CEACAM1 regulates insulin clearance in liver
|
|
|
- Pamela Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CEACAM1 regultes insulin lerne in liver Mtthew N. Poy 1, Yn Yng 1, Khijeh Rezei 1, Mts A. Fernström 1, Arhm D. Lee 2, Yoshiki Kio 3, Snr K. Erikson 4 & Soni M. Njjr 1 Pulishe online: 19 Ferury 2002, DOI: /ng840 We hypothesize tht insulin stimultes phosphoryltion of CEACAM1 whih in turn les to upregultion of reeptor-meite insulin enoytosis n egrtion in the heptoyte. We hve generte trnsgeni mie over-expressing in liver ominnt-negtive, phosphoryltion-efetive S503A-CEACAM1 mutnt. Supporting our hypothesis, we foun tht S503A-CEACAM1 trnsgeni mie evelope hyperinsulinemi resulting from impire insulin lerne. The hyperinsulinemi use seonry insulin resistne with impire gluose tolerne n rnom, ut not fsting, hyperglyemi. Trnsgeni mie evelope viserl iposity with inrese mounts of plsm free ftty is n plsm n hepti triglyeries. These finings suggest mehnism through whih insulin signling regultes insulin sensitivity y moulting hepti insulin lerne. Introution Insulin tivtes ifferent intrellulr signling pthwys y promoting protein phosphoryltion. The insulin reeptor is lign-tivte tyrosine kinse tht tivtes mny intrellulr protein sustrtes. Insulin-reeptor sustrtes (IRSs) hve een shown to influene insulin signling in ifferent tissues y promoting the tivtion of phosphtiylinositol-3 (PI-3) kinse n set of PIP-epenent serine/threonine protein kinses 1. It is likely, however, tht itionl sustrtes re lso require for insulin tion. For exmple, pthwy meite y phosphoryltion of the proto-onogene -l n le to gluose uptke inepenent of PI-3 kinse in response to insulin 2. Similrly, α 2 - Heremns Shmi glyoprotein (α 2 -HSG) inhiits signling through the insulin reeptor kinse 3, s n the plsm ell memrne glyoprotein-1 (PC-1) 4. We showe previously tht the trnsmemrne glyoprotein CEACAM1 is phosphorylte in response to insulin in heptoytes 5. The insulin reeptor kinse phosphoryltes single tyrosine resiue (Tyr488) in the intrellulr omin of CEACAM1. In ition, CEACAM1 is phosphorylte y serine/threonine kinses on Ser503 in the sene of insulin. Sustituting Al for Ser503 effetively olishe CEACAM1 phosphoryltion y either serine/threonine or tyrosine kinses, suggesting tht phosphoryltion on Ser503 is require for susequent tyrosine phosphoryltion y the insulin reeptor kinse. The funtion of CEACAM1 remins elusive. It hs een propose to t s ell hesion moleule 6. It is lso known to suppress tumor growth in ells of epithelil origin 7 10, to ownregulte the mitogeni effets of insulin n to upregulte reeptor-meite insulin enoytosis n egrtion Phosphoryltion of CEACAM1 seems to e require for its effet on ell prolifertion n insulin egrtion 12,13. In vitro stuies suggest tht upon its phosphoryltion y the insulin reeptor kinse, CEACAM1 ins iniretly to the reeptor to unergo internliztion in lthrin-ote vesiles 14 s prt of the insulin enoytosis omplex. Beuse reeptor-meite insulin enoytosis n egrtion in the heptoyte onstitutes the prinipl mehnism of insulin lerne, whih ours mostly in liver 15, we hve propose tht CEACAM1 phosphoryltion moultes hepti insulin lerne, ontriuting to the regultion of systemi insulin onentrtions. Beuse of the presene of two losely relte Cem genes in mouse (s oppose to one gene in rt n humns) 16, we generte mouse moel of funtionl intivtion of Cem1 ering ominnt-negtive, phosphoryltion-efetive CEACAM1 mutnt (from S503A rt) in liver. We report tht over-expression of the S503A minigene restrite to liver results in hyperinsulinemi ue to impire insulin lerne, with seonry hepti insulin resistne n impire gluose tolerne in the liverspeifi S503A CEACAM1 mutnt (L-SACC1) mie. These t inite new mehnisti link etween insulin signling n regultion of peripherl insulin sensitivity. Results Phosphoryltion of CEACAM1 in L-SACC1 mie We hrterize n re to homozygosity mouse line (F0 113) rrying six opies of the rt Cem1 S503A trnsgene. After phosphorylting liver lystes in the presene of [γ- 32 P]ATP, we immunopreipitte proteins with speifi ntioies ginst rt CEACAM1 (α-rcc1; Fig. 2) n mouse BGP, the rt CEA- CAM1 homolog (Fig. 2). In ontrst to the wil type (Fig. 2, lnes 3 n 4), insulin file to stimulte CEACAM1 phosphoryltion in homozygous L-SACC1 (L-SACC1 homo ) mie (Fig. 2, lnes 1 n 2). Overexpressing this mutnt i not signifintly 1 Deprtments of Phrmology n Therpeutis, n 2 Physil Therpy, Meil College of Ohio, 3035 Arlington Avenue, HSi Builing Room 270, Toleo, Ohio 43614, USA. 3 Seon Deprtment of Internl Meiine, Koe University Shool of Meiine, Kusunoki-ho, Chuo-ku, Koe, Jpn. 4 Deprtment of Meiine, Sn Frniso n the Veterns Affirs Meil Center, University of Cliforni, Sn Frniso, Cliforni, USA. Corresponene shoul e resse to S.M.N. (e-mil: snjjr@mo.eu). 270 nture genetis volume 30 mrh 2002
2 erese phosphoryltion of either the insulin reeptor (Fig. 2, lnes 1 n 2) or IRS-2 (Fig. 2e, lnes 1 n 2), mjor sustrte of the insulin reeptor kinse in liver. These results inite tht olishing CEACAM1 phosphoryltion in liver oes not interfere with phosphoryltion of other sustrtes of the insulin reeptor. It is thus possile tht IRS-epenent signling pthwys n the insulin tions they meite re not ltere in L-SACC1 mie. The S503A trnsgene uses hyperinsulinemi L-SACC1 homo mie showe inrese oy weight (Fig. 3; P<0.05) n viserl iposity t ll ges exmine (P<0.05; Fig. 3). By ontrst, hemizygous (L-SACC1 hemi ) mie were not ifferent from wiltype mie, onsistent with gene-osge effet (Fig. 3). Liver, kiney n musle funtions were unltere (Tle 1). L-SACC1 homo mie t two n eight months showe % inrese in plsm insulin levels ompre with ge-mthe wiltype mie (Fig. 4[i]). Insulin lerne, mesure s fsting molr C-peptie/insulin rtio, ws signifintly reue in L-SACC1 homo mie (Fig. 4[iii]). Moreover, the mount of plsm resiul [ 125 I]-insulin t min fter til injetion ws % higher in L-SACC1 thn wiltype nimls (Fig. 4). Insulin internliztion ws erese y pproximtely 50% (P<0.05) in heptoytes of L-SACC1 homo mie (Fig. 4). In ition, insulin-inue internliztion of insulin reeptors n CEA- CAM1, s mesure y the loss of iotin-lele surfe memrne proteins 14, ws reue in L-SACC1 ompre with wiltype nimls (insulin reeptor: 49.4% in L-SACC1 versus 82.1% in wiltype; CEACAM1: 13.7% in L-SACC1 versus 41.3 in wiltype; Fig. 4). Beuse CEACAM1 unergoes internliztion with the insulin reeptor s prt of the insulin enoytosis omplex 14, these finings inite tht reeptor-meite insulin internliztion n egrtion were erese in L-SACC1 mie. Tht C-peptie levels in L-SACC1 homo mie were milly inrese (Fig. 4[ii]; P<0.05) ws further supporte y unltere β-ell mss (1.611 ± in L-SACC1 versus ± 0.75 in wiltype, P>0.05). Tken together, these finings suggest tht the primry normlity of insulin metolism in L-SACC1 mie is impire insulin lerne rther thn inrese insulin seretion. To ress whether hyperinsulinemi ws primry effet of the trnsgene or seonry to insulin resistne, we exmine insulin sensitivity y intrperitonel insulin tolerne. After insulin injetion, gluose levels erese to similr extent in L-SACC1 homo n ontrols (wiltype n L-SACC1 hemi mie) t two n eight months of ge (Fig. 4e). This suggests tht peripherl tissues mintine insulin sensitivity in L-SACC1 homo mie. In ontrol mie, gluose levels returne to norml within three hours, wheres in L- SACC1 homo they remine suppresse. These results support the possiility tht injete insulin ws lere less effiiently. Seonry insulin resistne in L-SACC1 mie L-SACC1 homo mie evelope mil rnom hyperglyemi t 2 8 months (Fig. 5), initing insulin resistne in these mie. Fsting gluose levels were unltere, however, t two months (Fig. 5; 113 ± 37 in L-SACC1 homo versus 133 ± 41 in wiltype, P>0.05) or ten months (Fig. 5; 143 ± 19 in L-SACC1 homo versus 124 ± 29 in wiltype, P>0.05). Moreover, L-SACC1 homo mie were gluose intolernt (Fig. 5). The isrepny etween their sensitivity to insulin in n insulin tolerne test n their gluose intolerne proly hs severl uses. First, the lrge oses of insulin use in the insulin tolerne test re suffiient to overome the mil egree of peripherl insulin resistne. Seon, the egree of hypoglyemi ourring uring n insulin tolerne test epens lrgely on insulin-epenent gluose uptke tht ours primrily in skeletl musle, wheres hyperglyemi following n intrperitonel gluose injetion in roents isproportiontely epens on gluose utiliztion in liver. Thus, the preition from these experiments woul e tht L-SACC1 hs seonry hepti with Fig. 1 Genertion of L-SACC1 mie., Suloning of Apo A-1 promoter upstrem of Cem1 rt minigene ering Ser Al muttion on 503. The muttion rete new PstI site (*) without hnging the reing frme of the rt mutnt protein., Dominnt-negtive effet of rt S503A CEACAM1. SV40-trnsforme mouse heptoytes were trnsfete with rt S503A CEACAM1 mutnt (lnes 3, 4) or left untrnsfete (UT; lnes 1, 2). Internliztion of the insulin reeptor ws mesure s the loss of the iotin-lele α-suunit of the insulin reeptor (IR-α) from the surfe in the presene (even lnes) versus sene (o lnes) of insulin., Southern lot of HinIII/PstI-igeste genomi DNA from niml tils, using [ 32 P]-lele Apo A-1 promoter/s503a Cem1 minigene s proe. In the representtive gel, ns erive from the trnsgene were etete in the F0 mouse 113 in ition to the ns erive from the enogenous gene tht is lso etete in wiltype (WT) nimls., Western lot of liver-speifi expression of S503A CEACAM1 proteins. Plsm memrne proteins from livers n smll intestines of F1 progeny n WT mie were prepre y etergent extrtion n prtil purifition on letin hromtogrphy. Equl mounts (300 mg) of glyoproteins were immunopreipitte with R2-6, polylonl rt CEACAM1 ntioy tht ross-rets with the mouse protein. After nlysis on 7% SDS PAGE, proteins were immunolotte with α-295, polylonl rt CEACAM1 ntioy, n etete y ECL. nture genetis volume 30 mrh
3 insignifint musle insulin resistne. In ft, insulin inue omprle rise in the rte of gluose uptke in soleus musle of 2-month wiltype n L-SACC1 mie t sumximl onentrtions (1.2 nm; 5.20 ± 0.98 in wiltype versus 3.73 ± 0.54 nmol g 1 min 1 in L-SACC1, P<0.05; Fig. 5). Similr results were otine in epitrohleris musles of mie t two n six months (t not shown). In ition, gluose trnsporter-4 (GLUT4) mrna levels were not ltere in soleus musle of L-SACC1 mie (Fig. 5). Moreover, the triglyerie ontent in soleus musle of 8-month L-SACC1 mie ws norml (66 ± 16 in L-SACC1 mie versus 45 ± 9 mg mg 1 protein in wiltype, P>0.05). These finings inite tht L-SACC1 mie o not evelop signifint musle insulin resistne. The reeptor numer in heptoytes ws reue y hlf in L-SACC1 homo mie t two n eight months (pproximtely 2.4 ± in L-SACC1 versus pproximtely 5.62 ± reeptors per ell in wiltype, P<0.05). Moreover, the ffinity of insulin ining (K ) ws virtully unhnge (4.97 ± in L-SACC1 versus 6.55 ± in wiltype, P>0.05). Stey-stte mrna enoing rte-ontrol enzyme for hepti gluoneogenesis, phosphoenolpyruvte roxykinse (PEPCK), ws onsistently signifintly higher (y pproximtely %) in homozygous L-SACC1 t ll ges exmine (Fig. 5e). This suggests tht primry hyperinsulinemi use seonry hepti insulin resistne in L-SACC1 mie. In ontrst, mrna enoing rte-ontrol enzyme in glyogenolysis, glyogen 6-phosphtse (G-6-Pse), ws 35 70% lower in L-SACC1 homo thn in wiltype mie (Fig. 5e). The erese in G-6-Pse oul ounter-regulte the positive effet of elevte PEPCK on hepti gluose proution. This is onsistent with onition of hepti insulin resistne seonry to hyperinsulinemi without signifint inrese in fsting gluose levels n evelopment of ietes in L-SACC1 mie. e Fig. 2 Speifi ltertion of hepti CEACAM1 phosphoryltion in L-SACC1 mie. e, Glyoproteins from liver lystes of wiltype n L-SACC1 homozygous mie t 2 mo were letin-purifie n phosphorylte in the presene ( ) or sene (,e) of [γ- 32 P]ATP. Proteins were then immunopreipitte (Ip) with ntioies ginst mouse iliry glyoprotein (α-mbgp, the mouse CEA- CAM1 homolog; ); rt CEACAM1 (α-rcc1; ); IR-β suunit (IR-β; ) n IRS-2 (e). Phosphoryltion of proteins ws etete y utoriogrphy ( ) n immunolotting (I) with α-phosphotyrosine ntioy (α-ptyr; -e). To ount for the mount of rt CEACAM1 in the immunopellets, lot ws reproe with α-rcc1 (). Tle 1 Biohemistry of norml liver, kiney n musle in homozygous L-SACC1 mie WT L-SACC1 homo Liver funtion Asprtte minotrnsferse (µm) ± ± 52.3 Alnine minotrnsferse (µm) 48.7 ± ± 20.9 Alkline phosphtse (µm) 48.0 ± ± 21.5 Biliruin: totl (mg/l) 0.18 ± ± 0.09 Biliruin: iret (mg/l) 0.09 ± ± 0.05 Cholesterol: totl (mg/l) 98.5 ± ± 9.83 Cholesterol: HDL (mg/l) 83.2 ± ± 7.20 Musle funtion: Cretine kinse (µm) ± ± Kiney funtion: Bloo ure nitrogen (mg/l) 27.5 ± ± 3.90 The levels of severl enzymes n of holesterol, iliruin n loo ure nitrogen were etermine in fsting wiltype (WT) n homozygous (homo) L-SACC1 mie t 8 mo. All ssys were rrie out in triplite. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.e.m.. P>0.05 versus WT mie in ll etermintions. Unltere pnreti β-ell funtion in L-SACC1 mie To exmine pnreti β-ell funtion, we mesure insulin seretion in response to gluose. Clultion of the re uner the urve (Fig. 6) revele tht the first-phse insulin response to gluose ws not ltere (P>0.05) in 10-month L-SACC1 homo mie (4.680 ± u.) ompre with ontrols (wiltype: ± n L-SACC1 hemi : ± u.). Similr results were otine in mie t two months (t not shown). This suggests tht hyperinsulinemi n hepti insulin resistne i not signifintly impir β-ell funtion in L-SACC1 homo mie, in greement with no evelopment of ietes in these mie. Altere ft metolism in L-SACC1 mie Beuse elevte FFA levels influene hepti utoregultion of gluose proution, perhps y stimulting gluoneogenesis n ownregulting glyogenolysis in mie 17, we exmine fsting plsm FFA levels in L-SACC1 homo mie. Plsm FFA were signifintly elevte in these mie (Tle 2; P<0.05). This ws ssoite with inrese plsm (Tle 2) n hepti triglyerie ontent (18 ± 1 in L-SACC1 mie versus 10 ± 3 mg mg 1 protein in wiltype, P<0.05). Disussion We hve emonstrte tht over-expression of phosphoryltionefetive Cem1 trnsgene in mouse liver ts in ominntnegtive mnner to inhiit CEACAM1 funtion n results in hyperinsulinemi without ltering liver funtion or insulin-signling through other pthwys. This is in mrke ontrst to mie ering liver-speifi ltion of the insulin-reeptor gene (LIRKO) tht hve ltere liver funtion n IRS-epenent signling pthwys 18. Hyperinsulinemi in L-SACC1 mie is onsistent with the hypothesis tht CEACAM1 is prt of omplex of proteins require for internliztion of the insulin-reeptor omplex 11,12,14,19. Tht hyperinsulinemi in L-SACC1 mie is primrily ue to erese hepti lerne is supporte y severl finings: (i) the inrese in insulin levels is not prllele y proportionl inrese in C-peptie levels (ii) β-ell mss is not ommensurte to the extent of hyperinsulinemi (iii) L-SACC1 mie re more sensitive to exogenously ministere insulin thn nontrnsgeni littermtes n (iv) L-SACC1 mie evelope intr-ominl viserl iposity n elevte plsm FFA, whih re ommonly ssoite with impire insulin lerne Other finings support the hypothesis tht rnom hyperglyemi n impire gluose tolerne in L-SACC1 mie re proly ue to hepti insulin resistne: (i) erese numers n internliztion of insulin reeptors with erese internliztion of insulin n CEACAM1 in primry heptoytes erive 272 nture genetis volume 30 mrh 2002
4 from L-SACC1 mie (ii) elevte PEPCK mrna levels (iii) norml insulin-epenent gluose uptke in isolte musle, suggesting tht hyperglyemi in L-SACC1 mie is ue to inrese hepti gluose proution rther thn impire musle gluose uptke n (iv) elevte plsm FFA in L-SACC1 mie. This woul ontriute to hepti insulin resistne y stimulting hepti synthesis n output of gluose 26 n triglyeries 27. The phenotype of L-SACC1 mie is onsistent with the seonry hepti insulin resistne oserve in reipients of pnres trnsplnts, in whom systemi elivery of insulin is ssoite with hyperinsulinemi n erese first-pss insulin lerne Fig. 3 Growth urves of ge-mthe wiltype n L-SACC1 mie., Wiltype (WT), L-SACC1 homo n L-SACC1 hemi mie were weighe t 2 12 mo. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.. from six litters n represent 20 mie per genotype. P<0.05 for L-SACC1 homo versus WT, n P>0.05 for L-SACC1 hemi versus WT., Viserl ipose tissues from the ominl region were ollete from t lest 15 L-SACC1 homo n WT mie n weighe n mesure s perentge of totl oy weight. Vlues re expresse s men ± s..; P<0.05 for L-SACC1 versus WT. in liver 28,29. Although hyperinsulinemi in L-SACC1 mie is similr to tht of LIRKO mie, the mehnism of its evelopment iffers in these two moels. In L-SACC1 mie, hyperinsulinemi resulte minly from impire insulin lerne n, in turn, use seonry hepti insulin resistne, wheres in the LIRKO mouse, primry hepti insulin resistne use impire insulin lerne, insulin hyperseretion n extreme hyperinsulinemi 18. Nevertheless, neither mouse moel of hepti insulin resistne evelope ietes, supporting the notion tht itionl tissues must e involve for the evelopment of overt type 2 ietes. e Fig. 4 Hyperinsulinemi in L-SACC1 mie is ue to impire insulin lerne., Plsm insulin (i) n C-peptie (ii) levels were mesure in whole venous loo rwn etween 11:00 m n 1:00 pm from 2-mo n 8-mo ge-mthe wiltype (WT) n L-SACC1 homo mie fste overnight. Insulin lerne ws lulte s the molr rtio of C-peptie to insulin (iii). Dt represent t lest three sets of experiments with t lest 30 mie of eh genotype. Vlues re expresse s men ± s... Asterisks inite sttistilly signifint ifferene (P<0.05 y one ftor ANOVA)., Metoli lerne of [ 125 I]-insulin injete in til vein ws mesure in 8-mo WT (open squres) n L-SACC1 homo mie (lose irles). Vlues re expresse s men ± s.e.m. of the perent of the mount of plsm insulin t 7.5 min from eight mie of eh genotype., [ 125 I]-insulin internliztion in primry heptoytes erive from ge-mthe WT (open squres) n L-SACC1 mie (lose irles) ws mesure. After ining, [ 125 I]-insulin ws llowe to internlize t 37 C for 0 90 min, s inite on the horizontl xis. Internlize lign ws plotte on the vertil xis s perent of speifilly oun lign. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.. from triplite experiments rrie out on t lest three ge-mthe mie of eh genotype., Primry heptoytes erive from WT n L-SACC1 homo mie were trete with uffer (, lnes) or insulin (+, lnes) efore the leling of ell-surfe proteins with iotin. Cells were lyse n the proteins immunopreipitte with polylonl ntioies ginst mouse CEACAM1 (CC1) n the α-suunit of the insulin reeptor (IR-α) prior to nlysis y 7% SDS PAGE, immunolotting with HRP-lele streptviin n etetion y ECL. The mount of CC1 n IR-α internlize in response to insulin ws lulte s the ifferene in the mount of iotin-lele proteins efore n fter insulin tretment reltive to the mount of iotin-lele proteins in the sene of insulin (grph). Experiments were repete on t lest three mie for eh genotype. e, Insulin tolerne test. Gluose levels were mesure in venous loo from ge-mthe wiltype (WT, open squres), L-SACC1 hemi (open irles) n L-SACC1 homo (lose irles) L- mie injete i.p. with insulin (0.125 U kg 1 ) n fste overnight. Dt represent the men ± s.. of 24 mie from eh genotype. *Sttistilly signifint ifferene (P<0.05), WT versus L-SACC1 hemi. nture genetis volume 30 mrh
5 Fig. 5 Seonry insulin resistne in L-SACC1 mie., Rnom gluose levels were mesure in venous loo rwn t 10:00 m from 15 nesthetize ge-mthe mie. Dt re the men of two etermintions per mouse rrie out seven ys prt t the sme time perio. Vlues re expresse s men ± s... Asterisks enote sttistilly signifint ifferene (P<0.05) etween L-SACC1 homo mie n ontrols (WT n L- SACC1 hemi )., Gluose tolerne test. Whole-loo gluose ws etermine t min fter gluose injetion (2 mg kg 1 ) of gemthe 2 mo n 10 mo WT n L-SACC1 homo mie fste overnight. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.. for t lest 12 mie in eh group., Insulin-epenent 2-eoxy-Dgluose (2-DG) uptke ws mesure in insulin-trete (1.2 nm) isolte soleus musles from gemthe 2-mo mie tht h een fste. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.. of eight smples for eh mouse genotype.,e, Poly (A) mrna ws purifie from soleus musle () n from livers (e) of ge-mthe WT n L-SACC1 homo mie t 2 8 mo. Results re representtive of t lest four mie from eh genotype t eh ge. e Hyperinsulinemi in L-SACC1 mie i not prllel the extent of the metoli ltertion with hyperglyemi, suggesting tht itionl mehnisms unerlie insulin resistne. The ssoition of hepti insulin resistne with elevtion in FFAs n inrese viserl iposity provies potentil mehnism to explin this pprent isrepny. Our moel supports the hypothesis tht erese insulin lerne in the presene of inrese ominl iposity n irulting FFA provies n lterntive ompenstory mehnism of peripherl insulin resistne 30,31. Hypertriglyeriemi in L-SACC1 mie my t lest prtilly e ttriute to hyperinsulinemi 32 n to inrese gluoseinue e novo hepti ftty-i synthesis n lipogenesis. The inrese in plsm triglyeries my, in turn, promote elevtion in plsm FFA. For instne, it is possile tht not ll unesterifie ftty is relese from hyrolysis of triglyeries y lipoprotein lipse re trnsporte into ipoytes; some my remin lumin-orne in the loo. Bse on the Rnle yle 33,34, it is resonle to preit tht hroni stimultion of gluose uptke in musle y hronilly elevte insulin levels woul ompete with FFA uptke in musle n erese FFA oxition n lerne. We therefore hypothesize tht elevtion in plsm FFA in our moel results from inrese triglyerie relese from liver rther thn from inrese lipolysis in ipoytes. This is in greement with oservtions of unltere lipolysis with ttennt eese FFA reesterifition in the peripherl tissues of oese sujets with higher insulin onentrtions thn their len ontrols 35. Alterntively, elevte plsm FFA oul result from inrese e novo tissue lipogenesis in proportion to inrese insulin levels in L-SACC1 mie, s hs een reporte in hyperinsulinemi-euglyemi norml rts 36. Further stuies re require to sertin the nture of the isturne in ft metolism. Notly, the extent of impirment of ft metolism is isproportionte to the extent of insulin resistne. For instne, mie with primry hepti insulin resistne i not evelop elevte FFA espite hving higher insulin levels thn L-SACC1 trnsgenis 18,37. This suggests tht impirment of ft metolism in L-SACC1 mie is relte to the mehnism of their insulin resistne (tht is, seonry to impire insulin lerne rther thn primry geneti efet in insulin reeptor expression). Altere ft metolism my explin the persistene of hyperglyemi, gluose intolerne n insulin resistne in L-SACC1 mie s oppose to LIRKO mie tht regine hepti insulin sensitivity t six months of ge. The inrese in triglyerie ontent in livers of L-SACC1 trnsgenis my lso suggest tht the impirment of ft metolism is seonry to the hnge of hepti insulin sensitivity rought out y the trnsgene, n not to sustrte reistriution s, for instne, in musle-speifi insulin reeptor knokouts 38. The inrese in liver triglyeries my ontriute to hepti insulin resistne tht, in turn, my result from hyperinsulinemi. These stuies emonstrte novel mehnism y whih Fig. 6 Norml pnreti β-ell funtion in L-SACC1 homo mie. We mesure insulin seretion in response to gluose injetions in 10-mo wiltype (WT, open squres), L-SACC1 hemi (open irles) n L-SACC1 homo (open squres) mie tht h een fste. Whole loo ws rwn t inite time points from retrooritl sinuses to etermine plsm insulin level. Dt represent the verge of t lest two sets of experiments using minimum of 12 mie of eh genotype. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.e.m nture genetis volume 30 mrh 2002
6 Tle 2 Elevte levels of free ftty i n triglyeries in plsm of L-SACC1 mie Plsm free ftty is Plsm triglyeries (meq L 1 ) (mg/l) Genotype (n) 2 mo 8 mo 2 mo 8 mo WT (24) ± ± ± ± 4.34 L-SACC1 (21) ± 0.02* ± 0.05* 94.6 ± 9.73* ± 8.80* Fsting plsm FFA n triglyeries were etermine in ge-mthe mie t 2 mo n 8 mo. The numer of mie teste is inite in prentheses. All ssys were rrie out in triplite. Vlues re expresse s men ± s.e.m.. *P<0.05 versus WT mie. CEACAM1-epenent insulin signling in heptoytes is linke to regultion of hepti insulin sensitivity y moulting insulin metolism in liver. They lso provie in vivo eviene of the iret role of insulin lerne in liver in mintining rohyrte n ft homeostsis. Methos Genertion of liver-speifi S503A CEACAM1 mie (L-SACC1). We sulone the 490-p frgment 5 of the trnsltion strt site in genomi DNA of humn polipoprotein A-1 (Apo A-1) 39,40 upstrem of Cem1 DNA (from S503A rt) into n EoRI site 41 in pgem9z. We introue intron 1 of rt Cem1 etween NeI t nt 10 in exon 1 n BmHI t nt 313 in exon 2 (ref. 41). We re-sulone the NotI-exise Apo A-1/S503A Cem1 minigene in pdna3 (Fig. 1). As seen with lign-inue reeptor internliztion, ition of insulin erese surfe expression of iotinlele insulin reeptor 14 in untrnsfete SV-40 trnsforme heptoytes (UT; Fig. 1, lnes 2 versus 1). In ontrst, in heptoytes expressing the minigene, internliztion of the insulin reeptor in the presene of insulin ws inhiite (Fig. 1, lnes 4 versus 3), suggesting tht the mutnt is ominnt-negtive. We exise the promoter-minigene-polyenyltion DNA frgment n injete it into the pronulei of single-ell fertilize mouse emryos erive from C57BL/6 FVB mtings. We ientifie four F0 founers y Southern-lot nlysis of genomi DNA from HinIII/PstIigeste til n proing with [ 32 P]-lele promoter/s503a Cem1 minigene (Fig. 1) 41,42. Northern-lot nlysis on poly(a) mrna (Amion; t not shown) n western-lot nlysis using polylonl α- CEACAM1 ntioy tht ross-rets with rt n mouse proteins inite tht the rt trnsprotein ws etete t high levels in liver of trnsgeni F1 mie (Fig. 1) ut not in intestines (Fig. 1) or kineys (t not shown). Animl husnry. We re hemizygous mie (L-SACC1 hemi ) to homozygosity y rother/sister mtings. We onfirme homozygosity y quntittive Southern lot n empirilly y mting homozygous mie (L-SACC1 homo ). Animls were kept in 12-h rk light yle n fe stnr how liitum. All proeures esrie elow were pprove y the Institutionl Animl Cre n Utiliztion Committee. Phosphoryltion. We issete livers from nesthetize nimls n froze them immeitely efore lysis n prtil purifition y letin hromtogrphy 5. After rrying out insulin-inue phosphoryltion in the presene of [γ- 32 P]ATP 5, we immunopreipitte proteins with nti-iliry glyoprotein (BGP, the mouse homolog of rt CEACAM1) or nti-rt CEACAM1 ntioies n nlyze them using SDS PAGE n utoriogrphy. For insulin-reeptor n IRS-2 phosphoryltion, we rrie out the retion in the sene of [γ- 32 P]ATP, immunopreipitte proteins with monolonl ntioies ginst the IR-β suunit or IRS-2, immunolotte with ntiphosphotyrosine ntioies (α-ptyr) n etete proteins y enhne hemiluminesene (ECL; Amershm Phrmi Bioteh). Phenotypi nlysis. We mesure loo gluose levels using gluometer (Au-hek, Boehringer Mnnheim), plsm insulin n C-pepties with rioimmunossys (RIA, Lino), fsting plsm free ftty is (FFA) using the NEFA C kit (Wko) n triglyeries using the Infinity Triglyeries regent (Sigm). We etermine tissue-triglyerie ontent in homogenize tissues y extrting lipi with CHCL 3 :CH 3 OH (2:1, v:v), rying uner N 2, resuspening in ethnol, n mesuring triglyeries levels s the ifferene etween free n totl glyerol 43. Liver, musle n kiney funtions were ssye y Anlytis. Metoli lerne ssy. We fste ge-mthe 8-mo mle mie for 18 h (from 5:00 pm to 12:00 pm the next y) prior to intrvenous til vein injetion with 0.05 µg of humn reominnt [ 125 I]-insulin 44. We ollete venous loo smples (100 µl per mouse) t 7.5, 15, 60 n 90 min fter injetion, ounte 50 ml plsm n mesure resiul insulin in pm ml 1 plsm. Insulin tolerne test. We fste mie for 19 h (from 4:00 pm to 11:00 m the next y) prior to intrperitonel injetion (i.p.) with insulin (0.125 mu g 1 oy weight). We rew venous loo from the retro-oritl sinuses t 0, 30, 60 n 180 min fter insulin injetion to etermine loo gluose levels. Intrperitonel gluose tolerne test n insulin seretion. We injete mie fste overnight with gluose (2 mg kg 1 oy weight) i.p. n rew venous loo from the retro-oritl sinuses t 0, 15, 30, 60 n 120 min fter injetion to etermine gluose levels. We simultneously mesure serete insulin from β-ells in plsm t 2, 7 n 30 min. Morphometri nlysis of pnres. Pnret were setione into 5- mm 3 portions, fixe in 10% formlin-pbs (ph 7.4), ethnol-ehyrte n prffin-emee 37,45. We mounte onseutive setions on glss slies, rehyrte, permeilize in 0.1% Triton X-100 n immunostine with mouse insulin ntioies (Sigm). We systemtilly viewe setions with Nikon Optiphot-2 mirosope (Nikon) n Spot vieo mer (Dignosti Instruments) with umulting imges from eight non-overlpping fiels of mm 2. We exmine t lest three setions from three nimls per genotype for totl of 18 inepenent setions. We tre n nlyze β-ells in NIH Imge v Dt were expresse s perentge of the totl re ontining insulin-lele ells. Primry heptoytes. We isolte heptoytes y perfusing with 1 mg ml 1 ollgense in L-15 meium ontining 1 mg ml 1 gluose (Gio BRL). We plte ells t ells per well n inute t 37 C in DMEM-FBS-peniillin-streptomyin (Gio BRL). We refe ultures with DMEM fter 2-h tthment perio 46. Lign ining n internliztion. We grew primry heptoytes for 24 h prior to [ 125 I]-insulin (10 pm) ining t 4 C in uffer F (100 mm HEPES, ph 7.4, 120 mm NCl, 1.2 mm MgSO 4, 1 mm EDTA, 15 mm CH 3 COON, 10 mm gluose, 1% BSA). We remove unoun insulin n inute ells t 37 C for 0 90 min efore inuting them in 0.1% BSA-PBS (ph 3.5) for 10 min 11. We ounte the i wsh s surfe-oun, non-internlize insulin n NOH-soluilize ells s internlize ell-ssoite lign. We lulte internlize insulin s perent ell-ssoite per speifilly oun lign (the sum of surfe-oun plus ell-ssoite lign). Biotin leling of surfe memrne proteins. After inution of primry heptoytes in the sene or presene of 100 nm insulin t 37 C for 5 min, we inute ells with iotin s previously esrie 14. Following lysis in 1% Triton-X, proteins were immunopreipitte with monolonl ntioy ginst BGP (mouse homolog of rt CEACAM1), eletrophorese, immunolotte with HRP-onjugte streptviin n etete with ECL. Insulin-reeptor quntifition. We inute primry heptoytes t 37 C in triplite pltes for 24 h efore inuting t 4 C for 5 h in Buffer F supplemente with insulin (0, 1, 5, 10, 100 n 1,000 ng ml 1 ) n [ 125 I]-lele insulin (20 pm; pm ml 1 ). NOH-lyse ells were ounte n the IR numer etermine y Sthr-plot nlysis using the SCAFIT v. 4.7 progrm (Ntionl Institutes of Helth). Gluose uptke in isolte musle. As esrie previously 47,48, we remove soleus musle from hinlims of fste mie 47,48, pre-equilirte it for 1 h in oxygente Kres-Henseleit uffer ontining 2 mm pyruvte, 36 mm mnnitol n 0.1% BSA with or without 1,200 pm insulin, n inute it t 30 C t 95% O 2, 5% CO 2 for 20 min in 2-eoxy-D- nture genetis volume 30 mrh
7 [l,2-3 H]gluose (1 mm), [U- 14 C]mnnitol (39 mm) n 0.1% BSA. Musles were immeitely lotte n frozen in liqui nitrogen, n store t 80 C efore igestion, ounting n mesuring of intrellulr 2-DG umultion in nmol g wet musle 1 min 1. Sttistil proeures. We nlyze t with Sttview softwre (Aus onepts) using one-ftor ANOVA nlysis. P vlues less thn 0.05 were onsiere to e sttisilly signifint. Aknowlegments We thnk D. Aili, S.F. Previs n G.I. Shulmn for ritil reing of the mnusript n for helpful sientifi isussions, n E.M. Ruin n N. Beuhemin for proviing the polipoprotein A-1 promoter DNA n ntimouse BGP ntioies, respetively. We thnk S. Roson, E. Tietz n S. Lilly for ssistne in immunohistohemistry n mirosopy, n T. Di n R. Ruh for ssistne in primry heptoytes. We lso thnk the Ohio University Eison Biotehnology Institute Collortive Trnsgenis, Athens, Ohio for performing DNA miroinjetions s prt of their servie grnt support (to S.M.N.). This work ws hiefly supporte y two grnts from the Ntionl Institutes of Helth Ntionl Institute of Dietes & Digestive & Kiney Diseses (to S.M.N.), n prtilly y Sigm-Tu Reserh (to S.M.N.) n the Deprtment of Veterns Affirs (to S.K.E.). M.N.P. ws prtilly supporte y the Institutionl Pre-otorl Ntionl Reserh Servie Awr fellowship from the Ntionl Institutes of Helth. Competing interests sttement The uthors elre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. Reeive 30 Otoer; epte 12 Deemer Bker, J.M. et l. Insulin stimultion of phosphtiylinositol 3-kinse tivity mps to insulin reeptor regions require for enogenous sustrte phosphoryltion. J. Biol. Chem. 267, (1992). 2. Bumnn, C.A. et l. CAP efines seon signlling pthwy require for insulin-stimulte gluose trnsport. Nture 407, (2000). 3. Mthews, S.T. et l. Alph2-HSG, speifi inhiitor of insulin reeptor utophosphoryltion, interts with the insulin reeptor. Mol. Cell. Enorinol. 164, (2000). 4. Mux, B.A. & Golfine, I.D. Memrne glyoprotein PC-1 inhiition of insulin reeptor funtion ours vi iret intertion with the reeptor α-suunit. Dietes 49, (2000). 5. Njjr, S.M. et l. Insulin-stimulte phosphoryltion of reominnt pp120/ha4, n enogenous sustrte of the insulin reeptor tyrosine kinse. Biohemistry 34, (1995). 6. Cheung, P.H. et l. Cell-CAM105 isoforms with ifferent hesion funtions re oexpresse in ult rt tissues n uring liver evelopment. J. Biol. Chem. 268, (1993). 7. Hsieh, J.-T. et l. Tumor suppressive role of n nrogen-regulte epithelil ell hesion moleule (C-CAM) in prostte rinom ell revele y sense n ntisense pprohes. Cner Res. 55, (1995). 8. Luo, W., Woo, C.G., Erley, K., Hung, M.C. & Lin, S.H. Suppression of tumorigeniity of rest ner ells y n epithelil ell hesion moleule (C- CAM1): the hesion n growth suppression re meite y ifferent omins. Onogene 14, (1997). 9. Rosenerg, M. et l. The expression of mouse iliry glyoprotein, rinoemryoni ntigen-relte gene, is own-regulte in mlignnt mouse tissues. Cner Res. 53, (1993). 10. Neumier, M., Pulult, S., Chn, A., Mtthes, P. & Wgener, C. Biliry glyoprotein, potentil humn ell hesion moleule, is own-regulte in oloretl rinoms. Pro. Ntl A. Si. USA 90, (1993). 11. Li Clzi, S., Choie, C.V. & Njjr, S.M. Differentil effet of pp120 on insulin enoytosis y two vrint insulin reeptor isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. 273, E (1997). 12. Formisno, P. et l. Reeptor-meite internliztion of insulin. Potentil role of pp120/ha4, sustrte of the insulin reeptor kinse. J. Biol. Chem. 270, (1995). 13. Soni, P., Lkkis, M., Poy, M.N., Fernstrom, M.A. & Njjr, S.M. The ifferentil effets of pp120 (Cem 1) on the mitogeni tion of insulin n insulin-like growth ftor 1 re regulte y the nononserve tyrosine 1316 in the insulin reeptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, (2000). 14. Choie, C.V., Howr, M.J., Poy, M.N., Hnkin, M.H. & Njjr, S.M. Insulin stimultes pp120 enoytosis in ells o-expressing insulin reeptors. J. Biol. Chem. 273, (1998). 15. Dukworth, W.C., Bennett, R.G. & Hmel, F.G. Insulin egrtion: progress n potentil. Enor. Rev. 19, (1998). 16. Hn, E. et l. Differenes in tissue-speifi n emryoni expression of mouse Cem1 n Cem2 genes. Biohem. J. 355, (2001). 17. Chen, X., Iql, N. & Boen, G. The effets of free ftty is on gluoneogenesis n glyogenolysis in norml sujets. J. Clin. Invest. 103, (1999). 18. Mihel, M.D. et l. Loss of insulin signling in heptoytes les to severe insulin resistne n progressive hepti ysfuntion. Mol. Cell 6, (2000). 19. Njjr, S.M., Choie, C.V., Soni, P., Whitmn, C.M. & Poy, M.N. Effet of pp120 on reeptor-meite insulin enoytosis is regulte y the juxtmemrne omin of the insulin reeptor. J. Biol. Chem. 273, (1998). 20. Sveerg, J., Stroml, G., Wirth, A., Smith, U. & Bjorntorp, P. Ftty is in the portl vein of the rt regulte hepti insulin lerne. J. Clin. Invest. 88, (1991). 21. Esor, O. et l. Hepti insulin lerne inreses fter weight loss in oese hilren n olesents. Am. J. Me. Si. 317, (1999). 22. Bosello, O. et l. Moifitions of ominl ft n hepti insulin lerne uring severe lori restrition. Ann. Nutr. Met. 34, (1990). 23. Peiris, A.N., Mueller, R.A., Smith, G.A., Struve, M.F. & Kisseh, A.H. Splnhni insulin metolism in oesity. Influene of oy ft istriution. J. Clin. Invest. 78, (1986). 24. Sveerg, J., Bjorntorp, P., Smith, U. & Lonnroth, P. Free-ftty i inhiition of insulin ining, egrtion, n tion in isolte rt heptoytes. Dietes 39, (1990). 25. Hennes, M.M., Shrgo, E. & Kisseh, A.H. Reeptor n postreeptor effets of free ftty is (FFA) on heptoyte insulin ynmis. Int. J. Oes. 14, (1990). 26. Ferrnnini, E., Brrett, E.J., Bevilqu, S. & DeFronzo, R.A. Effet of ftty is on gluose proution n utiliztion in mn. J. Clin. Invest. 72, (1983). 27. Kisseh, A.H., Alfrsi, S., Ams, P.W. & Wynn, V. Role of insulin resistne in ipose tissue n liver in the pthogenesis of enogenous hypertriglyeriemi in mn. Dietologi 12, (1976). 28. Rooney, D.P. & Roertson, R.P. Hepti insulin resistne fter pnres trnsplnttion in type I ietes. Dietes 45, (1996). 29. Diem, P., Ai, M., Remon, J.B., Sutherln, D.E. & Roertson, R.P. Systemi venous ringe of pnres llogrfts s inepenent use of hyperinsulinemi in type I ieti reipients. Dietes 39, (1990). 30. Bergmn, R.N. & Aer, M. Free ftty is n pthogenesis of type 2 ietes mellitus. Trens Enorinol. Met. 11, (2000). 31. Bergmn, R.N. Non-esterifie ftty is n the liver: why is insulin serete into the portl vein? Dietologi 43, (2000). 32. Reven, G.M. & Chen, Y.D. Role of insulin in regultion of lipoprotein metolism in ietes. Dietes Met. Rev. 4, (1988). 33. Rnle, P.J., Grln, P.B., Newsholme, E.A. & Hles, C.N. The gluose ftty i yle in oesity n mturity onset ietes mellitus. Ann. NY A. Si. 131, (1965). 34. Rnle, P.J., Priestmn, D.A., Mistry, S. & Hlsll, A. Mehnisms moifying gluose oxition in ietes mellitus. Dietologi 37, S (1994). 35. Nestel, P.J., Ishikw, T. & Golrik, R.B. Diminishe plsm free ftty i lerne in oese sujets. Metolism 27, (1978). 36. Koopmns, S.J., Kushwh, R.S. & DeFronzo, R.A. Chroni physiologi hyperinsulinemi impirs suppression of plsm free ftty is n inreses e novo lipogenesis ut oes not use yslipiemi in onsious norml rts. Metolism 48, (1999). 37. Kio, Y. et l. Tissue-speifi insulin resistne in mie with omine muttions in the insulin reeptor, IRS-1, n IRS-2. J. Clin. Invest. 105, (2000). 38. Kim, J.K. et l. Reistriution of sustrtes to ipose tissue promotes oesity in mie with seletive insulin resistne in musle. J. Clin. Invest. 105, (2000). 39. Wlsh, A., Ito, Y. & Breslow, J.L. High levels of humn polipoprotein A-I in trnsgeni mie result in inrese plsm levels of smll high ensity lipoprotein (HDL) prtiles omprle to humn HDL. J. Biol. Chem. 264, (1989). 40. Bish, J.G., Simon, T.C., Goron, J.I. & Breslow, J.L. Chrteriztion of n enhner element in the humn polipoprotein C-III gene tht regultes humn polipoprotein A-I gene expression in the intestinl epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 270, (1995). 41. Njjr, S.M. et l. pp120/eto-atpse, n enogenous sustrte of the insulin reeptor tyrosine kinse, is expresse s two vrily splie isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 268, (1993). 42. Njjr, S.M. et l. Cloning n hrteriztion of funtionl promoter of the rt pp120 gene, enoing sustrte of the insulin reeptor tyrosine kinse. J. Biol. Chem. 271, (1996). 43. Folh, J., Lees, M. & Slone-Stnley, G.H. A simple metho for the isoltion n purifition of totl lipis from niml tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, (1957). 44. Monon, C.E., Olefsky, J.M., Dolks, C.B. & Reven, G.M. Removl of insulin y perfuse rt liver: effet of onentrtion. Metolism 24, (1975). 45. Cinti, S., Eerh, S., Cstellui, M. & Aili, D. Lk of insulin reeptors ffets the formtion of white ipose tissue in mie. A morphologil n ultrstruturl nlysis. Dietologi 41, (1998). 46. Ruh, R.J. & Klunig, J.E. Kinetis of phenoritl inhiition of interellulr ommunition in mouse heptoytes. Cner Res. 48, (1988). 47. Lee, A.D., Gulve, E.A., Chen, M., Shluter, J. & Holloszy, J.O. Effets of C2+ ionophore ionomyin on insulin-stimulte n sl gluose trnsport in musle. Am. J. Physiol. 268, R (1995). 48. Lee, C.H. et l. Nk ssoites with the SH2 omin-oking protein IRS-1 in insulin-stimulte ells. Pro. Ntl A. Si. USA 90, (1993). 276 nture genetis volume 30 mrh 2002
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
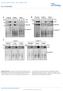
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
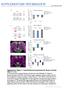
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
c-abl inhibition mitigates diet-induced obesity through improving insulin sensitivity of subcutaneous fat in mice
 Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
Dietologi (7) :9 9 DOI.7/s--- ARTICLE -Al inhiition mitigtes iet-inue oesity through improving insulin sensitivity of suutneous ft in mie Rong Wu, & Jin-gung Sun, & Ji-qiu Wng & Binhu Li & Qingsong Liu
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
b-sitosterol activates Fas signaling in human breast cancer cells
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
ARTICLE IN PRESS Phytomeiine 14 (2007) 747 754 www.elsevier.e/phyme -Sitosterol tivtes Fs signling in humn rest ner ells A.B. Aw,, M. Chinnm, C.S. Fink, P.G. Brfor Deprtment of Exerise n Nutrition Sienes
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Transcription factor Ets-1 links glucotoxicity to pancreatic beta cell dysfunction through inhibiting PDX-1 expression in rodent models
 Dietologi () 9: DOI.7/s ARTICLE Trnsription ftor Ets links gluotoxiity to pnreti et ell ysfuntion through inhiiting PDX expression in roent moels Fng Chen & Min Sh & Ynyng Wng & Tijun Wu & Wei Shn & Ji
Dietologi () 9: DOI.7/s ARTICLE Trnsription ftor Ets links gluotoxiity to pnreti et ell ysfuntion through inhiiting PDX expression in roent moels Fng Chen & Min Sh & Ynyng Wng & Tijun Wu & Wei Shn & Ji
Parathyroid hormone related peptide is a naturally occurring, protein kinase A dependent angiogenesis inhibitor
 Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
Prthyroi hormone relte peptie is nturlly ourring, protein kinse A epenent ngiogenesis inhiitor MANJIRI M. BAKRE 1, YUHONG ZHU 1, HONG YIN 1, DOUG W. BURTON 2, ROBERT TERKELTAUB 2, LEONARD J. DEFTOS 2 &
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Inhibition of Dexamethasone-induced Fatty Liver Development by Reducing mir-17-5p Levels
 originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
originl rtile Inhiition of Dexmethsone-inue Ftty Liver Development y Reuing -5p Levels Willim W Du,, Fengqiong Liu 3, Sze Wn Shn,, Xini Ciny M,, Shn Gupt,, Tinru Jin 4, Dvi Spner, Sergey N Krylov 5, You
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
ARTICLE. Keywords AMPK. Cholesterol. Insulin resistance. Intestine. Isoflavones. Liver. LXRα. LXRβ. Mice. Soy protein
 Dietologi () 55:469 478 DOI.7/s5--599-9 ARTICLE Soy protein isoflvones ifferentilly regulte liver X reeptor isoforms to moulte lipi metolism n holesterol trnsport in the liver n intestine in mie M. González-Grnillo
Dietologi () 55:469 478 DOI.7/s5--599-9 ARTICLE Soy protein isoflvones ifferentilly regulte liver X reeptor isoforms to moulte lipi metolism n holesterol trnsport in the liver n intestine in mie M. González-Grnillo
Macrophage mtorc1 disruption reduces inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice
 Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
Dietologi (1) 7:393 DOI 1.17/s-1-33- ARTICLE Mrophge mtorc1 isruption reues inflmmtion n insulin resistne in oese mie Hongfeng Jing & Mrit Westerterp & Chunjiong Wng & Yi Zhu & Ding Ai Reeive: 1 April
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
DOI:./n BJ RAS:ER Herrnz et l Supplementry Figure HFFF RAS:ER.. mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF mrna Expression..... ILα ILβ IL IL CCL INH VEGF + OHT Torin NVP-BEZ + OHT shmtor. shmtor.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Original article HIV-1 Tat protein impairs adipogenesis and induces the expression and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in human SGBS adipocytes
 Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
Antivirl Therpy 2012; 17:529 540 (oi: 10.3851/IMP2021) Originl rtile HIV-1 Tt protein impirs ipogenesis n inues the expression n seretion of proinflmmtory ytokines in humn SGBS ipoytes Juliet Díz-Delfín
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Opposite metabolic response to fenofibrate treatment in pregnant and virgin rats
 Opposite metoli response to fenofirte tretment in pregnnt n virgin rts An Sori, Crlos Boos, n Emilio Herrer 1 Fult e Cienis Experimentles y e l Slu, Universi Sn Plo-CEU, Ctr. Boill el Monte km 5,300, E-28668
Opposite metoli response to fenofirte tretment in pregnnt n virgin rts An Sori, Crlos Boos, n Emilio Herrer 1 Fult e Cienis Experimentles y e l Slu, Universi Sn Plo-CEU, Ctr. Boill el Monte km 5,300, E-28668
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. p53 locus. Targeting vector DTA LSL. Targeted allele
 Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Vol 445 8 Ferury 27 oi:1.138/nture5541 Restortion of funtion les to tumour regression in vivo Anre Ventur 1, Dvi G. Kirsh 1,2, Mrgret E. MLughlin 1, Dvi A. Tuveson 1, Jn Grimm 3, Lur Lintult 1, Jmie Newmn
Role of the EGF receptor in PPARγ-mediated sodium and water transport in human proximal tubule cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:1174 1182 DOI 1.17/s125-13-2835-y ARTICLE Role of the EGF reeptor in PPARγ-meite soium n wter trnsport in humn proximl tuule ells S. S & J. Zhng & R. Yong & D. Yghoin & M. G. Wong &
Dietologi (213) 56:1174 1182 DOI 1.17/s125-13-2835-y ARTICLE Role of the EGF reeptor in PPARγ-meite soium n wter trnsport in humn proximl tuule ells S. S & J. Zhng & R. Yong & D. Yghoin & M. G. Wong &
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Beneficial Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training Combined with Rosiglitazone on Glucose Metabolism in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
 Originl Artile Oesity n Metoli Synrome Dietes Met J 217;41:474-485 https://oi.org/1.493/mj.217.41.6.474 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Benefiil Effets of Aeroi Exerise Trining
Originl Artile Oesity n Metoli Synrome Dietes Met J 217;41:474-485 https://oi.org/1.493/mj.217.41.6.474 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Benefiil Effets of Aeroi Exerise Trining
Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters
 Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
Len, ut not oese, ft is enrihe for unique popultion of regultory T ells tht ffet metoli prmeters Mrkus Feuerer,5, Lur Herrero 2,5, Dniel Cipollett,4,5, Afi Nz 2, Jmie Wong,5, Ali Nyer 2, Jongsoon Lee 2,
BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Effect of age and moderate food restriction on insulin sensitivity in Wistar rats: role of adiposity
 131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
131 Effet of ge nd moderte food restrition on insulin sensitivity in Wistr rts: role of diposity Fernndo Esrivá, M Luí Gvete, Ysmín Fermín 1, Corli Pérez 1, Nild Gllrdo 2, Crmen Alvrez, Antonio Andrés
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
 Vol 457 26 Ferury 29 oi:1.138/nture7617 Deficiency of -rrestin-2 signl complex contriutes to insulin resistnce Bing Lun 1, Jin Zho 1, Hiy Wu 3, Boyu Dun 1, Gungwen Shu 1, Xioying Wng 4, Dngsheng Li 2,
Vol 457 26 Ferury 29 oi:1.138/nture7617 Deficiency of -rrestin-2 signl complex contriutes to insulin resistnce Bing Lun 1, Jin Zho 1, Hiy Wu 3, Boyu Dun 1, Gungwen Shu 1, Xioying Wng 4, Dngsheng Li 2,
Methyl-β-cyclodextrin alters adipokine gene expression and glucose metabolism in swine adipose tissue*
 University of Nebrsk - Linoln DigitlCommons@University of Nebrsk - Linoln Publitions from USDA-ARS / UNL Fulty U.S. Deprtment of Agriulture: Agriulturl Reserh Servie, Linoln, Nebrsk 213 Methyl-β-yloextrin
University of Nebrsk - Linoln DigitlCommons@University of Nebrsk - Linoln Publitions from USDA-ARS / UNL Fulty U.S. Deprtment of Agriulture: Agriulturl Reserh Servie, Linoln, Nebrsk 213 Methyl-β-yloextrin
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Torenia concolor Lindley var. formosana Yamazaki extracts improve inflammatory response and lipid accumulation via PPARs activation
 BioMeiine (ISSN 2211-8039) Septemer 2017, Vol. 7, No. 3, Artile 18 Pges 29-36 DOI: 10.1051/mn/2017070318 Originl rtile Toreni onolor Linley vr. formosn Ymzki extrts improve inflmmtory response n lipi umultion
BioMeiine (ISSN 2211-8039) Septemer 2017, Vol. 7, No. 3, Artile 18 Pges 29-36 DOI: 10.1051/mn/2017070318 Originl rtile Toreni onolor Linley vr. formosn Ymzki extrts improve inflmmtory response n lipi umultion
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor
 Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Brin-erive neurotrophi ftor regultes energy lne ownstrem of melnoortin-4 reeptor Boji Xu 1,5,Evn H Gouling 2,Keling Zng 1,Dvi Cepoi 3,Roger D Cone 3,Kevin R Jones 4,Lurene H Teott 2 & Louis F Reihrt 1
Farnesoid X receptor inhibits glucagon-like peptide-1 production by enteroendocrine L cells
 Reeive 27 Mr 215 Aepte 25 My 215 Pulishe 2 Jul 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8629 Frnesoi X reeptor inhiits glugon-like peptie-1 proution y enteroenorine L ells Mohme-Smi Trelsi 1,2,3,4, Mehi Doui 1,2,3,4, Jnne
Reeive 27 Mr 215 Aepte 25 My 215 Pulishe 2 Jul 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8629 Frnesoi X reeptor inhiits glugon-like peptie-1 proution y enteroenorine L ells Mohme-Smi Trelsi 1,2,3,4, Mehi Doui 1,2,3,4, Jnne
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
INTRODUCTION. Ji-Hye Lee 1, Seon-Mi Yu 1, Eun-Kyung Yoon, Won-Kil Lee, Jae-Chang Jung*, Song-Ja Kim
 J Koren Me Si 27; 22: 89-7 ISSN -8934 Copyright The Koren emy of Meil Sienes 2,4 5-Deoxy- -ProstglninJ2 Regultes Deifferentition through Peroxisome Prolifertor-tivte Reeptor- -Depenent Pthwy ut Not Expression
J Koren Me Si 27; 22: 89-7 ISSN -8934 Copyright The Koren emy of Meil Sienes 2,4 5-Deoxy- -ProstglninJ2 Regultes Deifferentition through Peroxisome Prolifertor-tivte Reeptor- -Depenent Pthwy ut Not Expression
ER-α36 mediates cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells through EGFR/HER-2/ ERK signaling pathway
 Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
Zhu et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (218) 37:123 https://oi.org/1.1186/s134618798z RESEARCH Open Aess ERα36 meites ispltin resistne in rest ner ells through /HER2/ signling pthwy Linlin
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pancreatitis in obese mice
 Artile Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pnretitis in oese mie Mri Pini,* Dvin H. Rhoes,* Krl J. Cstellnos,* Anrew R. Hll, Roert J. Cy, Rohini Chennuri, Eileen F. Gry, n Gimil Fntuzzi*, Deprtments of *Kinesiology
Artile Role of IL-6 in the resolution of pnretitis in oese mie Mri Pini,* Dvin H. Rhoes,* Krl J. Cstellnos,* Anrew R. Hll, Roert J. Cy, Rohini Chennuri, Eileen F. Gry, n Gimil Fntuzzi*, Deprtments of *Kinesiology
Peroxiredoxin 1 has an anti-apoptotic role via apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and p38 activation in mouse models with oral precancerous lesions
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 12: 413-420, 2016 Peroxireoxin 1 hs n nti-poptoti role vi poptosis signl-regulting kinse 1 n p38 tivtion in mouse moels with orl prenerous lesions JIANFEI ZHANG, XINYING JING, WENWEN NIU,
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 12: 413-420, 2016 Peroxireoxin 1 hs n nti-poptoti role vi poptosis signl-regulting kinse 1 n p38 tivtion in mouse moels with orl prenerous lesions JIANFEI ZHANG, XINYING JING, WENWEN NIU,
Regulation of NKT cell-mediated immune responses to tumours and liver inflammation by mitochondrial PGAM5-Drp1 signalling
 Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
Reeive Mr Aepte Aug Publishe 8 Sep DOI:.8/nomms97 Regultion of NKT ell-meite immune responses to tumours n liver inflmmtion by mitohonril PGAM-Drp signlling Young Jun Kng, Bo-Rm Bng, Kyung Ho Hn, Lixin
Capsid-specific T-cell Responses to Natural Infections With Adeno-associated Viruses in Humans Differ From Those of Nonhuman Primates
 originl rtile See pge 1923 Cpsi-speifi T-ell Responses to Nturl Infetions With Aeno-ssoite Viruses in Humns Differ From Those of Nonhumn Primtes Hu Li 1, Mrio O Lsro 1, Bei Ji 1,2, Shih Wen Lin 1,3, Lriss
originl rtile See pge 1923 Cpsi-speifi T-ell Responses to Nturl Infetions With Aeno-ssoite Viruses in Humns Differ From Those of Nonhumn Primtes Hu Li 1, Mrio O Lsro 1, Bei Ji 1,2, Shih Wen Lin 1,3, Lriss
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Hydrodynamic Delivery of mil10 Gene Protects Mice From High-fat Diet-induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Hydrodynmi Delivery of mil Gene Protets Mie From High-ft Diet-indued Oesity nd Gluose Intolerne Mingming Go, Chuno Zhng, Yongjie M, Le Bu, Linn Yn
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Allergology Interntionl. ;6:8-9 DOI:. llergolint.-oa-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elevte Serum IgE ginst MGL_ in Ptients with Atopi Dermtitis n Cholinergi Urtiri Mkiko Hirgun, Tkki Hirgun,KoriIshii, Hienori Suzuki,,
Allergology Interntionl. ;6:8-9 DOI:. llergolint.-oa-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Elevte Serum IgE ginst MGL_ in Ptients with Atopi Dermtitis n Cholinergi Urtiri Mkiko Hirgun, Tkki Hirgun,KoriIshii, Hienori Suzuki,,
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Lethal graft-versus-host disease in mouse models of T cell receptor gene therapy
 r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
r t i l e s Lethl grft-versus-host isese in mouse moels of T ell reeptor gene therpy Gvin M Benle,6, Crsten Linnemnn,6, Ann I Hooijks, Lur Bies, Moniek A e Witte, Annelies Jorritsm, Anrew D M Kiser, Nine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha Therapy in Crohn s Disease: Clinical and Health Economic Aspects
 Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-α Therpy in Crohn s Disese Anti-Tumour Nerosis Ftor-lph Therpy in Crohn s Disese: Clinil n Helth Eonomi Aspets Fion MGuire, 5th yer Meiine ABSTRACT Ojetives: Crohn s isese is hroni,
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Alternative rapamycin treatment regimens mitigate the impact of rapamycin on glucose homeostasis and the immune system.
 Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Aging Cell (216) 15, pp28 38 Doi: 1.1111/el.1245 Alterntive rpmyin tretment regimens mitigte the impt of rpmyin on gluose homeostsis nd the immune system Aging Cell Sestin I. Arriol Apelo, 1,2 Joshu C.
Serum mir-21 may be a Potential Diagnostic Biomarker for Diabetic Nephropathy
 417 Serum mir-21 my e Potentil Dignosti Biomrker for Dieti Nephropthy Authors J. Wng 1, L. Dun 2, L. Tin 1, J. Liu 1, S. Wng 3, Y. Go 4, J. Yng 5 Affilitions Affilition resses re liste t the en of the
417 Serum mir-21 my e Potentil Dignosti Biomrker for Dieti Nephropthy Authors J. Wng 1, L. Dun 2, L. Tin 1, J. Liu 1, S. Wng 3, Y. Go 4, J. Yng 5 Affilitions Affilition resses re liste t the en of the
Supplemental Figures and Legends
 Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Supplementl Figures n Legens Epigeneti trgeting of Hegehog trnsriptionl output through BET romoomin inhiition Yujie Tng 1,2, Shrreh Gholmin 2, Simone Shuert 1,2, Mine I. Willrson 3, Alex Lee 4, Prtiti
Docosapentaenoic Acid (22:5n-3) Downregulates mrna Expression of Pro-inflammatory Factors in LPS-activated Murine Macrophage Like RAW264.
 Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 217 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety oi : 1.565/jos.ess17111 Doospentenoi Ai (22:5n-3) Downregultes mrna Expression of Pro-inflmmtory Ftors in LPS-tivte Murine Mrophge Like RAW264.7
Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 217 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety oi : 1.565/jos.ess17111 Doospentenoi Ai (22:5n-3) Downregultes mrna Expression of Pro-inflmmtory Ftors in LPS-tivte Murine Mrophge Like RAW264.7
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Systemic delivery of genes to striated muscles using adeno-associated viral vectors
 24 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturemeiine Systemi elivery of genes to strite musles using eno-ssoite virl vetors Pul Gregorevi,4,Mihel J Blnkinship,4,Jmes M Allen 2,Roert W Crwfor,Leonr Meuse,
24 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturemeiine Systemi elivery of genes to strite musles using eno-ssoite virl vetors Pul Gregorevi,4,Mihel J Blnkinship,4,Jmes M Allen 2,Roert W Crwfor,Leonr Meuse,
Pellino3 targets the IRF7 pathway and facilitates autoregulation of TLR3- and viral-induced expression of type I interferons
 Pellino3 trgets the pthwy n filittes utoregultion of TLR3- n virl-inue expression of type I interferons Jku Sienienko 1,, Ruihri Jkson 1,, Mrk Mellett 1,, Nezir Delgi 1, Shuo Yng 1, Bingwei Wng 1, Lis
Pellino3 trgets the pthwy n filittes utoregultion of TLR3- n virl-inue expression of type I interferons Jku Sienienko 1,, Ruihri Jkson 1,, Mrk Mellett 1,, Nezir Delgi 1, Shuo Yng 1, Bingwei Wng 1, Lis
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
 nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
 Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Increasing the usage level of corn and distillers grains in market turkey diets through the use of supplemental amino acids
 Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
Inresing the usge level of orn n istillers grins in mrket turkey iets through the use of supplementl mino is August 014 By: Sny Noll University of Minnesot Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... INTRODUCTION...
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Hyun-Suk Ko, 1 Hyo-Jeong Lee, 1 Hyo-Jung Lee, 1,2 Eun Jung Sohn, 1 Miyong Yun, 1 Min-Ho Lee, 3 and Sung-Hoon Kim 1. 1.
 Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume 13, Artile ID 94737, 1 pges http://x.oi.org/1.1155/13/94737 Reserh Artile Essentil Oil of Pinus koriensis Exerts Antioesi n Hypolipiemi Ativity vi Inhiition
Eviene-Bse Complementry n Alterntive Meiine Volume 13, Artile ID 94737, 1 pges http://x.oi.org/1.1155/13/94737 Reserh Artile Essentil Oil of Pinus koriensis Exerts Antioesi n Hypolipiemi Ativity vi Inhiition
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Regular Paper. Introduction
 Regulr Pper Serotonin, Tryptophn-Derive Signl Conserve in Plnts n Animls, Regultes Root System Arhiteture Proly Ating s Nturl Auxin Inhiitor in Ariopsis thlin Rmón Pelgio-Flores, Rny Ortíz-Cstro, Alfonso
Regulr Pper Serotonin, Tryptophn-Derive Signl Conserve in Plnts n Animls, Regultes Root System Arhiteture Proly Ating s Nturl Auxin Inhiitor in Ariopsis thlin Rmón Pelgio-Flores, Rny Ortíz-Cstro, Alfonso
Endogenous GIP ameliorates impairment of insulin secretion in proglucagon-deficient mice under moderate beta cell damage induced by streptozotocin
 Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
