Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
|
|
|
- Annabel Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doc. MVDr. Květuše Lovásová, PhD. doc. MUDr. Adriana Boleková, PhD. MUDr. Stanislav Matéffy Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton) Neurocranium Frontal bone Squamous part: external surface frontal tuber, glabella, superciliary arch, supraorbital margin, supraorbital notch (supraorbital foramen), frontal notch (frontal foramen), zygomatic process, temporal line Frontal sinus - septum of frontal sinuses internal surface groove for superior sagittal sinus, frontal crest, foramen cecum Orbital part (paired): Fossa for lacrimal gl. (lacrimal fossa), trochlear spine, trochlear fovea, ethmoidal notch, impressions of cerebral gyri (digitate impressions) Nasal part: nasal spine Anterior/posterior ethmoidal foramen (between orbital part of frontal bone and orbital plate of ethmoidal labyrinth of ethmoid) Ethmoidal bone (Ethmoid) Cribriform plate: crista galli - ala of crista galli (paired), cribriform foramina Perpendicular plate Ethmoidal labyrinth (paired): anterior/middle/posterior ethmoidal cells, ethmoidal bulla, orbital plate, supreme/superior nasal concha, middle nasal concha - uncinate process Sphenoidal bone (Sphenoid) Body of sphenoid:
2 sella turcica (Turkish saddle), hypophyseal fossa, dorsum sellae, posterior clinoid process, prechiasmatic sulcus, carotid sulcus, sphenoidal lingula, sphenoidal rostrum, sphenoidal crest, sphenoidal sinus - septum of sphenoidal sinuses, sphenoidal conchae/apertures Lesser wing (paired): jugum sphenoidale (sphenoidal yoke), anterior clinoid process, optic canal Superior orbital fissure Greater wing (paired): cerebral surface impressions of cerebral gyri (digitate impressions), cerebral yokes, foramen rotundum/ovale/spinosum temporal surface infratemporal crest infratemporal surface foramen ovale/spinosum, spine of sphenoid, sulcus of auditory tube orbital surface maxillary surface foramen rotundum Pterygoid process (paired): lateral plate pterygospinous process Pterygoid notch - pterygoid fossa, scaphoid fossa medial plate pterygoid hamulus pterygoid canal (Vidian) Foramen lacerum (after maceration of skull) Temporal bone (paired) Petrous part: apex of petrous part anterior surface trigeminal impression, groove for greater/lesser petrosal n., hiatus for greater/lesser petrosal n., arcuate eminence, tegmen tympani Superior border - groove for superior petrosal sinus posterior surface internal acoustic opening - internal acoustic meatus, subarcuate fossa, external opening of vestibular aquaeduct (vestibular canaliculus), posterior border - jugular notch, groove for inferior petrosal/sigmoid sinus, mastoid foramen Jugular foramen (partially bounded by jugular notch)
3 inferior surface musculotubal canal - septum of musculotubal canal canal for tensor tympani m., canal for auditory tube, carotid canal - caroticotympanic canaliculi, jugular fossa - mastoid canaliculus, external opening of cochlear canaliculus, petrosal fossula - tympanic canaliculus, styloid process, stylomastoid foramen, mastoid process, mastoid notch, occipital groove, mastoid foramen Tympanic part: external acoustic opening - external acoustic meatus, tympanic sulcus Tympanomastoid/tympanosquamous/petrotympanic/petrosquamous fissure Squamous part: zygomatic process, mandibular fossa - articular tubercle, groove for middle temporal a. Parietal bone (paired) frontal/occipital/sphenoid/mastoid angle external surface parietal tuber (parietal eminence), superior/inferior temporal line, parietal foramen internal surface groove for superior sagittal sinus, parietal foramen, groove for middle meningeal a. frontal/occipital/sagittal/squamous border Occipital bone Basilar part: pharyngeal tubercle, clivus, groove for inferior petrosal sinus Lateral part (paired): occipital condyle, hypoglossal canal, jugular tubercle, condylar fossa - condylar canal, jugular notch - intrajugular process, jugular process Jugular foramen (partially bounded by jugular notch) Squamous part: external surface external occipital protuberance, external occipital crest, supreme (highest)/superior/inferior nuchal line internal surface internal occipital protuberance, cruciform eminence, internal occipital crest, groove for superior sagittal sinus, groove for transverse/sigmoid sinus, cerebral/cerebellar fossa Foramen magnum
4 Calvaria (cranial vault) Frontal bone (partially), parietal bones, occipital bone (partially) Splanchnocranium Mandible Body of mandible: base of mandible: mental protuberance - mental tubercle, mental foramen, oblique line, mental spine, digastric fossa, sublingual/submandibular fossa, mylohyoid line alveolar part: alveolar arch, alveolar juga (alveolar yokes), dental alveoli - interradicular septa, interalveolar septa, Angle of mandible masseteric/pterygoid tuberosity Ramus of mandible (paired): coronoid process - temporal crest mandibular notch condylar process - head of mandible, neck of mandible - pterygoid fovea, mandibular foramen - mandibular canal, lingula of mandible, mylohyoid groove Maxilla (paired) Body of maxilla: orbital surface infraorbital groove, infraorbital canal, infraorbital margin anterior surface infraorbital foramen, canine fossa, anterior nasal spine, nasal notch infratemporal surface maxillary tuberosity - alveolar foramina and canals nasal surface lacrimal groove, conchal crest, lacrimal margin, greater palatine groove, maxillary hiatus maxillary sinus: zygomatic/frontal/ /palatine/alveolar recess Processes of maxilla: frontal process anterior lacrimal crest, lacrimal groove, ethmoidal crest alveolar process alveolar arch, juga alveolaria (alveolar yokes), dental alveoli - interradicular septa, interalveolar septa zygomatic process
5 palatine process incisive foramen - incisive canal, incisive suture, median palatine suture - palatine torus, transverse palatine suture, palatine grooves and spines, nasal crest Piriform aperture: bodies and frontal processes of maxillae and nasal bones Zygomatic bone (paired) orbital surface zygomaticoorbital foramen lateral surface zygomaticofacial foramen temporal surface zygomaticotemporal foramen temporal/frontal process Zygomatic arch: zygomatic process of temporal bone and temporal process of zygomatic bone Palatine bone (paired) Horizontal plate: nasal/palatine surface, nasal/palatine crest, posterior nasal spine Perpendicular plate: maxillary surface, nasal surface - conchal/ethmoidal crest, greater palatine groove, pyramidal process - lesser palatine foramina orbital process sphenopalatine notch - sphenopalatine foramen sphenoidal process Greater palatine foramen - greater palatine canal bounded by greater palatine groove of body of maxilla and perpendicular plate of palatine bone Inferior nasal concha (paired) Lacrimal bone (paired) posterior lacrimal crest, lacrimal groove, fossa for lacrimal sac Nasal bone (paired) Vomer Auditory ossicles: malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup) part of the middle ear (paired) Hyoid bone: body, greater/lesser horn in the anterior region of the neck Skull cavities On the internal cranial base: Anterior view of the skull: Lateral view of the skull: Anterior/Middle/Posterior cranial fossae Osseous (bony) nasal cavity, Orbit Temporal/Infratemporal/Pterygopalatine fossae
6 Cervical vertebrae (C1 C7) Cervical vertebrae C3 C6 Body: uncal process Arch: Lamina spinous process (bifurcated, C7 vertebra prominens) transverse process transverse foramen (for vertebral a. and v.), anterior tubercle (C6 carotid tubercle) and posterior tubercle, groove for spinal n. superior and inferior articular processes Pedicle superior and inferior vertebral notches (intervertebral foramen) Vertebral foramen triangular shaped Atlas (C1) Lateral mass (paired): superior articular surface joins by occipital condyle inferior articular surface joins by superior articular surface of C2 transverse process, transverse foramen Anterior arch: anterior tubercle, dental fovea joins by dens of axis Posterior arch: posterior tubercle, groove for vertebral a. Vertebral foramen Axis (C2) Body: dens of axis apex of dens, anterior and posterior articular surfaces Arch: Lamina spinous process transverse process anterior and posterior tubercles, transverse foramen, groove for spinal n. superior and inferior articular processes Pedicle superior and inferior vertebral notches (intervertebral foramen) Vertebral foramen Joints of head and neck Unmovable joints of skull Fibrous joints of skull (cranial syndesmoses): Cranial sutures coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, squamous sutures median and transverse palatine sutures
7 Fontanelles (fonticles) anterior, posterior, sphenoidal and mastoid fontanelles Gomphosis (dentoalveolar syndesmosis) Cartilaginous joints of skull (cranial synchondroses): Sphenooccipital synchondrosis disappears in the 18 th year of life Sphenopetrosal and petroocipital synchondroses (permanent) foramen lacerum (after maceration of skull) Osseous joints of skull (cranial synostoses): after ossification of sutures Movable joint of skull Synovial joint - temporomandibular joint Articular disc insertion of lateral pterygoid m. Direct ligaments lateral and medial ligg. Indirect ligaments stylomandibular lig. (angular tract - separates parotid and submandibular gll.) sphenomandibular lig. - protects maxillary a. pterygomandibular lig. (buccopharyngeal raphe) pterygospinous lig. Craniovertebral joints Atlantooccipital joints: anterior atlantooccipital membrane (from anterior longitudinal lig.) tectorial membrane (from posterior longitudinal lig.) posterior atlantoocipital membrane (from ligg. flava) Atlantoaxial joints: median atlantoaxial joint cruciform lig. of atlas, alar ligg., apical lig. of dens lateral atlantoaxial joints Muscles of head Mimetic mm. (muscles of facial expression) i.: facial n. Epicranius m.: complex of muscles attached to epicranial aponeurosis occipitofrontal m. frontal and occipital bellies temporoparietal m. Muscles of auricle: superior, anterior and posterior auricular mm.
8 Muscles of eye slit: orbicularis oculi m. orbital, palpebral and lacrimal parts depressor supercilii m. corrugator supercilii m. procerus m. Muscles of nose: nasalis m. transverse and alar parts depressor septi nasi m. Muscles of oral slit: orbicularis oris m. marginal and labial parts levator labii superioris m. levator labii superioris alaeque nasi m. zygomatic major and minor mm. levator anguli oris m. risorius m. depressor anguli oris m. depressor labii inferioris m. mentalis m. transversus menti m. buccinator m. the only deep muscle of head and the only mimetic muscle covered by fascia, is pierced by parotid duct Masticatory mm. (chewing mm.) innervated by branches of mandibular n. (V/3) masseter m. superficial and deep parts temporalis m. medial pterygoid m. superficial and deep parts lateral pterygoid m. superior and inferior heads (depressor of mandible) Muscles of neck Platysma m. (i.: cervical br. of facial n.) only mimetic m. of neck Sternocleidomastoid m. (i.: accessory n.) - sternal and clavicular parts, between their origins: minor supraclavicular fossa
9 Suprahyoid mm.: digastric m. anterior (i.: mylohyoid n.) and posterior (i: facial n.) bellies stylohyoid m. (i.: facial n.) mylohyoid m. mylohyoid raphe (i.: mylohyoid n.) geniohyoid m. = oral diapdragm (i: hypoglossal n.) Infrahyoid mm.: (i: cervical ansa) sternohyoid m. sternothyroid m. thyrohyoid m. omohyoid m. superior and inferior bellies Scalene mm: (i: anterior brr. of cervical spinal nn.) anterior, middle and posterior scalene mm. Scalene gap (fissure) between anterior and middle scalene mm. and 1st rib for subclavian a. and trunks of brachial plexus Prevertebral mm (deep cervical mm.): (i: anterior brr. of cervical spinal nn.) longus colli m. longus capitis m. rectus capitis anterior and lateral mm. Vessels of head and neck Common carotid a. in carotid sheath with internal jugular v. and vagus n. Right: starts from brachiocephalic trunk (shorter) Left: starts from aortic arch (longer) Carotid bifurcation (level of C3-4, carotid body chemoreceptor for O2 and CO2 External carotid a. Anterior branches: Superior thyroid a. runs medially below hyoid bone infrahyoid br. superior laryngeal a. - pierces thyrohyoid membrane with superior laryngeal n. sternocleidomastoid br. cricothyroid br. glandular brr. anterior and posterior
10 Lingual a. runs medially below hyoglossus m. suprahyoid br. anastomoses with infrahyoid br. of superior thyroid a. dorsal lingual brr. sublingual a. deep lingual a. Facial a. runs medially to stylohyoid m. and posterior belly of digastric m., pierces submandibular gl. and runs to face ventrally to insertion of masseter m. ascending palatine a. for palatine tonsil submental a. accompanies submental v. and mylohyoid n. glandular brr. for submandibular gl. inferior labial a. superior labial a. septal nasal br., lateral nasal a. angular a. anastomoses with dorsal nasal a. (from ophthalmic a.) Medial branch: Ascending pharyngeal a. posterior meningeal a. Posterior branches: Occipital a. runs in the occipital groove medially to mastoid notch Posterior auricular a. stylomastoid a. (into stylomastoid foramen) Terminal branches: Superficial temporal a. in front of auricle accompanied auriculotemporal n. and superficial temporal v. transverse facial a. runs below zygomatic arch zygomaticoorbital a. runs above zygomatic arch middle temporal a. frontal and parietal brr. for anastomosis with ophthalmic and occipital aa. Maxillary a. 3 parts: Mandibular part: between neck of mandible and sphenomandibular lig. inferior alveolar a. with inferior alveolar n. to mandibular canal mylohyoid br., dental and peridental brr., mental br. middle meningeal a. passes through foramen spinosum Pterygoid part: branches for muscles deep temporal aa., masseteric a., pterygoid brr., buccal a.
11 Pterygopalatine part: in pterygopalatine fossa superior posterior alveolar a. into maxillary tuberosity infraorbital a. superior anterior alveolar a. descending palatine a. sphenopalatine a. - nasopalatine a. pterygoid canal a. Internal carotid a. Carotid sinus mechanoreceptors for blood pressure Ophthalmic a. accompanies optic n. into optic canal central retinal a. lacrimal a. lateral palpebral aa. medial palpebral aa. anterior ethmoidal aa. (anterior meningeal a.) and posterior ethmoidal aa. supraorbital a. through supraorbital foramen/notch supratrochlear a. through frontal foramen/notch dorsal nasal a. Subclavian a. Right: from brachiocephalic trunk (shorter) Left: from aortic arch (longer) passes through scalene gap Intrascalenic part: Vertebral a. through transverse foramina C6 C1 Internal thoracic a. through superior thoracic aperture into thoracic cavity Thyrocervical trunk inferior thyroid a. ascending cervical a. with phrenic n. in front of anterior scalene m. suprascapular a. runs up to superior transverse scapular lig. Interscalenic part: Costocervical trunk in scalene gap deep cervical a. spinal brr. supreme intercostal a. for two first intercostal spaces Extrascalenic part: Transverse cervical a. pierces trunks of brachial plexus
12 Superficial veins: External jugular v. from occipital v. and posterior auricular v. receives: anterior jugular v., suprascapular v., transverse cervical v. Anterior jugular v. from submental vv. forms: jugular venous arch or v. mediana coli Deep veins: Internal jugular v. originates from sigmoid sinus, passes through jugular foramen, runs ventrolaterally to common carotid a. in carotid sheath accompanied vagus n. Receives veins from head and neck: retromandibular v. connection of superficial temporal v. and maxillary vv. superficial temporal v. frontal and parietal brr. maxillary vv. from pterygoid plexus facial v. runs straight at the face laterally to facial a. angular v. from supraorbital and supratrochlear vv. deep facial v. connection with pterygoid plexus superior and inferior labial vv. submental v. lingual v. deep lingual v. (for rapid absorption of medicaments) superior and middle thyroid vv. Subclavian v. passes in front of scalene fissure and opens in venous angle receives: external jugular v. Venous angle connection of internal jugular v. and subclavian v. behind sternoclavicular joint Right: receives right lymphatic duct Left: receives thoracic duct Vertebral v., inferior laryngeal v. and inferior thyroid v. open to brachiocephalic v. Lymphatic nodes of head: occipital lnn. mastoid (retroauricular) lnn. parotid lnn. facial (buccal) lnn. submental lnn.
13 submandibular lnn. main lymphatic nodes of head Superficial cervical lnn. anterior and lateral lnn. Deep cervical lnn. along internal jugular v.: jugulodigastric and juguloomohyoid lnn. retropharyngeal lnn. lingual lnn. along transverse cervical vessels: virchow's ln. along accessory n. by cranial, spinal and autonomic nerves Innervation of head and neck Cranial nerves: Olfactory n. (CN I) through cribriform plate of ethmoidal bone Optic n. (CN II) passes through optic canal accompanied ophthalmic a. Oculomotor n. (CN III) passes through superior orbital fissure (for rectus superior, inferior and medialis mm., inferior oblique m., levator palpebrae superioris m.) Trochlear n. (CN IV) passes through superior orbital fissure (for superior oblique m.) Trigeminal n. (CN V) trigeminal ggl. (semilunar ggl.) in trigeminal impression, sensory innervation of head and motor innervation for masticatory mm. Ophthalmic n. (CN V/1) passes through superior orbital fissure, sensory Lacrimal n. Frontal n. supraorbital n.: lateral br. (supraorbital foramen/notch) medial br. (frontal foramen/notch) supratrochlear n. Nasociliar n. anterior ethmoidal n.: medial, lateral, external nasal brr. posterior ethmoidal n. infratrochlear n. Maxillary n. (CN V/2) through foramen rotundum into pterygopalatine fossa, sensory Zygomatic n. zygomaticofacial br., zygomaticotemporal br. Infraorbital n. superior alveolar nn. superior dental plexus
14 pes anserinus minor: inferior palpebral brr. external and internal nasal brr. superior labial brr. Pterygopalatine nn. to pterygopalatine ggl. Mandibular n. (CN V/3) passes through foramen ovale into infratemporal fossa Motor branches: masseteric n., deep temporal, lateral and medial pterygoid nn. n. to tensor tympani, n. to tensor veli palatini Sensory branches: meningeal br. buccal n. auriculotemporal n. lingual n.: communicating br. to chorda tympani Mixed branch: inferior alveolar n. mandibular canal mylohyoid n. motor inferior dental plexus sensory mental n. sensory, through mental foramen Abducent n. (CN VI) passes through superior orbital fissure (for rectus lateralis m.) Facial n. (CN VII) enters internal acoustic pore, leaves stylomastoid foramen Intracranial branches: in petrosal part of temporal bone stapedius n. greater petrosal n. chorda tympani PS + taste fibres for anterior 2/3 of tongue Extracranial branches: posterior auricular n. digastric and stylohyoid brr. intraparotid plexus (pes anserinus major) for mimetic mm.: temporal brr. zygomatic brr. buccal brr. marginal mandibular br. cervical br. Vestibulocochlear n. (CN VIII) into internal acoustic porus, balance and hearing Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) through ventromedial part of jugular foramen tympanic n. lesser petrosal n. Jacobson's anastomosis (for parotid gl.)
15 carotid sinus n. from carotid body and sinus pharyngeal br. to pharyngeal plexus tonsillar brr. lingual brr. Vagus n. (CN X) through ventromedial part of jugular foramen, runs into carotid sheath between to common carotid a. and internal jugular v. meningeal br. auricular br. pharyngeal br. to pharyngeal plexus carotid body n. superior laryngeal n. internal br. sensory, pierces thyrohyoid membrane together with superior laryngeal vessels external br. motor (for cricothyroid m.) recurrent laryngeal n.: right loops around subclavian a. left loops around aortic arch superior and inferior cervical cardiac brr. Accessory n. (CN XI) spinal root: from spinal cord through foramen magnum to skull cranial root: from medulla oblongata both roots leave skull through ventromedial part of jugular foramen and split to: internal br. - joins vagus n. external br. - for trapezius and sternocleidomastoid mm. Hypoglossal n. (CN XII) through hypoglossal canal, for motor innervation of all muscles of tongue except of palatoglossus m. Spinal nerves: Cervical plexus anterior brr. of spinal nn. C1 C4 Motor nerves: cervical ansa innervates infrahyoid mm. superior (anterior) root: C1 runs together with hypoglossal n. inferior (posterior) root: C2 C3
16 phrenic n. runs in front of anterior scalene m., innervates diaphragm muscular brr. for deep cervical mm. Sensory nerves from punctum nervorum: transverse cervical n. connection with cervical br. of facial n. lesser occipital n. greater auricular n. accompanies external jugular v. supraclavicular nn. medial, intermediate and lateral nn. Brachial plexus anterior brr. of spinal nn. C5 Th1 Supraclavicular part Trunks: superior, middle, inferior through scalene fissure dorsal scapular n. suprascapular n. long thoracic n. subclavian n. Autonomic nerves: Sympathetic fibres run along vessels. Sympathetic ganglia of neck: superior cervical ggl. (C2 C3) middle cervical ggl. (C6) inferior cervical = cervicothoracic = stellate ggl. (C7) Parasympathetic fibres run inside of cranial nerves. Parasympathetic ganglia of head and neck: ciliary ggl. (CN III) - head pterygopalatine ggl. (CN VII) - head submandibular ggl. (CN VII) - neck otic ggl. (CN IX) - head
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of
![function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of function - sensory & postganglionic sympathetic [communication from the internal carotid plexus in the cavernous sinus] innervation of the mucosa of](/thumbs/74/71276096.jpg) Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
Nerves I. Cranial nerves A. Olfactory (CN I) 1. Olfactory bulb 2. Olfactory tract B. Optic n. (CNII) function - carries visual sensory information from the neural retina to the diencephalon & midbrain
University of Palestine. Final Exam 1 st Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
Question One: MCQ: 1- The coronal suture joins the a) frontal and parietal bones. b) left and right parietal bones. c) parietal and occipital bones. d) parietal, squamous temporal and greater wing of the
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes
 Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Head & Neck Radiology (I) Waseem Jerjes Lamboid Suture Frontal Sinus Left Orbit (roof) Left Supraorbital Margin Left Frontozygomatic Suture Left Superior Orbital Fissure Rt Petrous Ridge of Temporal Bone
Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically
 CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德
 Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Face and Scalp 解剖學科鄭授德 本教材之圖片取自於 1 Gray s Anatomy for Students, 3rd ed, 2015, by Drake, Vogl, and Mitchell 2 Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 7th ed, 2014, by Moore, Dalley, and Agur 3 Clinically Oriented
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 1 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 1 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577040/ Section 1 Head and Neck (84 cards) Plate 1-1 Skull: Anterior View 1.1 Frontal bone 1.2 Supra-orbital notch
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 1 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577040/ Section 1 Head and Neck (84 cards) Plate 1-1 Skull: Anterior View 1.1 Frontal bone 1.2 Supra-orbital notch
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved
 HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
HEAD & NECK BY NUMBERS THIRD EDITION Copyright 2013, Anatomy Numbers (Phoenix, AZ) All rights reserved No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
The Axial Skeleton. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Nose & Mouth OUTLINE. Nose. - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls. - Paranasal Sinuses. - Neurovascular Structures. Mouth. - Oral Cavity & Its Contents
 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Nose & Mouth OUTLINE Nose - Nasal Cavity & Its Walls - Paranasal Sinuses - Neurovascular Structures Mouth - Oral Cavity & Its
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
EXAM NUMBER STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 7 October 28, PART l. Answer in the space provided. (9 pts)
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 7 October 28, 2005 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (9 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (3 pts) a. _Frontal Sinus b. _Lateral Posterior Inferior Nasal
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 7 October 28, 2005 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (9 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (3 pts) a. _Frontal Sinus b. _Lateral Posterior Inferior Nasal
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory fibers to the skin of the clavicular area
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY WRITTEN EXAM 2 -- October 10, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Each of the following statements is CORRECT EXCEPT: A. The supraclavicular nerves supply sensory
CN I Olfactory. CN II Optic. CN III Oculomotor. Special Sensory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb. Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid
 CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
External Occipital Protuberance
 Osteology Exterior Skull Frontal Bone Glabella Superciliary Arch Supraorbital Notch/Foramen Nasion (junction w/ Nasal bone) Frontal/Metopic Suture (usually absent in adult, b/w ossification centers of
Osteology Exterior Skull Frontal Bone Glabella Superciliary Arch Supraorbital Notch/Foramen Nasion (junction w/ Nasal bone) Frontal/Metopic Suture (usually absent in adult, b/w ossification centers of
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND. Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy
 FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy THE FACE THE SCALP The scalp is composed of five layers: Skin ConnecAve Assue Aponeurosis Loose connecave Assue Pericranium
FACE CN V & VII PAROTID GLAND Jacek Baj, MD, PhD Department of Human Anatomy THE FACE THE SCALP The scalp is composed of five layers: Skin ConnecAve Assue Aponeurosis Loose connecave Assue Pericranium
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
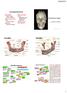 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Chapter 27: The ear, intracranial region and cranial nerves. Ear. The External Ear. This consists of the auricle and the external acoustic meatus.
 Chapter 27: The ear, intracranial region and cranial nerves Ear The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. It is divided into an external ear directing sound waves to the tympanic membrane, a middle
Chapter 27: The ear, intracranial region and cranial nerves Ear The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. It is divided into an external ear directing sound waves to the tympanic membrane, a middle
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
