site Position D E 5 5 TR DS 3 TR 3 3 Magnitude Period (nucleotide) Magnitude Period (nucleotide) High - 5 TR High - DS High - 3 TR Low - 5 TR Low - DS Low - 3 TR Magnitude Period (nucleotide) High - 5 TR High - DS High - 3 TR Low - 5 TR Low - DS Low - 3 TR F P < 2.2E-16 P =.955 P = 2.1E-1 No m 6 Single m 6 Multiple m 6 s..3.2 MM P = 9.E-13 m 6 ontrol Position
9 Supplemental Figure lobal pattern of mrn structurome in rice. () verage DMS reactivity in selected regions of mrns with more than one stop per nucleotide mrns filtered by length were used for this analysis. Wilcoxon rank-sum test (when alternative hypothesis was "less") was used for P value calculation between 5 TR and DS, DS and 3 TR. P values were shown in the corresponding region. (B) verage DMS reactivity around the alternative splice sites between spliced and unspliced events in 5 splice site and spliced and 6 35 unspliced events in 3 splice site. ()-(E) Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of average DMS reactivity of selected regions in all the mrns (), mrns with high and low mrn content (D), mrns with high and low translation efficiency (E). (F) Effect of the number of m 6 peaks on ini index in 3 TR. (Yellow) 7 38 transcripts without m 6 peaks; (orange) 2 6 transcripts with single m 6 peak; (red) 2 75 transcripts with multiple m 6 peaks. P values were calculated by Wilcoxon rank-sum test. () DMS reactivity pattern around the conserved motif (MM, M = or ) identified in m 6 -seq (Li et al., 21). 221 motifs with m 6 and 19 motifs without m 6 were analyzed. P values were calculated by Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test.
10 DMS reactivity DMS reactivity content content 1 High content Low content TR DS... DS 3 TR Position Position.2 B.5 High content Low content P =.2657 P =.19 P = 3.26E-7 P = 1.11E TR DS... DS 3 TR Position Position.1 3 Magnitude Period (nucleotide) High - 5 TR High - DS High - 3 TR Low - 5 TR Low - DS Low - 3 TR
11 Supplemental Figure 5 Effect of content on the global pattern of mrn structurome in rabidopsis. ()-(B) verage content () and average DMS reactivity (B) of transcripts with the highest 15% and lowest 15% mrn content with more than one stop per nucleotide (11 27 in total) in rabidopsis. P values between two groups were calculated by KS test. () DFT of average DMS reactivity of selected regions in mrns with high and low mrn content.
12 O. sativa DMS - + B. thaliana DMS P =.66 P = 1.385E-6 1 el reactivity O. sativa. thaliana Lane P =.77 P = 7.389E Sequence identity: O. sativa. thaliana Relative DMS reactivity Nucleotide position Lane Nucleotide position O. sativa thaliana Structure-Seq DMS reactivity.8.2 /
13 Supplemental Figure 6 omparison of 25S rrn fragment in rice and rabidopsis. The fragments are from 695 nt to 8 nt in rice and from 73 nt to 85 nt in rabidopsis. () el-based probing in rice and rabidopsis. Lane 1 and 2, without and with 2.5% DMS treatment; lane 3 to 6, /// sequencing lanes. The positions of each well-visible and are coloured by red and blue, respectively. (B) omparison of gel reactivity (top) and relative DMS reactivity (bottom) in rice and rabidopsis. In the sequence alignment, mismatches are highlighted in a green background, best matches are highlighted in a purple background, and the region with highly conserved in vivo RN secondary structure is marked in white. Pairwise alignments were performed in EMBOSS Needle. P and P value were shown in the corresponding region. () Phylogenetic structure of the fragments coloured by DMS reactivity. The orange line represents the highly conserved structure probing region identified in gel-based probing and Structure-seq analysis. The probed sites using gel-based probing (Supplemental Figure 6 and 6B top) and Structure-seq (Supplemental Figure 6B bottom) show very similar DMS modification patterns between rice and rabidopsis. The pattern of DMS reactivity is consistent with the phylogeny-derived structures (Supplemental Figure 6).
14 B Reactivity Reactivity 1.5 T LO_Os2g T Sequence identity: T Reactivity 2.5 Reactivity LO_Os9g735.1 LO_Os2g LO_Os9g735.1 T Sequence identity:.5 LO_Os2g in vivo LO_Os9g735.1 in vivo T in vivo T in vivo
15 Supplemental Figure 7 Two individual examples for two kinds of relationship between sequence identity and structure similarity. High sequence identity and high structure similarity (group-1) () and low sequence identity and low structure similarity (group-) (B) exhibit two kinds of relationship between sequence identity and structure similarity. The results in rice are coloured with red and the ones in rabidopsis with blue. The reactivity is compared based on the sequence alignment of selected regions. Best matched regions are coloured in a light purple background, the mismatches on and in a green background, and the mismatches on and in a yellow background. rc diagrams were shown to compare in vivo RN secondary structure in the selected regions.
16 Supplemental Table 1 libraries orrelation of stop counts in different replicates of Structure-seq Pearson correlation coefficient (P) 18S rrn a 25S rrn a (-) DMS replicate 1 vs. (-) DMS replicate (+) DMS replicate 1 vs. (+) DMS replicate (-) DMS replicate 1 vs. (+) DMS replicate (-) DMS replicate 2 vs. (+) DMS replicate a: ll the P values of P are less than 2.2E-16. 1
17 Supplemental Table 2 O enrichment of the highest and lowest 1% PPV in rice ID ene set name P value -log1(p value) Fold enrichment enes with the highest 1% PPV O:51171 Regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process 1.68E O:6255 Regulation of macromolecule metabolic process 3.62E O:168 Regulation of gene expression 2.E O:6355 Regulation of transcription, DNdependent 1.51E O:1876 Lipid localization 3.77E enes with the lowest 1% PPV O:167 RN metabolic process 7.28E O:55 ell redox homeostasis.5e O:6811 Ion transport 1.E O:7165 Signal transduction 9.66E O:15979 Photosynthesis 6.13E
18 Supplemental Table 3 orrelation of m 6 modification and ini index in rice Region mrn a 5 TR b DS c 3 TR d m 6 enrichment vs. ini index P P value m 6 peak density vs. ini index P P value < 2.2E E E-8 < 2.2E-16 a: transcripts were analyzed; b: 282 transcripts were analyzed; c: transcripts were analyzed; d: 7 25 transcripts were analyzed. 3
19 Supplemental Table verage content a in our analyzed populations Region (mrn) (5' TR) (DS) (3' TR) Rice (n = 11,87).5 ± ± ±.91.1 ±.2. thaliana (n = 7,2).2 ± ± ± ±.38 a: Mean and SD are shown.
20 Supplemental Table 5 Details of enriched O terms listed in Figure 5B to 5E ID ene set name P value -log1(p value) Fold enrichment High sequence identity, high structure similarity O:3197 hromatin assembly 6.25E O:726 Small TPase mediated signal transduction 6.55E O:921 Ribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process 3.76E O:61 Tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediate metabolic process 1.16E O:613 Translational initiation 1.75E O:6511 biquitin-dependent protein catabolic process 1.2E O:6352 DN-dependent transcription, initiation 3.3E High sequence identity, low structure similarity O:16192 Vesicle-mediated transport 1.5E O:283 Small molecule biosynthetic process 1.98E O:271 ellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process 6.53E O:1651 arbohydrate biosynthetic process 2.1E O:925 lucan biosynthetic process 3.55E O:69 luconeogenesis 7.77E O:15995 hlorophyll biosynthetic process 1.81E Low sequence identity, high structure similarity O:6869 Lipid transport 9.81E O:51171 Regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process 2.6E O:1556 Regulation of macromolecule biosynthetic process 3.E O:89 Regulation of primary metabolic process 6.7E O:6351 Transcription, DN-dependent 8.9E O:51252 Regulation of RN metabolic process 1.3E O:55 ell redox homeostasis 5.89E O:318 Nicotianamine biosynthetic process 7.99E Low sequence identity, low structure similarity O:5992 Trehalose biosynthetic process 1.8E O:6793 Phosphorus metabolic process 2.6E O:3687 Post-translational protein modification 3.7E O:2221 Response to chemical stimulus.88e O:668 Protein phosphorylation 1.5E O:6979 Response to oxidative stress 7.6E O:255 ell wall modification 8.3E
21 6
Supplemental Information. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method. for Genome-wide 5hmC Profiling. of Rare Cell Populations
 Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Molecular ell, Volume 63 Supplemental Information Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for enome-wide hm Profiling of Rare ell Populations Dali Han, Xingyu Lu, lan H. Shih, Ji Nie, Qiancheng You, Meng Michelle
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splicing at the major splice donor site is controlled by highly conserved RNA sequence and structural elements
 Journal of eneral Virology (2015), 96, 3389 3395 DOI 10.1099/jgv.0.000288 Short ommunication Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splicing at the major splice donor site is controlled by highly conserved
Journal of eneral Virology (2015), 96, 3389 3395 DOI 10.1099/jgv.0.000288 Short ommunication Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splicing at the major splice donor site is controlled by highly conserved
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
Hao D. H., Ma W. G., Sheng Y. L., Zhang J. B., Jin Y. F., Yang H. Q., Li Z. G., Wang S. S., GONG Ming*
 Comparison of transcriptomes and gene expression profiles of two chilling- and drought-tolerant and intolerant Nicotiana tabacum varieties under low temperature and drought stress Hao D. H., Ma W. G.,
Comparison of transcriptomes and gene expression profiles of two chilling- and drought-tolerant and intolerant Nicotiana tabacum varieties under low temperature and drought stress Hao D. H., Ma W. G.,
WHITE PAPER. Increasing Ligation Efficiency and Discovery of mirnas for Small RNA NGS Sequencing Library Prep with Plant Samples
 WHITE PPER Increasing Ligation Efficiency and iscovery of mirns for Small RN NGS Sequencing Library Prep with Plant Samples ioo Scientific White Paper May 2017 bstract MicroRNs (mirns) are 18-22 nucleotide
WHITE PPER Increasing Ligation Efficiency and iscovery of mirns for Small RN NGS Sequencing Library Prep with Plant Samples ioo Scientific White Paper May 2017 bstract MicroRNs (mirns) are 18-22 nucleotide
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
RNA interference (RNAi)
 RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
RN interference (RNi) Natasha aplen ene Silencing Section Office of Science and Technology Partnerships Office of the Director enter for ancer Research National ancer Institute ncaplen@mail.nih.gov Plants
Figure S1, Beyer et al.
 Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
Novel PRD-like homeodomain transcription factors and retrotransposon elements in early human
 Novel PRD-like homeodomain transcription factors and retrotransposon elements in early human development Virpi öhönen, Shintaro Katayama, Liselotte Vesterlund, Eeva-Mari Jouhilahti, Mona Sheikhi, Elo Madissoon,
Novel PRD-like homeodomain transcription factors and retrotransposon elements in early human development Virpi öhönen, Shintaro Katayama, Liselotte Vesterlund, Eeva-Mari Jouhilahti, Mona Sheikhi, Elo Madissoon,
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
If DNA resides in the nucleus, and proteins are made at the ribosomes, how can DNA direct protein production?
 Protein Synthesis If DN resides in the nucleus, and proteins are made at the ribosomes, how can DN direct protein production? cell nucleus? ribosome Summary of Protein Synthesis DN deoxyribonucleic acid
Protein Synthesis If DN resides in the nucleus, and proteins are made at the ribosomes, how can DN direct protein production? cell nucleus? ribosome Summary of Protein Synthesis DN deoxyribonucleic acid
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016
 Name: Date: Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016 nswer the following questions about the process shown above. 1. What are the reactants in this process? 2. What are the products in this process?
Name: Date: Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016 nswer the following questions about the process shown above. 1. What are the reactants in this process? 2. What are the products in this process?
Breast cancer. Risk factors you cannot change include: Treatment Plan Selection. Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data
 Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
Breast cancer Inferring Transcriptional Module from Breast Cancer Profile Data Breast Cancer and Targeted Therapy Microarray Profile Data Inferring Transcriptional Module Methods CSC 177 Data Warehousing
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
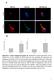 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Macromolecules Cut & Paste
 Macromolecules Cut & Paste Adapted from http://mrswords.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/2/4/15244382/ch_6-3_life_molecules_cut-out_lab.pdf INTRODUCTION Many of the molecules in living cells are so large that they
Macromolecules Cut & Paste Adapted from http://mrswords.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/2/4/15244382/ch_6-3_life_molecules_cut-out_lab.pdf INTRODUCTION Many of the molecules in living cells are so large that they
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
D. glycerol and fatty acids 4. Which is an example of an inorganic compound?
 Name: ate: 1. Glucose and maltose are classified as organic compounds because they are both 3. Which process is most directly responsible for the production of O 2 in these sugar solutions?. carbon-containing
Name: ate: 1. Glucose and maltose are classified as organic compounds because they are both 3. Which process is most directly responsible for the production of O 2 in these sugar solutions?. carbon-containing
Biology Unit 2 Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Date/Hour
 Biology Unit 2 Name Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Date/our Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body
Biology Unit 2 Name Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Date/our Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas. (a) Illustration of the plant organs and nodule infection time points analyzed. (b) Proteomic workflow
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental design and workflow utilized to generate the WMG Protein Atlas. (a) Illustration of the plant organs and nodule infection time points analyzed. (b) Proteomic workflow
Figure 1. Dnmt3b expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. (A) Representative images
 Figure Legends Figure. expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. () Representative images showing that Dnmta is not expressed in chondrocytes from mo W articular cartilage [Dnmta expression
Figure Legends Figure. expression in murine and human knee joint cartilage. () Representative images showing that Dnmta is not expressed in chondrocytes from mo W articular cartilage [Dnmta expression
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be
Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules
 Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational Methods
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
AMERICAN NATIONAL SCHOOL General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 MERIN NTIONL SHOOL General ertificate of Education dvanced Level IOLOGY 9700/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice lass 1 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft pencil (type or H is
MERIN NTIONL SHOOL General ertificate of Education dvanced Level IOLOGY 9700/01 Paper 1 Multiple hoice lass 1 dditional Materials: Multiple hoice nswer Sheet Soft clean eraser Soft pencil (type or H is
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be
Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight. All compounds can be
Retroviral RNA Processing and stability
 Retroviral RN Processing and stability m 7 gag pol env src Karen Beemon Johns Hopkins niversity m 7 env src m 7 src Retroviruses hijack host cell gene expression machinery to generate progeny virions Simple
Retroviral RN Processing and stability m 7 gag pol env src Karen Beemon Johns Hopkins niversity m 7 env src m 7 src Retroviruses hijack host cell gene expression machinery to generate progeny virions Simple
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0267398221* BIOLOGY 9700/41 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions May/June 2016 2 hours Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level *0267398221* BIOLOGY 9700/41 Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions May/June 2016 2 hours Candidates answer
Unit 3 Review Game Page 1
 Unit 3 Review Game Page 1 1 What best characterizes the role of TP in cellular metabolism? It is catabolized to carbon dioxide and water. The G associated with its hydrolysis is positive. The charge on
Unit 3 Review Game Page 1 1 What best characterizes the role of TP in cellular metabolism? It is catabolized to carbon dioxide and water. The G associated with its hydrolysis is positive. The charge on
FCC2 5CY7 FCC1 5CY8. Actinonin 5CVQ
 Table S1. Data collection and refinement statistics Data collection Apo 5E5D MA 5CPD MAS 5CP0 Actinonin 5CVQ FCC1 5CY8 FCC2 5CY7 FCC 5CWY FCC4 5CVK FCC5 5CWX FCC6 5CVP X-ray source 17A-KEK PAL4A PAL4A
Table S1. Data collection and refinement statistics Data collection Apo 5E5D MA 5CPD MAS 5CP0 Actinonin 5CVQ FCC1 5CY8 FCC2 5CY7 FCC 5CWY FCC4 5CVK FCC5 5CWX FCC6 5CVP X-ray source 17A-KEK PAL4A PAL4A
FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements.
 FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements. Under the right physical conditions, every microorganism
FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements. Under the right physical conditions, every microorganism
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA AGING, July 2014, Vol. 6 No. 7
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
BCH 4054 December 13, 1999
 BH 4054 December 13, 1999 FINL EXM This exam consists of six pages. Make sure you have one of each. For questions indicating a choice, answer only one of the choices. (If you answer both, you need to indicate
BH 4054 December 13, 1999 FINL EXM This exam consists of six pages. Make sure you have one of each. For questions indicating a choice, answer only one of the choices. (If you answer both, you need to indicate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature22359 Supplementary Discussion KRAS and regulate central carbon metabolism, including pathways supplied by abundant fuels like glucose and glutamine. Under control
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature22359 Supplementary Discussion KRAS and regulate central carbon metabolism, including pathways supplied by abundant fuels like glucose and glutamine. Under control
Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating enzymatic activity.
 Name: Enzymes in Action Objectives: You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating
Name: Enzymes in Action Objectives: You will use the model pieces in the kit to: Simulate enzymatic actions. Explain enzymatic specificity. Investigate two types of enzyme inhibitors used in regulating
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Topic 3: The chemistry of life (15 hours)
 Topic : The chemistry of life (5 hours). Chemical elements and water.. State that the most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen...2 State that
Topic : The chemistry of life (5 hours). Chemical elements and water.. State that the most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen...2 State that
Genetic information flows from mrna to protein through the process of translation
 Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project
 Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Immediate late genes decode ERK signal duration Florian Uhlitz et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV. cquired samples from HEK9ΔRF:ER cells. Microarrays - Untreated I +U6-5 6 7
Molecular Systems iology Immediate late genes decode ERK signal duration Florian Uhlitz et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV. cquired samples from HEK9ΔRF:ER cells. Microarrays - Untreated I +U6-5 6 7
Macromolecule Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. ll living things contain which element?. helium. sodium. copper. carbon 4. Which of the following compounds is most likely to be part of living organisms?. 6 H 12 O 6. F 3. Mol 2. si 2. Plants
Name: ate: 1. ll living things contain which element?. helium. sodium. copper. carbon 4. Which of the following compounds is most likely to be part of living organisms?. 6 H 12 O 6. F 3. Mol 2. si 2. Plants
Phylogenetic Methods
 Phylogenetic Methods Multiple Sequence lignment Pairwise distance matrix lustering algorithms: NJ, UPM - guide trees Phylogenetic trees Nucleotide vs. amino acid sequences for phylogenies ) Nucleotides:
Phylogenetic Methods Multiple Sequence lignment Pairwise distance matrix lustering algorithms: NJ, UPM - guide trees Phylogenetic trees Nucleotide vs. amino acid sequences for phylogenies ) Nucleotides:
Chapter 4. Cellular Metabolism
 hapter 4 ellular Metabolism opyright he Mcraw-ill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction. living cell is the site of enzyme-catalyzed metabolic reactions that maintain
hapter 4 ellular Metabolism opyright he Mcraw-ill ompanies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction. living cell is the site of enzyme-catalyzed metabolic reactions that maintain
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Studying Alternative Splicing
 Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
Studying Alternative Splicing Meelis Kull PhD student in the University of Tartu supervisor: Jaak Vilo CS Theory Days Rõuge 27 Overview Alternative splicing Its biological function Studying splicing Technology
3. Hydrogen bonds form between which atoms? Between an electropositive hydrogen and an electronegative N, O or F.
 Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and covalent bond. Provide an example for each. Ionic: occurs between metals and non-metals, e.g., NaCl Covalent: occurs between two non-metals;
Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and covalent bond. Provide an example for each. Ionic: occurs between metals and non-metals, e.g., NaCl Covalent: occurs between two non-metals;
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome
 RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome How do novel structures or functions evolve? A more relevant example Symbiosis and Nitrogen Fixation Limpens & Bisseling (23) Curr. Opin.
RNA-Seq Atlas of Glycine max: A guide to the Soybean Transcriptome How do novel structures or functions evolve? A more relevant example Symbiosis and Nitrogen Fixation Limpens & Bisseling (23) Curr. Opin.
SOUTHERN CONNECTICUT STATE UNIVERSITY CHE 451 Biochemistry II Spring Semester, 2011
 SOUTHERN CONNECTICUT STATE UNIVERSITY CHE 451 Biochemistry II Spring Semester, 2011 Name: Dr. J. Pang Office: 323 Jennings Hall Phone: 203-392-6272 E-mail: pangj1@southernct.edu Office Hours: MTWF 11-12
SOUTHERN CONNECTICUT STATE UNIVERSITY CHE 451 Biochemistry II Spring Semester, 2011 Name: Dr. J. Pang Office: 323 Jennings Hall Phone: 203-392-6272 E-mail: pangj1@southernct.edu Office Hours: MTWF 11-12
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells. Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010
 Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010 Introduction The Warburg Effect Cancer cells metabolize glucose differently Primarily
Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010 Introduction The Warburg Effect Cancer cells metabolize glucose differently Primarily
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15
 Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Supplemental Figure S1. Sequence feature and phylogenetic analysis of GmZF351. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of GmZF351, AtTZF1, SOMNUS, AtTZF5,
 Supplemental Figure S. Sequence feature and phylogenetic analysis of GmZF35. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of GmZF35, AtTZF, SOMNUS, AtTZF5, and OsTZF. Characters with black background indicate conserved
Supplemental Figure S. Sequence feature and phylogenetic analysis of GmZF35. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of GmZF35, AtTZF, SOMNUS, AtTZF5, and OsTZF. Characters with black background indicate conserved
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Name: Due on Wensday, December 7th Bioinformatics Take Home Exam #9 Pick one most correct answer, unless stated otherwise!
 Name: Due on Wensday, December 7th Bioinformatics Take Home Exam #9 Pick one most correct answer, unless stated otherwise! 1. What process brought 2 divergent chlorophylls into the ancestor of the cyanobacteria,
Name: Due on Wensday, December 7th Bioinformatics Take Home Exam #9 Pick one most correct answer, unless stated otherwise! 1. What process brought 2 divergent chlorophylls into the ancestor of the cyanobacteria,
Supporting Information
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Supporting Information Variances and biases of absolute distributions were larger in the 2-line
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma
 Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro
 Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Supplementary Material Mnemonic representations of transient stimuli and temporal sequences in the rodent hippocampus in vitro Robert. Hyde and en W. Strowbridge Mossy ell 1 Mossy ell Mossy ell 3 Stimulus
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity
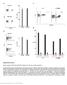 Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Supplementary Figure 1 Binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers and recovery of antigen specificity (a, b) Fluorescent-based determination of the binding capacity of DNA-barcoded MHC multimers (+barcode)
Metabolism. Metabolic pathways. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Core Lab #3 Investigating Diabetes Mellitus
 Name: Introduction Diabetes is a malfunction of one of the major homeostatic mechanisms in the body the endocrine system. Two hormones, insulin and glucagon control the level of sugar in the blood. The
Name: Introduction Diabetes is a malfunction of one of the major homeostatic mechanisms in the body the endocrine system. Two hormones, insulin and glucagon control the level of sugar in the blood. The
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function
 Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION MODIFIED LANGUAGE
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED GCE BIOLOGY Communication, Homeostasis and Energy F214 * OCE / 2 3852* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Insert (inserted) Other Materials
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED GCE BIOLOGY Communication, Homeostasis and Energy F214 * OCE / 2 3852* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Insert (inserted) Other Materials
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Name Date Period. Macromolecule Virtual Lab. Name: Go to the website:
 Macromolecule Virtual Lab Name: Go to the website: http://faculty.kirkwood.edu/apeterk/learningobjects/biologylabs.htm The most common organic compounds found in living organisms are lipids, carbohydrates,
Macromolecule Virtual Lab Name: Go to the website: http://faculty.kirkwood.edu/apeterk/learningobjects/biologylabs.htm The most common organic compounds found in living organisms are lipids, carbohydrates,
Metabolism. Topic 11&12 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism. Metabolic Balancing Act. Topics. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes
 Topic 11&12 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic Balancing Act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Topic 11&12 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic Balancing Act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Organic Chemistry Worksheet
 Organic Chemistry Worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Organic Compounds 1. Organic molecules exist in all living cells. In terms of biochemistry, what does the term organic mean? 2. Identify the monomer
Organic Chemistry Worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Organic Compounds 1. Organic molecules exist in all living cells. In terms of biochemistry, what does the term organic mean? 2. Identify the monomer
Microbial Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Functionally important structural elements of U12 snrna
 Published online 6 July 2011 Nucleic cids Research, 2011, Vol. 39, No. 19 8531 8543 doi:10.1093/nar/gkr530 Functionally important structural elements of 12 snrn Kavleen Sikand 1,2 and irish. Shukla 1,2,
Published online 6 July 2011 Nucleic cids Research, 2011, Vol. 39, No. 19 8531 8543 doi:10.1093/nar/gkr530 Functionally important structural elements of 12 snrn Kavleen Sikand 1,2 and irish. Shukla 1,2,
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Expanded View Figures
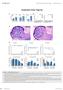 The EMO Journal Dnmt regulates translational fidelity Francesca Tuorto et al Expanded View Figures x E3 cells/µl W g/l HG x e3 cells/µl PLT % of cell type 8 day 8 month % of cell type 8 day 8 month 8 day
The EMO Journal Dnmt regulates translational fidelity Francesca Tuorto et al Expanded View Figures x E3 cells/µl W g/l HG x e3 cells/µl PLT % of cell type 8 day 8 month % of cell type 8 day 8 month 8 day
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
Chapter 8. An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
 Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
2 3 Carbon Compounds. Proteins. Proteins
 2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
2 3 Carbon Compounds Slide 1 of 37
 1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 2 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. 3 of 37 Macromolecules Macromolecules Macromolecules
Biology 1 of 37 2 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. 3 of 37 Macromolecules Macromolecules Macromolecules
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Aim 19: Cellular Respiration
 1. During the process of cellular respiration, energy is released from A) carbon dioxide B) oxygen atoms C) water molecules D) chemical bonds 2. The energy used to obtain, transfer, and transport materials
1. During the process of cellular respiration, energy is released from A) carbon dioxide B) oxygen atoms C) water molecules D) chemical bonds 2. The energy used to obtain, transfer, and transport materials
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration
 AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name: Date: Period Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take
AP Biology Reading Guide Name: Date: Period Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take
