label the basement membrane). Different fixation methods of EB-perfused P8 mice to optimize the combination
|
|
|
- Jared Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of the tissue fixation protocol to combine EB perfusion and IB4 endothelial tip cell staining in the postnatal mouse brain. a-l Labeling of EB-perfused P8 mice with biotinylated IB4 in combination with immunfluorescence (e.g. LN to label the basement membrane). Different fixation methods of EB-perfused P8 mice to optimize the combination of EB perfusion with IB4 endothelial tip cell labeling and antibody stainings were tested. Combinations of
2 immersion-fixation with 4% FA and different amounts of GA were used. Subsequently, 40 µm coronal brain sections were labeled with biotinylated IB4 to visualize blood vessel endothelial cells (red) and with an antibody against LN (green) to test if antigenicity is still present despite GA treatment (a-l,). EB (perfused blood vessels, cyan). Whereas postfixation in 4% FA only (no GA) resulted in a considerable loss of the EB signal (a-d), the combination of 4% FA % GA (e-h) or 4% FA % GA (i-l) were optimal for combination of the different label procedures (IB4, LN) with EB-perfused vessels. Scale bars: 50 µm (a-l).
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Classical endothelial tip cell markers in direct comparison to IB4 labeling in the P8 mouse brain cortex. Immunofluorescent labeling of 40 µm P8 coronal mouse brain sections labeled with the classical endothelial tip cells markers VEGFR2 (a-d, green), VEGFR3 (e-h, green) and Dll4 (i-l, green) and with biotinylated IB4 to visualize blood vessel endothelial (tip) cells (red). Cell nuclei (DAPI, blue).
4 a-l IB4 as well as antibodies against VEGFR2 (a-d), VEGFR3 (e-h) or Dll4 (i-l) visualize CNS blood vessel structures and endothelial tip-, stalk-, and phalanx cells. Boxed areas (a,b,e,f,i,j) highlight endothelial tip cells that are enlarged on the right hand (c,d,g,h,k,l). White arrowheads (a,b,i,j) mark additional endothelial tip cells c,d,g,h,k,l IB4 + endothelial tip cells with clearly identifiable, multiple filopodia forming a typical hand-like structure (c,g,k). Note that neither VEGFR2 (d), VEGFR3 (h) nor Dll4 (l) label endothelial tip cell filopodia as accurately as IB4. As filopodia are the key morphological criterion for identifying endothelial tip cells, the classical tip cell markers VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and Dll4 do not facilitate the identification of endothelial tip cells in the postnatal mouse brain. Moreover, none of these markers allows a clear delineation of endothelial stalk- or phalanx cells from endothelial tip cells (d,h,l). Scale bars: 50 µm (a,b,e,f,i,j) ; 10 µm (c,d,g,h,k,l).
5 Supplementary Figure 3
6 Immunofluorescence of perivascular cells in the vicinity of endothelial tip cells in the P8 mouse brain cortex. a-p All samples used for the immunofluorescence shown in this figure have been immersion fixed with 4% FA and 0.025% GA, which was the final fixation protocol of the present study. This ensures optimal retaining of EB inside the vessels but also good antigenicity for a variety of cellular markers (see also Supplementary Fig. S1). For example a-d shows GFAP + astrocytes and GFAP + radial glia (green), IB4 + blood vessel endothelial cells (red) including an endothelial tip cell and an established blood vessel in the P8 mouse brain cortex. Endothelial tip cell filopodia do not follow a template of GFAP + astrocytes and radial glia (a). Boxed area with zoom on endothelial tip cell is enlarged in b-d. Cell nuclei (DAPI, blue). e-h PDGFRB + pericytes (green) and IB4+ blood vessels (red) in the P8 mouse cortex. Boxed area is enlarged in f-h. Endothelial tip cell filopodia are PDGFRB -. Cell nuclei (DAPI, blue). i-l LN + (green) common basement membrane of IB4 + blood vessels (red) and PDGFRB + pericytes. Boxed area with zoom on endothelial tip cell is enlarged in j-l. Note the faint LNstaining of endothelial tip cell filopodia at the base of the endothelial tip cell body (l). Cell nuclei (DAPI, blue). Note that no pericytes are present at the tip cell (f,h) whereas LN is ensheathing the tip cell body (j,l). m-p Nf160 + axons (cyan) and IB4+ endothelial tip cell (red, filopodia) in the P8 mouse corpus callosum. Boxed area with zoom on endothelial tip cell is enlarged in n-p. Cell nuclei (DAPI, blue). Scale bars: 50 µm (a,e,i,m); 10 µm (b-d, f-h, j-l, n-p).
Supplementary information. Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic
 Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Supplementary information Nkx2.1 regulates the generation of telencephalic astrocytes during embryonic development Shilpi Minocha 1*, Delphine Valloton 1*, Yvan Arsenijevic 2, Jean-René Cardinaux 3, Raffaella
Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial tip cells in the postnatal mouse brain
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Quantitative assessment of angiogenesis, perfused blood vessels and endothelial
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram of BBB and brain chips.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
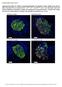 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of astrocytes. Primary astrocytes were separated from the glial cultures using a mild trypsinization protocol. Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunofluorescent
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/3/e1400244/dc1 Supplementary Materials for PlGF-induced VEGFR1-dependent vascular remodeling determines opposing antitumor effects and drug resistance to
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/3/e1400244/dc1 Supplementary Materials for PlGF-induced VEGFR1-dependent vascular remodeling determines opposing antitumor effects and drug resistance to
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND MOVIE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: GFAP positive nerves in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. (A) Images of nerves stained for GFAP (green), S100 (red) and DAPI
!! INL!!!! ONL!! IS/OS!!
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES GCL INL ONL IS/OS RPE Choroid GR MR A B C HSD2 Cc RPE CV D Cc RPE CV E RPE Cc CV F RPE Cc CV Figure S1 Figure S1: Immunohistochemistry eidence for glucocorticoid receptor (GR), mineralocorticoid
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES GCL INL ONL IS/OS RPE Choroid GR MR A B C HSD2 Cc RPE CV D Cc RPE CV E RPE Cc CV F RPE Cc CV Figure S1 Figure S1: Immunohistochemistry eidence for glucocorticoid receptor (GR), mineralocorticoid
Nogo-A is a negative regulator of CNS angiogenesis
 Nogo-A is a negative regulator of CNS angiogenesis Thomas Wälchli a,b,c,1, Vincent Pernet a,b,1, Oliver Weinmann a,b, Jau-Ye Shiu d, Anna Guzik-Kornacka a,b, Guillaume Decrey c, Deniz Yüksel e,f, Hannah
Nogo-A is a negative regulator of CNS angiogenesis Thomas Wälchli a,b,c,1, Vincent Pernet a,b,1, Oliver Weinmann a,b, Jau-Ye Shiu d, Anna Guzik-Kornacka a,b, Guillaume Decrey c, Deniz Yüksel e,f, Hannah
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Boucher et al NCOMMS B
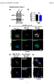 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Supplementary Figure 1 Genetic labeling of microglia Male and female 2-3 month-old CreERT2;R26-tdTomato mice or CreERT2;R26-tdTomato;Iba1-eGFP transgenic mice were treated with 1x, 2x (48 h apart), or
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
Collagen VI Ablation Retards Brain Tumor Progression Due to Deficits in Assembly of the Vascular Basal Lamina
 The American Journal of Pathology, Vol. 180, No. 3, March 2012 Copyright 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.006
The American Journal of Pathology, Vol. 180, No. 3, March 2012 Copyright 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.11.006
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the
 In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a,
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Supplementary Materials
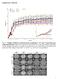 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo
 Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and
 Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Relative SOD1 activity. Relative SOD2 activity. Relative SOD activity (Infected:Mock) + CP + DDC
 Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the. development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation Dimitrios Davalos, Jae Kyu Ryu, Mario Merlini, Kim
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Supplementary Figure 1 Representative images of an in vitro comparison of several AAV serotypes regarding egfp expression in cochlear explants of CBA/CaJ mice. (A-F): Results after incubation at equal
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Neurons vs. glia. Traditionally, glia have been viewed as passive cells that help to maintain the function of neurons.
 GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
Image-Guided Radiotherapy Targets Macromolecules. through Altering the Tumor Microenvironment
 Supporting Information Image-Guided Radiotherapy Targets Macromolecules through ltering the Tumor Microenvironment uthors: Oliver K. ppelbe,, Qingbei Zhang,, harles. Pelizzari, Ralph R. Weichselbaum,,
Supporting Information Image-Guided Radiotherapy Targets Macromolecules through ltering the Tumor Microenvironment uthors: Oliver K. ppelbe,, Qingbei Zhang,, harles. Pelizzari, Ralph R. Weichselbaum,,
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration
 An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Lymphatic endothelial cells support tumor growth in breast cancer Esak Lee a, Niranjan B. Pandey a, and Aleksander S. Popel a,b a Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins
Supplementary Information Lymphatic endothelial cells support tumor growth in breast cancer Esak Lee a, Niranjan B. Pandey a, and Aleksander S. Popel a,b a Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins
NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration
 Article NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration Shin H. Kang, 1 Masahiro Fukaya, 2,4 Jason K. Yang, 1 Jeffrey D. Rothstein,
Article NG2 + CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration Shin H. Kang, 1 Masahiro Fukaya, 2,4 Jason K. Yang, 1 Jeffrey D. Rothstein,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and
 OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal
 Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Lack of cadherins Celsr2 and Celsr3 impairs ependymal ciliogenesis, leading to fatal hydrocephalus Fadel TISSIR, Yibo QU, Mireille MONTCOUQUIOL, Libing ZHOU, Kouji KOMATSU, Dongbo SHI, Toshihiko FUJIMORI,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
Supplementary legends
 Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination
 Supplemental Information Title: M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination Authors: Veronique E. Miron, Amanda Boyd, Jing-Wei Zhao, Tracy J. Yuen, Julia M.
Supplemental Information Title: M2 microglia/ macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination Authors: Veronique E. Miron, Amanda Boyd, Jing-Wei Zhao, Tracy J. Yuen, Julia M.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Formaldehyde scavengers function as novel antigen retrieval agents
 Supplementary Information Formaldehyde scavengers function as novel antigen retrieval agents Craig T Vollert 1, Wilna J Moree 2, Steven Gregory 1, Steven J Bark 2, & Jason L Eriksen* 1 1 Department of
Supplementary Information Formaldehyde scavengers function as novel antigen retrieval agents Craig T Vollert 1, Wilna J Moree 2, Steven Gregory 1, Steven J Bark 2, & Jason L Eriksen* 1 1 Department of
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Table 1
 Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Absolute %) Immature Pool (Absolute %) A10 EC Control A10 EC Control A10 EC Control
 Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Asolute %) Immature Pool (Asolute %) A10 EC A10 EC A10 EC Myeloid 50.7 57.5 37.5 46.2 13.2 11.3 Erythroid 38.3 23.2 33.3 16.8 9.3 6.3 Lymphocytes 13.8 19.0 - - -
Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Asolute %) Immature Pool (Asolute %) A10 EC A10 EC A10 EC Myeloid 50.7 57.5 37.5 46.2 13.2 11.3 Erythroid 38.3 23.2 33.3 16.8 9.3 6.3 Lymphocytes 13.8 19.0 - - -
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
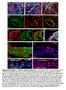 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1: Uncropped western blots for Figure 1B. Uncropped blots shown in Figure 1B, showing that NOTCH intracellular domain (NICD) is
 Supplementary Figure 1: Uncropped western blots for Figure 1B. Uncropped blots shown in Figure 1B, showing that NOTCH intracellular domain (NICD) is increased with exposure of HUVEC to 1h FSS, and that
Supplementary Figure 1: Uncropped western blots for Figure 1B. Uncropped blots shown in Figure 1B, showing that NOTCH intracellular domain (NICD) is increased with exposure of HUVEC to 1h FSS, and that
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization
 Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from
 Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Ophthalmology, Radiation Oncology,
 Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Supporting Online Material Journal: Nature Neuroscience Article Title: Corresponding Author: All Authors: Affiliations: Tanycytes of the Hypothalamic Median Eminence Form a Diet- Responsive Neurogenic
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1:
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Cord blood monocytes as a source of cell therapy products for treatment of brain injuries ISCT/CBA 2015 Cord Blood Workshop Wednesday, May 27, 2015
 Cord blood monocytes as a source of cell therapy products for treatment of brain injuries ISCT/CBA 2015 Cord Blood Workshop Wednesday, May 27, 2015 Andrew E. Balber, PhD Senior Scientific Advisor CT 2,
Cord blood monocytes as a source of cell therapy products for treatment of brain injuries ISCT/CBA 2015 Cord Blood Workshop Wednesday, May 27, 2015 Andrew E. Balber, PhD Senior Scientific Advisor CT 2,
Constitutional mislocalization of Pten drives precocious maturation in oligodendrocytes and aberrant myelination in model of autism spectrum disorder
 Lee et al. Translational Psychiatry (2019) 9:13 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0364-7 Translational Psychiatry ARTICLE Constitutional mislocalization of Pten drives precocious maturation in oligodendrocytes
Lee et al. Translational Psychiatry (2019) 9:13 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0364-7 Translational Psychiatry ARTICLE Constitutional mislocalization of Pten drives precocious maturation in oligodendrocytes
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
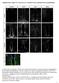 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table.
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
SOPten flox/flox (KO) Pten flox/flox (WT) flox allele 6.0 kb. Pten. Actin. ! allele 2.3 kb. Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al.
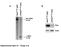 s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
c-abl PDGFRα PDGFRβ VEGFR-1 VEGFR-2 FLT-3 c-fms c-kit Ref. 2 (ND) 9.4 (ND) Supplementary Table 2. Chemical structure of the RTKIs used in this study.
 SUPPLEMETARY DATA Supplementary Table 1. Upper and lower entries in each cell represent IC50 (nm) values determined by a biochemical kinase assay or cellular tyrosine kinase phosphorylation, respectively.
SUPPLEMETARY DATA Supplementary Table 1. Upper and lower entries in each cell represent IC50 (nm) values determined by a biochemical kinase assay or cellular tyrosine kinase phosphorylation, respectively.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/385/ra70/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The interaction of heparan sulfate proteoglycans with endothelial transglutaminase-2 limits VEGF 165 -induced angiogenesis
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/385/ra70/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The interaction of heparan sulfate proteoglycans with endothelial transglutaminase-2 limits VEGF 165 -induced angiogenesis
Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration
 Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Brain anatomy tutorial. Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics
 Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
