CT-2A * * * * * * NRRP (particles per cell)
|
|
|
- Mark Brendan Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CT-2A Viability (%) TNF-α: AT-46 GDC-917 LCL161 Monomer AZD-5582 Birinapant Dimer Supplementary Figure 1. s potently synergize with TNF-α to induce the death of glioblastoma cells. Viability of mouse glioblastoma CT-2A cells to the treatment of.1% BSA or.1 ng ml -1 TNF-α and vehicle or 5 μm of the indicated monomeric or dimeric for h. Viability was assessed by Alamar blue. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 4. Representative data from two independent experiments using biological replicates. Statistical significance was compared to vehicle and BSA treatment using ANOVA using Dunnett s multiple comparison test. Significance is reported if p <.1 (). Viable cells (%) NRRP (particles per cell) CT-2A DBT Supplementary Figure 2. s synergize with non-replicating rhabdovirus-derived particles (NRRPs) to induce the death of glioblastoma cells. Alamar blue viability assays of mouse glioblastoma CT-2A or DBT-cells to the treatment of vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () and increasing numbers of NRRPs for h. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 3. Representative data from two independent experiments using biological replicates.
2 a Viable cells (%) K51 NT sirna: cflip sirna: BSA TNF-α VSV 51 G (MOI) SF539 Viable cells (%) NT sirna: cflip sirna: BSA TNF-α VSV 51 G (MOI) 12 GM38 Viable cells (%) NT sirna: cflip sirna: BSA TNF-α VSV 51 G (MOI) b SF539 NT sirna: cflip sirna: cflip β-tubulin K51 GM Supplementary Figure 3. Resistance to -based combinations in glioblastoma cells is circumvented with downregulation of cflip. (a) Primary mouse NF1-/p53-/ (K51) or human (SF539) glioblastoma cells or human non-transformed cells (GM38) were transfected with nontargeting (NT) or cflip sirna for h and subsequently treated for h with vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () and BSA,.1 ng ml -1 TNF-α or the indicated MOI of a nonspreading version of VSVΔ51 (VSVΔ51ΔG). Viability was determined by Alamar blue. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 4. Representative data from three independent experiments using biological replicates. Statistical significance was compared to vehicle and BSA treatment using ANOVA using Dunnett s multiple comparison test. Significance is reported if p <.1 (). (b) Efficacy of NT sirna or sirna targeting cflip from the experiment in (a).
3 a PBS CT-2A b Coronal Horizontal CT-2A PBS Supplementary Figure 4. Establishment of a mouse syngeneic orthotopic model of glioblastoma. MRI (a) and gross (b) images of a C57BL/6 mouse injected intracranially with PBS or 5x14 CT-2A cells and sacrificed at days post-implantation. Scale bar, 2 mm. Ruler is in cm with mm divisions. Cortex Cerebellum Spleen (h): ciap1/2 XIAP β-tubulin ciap1/2 XIAP β-tubulin ciap1/2 XIAP β-tubulin Supplementary Figure 5. treatment does not induce the downregulation of the IAPs in brain tissue from non-tumor bearing mice. Mice were treated with mg kg -1 of LCL161 () for the indicated time, and tissues were processed for Western Blotting using the indicated antibodies. n = 2 for each timepoint. (h): ciap1/2 XIAP β-tubulin CT-2A brain tumours Supplementary Figure 6. Degradation of ciap1/2 and XIAP in intracranial gliomas upon intratumoral injection of a. Mice with 21 d intracranial CT-2A tumors were treated by stereotactic injection (at the same coordinates as with the initial tumor implantation) with 1 μl of μm LCL161 (), and tumors were processed at the indicated times post-treatment for Westerm blotting using the indicated antibodies. n = 2 for control and n = 3 for -treated mice at the indicated post-treatment time.
4 Survival probability poly(i:c) treatment in C57BL/6 mice n = Time (days post-treatment) Supplementary Figure 7. Intracranial treatment of poly(i:c) does not cause mortality. Kaplan-Meier curve depicting survival of mice that received three 1 μl intracranial treatments of 5 μg poly(i:c). Treatments were on days, 3, and 7. Normalized counts SNB PD-L1 (BV421) PD-L2 (AF647) HLA-A,B,C (PE) HLA-DR/DP/DQ (BV65) Isotype control BSA TNF-α IFN-β VSV 51 Supplementary Figure 8. treatment does not abrogate expression of checkpoint inhibitor molecules or MHC I/II proteins. SNB cells were treated for 24 h with vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () and 1 ng ml -1 TNF-α, 25 U ml -1 IFN-β or.1 MOI of VSVΔ51, and viable cells (Zombie Green negative) were processed for flow cytometry using the indicated antibodies. Representative data from three independent experiments.
5 Spots per 1, cells IFN-γ CD8 T-cell Naïve: Cured: Cancer cell EMT6: line 4T1: α-pd-1: GrzB Supplementary Figure 9. CD8 T-cells cells from mice previously cured of mammary tumors recognize the same tumor cell type. CD8 T-cells were enriched from naïve mice or mice previously cured of EMT6 tumors, and subjected to ELISpot assays for the detection of IFN-γ and GrzB. Cancer cells (EMT6, 4T1) were cocultured with CD8 T-cells (12:1 ratio) and 1 μg ml -1 of control IgG or α-pd-1 for h. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 3 of mice for naïve or cured groups. Significance was compared to naïve CD8 T-cell co-incubated with EMT6 cells as assessed by ANOVA with Dunnett s multiple comparison test. p <.1;, p <.1. FSC 25K 2K 15K K CD45 (BV65) Counts CD45 CD K CD3 (APC-Cy7) CD3 (APC-Cy7) CD8 (PE) CD8 (PE) Normalized counts CD45 CD3 CD45 CD3 CD PD-1 (BV421) PD-1 (BV421) Normalized counts PD-1 (BV421) PD-1 (BV421) Supplementary Figure 1. treatment leads to the upregulation of PD-1 in CD8 T-cells. Mice bearing intracranial CT-2A tumors were treated with mg kg -1 LCL161 orally () on post-implantation days 14, 16, 21 and 23. Viable cells from CT-2A tumors were processed for flow cytometry using the antibodies CD45 (BV65), CD3 (APC-Cy7), CD8 (PE) and PD-1 (BV421). Data represented as box and whisker plots are in Fig. 4b.
6 a Viable cells (%) TNF-α: IFN-α: IFN-β: MPC-11 b Normalized To Mode MPC PE-Cy7 IgG α-pd-l1 c α-pd-1 (i.p.): (p.o.): Survival probability MPC Time (d post-implantation) (4) (7) (4) (4) (4) (4) IgG α-pd-1 α-ctla-4 d IgG α-ctla-4 α-pd-1 3. Time (d post-implantation) x1 6 Supplementary Figure 11. s synergize with immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of a mouse model of multiple myeloma. (a) MPC-11 cells were treated with vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () and.1 ng ml -1 TNF-α, 25 U ml -1 IFN-α or 25 U ml -1 IFN-β. Viability was determined by Alamar blue at h post-treatment. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 4. Statistical significance was compared to vehicle and BSA treatment using ANOVA using Dunnett s multiple comparison test. Significance is reported if p <.1 (). Representative data from three independent experiments using biological replicates. (b) MPC-11 cells were dissociated and processed for flow cytometry with PE-Cy7-conjugated isotype IgG or PD-L1. Representative data from two independent experiments. (c) Mice were injected with murine MPC-11 cells intravenously, and 5 days later were treated at the indicated time points with combinations of vehicle or mg kg -1 LCL161 orally and 25 μg of IgG, α-pd-1 or α-ctla4 intraperitoneally. Data represents the Kaplan-Meier curve depicting mouse survival. Log-rank with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison:, p <.5. Numbers in parentheses represent number of mice per group. Representative data from two independent experiments. (d) Representative IVIS images from mice described in (c) were acquired at indicated time points. Scale: p/sec/cm2/sr.
7 a Viable cells (%) TNF-α: IFN-β: VSV 51: EMT6 b Normalized counts 1 EMT PE-Cy7 IgG α-pd-l1 c VSV 51 (i.t.): α-pd-1 (i.p.): (p.o.): Tumour volume (mm 3 ) 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 EMT6 mammary tumors Time (d post-treatment) Survival probability EMT6 mammary tumors Time (d post-treatment) (4) (5) (4) (5) PBS VSV 51 α-pd1 Supplementary Figure 12. The combination of s with antibodies targeting immune checkpoint inhibitors in a mouse model of mammary cancer. (a) Viability assay of EMT6 cells treated with vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () and.1 ng ml -1 TNF-α, 25 U ml -1 IFN-β or.1 MOI of VSVΔ51 for h. Error bars, mean, s.d. n = 4. Statistical significance was compared to vehicle and BSA treatment using ANOVA using Dunnett s multiple comparison test. Significance is reported if p <.1 (). Representative data from three independent experiments using biological replicates. (b) EMT6 cells were dissociated and processed for flow cytometry with PE-Cy7-conjugated isotype IgG or PD-L1. Representative data from three independent experiments. (c) Mice bearing ~ mm 3 EMT6-Fluc tumors were treated at the indicated post-implantation times with PBS or 5x1 8 PFU of VSVΔ51 intratumorally, and then with vehicle or 5 mg/kg LCL161 () orally and 25 μg of IgG or α-pd-1 intraperitoneally. Left panel depicts tumor growth. Error bars, mean, s.e,m. Right panel represents the Kaplan-Meier curve depicting mouse survival. Log-rank with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison:, p <.5;, p <.1. Numbers in parentheses represent number of mice per group.
8 a TNF-α (pg ml -1 ) IL-6 (pg ml -1 ) IL-17 (pg ml -1 ) IFN-γ (pg ml GrzB (ng ml -1 ) -1 ) CT-2A: Naïve: Splenocytes Cured: mab α-pd-1: α-pd-l1: b IFN-γ (pg ml -1 ) IL-6 (pg ml -1 ) IL-17 (pg ml -1 ) 3, 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 4 GrzB (ng ml -1 ) TNF-α (pg ml -1 ) IL-1 (pg ml -1 ) Supplementary Figure 13. The inclusion of s increases the immune response in the presence of glioblastoma cells. (a) The expression of the indicated factors was detected by ELISA from cell culture supernatants of CT-2A cells that were co-incubated for h with splenocytes derived from naïve mice or mice previously cured with intracranial CT-2A tumors by and anti-pd-1 cotreatment (1:2 ratio of CT-2A cells to splenocytes). Data represented as heat maps is in Fig. 5a. Crosses depicts mean, solid horizontal line depicts median, box depicts 25th to th percentile, and whiskers depicts min-max range of the values. Statistical significance was compared to naïve CD8 T-cell as assessed by ANOVA with Dunnett s multiple comparison test., p <.5; p <.1;, p <.1. (b) The indicated cytokines were determined by ELISA from CT-2A cells that were cocultured with splenocytes derived from naïve or cured mice and treated with vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () for h. Heat map plots are shown in Fig. 5a.. Crosses depicts mean, solid horizontal line depicts median, box depicts 25th to th percentile, and whiskers depicts min-max range of the values. Statistical significance was compared to vehicle and IgG treated T-cells as assessed by ANOVA with Dunnett s multiple comparison test. p <.1;, p <.1. CT-2A: : α-pd-1:
9 pg ml -1 5 IFN-β 15 5 IFN-γ 1 5 IL-1α IL-1β IL-6 IL-1 IL-12p7 IL-17A : α-pd-1: pg ml -1 5 IL IL GM-CSF MCP TNF-α : α-pd-1: Supplementary Figure 14. Combinatorial and immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment leads to the increased systemic presence of proinflammatory cytokines. Serum from mice depicted in Fig. 6a was processed for multiplex ELISA for the quantitation of the indicated proteins. Crosses depicts mean, solid horizontal line depicts median, box depicts 25th to th percentile, and whiskers depicts min-max range of the values. Significance was compared to vehicle and IgG treated mice as assessed by ANOVA with Dunnett s multiple comparison test., p <.5. n = 6 for each treatment group. Data represented as heat maps is in Fig. 7e.
10 : α-pd-1: Min Tnfsf11 Inhba Tgfb1 Tgfb3 Bmp1 Ccl11 Il17c Il1f8 Tnfsf9 Inhbe Cd4l Angpt4 Tgfb2 Bmp8a Amh Ntf5 Il17b Nodal Gdf5 Gdf11 Inhbc Gdf1 Il1f6 Bmp8b Cd7 Ccl21a Ccl8 Ccl28 Eda Lefty2 Fgf16 Tnfsf12 Lta Tnfsf8 Ltb Tnfsf15 Gdf3 Tnfsf1 Ccl17 Il1a Bmp5 Ccl19 Tnfsf13b Ccl3 Cxcl16 Cxcl2 Cxcl3 Gdf15 Tnfsf14 Il24 Fgf2 Il23a Egf Il1b Tnfsf4 Cxcl1 Cxcl11 Ccl24 Ccl2 Ccl4 Ccl5 Fasl Gdnf Ccl22 Tnf Cxcl9 Cxcl13 Il2 Ccl7 Il1rn Il19 Ifnb1 Ccl25 Fgf15 Fgf22 Bmp7 Bmp4 Gdf1 Il17d Mstn Il18 Inhbb Inha Bmp2 Gdf7 Efnb2 Cxcl5 Cxcl14 Bmp6 Fgf9 Ntf3 Fgf13 Fgf5 Nrg3 Fgf14 Bdnf Nrg4 Gas6 Ccl2 Il1f5 Bmp3 Ccl27 Fgf1 Cxcl1 Bmp15 Fgf21 Ppbp Pdgfd Epo Il12a Fgf12 Prl Fgf17 Csf3 Pdgfc Fgf11 Nrg1 Gdf9 Il11 Il1 Tnfsf18 Bmp1 Il4 Osm Efna4 Il17f Ifne1 Fgf7 Efnb1 Vegfc Ngfb Il9 Il13 Ifng Gh Il15 Clc Il12b Tslp Angpt2 Fgf4 Figf Il6 Hgf Angpt1 Cxcl12 Lefty1 Fgf18 Ctf1 Zfp91 Lep Il5 Csf1 Vegfa Igf1 Fgf6 Max Supplementary Figure 15. Proinflammatory cytokine and chemoattractant chemokine gene signatures are upregulated with and immune checkpoint inhibitor combinatorial treatment. Mice were treated as in Fig. 6a, and intracranial CT-2A tumors were processed for quantitation of 176 cytokine and chemokine genes by RT-qPCR. Shown are normalized heat maps of major groups identified by hierarchical clustering. n = 4 for each treatment group.
11 CD8 Proportion (%) CD8 CT-2A: : α-pd-1: CT-2A: : α-pd-1: 1 3 CFSE Supplementary Figure 16. s enhance clonal expansion of CD8 T-cells in the presence of glioblastoma target cells. Isolated splenic CD8 T-cells derived from mice previously cured of CT-2A tumors were loaded with CFSE and co-incubated with CT-2A cells (1:1 ratio) for 96 h in the presence of vehicle or 5 μm LCL161 () or 2 μg ml -1 of control IgG or anti-pd1. Viable cells were processed for flow cytometry. Significance was compared to vehicle and IgG treated mice as assessed by ANOVA with Dunnett s multiple comparison test., p <.5;, p <.1;, p <.1. n = 5 for each treatment group.
12 2 3 4 Polarization Sensitization to TNF-α Co-stimulation (e.g. CD4L) Macrophage (M1>>M2) Tumor TNFα Engulfment or immunogenic cell death 1 Cytokine and chemokine production (e.g. TNF-α) Immune cell recruitment T-cell 6 5 APC (DC) Tumor Co-stimulation antigen (e.g. GITR, CD27, presentation 4-1BB, OX4L) Reversal of immune checkpoint blockade (e.g. α-pd-1, α-pd-l1) CTL Supplementary Figure 17. s are immunoregulatory drugs that act on tumor and immune cells to eradicate cancer through the innate and adaptive immune systems. Shown is a model depicting the single agent and combinatorial immunomodulatory effects of Smac mimetics based on our results and previously published findings. The effects of IAP antagonism on these immune or tumor cells are outlined below: (1) s stimulates the production of cytokines and chemokines from various immune cells, such as macrophages or T-cells, which results in infiltration of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment 1-3. (2) treatment decreases the immunosuppressive macrophage M2 population and concomitantly increases the pro-inflammatory M1 population 4. (3) s deplete ciap1 and ciap2 to sensitize tumors to death by immune ligands, such as TNF-α or TRAIL 1,5-8. Tumor cell death is sensed by the immune system resulting in the priming of a cytotoxic T-cell (CTL) response. (4) s stimulate the TNF/TNFR family member CD4L/CD4 signaling pathway on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) to promote the differentiation and maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages 9. APCs present tumor antigens to the immune system and further release cytotoxic inflammatory cytokines. (5) As a consequence of degrading ciap1 and ciap2 by treatment, s activate the alternative NF-κB pathway, removing the need for a TNF superfamily ligand (such as 4-1BB) and therefore providing a T-cell costimulatory signal 1, 11. (6) s have been shown to increase CTL and natural killer cell mediated cell death 12, 13. Granzyme B-mediated cell death is blocked by the X-linked IAP, XIAP, and this block can be overcome by the mitochondrial release of Smac or by its drug mimic,
13 a ciap1/2 ciap1/2 XIAP XIAP E7 E7 b cflip β-tubulin cflip β-tubulin cflip β-tubulin c ciap1/2 XIAP E ciap1/2 XIAP E ciap1/2 XIAP E d ciap1/2 XIAP E7 Supplementary Figure 18. Full-length blots pertaining to (a) Fig. 2a, (b) Supplementary Fig. 3b, (c) Supplementary Fig. 5 and (d) Supplementary Fig. 6.
14 Suppplementary References 1. Beug, S.T. et al. Smac mimetics and innate immune stimuli synergize to promote tumor death. Nat Biotechnol 32, (214). 2. Infante, J.R. et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of LCL161, an oral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 32, (214). 3. Erickson, R.I. et al. Toxicity profile of small-molecule IAP antagonist GDC-152 is linked to TNF-alpha pharmacology. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 131, (213). 4. Lecis, D. et al. Smac mimetics induce inflammation and necrotic tumour cell death by modulating macrophage activity. Cell death & disease 4, e92 (213). 5. Vince, J.E. et al. IAP antagonists target ciap1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 131, (27). 6. Gaither, A. et al. A Smac mimetic rescue screen reveals roles for inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in tumor necrosis factor-alpha signaling. Cancer Res 67, (27). 7. Li, L. et al. A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL- and TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Science, (24). 8. Fulda, S., Wick, W., Weller, M. & Debatin, K.M. Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med 8, (22). 9. Muller-Sienerth, N. et al. SMAC mimetic BV6 induces cell death in monocytes and maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells. PLoS One 6, e21556 (21). 1. Zarnegar, B.J. et al. Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors ciap1, ciap2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nature Immunology 9, (28). 11. Dougan, M. et al. IAP inhibitors enhance co-stimulation to promote tumor immunity. The Journal of experimental medicine 27, (21). 12. Kashkar, H. et al. XIAP targeting sensitizes Hodgkins Lymphoma cells for cytolytic T cell attack. Blood (26). 13. Brinkmann, K. et al. Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC) mimetic potentiates tumor susceptibility toward natural killer cell-mediated killing. Leukemia & lymphoma 55, (214). 14. Goping, I.S. et al. Granzyme B-induced apoptosis requires both direct caspase activation and relief of caspase inhibition. Immunity 18, (23). 15.Ravi, R. et al. Resistance of cancers to immunologic cytotoxicity and adoptive immunotherapy via X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein expression and coexisting defects in mitochondrial death signaling. Cancer Res 66, (26).
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3922
 Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
NKTR-214 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology
 plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
plus NKTR-262, a Scientifically-Guided Rational Combination Approach for Immune Oncology Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics World Preclinical Congress, 2017
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator
 Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator Yvonne Mowery, MD, PhD February 20, 2017 Tumor/Immune System Balance Kalbasi, JCI 2013 UNC-Duke-NC State-Wake Forest Spring 2017 2 RT Can Shift Balance Toward Elimination
Radiation Therapy as an Immunomodulator Yvonne Mowery, MD, PhD February 20, 2017 Tumor/Immune System Balance Kalbasi, JCI 2013 UNC-Duke-NC State-Wake Forest Spring 2017 2 RT Can Shift Balance Toward Elimination
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS.
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS. (a) Survival curves. WT Sham (n=5), WT CLP or WT CLP antibiotic
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS. (a) Survival curves. WT Sham (n=5), WT CLP or WT CLP antibiotic
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Supplementary Figure 1. ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons
 Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Supplementary Figure 1 ETBF activate Stat3 in B6 and Min mice colons a pstat3 controls Pos Neg ETBF 1 2 3 4 b pstat1 pstat2 pstat3 pstat4 pstat5 pstat6 Actin Figure Legend: (a) ETBF induce predominantly
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL).
 Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune
 Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Dual Targeting Nanoparticle Stimulates the Immune System to Inhibit Tumor Growth Alyssa K. Kosmides, John-William Sidhom, Andrew Fraser, Catherine A. Bessell, Jonathan P. Schneck * Supplemental Figure
Supplemental Information. Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Induces Dynamic Changes. in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells
 Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Immunity, Volume 50 Supplemental Information Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy Induces Dynamic Changes in PD-1 CD8 + Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Sema Kurtulus, Asaf Madi, Giulia Escobar, Max Klapholz, Jackson
Page 39 of 44. 8h LTA & AT h PepG & AT h LTA
 Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations. Tumor Immunology (Cancer)
 Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
Tumor Immunology (Cancer) Tumors arise from accumulated genetic mutations Robert Beatty MCB150 Mutations Usually have >6 mutations in both activation/growth factors and tumor suppressor genes. Types of
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity
 NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
NKTR-255: Accessing IL-15 Therapeutic Potential through Robust and Sustained Engagement of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Peiwen Kuo Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics August 31 st, 2018 Emerging
Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D.
 Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a.
 pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
pplementary Figur Supplementary Figure 1. a. Quantification by RT-qPCR of YFV-17D and YFV-17D pol- (+) RNA in the supernatant of cultured Huh7.5 cells following viral RNA electroporation of respective
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy
 Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Reprogramming Tumor Associated Dendritic Cells for Immunotherapy Edgar Engleman, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Medicine Stanford University Disclosures: Founder of Dendreon, a biotechnology company that
Innate Immunity II. Integration. Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2
 Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis
 Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis Vincent Laufer Rheumatology JC October 17 Disclosures NIH 2
Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis Vincent Laufer Rheumatology JC October 17 Disclosures NIH 2
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
NK cell flow cytometric assay In vivo DC viability and migration assay
 NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
NK cell flow cytometric assay 6 NK cells were purified, by negative selection with the NK Cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi iotec), from spleen and lymph nodes of 6 RAG1KO mice, injected the day before with
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies
 NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
NKTR-255: Accessing The Immunotherapeutic Potential Of IL-15 for NK Cell Therapies Saul Kivimäe Senior Scientist, Research Biology Nektar Therapeutics NK Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy, September 26-27,
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression
 Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression Hassane M. Zarour,, MD Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation
Tumor Microenvironment and Immune Suppression Hassane M. Zarour,, MD Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology-Oncology, University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, PAMB 650/720 - Fall 2008 Lecture 16 Tumor Immunology M. Nagarkatti Teaching Objectives: Introduction to Cancer Immunology Know the antigens expressed by cancer cells Understand
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang
 Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells are more responsive to IFN-γ. (A) Flow
 A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat.Immunol. 12, 568 575 (2011) The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF Mohamed El-Behi, Bogoljub Ciric, Hong
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat.Immunol. 12, 568 575 (2011) The encephalitogenicity of TH17 cells is dependent on IL-1- and IL-23- induced production of the cytokine GM-CSF Mohamed El-Behi, Bogoljub Ciric, Hong
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al
 Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
 Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
Novel RCC Targets from Immuno-Oncology and Antibody-Drug Conjugates Christopher Turner, MD Vice President, Clinical Science 04 November 2016 Uveal Melanoma Celldex Pipeline CANDIDATE INDICATION Preclinical
The g c Family of Cytokines Prof. Warren J. Leonard M.D.
 The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Immunity and Cancer. Doriana Fruci. Lab di Immuno-Oncologia
 Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
Immunity and Cancer Doriana Fruci Lab di Immuno-Oncologia Immune System is a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to defend the body against attacks of foreign invaders (pathogens, cancer
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation
 Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation C. Andrew Stewart,, Werner Müller, Giorgio Trinchieri J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4859-4874. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65180.
Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation C. Andrew Stewart,, Werner Müller, Giorgio Trinchieri J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4859-4874. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65180.
ASCO Annual Meeting 2013, May 31 June , Chicago, IL
 Phase I Study of Safety and Pharmacokinetics of GDC-0917, an Antagonist of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma 1 A Tolcher, 1 K Papadopoulos, 1 A Patnaik,
Phase I Study of Safety and Pharmacokinetics of GDC-0917, an Antagonist of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors or Lymphoma 1 A Tolcher, 1 K Papadopoulos, 1 A Patnaik,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/8/352/352ra110/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Spatially selective depletion of tumor-associated regulatory T cells with near-infrared photoimmunotherapy
Supplementary figure 1. Systemic delivery of anti-cd47 antibody controls tumor growth in
 T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors
 Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors Tibor Keler, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Enhancing immunity with immune modulating
Evaluation of an Agonist Anti-CD27 Human Antibody (Varlilumab) and its Potential for Combination With Checkpoint Inhibitors Tibor Keler, PhD Chief Scientific Officer Enhancing immunity with immune modulating
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis
 Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis rasseit and Steiner et al. .. Supplementary Figure 1 % of initial
Supplementary information CD4 T cells are required for both development and maintenance of disease in a new model of reversible colitis rasseit and Steiner et al. .. Supplementary Figure 1 % of initial
TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0085 TITLE: MODULATION OF T CELL TOLERANCE IN A MURINE MODEL FOR IMMUNOTHERAPY OF PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: ARTHUR A HURWITZ, Ph.d. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Posters and Presentations
 Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
Posters and Presentations June 2017: American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual - Preliminary Correlative Analysis of PD-L1 expression from the SUNRISE Study. View April 2017: American Association
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up. Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins
 Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins The hostile immune microenvironment within a tumor Stat3 Stat3 NK Lytic
Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins The hostile immune microenvironment within a tumor Stat3 Stat3 NK Lytic
Biogen Idec Oncology Pipeline. Greg Reyes, MD, PhD SVP, Oncology Research & Development
 Biogen Idec Oncology Pipeline Greg Reyes, MD, PhD SVP, Oncology Research & Development March 25, 2009 Biogen Idec Strategy in Lymphoma / Leukemia CLL RITUXAN NHL FC-RITUXAN GA101 RITUXAN-CVP RITUXAN-CHOP
Biogen Idec Oncology Pipeline Greg Reyes, MD, PhD SVP, Oncology Research & Development March 25, 2009 Biogen Idec Strategy in Lymphoma / Leukemia CLL RITUXAN NHL FC-RITUXAN GA101 RITUXAN-CVP RITUXAN-CHOP
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach
 Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Oncolytic Immunotherapy: A Local and Systemic Antitumor Approach Oncolytic immunotherapy Oncolytic immunotherapy the use of a genetically modified virus to attack tumors and induce a systemic immune response
Spleen. mlns. E Spleen 4.1. mlns. Spleen. mlns. Mock 17. Mock CD8 HIV-1 CD38 HLA-DR. Ki67. Spleen. Spleen. mlns. Cheng et al. Fig.
 C D E F Mock 17 Mock 4.1 CD38 57 CD8 23.7 HLA-DR Ki67 G H I Cheng et al. Fig.S1 Supplementary Figure 1. persistent infection leads to human T cell depletion and hyper-immune activation. Humanized mice
C D E F Mock 17 Mock 4.1 CD38 57 CD8 23.7 HLA-DR Ki67 G H I Cheng et al. Fig.S1 Supplementary Figure 1. persistent infection leads to human T cell depletion and hyper-immune activation. Humanized mice
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway
 Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
Therapeutic effect of baicalin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is mediated by SOCS3 regulatory pathway Yuan Zhang 1,2, Xing Li 1,2, Bogoljub Ciric 1, Cun-gen Ma 3, Bruno Gran 4, Abdolmohamad
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Approved for public release; distribution unlimited
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation
 MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
Supplemental Materials for. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to. FTY720 during neuroinflammation
 Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation. mammary cancer model. Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler
 Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Therapeutic efficacy of MUC1- specific CTL and CD137 costimulation in a spontaneous mammary cancer model Pinku Mukherjee & Sandra Gendler Goal of Immunotherapy Boosting the low level anti-tumor immune
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D.
 Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Online supplement. Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated
 Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
Online supplement Phenotypic, functional and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages Abdullah Al Tarique*, Jayden Logan *, Emma Thomas *, Patrick G Holt *, Peter
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x
 Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained with hematoxylin from caerulein-treated WT and mir-21
Supplementary Figure 1. Dynamic Response of WT and mir-21 -/- mice to caerulein. (a) Representative histological sections of mouse pancreas stained with hematoxylin from caerulein-treated WT and mir-21
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents
 Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents Chad May, PhD Senior Director Targeted Immunotherapy Oncology Research Unit, Pfizer 7 th Annual World ADC October 10, 2016 Cancer-Immunity Cycle Innate Immunity
Combining ADCs with Immuno-Oncology Agents Chad May, PhD Senior Director Targeted Immunotherapy Oncology Research Unit, Pfizer 7 th Annual World ADC October 10, 2016 Cancer-Immunity Cycle Innate Immunity
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine
 Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics SMI Cancer Vaccines, September 2017 Nektar Therapeutics
Enhanced Cancer Vaccine Effectiveness with NKTR-214, a CD122-Biased Cytokine Jonathan Zalevsky SVP, Biology and Preclinical Development Nektar Therapeutics SMI Cancer Vaccines, September 2017 Nektar Therapeutics
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
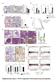 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
