Designer receptors show role for ventral pallidum input to ventral tegmental area in cocaine seeking
|
|
|
- Blaise Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Designer reeptors show role for ventrl pllium input to ventrl tegmentl re in oine seeking Stephen V Mhler 1, Elen M Vzey 1, Jo T Bekley 1, Coly R Keistler 1, Ellen M MGlinhey 1, Jennifer Kufling 1, Steven P Wilson 2, Krl Deisseroth 3, John J Woowr 1 & Gry Aston-Jones 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. The ventrl pllium is entrlly positione within mesoortiolimi rewr iruits, n its ense projetion to the ventrl tegmentl re () regultes neuronl tivity there. However, the ventrl pllium is heterogeneous struture, n how this omplexity ffets its role within wier rewr iruits is unler. We foun tht projetions to from the rostrl ventrl pllium (), ut not the ul ventrl pllium (), were roustly Fos tivte uring ue-inue reinsttement of oine seeking rt moel of relpse in ition. Moreover, esigner reeptor meite trnsient intivtion of neurons, their terminls in or funtionl onnetivity etween n opmine neurons loke the ility of rug-ssoite ues (ut not oine prime) to reinstte oine seeking. In ontrst, neuronl inhiition loke oine-prime, ut not ue-inue, reinsttement. This oule issoition in ventrl pllium suregionl roles in rug seeking is likely to e importnt for unerstning the mesoortiolimi iruits unerlying rewr seeking n ition. The ventrl pllium is ruil noe in the ventrl stritopllil iruits unerlying rewr-relte ehviors, with mjor reiprol onnetions to the umens, extene mygl, limi thlmus, sustnti nigr (SN) n 1. Ventrl pllium neurons respon to rewrs n their ues in nimls n humns n re neessry for rewr-seeking ehviors, leing to hypotheses tht the ventrl pllium helps trnslte motivtionl sttes into ppetitive ehviors 5 7. However, the ventrl pllium is heterogeneous struture, exhiiting meil-lterl n rostrl-ul vrition in histologil mrkers n onnetivity ptterns 1,,. Notly, the ventromeil ventrl pllium (most of whih is lote suommissurlly, rostrl of regm in rt: ) reeives ense fferents from the nuleus umens shell n projets strongly to the meioorsl thlmus n. The orsolterl ventrl pllium (most of whih is lote sulentiulrlly, ul of regm: ) inste reeives fferents from the umens ore n projets to SN n the suthlmi nuleus, in ition to 1,9. This topogrphy implies the involvement of ventrl pllium suregions in funtionlly istint mesolimi iruits. Funtionl heterogeneity etween ventrl pllium suregions hs lso een reporte. In vitro, n neurons iffer in severl wys: mny neurons hve spiny enrites, glutmtergi fferents, hyperpolrize memrne potentils n no spontneous tion potentils 1. Interestingly, these hrteristis re more typil of umens meium spiny neurons thn lssil ventrl pllium neurons. In ontrst, neurons hve more lssilly pllil hrteristis, inluing spiny enrites, GABAergi inputs, epolrize memrne potentils n spontneous tion potentils. Notly, neuronl firing uring rt oine self-ministrtion vries epening on meiolterl n rostroul loliztion within the ventrl pllium 11, n ventrl pllium rostroul vrition exists in neuronl ytorhiteture, in vivo firing rtes, sensitivity to the rewring effets of eletril stimultion n miroinjete rugs, opioi gonist inue heoni responses to tstes n funtionl mgneti resonne imging (fmri) tivtion to emotionlly rousing pitures However, little is known out how suh heterogeneity ontriutes to the funtions of the ventrl pllium within wier mesolimi iruits. In rts, provies tonilly tive GABA inputs to n SN tht gte the firing of supopultions of opmine neurons n moulte rewr seeking 2. However, ventrl pllium neurons re lso utely tivte y rewr-ssoite ues 6,21,22, n ventrl pllium projetions to re tivte uring ue-inue reinsttement of oine seeking 23. How oes funtionl-ntomil heterogeneity ffet the regultion of y the ventrl pllium n the role of this iruit in rug seeking? We sought to exmine the roles of ventrl pllium suregions n their projetions in relpse to oine seeking. We exmine Fos tivtion of n projetions to n intivte these suregions or their projetions to mirin opminergi regions uring reinsttement of oine seeking using esigner reeptors exlusively tivte y esigner rugs (DREADDs) 2. DREADDs utilize enogenous G-protein signling pthwys ut o not ffet neuronl tivity in the sene of their otherwise inert, exogenously ministere lign, lozpine-n-oxie (). The G i -ouple (hmdi) DREADDs use here therey llow trnsient intivtion of efine neuronl popultions 25. We lso show tht they n e use to mnipulte xonl terminls of DREADD-expressing neurons 1 Deprtment of Neurosienes, Meil University of South Crolin, Chrleston, South Crolin, USA. 2 Deprtment of Phrmology, Physiology n Neurosiene, Shool of Meiine, University of South Crolin, Columi, South Crolin, USA. 3 Deprtment of Bioengineering n Psyhitry n Behviorl Sienes, Stnfor University, Stnfor, Cliforni, USA. Corresponene shoul e resse to S.V.M. (mhler@mus.eu). Reeive 12 Deemer 213; epte 2 Jnury 21; pulishe online 2 Mrh 21; oi:1.13/nn.366 nture NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL
2 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Figure 1 hmdi inhiitory DREADD expression n funtion. () The Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP lentivirus use to express hmdi DREADDs uner neuronl-speifi humn synpsin promoter (Syn) in or. LTR, long terminl repet; IRES, internl riosome entry site; egfp, enhne GFP; WPRE, WHV post-trnsriptionl regultory element; SD, splie onor site; Psi, enpsition signl; GA, trunte GAG sequene; RRE, Rev response element. () Typil stining for HA-tgge hmdi fter ilterl injetions into. Sle r, 1 mm. () HA-tgge hmdi reeptors re expresse on ell oies n proesses (lk stining) in the ventrl pllium (neutrl re ounterstin). Sle r, 5 µm. () Typil HA expression (green) in ontine lrgely within the ventrl pllium orers (efine with sustne P ounterstin in re). (e) Typil HA expression in ontine lrgely within the ventrl pllium orers (s efine in ). Imges in e re representtive of DREADD expression seen in the experimentl groups (with n numers liste in the min text). The with of the imges in n e is 2.65 mm. (f) Inhiition of firing rtes in neurons (n = 2 totl) from nimls with Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP expression in or n lol pplition of 1 µm onto extrellulrly reore ventrl pllium (VP) neurons in vivo (with oule-rrel glss pipette). (g) Typil hnge in ishrge rte of ventrl pllium neuron (wveform inset) fter lol pplition (she region). to intivte prtiulr monosynpti pthwys (for exmple, -) or to isrupt funtionl onnetivity etween speifi neuronl popultions (for exmple, n opmine neurons). We emonstrte oule issoition etween the rostrl n ul ventrl pllium in ue s ompre to oine-prime reinsttement, respetively, n show tht ue oine seeking is epenent on projetions to n omplex intertions with opminergi n nonopminergi neurons there. RESULTS Vlition of ventrl pllium DREADDs We use DREADD-se strtegy to remotely ontrol ventrl pllium neurons in vivo n mnipulte the ventrl pllium iruit. We injete synpsin-riven lentivirl vetor yieling expression of the G i -ouple DREADD, hmdi 2, or ontrol virus lking the DREADD gene (Syn-GFP) into or n llowe nimls to survive for t lest 6 weeks efore nlyzing the rin tissue for virus expression. The Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP virus (Fig. 1) use roust hmdi expression within or (visulize with immunoretivity for the hemgglutinin (HA) tg or GFP reporter). These injetions yiele limite expression outsie the orers of the ventrl pllium (<3% leling outsie the ventrl pllium orers; Figs. 1 n 2 n Supplementry Fig. 1). The Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP n Syn-GFP viruses yiele omprle zones of somti GFP or hmdi expression entere t the injetion site (GFP:.2 (.21) mm 3 (men (s.e.m.)); hmdi:.9 (.5) mm 3 ). f 5 LTR +. mm HA SP VP neurons 79% (19) (5) Inhiite Not inhiite SD-Psi- GA-RRE g Spikes per 1 s Syn HA tg hmdi e HA + n Nissl IRES Promoters or filittors.72 mm egfp tg HA + proesses 1 ms WPRE Nissl only 3 LTR Enoe proteins We then use in vivo eletrophysiology to funtionlly vlite hmdi reeptor expression. In isofluorne-nesthetize rts, lol miroinjetion (6 nl, 1 µm) inhiite ventrl pllium neurons (n = 2 ells, 6.3 ± 6.6% (men ± s.e.m., normlize to the pre- firing rte for eh ell) erese in firing, Z = 2.5, P =.11; Fig. 1f,g). Lol miroinjetion of similrly ffete neurons (11/13 ells inhiite) n neurons (/11 inhiite), with 5.2 ±.7% n 63.2 ± 1.6% inhiition, respetively. Pre- firing rtes in (6. ± 2. Hz) were lower thn in (2. ± 5.3 Hz, P =.7, t 12 = 3.26), s reporte previously 1,12. Doule issoition of ventrl pllil roles in reinsttement Next we exmine whether trnsient DREADD-meite inhiition of or woul ttenute either ue or oine-prime (1 mg per kg oy weight) reinsttement of oine seeking fter Time (min) 57 VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 nture NEUROSCIENCE
3 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Figure 2 Effets of intivting the rostrl or ul ventrl pllium on reinsttement of oine seeking. () Dily oine infusions n tive or intive lever presses (men ± s.e.m.) for the lst 6 ys of riterion self ministrtion (>1 infusions per y) n tive or intive lever presses for the first 7 ys of extintion trining. () Ative lever presses uring ue-inue reinsttement fter ifferent oses of the DREADD gonist (the vrious oses re istinguishe y r shing: vehile or.1, 1, 1 or 2 mg per kg oy weight) in nimls with ilterl or Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP virus expression, ilterl ventrl pllium ontrol virus (Syn-GFP) expression or no virus expression. Intive lever presses uring reinsttement re shown with overli lk rs. P =.1 for vehile ompre to 1 mg per kg oy weight ; P =.15 for vehile ompre to 2 mg per kg oy weight (nlysis of vrine (ANOVA) with Bonferroni orretion post ho). () Ative n intive lever presses uring oine-prime reinsttement fter vehile or ifferent oses of (1 or 2 mg per kg oy weight) in nimls with or Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP virus expression or ontrol nimls (Syn-GFP or no virus expression). P =. for vehile ompre to 2 mg per kg oy weight (ANOVA with Bonferroni orretion post ho). The t in n re shown s the men ± s.e.m. () The ntomil loliztion of virus expression sites (s visulize with HA or GFP immunoretivity) represente for nimls injete with Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP in (lk res) or (gry res) or with Syn-GFP (gry res; inset). oine self-ministrtion n extintion (Fig. 2). (,.1, 1, 1 or 2 mg per kg oy weight) ttenute ue reinsttement in rts with hmdi expression in ut not in nimls with omprle DREADD expression in (: n = 16 rts, F,39 =., P =.; : n = 17 rts, F,6 =.59, P =.6; Fig. 2). In ontrst, (, 1 or 2 mg per kg oy weight) injetions ttenute oine-prime reinsttement only in nimls with hmdi expression in ut not in (: F 2,29 =.5, P =.6; : F 2,31 = 3., P =.; Fig. 2), reveling oule issoition etween n for reinsttement eliite y ues s ompre to oine. The zones in whih hmdi inhiition ws most effetive t reuing ue reinsttement were entere in, wheres effetive sites for oine-prime reinsttement were entere in (ue, ventrl pllium site rug intertion: F 1,16 = 7.35, P =.15; prime, ventrl pllium site rug intertion: F 1,25 =.5, P =.37). Inhiition of the ventrl pllium ws suffiient for these effets, s ses with miniml (<5%) hmdi expression outsie the ventrl pllium orers showe equivlent reinsttement effets s those with more (<3%) enrohment of expression into jent res (Supplementry Fig. 1). h no effet in nimls with either or infusions Self ministrtion Coine infusions Ative lever Intive lever Extintion Self-ministrtion y Extintion y Vehile.1 mg per kg 1 mg per kg 1 mg per kg 2 mg per kg hmdi Intive Intive Intive Intive Vehile 1 mg per kg 2 mg per kg hmdi Intive Intive Intive Control nimls GFP virus No virus GFP virus injetions (Syn-GFP, lking the hmdi gene; n = 5 rts; ue: F 2,11 =.5, P =.5; prime: F 1, =.5, P =.3) or no virus expression (n = 9 rts; ue: F 2,1 =.7, P =.; prime: F 2,2 =.2, P =.76; ontrol groups omine, ue: F 2,2 =.77, P =.7; prime: F 2,31 =.22, P =.; Fig. 2,). Fos tivtion of - projetions uring reinsttement We next ske whether the role of in ue reinsttement ehvior involves projetions to. First we exmine Fos expression in or -projeting neurons uring ue VP GFP Perentge Fos + -projeting neurons CS+ Ext CS Loo Ative lever presses : r =.7 : r = Perentge Fos + -projeting neurons Figure 3 Rostrl ventrl pllium projetions to re Fos tivte uring ue reinsttement. () Preominntly ipsilterl projetions from n to igrmme in the horizontl plne. () Axon terminls in express the nterogrely trnsporte, HA-tgge hmdi reeptor (lk xonl proesses) fter Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP injetion in ipsilterl (re Nissl ounterstin in ). Coronl view, sle r, 5 µm. The imge is representtive of ventrl pllium xonl DREADD expression in of the experimentl nimls (with n numers liste in the min text). () Perentges (men ± s.e.m.) of -projeting (CT + ) or ells tht express Fos fter ue-inue reinsttement (CS+) or ontrol ehviorl onitions in whih nimls were expose to the extinguishe self-ministrtion environment without ues or oine (Ext), tone or light stimulus not ssoite with oine (CS ) or loomotion-enhning novel environment (Loo). A greter proportion of -projeting neurons in were Fos tivte in CS+ thn in ontrol nimls (P =.1 for CS+ ompre to Ext; P =.5 for CS+ ompre to CS ; P =.25 for CS+ ompre to Loo; one-wy ANOVA with post ho Tukey HSD). No signifint ehvior-speifi tivtion of -projeting neurons ws etete in. The t re shown s the men ± s.e.m. () Correltion of ue-inue reinsttement ehvior with Fos tivtion of -projeting neurons in (P =.2, Person orreltion) n (P =.16, nonsignifint Person orreltion). nture NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL
4 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Figure Intivting rostrl ventrl pllium fferents moultes ell firing. () hmdi reeptors (green) re expresse on xon terminls in the viinity of TH-lele opmine neurons (re) in. Sle r, 3 µm. The imge is representtive of ventrl pllium xonl DREADD expression in of experimentl nimls (with n numers liste in the Online Methos). () Slie eletrophysiology experiments in whih reore neurons were fille with iotin, lele with viin (re) n ientifie s opminergi y oleling for TH (green). Sle r, 1 µm. () Representtive tres from opmine neurons in seline onitions (top, lk) n fter (ottom, re; vertil sles, 2 pa; horizontl sles, 2 ms). () The effet of on the umultive istriution or men (inset) sipsc mplitue. In the lrger grph, the t re represente s the men ± s.e.m.; the lines in the inset onnet rw vlues for iniviul ells, n the rs show the men ± s.e.m. (e) The shift in IEI umultive istriution (P =.2 for seline ompre to ; two-wy ANOVA) n men sipsc frequeny (P =.6 for seline ompre to (inset); t test) fter. The t in the lrger grph re shown s the men ± s.e.m.; the lines in the inset onnet rw vlues for iniviul ells, n the rs show the men ± s.e.m. (f) In vivo exittion of puttively opminergi type 1 neurons (n = 9 totl) in y lol pplition of in the viinity of hmdi-expressing terminls in. (g) Rte histogrm emonstrting the effet of lol pplition in vivo (6 nl; she region) on the firing of type 1 neuron (wveform inset) in of -hmdi niml. (h) Inhiition of fst-firing, short-wveform type 2 neurons (n = 1 totl) y lol pplition of in vivo in the viinity of hmdi-expressing terminls in. (i) Exmple hnge in the ishrge rte of type 2 neuron (wveform inset) in fter lol pplition in vivo (6 nl; she region) in -hmdi niml. reinsttement or ontrol ehviors (Fig. 3 n Supplementry Fig. 2). We injete the retrogre trer holer toxin β suunit (CT) into the rostrl or ul. We trine nimls (n = 25) to intrvenously self-minister oine plus onurrently presente ues, extinguishe this ehvior n then gve them 2-h ue-inue reinsttement test or ontrol ehviorl test (Online Methos). We euthnize the nimls immeitely fter this test session n o-stine ventrl pllium slies for Fos n CT. In, -projeting (CT + ) neurons were Fos tivte uring ue oine seeking (n = rts) ut not uring exposure to the extinguishe self-ministrtion hmer (n = 7), novel environment (n = 6) or fmilir, non oine ssoite stimulus (n = ; F 3,21 = 6.6, P =.2; Fig. 3). Unlike, projetions to were not signifintly tivte uring ue reinsttement (F 3,21 = 2.3, P =.11; Fig. 3 n Supplementry Fig. 2). Moreover, in iniviul ue oine-seeking nimls, the egree of Fos tivtion of fferents from, ut not, ws positively orrelte with the egree of ue-inue oine-seeking ehvior (: r =.7, P =.2; : r =.5, P =.16; Fig. 3 n Supplementry Fig. 2), Cumultive proility f h 1..5 Bseline Type 1 neurons (1) 9% () Exite Not exite 71% (1) () Inhiite Not inhiite Amplitue i g Spikes per 1 s Spikes per 1 s 6 2 Amplitue (pa) e Cumultive proility Bseline 2 ms Merge initing tht more tivity in efferents to is ssoite with more ue-triggere rug seeking. Vliting inhiition of - projetion with DREADDs The hmdi DREADD is trffike xonlly, s eviene y numerous HA + fiers n terminls tht re relily oserve in the ventrl mirin fter injetion of hmdi vetor in or (Figs. 3 n n Supplementry Fig. 3,e). We exmine whether moultion of G i -ouple signling in ventrl pllium xon terminls in y lol pplition woul lter the tivity of neurons. First we reore spontneous inhiitory postsynpti urrents (sipscs) from opmine neurons (verifie y tyrosine hyroxylse (TH) immunoretivity) in slies from rts tht Rostrl Bseline IEI Meil Bseline Bseline ,2 1,5 Amplitue (pa) Time (ms) Type 2 neurons TH HA 2 ms Time (min) TH Aviin Time (min) 1 5 Frequeny (Hz) 5 VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 nture neuroscience
5 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. were injete t lest 6 weeks previously with the hmdi vetor in (n = 7 rts; Fig.,). Perfusion with 5 µm h no effet on sipsc mplitue (t 6 =.9, P =.3; Fig. ) ut erese the frequeny (t 6 = 2.5, P =.6) n shifte the umultive istriution of interevent intervls (IEIs) to the right (min effet of IEI urtion: F 21,26 = 22.1, P =.1; tretment: F 1,26 = 1.2, P =.2; Fig. e). In slies from Syn-GFP injete nimls (n = 5 ells), whih lso expresse GFP in neurons n xons, h no effet on sipsc mplitue (t =.7, P =.67) or IEIs (t =.39, P =.; Supplementry Fig. ). These finings inite tht tivtion of hmdi DREADDs on ventrl pllium terminls in erese GABA relese onto opmine neurons. We onfirme this fining in vivo, emonstrting tht intr- miroinjetion of in rts previously injete with Syn-hMDi- HA-GFP in (-hmdi rts) signifintly inrese the firing rte (2.5 ± 5.2% inrese) in of 9 type 1 neurons (those meeting onventionl eletrophysiologil riteri for opmine neurons 26 ; P =.3; t 7 = 2.63; Fig. f,g). Conversely, 1 of 1 fst-spiking, shortwveform type 2 neurons (not onventionlly opmine-like) were inhiite ( 6.5 ± 12.% hnge in ishrge) fter intr- miroinjetion of in -hmdi rts (P =.3; t 9 = 3.93; Fig. h,i). Inhiiting terminls in loks ue reinsttement Next we exmine effets of intivting ventrl pllium terminls in on ue or oine-prime reinsttement ehvior. We miroinjete (in ounterlne orer on seprte ys) -hmdi nimls (n = 2) with (1 mm,.3 µl per sie) or vehile (rtifiil ererospinl flui (CSF)) into (n = 17 rts) or SN (n = 11) 5 min efore ue or prime reinsttement (two tests eh per niml; Fig. 5). We lso injete -hmdi nimls (n = 9) with ( or 1 mm,.3 µl) into n then teste them on ue or prime reinsttement (Fig. 5 n nnule sites in Supplementry Fig. 5). Inhiition of terminls in with lol seletively ttenute ue ut not prime reinsttement (ue: F 1,16 = 27.7, P =.75; prime: F 1,16 =.1, P =.92; Fig. 5), initing tht tivtion of the projetion to is require for rug ues to rive reinsttement of oine seeking. In ontrst, intivting terminls in SN or terminls in h no effets on ue or prime reinsttement (-SN inhiition, ue: F 1,1 =.21, P =.66; prime: F 1,1 =.1, P =.92; - inhiition, ue: F 1, =., P =.39, prime: F 1, =.37, P =.56; Fig. 5,f). This result inites tht lthough is neessry for oine-prime reinsttement (Fig. 2), its trgets re not essentil for this tion. Intivting projetions to in the sene of ues or priming injetions file to ffet rug seeking fter extintion (n = rts; vehile tive lever presses:.7 ± 6.7 (men ± s.e.m.); :.3 ± 1.7; F 1,3 = 3.9, P =.1). In -hmdi (n = 11) or -hmdi (n = 6) nimls, neither intr- (n = 17) nor intr-sn (n = 6) h signifint effet on generl loomotor ehvior in fmilir environment (no min effet of rug or rug time intertions; F s < 1.7, P s >.11; Fig. 5,e,g), initing tht reinsttement effets of - inhiition re more likely motivtionl thn motori in nture. interts with opmine neurons in reinsttement is omplex struture, with opmine, GABA n glutmte projetion neurons, s well s interneurons n other lol onnetivity Beuse ventrl pllium projetions moulte opmine n nonopmine neuron firing in 32 (Fig. ), we ske whether reinsttement ehvior is ffete y ontrhemispheri isonnetion of from opmine neurons. In trnsgeni rts tht express Cre reominse in TH neurons (THøCre + rts) 33, we unilterlly trnsue neurons with the Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP lentivirus esrie ove. We lso injete oule-floxe hmdi enossoite virus (AAV) (DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry; Fig. 6) into the ontrlterl (n = 9 rts) or SN (n = ), yieling relile n ntomilly restrite hmdi expression in unilterl opmine neurons (Fig. 6, n Supplementry Fig. 6). A systemi injetion in these nimls therefore funtionlly isonnete inputs from mirin opmine ells ilterlly while spring onnetivity with nonopminergi neurons (Fig. 6). Control groups onsiste of Cre + nimls with unilterl DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry injetions ut no virus in (n = 6 rts) or Cre littermtes (n = 1) with unilterl hmdi n ontrlterl injetions of DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry (ut no hmdi expression). As shown in Figure 6, ue-inue reinsttement ws mrkely ttenute y isrupting the - opmine iruit in this mnner (F 1, = 37.97, P =.3; Fig. 6e). We foun no effets fter similrly isonneting from SN opmine neurons (F 1,7 =.29, P =.61) or fter unilterlly intivting either (F 1,9 =.6, P =.1) or opmine neurons (F 1,5 =.57, P =.) (Fig. 6e). This result inites tht intt onnetivity etween (not ) SN miroinjetion 6 2 Intive Ext Cue Prime Vehile Intive Bem reks ( 1) Bem reks ( 1) Horizontl loomotion Rering 12 Time in session Intive Intive Ext Cue Prime e Bem reks ( 1) Bem reks ( 1) Horizontl loomotion 9 6 Rering Time in session (min) f 6 2 SN Intive Intive Ext Cue Prime g Bem reks ( 1) Bem reks ( 1) SN Horizontl loomotion 9 6 Rering Time in session (min) Figure 5 Intivting rostrl ventrl pllium projetion to loks ue reinsttement. () Projetions from to or SN or from to were trnsiently intivte y lol mirin miroinjetion of mong ventrl pllium xon terminls expressing hmdi reeptors. () The effet of intivtion of terminls from on ue-inue (Cue) n oine-prime (Prime) reinsttement of oine seeking (n = 17). Also shown re tive lever pressing uring the lst y of extintion trining (Ext, rs t left) n reinsttement fter tretment of with vehile (white rs) or (gry rs). Intive lever presses re represente with lk rs t the ottom. P =.75; two-wy ANOVA. () Effets on horizontl (top grph) n vertil (rering; ottom grph) loomotion in fmilir environment fter intivting projetions to (n = 11). Loomotion (em reks) uring 3 min ins in the 2-h session is shown fter miroinjetion of vehile (lk lines) or (gry lines). (,e) Effets on ue-inue n oine-prime reinsttement (n = 9), s well s horizontl loomotion n rering (n = 6), fter intivtion of efferents to. (f,g) Effets on reinsttement (n = 11) or loomotive ehvior (n = 6) fter intivtion of projetions to SN. All t re shown s the men ± s.e.m. nture NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 51
6 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Figure 6 Funtionl isonnetion of rostrl ventrl pllium projetion to opmine neurons loks ue-inue reinsttement. () A DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry AAV onstrut tht ws use to seletively express mcherry-tgge hmdi reeptors in opmine ells in THøCre + trnsgeni rts. ITR, inverte terminl repet. () hmdi expression in representtive niml with DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry injetion in. Immunoleling for TH ientifies opmine neurons (green), n mcherry (re) ientifies hmdi-expressing neurons in. Nerly ll hmdi-expressing neurons were opminergi. -injete nimls i not show sustntil hmdi expression lterlly in SN or in the ontrlterl. Sle r, 5 µm. The inset on the right shows hmdi + TH + ell t high mgnifition (imge with, 5 µm). () hmdi expression in representtive niml with DIO-Syn-hMDimCherry injetion in SN. Miniml expression in ws oserve. Sle r, 5 µm. Equivlent expression ws oserve in ehviorlly teste rts;, n = 9; SN, n =. () Unilterl Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP injetions were me in, n DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry injetions were me in the ontrlterl or SN of THøCre + rts or of Cre littermtes. When systemi ws ministere, seril onnetivity etween the ventrl pllium n mirin opmine popultions is ompromise ilterlly y unilterl hmdi inhiition of n ontrlterl hmdi inhiition of opmine neurons. (e) Ative n intive lever pressing uring ue-inue reinsttement in nimls with - opmine (DA) ontrlterl isonnet. Pressing uring lte extintion (gry r t left) n ue reinsttement fter vehile (white rs) or (1 mg per kg oy weight; re rs) is shown. Contrlterl isonnet nimls were THøCre + rts tht reeive unilterl Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP injetions n ontrlterl or SN DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry injetions. Unilterl intivtion rts (-hmdi) were Cre n reeive unilterl hmdi virus plus ontrlterl opmine hmdi virus (lthough the ltter i not use hmdi expression in these Cre rts). Unilterl opmine intivtion rts ( opmine hmdi) were Cre + n reeive only unilterl opmine hmdi virus. Only ontrlterl n (not SN) opmine popultions is require for onitione ues to trigger oine seeking uring reinsttement. Further exmintions of the nture of the - iruit GABAergi ventrl pllium projetions to n tonilly inhiit opmine neurons 5, n intivting this projetion with DREADDs n isinhiit opmine neurons (Fig. ). We therefore e e TH mcherry TH mcherry ITR Merge Dorsl Dorsl Syn Meil Meil Vehile (1 mg per kg) Extintion Merge Floxe hmdi DREADD AAV 6993 p ske whether isinhiition of opmine neurons oul hve ontriute to the ttenution of reinsttement we oserve fter intivting inputs to with DREADDs. If so, then iret isinhiition of opmine neurons with the GABA A ntgonist gzine shoul lso ttenute reinsttement. Inste we oserve tht intr- gzine (1 µm,.3 µl) strongly inrese ue reinsttement (n = 6 rts; F 2,17 = 9.3, P =.2; vehile s ompre f Intive loxp m Cherry hmdi tg lox 2722 Contrlterl isonnet Intive g WPRE opmine hmdi VP Intive 3 ITR Unilterl ontrols SN Intive - DA -SN DA DA isonnetion of from opmine neurons reue ue reinsttement elow ontrol levels. P =.3; repete-mesures ANOVA. The group n numers re liste in the min text. The t re shown s the men ± s.e.m. hmdi Cells per mm Vehile Gzine (1 µm) Fos + TH + neurons Totl TH + neurons Perentge TH + ells with Fos % 75.3% Veh Gzine (1 µm) Figure 7 GABA A -meite isinhiition of opmine neurons enhnes ue-inue reinsttement. () Exmple of Fos stining fter nery gzine miroinjetion (1 µm,.3 µl). () Exmple TH stining of the sme tissue. () Overly of Fos n TH stining. () Mgnifie view of the Fos n TH overly. Arrows point to olele neurons. Stining typil of gzine-injete rts (n = 5). Sle rs ( ), 1 µm. (e) Fos inution in, n numer of, TH + neurons fter miroinjetion of vehile (n = 3) or gzine (n = 5). (f) The perentge of TH + neurons tht expresse Fos fter injetion of vehile (veh) or gzine. (g) Gzine injetion sites within from ue-inue reinsttement nimls. Gzine ws injete t equivlent sites s in the Fos- n TH-stine setion in. (h) Ative n intive lever pressing uring ue reinsttement fter injetion of vehile or gzine (1 µm; n = 6). In suset of nimls (n = ), gzine (1 µm) roustly inrese pressing oth levers, whih ws proly relte to intense nonspeifi loomotor tivtion. P =.2; one-wy ANOVA. All t re shown s the men ± s.e.m. h 12 gzine injetion sites Ative lever Intive lever Ext 1 1 gzine (µm) 52 VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 nture neuroscience
7 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. to 1 µm gzine tive lever: t 6 = 2.62, P =.; Fig. 7g,h) n roustly inue Fos in nery opmine neurons (vehile, n = 3; gzine, n = 5 rts; no effet on numer of TH + ells: t 6 =.2, P =.; totl Fos + TH + ells: t. = 5.55, P =.1; perentge Fos + TH + ells: t 6 =., P =.1; Fig. 7 f). This fining inites tht simple isinhiition of opmine neurons is proly not the mehnism y whih inhiiting inputs to reues ue reinsttement. In ition to GABA projetions, sens numerous VGlut2 + efferents to 3 ; we ske whether this glutmtergi projetion is require for ue reinsttement. We use unilterl DREADD-se inhiition n ontrlterl miroinjetion of oktil of the AMPA n NMDA ntgonists 6-yno-7-nitroquinoxline-2,3- ione (CNQX) n ( )-2-mino-5-phosphonovleri i (AP5) (.7 n 1.6 mm, respetively) to ilterlly ompromise glutmte projetions from to. This i not ffet ue reinsttement (n = 5 rts; t = 1.2, P =.29; Supplementry Fig. 7). In ontrst, reinsttement ws ttenute when ll neurons were inhiite (with lofen n musimol,.3 n.3 mm, respetively) ontrlterlly to DREADD-intivte (- isonnet, n = 1 rts, t 9 = 2.1, P =.2; no effet of unilterl lofen n musimol lone, n =, t 7 = 1.3, P =.3; Supplementry Fig. 7). In slies, we lso explore whether inhiiting inputs to woul erese spontneous exittory trnsmission (sepscs) onto opmine neurons. (5 µm) h no effet on sepsc mplitue (t 5 =.22, P =.3) or frequeny (t 5 =.3, P =.6) in TH + ells (n = 6 ells; Supplementry Fig. ). These finings inite tht glutmtergi projetions to o not moulte opmine neurons iretly n re proly not neessry for ue reinsttement. DISCUSSION Here we esrie n - pthwy tivte y, n neessry for, onitione ue-inue reinsttement of oine seeking in rts. The involvement of the ventrl pllium in reinsttement epens ritilly on oth the rostroul position within the ventrl pllium n the mens y whih rug seeking is reinstte (ues or oine prime). Cue-triggere rug seeking speifilly requires oth projetions to n funtionl intertions etween inputs n opmine n nonopmine neurons. In ition to esriing oule issoition etween ventrl pllium suregions in rug seeking, we lso vlite the use of G i -ouple DREADDs to intivte speifi neuronl pthwys through moultion of DREADD-expressing terminls n to funtionlly isonnet rin iruits in vivo. Ventrl pllium roles in rewr seeking Muh previous reserh hs fouse on the portion of the ventrl pllium ul of regm in rts (), whih showe tht the ventrl pllium is n importnt noe in mesoortiolimi rewr iruits. Lesions or phrmologil intivtion of reue rug or foo seeking 13,35 3. Mny of these ventrl pllium neurons re spontneously tive, n their GABAergi projetion to tonilly inhiits popultions of opmine neurons there 5. Ventrl pllium efferents to re lso utely tivte y rewrs n ssoite ues. For exmple, ventrl pllium projetions in rts re Fos-tivte fter ute mphetmine ministrtion, oine self-ministrtion or ue reinsttement of oine seeking 23,39,, n ventrl pllium neurons phsilly fire when slient rewrs n their ues re experiene 6,11. In nonhumn primtes, ventrl pllium neurons lso fire in reltion to rewr ntiiption, n ventrl pllium intivtion ompromises moultion of rewr seeking on the sis of rewr expettion 22. Similrly, the ventrl pllium is fmri-tivte y ues for rug or nturl rewrs in humns 1. Our report therefore supports n sustntilly expns on the known roles for the ventrl pllium in rewr seeking. Heterogeneity within the ventrl pllium Antomilly, oth rostroul n meiolterl heterogeneity exists in ventrl pllium ell morphology, trnsmitter ontent, soures of fferents n efferent trgets 6,1,16,2,3. A lrge proportion of the suommissurl onsists of neurotensin-positive ventromeil suregion, whih reeives fferents from the meil umens shell n sens efferents to the meioorsl thlmus n. In ontrst, lrge proportion of the sulentiulr onsists of linin-positive orsolterl suregion tht reeives umens ore inputs n projets to SN n the suthlmi nuleus 1. (n the jent ul umens shell) hs een esrie s trnsition zone etween the umens n tritionl (ul) ventrl pllium, with onnetivity n morphologil fetures istint from those of the rostrl umens, pllil or extene mygl regions 1,2. Supporting this view, n the ul ventromeil umens shell projet similrly to, n Fos tivtion of oth projetions is orrelte with ue-inue reinsttement ehvior (Fig. 3) 23. Previous eviene supports role for in onitione motivtion n for in the rewring n priming effets of reinforers themselves. For exmple, (ut not ) is Fostivte uring motivte ehviors triggere y Pvlovin ues for speifi slient rewrs n is neessry for these ues to trigger seeking ehviors,5. (not ) is fmri-tivte when people view highly slient, isgusting photogrphs, gin initing role in onitione motivtionl sttes 1. In ontrst, GABA gonists miroinjete into reue oine-prime n stress-inue reinsttement of oine seeking 35,36, in lignment with our oservtion tht DREADD-se inhiition of neurons loke prime reinsttement (lthough to our knowlege ours is the first report of role for the ventrl pllium, n more speifilly,, in ue reinsttement of oine seeking). Aitionlly, (not ) hs een linke to the heoni evlution of primry rewrs in nimls n humns 1,19. Here we exmine the funtions of n in ue n prime reinsttement of oine seeking. We showe tht (not ) is neessry for ues to trigger oine seeking, wheres (not ) is neessry for oine prime to eliit reinsttement. Therefore, the ventrl pllium in generl is ritilly involve in promoting relpse-relte rug seeking, ut its rostrl n ul spets ifferentilly meite the motivtionl properties of previously lerne ues s ompre to oine itself. - projetion speifilly meites ue rug seeking To exmine the wier neurl iruits with whih n intert to rive reinsttement, we fouse on ventrl pllium projetions to. First we showe tht ut not projetions to re Fos tivte in proportion to ue reinsttement. To test whether these efferents to re lso neessry for reinsttement, we inue hmdi DREADD expression in or neurons n then miroinjete the DREADD gonist iretly into. This llowe us to speifilly inhiit ventrl pllium projetions ut not other ventrl pllium efferents. When projetions to (ut not the jent SN) were intivte in this mnner, ue-inue reinsttement ws olishe, ut prime reinsttement ws spre. In ontrst, similr inhiition nture NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 53
8 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. of projetions to file to ffet either ue or prime reinsttement. Therefore, projetions to re seletively reruite uring ue reinsttement n re neessry for ues to trigger reinsttement, wheres is neessry for oine prime to promote reinsttement through -inepenent iruitry. iniretly moultes opmine neurons in reinsttement We ientifie funtionl iruit ontining n (ut not or SN) opmine neurons tht is neessry for ues to eliit reinsttement y funtionlly isonneting from opmine neurons through hmdi inhiition of in one hemisphere n simultneous hmdi inhiition of opmine neurons in the ontrlterl hemisphere. This seletive, ilterl iruit isruption reue ue-inue reinsttement, initing tht seril onnetivity etween n opmine neurons is require for ues to trigger oine seeking. Ventrl pllium projetions to re preominntly GABAergi 3,5,32, n onsistent with previous reports 32, we oserve tht DREADD-se inhiition of inputs to isinhiite opmine neurons y eresing sipsc frequeny. However, inisriminte isinhiition of opmine neurons is unlikely to ount for the ttenute reinsttement tht we oserve fter - intivtion. When we iretly isinhiite opmine neurons (s eviene y roust Fos inution) with miroinjetions of the GABA A ntgonist gzine, ue reinsttement ws inste inrese (Fig. 7). It is therefore likely tht reinsttement loke y inhiition of inputs to involves ifferentil moultion of heterogeneous neuronl supopultions, possily inluing inhiition of nonopminergi neurons. Notly, this moultion ppers to e le to supersee reinsttement-promoting effets of opmine neuron isinhiition, whih n lso our when the - iruit is intivte. Systemti mpping of inputs to neuronl supopultions will e require to further hrterize the omplexities of this new, ition-relte iruit. In ition to GABA efferents, sens sustntil VGlut2- ontining projetions to 3. However, DREADD-se inhiition of - projetions i not reue spontneous exittory trnsmission to TH + ells, n ontrlterl isonnet se isruption of glutmte projetions to i not ffet ue reinsttement, rguing ginst reinsttement-relte glutmtergi - projetion. Conlusions Here we showe tht projetions to re tivte uring, n re neessry for, ue-inue reinsttement n tht this requires moultion of opmine neurons. However, this moultion proly oes not involve iret GABAergi or glutmtergi projetions onto opmine neurons. Inste, inhiiting inputs to yiele oth exittion of type 1 neurons n inhiition of type 2 neurons in vivo (Fig. ). Type 1 neurons, whih isplye onventionlly opminergi eletrophysiologil hrteristis, were exite y ventrl pllium inhiition, onsistent with our fining tht intivtion of inputs to ttenutes GABA inputs to TH + neurons (Fig. e). However, inisriminte isinhiition of opmine neurons with GABA A ntgonist i not impee reinsttement ut inste roustly filitte it. Therefore, lthough our isonnetion stuy revele tht opmine neurons re neee for ventrl pllium regultion of relpse, the role of the ventrl pllium in reinsttement oes not epen on generl isinhiition of opmine neurons in. One possiility is tht ventrl pllium neurons seletively regulte selet supopultion of opmine neurons uring ue rug seeking. Notly, ontins fst-firing, thin-wveform opmine neurons 6,7, n it is possile tht these oul e the type 2 neurons whose tivity is suppresse fter - intivtion (Fig. h,i). However, this possiility seems unlikely, s inhiitory inputs to opmine neurons reore in vitro here were nerly lwys reue y DREADD-se intivtion of - projetions (Fig. e). Therefore, we hypothesize tht omplex, supopultion-speifi ventrl pllium moultion of neurons is neessry for ues to eliit relpse to oine seeking. These finings ll for itionl reserh to hrterize the reltive onnetivity of ventrl pllium GABA, glutmte, etylholine n peptie-ontining neurons with neuronl supopultions n to further efine the roles for eh in rewr seeking. In summry, we hve esrie new pthwy, the projetion from to, tht is neessry for onitione rug seeking in moel of relpse in ition. Furthermore, this iruit-ehvior reltionship requires moultion of oth nonopmine n opmine neurons. We lso showe tht ventrl pllium suregions hve qulittively ifferent roles in rug-seeking ehvior eliite y either onitione stimuli or the rug itself. Together these finings oth expn the known iruitry of onitione motivtion n lso highlight importnt next iretions for untngling the neurl sustrtes of rewr-seeking ehvior, espeilly in ppetitive isorers suh s rug ition. Methos Methos n ny ssoite referenes re ville in the online version of the pper. Note: Any Supplementry Informtion n Soure Dt files re ville in the online version of the pper. Aknowlegments We thnk P. Do, M.J. Gilstrp n E.C. Lin for ssistne with ehviorl testing n immunohistohemistry n B.L. Roth (Deprtment of Phrmology, University of North Crolin) for DREADD onstruts n onsulttion on DREADDs. ws supplie y US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (NIH) Ntionl Cner Institute (NCI) uner the uspies of NS62-1 n y the Ntionl Institute of Mentl Helth (NIMH) Chemil Synthesis n Drug Supply Progrm. Reserh ws supporte y NIH grnts F32 DA26692, K99 DA35251 (S.V.M.), F31 DA391 (J.T.B.), R21 DA2537 (G.A.-J. n S.P.W.), R1 DA13951 (J.J.W.), R37 DA621 n P5 DA15369 (G.A.-J.). This projet ws supporte y the Ntionl Center for Reserh Resoures n the Offie of the Diretor of the Ntionl Institutes of Helth through grnt numer C6 RR1555. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS S.V.M. ttine funing, esigne n onute experiments, performe surgeries, nlyze t n wrote the mnusript. E.M.V. esigne n onute nesthetize eletrophysiology experiments, nlyze these t n wrote the mnusript. J.T.B. esigne n onute slie eletrophysiology experiments, nlyze these t n wrote the mnusript. C.R.K. onute ehviorl experiments n wrote the mnusript. E.M.M. performe surgeries for n onute ehviorl n immunohistohemil experiments. J.K. onute immunohistohemil n onfol mirosopy experiments. S.P.W. ttine funing n ontriute the Syn-GFP virl onstrut. K.D. ontriute the THøCre trnsgeni rt line. J.J.W. ttine funing, esigne n onute slie eletrophysiology experiments n wrote the mnusript. G.A-J. ttine funing, esigne experiments n wrote the mnusript. COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS The uthors elre no ompeting finnil interests. Reprints n permissions informtion is ville online t reprints/inex.html. 1. Zhm, D.S. & Heimer, L. Two trnspllil pthwys originting in the rt nuleus umens. J. Comp. Neurol. 32, 37 6 (199). 5 VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 nture neuroscience
9 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. 2. Zhm, D.S., Willims, E. & Wohltmnn, C. Ventrl stritoplliothlmi projetion: IV. Reltive involvements of neurohemilly istint suterritories in the ventrl pllium n jent prts of the rostroventrl forerin. J. Comp. Neurol. 36, (1996). 3. Klivs, P.W., Churhill, L. & Klitenik, M.A. GABA n enkephlin projetion from the nuleus umens n ventrl pllium to the ventrl tegmentl re. Neurosiene 57, (1993).. Her, S.N. & Nut, W.J. Rmifitions of the glous pllius in the rt s inite y ptterns of immunohistohemistry. Neurosiene 9, (193). 5. Floreso, S.B., West, A.R., Ash, B., Moore, H. & Gre, A.A. Afferent moultion of opmine neuron firing ifferentilly regultes toni n phsi opmine trnsmission. Nt. Neurosi. 6, (23). 6. Smith, K.S., Tinell, A.J., Alrige, J.W. & Berrige, K.C. Ventrl pllium roles in rewr n motivtion. Behv. Brin Res. 196, (29). 7. Mogenson, G.J., Bruzynski, S.M., Wu, M., Yng, C.Y. & Yim, C.Y. From motivtion to tion: review of opminergi regultion of limi to nuleus umens to ventrl pllium to peunulopontine nuleus iruitries involve in limi-motor integrtion. in Limi Motor Ciruits in Neuropsyhitry (es. Klivs, P.W. & Brnes, C.D.) (CRC Press, Bo Rton, Flori, 1993).. Churhill, L. & Klivs, P.W. A topogrphilly orgnize γ-minoutyri i projetion from the ventrl pllium to the nuleus umens in the rt. J. Comp. Neurol. 35, (199). 9. Heimer, L., Zhm, D.S., Churhill, L., Klivs, P.W. & Wohltmnn, C. Speifiity in the projetion ptterns of uml ore n shell in the rt. Neurosiene 1, (1991). 1. Kuphik, Y.M. & Klivs, P.W. The rostrl suommissurl ventrl pllium is mix of ventrl pllil neurons n neurons from jent res: n eletrophysiologil stuy. Brin Strut. Funt. 21, (213). 11. Root, D.H. et l. Differentil roles of ventrl pllium suregions uring oine self-ministrtion ehviors. J. Comp. Neurol. 521, 55 5 (213). 12. Yng, C.R. & Mogenson, G.J. Ventrl pllil neuronl responses to opmine reeptor stimultion in the nuleus umens. Brin Res. 9, (199). 13. MBrie, W.J., Murphy, J.M. & Ikemoto, S. Loliztion of rin reinforement mehnisms: intrrnil self-ministrtion n intrrnil ple-onitioning stuies. Behv. Brin Res. 11, (1999). 1. Pngis, G., Miliressis, E., Angnostkis, Y. & Spyrki, C. Ventrl pllium selfstimultion: movele eletroe mpping stuy. Behv. Brin Res. 6, (1995). 15. Bengtson, C.P. & Osorne, P.B. Eletrophysiologil properties of holinergi n nonholinergi neurons in the ventrl pllil region of the nuleus slis in rt rin slies. J. Neurophysiol. 3, (2). 16. Zhm, D.S. & Heimer, L. Ventrl stritopllil prts of the sl gngli in the rt: I. Neurohemil omprtmenttion s reflete y the istriutions of neurotensin n sustne P immunoretivity. J. Comp. Neurol. 272, (19). 17. Johnson, P.I., Stellr, J.R. & Pul, A.D. Regionl rewr ifferenes within the ventrl pllium re revele y miroinjetions of µ opite reeptor gonist. Neurophrmology 32, (1993). 1. Cler, A.J. et l. Disgust sensitivity preits the insul n pllil response to pitures of isgusting foos. Eur. J. Neurosi. 25, (27). 19. Smith, K.S. & Berrige, K.C. The ventrl pllium n heoni rewr: neurohemil mps of surose liking n foo intke. J. Neurosi. 25, (25). 2. Gre, A.A., Floreso, S.B., Goto, Y. & Loge, D.J. Regultion of firing of opminergi neurons n ontrol of gol-irete ehviors. Trens Neurosi. 3, (27). 21. Tinell, A.J., Berrige, K.C. & Alrige, J.W. Ventrl pllil representtion of pvlovin ues n rewr: popultion n rte oes. J. Neurosi. 2, (2). 22. Thin, Y. & Hikosk, O. The primte ventrl pllium enoes expete rewr vlue n regultes motor tion. Neuron 76, (212). 23. Mhler, S.V. & Aston-Jones, G.S. Fos tivtion of seletive fferents to ventrl tegmentl re uring ue-inue reinsttement of oine seeking in rts. J. Neurosi. 32, (212). 2. Armruster, B.N., Li, X., Push, M.H., Herlitze, S. & Roth, B.L. Evolving the lok to fit the key to rete fmily of G protein ouple reeptors potently tivte y n inert lign. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 1, (27). 25. Ferguson, S.M. & Neumier, J.F. Grteful DREADDs: engineere reeptors revel how neurl iruits regulte ehvior. Neuropsyhophrmology 37, (212). 26. Ungless, M.A. & Gre, A.A. Are you or ren t you? Chllenges ssoite with physiologilly ientifying opmine neurons. Trens Neurosi. 35, 22 3 (212). 27. Ikemoto, S. Dopmine rewr iruitry: two projetion systems from the ventrl mirin to the nuleus umens-olftory tuerle omplex. Brin Res. Rev. 56, 27 7 (27). 2. Morles, M. & Pikel, V.M. Insights to rug ition erive from ultrstruturl views of the mesoortiolimi system. Ann. NY A. Si. 12, 71 (212). 29. Fiels, H.L., Hjelmst, G.O., Mrgolis, E.B. & Niol, S.M. Ventrl tegmentl re neurons in lerne ppetitive ehvior n positive reinforement. Annu. Rev. Neurosi. 3, (27). 3. vn Zessen, R., Phillips, J.L., Buygin, E.A. & Stuer, G.D. Ativtion of GABA neurons isrupts rewr onsumption. Neuron 73, (212). 31. Stmtkis, A.M. et l. A unique popultion of ventrl tegmentl re neurons inhiits the lterl henul to promote rewr. Neuron, (213). 32. Hjelmst, G.O., Xi, Y., Mrgolis, E.B. & Fiels, H.L. Opioi moultion of ventrl pllil fferents to ventrl tegmentl re neurons. J. Neurosi. 33, (213). 33. Witten, I.B. et l. Reominse-river rt lines: tools, tehniques, n optogeneti pplition to opmine-meite reinforement. Neuron 72, (211). 3. Geisler, S., Derst, C., Veh, R.W. & Zhm, D.S. Glutmtergi fferents of the ventrl tegmentl re in the rt. J. Neurosi. 27, (27). 35. MFrln, K. & Klivs, P.W. The iruitry meiting oine-inue reinsttement of rug-seeking ehvior. J. Neurosi. 21, (21). 36. MFrln, K., Dvige, S.B., Lpish, C.C. & Klivs, P.W. Limi n motor iruitry unerlying footshok-inue reinsttement of oine-seeking ehvior. J. Neurosi. 2, (2). 37. Roleo, P. & Koo, G.F. Two isrete nuleus umens projetion res ifferentilly meite oine self-ministrtion in the rt. Behv. Brin Res. 55, (1993). 3. Frrr, A.M. et l. Forerin iruitry involve in effort-relte hoie: injetions of the GABA A gonist musimol into ventrl pllium lter response llotion in foo-seeking ehvior. Neurosiene 152, (2). 39. Colussi-Ms, J., Geisler, S., Zimmer, L., Zhm, D.S. & Bero, A. Ativtion of fferents to the ventrl tegmentl re in response to ute mphetmine: oulelelling stuy. Eur. J. Neurosi. 26, (27).. Geisler, S. et l. Prominent tivtion of rinstem n pllil fferents of the ventrl tegmentl re y oine. Neuropsyhophrmology 33, (2). 1. Chilress, A.R. et l. Prelue to pssion: limi tivtion y unseen rug n sexul ues. PLoS ONE 3, e156 (2). 2. Zhm, D.S. Is the uomeil shell of the nuleus umens prt of the extene mygl? A onsiertion of onnetions. Crit. Rev. Neuroiol. 12, (199). 3. Tripthi, A., Prens, L. & Mengul, E. Axonl rnhing ptterns of ventrl pllil neurons in the rt. Brin Strut. Funt. 21, (213).. Leung, B.K. & Blleine, B.W. The ventrl strito-pllil pthwy meites the effet of preitive lerning on hoie etween gol-irete tions. J. Neurosi. 33, (213). 5. Roinson, M.J. & Berrige, K.C. Instnt trnsformtion of lerne repulsion into motivtionl wnting.. Curr. Biol. 23, (213). 6. Lmmel, S. et l. Unique properties of mesoprefrontl neurons within ul mesoortiolimi opmine system. Neuron 57, (2). 7. Luo, A.H., Georges, F.E. & Aston-Jones, G.S. Novel neurons in ventrl tegmentl re fire seletively uring the tive phse of the iurnl yle. Eur. J. Neurosi. 27, 22 (2).. Roinson, T.E. & Berrige, K.C. Aition. Annu. Rev. Psyhol. 5, (23). nture NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 17 NUMBER APRIL 21 55
10 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. ONLINE METHODS Sujets. 159 mle Sprgue-Dwley rts (25 35 g; Chrles River) n 5 outre mle Long-Evns THøCre rts (hemizygous Cre +, n = 35; Cre littermtes, n = 1) 33 were single or pir house in 12 h, 12 h reverse light yle vivrium (ll tests were onute in the rk perio). No sttistil methos were use to preetermine smple sizes, ut they were similr to those reporte in previous pulitions 15,19,23,9. All proeures were pprove y the Meil University of South Crolin s Institutionl Animl Cre n Use Committee. Surgil proeures. Animls were nesthetize with ketmine, xylzine n meloxim (56.5,.7 n 1. mg per kg oy weight, respetively) n implnte with inwelling jugulr theters. They then reeive 2 3 nl injetions of.5% CT unilterlly in or 1 µl unilterl or ilterl virus injetions into, or. CT n ventrl pllium lentivirus injetions were me y pneumti pressure using glss pipette (for CT, 15 2 µm tip; for lentivirus, 3-5 µm tip) over 5 min n left in ple for 15 2 min. In THøCre nimls, mirin injetions of n AAV floxe DIO-Syn-hMDi-mCherry virus were me over 1 min through Hmilton miroinjetion syringe. For ilterl or gzine or unilterl glutmte ntgonist or GABA gonist miroinjetions in ehving nimls, guie nnule were implnte 2 mm orsl to or SN. Virl onstruts. To trnsue ventrl pllium neurons with hmdi DREADDs, we use synpsin promoter riven lentivirl vetor with GFP reporter ustom pkge (VSV-G envelope) y the University of Pennsylvni vetor ore. To ssist with ientifition, the hmdi hs n N-terminl HA tg n n IRES GFP reporter (Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP; Fig. 1). A Syn-GFP lentivirus (lking the DREADD gene) ws use to ontrol for nonspeifi virus effets (Fig. 2, n Supplementry Fig. 5). In THøCre trnsgeni rts 33, n AAV ontining oule-floxe, inverte open reing frme hmdi-mcherry sequene (DIO-Syn-hMDimCherry; University of North Crolin Vetor Core) ws miroinjete into the ventrl mirin to express hmdi reeptors seletively in TH neurons of or SN (Fig. 6). Loliztion of DREADD expression. hmdi reeptor expression in ell oies n proesses ws visulize with immunohistohemistry for HA, GFP or mcherry tgs (esrie elow). Continment of trnsution sites within or, or within or SN opmine ells, ws onfirme y o-stining for sustne P (SP; efining orers of the ventrl pllium) or TH (efining n SN) n rin tls 5. A synpsin promoter virus ws employe in the ventrl pllium, so some expression ws oserve outsie the orers of or in most nimls. Animls with more thn 3% of DREADD expression oserve outsie or were exlue from nlyses (n = 7). For nimls with virus injetions, no more thn 2% of DREADD-expressing tissue enrohe into (i.e., ul of regm) or vie vers. Animls injete with the Syn-GFP ontrol virus in the ventrl pllium h omprle GFP expression ptterns to the hmdi-injete nimls. For THøCre rts, hmdi expression ws roust in either or SN n ws restrite lmost exlusively to TH + ell oies n proesses (perentge mcherry + neurons oexpressing TH (men ± s.e.m.): 97.5 ±.7%; Fig. 6, n Supplementry Fig. 6). mcherry expression ws not oserve in the ontrlterl hemisphere, n expression i not exten sustntilly into SN of -injete nimls or into of SNinjete nimls (Fig. 6,). Eletrophysiologil vlition of DREADD-se inhiition of ventrl pllium neurons n efferents. Brin slies from nimls injete in the ventrl pllium with Syn-hMDi-HA-GFP (n = 6 rts) or Syn-GFP (n = 2) were prepre s previously esrie 9. Slie physiology t olletion n nlyses were not performe lin to the experimentl group. Horizontl setions ontining were trnsferre to 32 3 C hmer ontining rogen-ule CSF solution. Slies were trnsferre to reoring hmer n perfuse with 32 C CSF t 2 ml per min. Neurons were visully ientifie uner infrre light using Dot grient ontrst imging. Reoring pipettes with resistne of 1 3 MΩ were fille with internl solution ontining (in mm) CsCl (12), -(2-hyroxyethyl)- 1-piperzineethnesulfoni i (1), MgCl 2 (2), ethylene glyol tetreti i (1), N 2 ATP (2), NGTP (.3) n.2% ioytin; 295 mosm, ph 7.3. To isolte sipscs, reoring CSF ws supplemente with AMPA n NMDA ntgonists (NBQX n AP5; 1 µm n 1 µm, respetively; Am), n for sepsc reorings, pirotoxin (1 µm; Toris) ws e to the CSF. Neurons meil to the nuleus of the essory opti trt were trgete for pth lmp (in the viinity of ense, GFP-expressing fferents), n whole-ell moe ws hieve while holing the ell t 7 mv. Dt were quire using n Axon MultiClmp 7B mplifier n n ITC-1 igitl interfe (HEKA Instruments) ontrolle y AxogrphX softwre. Reorings were filtere t khz n quire t 1 khz, n sipscs were etete n nlyze using the templte-mthing event-etetion lgorithm in AxogrphX. Detetion prmeters were set t mplitue > pa, n quire events were visully inspete efore verging. We reore t lest 15 spontneous urrents uring seline perio n fter 1 min of 5 µm perfusion. Series resistne (R s ) ws monitore throughout the reoring, n n experiment ws isontinue if the R s exeee 25 MΩ or hnge more thn 25%. In vivo eletrophysiology t olletion n nlyses were performe in isofluorne-nesthetize rts y n experimenter lin to experimentl onitions. Glss reoring pipettes (5 12 MΩ) were fille with 2% pontmine sky lue in.5 M soium ette. A glss injetion pipette (2-µm tip) glue ~15 µm ehin the reoring tip elivere 6 nl of 1 µm to the ventrl pllium or neurons with rief pneumti pulses. Multiple pplitions ourre in eh niml in ifferent ells, eh seprte y >3 min. Signls were mplifie n filtere (.3 5 khz) using Moel 16 Neuroproe Amplifier (A-M Systems) n BMA 2 Biomplifier (CWE) efore igitl onversion n reoring to Spike 2 (v5.21) with Miro 11 MkII interfe (CED). Boy temperture ws mintine t C throughout the reorings. Reore ventrl pllium neurons were lote ner previous virus injetions n were ientifie y their firing rtes n wveforms, s reporte previously 12. For onfirmtion of reoring lotions, mrkings 1 mm ove n immeitely elow reoring trks in eh ventrl pllium n site were me y iontophoreti ye eposits immeitely efore perfusion. type 1 neurons were ientifie y eletrophysiologil riteri tritionlly esriing opmine neurons 26, inluing (i) iphsi or triphsi wveform >2.5 ms in urtion, (ii) >1.1 ms from spike onset to negtive trough n (iii) spontneous firing rte <1 Hz. All ells inlue in nlyses were from onfirme reorings in the ventrl pllium or. Drugs n trt trers. Coine HCl (NIDA) ws issolve in.9% sterile sline. CT (Sigm) ws issolve t.5% in.1 M PBS. ws supplie y NIH NCI uner the uspies of NS62-1. For systemi ministrtion, (,.1, 1, 1 or 2 mg per kg oy weight) ws issolve in 5% imethyl sulfoxie n then ilute to 1 ml per kg oy weight volume with.9% sline. For intrrnil ministrtion, ws issolve in CSF to 1 µm (in vivo eletrophysiology) or 1 mm (ehviorl miroinjetion) or 5 µm in vitro. Gzine (1 or 1 µm), lofen n musimol (.3 n.3 mm, respetively), n CNQX n AP5 (.7 n 1.6 mm, respetively; ll from Sigm) were issolve in CSF for.3 µl miroinjetions. Behviorl trining n testing proeures. Behviorl trining n testing took ple in stnr Me Assoites opernt hmers esrie elsewhere 23. Rts unerwent ten ily 2-h self-ministrtion sessions (>1 oine infusions per y,.2 mg, 5 µl infusion). Pressing one lever yiele 3.6-s oine infusion, tone n light ove the tive lever (FR1 sheule), followe y 2-s timeout uring whih pressing ws reore ut i not yiel oine or ues (Fig. 2). Intive lever presses were reore ut h no onsequenes. Animls then reeive t lest 7 of extintion trining (until the riterion of <25 presses for 2 onseutive ys ws rehe) uring whih lever presses yiele neither oine nor ues. During 2-h ue-inue reinsttement tests, tive lever presses yiele oine ues ut no oine. For oine priming tests, 1 mg per kg oy weight oine ws ministere intrperitonelly (i.p.) immeitely efore the 2-h test uring whih lever presses yiele neither oine nor ues. For the CT n Fos experiment, nimls were perfuse immeitely fter one of the following 2-h test sessions: CS+ reinsttement, n itionl extintion session, exposure to novel environment or exposure to isrete CS (further etils re liste in ref. 23). nture NEUROSCIENCE oi:1.13/nn.366
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Climbing fibers encode a temporal-difference prediction error during cerebellar learning in mice
 Climing fiers enoe temporl-ifferene preition error uring ereellr lerning in mie Shogo Ohme & Jvier F Mein npg 25 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Climing fier inputs to Purkinje ells re thought to
Climing fiers enoe temporl-ifferene preition error uring ereellr lerning in mie Shogo Ohme & Jvier F Mein npg 25 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Climing fier inputs to Purkinje ells re thought to
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Increasing the usage level of corn and distillers grains in market turkey diets through the use of supplemental amino acids
 Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Non-redundant odor coding by sister mitral cells revealed by light addressable glomeruli in the mouse
 Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Neuroligin-1 dependent competition regulates cortical synaptogenesis and synapse number
 Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
Neural mechanisms mediating optimism bias. Positive Negative t-test (P) Correlation with optimism
 oi:.8/nture68 Neurl mehnisms meiting optimism is Tli Shrot,, Alison M. Riri, Cne M. Rio & Elizeth A. Phelps Humns expet positive events in the future even when there is no eviene to support suh expettions.
oi:.8/nture68 Neurl mehnisms meiting optimism is Tli Shrot,, Alison M. Riri, Cne M. Rio & Elizeth A. Phelps Humns expet positive events in the future even when there is no eviene to support suh expettions.
Diversity and wiring variability of olfactory local interneurons in the Drosophila antennal lobe
 Diversity n wiring vriility of olftory lol interneurons in the Drosophil ntennl loe Y-Hui Chou 1,3, Mri L Spletter 1,3, Emre Yksi 2,3, Jonthn C S Leong 1, Rhel I Wilson 2 & Liqun Luo 1 21 Nture Ameri,
Diversity n wiring vriility of olftory lol interneurons in the Drosophil ntennl loe Y-Hui Chou 1,3, Mri L Spletter 1,3, Emre Yksi 2,3, Jonthn C S Leong 1, Rhel I Wilson 2 & Liqun Luo 1 21 Nture Ameri,
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
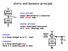 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor
 Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
nature letters to nature ... Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1 advance online publication
 vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
VTA CRF neurons mediate the aversive effects of nicotine withdrawal and promote intake escalation
 CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
Short term pre and post operative stress prolongs incision induced pain hypersensitivity without changing basal pain perception
 Co et l. Mol Pin () 11:73 DOI 1.11/s99--77-3 Moleulr Pin RESEARCH Open Aess Short term pre n post opertive stress prolongs inision inue pin hypersensitivity without hnging sl pin pereption Jing Co 1,,
Co et l. Mol Pin () 11:73 DOI 1.11/s99--77-3 Moleulr Pin RESEARCH Open Aess Short term pre n post opertive stress prolongs inision inue pin hypersensitivity without hnging sl pin pereption Jing Co 1,,
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
Parathyroid hormone related peptide is a naturally occurring, protein kinase A dependent angiogenesis inhibitor
 Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha Therapy in Crohn s Disease: Clinical and Health Economic Aspects
 Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
LETTER. Aberrant light directly impairs mood and learning through melanopsin-expressing neurons
 oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Presynaptic glycine receptors as a potential therapeutic target for hyperekplexia disease
 Presynpti glyine reeptors s potentil therpeuti trget for hyperekplexi isese Wei Xiong 1,2, Sho-Rui Chen 3, Liming He 4, Kejun Cheng, Yi-Lin Zho 3, Hong Chen 3, De-Pei Li 3, Gregg E Homnis 6,7, John Peever
Presynpti glyine reeptors s potentil therpeuti trget for hyperekplexi isese Wei Xiong 1,2, Sho-Rui Chen 3, Liming He 4, Kejun Cheng, Yi-Lin Zho 3, Hong Chen 3, De-Pei Li 3, Gregg E Homnis 6,7, John Peever
CSE 5311 Notes 2: Binary Search Trees
 S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
A savings procedure based construction heuristic for the offshore wind cable layout optimization problem
 A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is involved in learning and neuroprotection
 Glugon-like peptie-1 reeptor is involve in lerning n neuroprotetion Mtthew J During 1,2,Lei Co 2,Dvi S Zuzg 2,Jeremy S Frnis 1,Helen L Fitzsimons 1,2,Xingyng Jio 2, Ross J Bln 2,Mtthis Klugmnn 1,Willim
Glugon-like peptie-1 reeptor is involve in lerning n neuroprotetion Mtthew J During 1,2,Lei Co 2,Dvi S Zuzg 2,Jeremy S Frnis 1,Helen L Fitzsimons 1,2,Xingyng Jio 2, Ross J Bln 2,Mtthis Klugmnn 1,Willim
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
 nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, demyelinating, degenerative
 Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Electrophysiological Effects of Neurotensin on Globus Pallidus Neurons of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rats
 Originl Pper Neurosignls 29;17:153 161 DOI: 1.1159/19947 Reeived: Jnury 22, 28 Aepted fter revision: July 23, 28 Pulished online: Ferury 7, 29 Eletrophysiologil Effets of Neurotensin on Glous Pllidus Neurons
Originl Pper Neurosignls 29;17:153 161 DOI: 1.1159/19947 Reeived: Jnury 22, 28 Aepted fter revision: July 23, 28 Pulished online: Ferury 7, 29 Eletrophysiologil Effets of Neurotensin on Glous Pllidus Neurons
Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. p53 locus. Targeting vector DTA LSL. Targeted allele
 Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Supplemental Figures and Legends
 Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Evaluation of 99m Tc labeled PSMA SPECT/CT imaging in prostate cancer patients who have undergone biochemical relapse
 [Downloe free from http://www.jnrology.om on Thursy, Ferury 16, 2017, IP: 5.170.11.223] Asin Journl of Anrology (2017) 19, 1 5 2017 AJA, SIMM & SJTU. All rights reserve 1008 682X www.sinro.om; www.jnrology.om
[Downloe free from http://www.jnrology.om on Thursy, Ferury 16, 2017, IP: 5.170.11.223] Asin Journl of Anrology (2017) 19, 1 5 2017 AJA, SIMM & SJTU. All rights reserve 1008 682X www.sinro.om; www.jnrology.om
Opponent appetitive-aversive neural processes underlie predictive learning of pain relief
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
Rotoroll OK! User's Guide
 Rotoroll Pge Sfety preution. The user must never open Rotoroll to inspet it, reple prts or unertke repirs. The reeling mehnisms spring my pop out of its set n use mge n injury to persons, nimls n ojets
Rotoroll Pge Sfety preution. The user must never open Rotoroll to inspet it, reple prts or unertke repirs. The reeling mehnisms spring my pop out of its set n use mge n injury to persons, nimls n ojets
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
b-sitosterol activates Fas signaling in human breast cancer cells
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Macrophage mtorc1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice
 Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Systemic delivery of genes to striated muscles using adeno-associated viral vectors
 24 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturemeiine Systemi elivery of genes to strite musles using eno-ssoite virl vetors Pul Gregorevi,4,Mihel J Blnkinship,4,Jmes M Allen 2,Roert W Crwfor,Leonr Meuse,
24 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturemeiine Systemi elivery of genes to strite musles using eno-ssoite virl vetors Pul Gregorevi,4,Mihel J Blnkinship,4,Jmes M Allen 2,Roert W Crwfor,Leonr Meuse,
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Lethal graft-versus-host disease in mouse models of T cell receptor gene therapy
 r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
 Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
