Original Article Overexpression of chromosome kinesin protein KIF4A enhance cisplatin resistance in A549/DDP cells
|
|
|
- James O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article Overexpression of chromosome kinesin protein KIF4A enhance cisplatin resistance in A549/DDP cells Ning Xiao 1*, Chenghua Fu 2*, Yani Lin 3, Zhixiong Dong 2, Lina Pan 2, Weiwen Chen 3, Jian Zhao 1 1 Department of Thoracic Surgery, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China; 2 College of Life Science/Tianjin Key Laboratory of Cyto-Genetical and Molecular Regulation, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin, China; 3 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China. * Equal contributors. Received December 9, 2015; Accepted February 18, 2016; Epub March 1, 2016; Published March 15, 2016 Abstract: Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is the most effective method for treating lung cancer currently; however, cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells has become a major obstacle to the successful treatment of lung cancer. The specific molecular mechanism of drug-resistant in lung cancer cells remains unclear. So we applied the A549 lung cancer cell line and cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP lung cancer cell line to study the possible molecular mechanism of drug-resistance in lung cancer cells in this study. By RT-PCR and Western blot assays, we found the expression of chromosome kinesin coding gene KIF4A was significantly higher in A549/DDP cells than in A549 cells, both at mrna level and protein level. Then, KIFA4 overexpressed A549 cells and endogenous KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells were correspondingly constructed by cell transfection or RNAi technology, then treated by cisplatin, and changes of cell proliferation and DNA damage in these cells were detected by MTT assay and γh2ax detection. Results showed that after cisplatin treatment, cell proliferation capacity was not significantly decreased and DNA damage was decreased in the KIF4A overexpressed A549 cells, while cell proliferation capacity reduced significantly and DNA damage occurred apparently in KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells. Our research indicates that KIF4A may be involved in the regulatory process of cisplatin resistance in A549 lung cancer cells, and could be used as a new biological target for treatment of cisplatin resistant lung cancer. Keywords: KIF4A, cisplatin resistance, enhance, A549/DDP cells Introduction Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers and has the highest mortality rate in the world, causing about 13 million deaths every year [1-3]. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of all lung cancers [1-3]. Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is considered as the most effective treatment for lung cancer [4]. In cancer cells, cisplatin can induce DNA damage through intra- and inter-chain crosslinking with DNA, leading to tumor cell death, to achieve the therapeutic purposes [5-7]. However, the cisplatin-resistant lung cancers act as the main obstacle to the successful treatment of lung cancers [8, 9]. Therefore, it is extremely urgent to study the mechanism of drug resistance in lung cancer. Kinesin superfamily proteins are molecular motor proteins, which can do directional movement along microtubules [10]. KIFs family proteins play important roles in intracellular transport processes, and are very necessary in mitosis and maintaining cell morphology [10]. Chromosome kinesin KIF4A is a multifunctional protein, which is involved in intracellular material transport, cell mitosis regulation, DNA repair, immune cell activation and development of the nervous system [11-16]. KIF4A has been reported to closely relate to the development of a variety of tumors [17, 18], especially in lung cancer tissues. KIF4A mrna and protein are highly expressed in lung cancer cells, meanwhile inhibiting the expression of KIF4A result in reduced growth and invasive ability in lung cancer cells, indicating that KIF4A plays a key role in the processes of cell growth and proliferation in cancer cells [19, 20]. However, it remains unclear whether KIF4A is associated with drug resistance in lung cancer cells.
2 Our pilot experiment found that after cisplatin treatment, there was apparent DNA damage in KIF4A low-expressed A549 lung cancer cells, but not in KIF4A high-expressed A549 lung cancer cells. We further explored the role of KIF4A in the processes of drug resistant in lung cancer cells. We found the chemosensitivity to cisplatin was reduced in KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells, while increased in KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells. These results suggest that KIF4A may be use as a new biological target for treatment of cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells. Materials and methods Cell lines, plasmids and reagents A549 and A549/DDP cell lines kept in our laboratory. They were cultured in RPMI-1640 culture medium supplemented with 10% FBS, and incubated at 37 C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO 2. The pegfp-c1 and pegfp-kif4a plasmids were laboratory self-prepared. Lipofectamine 2000 purchased from Invitrogen Inc. (Invitrogen Co., Carlsbad, CA, USA) and cisplatin purchased from Sigma (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA). Rabbit anti-kif4a antibody was laboratory self-prepared. Rabbit anti-gfp antibody, mouse anti-tubulin antibody, mouse anti-γh2ax, and rabbit anti-h2ax antibody were purchased from Sigma. All the secondary antibodies purchased from Jackson Immuno- Research Inc (West Grove, PA, USA). Western blot Cell lysates were prepared with 50 mmol/l Tris-HCl (ph 8.0), 150 mmol/l NaCl, 0.5% NP-40, 0.5% dexycholate-na, and 0.1% SDS plus protease inhibitor cocktail from Sigma Inc. Equal amounts of cell lysis samples were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE for Western Blot analysis. The primary antibodies, including purified anti-kif4a antibody (1:1000), anti-gfp antibody, anti-γh2ax antibody, and anti-h2ax antibody, were used for detecting the expression of endogenous KIF4A, over-expressed GFP-KIF4A, endogenous γh2ax, and endogenous H2AX respectively. Tubulin antibody for detecting the expression of endogenous tubulin was used as an internal reference. Secondary antibodies were HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse antibodies (1:10000). Che- miluminescence was used for color development. Immunofluorescence staining Immunofluorescence staining experiment was performed as follows. Cells were fixed by formalin fixative solution (PBS buffer supplemented with 3% formaldehyde and 2% sucrose) for 15 minutes. After blocking by goat serum (PBS buffer supplemented with 10% goat serum and 0.4% Triton X-100) for 30 minutes, cells were incubated with the primary antibodies, including anti-γh2ax antibody, anti-kif4a antibody, anti-gfp antibody and anti-tubulin antibody, for 2 hours at room temperature. Then cells were incubated with Texas Red-labeled goat secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature in the dark. Finally, cells were incubated with DAPI for DNA staining for 3 minutes at room temperature in the dark. MTT A549 and A549-DDP cells were seed in a 96-well tissue culture plates at 5000 cells/ well, and cultured in RPMI-1640 medium. MTT analysis was performed after incubation for 0 day, 2 days and 4 days. For MTT assay, 20 µl of MTT (5 mg/ml) was added to each well and incubated for 4 h. After carefully removing the medium, 200 μl DMSO was added to each well. After 30 minutes, the absorbance value of each well was read at a wavelength of 570 nm on a microplate reader (BIO-RAD680, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), and cell proliferation curve was drawn according to the absorbance value. All these assays were performed independently in triplicate. RT-PCR Total RNA was extracted by Trizol according to the manufacturer s protocol. Then 2 μg RNA was reverse transcribed into cdna. The cdna was used as a template for PCR to detect the expression of KIF4A in A549 cells and A549/ DDP cells. The expression of β-actin was set as an internal control. The primer sequences were as follows: β-actin: sense primer 5 -TCGTGCGTGACATTAA- GGAG-3 ; Antisense primer 5 -ATGCCAGGGT- ACATGGTGGT-3 ; KIF4A: sense primer 5 -TGAA- CTCCCAGTCGTCC-3 ; Antisense primer 5 -GC- ACTGATTACATTTCCC Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
3 Figure 1. KIF4A is overexpressed in A549/DDP cells. A. MTT analysis was performed to detect cell survival of A549 cells and A549/DDP cells after treatment with DDP. Compared with 0 h, *P < B. Western blot was conducted to analyze expression of KIF4A in A549 and A549/DDP cells by using specific anti-kif4a antibody. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. C. RT-PCR was performed to detect the mrna expression level of KIF4A in A549 and A549/DDP cells. Actin was used as a control. Statistical analysis All data were analyzed using SPSS 17.0 software package (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). All values were expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD) from at least three independent experiments, and statistical significance was defined as P < Results Chromosome kinesin molecule KIF4A is highly expressed in A549/DDP cells Kinesin molecule KIF4A is closely related to the development of lung cancer [20], but the relationship between KIF4A and drug resistance in lung cancer remains unclear. In order to study the correlation between KIF4A and drug resistance in lung cancer cells, A549 lung cancer cells and cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP lung cancer cells were applied. The chemosensitivity to cisplatin drugs was detected by MTT assay. After treatment by different concentrations of cisplatin, the relative survival rates of A549 cells and A549/DDP cells at 48 h and 96 h were detected. Results showed that the A549 cells were more sensitive to cisplatin in time gradient and concentration gradient with respect to A549/DDP cells (Figure 1A). On this basis, the mrna and protein levels of KIF4A gene in A549 and A549/DDP cells were further examined. The mrna and protein of KIF4A were analyzed by RT-PCR and Western blot assay, respectively. As shown in Figure 1B and 1C, both the mrna level and protein level of KIF4A were higher in cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP lung cancer cells than in A549 lung cancer cells, and the corresponding ratio was 7.4 and 2.3 times. These results indicate that the chromosomal kinesin molecule KIF4A may be involved in the regulation the chemosensitivity of A549 lung cancer cells to cisplatin. Chromosome kinesin KIF4A decreases the chemosensitivity of A549/DDP lung cancer cells to cisplatin The chromosome kinesin molecule KIF4A expressed at a very high level in cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP lung cancer cells suggests that KIF4A may be involved in the regulation of cell resistant to cisplatin in lung cancer cells. In order to study the role of KIF4A in the process of resistant to cisplatin, cell transfection was applied for over expressing exogenous KIF4A in A549 cells, and RNAi technology was also applied for interfering the expression of endogenous KIF4A in A549/DDP cells. Then changes in cell growth and proliferation were studied Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
4 Figure 2. KIF4A overexpression in A549 cells and KIF4A expression interfered in A549/DDP cells reverses the chemosensitivity to cisplatin respectively. A. A549 cells grown in a 6-well plate were transfected with 1000 ng of pegfp-c1, or pegfp-kif4a. Twenty-four hours later, cells were lysed, and the lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-kif4a and anti-tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as a loading control. B. MTT analysis of the chemosensitivity to cisplatin in pegfp-c1 or pegfp-kif4a overexpressed A549 cells. C. A549/DDP cells grown in a 6-well plate were transfected with 1000 ng of NS Si RNA, or KIF4A Si RNA. After 36 hours, cells were lysed, and the lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-kif4a and anti-tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as a loading control. D. MTT analysis of the chemosensitivity to cisplatin in NS Si RNA or KIF4A Si RNA transfected A549/DDP cells. By MTT assay, we found that after treated with different concentrations of cisplatin for 48 hours, the cell proliferation capacity was significantly decreased with increasing of cisplatin concentration in GFP over-expressed A549 cells. However, at the same treatment concentration of cisplatin, the cell proliferation capacity was far higher in GFP-KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells than in control A549 cells (Figure 2A and 2B). These results suggested that GFP- KIF4A over expression reduced the chemosensitivity of A549 lung cancer cells to cisplatin. Then, we examined the chemosensitivity of KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells to cisplatin. Results showed that under the high concentrations of cisplatin treatment, compared with that in the nonsense sirna transfected A549/DDP cells, the expression of KIF4A was significantly reduced and the cell proliferation capacity was also significantly decreased in KIF4A sirna transfected A549/DDP cells (Figure 2C and 2D). These results indicate that decreasing the expression of KIF4A in A549/ DDP cells would enhance the chemosensitivity of the cells to cisplatin drugs. Chromosome kinesin KIF4A inhibits the DNA damage of A549/DDP cells induced by cisplatin The chemotherapy cisplatin achieves the purpose of killing tumor cells by inducing DNA dam Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
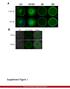
5 Figure 3. DDP induced DNA Damage in A549 cells not A549/DDP cells. A. Western blotting analysis of γh2ax expression level after DDP treatment in A549 and A549/DDP cells. A549 and A549/DDP cells were treated with DDP for 16 h, and then cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-kif4a, anti-γh2ax or anti-h2ax antibodies. α-tubulin was used as a loading control. B. Immunostaining analysis of γh2ax expression level after DDP 3335 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
6 treatment in A549 and A549/DDP cells. A549 and A549/DDP cells were treated by DDP for 16 h, and then the cells were fixed for immunostaining analysis with mouse anti-γh2ax antibody. DNA was labeled with DAPI. Representative images were shown. The scale bar represents 5 μm. age through DNA cross-linking [6]. When DNA damage occurs, the histone H2AX in the injury site will be phosphorylated to γh2ax, which clusters at the injury site (foci). Therefore, the expression level and intracellular localization of γh2ax is a sign of DNA damage. As results of Western blot and immunofluorescence staining assays shown (Figure 3A and 3B), after treated with 1 μg/ul cisplatin for 16 hours, the expression level of γh2ax was significantly increased in A549 cells, and γh2ax clustered in the nucleus. These results indicate that there is apparent DNA damage occurred in the cells. Instead, there was no apparent γh2ax expression and nucleus cluster in A549/DDP cells under the condition of 1 μg/ul cisplatin drug treatment (Figure 3A and 3B). In order to study whether KIF4A was involved in the drug resistant of lung cancer cells, GFP or GFP-KIF4A was overexpressed in A549 cells, then the cells were treated with cisplatin for 16 h, and the changes of γh2ax were detected by Western blot and immunofluorescence staining assay. Western blot results showed after cisplatin treatment, unlike that in the GFP overexpressed A549 cells, intracellular γh2ax expression level was not significantly increased in GFP-KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells (Figure 4A). Results of immunofluorescence staining assay also showed that after cisplatin treatment, the amounts of γh2ax staining foci were significantly reduced in KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells relative to the control cells (Figure 4C). These results indicated that no obvious DNA damage was observed after treated with cisplatin in GFP-KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells. Subsequently, intracellular expression levels and localization of γh2ax were compared between nonsense sirna transfected and KIF4A sirna transfected A549/DDP cells after cisplatin treatment. Different from that in the nonsense sirna transfected A549/DDP cells, γh- 2AX was significantly up-regulated and clustered in the nucleus of KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells (Figure 4B and 4D). This suggested that reduced expression of KIF4A in A549/DDP cells resulted in significant DNA damage after cisplatin treatment. All these re- sults indicate that chromosomal kinesin molecule KIF4A can inhibit the DNA damage of A549 or A549/DDP cells induced by cisplatin. Discussion Although there are a large number of studies focused on lung cancer, lung cancer remains as one of the most common cancers with the highest mortality rate in the world [3]. Resistance to antitumor drugs becomes one of the important factors for the death of lung cancer patients [21]. In order to investigate the mechanism of drug resistance in lung cancer, we discussed the key role of chromosome kinesin molecule KIF4A in cisplatin resistance in lung cancer. It has been reported that kinesin molecule KIF4A were highly expressed in most lung cancer cells and clinical samples [20], while KIF4A was barely detectable in A549 cells. In our study, we also found that KIF4A was barely detectable in A549 cells, while obviously expressed in cisplatin-resistant A549/DDP cells. Meanwhile by MTT assays, we found the chemosensitivity to cisplatin was decreased in KI- F4A over-expressed A549 cells while increased in KIF4A expression interfered A549/DDP cells. Moreover, after cisplatin treatment, the amounts of DNA damage were fewer in KIF4A over-expressed A549 cells than controls, while much more in KIF4A expression interfered in A549/DDP cells. Thus, chromosomal kinesin molecule KIF4A reduced the chemosensitivity of A549 and A549/DDP cells to chemotherapeutic cisplatin drugs. We speculate that KIF4A may be involved in cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells in two ways. Firstly, as has been reported in the literature, the multidrug resistance ABC (ATP-binding cassette transporter) superfamily proteins played important roles in cancer drug resistance, and two superfamily members transporter protein LRP (lung resistance-related protein) and MVP (major vault protein) were closely related to lung cancer drug resistance [22]. After been expressed within the cytoplasm, the superfamily transporter proteins need to be transported to cell membrane to play their corresponding roles. As a member of kinesin su Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
7 3337 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
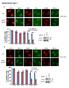
8 Figure 4. The mechanism of KIF4A in inhibiting the induced DNA damage of cisplatin to A549/DDP cells. A. A549 cells were transfected with control pegfp-c1 or pegfp-kif4a for 24 h, and then treated with DDP for 16 h. Cells were lysed, and the lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-kif4a, anti-γ-h2ax antibody and anti-tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as a loading control. B. A549/DDP cells were transfected with control NS Si RNA or KIF4A SiRNA for 36 h, and then treated with DDP for 16 h. cells were lysed, and the lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-kif4a, anti-γ-h2ax and anti-tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as a loading control. C. DDP induced the phosphorylation of H2AX in A549 cells. A549 cells were transfected with control pegfp-c1 or pegfp-kif4a for 24 h, and then treated with DDP for 16 h. The cells were fixed and stained with anti-γh2ax antibody. DNA was labeled with DAPI. D. A549/DDP cells were transfected with control NS Si RNA or KIF4A SiRNA for 36 h, and then treated with DDP for 16 h. The cells were fixed and stained with anti-kif4a or anti-γh2ax antibodies. DNA was labeled with DAPI. Representative images were shown. The scale represents 5 μm. perfamily proteins, kinesin molecule KIF4A can transport subcellular structure or biological macromolecule in cells. Therefore, KIF4A may be involved in the process of transporting transporter proteins to cell membrane, and then pumping the chemotherapy cisplatin drugs out of cells. Secondly, previous study shows that KIF4A may also directly participate in the regulation of DNA damage repair pathways [23]. In addition, knockout KIF4A gene in mice resulted in increased chemosensitivity of cells to ionizing radiation and DNA damage [23]. Meanwhile KIF4A may affect the processes of DNA damage repair by regulating the expression and function of breast cancer-related genes BRCA2 and homologous repair gene Rad51 [17, 23]. Therefore, high expression KIF4A may antagonize the induced DNA damage caused by cisplatin drugs though promoting the repair of DNA damage in cells. In conclusion, our study was the first to report the key role of chromosome protein KIF4A in the process of cisplatin resistance in lung cancer. Our findings may provide a new target for the effective prevention and for the treatment of drug-resistant lung cancer. Acknowledgements This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No , No , and No ), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET ), Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (12JC2DJC21400, 14JCYBJC24200), Doctor Foundation of Tianjin Normal University (52XB1104, 52XB1005), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2015HM047). Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Jian Zhao, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, 107 Wenhuaxi Road, Jinan , Shandong, China. Tel: ; Fax: ; zhaojianjn@hotmail. com References [1] Arya SK and Bhansali S. Lung cancer and its early detection using biomarker-based biosensors. Chem Rev 2011; 111: [2] Webb JD and Simon MC. Novel insights into the molecular origins and treatment of lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: [3] Haura EB, Camidge DR, Reckamp K, Chiappori A, Johnson F, Herbst R, Wong K and Carbone D. Molecular origins of lung cancer: prospects for personalized prevention and therapy. J Thorac Oncol 2010; 5 Suppl 3: S [4] Maneechawakajorn J and Suksuperm J. Quality of life in advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy of platinum combination in old versus new standard chemotherapy regimen. J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 Suppl 11: S [5] Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012; 31: [6] Pan H, Mukhopadhyay P, Rajesh M, Patel V, Mukhopadhyay B, Gao B, Haskó G and Pacher P. Cannabidiol attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by decreasing oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation, and cell death. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2009; 328: [7] Dasari S and Tchounwou PB. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 2014; 740: [8] Gillet JP, Calcagno AM, Varma S, Marino M, Green LJ, Vora MI, Patel C, Orina JN, Eliseeva TA, Singal V, Padmanabhan R, Davidson B, Ganapathi R, Sood AK, Rueda BR, Ambudkar SV and Gottesman MM. Redefining the relevance of established cancer cell lines to the study of mechanisms of clinical anti-cancer drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011; 108: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
9 [9] Chen D, Milacic V, Frezza M and Dou QP. Metal complexes, their cellular targets and potential for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des 2009; 15: [10] Hancock WO. Bidirectional cargo transport: moving beyond tug of war. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014; 15: [11] Heintz TG, Heller JP, Zhao R, Caceres A, Eva R and Fawcett JW. Kinesin KIF4A transports integrin beta1 in developing axons of cortical neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 2014; 63: [12] Sabo Y, Walsh D, Barry DS, Tinaztepe S, de Los Santos K, Goff SP, Gundersen GG and Naghavi MH. HIV-1 induces the formation of stable microtubules to enhance early infection. Cell Host Microbe 2013; 14: [13] Bastos RN, Cundell MJ and Barr FA. KIF4A and PP2A-B56 form a spatially restricted feedback loop opposing Aurora B at the anaphase central spindle. J Cell Biol 2014; 207: [14] Nunes Bastos R, Gandhi SR, Baron RD, Gruneberg U, Nigg EA and Barr FA. Aurora B suppresses microtubule dynamics and limits central spindle size by locally activating KIF4A. J Cell Biol 2013; 202: [15] Subramanian R, Ti SC, Tan L, Darst SA and Kapoor TM. Marking and measuring single microtubules by PRC1 and kinesin-4. Cell 2013; 154: [16] Martinez NW, Xue X, Berro RG, Kreitzer G and Resh MD. Kinesin KIF4 regulates intracellular trafficking and stability of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag polyprotein. J Virol 2008; 82: [17] Wang H, Lu C, Li Q, Xie J, Chen T, Tan Y, Wu C and Jiang J. The Role of Kif4A in Doxorubicin- Induced Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol Cells 2014; 37: [18] Minakawa Y, Kasamatsu A, Koike H, Higo M, Nakashima D, Kouzu Y, Sakamoto Y, Ogawara K, Shiiba M, Tanzawa H and Uzawa K. Kinesin family member 4A: a potential predictor for progression of human oral cancer. PLoS One 2013; 8: e [19] Rouam S, Moreau T and Broët P. Identifying common prognostic factors in genomic cancer studies: a novel index for censored outcomes. BMC Bioinformatics 2010; 11: 150. [20] Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N, Yasui W, Inai K, Nishimura H, Tsuchiya E, Kohno N, Nakamura Y and Daigo Y. Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: [21] O Grady S, Finn SP, Cuffe S, Richard DJ, O Byrne KJ and Barr MP. The role of DNA repair pathways in cisplatin resistant lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 2014; 40: [22] Kelderman S, Schumacher TN and Haanen JB. Acquired and intrinsic resistance in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Oncol 2014; 8: [23] Wu G, Zhou L, Khidr L, Guo XE, Kim W, Lee YM, Krasieva T and Chen PL. A novel role of the chromokinesin Kif4A in DNA damage response. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):
Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 3503-3507, 2015 Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A CHENG LIANG ZHU 1, DUO ZHI CHENG 2, FANG LIU 3, XIAO HONG YAN 3, KAI LANG WU 3, FU
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 3503-3507, 2015 Hepatitis B virus upregulates the expression of kinesin family member 4A CHENG LIANG ZHU 1, DUO ZHI CHENG 2, FANG LIU 3, XIAO HONG YAN 3, KAI LANG WU 3, FU
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation
 Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Multiple mechanisms underlying acquired resistance to taxanes in selected docetaxelresistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 Wang et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Multiple mechanisms underlying acquired resistance to taxanes in selected docetaxelresistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells Harris Wang 1, The Vo 1, Ali Hajar
Wang et al. BMC Cancer 2014, 14:37 RESEARCH ARTICLE Multiple mechanisms underlying acquired resistance to taxanes in selected docetaxelresistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells Harris Wang 1, The Vo 1, Ali Hajar
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
http / / cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology COX-2 NTera-2 NTera-2 RT-PCR FasL caspase-8 caspase-3 PARP.
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein
![2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein](/thumbs/86/94743397.jpg) Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-J4JVV9
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Human Cathepsin D ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-J4JVV9
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3
 Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology MKL P1. 3, Changjun ZHU 3) 1) 2) 3 MKLP1 . MKLP1
 ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ 2005 8 Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 21 (4) :554 560 esirna MKLP1 1) 2) 3, 3, Changjun ZHU 3) 1) 1),,, 1) 3, Wei J IANG 3) ( 1), 250012 ; 2), 250012
ISSN 100727626 CN 1123870ΠQ 2005 8 Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 21 (4) :554 560 esirna MKLP1 1) 2) 3, 3, Changjun ZHU 3) 1) 1),,, 1) 3, Wei J IANG 3) ( 1), 250012 ; 2), 250012
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
Mouse Myeloperoxidase/MPO ELISA Kit
 OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Mouse Myeloperoxidase/MPO ELISA Kit Catalog
OriGene Technologies, Inc 9620 Medical Center Dr., Suite 200, Rockville, MD 20850 Phone: 1.888.267.4436 Fax: 301-340-9254 Email: techsupport@origene.com Web: Mouse Myeloperoxidase/MPO ELISA Kit Catalog
Yuriko Saiki, 1 Takenori Ogawa, 1, 2 Kiyoto Shiga, 2 Makoto Sunamura, 1, 3 Toshimitsu Kobayashi, 2 and Akira Horii 1. 1.
 International Otolaryngology Volume 211, Article ID 521852, 4 pages doi:1.1155/211/521852 Research Article A Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line with Acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum-resistance
International Otolaryngology Volume 211, Article ID 521852, 4 pages doi:1.1155/211/521852 Research Article A Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line with Acquired cis-diamminedichloroplatinum-resistance
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this. study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319,
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319, NCI-H1373, PC-3, PC-9,
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319, NCI-H1373, PC-3, PC-9,
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit
 AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Figure S1. Schematic presentation of genomic replication of idsiv after transfection and infection. After transfection of idsiv plasmid DNA into 293T
 Figure S1. Schematic presentation of genomic replication of idsiv after transfection and infection. After transfection of idsiv plasmid DNA into 293T cells, the RNA genomes with all modifications are generated
Figure S1. Schematic presentation of genomic replication of idsiv after transfection and infection. After transfection of idsiv plasmid DNA into 293T cells, the RNA genomes with all modifications are generated
The effect of elemene reversing the multidurg resistance of A549/DDP lung cancer cells
 213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
213 12 33 12 TUMOR Vol. 33, December 213 www.tumorsci.org 161 Basic Research DOI: 1.3781/j.issn.1-7431.213.12. 5 Copyright 213 by TUMOR A549/DDP 1, 2 2 1 3 4 1 1 1. 3619 2. 355 3. 3611 4. 361 elemene cisplatin
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Alpha-Tubulin Housekeeping 10,000 tests
 Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
