MASSAGENERD.COM Presents. 47 Muscles. With. TrP s. (Anterior) By Ryan Hoyme CMT, NCTMB, HST
|
|
|
- Madeleine Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MASSAGENERD.COM Presents 47 Muscles With TrP s (Anterior) By Ryan Hoyme CMT, NCTMB, HST
2 Legal Disclaimer All models are at least 18 years of age. The techniques, ideas, and suggestions in this document are not intended as a substitute for proper medical advice! Consult your physician or health care professional before performing or receiving a massage, particularly if you are pregnant or nursing, or if you are elderly, or if you have any chronic or recurring conditions. Any application of the techniques, ideas, and suggestions in this document is at the reader's sole discretion and risk. The author and publisher of this document and their employers are not liable or responsible to any person or entity for any errors contained in this document, or for any special, incidental, or consequential damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by the information contained in this document. Copyright Ryan Jay Hoyme 2
3 Scalenus Anterior (skay-lee-nus) - Triangular with unequal sides Scalenus Medius (skay-lee-nus) - Triangular with unequal sides Scalenus Posterior (skay-lee-nus) - Triangular with unequal sides TrP Location The TrP s are just posterior and under the SCM. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Scaleni or Pectoralis Minor Back Pain (Upper) - Scaleni, Levator scapulae, Rhomboids, Latissimus dorsi, Serratus posterior superior, Thoracic paraspinals Breathing problems - Tight Innercostals, Pectoralis Major, and or Scalenes. 3
4 Platysma - Most superficial neck muscle (Covers SCM) Sternocleidomastoid (STER-no-CLY-do-mas-toyd) - Connecting to sternum, clavicle and mastoid process (Tightness can cause vertigo or torticollis / only muscle that move the head and are not connected to the ribs) TrP Location For the SCM you have the client flex their neck and then rotate it to find the SCM and then pinch it (Safest way) Stiff Neck (Acute) - Levator scapulae, Sternocleidomastoid, Upper Trapezius Atypical Facial Neuralgia - Sternocleidomastoid (sternal division), Facial muscles Headache (Tension/Migraine) - Sternocleidomastoid, Upper trapezius, Posterior cervicals, Temporalis Earache (Drum normal) - Deep masseter, Sternocleidomastoid (clavicular division) Wryneck -Tightness and hard to rotate the head could be the Sternocleidomastoid. Whiplash - Head whipping back and forth or side to side in a fast jerky movement. Could be any of the neck muscles. 4
5 Masseter (MAS-sit-er) - Chew TrP Location Place your hand on their cheek region and have them open and close their mouth to feel the muscle Jaw Pain, TMJ Dysfunction - Lateral pterygoid or Masseter Earache (Drum normal) - Deep masseter, Sternocleidomastoid (clavicular division) 5
6 Lateral Pterygoid (TER-ih-goyd) - Wing shaped Medial Pterygoid (TER-ih-goyd) - Wing shaped TrP Location Superior TrP is superior to the Masseter. The inferior TrP is Inferior to the Superior TrP. Jaw Pain, TMJ Dysfunction - Lateral pterygoid or Masseter 6
7 Buccinator (BUK-sin-ate-or) - Trumpeter Orbicularis Oculi (or-bik-you-lar-iss OK-you-li) - Small disk belonging to the ear (Winking muscle) Orbicularis Oris (or-bik-you-lar-iss OR-iss) - Small disk belonging to the mouth (Kissing muscle) Zygomaticus Major (ZYE-go-MAT-ik-us) - Connected to the connector Zygomaticus Minor (ZYE-go-MAT-ik-us) - Connected to the connector TrP Location Buccinator is medial to the Masseter TrP s. TrP Location Orbicularis oculi & Zygomaticus ore around the eye socket. 7
8 Temporalis (TEMP-OR-al-ISS) - Temple of head TrP Location Locate the temporal pulse and keep going posterior to find the TrP s Headache (Tension/Migraine) - Sternocleidomastoid, Upper trapezius, Posterior cervicals, Temporalis 8
9 Deltoid (DEL-toyd) - Triangular (Shoulder pad muscle / Anterior, Lateral (or middle) and Posterior / Antagonist to itself) TrP Location 4 TrP s are on the lateral deltoid and there is one on each of the other deltoids (Anterior & Posterior) Arthritis of Shoulder - Infraspinatus or Deltoid Bursitis of shoulder (Subdeltoid) - Infraspinatus, Deltoid, Supraspinatus 9
10 Coracobrachialis (KORE-a-koe-BRAY-kee-AL-iss) - Crows beak of the arm Subclavius (sub-klave-ee-us) - Below the clavicle TrP Location Coracobrachialis; pinch the anterior part of the axillary region TrP Location Subclavius; Under the clavicle TrP Location Sternalis; ½ way down the sternum and ½ inch off it Not many people have the sternalis and subclavius muscle 10
11 Biceps Brachii (BI-seps BRAY-kee-eye) - Two heads and of the arm (Corkscrew muscle) Brachialis (BRAY-kee- AL-iss) - Arm (Strongest elbow flexor / superficial lateral forearm) Pectoralis Major (PEKtor-al-iss) - Chest Pectoralis Minor (PEKtor-al-iss) - Chest TrP Location Pectoralis minor; have the client in the supine position, anterior part of the axillary, then place your fingers on the anterior ribs and finally have the client perform horizontal adduction to go more medially under the Pectoralis major TrP Location Pectoralis Major; ask the client where their areola is as a landmark (Never put pressure on it). You can use a towel over the pects or use the client s fingers to find the TrP s on woman. TrP Location Brachialis; have the client flex their bicep and it is under the lower portion of the bicep on the lateral side Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Scaleni or Pectoralis (Tightness equals rounded shoulders and or constriction of chest wall Minor) Mastectomy - Removal of the breast tissue. Pectoralis minor and Pectoralis major could be affected. Breathing problems - Tight Innercostals, Pectoralis Major, and or Scalenes. 11
12 Abductor Digiti Minimi Manus (ab- DUCK-tur DIH-jih-tee MIN-ih-mee MANus) - Lead away, digits, smallest and hand Abductor Pollicis Brevis (ab-duck-tur POLL-is-iss BREV-us) - Lead away, thumb and short Abductor Pollicis Longus (ab-duck-tur POLL-is-iss LONG-us) - Lead away, thumb and long Adductor Pollicis (ad-duck-tur POLL-isiss) - Lead towards and thumb Brachioradialis (BRAY-kee-oh-RAY-dee- AL-iss) - Arm and radius TrP Location Brachioradialis; 2 inches inferior to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus TrP Locations - Adductor Pollicis & Opponens Pollicis; Just inferior to the index finger on the palm side TrP Locations Dorsal Interosseous; on the dorsal part of the hand Hypothenar eminence - Opponens digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi brevis, and Abductor digiti minimi Thenar eminence - Opponens pollicis, Abductor pollicis brevis, and Flexor pollicis brevis De Quervain s Syndrome (Washerwoman's Sprain) - Stenosing tenosynovitis of the short extensor (extensor pollicis brevis) and long abductor tendon (abductor pollicis longus) of the thumb. 12
13 Palmaris Longus (pal- MAR-iss LONG-us) - Palm and long Pronator Quadratus (PRO-nay-tor kwad- RATE-us) - Causes pronation and square shaped Pronator Teres (PROnay-tor TER-eez) - Causes pronation and round/smooth Supinator (SOOP-in- ATE-or) - Causes supination TrP Location Palmaris Longus; one inch inferior to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and go medial about 1 ½ inches (Make sure you are not on the Flexor carpi ulnaris) TrP Location Pronator Quadratus; find the carpals on the radial side and go superior 1 inch (Try not to push pressure one the radius bone and not on the radial pulse; so just go at an angle) TrP Location Pronator Teres; find the medial epicondyle of the humerus and go inferior 1/2 inch and one inch medial TrP Location Supinator; find lateral epicondyle of humerus, then go inferior one inch and medial one inch (Hook under Brachioradialis) Tennis Elbow (Epicondylitis) - Supinator, Wrist Extensors, Triceps brachii Radial Tunnel Syndrome -This syndrome is often misdiagnosed as chronic lateral epicondylitis, because patients complain of lateral elbow pain at the forearm. Stretch the supinator muscle. Pronator Teres Syndrome - A Cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and it is a Nerve entrapment at the pronator teres muscle area. The median nerve can get entrapped between the humeral and ulnar heads of the pronator teres muscle. The patient will complain of pain and tingling in the palmar and dorsal aspect of the hand, palm, and fingers. Dupuytren s contracture - This relatively common disorder is characterized by hyperplasia of the palmar fascia and related structures, with nodule formation and contracture of the palmar fascia. 13
14 Flexor Carpi Radialis (FLEXS-or KAR-pee- RAY-dee-AL-iss) - Bend, wrist and radius Flexor Carpi Ulnaris (FLEXS-or KAR-pee- ul-nar-iss) - Bend, wrist and ulna Flexor Digiti Minimi Manus (FLEXS-or DIH-jih-tee MIN-ihmee MAN-us) - Bend, digits, smallest and hand Flexor Digitorum Profundus (FLEKS-or DIH-jih-TOR-um pro- FUND-us) - Bend, digits and deep Flexor Digitorum Superficialis (FLEKS-or DIH-jih-TOR-um SOO-per-fish-ee-AL-us) - Bend, digits and top of surface Flexor Pollicis Brevis (FLEXS-or POLL-is-iss BREV-us) - Bends, thumb and short Flexor Pollicis Longus (FLEKS-or POLL-is-iss LONG-us) - Bend, thumb and long TrP Location Flexor Carpi Radialis; find the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and go down 2 inches and one inch medial (Make sure you are not on the median nerve) TrP Location Flexor Carpi Ulnaris; find the medial epicondyle of the humerus and go inferior 1 inch and one inch medial (Most medial forearm muscle). TrP Location Flexor Digitorum; the TrP s are on each side of the median nerve. TrP Location Flexor Pollicis Longus; find the carpals on the radial side and go superior 2 inches (Try not to push pressure one the radius bone and not on the radial pulse; so just go at an angle) Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - There are 9 tendons and the median nerve pass through the tunnel from the forearm to the hand. Increased pressure in the tunnel form inflammation in one or many of the tendons irritate the median nerve. Flexor Retinaculum, Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, Flexor Digitorum Profundus, and or the Palmaris Longus. Golfer's Elbow (Medial epicondylitis) - Inflammation of the medial epicondyle. Palmaris Longus, Flexor Digitorum Superficialis, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris, or Pronator Teres. Guyon's canal syndrome - a common nerve compression affecting the ulnar nerve as it passes through a tunnel in the wrist called Guyon's canal. This problem is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome, but involves a completely different nerve. Sometimes both conditions can be causing a problem in the same hand. Flexor Carpi Ulnaris tunnel syndrome - This muscle tunnel syndrome represents entrapment of the ulnar nerve between the humeral and ulnar heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. 14
15 External Abdominal Oblique (ab-dahm-in-al oh- BLEEK) - Abdomen and slant Internal Abdominal Oblique (ab-dahm-in-al oh-bleek) - Abdomen and slant (The fibers go vertical) Rectus Abdominis (REK-tus ab-dahm-in-iss) - Straight and abdomen (Horizontal layer of connective tissue every few inches / six pack muscle) Transversus Abdominis (Trans-VER-sus ab-dahmin-iss) - Lying crosswise and abdomen (Deepest abdominal muscle / Wraps around the internal organs) TrP Location Never push straight down on the abdomen (Especial above the navel) TrP Location Rectus abdominis; have the client perform a sit-up to find the rectus abdominis Costals - Internal and External Diaphragm - Prime mover in inspiration Internal Intercostals (inter- KOS-talz) - Between ribs External Intercostals (inter- KOS-talz) - Between ribs Duodenal ulcer - Rectus abdominus Back Pain (Lower) - Quadratus lumborum, Thoracolumbar paraspinals, Gluteus (maximus / medius), Rectus abdominis, Iliopsoas Hockey player's syndrome - Involves a tear of the external oblique aponeurosis, associated with inguinal nerve entrapment. Inguinal hernias - result from a weakness or tear of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal (transversus abdominis). Frequent Urination - Tight abdominus rectus muscle and floor of the pelvis. 15
16 Iliacus (ILL-ee-AK-us) - Hip Psoas Major (SO-as) - Loins (Strongest hip flexor / strongest posture muscle) Psoas Minor (SO-as) - Loins (Missing in most cadavers) TrP Location Psoas; find the rectus abdominus and perform the technique straight down on the external obliques (Never above the navel region and not on the rectus abdominis. Once you have gone as far as you can, then hook your fingers towards their spine TrP Location Iliacus; find their hip bone and hook your fingers under it Iliopsoas - Group of psoas major, psoas minor, and iliacus Appendicitis - Rectus abdominus or Psoas Back Pain (Lower) - Quadratus lumborum, Thoracolumbar paraspinals, Gluteus (maximus / medius), Rectus abdominis, Iliopsoas Groin Pain - Adductors or Iliopsoas Psoas Syndrome - Chronic psoas shortening and weakness may occur due to sleeping in the fetal position, exercise programs emphasizing repetitive hip flexion, and sedentary life styles. Some people don t have the Psoas minor 16
17 Rectus Femoris (REK-tus FEM-oriss) - Straight and relates to the thigh (Only quad muscle that crosses two joints and has two actions) Vastus Intermedius (VAS-tus inter- MEE-dee-us) - Large Vastus Lateralis (VAS-tus LATter-al-us) - Large Vastus Medialis (VAS-tus MEEdee-al-us) - Large TrP Location Rectus femoris; have the client tense up their anterior part of their leg and for the superior TrP, find their ASIS and go inferior about 2 inches and medial 2 inches. For their lower TrP, fin patella (Knee cap) and go 2-3 inches superior TrP Location Vastus intermedius; have the client tense up their anterior part of their leg and for the TrP, find their ASIS and go inferior about 3 inches and hook under the rectus femoris. TrP Location Vastus lateralis; Use the rectus femoris and the IT band as landmarks (The Vastus lateralis is in between both of them) TrP Location Vastus medialis; have the client tense up their anterior part of their leg and find patella (Knee cap) and go 2 inches superior and one inch medial. The other TrP is 3-4 inches superior of the patella and one inch medial. Arthritis of Knee - Rectus femoris, Vastus medialis, Vastus lateralis Bursitis of the hip (Trochanteric) - Gastrocnemius, Vastus lateralis, Tensor fasciae latae or Quadratus lumborum Arthritis of Hip - Tensor fasciae latae, Vastus lateralis Rapid Extension (problems with) - Vastus Medialis, Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis. Displaced Patella (Dancers) - Quadriceps asymmetrically tight. Classical ballet ranks above contact sports for injury. 17
18 Adductor Brevis (ad- DUCK-tur BREV-us) - Lead towards and short Adductor Longus (ad- DUCK-tur LONG-us) - Lead towards and long Gracilis (gra-sil-iss) - Slender (The gracilis and the femoral shaft form the letter V ) Pectineus (PEK-tih-NEEus) - Pubic bone (Medial to the femoral artery and considered an extension of the iliopsoas muscle) Sartorius (sar-tor-ee-us) - Tailor (Longest muscle) TrP Location Pectineus; one inch below the femoral triangle TrP Location Adductor Brevis & Longus; 2 and 3 inches below the femoral triangle TrP Location Sartorius; find the ASIS and map out a curved line all the way down to the medial part of the knee and you will find many TrP s TrP Location Gracilis; use the medial side of the knee and keep going superior and then you will find many TrP s Meralgia Paresthetica - Tensor fasciae latae or Sartorius Appendicitis - Rectus abdominus or Psoas Sexual Dysfunction - Piriformis, Adductors Groin Pain - Adductors or Iliopsoas Adductor longus - While the adductor longus, adductor magnus, adductor brevis, and pectineal muscles are all adductors of the hip, of these the adductor longus is most often injured in sports. 18
19 Extensor Digitorum Longus (ex-sten-sur DIH-jih-TOR-um LONG-us) - Stretches, digits and long Extensor Hallucis Longus (ex-sten-sur HAL-uh-iss LONG-us) - Stretches, big toe and long Tibialis Anterior (TIBee-AL-iss) - Related to shin bone (Weakness causes flat foot / Tightness causes high arch / prone to shin splints) TrP Location Tibialis Anterior; find the patella and go inferior 2-3 inches and the TrP s are just lateral to the tibia bone (Not on it) TrP Location Extensor digitorum longus; it is in between the tibialis anterior and the peroneus muscles (About same area as Tibialis anterior TrP s, but laterally ½-1 inch) TrP Location Extensor hallucis longus; it is in between the tibialis anterior and the peroneus muscles (Lower ½ of the shin) Pes Cavus - Higher than normal arch in the foot and could be a tight Tibialis Anterior muscle. Pes Planus - Is flat feet, not enough of an arch, weakness in the soleus-gastroc group or tibialis anterior. Shin Splints - Overly tight (hypertonic) Tibialis anterior muscle & could also be Extensor hallucis longus, Extensor digitorum longus, or Tibialis posterior. Injuries that result in small tears in the fibers of these muscles probably cause the pain known as shin splints. Inverted foot or clubfoot - tibialis anterior muscle could be one of the causes. Hammertoes - Are caused by tight extensor digitorum longus. Bunions - Can be caused by tightened extensor hallucis longus. Dorsiflexor weakness - Foot slaps down when walking, weakness in the dorsi-flexor muscles. 19
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Occipitalis (Head) ock-sip-i-tal-is. Temporalis TEM-per-AL-is. Frontalis Fron-TAL-is. Corrugator COR -oo-gay-tor
 As a revision aid, try printing/cutting out the following labels and place them on your model s body. If there is no room, on the face/head for example, then place them on the table next to them. To help
As a revision aid, try printing/cutting out the following labels and place them on your model s body. If there is no room, on the face/head for example, then place them on the table next to them. To help
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8
 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
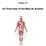 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Electrode Placement. Skin Preparation. Frontalis (FRL) (Specific) Temporalis Anterior (TA) (Specific) Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) (Specific)
 Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Lab Exercise 8. BIOPAC Exercise. Muscle Tissue. Muscles. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
The Massage Routine. Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position. Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes
 The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
The Massage Routine Start with your client lying face down - Prone Position Clean YOUR HANDS and CLIENTS FEET using antibacterial wipes!!!! GROUNDING FOR 3 BREATHS TUNE YOUR BREATHING WITH THE CLIENTS!!!
Appendix. Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance
 Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Systematic Anatomy (For international students)
 Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 11 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) The attachment of a muscle s tendon to the stationary bone is called the ; the attachment of the muscle s other tendon to the movable
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp ) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a
 The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
The Muscular System Outline 10.1 For any movement, muscles can act in one of three ways (pp. 321 322) A. Muscles only pull; they never push, and as a muscle shortens, the insertion is pulled toward the
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
The Muscular System. - composed of mostly skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood and connective tissue
 The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
