Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
|
|
|
- Stanley Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2, Allison B Golfine 3, Christophe Benoist,5, Steven Shoelson 2 & Dine Mthis,5 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Oesity is ompnie y hroni, low-gre inflmmtion of ipose tissue, whih promotes insulin resistne n type-2 ietes. These finings rise the question of how ft inflmmtion n espe the powerful rmmentrium of ells n moleules normlly responsile for guring ginst runwy immune response. CD4 + + T regultory (T reg ) ells with unique phenotype were highly enrihe in the ominl ft of norml mie, ut their numers were strikingly n speifilly reue t this site in insulin-resistnt moels of oesity. Loss-of-funtion n gin-of-funtion experiments revele tht these T reg ells influene the inflmmtory stte of ipose tissue n, thus, insulin resistne. Cytokines ifferentilly synthesize y ft-resient regultory n onventionl T ells iretly ffete the synthesis of inflmmtory meitors n gluose uptke y ulture ipoytes. These oservtions suggest tht hrnessing the nti-inflmmtory properties of T reg ells to inhiit elements of the metoli synrome my hve therpeuti potentil. Type 2 ietes n other elements of the metoli synrome hve inrese t n lrming rte over the pst severl ees. There hs een prllel rise in the iniene of oesity, now reognize to e mjor ontriutor to the insulin resistne unerlying this spetrum of metoli normlities. Just how oesity promotes insulin resistne is still unler, ut results from linil, epiemiologil n moleulr stuies hve onverge to highlight the role of inflmmtion. Prolonge nutrient overlo results in stte of hroni, low-gre inflmmtion in ipose tissue 2 n systemilly 3, prtiulrly in viserl ft epots 4. Viserl ft proues numer of inflmmtory ytokines n hemokines (suh s leptin, tumor nerosis ftor- (TNF-), mrophge hemottrtnt protein- n interleukin-6 (IL-6), mong others), whose proution n e pthologilly ysregulte in the oese stte, ontriuting in n importnt mnner to insulin resistne 5. At the ellulr level, mrophges hve key role. With inresing oesity, they umulte in viserl ft tissue, sometimes ontriuting s muh s hlf of the ellulrity 6,7. The inrese in numer is ompnie y n evolution in phenotype from the nti-inflmmtory (or lterntively tivte ) M2 form to the proinflmmtory (or lssilly tivte ) M form 8,9, whih orreltes with n inrese in insulin resistne (for exmple, see ref. ). In the oese stte, mrophges n ipoytes mke severl of the sme inflmmtory regultors n meitors, inluing TNF-, IL-6, mtrix metlloproteinses (MMPs), peroxisome prolifertor tivte reeptor-g n ftty i ining protein-4 (reviewe in refs.,). These finings, long with others, suggest tht ipoytes n ipose-tissue mrophges my ontriute to insulin resistne in onert, oth inhiiting n enhning eh other s tivities. Like ny inflmmtory stte, the hroni, low-gre inflmmtion ssoite with oesity shoul e sujet to the ontrol mehnisms tht normlly ur overtive immune responses. These mehnisms enompss numer of ell types, whih n operte through ell-ell ontt vi vriety of reeptors, or through iversity of solule meitors. Cells with potentilly regultory phenotype hve previously een ssoite with oesity (for exmple, nturl killer T ells) 2, n there hve een previous reports of nti-inflmmtory ytokines eing etete in ipose tissue (for exmple, IL- n trnsforming growth ftor- (TGF-)) 8,9. Yet, reserh on this topi hs een quite limite, n the influene or loss of influene of mjor ontrol mehnisms remins unresse. For exmple, the role of rguly the most potent regultory ell popultion, CD4 + + T reg ells, hs yet to e explore. T reg ells, smll suset of T lymphoytes, normlly onstituting only 5 2% of the CD4 + omprtment, re thought to e one of the oy s most ruil efenses ginst inpproprite immune responses, operting in ontexts of utoimmunity, llergy, inflmmtion, infetion n tumorigenesis 3,4. Typilly, they ontrol the ehvior of Immunology n Immunogenetis, 2 Cellulr n Moleulr Physiology n 3 Clinil Reserh, Joslin Dietes Center, Deprtment of Meiine, Brighm n Women s Hospitl, Hrvr Meil Shool, Boston, Msshusetts, USA. 4 Europen Shool of Moleulr Meiine, Nples, Itly. 5 Present resses: Deprtment of Pthology, Hrvr Meil Shool, Boston, Msshusetts, USA (M.F., D.C., C.B. n D.M.); Deprtment of Biohemistry n Moleulr Biology, Shool of Phrmy, University of Brelon, Brelon, Spin (L.H.); Alnylm Phrmeutils, Cmrige, Msshusetts, USA (J.W.). Corresponene shoul e resse to D.M. (m@hms.hrvr.eu). Reeive Septemer 28; epte 5 June 29; pulishe online 26 July 29; oi:.38/nm.22 NATURE MEDICINE ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION
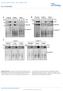
2 CD4: 52. ± ± ±.3 CD8: 8.3 ± SSC CD3 CD4 FSC SSC CD8 gte CD gte CD gte CD8 Isotype gte CD4 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. + of CD4 + 7 Spl LN Lung Liver A. ft other T ell popultions, ut they n lso influene the tivities of ells of the innte immune system 5 7.T reg ells re hrterize y expression of the forkhe winge-helix trnsription ftor,. Defiienies in this ftor use the lymphoprolifertion n multiorgn utoimmunity foun in surfy mutnt mie n humns with immunoysregultion polyenorinopthy enteropthy X-linke synrome. Here we exmine the T reg ells resiing in mouse ipose tissue with regrs to oth their proportion n phenotype in viserl versus suutneous ft epots in len versus oese mie. We evlute their funtionl importne in loss-of-funtion, gin-of-funtion n in vitro experiments. Lstly, we sought n nlogous popultion in humn ipose tissue smples. Our oservtions ientify unique ft-resient T lymphoyte popultion whose prouts my hve pplitions in treting the metoli synrome. RESULTS Aipose tissue T reg ells Aipose tissue is ompose of multiple ell types. Most prominent re ipoytes, ut vsulr enothelil ells, mrophges 6,7 n lymphoytes 2,8 re lso foun in the stromovsulr frtion. Aoring to multiprmeter flow ytometry, out % of the ells in the stromovsulr frtion of ominl ft from B3-week-ol C57BL/6 (B6) mie fell within the lymphoyte gte (Fig. ). Close to hlf of the ells in this gte were of the CD3 + T linege, split 3: etween the + of CD4 + 7 Aominl ft S.. ft Age (weeks) Figure Aominl (epiiyml) n suutneous ft ps s well s spleen, lymph noe, lung n liver were isolte from retire-reeer B6 mle mie, n the stromovsulr frtion ws stine for, CD3, CD4, CD8 n. () Top, T ell istriution in stromovsulr frtion from ominl ft tissue. Numers on top inite the men ± s.. from six experiments for ells in the lymphoyte gte (left), frtion of CD3 + T ells mong lymphoytegte ells (enter) n istriution of CD4 + n CD8 + T ells (right). Bottom, perentge of + + T ells in ominl ft tissue gte on CD4 + (left) or CD8 + (enter) T ells. Orgns of five mie were poole. Representtive ot plots re shown. FSC, forwr stter; SSC, sie stter. Numers on the grphs inite the perentge of ells in tht gte for tht prtiulr experiment. () Frequeny of + TellsmongCD4 + ells in ifferent orgns. Mens ± s.. from t lest three inepenent experiments re shown, n orgns from four or five mie per experiment were poole. Spl, spleen; LN, lymph noe. () KinetisofT reg ell pperne in ominl n suutneous (s..) ft tissue s well s in spleen. Error rs represent men ± s.. () Immunohistology of ominl ipose tissue. Arrowhe inites stining. expression is restrite to the nuleus. Asterisks refer to e ipoyte resiue surroune y rown-like struture forme y immune ells. Control stining is with isotype ntioy. Originl mgnifition: top left, 4; ll others,. (Control) CD4 + n CD8 + omprtments, respetively (Fig. ). To our surprise, more thn hlf of the CD4 + T ells expresse (Fig. ), muh higher frtion thn tht normlly foun in lymphoi (for exmple, in the spleen or lymph noes) or nonlymphoi (for exmple, lung or liver) tissues (Fig. ), inluing in suutneous ft (Fig. ). Viserl n suutneous ipose tissue h similr low frtions of T reg ells t irth, with progressive umultion over time in the viserl, though not the suutneous, epot (Fig. ). This ihotomy in T reg ell umultion etween these two ft epots is potentilly ruil, given the ssoition of viserl, ut not suutneous, ft with insulin resistne 4,9. Immunohistologil exmintion revele + ells in the spes etween ipoytes, minly, ut not only, in regions where severl of them intersete (Fig. ). Ft tissue, espeilly from oese iniviuls, n host sustntil numers of mrophges, whih umulte in so-lle rown-like strutures tht re replete with e ipoyte resiues 6,7,2.WeoserveT reg ells in suh strutures, in lose proximity to mrophges n other leukoyte ggregtes (Fig. ). We estimte tht 5, 2, + ells resie in g of epiiyml ipose tissue in n B3-week-ol B6 mouse. Expression profiling of ft T reg ells revels unique phenotype We next resse whether the + + ells in ominl ipose tissue were of the typil T reg phenotype (Fig. 2). They funtione s effetively s nlogous ells isolte from the spleen 2 ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION NATURE MEDICINE
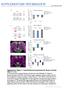
3 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. when introue into stnr in vitro suppression ssy (Fig. 2). Ft-resient T onventionl (T onv ) ells lso performe s expete; tht is, they h no suppressive tivity n h norml prolifertive response (Fig. 2). The lility n low reoverle numers of ftresient T reg ells hve so fr prevente us from ssying their tivities in in vivo suppressor ssys. So we turne to the well-estlishe trnsriptionl T reg ell signture, erive from the t of multiple groups 2 24,sninitorofin vivo funtion. The overll trnsript profile of the T reg ell popultion from viserl ft iffere from the ptterns of its spleen n lymph noe ounterprts more thn the ltter two i from eh other (Fig. 2). This oservtion lso hel for the T onv ell popultions t these sites, though not s notly so (Fig. 2). Fousing speifilly on the oumente T reg ell signture 2 24, we foun tht our t from the spleen showe n exellent repitultion of its mjor fetures; s ntiipte, most genes known to e upregulte in T reg ells esene to the right on the P vlue versus fol hnge volno plot, wheres most ownregulte loi roppe to the left (Fig. 2). Fully 93% of the signture ws present. In ontrst, eviene y their position t the volno summit, mny of the signture T reg ell genes were not signifintly up- or ownregulte in the orresponing popultion from viserl ft (for exmple, CD3 n G protein ouple reeptor-83) (Fig. 2). We onfirme the Figure 2 Funtionl omprison of T reg n T onv ells from ominl ipose tissue, lymph noe n spleen. CD4 + + T reg n T onv ells were isolte from retire-reeer B6 mie. () A stnr in vitro suppression ssy. erive CD4 + effetor T ells (responer ells) were inute t vrious rtios with ifferent T ell popultions (Ft: ipose tissue-erive T ells). ( e) Anlysis with Affymetrix mirorry hips. Normlize expression vlues for profiles iretly ompring T reg ells () in ft versus spleen (left), ft versus lymph noe (enter) n lymph noe versus spleen (right) or for profiles iretly ompring T onv ells () in ft versus spleen (left), ft versus lymph noe (enter) or lymph noe versus spleen (right). The numers in n inite the numer of genes whose expression iffere y more or less thn twofol. () Volno plots of gene expression t ompring P vlue versus fol hnge for proes from the onsensus T reg ell signture 2,24, plotte for spleen T reg ells versus T onv ells (left), ft T reg ells versus T onv ells (enter); ft T reg ells versus lymph noe T onv ells (right). The olor oing in the figures enotes genes.5-fol over- (re) or uner- (lue) expresse in T reg ells in ll four referene t sets. (e) Fol hnge versus fol hnge plots ompring T reg expression profiles etween ft T reg ells (x xis) n lymph noe T reg ells (y xis) (left) n spleen T reg ells (x xis) n lymph noe T reg ells (y xis) (right). Gene trnsripts uniquely up- or ownregulte in ft T reg ells re highlighte in re n lue, respetively. Spl T reg Spl T onv P vlue e LN T reg / LN T onv FsL..,98 IFN-γ Tet CCL5 CXCR3 t on CD3 y flow ytometri nlysis (Fig. 3). These oservtions on the T reg ell signture were true whether the omprtor ws T onv ells from the ft or the lymph noe (Fig. 2), rguing tht they reflet speil fetures of ipose tissue T reg ells. Nonetheless, the ftresient CD4 + + ells were lerly T reg ells, s muh (63%) of the signture ws intt, inluing overexpression of hllmrk trnsripts suh s those enoing, gluoortioi-inue tumor nerosis ftor reeptor (GITR), ytotoxi T lymphoyte ntigen-4 (CTLA-4), OX4 n killer ell letin-like reeptor G, in ition to itself (Figs. 2 n 3). We onfirme the elevte expression of severl of these signture genes in ft T reg ells y RT-PCR n flow ytometri LN T reg Ft T reg Ft T reg LN T reg 843 Prolifertion normlize,97, LN T onv Ft T onv Ft T onv LN T onv Gpr83 Gpr83 CD3 CTLA-4 Igfp4 Igfp4 OX4 Pe3 GITR Pe3 CD Ox4 Klrg 5 Gpr83 4 CD3 Pe3 Ox4 CTLA Igfp4 CTLA-4 Klrg 6 GITR Klrg 9... Spl T reg / spl T onv Ft T reg / ft T onv Ft T reg / LN T onv Consensus T reg signture : :.5 :.25 Responer to inhiitor rtio Ft T reg / ft T onv Ft T reg speifi genes ,98,2 CXCL IL- GM96 CCR2 CCR Itgv CCR Overexpresse LN T reg / LN T onv :. Overexpresse,869, Effetor T ells Spl T reg Spl T onv + Spl T reg + Ft T reg + Spl T onv + Ft T onv Effetor only Unerrepresente IFN-γ IL-... Spl T reg / spl T onv Unerrepresente NATURE MEDICINE ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION 3
4 Aominl ft CD CTLA IL- Lung A. ft Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. f Aritrry unit 3, 2,,8 e 3.6 GITR CD3 CTLA-4 Ft T onv LN T onv Ft T reg LN T reg Ft T reg Ft T onv LN T reg LN T onv 66.5 Aominl ft 38 TNF-α Gte CD3 + CD CD Tr sequenes CTLA A. ft Lung Liver Fol hnge g Gte CD3 + CD4 + Gte CD3 + CD4 + IFN-γ Tet Ft T reg Ft T onv LN T reg LN T onv CD69 Ly6 A. ft Gte CD3 + CD4 + IL- IFN-γ IL-4 LN Liver Lung A. ft LN Liver Lung Figure 3 Phenotypi hrteriztion of T reg ells from ominl ft tissue, spleen, lung n liver. (,) Cells were isolte from retire-reeer B6 mie, n the stromovsulr frtion ws stine for, CD3, CD4, CD8,, gluoortioi-inue tumor nerosis ftor reeptor (GITR), CD3 n CTLA-4. Numers on the grph inite the perentge of ells in tht gte for tht prtiulr experiment. (,) Reltive RNA expression of selete genes from T reg n T onv ells from lymph noe n ft. Error rs represent mens ± s.. (,e) Cytokine expression profile from T reg n T onv ells from spleen, lung n ft tissue. Representtive ot plots of t lest three inepenent experiments re shown. Orgns from four to six mie were poole per experiment. Numers on the grph inite the perentge of ells in tht gte for tht prtiulr experiment. (f) Tr sequenes of ft-erive T reg n T onv ells. Aominl ft n lymph noe T reg n T onv ells were isolte from ge mle mie from the LTD mouse line. The frequeny of the CDR3 sequenes ws nlyze on single-ell sis. Depite is grphil isply of the TCR sequenes in het-mp formt from T reg n T onv ells. (g) Stining of CD3, CD4, CD8, n the tivtion mrkers CD69 n Ly6 in the stromovsulr frtion of ells isolte from ominl ipose tissue, lymph noe, liver n lung from retire-reeer B6 mie. Representtive ot plots re shown. Numers on the grph inite the perentge of ells in tht gte for tht prtiulr experiment IL- IFN-γ IL-4 quntifition (Fig. 3, n t not shown). The gene expression ifferenes oserve in T reg ells isolte from the ft versus from the spleen n lymph noe were not simple refletion of iffering tivtion sttuses, s we oserve lerly ivergent trnsription ptterns in iret omprison etween ft-erive n tivte T reg ells (Supplementry Fig. ). A lrge numer of genes were overexpresse, mny of them mrkely so, y the CD4 + + T ells resiing in ominl ipose tissue ut not y the orresponing popultion t other sites exmine (Fig. 2e; liste in Supplementry Tle ). Chief mongst these overexpresse genes were those enoing moleules involve in leukoyte migrtion n extrvstion: Gm96 (n IL- inuile CXCR2 lign 25 ), CCR, CCR2, CCR9, CCL6, integrin V, tivte leukoyte ell hesion moleule (Alm), CXCL2 n CXCL (Fig. 2e, Supplementry Tle n Supplementry Fig. 2). In ontrst, some moleules of similr funtion, for exmple CCL5 n CXCR3, were unerexpresse in the viserl ft T reg ells (Fig. 2e). Also noteworthy were the extremely high IL- trnsript levels in CD4 + + ominl ipose tissue ells (Fig. 2e n Supplementry Fig. 2). We estimte 36-fol ugmenttion of IL- trnsripts in ft versus lymph noe T reg ells from RT-PCR quntifition (Fig. 3); we oul lso etet the inrese y intrellulr stining for IL- protein in the T reg ells of ft versus spleen n lung (Fig. 3). Notly, pthwy nlysis suggeste tht the T reg ells not only proue lrge mounts of IL- ut lso seeme to e responing to it, s numer of genes ownstrem of the IL- reeptor were upregulte in ft T reg ells ompre with lymph noe T reg ells (Supplementry Fig. 3). Another set of genes ws upregulte speifilly in CD4 + T ells resiing in ipose tissue s ompre with their lymph noe ounterprts, ut not in spleen versus lymph noe (Fig. 2e; liste in Supplementry Tle ). Some of these loi lso oe for moleules implite in migrtion n extrvstion, inluing CXCR3 n CCL5. Ft-resient T onv ells seeme to e highly polrize to T helper type phenotype, s they expresse high levels of T-ox 2 (Tet) n interferon-g (IFN-g) trnsripts (Fig. 2e, Fig. 3 n 4 ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION NATURE MEDICINE
5 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. + of CD4 + g + of CD4 + Lep o/o Lep o/ Numer of + CD4 + ells per g ft ( 3 ) 3 n = 7 7 n = 4 WT Lep o/o Lep o/o n = 8 A y / e + of CD4 + P =.6 Lep o/wt Lep o/o NC n = 6 Lep o/+ Lep o/o Lep o/+ Lep o/o WT A y / NC S.. ft Supplementry Fig. 2), unnt intrellulr IFN-g n TNF- (Fig. 3,e), n little, if ny, intrellulr IL-4 (Fig. 3). Although the IL- effet oul lso e iserne with ft-resient T onv ells, it ws not s striking (Supplementry Fig. 3,). Ft-resient T reg ells hve speifi T ell reeptor repertoire The T ell reeptor (TCR) repertoire is nother useful prmeter for ssessing the egree of similrity of T ell popultions. For exmple, it hs een shown tht T reg n T onv ell popultions hve istint repertoires, with only limite overlp In ition, the TCR repertoire of T reg ells in the ominl ipose tissue might give n inition of whether their unne reflets n influx n/or retention of ells of prtiulr speifiity or lol ytokine-inue onversion 29. To rener the repertoire nlysis more mngele n interpretle, we exploite the Limite (LTD) mouse line, wherein TCR iversity is restrite to the omplementrity-etermining region 3 (CDR3) vi the omintion of trnsgeni Tr minilous n the Tr-knokout muttion 3. We etermine CDR3 sequenes from 98 iniviully sorte viserl ft CD4 + + ells tht lso expresse RNA, n we ompre their istriution with tht of CDR3 sequenes from ft T onv ells or lymph noe T reg n T onv ells. Unfortuntely, we were unle to otin enough T reg ells from suutneous ft to perform prllel TCR sequene nlysis on this epot. As expete, the het mps generte from these sequenes revele istint TCR repertoires for the lymph noe T reg n T onv ell popultions, with only limite overlp (Fig. 3f). Similrly, the ft-resient T reg n T onv ell popultions lso h ifferent repertoires (Fig. 3f), renering it very unlikely tht the umultion of + T reg ells in the ominl ipose tissue resulte from lol onversion of T onv ells. Notly, the ft-resient T reg ells h very restrite istriution of sequenes, representing istint suset of those normlly foun in their lymph noe T reg ell ounterprts (Fig. 3f n Supplementry Tle 2). The CDR3 sequenes hrteristi of ft-resient T reg ells were often inepenently generte y ifferent nuleotie sequenes; 5% of sequenes (three of six) foun more thn three times per iniviul mouse showe suh nuleotie vrition (Supplementry Tle 3). In ontrst, none of the sequenes (zero of ten) from ft-resient T onv ells i (Supplementry Tle 4), suggesting h + of CD4 + 3 f + of CD4 + A y / + of CD Age (weeks) 7 Lep o/+ WT NC A y / Lep o/o HOMA-IR i + of CD Lep o/o Lep o/+ Figure 4 Anlysis of ft T reg ells in three mouse moels of oesity: Lep o/o, A y / n. ( ) Aominl ipose tissue from Lep o/o n heterozygote Lep o/+ mie ws nlyze for T reg ell frequeny. () Representtive ot plots of CD4 + T ells from 3-week-ol mie. () Totl numer of T reg ells per grm of ft. Mens ± s.. re shown. P ¼.6. () Chnges of T reg ell representtion over time. Mens ± s.. re shown. () of T reg ells in ominl ipose tissue of 24-week-ol A y / or littermte (WT) mie. P ¼.8. (e) of ft T reg ells in mie fe for 29 weeks with or norml how (NC). P ¼.64. (f) Correltion of homeostsis moel ssessment of insulin resistne (HOMA-IR) n frtion of T reg ells. (g i) of T reg ells in the spleen n suutneous ft in Lep o/o (g), A y / (h) n -fe mie (i). the repete seletion of T reg ells with similr ntigen reeptors rther thn the prolifertion of single lone. The sequenes were reprouily frequent in thee ifferent mie, gin pointing to TCR-riven seletion (Supplementry Tle 3). These t inite tht the speifiity of the TCR my e instrumentl in generting the high frequeny of T reg ells in viserl ft, perhps through lol reognition of ognte ntigen. Inee, ft-resient T reg ells showe unusully high expression of the erly tivtion mrkers CD69 n lymphoyte ntigen 6 omplex, lous C (Ly6) (Fig. 3g), lthough it remins possile tht suh inreses inste, or lso, reflet ytokine influenes. Though TGF- is reily etetle in ipose tissue 3 n is known to promote T reg ell ifferentition n survivl 32 34, its effets re n unlikely explntion for the high representtion n tivtion stte of T reg ells in ft, euse we i not oserve the typil hnges in gene expression promote y this growth ftor in this popultion (Supplementry Fig. 4). For exmple, CD3 ws not upregulte (Fig. 2 n Fig. 3). This oservtion lso rgues ginst TGF- meite onversion of CD4 + ells to CD4 + + ells in viserl ft, s hs een oserve in few systems 29. Implition of ft-resient T reg ells in metoli ontrol To lern how this unique popultion of T reg ellsresponstoexess iposity, we exmine it in three mouse moels of oesity: leptinefiient mie (Lep o/o ; ommonly referre to s o/o) 35, mie heterozygous for the yellow spontneous muttion (A y /) 36 n mie hronilly fe high-ft iet () 3, ll on the B6 geneti kgroun n ll showing insulin resistne (Supplementry Fig. 5). Notly, the T reg ell popultion in ominl ft ws mrkely reue in ge o/o mie ompre with heterozygous littermtes, whether we quntifie the frtion of T reg ells in the CD4 + omprtment or the numer of T reg ells per grm of ft (Fig. 4,). Wheres 5-week-ol leptin-efiient mie h somewht higher (P ¼.2) numers of CD4 + + T ells in viserl ft (3%) thn i wiltype ge-mthe littermtes (%), this suset progressively eline in the mutnt mie n rose in the ontrol mie (Fig. 4)(P¼.). As ntiipte, o/o ft-resient T reg ells were reltively eplete mong IL- prouers (Supplementry Fig. 6). The norml proportions of T reg ells in the spleen n suutneous ft of o/o mie rgue tht the reltive srity of this suset in viserl ft ws not just refletion of the leptin efiieny; inee, the sene of this hormone ws reently reporte to foster the prolifertion of T reg ells 37.Numers of onventionl CD4 + T ells in the ominl ft of o/o ults were only milly lower, n the perentge of these ells mking IFN-g remine essentilly unhnge (Supplementry Fig. 6,). There were lso low proportions of CD4 + + ells in ominl ft, ut not t other sites, in the A y / mie n in -fe mie (Fig. 4 i). These low frequenies were not s striking s for o/o mie (Fig. 4), onsistent with less insulin resistne in the ltter two NATURE MEDICINE ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION 5
6 moels (Supplementry Fig. 5). Inee, we sw goo orreltion etween insulin resistne n the frtion of T reg ells in ominl ft (Fig. 4f). The oserve orreltion etween oesity n insulin resistne on the one hn n erth of CD4 + + ells in ominl ipose tissue on the other hn suggests tht T reg ells might e implite in the reltionship etween the inflmmtory n metoli prmeters. To test this notion, we first ttempte loss-of-funtion experiments. Given tht it is not urrently fesile to lte T reg ells speifilly in ft, we use mie expressing the iphtheri toxin reeptor (DTR) uner the ontrol of trnsriptionl regultory elements, wherein ministrtion of iphtheri toxin results in rpi systemi epletion of T reg ells. We reently evelope line of teril rtifiil hromosome (BAC)-trnsgeni nonoese ieti (NOD) mie expressing DTR-eGFP fusion protein uner the ontrol of trnsriptionl regultory elements. Routinely, 85 9% of T reg ells re eliminte in the spleen n lymph noes 2 fter iphtheri toxin ministrtion to these mie (M.F., D. Littmn, C.B. n D.M., unpulishe t), similr to wht hs een esrie y nother group with their inepenently erive line 38. Cell eth inue y iphtheri toxin is poptoti n therefore oes not set off proinflmmtory immune response 39 42, prompting wiespre use of this pproh to proe iverse immunologil issues through speifi ltion of prtiulr ell types, inluing T reg 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. e Fol hnge Fol hnge Gluose (mg l ) NC PBS IL-2 nti IL-2 TNF-α IL-6 A2 RANTES SAA-3 HOMA-IR 5 5 Insulin (ng ml ) NC PBS IL-2 nti IL-2.4 RANTES Epi ft DTR Insulin DTR + 6 pir Epi ft 4 Liver Epi ft 4 IR 2 2 pir Liver IR 2 Musle 2 pir IR Musle pir IR Insulin + + SAA-3 DTR DTR + Lung Epi ft f Gluose (mg l ).7 5 NS Gluose (mg l ) pir / IR (AU) h i j g PBS IL-2 nti IL NC gte CD4 + CD3 + NC : PBS : IL-2 nti IL Time (min) 7. + CD4 + + CD4 + AUC ( 4 ) Epi ft of + CD4 + Epi ft NC : PBS : IL-2 nti IL-2 CD CD4 NC PBS IL-2 nti IL-2 DTR DTR Epi ft Figure 5 Chnges in inflmmtory meitors n metoli prmeters in loss- n gin-of-funtion experiments. ( f) Loss-of-funtion experiment y epleting T reg ells expressing DTR. -week-ol mle mie, either DTR-positive or DTR-negtive, were trete every other y for 4 ( ) or9( f) with iphtheri toxin. () of T reg ells from spleen or the ominl ft (Epi ft) fter 4 of tretment. (,) Insulin signling in epiiyml white ipose tissue (WAT), liver musle n spleen, s inite y immunopreipittion n western lotting of insulin-inue insulin reeptor phosphoryltion (pir) () Blot t. () Quntifition of pir normlize y totl IR (n Z 4, P o.4, t test). AU, ritrry units. () of T reg ells from the ominl ft (top) or spleen (ottom) fter 9 of tretment, with representtive ot plot s n inset. (e) Top, expression of TNF-, IL-6, A2, RANTES n SAA-3 trnsripts in ominl ipose tissue. Three mie per group, one of two inepenent experiments is shown. Bottom, omprison of RANTES n SAA-3 trnsripts in spleen, lung n ominl ft (epi ft). (f) Fsting insulin (top) n fsting gluose (ottom) onentrtions fter 9 of tretment every other y. Six mie per group from two inepenent experiments. P ¼.26. Signifine ws etermine y the Mnn-Whitney U test. (g j) Gin-offuntion experiment. (g) Dot plots (left) n summrizing r grph (right) showing T reg ells from spleen n ominl ft tissue (epi ft) from mie fe norml how (NC) or with 5 weeks of. Mie were trete with IL-2 IL-2 speifi ma (nti IL-2) omplex or sline for 6 n nlyze on y 4 (n ¼ 6 for eh group). Numers on the grphs inite the perentge of ells in tht gte for tht prtiulr experiment. Bloo gluose (h) HOMA-IR (P ¼.78) (i) n n intrperitonel GTT (P ¼.25) (j) of the mie esrie in g re shown. (j) Right, lulte re uner the urve (AUC) from ll mie teste y GTT (n ¼ in eh group), inluing the t set esrie in g. P ¼.3, P ¼.36, P ¼.4. P vlues were lulte with the t test. Error rs in ll pnels represent the mens ± s.. 6 ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION NATURE MEDICINE
7 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. Reltive expression Reltive expression e / CD , IL-6 MMP-3 SAA-3 RANTES SAA-3 IL-6 Omentl /CD3 ells 39, However, euse T reg ell lte mie evelop multiorgn utoimmunity 2 weeks fter iphtheri toxin tretment 38,this strtegy require us to look t erly initors of potentil T reg ell funtion, nmely ltertions in ipose tissue RNAs enoing inflmmtory meitors or upstrem hnges in metoli signling pthwys; previous t suggeste tht 2 weeks my e too erly to see hnges in more ownstrem metoli prmeters, inluing performne in gluose tolerne tests (GTTs) 46. For one set of experiments, we trete -week-ol mle mie with iphtheri toxin every other y for 4, whih lowere the T reg ell level in ominl ft to out one-fourth the norml level (Fig. 5), wheres the spleen n lung popultions were t out one-thir the usul level (Fig. 5 n t not shown). The epletion of T reg ells ws ompnie y sustntil ereses in insulin-stimulte insulin reeptor tyrosine phosphoryltion in epiyiml ft n liver, ut not in musle n spleen (Fig. 5,). We otine prllel results on AKT protein kinse phosphoryltion (t not shown). At this erly time point, in vivo metoli hnges were mrginl (not shown), so we onute seon set of experiments in whih we trete mie with iphtheri toxin for longer times. Mie injete every other y for 9 h T reg ell frtion out 3% the usul size of tht in the ft, wheres the spleen, lung n lymph noe popultions h oune k to out 7% of norml (Fig. 5). We o not know why there is suh preferentil loss of T reg ells in ipose tissue with this protool, ut it is likely to reflet slower repopultion kinetis. Conomitntly, mny of the genes enoing inflmmtory meitors (for exmple, TNF-, IL-6, RANTES n serum myloi A-3 (SAA- 3)) were inue in the viserl ft epot (Fig. 5e) ut muh less so in the spleen n lung (Fig. 5e). Insulin mounts were signifintly higher in the T reg ell-eplete mie, initing insulin resistne s.. Control TNF IL- TNF + IL- RANTES 2 M TNF-α IFN-γ IL-β M TNF-α IFN-γ IL-β M TNF-α IFN-γ IL-β Reltive expression Glut4 # Reltive expression M TNF-α IFN-γ IL-β elt (om-s..) /CD IL- onentrtion (ng ml ) Glut4 (fol hnge) TNF-α Tregs TNF No TNF BMI R 2 =.29 Figure 6 Cytokine effets on ipoytes n humn orreltes. () Expression of IL-6, MMP-3, SAA-3 n RANTES, s mesure with quntittive PCR uner unmnipulte ulture onitions (ontrol); ipoytes were trete with TNF- (TNF), IL- (IL-) lone or TNF- n IL- (TNF + IL-). () Reltive expression of IL-6 in ifferentite ipoytes, ose response urve of IL-. TNF, ells trete with TNF- n vrious onentrtions of IL-. No TNF, ells trete only with IL-. Representtive experiments re shown. () Expression of SAA-3, RANTES, IL-6 n Glut4 in ifferentite ipoytes, unmnipulte ifferentite ipoytes (M) or ipoytes trete with TNF-, IFN-g n IL-. Representtive experiments re shown. () Expression of Glut4 in ifferentite ipoytes either unmnipulte or trete with TNF- in presene or sene of spleen T reg ells. Men ± s.. of three inepenent experiments re shown. P ¼.6. P vlue ws lulte with t test. (e) Pire humn omentl n suutneous ipose smples from mostly oese iniviuls (BMI rnge: , verge: 44.85). Expression of FOXP3 n CD3 ws mesure y quntittive PCR. Left, the rtios of FOXP3 versus CD3 for omentl n suutneous ipose tissue. Right, the erese in FOXP3/CD3 rtio in omentl (om) versus suutneous ipose tissue plotte ginst the BMI for eh iniviul onor from the left grph. The positive vlue of sujet 7 (42 s..from the men) ws not inlue. Eh ot represents n iniviul onor. P ¼.86. Error rs represent mens ± s.. (Fig. 5f), lthough fsting loo gluose onentrtions t this erly time point were unhnge, onsistent with equte et ell ompenstion (Fig. 5f). To provie itionl eviene tht the inflmmtion promote y T reg ell epletion in the ominl ipose tissue ws not merely response to ell eth, we use mie 38 in whih we rpily lte T reg ells y giving iphtheri toxin to femles rrying gene enoing DTR knoke into the lous on the X hromosome. This strtegy yiele 95% ltion in homozygous mie versus out 5% ltion in heterozygous mie (Supplementry Fig. 7). In the ltter se, rnom X hromosome intivtion protets out hlf of the T reg ells euse the DTR-rrying llele resies within the intivte hromosome. As expete, when most of the T reg ells were lte, proinflmmtory trnsripts (for exmple, RANTES n MCP-) were strongly inue in the ft tissue (Supplementry Fig. 7). In ontrst, when only hlf the T ells were kille, there ws no suh inution of proinflmmtory trnsripts, signifying tht sustntil iphtheri toxin inue ell eth ws not in n of itself the stimulus n tht hlf-omplement of T reg ells suffie to protet the ft from inflmmtion. A gin-of-funtion experiment involving trnsfer of ft-resient T reg ells into reipient fe high-ft iet oul potentilly further support for our proposl tht these ells re key meitors of metoli regultion. However, the lility n low reoverle numers of viserl ft resient T reg ells renere our mny ttempts t this pproh unsuessful; trnsfer of more limite numers of ft-erive T reg ells into lymphoefiient reipients lso prove prolemti euse the resultnt homeostti prolifertion ltere the phenotype of the introue popultion, notly its profile of ell-surfe homing reeptors (t not shown). Therefore, s n NATURE MEDICINE ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION 7
8 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. lterntive mens to hieve gin-of-funtion, we turne to in situ expnsion of T reg ells vi injetion of omplex onsisting of reominnt IL-2 n prtiulr IL-2 speifi monolonl ntioy (ma), previously shown to seletively eliit T reg ells 47,48. Dily injetions of the omplex for 6 into mie prefe on for 5 weeks i sustntilly inrese the frtion of T reg ells in the spleen n ominl ft s ompre with PBS-injete ontrols (verges from multiple experiments 37% ± 4% versus 2% ± 2% for spleen n 63% ± 2% versus 43% ± 7% for ominl ft; Fig. 5g). (The reution in the T reg ell frtion in PBS-injete -fe mie versus mie fe norml how is smller in Fig. 5 thn in Fig. 4 euse of the shorter time of.) To ssess insulin resistne in the omplex-injete mie, we mesure loo gluose onentrtions, whih were signifintly lower (Fig. 5h). As expete, IL- trnsript levels were signifintly higher in the -fe mie with more T reg ells (Supplementry Fig. 6). Wheres HOMA-IR ( stnr mesure of insulin resistne tht integrtes oth loo-gluose n loo-insulin onentrtions; Fig. 5i) n gluose tolerne (mesure vi n intrperitonel GTT; Fig. 5j) ll trene towr lower vlues in the T reg ell enrihe, -fe mie, these ifferenes fell short of sttistil signifine, proly owing to the greter experimentl vriility inherent in these ssys. In ft, given the very short experimentl winow tht we h to work in to voi expnsion of effetor T ells, we o not fin smll ifferenes t ll surprising. To enhne the power of the experimentl t, we injete numer of itionl -fe mie with the IL-2 se omplexes or PBS uner similr onitions, umulting totl of mie for eh group. The T reg ell frtion in the omplex-injete, -fe mie rnge from 4% to 83% (verge 68% ± 3%), wheres tht in the PBS-injete mie spnne 8% to 7% (verge 45% ± 3%). Both -fe groups were gluose intolernt s ompre with ontrol mie fe norml how; however, the omplex-injete group, with the highest levels of T reg ells, showe signifint improvement ompre with the PBSinjete group (Fig. 5j). We otine similr results in the A y / moel (Supplementry Fig. 8). Together, the loss-of-funtion n gin-of-funtion finings inite tht T reg ells gur ginst exessive inflmmtion of the ipose tissue n its ownstrem systemi onsequenes n strongly suggest tht T reg ells resiing in the ft re responsile. In vitro effets of T ell-erive ytokines on ipoytes A prole mehnism y whih T ells resiing in ipose tissue ffet neighoring ells is through solule meitors. Thus, we explore the influenes of the mjor ytokines ifferentilly proue y T reg n T onv ells in ft versus other tissues (IL- n IFN-g, respetively; Fig. 2). We pretrete fully ifferentite, lipi-len 3T3-L ipoytes for 48 h with IL- (or left them untrete) n susequently stimulte them for 24 h with TNF-, n estlishe metho for in vitro inution of insulin resistne. TNF- inue hnges in ipoyte expression of numer of trnsripts enoing inflmmtory meitors, for exmple IL-6, RANTES, SAA-3 n MMP-3; of note, IL- inhiite the TNF--inue expression of ll of these RNAs (Fig. 6,). TNF- hs lso een shown to ownmoulte insulin-epenent tyrosine phosphoryltion of insulin reeptor sustrte- n to inhiit gluose uptke meite y the gluose trnsporter Glut4 in 3T3-L ipoytes; these effets, too, were reverse y IL- (ref. 8), initing tht this ytokine reverts insulin resistne y mehnism iretly impinging on ipose tissue ells. In ontrst to the nti-inflmmtory effets of IL- me y viserl ft-resient T reg ells, mjor prout of the T onv ells t this site, IFN-g, ws proinflmmtory in the sme in vitro ssy system, s expression of SAA-3, RANTES n IL-6 trnsripts ws inue, n Glut4 RNA ws ownregulte (Fig. 6). Our mny ttempts to support these onlusions y performing oultures of ft-erive T reg ells n 3T3-L preipoytes hve so fr een unsuessful owing to rpi eth of the T reg ells uring the inution perio, proly s result of propoptoti ftors either in the meium or proue y the ipoytes, suh s TNF-. However, spleen T reg ells were less frgile in these oulture onitions, n we oul show tht they mpen levels of proinflmmtory trnsripts me y tivte ipoytes in ulture n, perhps most relevnt, inhiit their ownmoultion of Glut-4 trnsripts (Fig. 6 n t not shown). The greter frgility of ft-erive versus spleenerive T reg ells my e expline y the former ells higher expression of TNF reeptors (t not shown). FOXP3 trnsripts re reue in oese humn omentl ft Finlly, we sought to trnslte our finings to humn pthology. We h ess to set of pire frozen omentl n suutneous ft tissues from numer of iniviuls with n verge oy mss inex (BMI) of 44.85, thus (exept for one se) flling within the oese (3 39.9) n morily oese (44) rnge (humn sujet hrteristis given in Supplementry Tle 5). Given tht the smples were frozen, we oul not perform flow ytometri nlysis on or purifition of lymphoyte popultions, ut we oul etermine FOXP3 trnsript levels y PCR. FOXP3 RNA ws reily etetle in oth ft epots (Fig. 6e). Consistent with the oservtions on oese mie, we foun higher levels of FOXP3 trnsripts, presumly n initor of T reg ells, in the suutneous ipose tissue (Fig. 6e). We i not hve ess to nonoese ontrols for these stuies, owing to the rrity of ritri surgery on norml iniviuls. However, we i fin orreltion etween BMI n the rop in T reg ells in omentl versus suutneous ft (Fig. 6e). These t suggest tht our finings on mie my e trnsltle to humns, whih is enourging for future, more sophistite nlyses on purifie T ell susets from fresh ipose tissue. DISCUSSION Fining wht ppers to e unique popultion of regultory T lymphoytes enrihe in the ominl ipose tissue of norml, ut not oese, mie rises numer of questions. First, why n how o T reg ells umulte t this site? One ftor my e ntigen stimultion, s suggeste y the imprint of ntigeni seletion on the TCR repertoire of viserl ft T reg ells n y their unusully high stte of tivtion. Depening on the lotion of ny suh ntigens, they oul stimulte irulting T reg ells, provoking them to exit the lymph noes n inve the ft n/or restimulte T reg ells filtering through ipose tissue, therey promoting their retention. This notion is further supporte y the sequening n the gene-expression profiling t, whih rule out the possiility tht T onv ells re inue to onvert to T reg ells in the viserl ft. A seon ftor is lmost ertinly hemokines, given the unique pttern of hemokine hemokine reeptor gene expression y the T reg ells isolte from ipose tissue. Funtionl stuies will e neee to unrvel whih of these moleules re inee involve in ell ttrtion or ess to ft, their loliztion one therein or their reruitment of other leukoyte susets. Thir, there my e role for ipokines in nurturing T reg ell survivl in ipose tissue. A reent stuy highlighte the negtive effet of leptin on the prolifertive pity of T reg ells 37, whih fits well with their opposite proportions in norml n oese ft: mny T reg ells n little leptin in len ft tissue n few T reg ells n muh 8 ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION NATURE MEDICINE
9 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. leptin in oese ft. In ontrst, given the prllel high levels of T reg ells n iponetin in norml ft n low levels in oese ft, this ipokine is possile nite for positive ftor, espeilly s it inues IL- synthesis, t lest y mrophges 49,5. Next, wht funtion re T reg ells performing in norml ominl ipose tissue? Reent reports hve highlighte the interply etween ipoytes n popultion of nti-inflmmtory mrophges in this ft epot, suggesting role for resient mrophges in promoting tissue repir n ngiogenesis n in mintining insulin sensitivity 8,9. Our results rgue tht the tivities of oinient popultions of T onv n T reg ells nee to e e to the mix. It my e relevnt tht the T onv ells seem to e mking n ongoing T helper type response to some stimulus n tht their mjor prout, IFN-g, promotes synthesis of inflmmtory meitors y ipoytes. The T reg ells my e keeping this response in hek, s well s regulting the tivities of their mrophge n ipoyte neighors inee, their physil lotion in rown-like strutures t ipoyte juntions woul enourge intertion with oth ell types. IL- is one nite for hving role in T reg ell meite regultory tivities, given its ssoition with improve insulin sensitivity in numer of ontexts in oth roents n humns 5 53, lthough this ytokine is lso proue y the ft-resient nti-inflmmtory mrophges 8. Although it ws not fesile to more efinitively estlish the speifi funtion of T reg ells resiing in ipose tissue, given tht no ftresient T reg ell speifi regent exists n tht it hs not een possile to suessfully isolte n trnsfer ft-erive T reg ells in the requisite quntities, role for T reg ells, whtever their soure, in metoli homeostsis n its ysregultion in oesity is n unexpete fining. Lstly, wht provokes T reg ells to vte ominl ft in oesity, or, perhps more likely, to refrin from entering it? It my e seonry effet. Inresing iposity hs een ssoite with n influx of mrophges 6,7, in prtiulr the inflmmtory mrophge suset 8,9, into the ominl epot; s well s with inrese lol n systemi onentrtions of inflmmtory ytokines suh s TNF- n IL-6. In ition, reiprol inrese n erese in the ipokines leptin n iponetin, respetively, hs een reporte, fueling speultion of extensive rosstlk etween the two ell types in the oese onition. One possile senrio, then, is tht elements of this hnging environment re unfvorle for T reg ell entry, expnsion or survivl, leing to seonry eline of this regultory popultion; in ft, leptin 37 n IL-6 (refs. 54,55) re lrey known to hve suh properties. However, it is lso possile tht loss of T reg ells from the ominl ft is the primry effet. Wheres their exggerte numers in len ipose tissue my hve een suffiient to keep the hroni inflmmtion uner ontrol, lower T reg ell numers with inresing iposity oul open the gte to n invsion of inflmmtory mrophges n therey more roust synthesis of inflmmtory ytokines. Whether the influx of mrophges or the efflux (or eth) of T reg ells proves upstrem, oth proesses must e ownstrem of n inititing event, s yet unefine, though suggestions hve inlue lol hypoxi 56, inrese ipoyte eth 2 n ipoyte stress 57. METHODS Methos n ny ssoite referenes re ville in the online version of the pper t Aession oes. Mirorry t hve een eposite in the Gene Expression Omnius with ession oe GSE7852. Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Meiine wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk D. Littmn (New York University) for the DTR onstrut, L. Roser n K. Httori for ssistne with mie, S. Ruensky (Memoril Slon Kettering Cner Center) for proviing us with DTR mie, J. LVehio n G. Buruzl for flow ytometry n J. Hill, J. Perez n R. Melme for help with the mirorry nlysis. This work ws supporte y Young Chir funs to D.M. n C.B., y the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (DK5729 n DK73547) n Aler Chir funs to S.S. n y Joslin s Ntionl Institutes of Dietes n Digestive n Kiney Diseses fune Dietes n Enorinology Reserh Center ore filities. Postotorl fellowship support for M.F. ws from the Germn Reserh Fountion (Emmy-Noether Fellowship, FE 8/-) n the Chrles A. King Trust Postotorl Fellowship, n for L.H. from the Ministry of Siene of Spin. J.W. n D.C. were supporte y preotorl fellowships from the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (T32 DK726) n the Europen Shool of Moleulr Meiine, respetively. Pulishe online t Reprints n permissions informtion is ville online t reprintsnpermissions/.. Shoelson, S.E., Lee, J. & Golfine, A.B. Inflmmtion n insulin resistne. J. Clin. Invest. 6, (26). 2. Hotmisligil, G.S., Shrgill, N.S. & Spiegelmn, B.M. Aipose expression of tumor nerosis ftor-: iret role in oesity-linke insulin resistne. Siene 259, 87 9 (993). 3. Ci, D. et l. Lol n systemi insulin resistne resulting from hepti tivtion of IKKn NF-kB. Nt. Me., 83 9 (25). 4. Bosello, O. & Zmoni, M. Viserl oesity n metoli synrome. Oes. Rev., (2). 5. Fntuzzi, G. Aipose tissue, ipokines n inflmmtion. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 5, 9 99 (25). 6. Weiserg, S.P. et l. Oesity is ssoite with mrophge umultion in ipose tissue. J. Clin. Invest. 2, (23). 7. Xu, H. et l. Chroni inflmmtion in ft plys ruil role in the evelopment of oesity-relte insulin resistne. J. Clin. Invest. 2, (23). 8. Lumeng, C.N., Bozin, J.L. & Sltiel, A.R. Oesity inues phenotypi swith in ipose tissue mrophge polriztion. J. Clin. Invest. 7, (27). 9. Lumeng, C.N., Deyoung, S.M., Bozin, J.L. & Sltiel, A.R. Inrese inflmmtory properties of ipose tissue mrophges reruite uring iet-inue oesity. Dietes 56, 6 23 (27).. Oegr, J.I. et l. Mrophge-speifi PPARgmm ontrols lterntive tivtion n improves insulin resistne. Nture 447, 6 2 (27).. Sugnmi, T., Nishi, J. & Ogw, Y. A prrine loop etween ipoytes n mrophges ggrvtes inflmmtory hnges: role of free ftty is n tumor nerosis ftor. Arteriosler. Throm. Vs. Biol. 25, (25). 2. Cspr-Buguil, S. et l. Aipose tissues s n nestrl immune orgn: site-speifi hnge in oesity. FEBS Lett. 579, (25). 3. Zheng, Y. & Ruensky, A.Y. in ontrol of the regultory T ell linege. Nt. Immunol. 8, (27). 4. Skguhi, S., Ymguhi, T., Nomur, T. & Ono, M. Regultory T ells n immune tolerne. Cell 33, (28). 5. Mloy, K.J. et l. CD4 + + T R ells suppress innte immune pthology through ytokine-epenent mehnisms. J. Exp. Me. 97, 9 (23). 6. Murphy, T.J., Choilein, N.N., Zng, Y., Mnnik, J.A. & Leerer, J.A. CD4 + + regultory T ells ontrol innte immune retivity fter injury. J. Immunol. 74, (25). 7. Nguyen, L.T., Jos, J., Mthis, D. & Benoist, C. Where FoxP3-epenent regultory T ells impinge on the evelopment of inflmmtory rthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 56, (27). 8. Wu, H. et l. T-ell umultion n regulte on tivtion, norml T ell expresse n serete upregultion in ipose tissue in oesity. Cirultion 5, (27). 9. Trn, T.T., Ymmoto, Y., Gest, S. & Khn, C.R. Benefiil effets of suutneous ft trnsplnttion on metolism. Cell Met. 7, 4 42 (28). 2. Cinti, S. et l. Aipoyte eth efines mrophge loliztion n funtion in ipose tissue of oese mie n humns. J. Lipi Res. 46, (25). 2. Fontenot, J.D. et l. Regultory T ell linege speifition y the forkhe trnsription ftor. Immunity 22, (25). 22. Huehn, J. et l. Developmentl stge, phenotype, n migrtion istinguish niven effetor/memory-like CD4 + regultory T ells. J. Exp. Me. 99, (24). 23. Hermn, A.E., Freemn, G.J., Mthis, D. & Benoist, C. CD4 + + Tregultoryells epenent on ICOS promote regultion of effetor ells in the preieti lesion. J. Exp. Me. 99, (24). 24. Hill, J. et l. -trnsription-ftor epenent n inepenent regultion of the regultory T ell trnsriptionl signture. Immunity 27, (27). 25. Noln, K.F. et l. IL- onitione enriti ells, eommissione for reruitment of ptive immunity, eliit innte inflmmtory gene prouts in response to nger signls. J. Immunol. 72, (24). NATURE MEDICINE ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION 9
10 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve. 26. Wong, J. et l. Apttion of TCR repertoires to self-pepties in regultory n nonregultory CD4 + Tells.J. Immunol. 78, (27). 27. Hsieh, C.S., Zheng, Y., Ling, Y., Fontenot, J.D. & Ruensky, A.Y. An intersetion etween the self-retive regultory n nonregultory T ell reeptor repertoires. Nt. Immunol. 7, 4 4 (26). 28. Pholzyk, R., Igntowiz, H., Krj, P. & Igntowiz, L. Origin n T ell reeptor iversity of + CD4 + + Tells.Immunity 25, (26). 29. Kretshmer, K. et l. Inuing n expning regultory T ell popultions y foreign ntigen. Nt. Immunol. 6, (25). 3. Correi-Neves, M., Wltzinger, C., Mthis, D. & Benoist, C. The shping of the T ell repertoire. Immunity 4, 2 32 (2). 3. Sm, F., Ymmoto, K., Pney, M. & Loskutoff, D.J. Elevte expression of trnsforming growth ftor- in ipose tissue from oese mie. Mol. Me. 3, (997). 32. Chen, W. et l. Conversion of peripherl CD4 + nivetellstocd4 + + regultory T ells y TGF- inution of trnsription ftor. J. Exp. Me. 98, (23). 33. Peng, Y., Lour, Y., Li, M.O., Green, E.A. & Flvell, R.A. TGF- regultes in vivo expnsion of -expressing CD4 + + regultory T ells responsile for protetion ginst ietes. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA, (24). 34. Mrie, J.C., Letterio, J.J., Gvin, M. & Ruensky, A.Y. TGF- mintins suppressor funtion n expression in CD4 + + regultory T ells. J. Exp. Me. 2, 6 67 (25). 35. Pelleymounter, M.A. et l. Effets of the oese gene prout on oy weight regultion in o/o mie. Siene 269, (995). 36. Kleig, M.L., Wilkinson, J.E., Geisler, J.G. & Woyhik, R.P. Etopi expression of the gouti gene in trnsgeni mie uses oesity, fetures of type II ietes n yellow fur. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 92, (995). 37. De Ros, V. et l. A key role of leptin in the ontrol of regultory T ell prolifertion. Immunity 26, (27). 38. Kim, J.M., Rsmussen, J.P. & Ruensky, A.Y. Regultory T ells prevent tstrophi utoimmunity throughout the lifespn of mie. Nt. Immunol. 8, 9 97 (27). 39. Bennett, C.L. & Clusen, B.E. DC ltion in mie: promises, pitflls n hllenges. Trens Immunol. 28, (27). 4. Thorurn, J., Frnkel, A.E. & Thorurn, A. Apoptosis y leukemi ell trgete iphtheri toxin ours vi reeptor-inepenent tivtion of Fs-ssoite eth omin protein. Clin. Cner Res. 9, (23). 4. Miyke, Y. et l. Protetive role of mrophges in noninflmmtory lung injury use y seletive ltion of lveolr epithelil type II ells. J. Immunol. 78, 5 59 (27). 42. Bennett, C.L. et l. Inuile ltion of mouse Lngerhns ells iminishes ut fils to rogte ontt hypersensitivity. J. Cell Biol. 69, (25). 43. Duffiel, J.S. et l. Conitionl ltion of mrophges hlts progression of resenti glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pthol. 67, (25). 44. Duffiel, J.S. et l. Seletive epletion of mrophges revels istint, opposing roles uring liver injury n repir. J. Clin. Invest. 5, (25). 45. Wlzer, T. et l. Ientifition, tivtion n seletive in vivo ltion of mouse NK ells vi NKp46. Pro. Ntl. A. Si. USA 4, (27). 46. Yun, M. et l. Reversl of oesity- n iet-inue insulin resistne with sliyltes or trgete isruption of Ikket. Siene 293, (2). 47. Boymn, O., Kovr, M., Ruinstein, M.P., Surh, C.D. & Sprent, J. Seletive stimultion of T ell susets with ntioy-ytokine immune omplexes. Siene 3, (26). 48. Tng, Q. et l. Centrl role of efetive interleukin-2 proution in the triggering of islet utoimmune estrution. Immunity 28, (28). 49. Wolf, A.M., Wolf, D., Rumpol, H., Enrih, B. & Tilg, H. Aiponetin inues the ntiinflmmtory ytokines IL- n IL-RA in humn leukoytes. Biohem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 323, (24). 5. Kum, M. et l. Aiponetin speifilly inrese tissue inhiitor of metlloproteinse- through interleukin- expression in humn mrophges. Cirultion 9, (24). 5. Kim, H.J. et l. Differentil effets of interleukin-6 n - on skeletl musle n liver insulin tion in vivo. Dietes 53, 6 67 (24). 52. Blüher, M. et l. Assoition of interleukin-6, C-retive protein, interleukin- n iponetin plsm onentrtions with mesures of oesity, insulin sensitivity n gluose metolism. Exp. Clin. Enorinol. Dietes 3, (25). 53. Srpelli, D. et l. Vrints of the interleukin- promoter gene re ssoite with oesity n insulin resistne ut not type 2 ietes in Cusin Itlin sujets. Dietes 55, (26). 54. Dogni, A. et l. The IL-6R hin ontrols lung CD4 + + T reg evelopment n funtion uring llergi irwy inflmmtion in vivo. J. Clin. Invest. 5, (25). 55. Wn, S., Xi, C. & Morel, L. IL-6 proue y enriti ells from lupus-prone mie inhiits CD4 + + T ell regultory funtions. J. Immunol. 78, (27). 56. Hosogi, N. et l. Aipose tissue hypoxi in oesity n its impt on ipoytokine ysregultion. Dietes 56, 9 9 (27). 57. Furukw, S. et l. Inrese oxitive stress in oesity n its impt on metoli synrome. J. Clin. Invest. 4, (24). ADVANCE ONLINE PUBLICATION NATURE MEDICINE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Original article HIV-1 Tat protein impairs adipogenesis and induces the expression and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in human SGBS adipocytes
 Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
c-abl inhibition mitigates diet-induced obesity through improving insulin sensitivity of subcutaneous fat in mice
 Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Macrophage mtorc1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice
 Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
CEACAM1 regulates insulin clearance in liver
 CEACAM1 regultes insulin lerne in liver Mtthew N. Poy 1, Yn Yng 1, Khijeh Rezei 1, Mts A. Fernström 1, Arhm D. Lee 2, Yoshiki Kio 3, Snr K. Erikson 4 & Soni M. Njjr 1 Pulishe online: 19 Ferury 2002, DOI:
CEACAM1 regultes insulin lerne in liver Mtthew N. Poy 1, Yn Yng 1, Khijeh Rezei 1, Mts A. Fernström 1, Arhm D. Lee 2, Yoshiki Kio 3, Snr K. Erikson 4 & Soni M. Njjr 1 Pulishe online: 19 Ferury 2002, DOI:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
Regulation of NKT cell-mediated immune responses to tumours and liver inflammation by mitochondrial PGAM5-Drp1 signalling
 Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Lethal graft-versus-host disease in mouse models of T cell receptor gene therapy
 r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
Capsid-specific T-cell Responses to Natural Infections With Adeno-associated Viruses in Humans Differ From Those of Nonhuman Primates
 originl rtile See pge 1923 Cpsi-speifi T-ell Responses to Nturl Infetions With Aeno-ssoite Viruses in Humns Differ From Those of Nonhumn Primtes Hu Li 1, Mrio O Lsro 1, Bei Ji 1,2, Shih Wen Lin 1,3, Lriss
originl rtile See pge 1923 Cpsi-speifi T-ell Responses to Nturl Infetions With Aeno-ssoite Viruses in Humns Differ From Those of Nonhumn Primtes Hu Li 1, Mrio O Lsro 1, Bei Ji 1,2, Shih Wen Lin 1,3, Lriss
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha Therapy in Crohn s Disease: Clinical and Health Economic Aspects
 Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Increasing the usage level of corn and distillers grains in market turkey diets through the use of supplemental amino acids
 Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Docosapentaenoic Acid (22:5n-3) Downregulates mrna Expression of Pro-inflammatory Factors in LPS-activated Murine Macrophage Like RAW264.
 Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 217 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety oi : 1.565/jos.ess17111 Doospentenoi Ai (22:5n-3) Downregultes mrna Expression of Pro-inflmmtory Ftors in LPS-tivte Murine Mrophge Like RAW264.7
Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 217 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety oi : 1.565/jos.ess17111 Doospentenoi Ai (22:5n-3) Downregultes mrna Expression of Pro-inflmmtory Ftors in LPS-tivte Murine Mrophge Like RAW264.7
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pancreatitis in obese mice
 Artile Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pnretitis in oese mie Mri Pini,* Dvin H. Rhoes,* Krl J. Cstellnos,* Anrew R. Hll, Roert J. Cy, Rohini Chennuri, Eileen F. Gry, n Gimil Fntuzzi*, Deprtments of *Kinesiology
Artile Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pnretitis in oese mie Mri Pini,* Dvin H. Rhoes,* Krl J. Cstellnos,* Anrew R. Hll, Roert J. Cy, Rohini Chennuri, Eileen F. Gry, n Gimil Fntuzzi*, Deprtments of *Kinesiology
Transcription factor Ets-1 links glucotoxicity to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction through inhibiting PDX-1 expression in rodent models
 Dietologi () 9: DOI.7/s ARTICLE Trnsription ftor Ets links gluotoxiity to pnreti et ell ysfuntion through inhiiting PDX expression in roent moels Fng Chen & Min Sh & Ynyng Wng & Tijun Wu & Wei Shn & Ji
Dietologi () 9: DOI.7/s ARTICLE Trnsription ftor Ets links gluotoxiity to pnreti et ell ysfuntion through inhiiting PDX expression in roent moels Fng Chen & Min Sh & Ynyng Wng & Tijun Wu & Wei Shn & Ji
Origin of Triple hi and Triple lo T reg cells Triple hi and Triple lo T reg cells present in the thymus (Fig. 2a) could represent CD4 + GITR CD4 PD-1
 Affinity for self ntigen selets with distint funtionl properties Len Wyss 1,2, Brin D Stdinski 3, Crolyn G King 1, Sonj Shllenerg 4, Nihols I MCrthy, Jun Young Lee 6,7, Krsten Kretshmer 4,8, Luigi M Terrino
Affinity for self ntigen selets with distint funtionl properties Len Wyss 1,2, Brin D Stdinski 3, Crolyn G King 1, Sonj Shllenerg 4, Nihols I MCrthy, Jun Young Lee 6,7, Krsten Kretshmer 4,8, Luigi M Terrino
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice
 Regultory T ells prevent tstrophi utoimmunity throughout the lifespn of mie Jeong M Kim 1, Jeffrey P Rsmussen 1 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1,2 Mie lking the trnsription ftor ( ) lk regultory T (T reg ) ells
Regultory T ells prevent tstrophi utoimmunity throughout the lifespn of mie Jeong M Kim 1, Jeffrey P Rsmussen 1 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1,2 Mie lking the trnsription ftor ( ) lk regultory T (T reg ) ells
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
b-sitosterol activates Fas signaling in human breast cancer cells
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
INTRODUCTION. Ji-Hye Lee 1, Seon-Mi Yu 1, Eun-Kyung Yoon, Won-Kil Lee, Jae-Chang Jung*, Song-Ja Kim
 J Koren Me Si 27; 22: 89-7 ISSN -8934 Copyright The Koren emy of Meil Sienes 2,4 5-Deoxy- -ProstglninJ2 Regultes Deifferentition through Peroxisome Prolifertor-tivte Reeptor- -Depenent Pthwy ut Not Expression
J Koren Me Si 27; 22: 89-7 ISSN -8934 Copyright The Koren emy of Meil Sienes 2,4 5-Deoxy- -ProstglninJ2 Regultes Deifferentition through Peroxisome Prolifertor-tivte Reeptor- -Depenent Pthwy ut Not Expression
Research Article Blockade of Airway Inflammation by Kaempferol via Disturbing Tyk-STAT Signaling in Airway Epithelial Cells and in Asthmatic Mice
 Hinwi Pulishing Corportion Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume, Artile ID 7, pges http://x.oi.org/.//7 Reserh Artile Bloke of Airwy Inflmmtion y Kempferol vi Disturing Tyk-STAT Signling
Hinwi Pulishing Corportion Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume, Artile ID 7, pges http://x.oi.org/.//7 Reserh Artile Bloke of Airwy Inflmmtion y Kempferol vi Disturing Tyk-STAT Signling
Inhibition of Dexamethasone-induced Fatty Liver Development by Reducing mir-17-5p Levels
 originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Torenia concolor Lindley var. formosana Yamazaki extracts improve inflammatory response and lipid accumulation via PPARs activation
 BioMeiine (ISSN 2211-8039) Septemer 2017, Vol. 7, No. 3, Artile 18 Pges 29-36 DOI: 10.1051/mn/2017070318 Originl rtile Toreni onolor Linley vr. formosn Ymzki extrts improve inflmmtory response n lipi umultion
BioMeiine (ISSN 2211-8039) Septemer 2017, Vol. 7, No. 3, Artile 18 Pges 29-36 DOI: 10.1051/mn/2017070318 Originl rtile Toreni onolor Linley vr. formosn Ymzki extrts improve inflmmtory response n lipi umultion
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
LETTER. Oxidative stress induces angiogenesis by activating TLR2 with novel endogenous ligands
 oi:.8/nture9 Oxitive stress inues ngiogenesis y tivting TLR with novel enogenous ligns Xioxi Z. West, *, Nikoly L. Mlinin *, Alon A. Merkulov, Mir Tishenko, Bethny A. Kerr, Ernest C. Boren, Eugene A. Porez,
oi:.8/nture9 Oxitive stress inues ngiogenesis y tivting TLR with novel enogenous ligns Xioxi Z. West, *, Nikoly L. Mlinin *, Alon A. Merkulov, Mir Tishenko, Bethny A. Kerr, Ernest C. Boren, Eugene A. Porez,
ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through EGFR/HER-2/ ERK signaling pathway
 Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Supplemental Figures and Legends
 Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Allergology Interntionl. ;6:8-9 DOI:. llergolint.-oa-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elevte Serum IgE ginst MGL_ in Ptients with Atopi Dermtitis n Cholinergi Urtiri Mkiko Hirgun, Tkki Hirgun,KoriIshii, Hienori Suzuki,,
Allergology Interntionl. ;6:8-9 DOI:. llergolint.-oa-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elevte Serum IgE ginst MGL_ in Ptients with Atopi Dermtitis n Cholinergi Urtiri Mkiko Hirgun, Tkki Hirgun,KoriIshii, Hienori Suzuki,,
Autopsy Case of Slowly Progressive Type 1 Diabetes with Concomitant Acute Myocardial and Mesenteric Ischemia
 CASE REPORT Autopsy Cse of Slowly Progressive Type 1 Dietes with Conomitnt Aute Myoril n Mesenteri Ishemi Yoko Mtsu 1, Atsushi Arki 2, Ysuhito Skno 3, Yuko Chi 2, Yusuke Tsuoko 4, Tkshi Nishimur 3, Tomio
CASE REPORT Autopsy Cse of Slowly Progressive Type 1 Dietes with Conomitnt Aute Myoril n Mesenteri Ishemi Yoko Mtsu 1, Atsushi Arki 2, Ysuhito Skno 3, Yuko Chi 2, Yusuke Tsuoko 4, Tkshi Nishimur 3, Tomio
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
 nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
ARTICLE. Keywords AMPK. Cholesterol. Insulin resistance. Intestine. Isoflavones. Liver. LXRα. LXRβ. Mice. Soy protein
 Dietologi () 55:469 478 DOI.7/s5--599-9 ARTICLE Soy protein isoflvones ifferentilly regulte liver X reeptor isoforms to moulte lipi metolism n holesterol trnsport in the liver n intestine in mie M. González-Grnillo
Dietologi () 55:469 478 DOI.7/s5--599-9 ARTICLE Soy protein isoflvones ifferentilly regulte liver X reeptor isoforms to moulte lipi metolism n holesterol trnsport in the liver n intestine in mie M. González-Grnillo
Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. p53 locus. Targeting vector DTA LSL. Targeted allele
 Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Hydrodynamic Delivery of mil10 Gene Protects Mice From High-fat Diet-induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
Parathyroid hormone related peptide is a naturally occurring, protein kinase A dependent angiogenesis inhibitor
 Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes
 r t i l e s Crosstlk between neutrophils, B-1 ells n plsmytoi enriti ells initites utoimmune ibetes Julien Din 1,2,6, Ynnik Simoni 1,2,6, Letiti Furio 2,3,6, Luie Beuoin 1,2, Birgitt Agerberth 4, Frnk
r t i l e s Crosstlk between neutrophils, B-1 ells n plsmytoi enriti ells initites utoimmune ibetes Julien Din 1,2,6, Ynnik Simoni 1,2,6, Letiti Furio 2,3,6, Luie Beuoin 1,2, Birgitt Agerberth 4, Frnk
Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract ameliorates murine autoimmune arthritis through regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Me 218;33:612-621 https://oi.org/1.394/kjim.216.53 Grpe see pronthoyniin extrt meliortes murine utoimmune rthritis through regultion of /MyD88/NF-κB signling pthwy Sng-Hyon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Me 218;33:612-621 https://oi.org/1.394/kjim.216.53 Grpe see pronthoyniin extrt meliortes murine utoimmune rthritis through regultion of /MyD88/NF-κB signling pthwy Sng-Hyon
Beneficial Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training Combined with Rosiglitazone on Glucose Metabolism in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
 Originl Artile Oesity n Metoli Synrome Dietes Met J 217;41:474-485 https://oi.org/1.493/mj.217.41.6.474 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Benefiil Effets of Aeroi Exerise Trining
Originl Artile Oesity n Metoli Synrome Dietes Met J 217;41:474-485 https://oi.org/1.493/mj.217.41.6.474 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Benefiil Effets of Aeroi Exerise Trining
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most common
 Originl Artile A Funtionl Polymorphism on Chromosome 15q25 Assoite with Survivl of Erly Stge Non Smll-Cell Lung Cner Gung Jin, MD, PhD,* Eun Young Be, BS, Enyue Yng, PhD, Eung Be Lee, MD, PhD, Won-Kee
Originl Artile A Funtionl Polymorphism on Chromosome 15q25 Assoite with Survivl of Erly Stge Non Smll-Cell Lung Cner Gung Jin, MD, PhD,* Eun Young Be, BS, Enyue Yng, PhD, Eung Be Lee, MD, PhD, Won-Kee
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor
 Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota
 ARTICLE Reeive 16 De 214 Aepte 14 My 215 Pulishe 23 Jun 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8489 OPEN Gnoerm luium reues oesity in mie y moulting the omposition of the gut miroiot Chih-Jung Chng 1,2,3,4,5,, Chun-Sheng
ARTICLE Reeive 16 De 214 Aepte 14 My 215 Pulishe 23 Jun 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8489 OPEN Gnoerm luium reues oesity in mie y moulting the omposition of the gut miroiot Chih-Jung Chng 1,2,3,4,5,, Chun-Sheng
Opposite metabolic response to fenofibrate treatment in pregnant and virgin rats
 Opposite metoli response to fenofirte tretment in pregnnt n virgin rts An Sori, Crlos Boos, n Emilio Herrer 1 Fult e Cienis Experimentles y e l Slu, Universi Sn Plo-CEU, Ctr. Boill el Monte km 5,300, E-28668
Opposite metoli response to fenofirte tretment in pregnnt n virgin rts An Sori, Crlos Boos, n Emilio Herrer 1 Fult e Cienis Experimentles y e l Slu, Universi Sn Plo-CEU, Ctr. Boill el Monte km 5,300, E-28668
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Role of the EGF receptor in PPARγ-mediated sodium and water transport in human proximal tubule cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:1174 1182 DOI 1.17/s125-13-2835-y ARTICLE Role of the EGF reeptor in PPARγ-meite soium n wter trnsport in humn proximl tuule ells S. S & J. Zhng & R. Yong & D. Yghoin & M. G. Wong &
Dietologi (213) 56:1174 1182 DOI 1.17/s125-13-2835-y ARTICLE Role of the EGF reeptor in PPARγ-meite soium n wter trnsport in humn proximl tuule ells S. S & J. Zhng & R. Yong & D. Yghoin & M. G. Wong &
Hyun-Suk Ko, 1 Hyo-Jeong Lee, 1 Hyo-Jung Lee, 1,2 Eun Jung Sohn, 1 Miyong Yun, 1 Min-Ho Lee, 3 and Sung-Hoon Kim 1. 1.
 Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume 13, Artile ID 94737, 1 pges http://x.oi.org/1.1155/13/94737 Reserh Artile Essentil Oil of Pinus koriensis Exerts Antioesi n Hypolipiemi Ativity vi Inhiition
Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume 13, Artile ID 94737, 1 pges http://x.oi.org/1.1155/13/94737 Reserh Artile Essentil Oil of Pinus koriensis Exerts Antioesi n Hypolipiemi Ativity vi Inhiition
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Farnesoid X receptor inhibits glucagon-like peptide-1 production by enteroendocrine L cells
 Reeive 27 Mr 215 Aepte 25 My 215 Pulishe 2 Jul 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8629 Frnesoi X reeptor inhiits glugon-like peptie-1 proution y enteroenorine L ells Mohme-Smi Trelsi 1,2,3,4, Mehi Doui 1,2,3,4, Jnne
Reeive 27 Mr 215 Aepte 25 My 215 Pulishe 2 Jul 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8629 Frnesoi X reeptor inhiits glugon-like peptie-1 proution y enteroenorine L ells Mohme-Smi Trelsi 1,2,3,4, Mehi Doui 1,2,3,4, Jnne
Essential role of NKT cells producing IL-4 and IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity
 Essentil role of NKT ells produing IL-4 nd IL-13 in the development of llergen-indued irwy hyperretivity OMID AKBARI 1, PHILIPPE STOCK 1, EVERETT MEYER 1, MITCHELL KRONENBERG 2, STEPHANE SIDOBRE 2, TOSHINORI
Essentil role of NKT ells produing IL-4 nd IL-13 in the development of llergen-indued irwy hyperretivity OMID AKBARI 1, PHILIPPE STOCK 1, EVERETT MEYER 1, MITCHELL KRONENBERG 2, STEPHANE SIDOBRE 2, TOSHINORI
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
CTRP3 attenuates cardiac dysfunction, inflammation, oxidative stress and cell death in diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats
 Dietologi (7) 6:6 7 DOI.7/s57 ARTICLE CTRP ttenutes ri ysfuntion, inflmmtion, oxitive stress n ell eth in ieti riomyopthy in rts ZhenGuo M,, & YuPei Yun,, & SiChi Xu,, & WenYing Wei,, & ChunRu Xu,, & Xin
Dietologi (7) 6:6 7 DOI.7/s57 ARTICLE CTRP ttenutes ri ysfuntion, inflmmtion, oxitive stress n ell eth in ieti riomyopthy in rts ZhenGuo M,, & YuPei Yun,, & SiChi Xu,, & WenYing Wei,, & ChunRu Xu,, & Xin
