Combined deletion of SCD1 from adipose tissue and liver does not protect
|
|
|
- Clarence Pierce
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Mdison, 433 Bcock Drive, Mdison, Wisconsin 5376 Running Title: Deletion of dipose nd liver SCD1 does not prevent oesity *Correspondence to e ddressed to: Jmes M. Ntmi University of Wisconsin-Mdison Deprtment of Biochemistry 433 Bcock Drive Mdison, WI 5376 Tel: Fx: e-mil: ntmi@iochem.wisc.edu revitions used: dipose SCD1 knockout (); gouti ( y /); ntisense oligonucleotide (SO); diet-induced oesity (DIO); ftty cid (F); glol SCD1 knockout (GKO); liver SCD1 knockout (); liver/dipose SCD1 knockout (L); monounsturted ftty cids (MUF); non-gouti (/); Scd1 flox/flox (); skin SCD1 knockout (SKO); steroyl-co desturse-1 (SCD1), sterol regultory element inding protein-1c (SREBP1c), triglycerides (TG) 1
2 strct Steroyl-Co desturse 1 (SCD1) ctlyzes the synthesis of monounsturted ftty cids (MUF) from sturted F nd mice with whole-ody or skin-specific deletion of SCD1 re resistnt to oesity. Here, we show tht mice lcking SCD1 in dipose nd/or liver re not protected from either genetic- (gouti; y /) or diet-induced oesity (DIO) despite roust reduction in SCD1 MUF products in oth sucutneous nd epididyml white dipose tissue. dipose SCD1 deletion hd no effect on glucose or insulin tolernce, or heptic triglyceride (TG) ccumultion. Interestingly, lck of SCD1 from liver lowered the MUF levels of dipose tissue, nd vice vers, s reflected y the chnges in F composition. Simultneous deletion of SCD1 from liver nd dipose resulted in synergistic lowering of tissue MUF levels, especilly in the y / model in which glucose tolernce ws lso improved. Lstly, we found tht liver nd plsm TG show nerly identicl genotype-dependent differences in F composition indicting tht F composition of plsm TG is predictive for heptic SCD1 ctivity nd TG F composition. The current study suggests tht SCD1 deletion from dipose nd/or liver is insufficient to elicit protection from oesity, ut supports the existence of extensive lipid crosstlk etween liver nd dipose tissue. Supplementry key words: steroyl-co, monounsturted ftty cid, desturse, desturtion index, olete, plmitolete, ftty cid composition, gouti, triglyceride, Cre-lox 2
3 Introduction Steroyl-Co desturse 1 (SCD1) ctlyzes the desturtion of sturted ftty cids (F), primrily plmitte (16:) nd sterte (18:), into the cis-monounsturted ftty cid (MUF) products plmitolete (16:1n7) nd olete (18:1n9), respectively. The metolic role for SCD1 hs een extensively explored in mice with nturlly occurring Scd1 muttions nd those with glol deletion of Scd1 (GKO mice) (1-3). These mice disply remrkle hypermetolic phenotype tht protects them from oesity, insulin resistnce nd heptic stetosis. To determine which tissue or tissues re primrily responsile for these metolic chnges, we hve employed the Cre-lox system to explore the tissue-specific contriutions of SCD1. We previously found tht mice with liver-specific deletion of Scd1 ( mice) re protected from high-crohydrte, ut not high-ft diet-induced oesity (DIO), unlike GKO mice tht re resistnt to oth high-ft nd high-crohydrte DIO (4). This indictes tht inhiition of liver SCD1 lone is insufficient to elicit the hypermetolism nd incresed energy expenditure necessry to compenste for the incresed energy intke ssocited with high-ft feeding. The reduced high-crohydrte diet-induced diposity in nd GKO mice ws ssocited with lock in crohydrte-induced increses in heptic sterol regultory element inding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) proteolytic processing, expression of F synthesis genes nd heptic triglyceride (TG) ccumultion. We recently reported tht mice with skin-specific deletion of Scd1 (SKO mice) recpitulted the hypermetolic phenotype oserved in GKO mice, indicting tht the skin is mjor contriutor to the ltered energy metolism oserved in GKO mice (5). In contrst, SKO mice hd norml crohydrte-induced increse in SREBP-1c mturtion nd F synthesis genes. These heptic oservtions highlight tht not ll of the phenotypes of the SCD1 GKO mice cn e ttriuted to SCD1 deletion in the skin. 3
4 Interestingly, mice intrperitonelly injected with Scd1-trgeted ntisense oligonucleotides (SO) re lso protected from the development of high-ft DIO nd insulin resistnce (6, 7). This SO therpy potently reduced SCD1 expression nd ctivity in the liver nd dipose tissue without ffecting SCD1 expression in the muscle or skin. This suggests tht inhiition of SCD1 in the liver nd dipose tissue elicits oesity resistnce vi mechnism tht is physiologiclly distinct from tht cused y skin SCD1 deletion. Since mice re not protected from high-ft DIO (4), we hypothesized tht deletion of dipose SCD1 ( mice), or comined deletion of liver nd dipose SCD1 (L mice), would elicit oesity resistnce nd other improved metolic prmeters previously oserved in SCD1 GKO mice nd those treted with SO. dipose SCD1 ws deleted from oth white nd rown dipose tissue y introducing the P2-Cre llele into our SCD1 flox/flox mice. Surprisingly, nd L mice were not protected from oesity despite roust reductions in dipose MUF content. These results indicte tht deletion or inhiition of SCD1 in the white nd rown dipose tissue, in the presence or sence of liver SCD1 ctivity, hs miniml effect on whole-ody energy expenditure. Our study lso revels tht dipose-derived F impct the F composition of liver, nd vice vers. Lstly, we report tht the MUF composition of plsm TG is strikingly similr to tht of liver TG nd cn potentilly e used s predictor of heptic SCD ctivity. 4
5 Mterils nd methods nimls, Genotyping nd Diets. FBP4(P2)-Cre mice were otined from Brr Khn t Beth Isrel Deconess Medicl Center (8) nd ckcrossed to C57BL/6J for t lest 1 genertions. To generte mice, we crossed C57BL/6J Scd1 flox/flox () mice (4), which trgets exon 3 of the Scd1 gene, with mice heterozygous for P2-Cre to generte compound heterozygous (Scd1 flox/+ ; P2-Cre/+) mice. Mle Scd1 flox/+ ;P2-Cre/+ mice were susequently mted with femle mice to generte Scd1 flox/flox ;P2-Cre/+ mice (). For litter expnsion, mle mice were red with either femle mice to produce or mice, or with femle Scd1 flox/flox ;lumin-cre/+ () mice (4) to produce,, or Scd1 flox/flox ;P2-Cre/+;lumin-Cre/+ (L) mice. lterntively, mle L mice were red with femle mice to generte,,, or L mice. To generte conditionl Scd1-deficient mice lso contining the yellow gouti ( y /) llele, we red mle or mice with femle C57BL/6J y / mice (Jckson Ls stock #21). The F1 mle y / Scd1 flox/+ ;lumin-cre/+ or y / Scd1 flox/+ ;P2-Cre/+ mice were then red with femle non-gouti (/) mice to generte y /, y / nd y / mice. For litter expnsion, mle y / or y / were red with femle / mice. lterntively, mle y / mice were red with femle / mice to generte y /, y /, y / nd y / L mice. Mice were mintined on 12 hr light/drk cycle with free ccess to food nd wter. Breeders were fed Purin 515 nd pups were wened t 3 wks of ge nd susequently fed cerel grin-sed, low-ft stndrd diet (SD; Purin 58). For DIO studies, mle mice were individully cged t 8 wks of ge nd fed either Purin 58 or high-ft diet (Reserch Diets RD12492; 6% kcl ft) for n dditionl 18 wks. For y /-induced oesity studies, mle mice 5
6 were individully cged t 4 wks of ge nd mintined on Purin 58 until 26 wks of ge. nimls were fsted for 4 hr nd scrificed y n overdose of isoflurne nesthesi. The genotyping protocol for distinguishing the Scd1 flox nd wild type Scd1 lleles hs een descried previously (4, 9). For reeding strtegies involving only one Cre trnsgene, we used generic Cre-recominse genotyping strtegy ville t the Jckson Lortories wesite (jxmice.jx.org). For L reeding schemes, we designed genotyping primers specific to either lumin-cre or P2-Cre. lumin-cre ws mplified using primer l-f (5 GC TGC GG CT TC TC 3 ) nd Cre-R (5 GTG CG CT TGC TGT CC TT 3 ) with 54 C nneling temperture. P2-Cre ws mplified using P2-F (5 TG TC TGG CCC CC TTG G 3 ) nd Cre-R with 51 C nneling temperture. ll in vivo experimentl procedures were performed in ccordnce with Ntionl Institutes of Helth Guidelines for the Cre nd Use of nimls nd were pproved y the Institutionl niml Cre nd Use Committee t the University of Wisconsin-Mdison. Immunolot nlysis of SCD1 Liver nd white dipose microsomes were prepred y sequentil centrifugtion. Tissues were first homogenized t 1 mg tissue/ml uffer in.1 M potssium phosphte uffer (ph=7.2) supplemented with 1 μg/ml leupeptin nd 1 mm PMSF. The homogente ws centrifuged t 1, x g for 15 min t 4 C. The superntnt ws susequently centrifuged t 1, x g for 1 h t 4 C. The pellet ws rinsed once nd resuspended in protese inhiitor free.1 M phosphte uffer. Brown dipose tissue ws homogenized t 1 mg tissue/ml in lysis uffer contining 1 mm PMSF, 1 μg/ml leupeptin, 5 μg/ml pepsttin nd 2 μg/ml protinin. SCD1 immunolotting ws performed on 1 μg of protein using polyclonl SCD1 ntiody (Snt Cruz; sc-14719). 6
7 Glucose nd insulin tolernce tests. For glucose tolernce tests, mice were fsted for four hours nd susequently injected i.p. with 1% dextrose t dose of 1 g/kg ody weight. Blood ws smpled y retrooritl puncture t, 2, 4, 9 nd 18 min post-injection. For insulin tolernce tests, non-fsted mice were injected i.p. with.75 U/kg ody weight of humn insulin (Novo Nordisk). Blood ws collected y retrooritl puncture t, 15, 3, 45 nd 6 min postinjection. Plsm glucose ws nlyzed using colorimetric glucose oxidse method. Tissue nd plsm lipid nlysis. Lipids were extrcted from pproximtely 3 mg of tissue or 1 μl of plsm lipids using modifiction of the Folch procedure (1). Smples were homogenized in 3 ml of CHCl 3 :MeOH (2:1) contining 1 mg/1 ml utylted hydroxytoluene. Heptdecnoic cid ws dded s n internl stndrd to correct for smple loss. Next, 1 ml of cidified sline (.1 N HCl,.9% NCl) ws dded. fter vigorous vortexing nd centrifugtion, the orgnic lyer ws isolted, dried under nitrogen gs nd sujected to TLC on silic gel-6 pltes (EMD Chemicls) in heptne/isopropyl ether/glcil cetic cid (6/4/3, v/v/v). The nds corresponding to stndrds were scrped nd trnsferred to screw cp glss tues contining pentdecnoic cid s n internl stndrd to control for trnsmethyltion efficiency. F were trnsmethylted in the presence of 14% oron trifluoride in methnol. The resulting methyl esters were extrcted with hexne nd nlyzed y gs liquid chromtogrphy s previously descried (11). Totl lipid contents were clculted from individul F content in ech frction. Rel-time quntittive PCR. Totl RN ws extrcted with TRI regent (Moleculr Reserch), treted with Turo DNse (mion), nd reverse trnscried using Multiscrie reverse trnscriptse (pplied Biosystems). Rel-time quntittive PCR ws performed on n BI StepOne Plus instrument using gene-specific primers nd Power SYBR Green mster mix 7
8 (pplied Biosystems). Quntifiction of given genes is expressed s mrn level normlized to housekeeping gene (rp) using the ΔΔCt method. Primer sequences re ville upon request. Dt nd sttisticl nlysis. Dt re expressed s men + SEM nd were compred y one- or two-wy NOV followed y Tukey s Post-hoc test in GrphPd Prism. Comprisons with P<.5 were considered significnt. 8
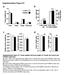
9 Results To generte mice deficient in dipose Scd1 (), we introduced the P2-Cre trnsgene into our Scd1 flox/flox () colony (4, 5). We lso generted mice with liver-specific deletion of Scd1 () tht expressed the lumin-cre trnsgene (4), nd crossed these with the mice to otin mice with simultneous deletion of Scd1 from oth the liver nd dipose (L). nd L mice were orn t the expected frequency nd were indistinguishle from mice. Importntly, nd L mice do not disply the closed eye fissures, dry skin nd lopeci previously oserved in glol (GKO) nd skin-specific (SKO) Scd1-deficient mice (5). Immunolot nlysis confirmed the deletion of Scd1 from white nd rown dipose tissue of nd L mice, nd from liver of nd L mice (Figure 1). Furthermore, F composition nlysis of TG from oth sucutneous dipose (Figure 1B-E) nd epididyml dipose (Supplementry Figure I) tissue reflects mrked decrese in the undnce of the SCD products plmitolete (16:1n7) nd olete (18:1n9) nd n increse in the SCD sustrtes plmitte (16:) nd sterte (18:) in nd L mice. Effect of dipose Scd1 deletion on oesity nd glucose tolernce To test whether dipose nd/or liver deletion of Scd1 influences the development of oesity, we used oth dietry (high-ft DIO) nd geneticlly-induced ( y / llele) oesity models compred to / mice fed stndrd diet. The high-ft DIO model utilizes hypercloric, semi-purified diet, which is highly undnt in the SCD product olete. Despite the mple MUF content of this high-ft diet, we hve previously shown tht oth GKO nd SKO mice, ut not mice, re remrkly resistnt to oesity on this diet due to hypermetolic phenotype (4, 5). y / mice hve uiquitous expression of the gouti protein, cusing leptin resistnce, incresed food intke nd decresed energy expenditure (2, 12). Thus, the y / model 9
10 llows for oesity-induction y feeding stndrd diet. We found no significnt difference in ody weight, epididyml or sucutneous white dipose weights due to dipose nd/or liver SCD1 deletion in either the DIO or y / models (Figure 2, C, D). dditionlly, food intke ws unffected (Figure 2E,F). Liver weight ws not significntly ffected in / mice fed stndrd or high-ft diet; however, liver weight ws reduced y loss of liver Scd1 in y / nd y / L compred to counterprts (Figure 2B). Fsting glucose s well s glucose nd insulin tolernce were not significntly ffected y dipose Scd1 deletion in / mice fed stndrd or high-ft diet (Figure 3-C). However, liver SCD1 deletion in oth y / L nd y / improved glucose tolernce (Figure 3D). Heptic SCD1 ctivity influences dipose F composition Liver nd dipose tissue TG levels nd their F composition cn e influenced directly y severl sources. First, dietry F, primrily in the form of TG-rich chylomicrons, cn e tken up into tissues vi lipoprotein lipse nd lipoprotein receptor-medited mechnisms. Second, cells cn de novo synthesize F from cetyl-co, nd the rte of de novo synthesis in liver is especilly responsive to dietry nutrients nd hormones such s glucose nd insulin, respectively (13). nd finlly, there is significnt lipid crosstlk etween the dipose nd liver vi the reciprocl exchnge of dipose-derived free F nd heptic derived TG-rich VLDL. Importntly, intrcellulr sturted F (plmitte nd sterte), regrdless of their origin, cn e converted to MUF vi SCD1. Liver SCD1 influenced dipose stores of olete nd the 18:1n9/18: rtio, ut not stores of plmitolete or 16:1n7/16: rtio, in y / mice, ut not / mice (Fig. 1 nd Supp. Fig. I). This suggests tht under conditions of high heptic lipogenesis, liver-derived TG contriute greter mount to dipose TG stores thn during conditions of low heptic lipogenesis. dditionlly, 1
11 the % composition of plmitte, plmitolete, sterte nd olete in dipose TG ws significntly ffected y loss of dipose SCD1 in the sucutneous ft, ut not epididyml ft, of / mice. Upon introgression of the y / llele, oth ft depots were significntly influenced y loss of SCD1 from liver or dipose. These ft-depot specific chnges suggest tht the F composition of ft depots sptilly-oriented closer to the liver, such s viscerl or epididyml ft, is influenced to greter extent y liver-derived F, especilly under sl lipogenic conditions. side from 16- nd 18-cron sturted F nd MUF, the other predominnt F found in dipose is linoleic cid (18:2n6), which comprises pproximtely 25% of dipose F. In / mice, loss of dipose nd/or liver SCD1 hd no significnt effect on the percent composition of 18:2n6 in epididyml or sucutneous ft (dt not shown). Loss of dipose SCD1 in y / mice hd lso no effect on the undnce of 18:2n6 (Supplementry Figure II). Interestingly, loss of liver SCD1 in oth y / nd y / L mice cused elevted levels of 18:2n6 in the epididyml nd sucutneous dipose stores (Supp. Fig. II). To further explore the reltionship etween liver SCD1 nd dipose 18:2n6 levels, we looked t 18:2n6 levels in liver TG nd plsm TG. In / mice, 18:2n6 levels in liver were non-significntly elevted y pproximtely 12% in oth nd L mice compred to nd (~28.7% in nd L compred to 25.5% in nd ), ut plsm 18:2n6 levels were unchnged. However, oth liver nd plsm 18:2n6 levels were incresed in y / nd y / L compred to y / nd y / mice (Supp. Fig. II). Thus, lck of heptic SCD1, when comined with the y / llele, leds to drmtic decrese in 18:1n9 vilility nd concomitnt increse in 18:2n6 enrichment of these liver nd plsm TG, which susequently influence the F composition of the dipose stores. Effect of liver nd dipose SCD1 on heptic nd TG composition 11
12 lthough y / nd y / L mice were not protected from oesity, their liver weights were significntly lower thn the y / nd y / (Fig. 2). We mesured heptic TG levels in oth y / nd / mice. Compred to their / counterprts, y / mice hd significntly elevted heptic TG levels (Figure 4). However, this y /-effect ws severely lunted y loss of liver SCD1 in oth y / nd y / L mice. Consistent with this oservtion, the percent composition of plmitte, plmitolete, sterte nd olete in heptic TG were ll significntly ffected y loss of heptic SCD1 in oth the y / nd y / L mice. (Figures 4 nd 5). Comined loss of liver nd dipose SCD1 lowered heptic TG, the 16:1n7/16: rtio nd the 18:1n9/18: rtio in high-ft fed L mice s well. (Supplementry Figure III). Deletion of liver nd/or dipose SCD1 did not influence heptic TG levels in the / mice nd hd more modest effect on the F composition. Thus, the heptic rte of F synthesis is n importnt determinnt for the ccumultion of SCD sustrtes in the sence of SCD1. In y / mice, the heptic 16:1n7/16: nd 18:1n9/18: rtios were predominntly determined y liver SCD1. nlysis of the desturtion indices of heptic lipids lso reveled prtil role of dipose SCD1 in determining the F composition of the liver. In oth y / nd / mice, the liver TG 16:1n7/16: rtio ws independently nd dditively influenced y loss of liver nd dipose SCD1 (Fig. 4). dipose deletion of SCD1 in y / mice lso reduced the heptic 18:1n9/18: rtio. However, dipose-specific deletion of SCD1 did not protect mice from high-ft DIO- or y /-induced heptic TG ccumultion (Fig. 4 nd Supp. Fig. III). Plsm TG F composition prllels heptic TG F composition In the fsted stte, plsm TG re predominntly trnsported y liver-derived VLDL, which otin their neutrl lipid core during the pre-secretory intrcellulr ssemly of these 12
13 prticles in heptocytes. Therefore, we compred the liver nd plsm TG mss, desturtion indices nd F compositions in oth y / nd / mice with liver nd/or dipose deletion of SCD1 (Fig. 4 nd 5). Similr to the pttern oserved for liver TG mss, plsm TG mss in / mice ws not ffected y loss of dipose nd/or liver SCD1 ut loss of liver SCD1 in y / nd y / L led to reduction of plsm TG levels. Strikingly, the desturtion indices (Fig. 4) nd F composition (Fig. 5) for liver nd plsm TG showed the sme genotype-dependent chnges, suggesting tht the F composition of plsm TG is predictive of oth liver TG F composition nd SCD1 ctivity. 13
14 Discussion lthough mice with glol deletion of Scd1 (GKO) disply remrkle oesity resistnce (2-4) nd insulin sensitivity (14), the importnce of dipose SCD1 for whole-ody energy metolism is uncler. SCD1 is highly expressed in oth white nd rown dipose tissue. Previous studies in mice with whole-ody deletion of SCD1 hve documented incresed insulin signling nd uncoupling protein expression in the white nd rown dipose tissue (15-17). Due to the simultneous deletion of Scd1 from ll tissues in GKO mice, it is uncler whether metolic chnges in prticulr tissue re direct effect of locl loss of SCD1 function, or n indirect effect stemming from loss of SCD1 in distl tissues. Tissue-specific deletion using the Cre-lox system relies upon the use of tissue-specific promoter to drive the expression of the Cre-recominse. The FBP4(P2)-Cre trnsgene is highly expressed in oth white nd rown dipose tissue (8, 18). The differentition of predipocytes into mture dipocytes leds to the ctivtion of severl dipose-specific genes, including Fp4 nd Scd1 (19). Therefore, it is likely tht the FBP4-Cre-medited deletion of Scd1 occurs sometime during or immeditely fter dipocyte differentition. It is noteworthy to cknowledge tht P2-Cre expression nd concomitnt deletion of Scd1 in our studies re likely not restricted to dipocytes. The P2-Cre trnsgene hs lso een detected during emryonic development (2), in mcrophges nd mcrophge rich tissues (21, 22), one mrrow (21), crdic nd skeletl muscle, intestine, stomch, pncres nd in the centrl nd peripherl nervous system (23). However, the endogenous P2 gene is predominntly expressed in dipocytes nd the P2-Cre-medited recomintion in these other tissues is likely incomplete due to the lower expression level of Cre. Nonetheless, P2-Cre medited deletion of Scd1 from 14
15 dipocytes nd potentilly other cell types filed to recpitulte the oesity resistnce oserved in GKO mice. We recently reported tht skin-specific deletion of SCD1 elicited hypermetolic phenotype comprle to tht oserved in GKO mice (5). These mice resisted dipocyte hypertrophy nd mintined insulin sensitivity when chllenged with high-ft feeding, nd this ws ssocited with incresed uncoupling protein expression in vriety of peripherl tissues such s white nd rown dipose tissue, muscle nd liver. Thus, ltered skin lipid metolism cn indirectly influence metolic flux nd cell signling in peripherl tissues. However, these dt do not necessrily exclude role for SCD1 in other tissues such s rown or white dipose tissue, ecuse the severity of the cutneous phenotypes in SKO mice my msk the contriutions of SCD1 in these tissues to glol energy homeostsis. Therefore, it is possile tht n extrcutneous mechnism for oesity resistnce lso exists in the GKO mouse. This is supported y studies in mice treted with Scd1-trgeted SO, which re reported to not ffect the skin (6, 7). However, the filure of dipose nd/or liver Scd1 deletion to prevent oesity in either the y / or DIO models strongly suggests tht loss of SCD1 function in these tissues is not the mechnism for oesity resistnce in the GKO mice or SO-treted mice. Furthermore, we did not oserve incresed expression of thermogenic genes (Ucp1, Ucp2, dr2, Dio2, Pprgc1) in the rown dipose tissue of or L mice (Supplementry Figure IV). Intrperitonel injected SOs result in the ccumultion of SOs in severl tissues. In ddition to the reported effects of SCD1 SOs on liver, white dipose nd rown dipose, we speculte tht the SO-medited oesity resistnce is due to dditionl inhiition of Scd1 in cells or tissues not trgeted y the lumin-cre nd P2-Cre. In the cse of the dipose tissue, the SO tretment my e eliciting effects on oth pre-dipocytes nd mture dipocytes, unlike the 15
16 P2-Cre medited recomintion tht requires ctivtion of the P2 promoter during dipocyte differentition. Inhiition of SCD1 during the pre-dipocyte stge my cuse distinct metolic chnges compred to deletion of Scd1 in the lte stges of or post-differentition. lterntively, the SO my e eliciting off trget effects on other genes contriuting to oesity resistnce, unlike the Cre-lox system which is specific to Scd1. Unlike the dult mouse liver, which expresses primrily Scd1, oth Scd1 nd Scd2 re highly expressed in the mouse dipose tissue (24). We found tht the expression of Scd2 in white nd rown dipose tissue ws unffected y deletion of Scd1 vi P2-Cre (Supp. Fig. IV). Therefore, it is lso possile tht the nti-oesity effects of pulished Scd1-trgeted SO (6, 7) re occurring due to the simultneous inhiition of oth Scd1 nd Scd2. This would predict tht there re two SCD-medited mechnisms to oesity resistnce in mice: 1) deletion of Scd1 in skin, or 2) inhiition of Scd1 nd Scd2 from the liver nd dipose. The filure of Scd1 deletion from the liver to protect ginst the y /-induced oesity is somewht surprising in light of our previous oservtions of reduced diposity in mice fed semi-purified high-crohydrte diet (4). Since the y / mice in our study were fed cerel grin-sed high-crohydrte, low-ft diet, we hypothesized tht lck of liver SCD1 would reduce heptic conversion of these dietry crohydrtes into TG, reduced liver VLDL TG secretion nd reduce overll ody diposity. lthough we did oserve reduced heptic MUF nd TG content, this is presumly insufficient to ffect overll energy homeostsis. The leptinresistnt phenotype of the y / mice results in oth incresed food intke nd decresed energy expenditure. Thus, hypermetolic response tht increses whole-ody energy expenditure, such s tht oserved in GKO nd SKO mice (5), my e necessry to comt the positive energy lnce tht exists in the y / nd DIO oesity chllenges. 16
17 Plmitolete (16:1n7) relesed into circultion from the dipose tissue hs een suggested to ct s eneficil lipokine tht improves metolic derngements including insulin resistnce nd heptic stetosis (25). The comined dipose deficiency of the P2 (FBP4) nd ml1 (FBP5) F inding proteins cused elevted levels of dipose 16:1n7 concomitnt with improved metolic phenotype (25), nd this predicts tht reducing norml levels of dipose 16:1n7 y deleting SCD1 would worsen metolism. However, deletion of dipose SCD1 in our study hd no ffect on ody weight, glucose or insulin tolernce in stndrd diet fed mice, s well s in two models of oesity (DIO nd y /), despite significnt lowering of dipose levels of 16:1n7. Furthermore, simultneous deletion of liver nd dipose SCD1 ctully hd eneficil effect of lowering liver TG levels nd improving glucose tolernce compred to control mice. The F rtios 16:1n7/16: nd 18:1n9/18: in liver TG hve een previously shown in humn studies to correlte very well with the F rtios found in plsm TG (26). In our current study, we found remrkle similrity etween the liver nd plsm TG F compositions tht reflected oth y /- nd SCD1-genotype effects. lthough the liver SCD1 genotype comprised mjority of the effect on the liver nd plsm 18:1n9/18: rtio, we found the 16:1n7/16: to e influenced y oth the liver nd dipose SCD1 genotype. dditionlly, we found the dipose 18:1n9/18: rtio to e influenced y heptic SCD1 in y / mice. Therefore, liver nd dipose F stores cn reciproclly influence the composition of one nother presumly due to the exchnge of liver-derived VLDL TG nd dipose-derived free F. We lso oserved tht the mgnitude of the heptic SCD1 genotype effect on these heptic F rtios ws drmticlly influenced y the presence or sence of the y / llele. Thus, diet nd genetic fctors tht 17
18 predispose n individul to insulin resistnce nd incresed heptic lipogenesis cn ffect the pprent correltion of heptic F rtios with heptic SCD1 levels. 18
19 cknowledgements: This work ws supported y NIH grnt R1-DK62388 (to J.M.N.) M.T.F ws supported y NIH postdoctorl trining grnt T32-DK7665 nd n mericn Hert ssocition postdoctorl fellowship. M.S.S ws supported y NIH predoctorl trining grnt T32-DK
20 References 1. Flowers, M. T., nd J. M. Ntmi. 28. Role of steroyl-coenzyme desturse in regulting lipid metolism. Current Opinion in Lipidology 19: Miyzki, M., H. Smpth, X. Liu, M. T. Flowers, K. Chu,. Dorzyn, nd J. M. Ntmi. 29. Steroyl-Co desturse-1 deficiency ttenutes oesity nd insulin resistnce in leptin-resistnt oese mice. Biochemicl nd Biophysicl Reserch Communictions 38: Ntmi, J. M., M. Miyzki, J. P. Stoehr, H. Ln, C. M. Kendziorski, B. S. Yndell, Y. Song, P. Cohen, J. M. Friedmn, nd. D. ttie. 22. Loss of steroyl-co desturse-1 function protects mice ginst diposity. Proceedings of the Ntionl cdemy of Sciences of the United Sttes of meric 99: Miyzki, M., M. T. Flowers, H. Smpth, K. Chu, C. Otzelerger, X. Liu, nd J. M. Ntmi. 27. Heptic steroyl-co desturse-1 deficiency protects mice from crohydrteinduced diposity nd heptic stetosis. Cell Met 6: Smpth, H., M. T. Flowers, X. Liu, C. M. Pton, R. Sullivn, K. Chu, M. Zho, nd J. M. Ntmi. 29. Skin-specific deletion of steroyl-co desturse-1 lters skin lipid composition nd protects mice from high ft diet-induced oesity. Journl of Biologicl Chemistry 284: Jing, G., Z. Li, F. Liu, K. Ellsworth, Q. Dlls-Yng, M. Wu, J. Ronn, C. Esu, C. Murphy, D. Szlkowski, R. Bergeron, T. Doeer, nd B. B. Zhng. 25. Prevention of oesity in mice y ntisense oligonucleotide inhiitors of steroyl-co desturse-1. J. Clin. Invest. 115: Brown, J. M., S. Chung, J. K. Swyer, C. Degirolmo, H. M. lger, T. Nguyen, X. Zhu, M. N. Duong,. L. Wiley, R. Shh, M.. Dvis, K. Kelley, M. D. Wilson, C. Kent, J. S. Prks, nd L. L. Rudel. 28. Inhiition of steroyl-coenzyme desturse 1 dissocites insulin resistnce nd oesity from therosclerosis. Circultion 118: el, E. D., O. Peroni, J. K. Kim, Y. B. Kim, O. Boss, E. Hdro, T. Minnemnn, G. I. Shulmn, nd B. B. Khn. 21. dipose-selective trgeting of the GLUT4 gene impirs insulin ction in muscle nd liver. Nture 49: Miyzki, M., W. C. Mn, nd J. M. Ntmi. 21. Trgeted disruption of steroyl-co desturse1 gene in mice cuses trophy of seceous nd meiomin glnds nd depletion of wx esters in the eyelid. J. Nutr. 131: Folch, J., M. Lees, nd G. H. Slone Stnley simple method for the isoltion nd purifiction of totl lipides from niml tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226: Miyzki, M., H. J. Kim, W. C. Mn, nd J. M. Ntmi. 21. Oleoyl-Co is the mjor de novo product of steroyl-co desturse 1 gene isoform nd sustrte for the iosynthesis of the Hrderin glnd 1-lkyl-2,3-dicylglycerol. Journl of Biologicl Chemistry 276: Brsh, G. S., nd M. W. Schwrtz. 22. Genetic pproches to studying energy lnce: perception nd integrtion. Nt Rev Genet 3: Flowers, M. T., nd J. M. Ntmi. 29. Steroyl-Co desturse nd its reltion to highcrohydrte diets nd oesity. Biochimic et Biophysic ct 1791:
21 14. Flowers, J. B., M. E. Rgli, K. L. Schueler, M. T. Flowers, H. Ln, M. P. Keller, J. M. Ntmi, nd. D. ttie. 27. Loss of steroyl-co desturse-1 improves insulin sensitivity in len mice ut worsens dietes in leptin-deficient oese mice. Dietes 56: Liu, X., M. Miyzki, M. T. Flowers, H. Smpth, M. Zho, K. Chu, C. M. Pton, D. S. Joo, nd J. M. Ntmi. 21. Loss of Steroyl-Co desturse-1 ttenutes dipocyte inflmmtion: effects of dipocyte-derived olete. rteriosclerosis, Thromosis, nd Vsculr Biology 3: Rhmn, S. M.,. Dorzyn, S. H. Lee, P. Dorzyn, M. Miyzki, nd J. M. Ntmi. 25. Steroyl-Co desturse 1 deficiency increses insulin signling nd glycogen ccumultion in rown dipose tissue. m J Physiol Endocrinol Met 288: E Lee, S. H.,. Dorzyn, P. Dorzyn, S. M. Rhmn, M. Miyzki, nd J. M. Ntmi. 24. Lck of steroyl-co desturse 1 upregultes sl thermogenesis ut cuses hypothermi in cold environment. Journl of Lipid Reserch 45: He, W., Y. Brk,. Hevener, P. Olson, D. Lio, J. Le, M. Nelson, E. Ong, J. M. Olefsky, nd R. M. Evns. 23. dipose-specific peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor gmm knockout cuses insulin resistnce in ft nd liver ut not in muscle. Proceedings of the Ntionl cdemy of Sciences of the United Sttes of meric 1: Christy, R. J., V. W. Yng, J. M. Ntmi, D. E. Geimn, W. H. Lndschulz,. D. Friedmn, Y. Nkeppu, T. J. Kelly, nd M. D. Lne Differentition-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 predipocytes: CCT/enhncer inding protein intercts with nd ctivtes the promoters of two dipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 3: Urs, S.,. Hrrington, L. Liw, nd D. Smll. 26. Selective expression of n P2/Ftty cid Binding Protein 4-Cre trnsgene in non-dipogenic tissues during emryonic development. Trnsgenic Res. 15: Mo, J., T. Yng, Z. Gu, W. C. Heird, M. J. Finegold, B. Lee, nd S. J. Wkil. 29. P2- Cre-medited inctivtion of cetyl-co croxylse 1 cuses growth retrdtion nd reduced lipid ccumultion in dipose tissues. Proceedings of the Ntionl cdemy of Sciences of the United Sttes of meric 16: Wng, Z. V., Y. Deng, Q.. Wng, K. Sun, nd P. E. Scherer. 21. Identifiction nd chrcteriztion of promoter cssette conferring dipocyte-specific gene expression. Endocrinology 151: Mrtens, K.,. Bottelergs, nd M. Bes. 21. Ectopic recomintion in the centrl nd peripherl nervous system y P2/FBP4-Cre mice: implictions for metolism reserch. FEBS Letters 584: Kestner, K. H., J. M. Ntmi, T. J. Kelly, Jr., nd M. D. Lne Differentitioninduced gene expression in 3T3-L1 predipocytes. second differentilly expressed gene encoding steroyl-co desturse. J. Biol. Chem. 264: Co, H., K. Gerhold, J. R. Myers, M. M. Wiest, S. M. Wtkins, nd G. S. Hotmisligil. 28. Identifiction of lipokine, lipid hormone linking dipose tissue to systemic metolism. Cell 134: Peter,.,. Cegn, S. Wgner, R. Lehmnn, N. Stefn,. Konigsriner, I. Konigsriner, H. U. Hring, nd E. Schleicher. 29. Heptic lipid composition nd steroyl-coenzyme desturse 1 mrn expression cn e estimted from plsm VLDL ftty cid rtios. Clinicl Chemistry 55:
22 Figure Legends Figure 1: Vlidtion of dipose SCD1 deletion y immunolot nd F composition. ) SCD1 protein expression in liver, epididyml white dipose, sucutneous white dipose, nd rown dipose. (LX), (L), () nd L(L); B,C) F composition of sucutneous ft in / (B) nd y / (C) mice fed stndrd diet were nlyzed y one-wy NOV. D) 16:1n7/16: nd E) 18:1n9/18: desturtion indices for sucutneous ft were nlyzed y two-wy NOV. Different letters indicte significnt differences (p<.5) etween SCD1 genotypes within the / or y / groups. *p<.5 for y / vs. /, for n=5-7 per group. Figure 2: Deletion of dipose nd/or liver SCD1 does not protect mice from oesity. ) Body weight, B) liver weight, C) epididyml ft pd weight nd D) sucutneous ft pd weight were mesured t scrifice in mle mice t 6-months of ge fter eing fed either stndrd diet (SD) for oth / nd y /, or high-ft diet (DIO) for /. Food intke for E) y / nd F) DIO mice were mesured over the course of five to seven dys. y / SD, / SD, nd / DIO groups were ech independently nlyzed y one-wy NOV. *p<.5 vs., n=5 to 11 per group. Figure 3: Effect of SCD1 deletion on glucose nd insulin tolernce. Glucose tolernce tests were performed in ) / mice fed stndrd diet, C) / mice fed high-ft diet (DIO) nd D) y / mice fed stndrd diet. Insulin tolernce tests (B) were done in / mice fed the stndrd diet. Tests were done t 5-6 months of ge. #, p<.5 vs. ; *, p<.5 vs. L; $, p<.5 vs. L, n=5 to 11 per group. 22
23 Figure 4: Effect of SCD1 deletion on liver nd plsm TG mss nd desturtion indices. ) Liver TG mss nd B) plsm TG mss in / nd y / mice fed stndrd diet. C,D) 16:1n7/16: TG desturtion index for liver (C) nd plsm (D). E,F) 18:1n9/18: desturtion index for liver (E) nd plsm (F). Dt were nlyzed y two-wy NOV. Different letters indicte significnt differences (p<.5) etween SCD1 genotypes within the / or y / groups. *p<.5 for y / vs. /, for n=5-7 per group. Figure 5: Effect of SCD1 deletion on liver nd plsm TG F composition. F composition of ) / liver TG, B) / plsm TG, C) y / liver TG nd D) y / plsm TG in mice fed stndrd diet. Dt were nlyzed y one-wy NOV. Different letters indicte significnt differences (p<.5) mongst SCD1 genotypes within the / or y / groups for n=5-7 per group. 23
24 Figure 1 L L LX LX L L L LX L L L LX LX L LX L Sucut. Ft L L L L L Epidid. Ft Brown Ft Liver LX LX LX L L L L L LX LX LX
25 Figure 1B-1E B % Totl D 16:1n7 / 16: / Sucutneous Ft 4 c 3 L 2 1 c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9)18:1(n7) Sucutneous Ft (16:1n7 / 16:).5.4 L C % Totl E 18:1n9 / 18: y/ Sucuteneous Ft 5 4 c 3 c 2 1 c c c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9)18:1(n7) Sucutneous Ft (18:1n9 / 18:) L 2 15 * c L 1 5 d. / y/ / y/
26 Figure 2 Body Weight (g) L Finl Body Weight B Tissue Weight (g) L Liver * * / SD y/ SD / DIO / SD y/ SD / DIO C Tissue Weight (g) E Epididyml White dipose L / SD y/ SD / DIO y/ Food Intke D Tissue Weight (g) F Sucutneous White dipose L / SD y/ SD / DIO DIO Food Intke Food Intke (g/dy) Food Intke (g/dy) L L
27 Figure 3 Non-gouti GTT, Stndrd Diet B Non-gouti ITT, Stndrd Diet Glucose (mg/dl) C Glucose (mg/dl) L Time (minutes) Non-gouti GTT, DIO L Glucose (mg/dl) D Glucose (mg/dl) Time (minutes) # L gouti GTT, Stndrd Diet # * * $ L Time (minutes) Time (minutes)
28 Figure 4 mg TG per g tissue Liver TG Mss * * * * L B Plsm TG (mg/dl) Plsm TG Mss *, * L * c,c / y/ / y/ C 16:1n7 / 16: Liver TG 16:1n7 / 16: c / * * c y/ L d D 16:1n7 / 16: Plsm TG 16:1n7 / 16: L *.1 c.5 c c. / y/ E 18:1n9 / 18: Liver TG 18:1n9 / 18: / * * c y/ * L c F 18:1n9 / 18: Plsm TG 18:1n9 / 18: * * / y/ L
29 Figure 5 % Totl C % Totl / Liver TG Ftty cid Composition c c c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9)18:1(n7) y/ Liver TG Ftty cid Composition c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9)18:1(n7) L L B % Totl D % Totl / Plsm TG Ftty cid Composition c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9) 18:1(n7) y/ Plsm TG Ftty cid Composition c 16: 16:1(n7) 18: 18:1(n9)18:1(n7) L L
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS
 Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance
 Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
How adaptations of substrate utilization regulate body composition
 (27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
(27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report July September 2018
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin
 Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY
 ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Effects of hepatic glycogen on food intake and glucose homeostasis are mediated by the vagus nerve in mice
 Dietologi (217) 6:176 183 DOI 1.17/s125-17-424-4 ARTICLE Effects of heptic glycogen on food intke nd glucose homeostsis re medited y the vgus nerve in mice Ilin López-Solddo 1,2 & Reec Fuentes-Romero 1
Dietologi (217) 6:176 183 DOI 1.17/s125-17-424-4 ARTICLE Effects of heptic glycogen on food intke nd glucose homeostsis re medited y the vgus nerve in mice Ilin López-Solddo 1,2 & Reec Fuentes-Romero 1
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Alpha linolenic acid in maternal diet halts the lipid disarray due to saturated fatty acids in the liver of mice offspring at weaning
 Shomonov-Wgner et l. Lipids in Helth nd Disese (2015) 14:14 DOI 10.1186/s12944-015-0012-7 RESEARCH Open Access Alph linolenic cid in mternl diet hlts the lipid disrry due to sturted ftty cids in the liver
Shomonov-Wgner et l. Lipids in Helth nd Disese (2015) 14:14 DOI 10.1186/s12944-015-0012-7 RESEARCH Open Access Alph linolenic cid in mternl diet hlts the lipid disrry due to sturted ftty cids in the liver
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF PIROXICAM
 IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
Effect of Different Dietary Energy Sources on Induction of Fatty Liver-Hemorrhagic Syndrome in Laying Hens
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 7 (12): 1232-1236, 2008 ISSN 1682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2008 Effect of Different Dietry Energy Sources on Induction of Ftty Liver-Hemorrhgic
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Science 7 (12): 1232-1236, 2008 ISSN 1682-8356 sin Network for Scientific Informtion, 2008 Effect of Different Dietry Energy Sources on Induction of Ftty Liver-Hemorrhgic
Roughage Type & Level & Grain Processing Interactions with Distiller s s Grains Diets. Matt May High Plains Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference
 Roughge Type & Level & Grin Processing Interctions with Distiller s s Grins Diets Mtt My High Plins Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference Why do we flke grin? Stem-flked corn (SFC) vs. dry-rolled rolled
Roughge Type & Level & Grin Processing Interctions with Distiller s s Grins Diets Mtt My High Plins Bio Fuels Co-Product Nutrition Conference Why do we flke grin? Stem-flked corn (SFC) vs. dry-rolled rolled
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
The Effect of Substituting Sugar with Artificial. Sweeteners on the Texture and Palatability of Pancakes
 The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Offspring subcutaneous adipose markers are sensitive to the timing of maternal gestational weight gain
 Gilin et l. Reproductive Biology nd Endocrinology (2015) 13:16 DOI 10.1186/s12958-015-0009-0 RESEARCH Open Access Offspring sucutneous dipose mrkers re sensitive to the timing of mternl gesttionl weight
Gilin et l. Reproductive Biology nd Endocrinology (2015) 13:16 DOI 10.1186/s12958-015-0009-0 RESEARCH Open Access Offspring sucutneous dipose mrkers re sensitive to the timing of mternl gesttionl weight
Optimizing Metam Sodium Fumigation in Fine-Textured Soils
 Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Implication of fermentable carbohydrates targeting the gut microbiota on conjugated linoleic acid production in high-fat-fed mice
 British Journl of Nutrition, pge 1 of 14 q The Authors 213 doi:1.117/s7114513123 Impliction of fermentle crohydrtes trgeting the gut microiot on conjugted linoleic cid production in high-ft-fed mice Céline
British Journl of Nutrition, pge 1 of 14 q The Authors 213 doi:1.117/s7114513123 Impliction of fermentle crohydrtes trgeting the gut microiot on conjugted linoleic cid production in high-ft-fed mice Céline
Physiology & Behavior
 Physiology & Behvior 1 (1) 376 387 Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Physiology & Behvior journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/ph Physiologicl nd ehviorl responses to intermittent strvtion
Physiology & Behvior 1 (1) 376 387 Contents lists ville t SciVerse ScienceDirect Physiology & Behvior journl homepge: www.elsevier.com/locte/ph Physiologicl nd ehviorl responses to intermittent strvtion
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Naringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflammation, metabolic dysregulation and atherosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice.
 Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Randomized Controlled Trial to Improve Adiposity, Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance in Obese African-American and Latino Youth
 nture publishing group rticles Rndomized Controlled Tril to Improve Adiposity, Inflmmtion, nd Insulin Resistnce in Obese -Americn nd Ltino Youth Rebecc E. Hsson 1, Tnj C. Adm 1, Jimie N. Dvis 1, Louise
nture publishing group rticles Rndomized Controlled Tril to Improve Adiposity, Inflmmtion, nd Insulin Resistnce in Obese -Americn nd Ltino Youth Rebecc E. Hsson 1, Tnj C. Adm 1, Jimie N. Dvis 1, Louise
obesità nel bambino: epidemiologia e prevenzione
 Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
Effect of Various Doses of Cinnamon on Lipid Profile in Diabetic Individuals
 Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Enhanced glutathione peroxidases (GPx) activity in young barley seedlings enriched with selenium
 Africn Journl of Biotechnology Vol. 10(55), pp. 11483-11487, 21 Septemer, 2011 Aville online t http://www.cdemicjournls.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.1480 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Acdemic Journls Full Length Reserch
Africn Journl of Biotechnology Vol. 10(55), pp. 11483-11487, 21 Septemer, 2011 Aville online t http://www.cdemicjournls.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB11.1480 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Acdemic Journls Full Length Reserch
Particle-size distribution of very low density plasma lipoproteins during fat absorption in man
 Prticle-size distriution of very low density plsm lipoproteins during ft sorption in mn EDWIN L. BIERMAN, THOMAS L. HAYES, JAMES N. HAWKINS, ALICIA M. EWING, nd FRANK T. LINDGREN Deprtment of Medicine,
Prticle-size distriution of very low density plsm lipoproteins during ft sorption in mn EDWIN L. BIERMAN, THOMAS L. HAYES, JAMES N. HAWKINS, ALICIA M. EWING, nd FRANK T. LINDGREN Deprtment of Medicine,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
Critical role of c-kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model
 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s15-1-5-5 ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel
Repeated bouts of high-intensity exercise and muscle glycogen sparing in the rat
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 26, 2159-2166 23 The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/je.416 2159 Repeted outs of high-intensity exercise nd muscle glycogen spring in the rt Ghzl Rj 1, Lmert Bräu
The Journl of Experimentl Biology 26, 2159-2166 23 The Compny of Biologists Ltd doi:1.1242/je.416 2159 Repeted outs of high-intensity exercise nd muscle glycogen spring in the rt Ghzl Rj 1, Lmert Bräu
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE
 THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
Erythroferrone is not required for the glucoregulatory and hematologic effects of chronic erythropoietin treatment in mice
 ORIGINL RESERCH Physiologicl Reports ISSN 51-817X Erythroferrone is not required for the glucoregultory nd hemtologic effects of chronic erythropoietin tretment in mice Richrd Coffey 1, Ugo Srdo,Leon Kutz,
ORIGINL RESERCH Physiologicl Reports ISSN 51-817X Erythroferrone is not required for the glucoregultory nd hemtologic effects of chronic erythropoietin tretment in mice Richrd Coffey 1, Ugo Srdo,Leon Kutz,
Accepted 10 January 2006
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 9, - Pulished y The Compny of Biologists doi:./je. Glycerol production in rinow smelt (Osmerus mordx) my e triggered y low temperture lone nd is ssocited with the ctivtion
The Journl of Experimentl Biology 9, - Pulished y The Compny of Biologists doi:./je. Glycerol production in rinow smelt (Osmerus mordx) my e triggered y low temperture lone nd is ssocited with the ctivtion
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
Effect of environmental stress on biochemical and physiological features in cultured fish
 Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
