Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
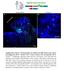
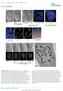
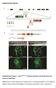
2 Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a) are generated to study the apical ectoderm ridge (AER), floor plate (FP) (b) and isthmus (c). (d-o) Triple staining of YAP (red), p21 (green), and Ki67 (orange) in the AER of the limb (d-g), floor plate of the neural tube (h-k), and isthmus (l-o) at E10.5 shows low Ki67 staining, high p21 expression, and the lack of nuclear YAP in each signaling center. Representative cells within the signaling centers (solid box) and the surrounding tissues (dashed box) are enlarged respectively. (p-r) Quantification of overlapping signals of YAP and DAPI in each signaling center (mean ± SEM, n=5, p<0.05). (s,u,w) Expression of S127 phosphorylated YAP in the signaling centers. (t,v,x) Expression of -catenin in the signaling centers. All quantifications are analyzed by using Student s t-test.yellow arrowheads indicate the signaling center in AER, the floor plate and the isthmus. Scale bar, 20 μm in d-o,s-x.
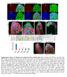
3 Supplementary Figure 2: Expression of constitutively active YAP induces ectopicc cell proliferation and inhibits the EK formation during tooth development. (a,b) Expression of a
4 constitutively activated YAP (Yap S127A ) at E13.5 results in increased nuclear YAP. (c,d) Expression of Yap S127A results in reduced p21 expression in the EK (open yellow arrowhead in d compared to yellow arrowhead in c). (e-h) Ki67 negative cells are decreased in numbers at the posterior region of the incisor tooth germ at E13.5 after Yap S127A expression (yellow arrowheads in g,h) compared to control (open yellow arrowheads in e,f). (i) Quantification of the number of p21 positive cells at the posterior region of the epithelium in the incisor tooth germ (mean ± SEM, n=3, p<0.05). (j) Quantification of the number of Ki67 negative cells at the posterior region of the dental epithelium in the incisor tooth germ (mean ± SEM, n=3, p<0.05). (k,l) Shh expression is decreased at E14.5 after Yap S127A expression in the molar tooth germ. (m,n) Expression of Yap S127A results in reduced p21 expression in the molar EK (open yellow arrowhead in l compared to yellow arrowhead in k). (o-r) Ki67 negative cells are decreased in numbers at the basal region of the molar tooth germ at E14.5 after Yap S127A expression (yellow arrowheads in q,r) compared to control (open yellow arrowheads in o,p). (s) Quantification of the number of p21 positive cells at the basal region of the epithelium in the molar tooth germ (mean ± SEM, n=3, p<0.05). (t) Quantification of the number of Ki67 negative cells at the basal region of the dental epithelium in the molar tooth germ (mean ± SEM, n=3, p<0.05). All quantifications are analyzed by using Student s t-test. Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 25 μm in a,b; 50 μm in c-e,g, m-n,o,q; 8 μm in f,h,p,r.
5 Supplementary Figure 3: Expression of a constitutively active YAP delays invagination of lingual epithelium. (a,b) Expression of a constitutively active YAP (Yap S127A ) results in delayed invagination of the lingual epithelium at E15.5. (c,d) Expression of Yap S127A results in reduced p21 expression in the EK (compare open yellow arrowhead in d to yellow arrowhead in c). (e,f) Ki67 negative cells are decreased in numbers at the posterior region of the incisor tooth germ at E15.5 after Yap S127A expression (yellow arrowhead in f) compared to the control (open yellow arrowhead in e). Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 75 μm in a,b; 50 μm in c-f.
6
7 Supplementary Figure 4: Activation of Axin2 CreER and Shh CreER in the EK is unable to fully induce nuclear YAP at E13.5. (a,d,g,j) Nuclear YAP is excluded from the EK with increased p21 and decreased Ki67 levels at E13.5. (b,c) After double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 in the EK, YAP begins to accumulate in the nucleus of EK cells (yellow arrowheads), although the majority of the cells exhibit low nuclear YAP. (e,f,h,i,k,l) p21 expression remains high and cell proliferation as assessed by Ki67 staining is unchanged after double deletion of Lats1 and Lats2 in the EK at E13.5. Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 50 μm in a-l.
8
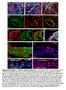
9 Supplementary Figure 5: Deletion of Ctnna1 results in varied phenotypes and actin organization and constriction defects with normal expression of other adherens junction proteins. (a-d) H&E staining shows that invagination occurs in 100% of control embryos. However, in the Ctnna1 cko, a range of abnormalities is observed (a total of 28 samples were used here). (e,f) H&E staining of E16.5 tooth germs shows complete loss of the developing incisor in the Ctnna1 cko. (g,h) Histological analysis at E12.5 did not show obvious changes after deletion of Ctnna1. (i,j) The level of E-cadherin in the dental epithelium is increased in the EK region at E13.5 in the Ctnna1 cko (j) compared with control (i). (k,l) The level of -catenin in the dental epithelium is not changed in the Ctnna1 cko at E13.5 (l) compared with control (k). (m-p) Actin organization and apical actin constriction (yellow and open yellow arrowheads) are disrupted at the apical side of the Ctnna1 cko epithelium at E13.5 (n,n ) compared with that in the control (m,m ). (q,r) TUNEL staining at E13.5 did not show obvious changes after deletion of Ctnna1. Asterisk in f indicates the missing of the tooth germ at E16.5 in the Ctnna1 cko. Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 100 μm in a-h; 25 μm in i-m,o,q,r; 12 μm in n,p.
10
11 Supplementary Figure 6: Disruption of cell-cell adhesion does not inhibit EK formation and tooth germ invagination during tooth development. (a-f) H&E staining shows that deletion of both copies of p120ctn and one copy of E-cadherin disrupts cell-cell adhesion as indicated by the gaps throughout the tissues during tooth development (dark arrowheads indicate the gaps within the tissues). (g,h) The EK is formed, based on the presence of p21 positive cells and ceased cell proliferation in the posterior region of the tooth germ epithelium at E13.5. (i,j) The formed EK is maintained throughout the cap stage, despite defective cell-cell adhesion. Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 100 μm in a-f; 50 μm in g-j.
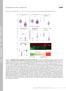
12 Supplementary Figure 7: 3D reconstructi ion of the E13.5 tooth germ and measurement of the condensed mesenchyme thickness. (a,b) 3D reconstructed E13.5 incisor tooth germs in the control and Ctnna1 cko. (c-f) Lateral to medial H&E stained sectionss of a control tooth germ. (g) The border of the condensed mesenchyme in the control tooth germ. Dark arrowheads and the blue lines indicate the boarder of condensedd dental mesenchyme. (h-k) Lateral to medical H&E stained sections of Ctnna1 cko tooth germ. (l) The border of the condensed mesenchyme in the Ctnna1 cko tooth germ. (g-l) High magnification shows the border off the condensed mesenchyme
13 in control and mutant of tooth germ. (m-n) Tracing the orientation of the long axis of cells in dental mesenchyme and its surrounding area marks the border of dental mesenchyme in control and Ctnna1 cko tooth germ. (o-p) Radial histograms displaying quantification of dental mesenchymal cell orientation in control and Ctnna1 cko tooth germ. (q) Quantification of cell orientation in dental mesenchyme and surrounding area (mean ± SEM, n=100, p<0.001). All quantifications are analyzed by using Student s t-test. Dark dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Green dotted lines outline the condensed cells in the mesenchyme surrounding the epithelium. Green lines outline the long axis of cells in dental mesenchyme and surrounding area. Red lines outline the border between dental and non-dental mesenchyme based on aligned cell orientation. Scale bars, 100 μm in c-f,h-k; 50 μm in g,l,m,n.
14 Supplementary Figure 8: E-catenin-YAP/TAZ axis induced EK formation is required for the cervical loop invagination during late tooth development. (a-d) Immunostaining of YAP showed that YAP is mostly ablated in the tooth germ epithelium off triple mutants at E13.5 and
15 E14.5. (e,f) The tooth germ was not rescued in K14 Cre ;Ctnna1 fl/fl ;Yap fl/+ ;Taz fl/fl mutants (asterisk). (g,h) The tooth germ was formed in K14 Cre ;Ctnna1 fl/fl ;Yap fl/fl ;Taz fl/+ mutants (asterisks). Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 25 μm in a-d; 100 μm in e,f; 400 μm in g,h.
16 Supplementary Figure 9: Deletion of Yap/Taz in the tooth germ epithelium shows no obvious effects on tooth development. (a,b) H&E staining of E14.5 tooth germs from the control and Yap/Taz double mutants. (c,d) Immunofluorescence staining of p21 shows thatt EKs are formed both in the control and Yap/Taz mutants. Dotted lines outline the epithelium of the incisor tooth germ. Scale bars, 100 μm in a,b; 50 μm in c,d.
a 0,8 Figure S1 8 h 12 h y = 0,036x + 0,2115 y = 0,0366x + 0,206 Labeling index Labeling index ctrl shrna Time (h) Time (h) ctrl shrna S G2 M G1
 (GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
(GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
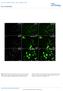
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a,
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
a b c periosteum parietal bone bone marrow dura periosteum suture mesenchyme osteogenic front suture mesenchyme 1
 coronary suture sagittal suture DOI: 10.1038/ncb3139 a b c e parietal bone suture mesenchyme parietal bone bone marrow ura ura ura f parietal bone ura suture mesenchyme bone g ura osteogenic front suture
coronary suture sagittal suture DOI: 10.1038/ncb3139 a b c e parietal bone suture mesenchyme parietal bone bone marrow ura ura ura f parietal bone ura suture mesenchyme bone g ura osteogenic front suture
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) Chimeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears.
 Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplementary Figure 1. himeric analysis of inner ears. (A-H) himeric inner ears with fluorescent ES cells and (I,J) Rainbow inner ears. (A,B) omposite images showing three colors in different vestibular
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. The expression of ephrin-b2 H2BGFP persists in the post-hearingonset organ of Corti and is specifically restricted to supporting cells. Sox2 immunolabeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2697 Figure S1 Cytokeratin 5 is a specific marker for basal and intermediate cells in all mouse prostate lobes. (a) Immunofluorescence staining showing co-localization of YFP with p63 in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Supplemental Information. Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier. to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc.
 Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor
 BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
Loss of RhoA promotes skin tumor formation. Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from
 Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplemental material Brooks and Wallingford, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201204072/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Quantification of ciliary compartments in control
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
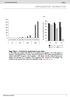 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons by multidirectional repulsion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Absolute %) Immature Pool (Absolute %) A10 EC Control A10 EC Control A10 EC Control
 Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Asolute %) Immature Pool (Asolute %) A10 EC A10 EC A10 EC Myeloid 50.7 57.5 37.5 46.2 13.2 11.3 Erythroid 38.3 23.2 33.3 16.8 9.3 6.3 Lymphocytes 13.8 19.0 - - -
Bone Marrow Pop. (% Total) Mature Pool (Asolute %) Immature Pool (Asolute %) A10 EC A10 EC A10 EC Myeloid 50.7 57.5 37.5 46.2 13.2 11.3 Erythroid 38.3 23.2 33.3 16.8 9.3 6.3 Lymphocytes 13.8 19.0 - - -
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4
 Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
F-actin VWF Vinculin. F-actin. Vinculin VWF
 a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
a F-actin VWF Vinculin b F-actin VWF Vinculin Supplementary Fig. 1. WPBs in HUVECs are located along stress fibers and at focal adhesions. (a) Immunofluorescence images of f-actin (cyan), VWF (yellow),
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 2 3 4 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table S1. Brain Tumors used in the study Code Tumor Classification Age Gender HuTuP51 Glioblastoma 57 Male HuTuP52 Glioblastoma 53 Male
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2610 Figure S1 FSMCs derived from MSLN CLN transgenic mice express smooth muscle-specific proteins. Beta-galactosidase is ubiquitously expressed within cultured FSMCs derived from MSLN
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm
 Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs. Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification
 icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
icamp: Cancer biology tutorial II: recent developments in tumor biology, experimental methodology, and reference identification Stem cells and the environment in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence (Medema,
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Teeth, orofacial development and
 Teeth, orofacial development and cleft anomalies Miroslav Peterka Variability of jaws in vertebrates. (A) cartilaginous fish shark; (B) an example of a bone fish; (C ) amphibian frog; (D) reptile - turtle;
Teeth, orofacial development and cleft anomalies Miroslav Peterka Variability of jaws in vertebrates. (A) cartilaginous fish shark; (B) an example of a bone fish; (C ) amphibian frog; (D) reptile - turtle;
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants (Sgpl1 -/- and Plekha1 -/- ). Using an antibody against CYP11a1 to label Leydig
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants (Sgpl1 -/- and Plekha1 -/- ). Using an antibody against CYP11a1 to label Leydig
Supplementary Figure 1. Satellite cell contribution to myofibers in whole. gastrocnemius/plantaris/soleus, diaphragm, and EOM of 12 or 20 month
 Keefe et al. p. 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Satellite cell contribution to myofibers in whole muscles. (a-l) Representative cross-sections through whole TA/EDL, gastrocnemius/plantaris/soleus, diaphragm,
Keefe et al. p. 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Satellite cell contribution to myofibers in whole muscles. (a-l) Representative cross-sections through whole TA/EDL, gastrocnemius/plantaris/soleus, diaphragm,
ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo
 Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Supplementary Information ROCK/Cdc42-mediated microglial motility and gliapse formation lead to phagocytosis of degenerating dopaminergic neurons in vivo Carlos Barcia* 1,2, Carmen M Ros 1,2, Valentina
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors
 Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors Ka-Cheuk Liu, Gunter Leuckx, Daisuke Sakano, Philip A. Seymour, Charlotte L. Mattsson, Linn Rautio, Willem Staels, Yannick Verdonck,
Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors Ka-Cheuk Liu, Gunter Leuckx, Daisuke Sakano, Philip A. Seymour, Charlotte L. Mattsson, Linn Rautio, Willem Staels, Yannick Verdonck,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of CerTN-L15 expressed in Arabidopsis roots. a. Ratiometric images of CerTN-L15 in roots under osmotic stress Ratiometric
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and
 OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
Supplemental Information. Helicobacter pylori Employs a Unique Basolateral. Type IV Secretion Mechanism for CagA Delivery
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Helicobacter pylori Employs a Unique Basolateral Type IV Secretion Mechanism for CagA Delivery Nicole Tegtmeyer, Silja Wessler, Vittorio Necchi,
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Helicobacter pylori Employs a Unique Basolateral Type IV Secretion Mechanism for CagA Delivery Nicole Tegtmeyer, Silja Wessler, Vittorio Necchi,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Advances in pancreatic islet monolayer culture on glass surfaces enable superresolution microscopy and insights into beta cell ciliogenesis and proliferation Edward A. Phelps,
Supplemental Table S1. Primers used in qrt-pcr analyses. Supplemental Figure S1, related to Figure 4. Extracellular matrix proteins
 Supplemental Material PDGFRb regulates craniofacial development through homodimers and functional heterodimers with PDGFRa Katherine A. Fantauzzo and Philippe Soriano Supplemental materials provided: Supplemental
Supplemental Material PDGFRb regulates craniofacial development through homodimers and functional heterodimers with PDGFRa Katherine A. Fantauzzo and Philippe Soriano Supplemental materials provided: Supplemental
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Supplemental Information. Induction of Expansion and Folding. in Human Cerebral Organoids
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
