Osteopathic Care for the Newborn and Infant. Overview. Laura Griffin, D.O, FAAO April 30, 2016
|
|
|
- Prudence Sanders
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Laura Griffin, D.O, FAAO April 30, 2016 Osteopathic Care for the Newborn and Infant Overview Review anatomy of fetal skull, attention to areas of potential dysfunction Learn common areas of somatic dysfunction in the newborn skull and physiologic implications of dysfunction in that area Learn how the forces of delivery can create dysfunction Discuss evaluation of newborn for somatic dysfunction, including overriding sutures and strain patterns Practice some basic treatment to address common dysfunctions Discuss issues in older children, including otitis media, GERD and scoliosis 1
2 Fetal Skull Vault bones are formed in membrane, squamous in nature Bone represents a thickening of the membrane Membranes remain continuous through sutures, even after fontanelles close Fetal Skull Fetal Skull Override is normal and desirable at birth Other than the temporal at the squamous suture, parietals should override everything else Parietals override frontals at the coronal suture and occipital at the lambdoid suture most physiologic Parietals override each other at the sagittal suture If override is asymmetrical, look for SBS strains Override is limited by the membranes 2
3 3
4 Principles of Newborn Osteopathic Treatment Balanced ligamentous tension Balanced membranous tension All techniques should be direct, don t exaggerate strain patterns 4
5 Occipital bone - fetal Squama Condylar parts Basilar part Four parts at birth which surround the foramen magnum: squama, the condylar parts and the base Occipital bone - adult Squama Condylar parts Basilar part 5
6 Fetal Skull Jugular Foramen formed between condylar part of occiput and petrous portion of temporal Hypoglossal canal just superior to condylar part of occiput Both affected by mechanical strain Fetal Skull Key features: Jugular foramen transmits CN s: IX (glossopharyngeal) X (vagus) XI (spinal accessory) Hypoglossal canal: transmits CN: XII (hypoglossal) Cranial Nerve Sensory Function Somatic Motor Function CN IX (glossopharyngeal) Touch & taste to posterior 1/3 of tongue, visceral sensory to carotid bodies One pharyngeal muscle (stylopharyngeus) Parasympathetic Motor Function Innervates (increases secretion of) parotid salivary gland CN X (vagus) CN XI (spinal accessory) Visceral sensory information from pharynx, larynx,, carotid bodies, heart, lungs, most abdominal organs General sensory information from external auditory canal, eardrum, and pharynx None Most pharyrngeal muscles; laryngeal muscles Trapezius muscle, sternocleidomastoid muscle Innervates smooth muscle and glands of heart, lungs, larynx, trachea, most abdominal organs None CN XII (hypoglossal) None Intrinsic tongue muscles and extrinsic tongue muscles None 6
7 Jugular Foramen Optic Canal Foramen ovale CN IX, X, XI CN XII Jugular Foramen Hypoglossal canal Hypoglossal Canal Hypoglossal Canal Clinical Significance Glossopharyngeal (IX): Primarily sensory, posterior third of tongue, sensory impairment can affect suck reflex Vagus (X): Visceral sensory to pharynx, larynx. Parasympathetic to viscera, poor function can cause decreased peristalsis, reflux 7
8 Jugular Foramen Optic Canal Foramen ovale CN IX, X, XI CN XII Jugular Foramen Hypoglossal canal Clinical Significance Spinal Accessory (XI): Motor to SCM, trapezius. Unilateral dysfunction can cause torticollis Bilateral dysfunction can cause arching which is frequently seen with reflux Hypoglossal (XII): Motor to tongue musculature, involved in suck and swallow reflexes 8
9 Sphenoid 3 portions at birth Lesser wings with basisphenoid 2 greater wing/pterygoid portions 9
10 Sphenoid Anterior view Sphenoid Posterior view Superior orbital fissure CNs III, IV, V1, VI 10
11 Sphenoid Superior orbital fissure transmits CN s: Oculomotor (III) Trochlear (IV) Ophthalmic (V 1) Abducent (VI) Impingement can cause strabismus, may not show up until later Sphenoid Superior orbital fissure (III, IV, V1, VI) Foramen rotundum (V2) Foramen ovale (V3) Sphenoid Foramen rotundum transmits maxillary nerve (V2): sensory to upper lip, teeth and gums, also palate Foramen ovale transmits mandibular (V3): motor to muscles of mastication, can affect ability to suck 11
12 Cranial base: Sphenoid and Occiput Cranial base: Sphenoid and Occiput Common strain patterns Torsion Sidebending-rotation Lateral strains Vertical strains Unresolved strains can contribute to plagiocephaly and FLK syndrome TORSION One axis: Antero-superior to Infero-posterior Sphenoid and occiput rotate in opposite directions Named for superior great wing of sphenoid 12
13 SIDEBENDING ROTATION Two axes: A-P and bilateral vertical axes Occiput and Sphenoid rotate same direction on AP axis; side-bend away from each other on parallel axes. Named for convexity 13
14 LATERAL STRAIN Bilateral vertical axes Shearing force at SBS causing Sphenoid and Occiput to rotate same direction on axes Named for position of base of sphenoid Head appears parallelogram 14
15 VERTICAL STRAINS Sphenoid and Occiput rotate same direction on parallel horizontal axes Named for position (superior/inferior) of base of Sphenoid COMPRESSION 15
16 Temporal Bone 2 portions at birth (may fuse just prior to birth): Petromastoid portion: contains auditory and vestibular apparatus Squamous portion Eustachian tube forms between the petrous and squamous portions Temporal bone 16
17 Frontal bone 2 halves at birth Separated by metopic suture Remains unfused in 10% of population Labor and Delivery Head engages in pelvis Usually left occiput anterior LOA 17
18 Forces of Delivery Head begins in flexion, as vertex is presenting Flexion limits ability to rotate, forces move inferiorly Can lead to SBS compression Forces of Delivery Head extends as occiput pivots on the pubic symphysis Transmits force to atlanto-axial joint, or becomes intra-osseous within the occiput itself Forces of Delivery Rotational component relates to presenting position Head returns to neutral upon delivery of head, called restitution Strains can also result from in utero positioning 18
19 Forces of Delivery Moulding should resolve in 2 days Crying and suckling helpbreastfeeding is better Harder to resolve forceps or mityvac deliveries Frequent cause of cephalohematoma and caput succedaneum C-sections may also not resolve spontaneously, especially after a trial of labor Evaluation of Newborn Regular physical exam Overlapping of sutures Cranial base strain patterns Cephalohematoma Caput succedaneum Facial asymmetry, subconjunctival hemorrhage, suck reflex 19
20 OCF for Infants Torticollis Plagiocephaly Otitis media Torticollis Sidebending and rotation in opposite directions in the cervical spine that can not be passively reversed Related to intrauterine postioning, CN XI irritation Plagiocephaly Abnormal shape/flattening of the cranium Need to distinguish between nonsynostotic (positional) vs. synostotic 20
21 Deformational plagiocephaly vs. lambdoid synostosis Brachiocephaly 21
22 Clinical Impact Neurodevelopment in Children with Single-Suture Craniosynostosis and Plagiocephaly without Synostosis Panchal, Jayesh M.B.B.S., F.R.C.S., M.B.A.; Amirsheybani, Hamid M.D.; Gurwitch, Robin Ph.D.; Cook, Vicki M.Ed.; Francel, Paul M.D., Ph.D.; Neas, Barbara Ph.D.; Levine, Norman M.D. Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery: November Volume Issue 6 - pp Showed increased incidence of cognitive and psychomotor development Clinical Impact Auditory ERPs Reveal Brain Dysfunction in Infants With Plagiocephaly Balan, Polina PhD*; Kushnerenko, Elena MSc*; Sahlin, Pelle MD, PhD ; Huotilainen, Minna PhD*; Näätänen, Risto PhD*; Hukki, Jyri MD, PhD Journal of Craniofacial Surgery: July/August Volume 13 - Issue 4 - pp Demonstrated an increased risk of auditory processing disorders Clinical Impact Avoiding the Sequela Associated With Deformational Plagiocephaly Habal, Mutaz B. MD, FRCSC; Leimkuehler, Teresa MS; Chambers, Christina MS; Scheuerle, Jane EdD; Guilford, Arthur M. PhD Journal of Craniofacial Surgery: July Volume 14 - Issue 4 - pp Increased incidence of strabismus 22
23 Otitis Media 31 million office visits annually 90% of children have 1 episode by age 2 One third of children have 6 or more episodes by age 7 Major cause of mortality in undeveloped nations Otitis Media Male = Female Incidence peaks between 6-18 months Recurrence more likely if first episode is diagnosed before 1 year of age Otitis Media Anatomic basis for age differences TM s almost face inferiorly Angle of Eustachian tube is more horizontal, moves inferiorly as face lengthens with age 23
24 Otitis Media Risk Factors Passive smoke exposure Bottle-feeding Group daycare Pacifier use (but may protect against SIDS) Winter/Spring Preceding viral URI Otitis Media Otitis Media Osteopathic Exam Age-dependent Respiratory mechanics Cervical spine: middle for diaphragm innervation & sympathetic ganglion Thoracic spine: upper for sympathetic input to the cranium and mechanical contribution to cranial motion 24
25 Otitis Media Osteopathic Exam cont d Visual inspection for cranial asymmetry Cranial base: sphenoid and occiput Temporal bones Jaw Otitis Media Osteopathic techniques Galbreath technique Thoracic lymphatic pumps Diaphragm Balanced ligamentous/membranous tension for the cranium Research Authors Mills, M V; Henley, C E; Barnes, L L B; Carreiro, J E; Degenhardt, B F; Worden, K Title Effect of osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) on recurrent acute otitis media in children 25
26 OM Research Multi-center, randomized, nonplacebo trial Used OMT as adjunctive care to traditional treatment Pediatricians were blinded to treatment 25 OMT and 32 controls OM Research OMT group received 6-9 treatments over a 6 month period Treatment was articulatory, myofascial release, BLT/BMT, facilitated positional release and/or counterstrain No HV/LA OM Research Showed significant differences in: Number of episodes of AOM Antibiotic usage Surgical intervention 26
27 Other Pediatric Pearls Always think about bone age, epiphyseal fusion etc. Indirect is always better than direct Don t be intimidated by moving targets. Toys and bubbles help catch their attention From Pediatric Manual Medicine, Carreiro, 2009, p. 3 Diagnoses that respond well to OMT in kids Scoliosis Not usually diagnosed until older, can mostly be treated like adults Home exercise involving postural control Sports injuries Asthma/bronchiolitis/other respiratory illnesses Colic/GERD Motor disorder/developmental delays Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Indirect BLT/functional when more acute, joint play when not inflamed 27
28 28
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
WELCOME TO KCUMB-COM ACOP
 WELCOME TO KCUMB-COM ACOP WELCOME TO THE CITY OF FOUNTAINS! Osteopathic Approach to the Pediatric Patient Objectives At the end of the workshop the attendee will be able to: Discuss the musculoskeletal
WELCOME TO KCUMB-COM ACOP WELCOME TO THE CITY OF FOUNTAINS! Osteopathic Approach to the Pediatric Patient Objectives At the end of the workshop the attendee will be able to: Discuss the musculoskeletal
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II. Nerves covered in other lectures. A reminder about embryology. Prof. Stuart Bunt
 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
OMT for the child with ENT problems
 SEATED INNOMINATE AND PELVIC BOWL BALANCED LIGAMENTOUS TENSION 1. The physician is seated behind the child with both hands, each contacting an innominate and the sacrum. The fingers contact the ASIS bilaterally
SEATED INNOMINATE AND PELVIC BOWL BALANCED LIGAMENTOUS TENSION 1. The physician is seated behind the child with both hands, each contacting an innominate and the sacrum. The fingers contact the ASIS bilaterally
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Cranial Nerves VII to XII
 Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
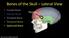 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Osteopathic Pediatrics. AOBP with thanks to: Dawn C. Dillinger, DO Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Eric Hegybeli, DO
 Osteopathic Pediatrics AOBP with thanks to: Dawn C. Dillinger, DO Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Eric Hegybeli, DO Osteopathic Tenants from the Pediatric Perspective The body functions as a unit A child
Osteopathic Pediatrics AOBP with thanks to: Dawn C. Dillinger, DO Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Eric Hegybeli, DO Osteopathic Tenants from the Pediatric Perspective The body functions as a unit A child
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017
 OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
OMT FOR CONCUSSIONS KIMBERLY WOLF, D.O. FEBRUARY 17, 2017 POTENTIAL SEQUENCE Address lymphatics including all transition zones/diaphragms Address somatic dysfunction in spine Focus on upper cervical spine
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Prevention Diagnosis
 Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
Prevention and Management of Positional Skull Deformities in Infants John Persing, MD, Hector James, MD, Jack Swanson, MD, John Kattwinkel, MD, Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Osteopathic Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction in Infants After Birth
 Osteopathic Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction in Infants After Birth Tammy Humphreys C170347 August 10, 2018 Osteopathy refers to three basic principles. 1) The body is a unit, wherein all systems aim
Osteopathic Treatment for Somatic Dysfunction in Infants After Birth Tammy Humphreys C170347 August 10, 2018 Osteopathy refers to three basic principles. 1) The body is a unit, wherein all systems aim
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES. Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa
 MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa SENR 2014 CRANIAL NERVES Olfactory: I Optic: II Oculomotor nerves: III, IV, VI Trigeminal nerve:
MRI ANATOMY OF THE CRANIAL NERVES Alexandra Borges Radiology Dpt. Instituto Português de Oncologia de Lisboa SENR 2014 CRANIAL NERVES Olfactory: I Optic: II Oculomotor nerves: III, IV, VI Trigeminal nerve:
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1
 Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord
 1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Authorized Osteopathic Thesaurus December, 2003 Terms
 s 100-199 USE (s) Elevated Rib Inhalation Rib Dysfunction Item number: 100 Broader (s) Related (s) End Feel Tissue Texture Abnormality Movement Barrier Item number: 101 Perceived quality of motion as an
s 100-199 USE (s) Elevated Rib Inhalation Rib Dysfunction Item number: 100 Broader (s) Related (s) End Feel Tissue Texture Abnormality Movement Barrier Item number: 101 Perceived quality of motion as an
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
Anatomy #9. Rashed AL-Jomared. The Cranial Nerves IX. Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji
 Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
OMT FOR THE NAS INFANT. Eren Ural OGME II
 OMT FOR THE NAS INFANT Eren Ural OGME II Objectives: 1. Review the signs and symptoms monitored for diagnosing Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome 2. Understand current medical management for Neonatal Abstinence
OMT FOR THE NAS INFANT Eren Ural OGME II Objectives: 1. Review the signs and symptoms monitored for diagnosing Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome 2. Understand current medical management for Neonatal Abstinence
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
The Axial Skeleton. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app.
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors We've split our Cranial Nerves lab activity into two parts. Part 1 is pre-lab exercises
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors We've split our Cranial Nerves lab activity into two parts. Part 1 is pre-lab exercises
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Applications of CranioSacral Therapy in Newborns and Infants, Part I
 Applications of CranioSacral Therapy in Newborns and Infants, Part I By John Upledger, DO, OMM CranioSacral Therapy has proven effective in identifying a number of disorders affecting children, including
Applications of CranioSacral Therapy in Newborns and Infants, Part I By John Upledger, DO, OMM CranioSacral Therapy has proven effective in identifying a number of disorders affecting children, including
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
THE USE OF OSTEOPATHIC MANUAL MEDICINE IN THE SPECIAL NEEDS POPULATION
 THE USE OF OSTEOPATHIC MANUAL MEDICINE IN THE SPECIAL NEEDS POPULATION AVA C. STANCZAK, D.O.,FACOP,CS PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS OCSA Copyright 2017 I have no relevant relationships/affiliations with any
THE USE OF OSTEOPATHIC MANUAL MEDICINE IN THE SPECIAL NEEDS POPULATION AVA C. STANCZAK, D.O.,FACOP,CS PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRICS OCSA Copyright 2017 I have no relevant relationships/affiliations with any
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Department of Neurosurgery. Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly
 Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
Department of Neurosurgery Differentiating Craniosynostosis from Positional Plagiocephaly The number of infants with head shape deformities has risen over the past several years, likely due to increased
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
