Stage 5: Immature endocrine Stage 4 cells were cultured for seven days in DM-F12 medium supplemented with 1% B27 and 1 µm ALK5 inhibitor.
|
|
|
- Sybil Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Data Research Design and Methods Differentiation of Human ES Cells Stage 1: Mesoendoderm 60-70% confluent adherent cultures of undifferentiated H1 cells plated on 1:30 Matrigel coated surfaces were exposed to RPMI 1640 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 2% fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin (Proliant; Ankeny, IA), 100 ng/ml activin-a (Pepro-tech; Rocky Hill, NJ), and 20 ng/ml of Wnt3A (R&D Systems) for day one only, and 8 ng/ml of FGF2 (Peprotech) for 3-4 days. Stage 2: Endoderm Progenitor Stage 1 cells were exposed to DM-F12 medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 2% fatty acidfree BSA, 50 ng/ml of FGF7 (Pepro-tech), and 0.25 µm Cyclopamine-KAAD (EMD; Gibbstown, NJ) for two days. Stage 3: Foregut Progenitor Cultures were continued for four days in DM-F12 medium supplemented with 0.25 µm Cyclopamine-KAAD, 2 µm retinoic acid (Sigma-Aldrich; St. Louis, MO), 50 ng/ml of FGF7, 100 ng/ml of Noggin (R&D Systems), and 1% (v/v) B27 (Invitrogen). Stage 4: Endocrine Precursor Stage 3 cells were cultured for three days in DM-F12 medium supplemented with 1 µm ALK5 inhibitor II (Axxora; San Diego, CA), 100 ng/ml of Noggin, 1 µm DAPT (γ-secretase inhibitor; EMD) and 1% B27. Stage 5: Immature endocrine Stage 4 cells were cultured for seven days in DM-F12 medium supplemented with 1% B27 and 1 µm ALK5 inhibitor. Stage 6: Mature endocrine Stage 5 cells were further cultured for an additional seven days in DM-F12 medium supplemented with 1% B27. Clusters were removed from the monolayer by treating with 1X Accutase (Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 min at room temperature. This was followed by aspiration of the enzyme, rinsing with DM-F12 basal media, and gentle scraping of cells using a cell scraper. In some cases, the cell suspension was passed through a 40 µm filter (BD Biosciences; Franklin Lakes, NJ) to retain large clusters. In general, harvested clusters were cultured in DM-F12 medium on non-adherent plates (Corning; Corning, NY) for 1 week in DM-F12, 1% B27 prior to transplantation. In some studies (eg. Supplementary Fig. S3D), harvested clusters were cultured for up to four weeks in DM-F12 + 1% B27. Targeted Screening of Kinase Inhibitor Libraries To identify small molecules that could upregulate endocrine marker expression, we performed a primary screen using EMD kinase inhibitor libraries I and II (Cat# and ; EMD Chemicals; Gibbstown, NJ). The readout for the primary screen was based on qrt-pcr for insulin, glucagon, NeuroD, PDX-1, and NKX2.2 expression. All compounds were administered at a concentration of 1 µmol/l during stage 3 and stage 4 of differentiation. Those compounds that resulted in a 2-fold or greater upregulation of one or more of these genes relative to vehicle control were selected for secondary screening. The six compounds selected for secondary screening were MAPK inhibitor (EMD Cat# ), Alk5 inhibitor II (Cat# ALX ; ENZO Life Sciences; Plymouth Meeting, PA), SMAD3 inhibitor (EMD Cat# ),
2 AKT inhibitor (EMD Cat# ), Raf Kinase inhibitor (EMD Cat# ), and MEK inhibitor (EMD Cat# ). Some experiments were performed using ALK5 inhibitor I (Cat# ALX ; ENZO Life Sciences). Secondary screening data are shown in supplemental figure 2. Flow Cytometry Following release of cells into suspension, cells were washed twice in staining buffer (PBS containing 0.2% BSA). For surface marker staining, 1x10 5-1x10 6 cells were re-suspended in 100 µl blocking buffer (0.5% human gamma-globulin diluted 1:4 in staining buffer). Directly conjugated primary antibodies (CD184 APC (Allophycocyanin)) were added to the cells at a final dilution of 1:20 and incubated for 30 min at 4 o C. For intracellular antibody staining, cells were first incubated with green fluorescent LIVE/DEAD cell dye (Invitrogen) for 30 min at 4 C, followed by a single wash in PBS. Next, cells were fixed in 250 µl of Cytofix/Cytoperm Buffer for 30 min at 4 C followed by two washes in BD Perm/Wash Buffer Solution (both BD Biosciences). Cells were resuspended in 100 µl staining/blocking solution consisting of Perm wash buffer with 2% normal goat serum (or appropriate species of the secondary antibody) and primary antibodies at the appropriate dilutions, incubated for 30 min at 4 C, and washed twice in Perm/Wash buffer before a further 30 min incubation in appropriate secondary antibodies. Antibodies used were as follows: rabbit anti-insulin (1:100; Cell Signaling; Danvers, MA), mouse anti-glucagon (1:1250; Sigma-Aldrich); rabbit anti-synaptophysin (1:100; Dako; Carpinteria, CA); goat anti-rabbit PE (1:200; Invitrogen); goat anti-mouse Alexa 647 (1:500; Invitrogen). Cells were washed twice in Perm/Wash buffer and analyzed using BD FACS Canto. At least 30,000 events were acquired for analysis. Immunocytochemistry hes cells were fixed in 4% PFA followed by two washes in PBS and permeabilized by incubating in 0.5% Triton X-100 for 20 min at room temperature, followed by blocking for 30 min at room temperature in 5% normal serum of the appropriate secondary antibody. Cells were stained overnight at 4 o C with primary antibody diluted in blocking buffer at the appropriate dilution. Primary antibodies used were goat anti-neurod (1:500; R&D Systems), mouse anti- Nkx6.1 (1:500; F55A12; This antibody developed by Ole D. Madsen was obtained from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank developed under the auspices of the NICHD and maintained by The University of Iowa, Department of Biology, Iowa City, IA 52242), rabbit anti-pdx-1 (1:500; Abcam), and sheep anti-ngn3 (1:500; R&D Systems). Cells were washed 3 times in PBS followed by incubation in the appropriate secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature. For visualization, cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoeschst or DAPI stain dye in antifade solution (all from Invitrogen). Cells were imaged using a Nikon TE2000 fluorescent microscope. Grafts harvested at d 125 or d 153 were fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde overnight at 4 C prior to being paraffin embedded and sectioned. All sections were cut at a thickness of 5 µm. Sections were subjected to 10 min heat-induced epitope retrieval (HIER) at 95 C using a 10 mmol/l citrate buffer, ph 6.0. Sections were incubated with mouse anti-glucagon (1:1000; Sigma-Aldrich), goat anti-glucagon (1:50; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA), guinea pig anti-insulin (1:1000; Millipore Corp., Billerica, MA), rabbit anti-pc1/3 (1:500; generously provided by Dr. Lakshmi Devi; Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY), rabbit anti-pc2 (1:500; Affinity BioReagents, Rockford, IL,), mouse anti-somatostatin (1:50; GeneTex, Inc., Irvine, CA), rabbit anti-ghrelin (1:1000; BioVision, Mountain View, CA,), rabbit anti-arx (1:1000; AbCam, Inc., Cambridge, MA), rabbit anti-pdx-1 (1:1000; generously provided by Dr. Joel Habener; Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA), or mouse antiproliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA; 1:200; BD Biosciences) as indicated in the text. Visualization of primary antibodies was achieved following incubation with secondary
3 antibodies conjugated to AlexaFluor 488, 555, 594, or 647 as required (1:1000; Invitrogen) or using the VECTASTAIN ABC kit (Vector Laboratories, Inc., Burlington, ON). Images were captured using a Retiga 2000R LCD camera (QImaging, Surrey, BC) in monochrome and pseudo-coloured (fluorescent images) or in RGB format (DAB images) using OpenLab v5 software (ImproVision, Lexington, MA). In Vivo Analysis of Transplanted Cells Routine blood glucose measurements were taken following a 4 h morning fast. Animals were fasted overnight (16 h) prior to initial blood glucose testing and blood collection for the fast/refeed test. All other metabolic tests were performed following a 4 h morning fast. Intraperitoneal arginine tests were performed via injection of 2 g/kg arginine (Sigma-Aldrich) prepared in saline. For the glucagon tolerance test, 1 µg/kg of glucagon (American Peptide Co.; Sunnyvale, CA) prepared in water was delivered by intraperitoneal injection. For insulin tolerance testing, 0.4 IU/kg of recombinant human insulin (Novolin GE; Novo Nordisk Canada; Mississauga, ON) was delivered by intraperitoneal injection. Where blood glucose levels dropped below 2 mm, a bolus injection of 100 µl 40% glucose was given and mice were subsequently excluded from the analysis. Oral glucose tolerance was tested via gavage of 2 g/kg glucose (40% solution prepared in saline). For all tests, blood glucose was tested via saphenous vein, and saphenous blood samples were collected at the indicated time points using heparinized microhematocrit tubes. Plasma was stored at -20 C and later assayed using a mouse insulin kit (Alpco Diagnostics), a human insulin/glucagon/glp NH2 triplex (Meso Scale Discovery; Gaithersburg, MD), or a glucagon bioassay kit (DiscoveRX; Fremont, CA). To boost the signal of the glucagon bioassay, isobutylmethylxanthine (IBMX) was added to each well at a final concentration of 250 µmol/l. Thirty days (STZ study), 125 or 153 days (studies in normal mice) after transplantation, survival nephrectomy was performed to remove the graft-bearing kidney. Engrafted kidneys and pancreata were fixed in 4% PFA and paraffin-sectioned for subsequent immunocytochemical analysis. qrt-pcr Total RNAs were extracted with the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen; Valencia, CA) and reverse-transcribed using the High Capacity cdna Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) according to manufacturer s instructions. cdna ( ng) was amplified by PCR using Taqman Universal Master Mix and Taqman Gene Expression Assays (see table S2 below) which were pre-loaded onto custom Taqman Arrays (all Applied Biosystems). Data was analyzed using Sequence Detection Software (Applied Biosystems) and normalized to undifferentiated human embryonic stem (hes) cells using the Ct method. In some cases part of the graft, harvested at d 125 or d 153 after transplantation, was dissected away from the kidney prior to fixation, and immediately immersed in RNAlater RNA stabilization solution (Qiagen), then incubated at 4 C for 24 h. Total cellular RNA was extracted from the grafts by first further dissecting away kidney tissue, then homogenizing the remaining tissue in QIAzol lysis reagent (Qiagen) using a rotor-type tissue homogenizer. RNA extraction was then performed using the mirneasy kit (Qiagen) with on-column DNase digestion as described in the manufacturer s instructions. cdna synthesis was performed using the RT 2 first strand cdna synthesis kit and mrna levels measured using a custom designed PCR array (SA Biosciences, Frederick, MD) run on a StepOne Plus Real Time PCR machine (Applied Biosystems). Data analysis was performed using the online RT 2 Profiler PCR Array Data Analysis Tool (SA Biosciences). Primers used are listed in Supplementary Table 2. Plasma GLP-1 Measurements
4 All experiments were approved by the UBC Animal Care Committee. Male Rag1 -/- mice (stock 2216) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME) at 8-10 weeks of age. Mice were maintained on a 12 h light/dark cycle and had ad libitum access to a standard irradiated diet (PicoLab 20; #5058l PMI International; St. Louis, MO). Blood samples were collected from the saphenous vein of conscious restrained mice at the indicated time points using heparinized microhematocrit tubes. Plasma was stored at -20 C and later assayed using a human insulin/glucagon/glp NH2 triplex (Meso Scale Discovery; Gaithersburg, MD). Supplemental Figure 1: Gene Expression Patterns in Differentiating hes Cells (A) Expression of mesoendodermal markers (CD184, GSC, Sox17, Cer, and Foxa2), extraembryonic markers (AFP, Sox7) and mesoderm markers (T) were assessed via qrt-pcr in stage 1 hes cell-derived cells. Data are expressed as mean fold stimulation over undifferentiated H1 cells. n=6. Error bars indicate SE. AFP, α-fetoprotein; CER, cerebus-like; CD184, CXCR4; GSC, goosecoid; T, brachyury. (B) Representative image of hes cell-derived cells expressing SOX17 and HNF3β. Nuclei are labeled with Hoechst Scale bars, 100 µm. (C) Expression of endodermal and endocrine markers at each differentiation stage (S2 to S6) and in stage 6 clusters (S6C) as measured by qrt-pcr. Data are expressed as fold induction versus adult human islets. n=3 for each stage of differentiation. Error bars indicate SE. (D) Representative images of hes cell-derived cells co-expressing NGN3 and NeuroD at stage 4. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI. Scale bars, 100 µm. (E) Representative images depicting the lack of NKX6.2 expression within PDX-1-expressing hes cell-derived cells at stage 4 of differentiation. Scale bars, 100 µm.
5 Supplemental Figure 2: Alk5 inhibition improves the efficiency of differentiation to endocrine cells. (A and B) Expression of endocrine markers following treatment with a 1 µmol/l concentration of 6 different kinase inhibitors was assessed via qrt-pcr at stage 3, 4, or 5 as indicated. +/- = compound treatment during stage 3 only; +/+ = compound treatment during stages 3 and 4; -/+ = compound treatment during stage 4 only. Compounds described in supplemental Research Design and Methods. n=2 for each group. (C) Expression of glucagon (green bars) and insulin (red bars) at stage 5 (solid bars) or stage 6 (hatched bars) following treatment with 1 µmol/l Alk5 inhibitor II as indicated. ND, not determined. (D) Endocrine marker expression was assessed via qrt-pcr in stage 4 following treatment with Alk5 inhibitor II at the indicated concentrations. Data are expressed as fold increase versus undifferentiated H1 cells; n=6. (E) Grouped data showing the total number of NGN3-expressing cells per mm 2 assessed at stage 5 following treatment with Alk5 inhibitor II at the indicated concentrations. * P<0.05 vs. 0 µm; P<0.05 vs. 1 µm. n=6.
6 Supplemental Figure 3: Morphological and subcellular characterization of hes cellderived cells. (A) Representative image showing colocalization of insulin (INS; red) and C-peptide (C-PEP; green) immunofluorescence in stage 6 clusters. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 µm. (B) Representative image of INS (red), glucagon (GCG; blue), and C-PEP (green) immunofluorescence in stage 6 clusters. Triple-positive cells are visualized as white cells. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C, D) Representative glucagon (GCG; green) and (C) somatostatin (SST; red) or (D) ghrelin (GHR; red) immunofluorescence in adult human islets (left) and stage 6 clusters (right). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 100 µm. (E and F) Ultrastructural appearance of Stage 6 clusters (E) and adult human islets (F) was assessed via transmission electron microscopy. Scale bar, 2.5 µm. Blue arrows indicate representative alpha cell secretory granules. Greek lettering indicates individual human islet cell type.
7 Supplemental Figure 4: hes cell-derived cells produce some GLP-1. (A) Plasma GLP-1 levels during an intraperitoneal arginine challenge (2 g/kg) performed in normal Rag Tm1Mom mice 62 days after transplantation with stage 6 clusters. n=4-7 per group; **p<0.01 versus control. (B) Plasma GLP-1 levels were measured following an overnight fast and after a 45 min refeeding period in normal Rag Tm1Mom mice 99 days after transplantation with stage 6 clusters. n=5-7 per group; **p<0.01 versus respective fasted; ### p<0.001 versus control fasted (Student s t-test).
8 Supplemental Figure 5: The diabetic milieu does not alter the fate specification of transplanted hes cell-derived cells. (A) Blood glucose in streptozotocin (STZ)-treated diabetic Rag Tm1Mom mice after a 4 h morning fast. Cell Tx mice received STZ (175 mg/kg) at day -8; following diabetes development they were transplanted with stage 6 clusters on day 0 and implanted with slow release insulin pellets (LinBit 1 and 2) as indicated. Linbits were explanted at day 27 and diabetes rapidly returned (n=5-8 animals/group). (B) Blood glucose following intraperitoneal arginine challenge (2 g/kg) performed 28 days posttransplantation and 2 d after Linbit removal (n=8). (C) Plasma glucagon levels in Cell Tx mice during arginine challenge in Panel B. Glucagon levels were below the level of detection (<40 ng/ml) in control mice (n=5-8). Data are expressed as mean ± SE. (D) Grafts were harvested at day 29, paraffin-sectioned and immunostained for glucagon (GCG; green) and insulin (INS; red). A representative image is shown. White arrowhead indicates insulin-positive cell. Scale bar, 100 µm. Merged image includes a DAPI nuclear stain (blue).
9 Supplemental Figure 6. Alpha cell mass quantification. Pancreata were harvested from control mice and hes cell recipients at d153 post-transplant. (A) Representative image of paraffin-sectioned pancreas immunostained for glucagon (brown). (B) Representative selection masks used to quantify alpha cell mass. Negative pixels appear blue and represent unstained pancreas area. Positive pixels appear red and orange. Scale bars, 50 µm. (C) Quantification of alpha cell mass in control mice and hes cell recipients. Data are plotted as mean ± SE. n=5-7 animals/group; *p<0.05.
10 Supplemental Table qrt-pcr Analysis of hes Cell Graft Supplemental Table 2. qrt-pcr Primers Applied Gene Biosystems Name Cat. Number AFP Hs _m1 ARX Hs _m1 CER1 Hs _m1 CXCR4 Hs _m1 FOXA2 Hs _m1 GAPDH Hs _m1 GCG Hs _m1 GSC Hs _m1 HNF4A Hs _m1 INS Hs _m1 NEUROD1 Hs _m1 NEUROG3 Hs _g1 NKX2.2 Hs _m1 NKX6.1 Hs _m1 PAX4 Hs _m1 PAX6 Hs _m1 PDX1 Hs _m1 SOX17 Hs _s1 SOX7 Hs _s1 T (Bry) Hs _m1
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
In vitro differentiation optimization Flow Cytometry
 In vitro differentiation optimization The effect of various basal media formulations were examined during stages 3 4 of the differentiation protocol. For these studies, conditions were as described for
In vitro differentiation optimization The effect of various basal media formulations were examined during stages 3 4 of the differentiation protocol. For these studies, conditions were as described for
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes. Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site
 Stem Cell Reports, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site Andrew R. Pepper, Rena
Stem Cell Reports, Volume 8 Supplemental Information Transplantation of Human Pancreatic Endoderm Cells Reverses Diabetes Post Transplantation in a Prevascularized Subcutaneous Site Andrew R. Pepper, Rena
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study
 Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
Supplementary Table 1. Antibodies and dilutions used in the immunohistochemical study Antigen Species Clone Source Dilution Insulin Guinea pig - Dako, Carpinteria, 1:200 Glucagon Rabbit - Dako, Carpinteria,
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes
 MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
MPB333:Molecular Endocrinology of Obesity and Diabetes The Use of Stem Cells as a Cure for Type 1 Diabetes January 15, 2010 Trish Labosky 9415C MRBIV trish.labosky@vanderbilt.edu In theory. 2. ~Easy and
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue
 Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Control Pancreatitis Supplementary Figure 2 A Panc Liver SI Spleen H 2 O B EZH2 fl/fl C EZH2 fl/fl 37bp EZH2 ERK2 D E 5 EZH2 fl/fl Fasting Glucose (mg/dl) 2 18 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2
Supplementary Figure 1 Control Pancreatitis Supplementary Figure 2 A Panc Liver SI Spleen H 2 O B EZH2 fl/fl C EZH2 fl/fl 37bp EZH2 ERK2 D E 5 EZH2 fl/fl Fasting Glucose (mg/dl) 2 18 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
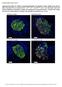 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name
 Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells. Prepared by: David Randolph at University of Alabama, Birmingham
 Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells Prepared by: David Randolph (drdrdr@uab.edu) at University of Alabama, Birmingham Goal: To obtain large numbers of highly pure primary CD4+ CD45RO- CD25- cells from
Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells Prepared by: David Randolph (drdrdr@uab.edu) at University of Alabama, Birmingham Goal: To obtain large numbers of highly pure primary CD4+ CD45RO- CD25- cells from
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1175194/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Vital Role for Interleukin-21 in the Control of a Chronic Viral Infection John S. Yi, Ming Du, Allan J. Zajac* *To whom
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination
 AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
Generation of Insulin-Producing Islet-Like Clusters from Human Embryonic Stem Cells
 EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Generation of Insulin-Producing Islet-Like Clusters from Human Embryonic Stem Cells JIANJIE JIANG, a MELINDA AU, a KUANGHUI LU, a ALANA ESHPETER, b GREGORY KORBUTT, b GREG FISK, a
EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS Generation of Insulin-Producing Islet-Like Clusters from Human Embryonic Stem Cells JIANJIE JIANG, a MELINDA AU, a KUANGHUI LU, a ALANA ESHPETER, b GREGORY KORBUTT, b GREG FISK, a
Supplementary Figures
 Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Inhibition of Pulmonary Anti Bacterial Defense by IFN γ During Recovery from Influenza Infection By Keer Sun and Dennis W. Metzger Supplementary Figures d a Ly6G Percentage survival f 1 75 5 1 25 1 5 1
Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells
 Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells Legends to Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. A. Suppression of p57 Kip2 in human islets does not
Avrahami et al., Suppression of p57kip2 allows successful replication of adult human -cells Legends to Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. A. Suppression of p57 Kip2 in human islets does not
IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
 IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells Jennifer A. Mitchel, Silvio Antoniak, Joo-Hyeon Lee, Sae-Hoon Kim, Maureen McGill, David I. Kasahara,
IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells Jennifer A. Mitchel, Silvio Antoniak, Joo-Hyeon Lee, Sae-Hoon Kim, Maureen McGill, David I. Kasahara,
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased β cell mass and islet diameter in βtsc2 -/- mice up to 35 weeks A: Reconstruction of multiple anti-insulin immunofluorescence images showing differences in β cell mass
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice
 Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
Impact of Sox9 Dosage and Hes1-mediated Notch Signaling in Controlling the Plasticity of Adult Pancreatic Duct Cells in Mice Shinichi Hosokawa 1,3,Kenichiro Furuyama 1,3, Masashi Horiguchi 1,3,Yoshiki
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Soltani et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102715108 SI Experimental Procedures Evaluation of Mice and Drug Administration. IPGTT, insulin tolerance test, and glucagon tolerance test were performed
Supporting Information Soltani et al. 10.1073/pnas.1102715108 SI Experimental Procedures Evaluation of Mice and Drug Administration. IPGTT, insulin tolerance test, and glucagon tolerance test were performed
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes
 University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
University of British Columbia Departments of Surgery and Cellular & Physiological Sciences Making Mature Human Islet Cells from Stem Cells to Model Disease and Treat Diabetes 2016 International Conference
Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro.
 Manuscript EMBO-2015-91058 Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. Holger A Russ, Audrey V Parent, Jennifer J Ringler, Thomas G Hennings, Gopika
Manuscript EMBO-2015-91058 Controlled induction of human pancreatic progenitors produces functional beta-like cells in vitro. Holger A Russ, Audrey V Parent, Jennifer J Ringler, Thomas G Hennings, Gopika
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Supplementary Materials and Methods Hepatocyte toxicity assay. Freshly isolated hepatocytes were incubated for overnight with varying concentrations (-25 µm) of sodium glycochenodeoxycholate (GCDC) or
Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
 v Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining Authors A. Cosma, S. Allgayer MATERIALS Date 01-02-2007 REAGENTS: Version 1.0 - PBMCs - Culture medium - Costimulating antibodies - Peptide pools
v Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining Authors A. Cosma, S. Allgayer MATERIALS Date 01-02-2007 REAGENTS: Version 1.0 - PBMCs - Culture medium - Costimulating antibodies - Peptide pools
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Table S1. qpcr primer list.
 Table S1. qpr primer list. Genes Forward primer Reverse primer NANOG AAATGGGAAGAATAGA GGTTAGTGGGTTA PAX6 TTTTGTTGGGAAATG TGGTTAAATTTAG ASL1 AAGATGAAAGAAAG GGAGTTTGATTAA NHLH GTGGATAGATATTT ATATTTTGGAATTT
Table S1. qpr primer list. Genes Forward primer Reverse primer NANOG AAATGGGAAGAATAGA GGTTAGTGGGTTA PAX6 TTTTGTTGGGAAATG TGGTTAAATTTAG ASL1 AAGATGAAAGAAAG GGAGTTTGATTAA NHLH GTGGATAGATATTT ATATTTTGGAATTT
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
In vitro bactericidal assay Fig. S8 Gentamicin protection assay Phagocytosis assay
 In vitro bactericidal assay Mouse bone marrow was isolated from the femur and the tibia. Cells were suspended in phosphate buffered saline containing.5% BSA and 2 mm EDTA and filtered through a cell strainer.
In vitro bactericidal assay Mouse bone marrow was isolated from the femur and the tibia. Cells were suspended in phosphate buffered saline containing.5% BSA and 2 mm EDTA and filtered through a cell strainer.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
MATERIALS. Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining- EFFECTOR 45RA PANEL
 v Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining- EFFECTOR 45RA PANEL Authors S. Kutscher, A. Cosma, MATERIALS REAGENTS: - PBMCs - Culture medium - Costimulating antibodies - Peptide pools including
v Peptide stimulation and Intracellular Cytokine Staining- EFFECTOR 45RA PANEL Authors S. Kutscher, A. Cosma, MATERIALS REAGENTS: - PBMCs - Culture medium - Costimulating antibodies - Peptide pools including
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
 Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Haekwon Kim Dept. of Biotechnology Seoul Women s University Introduction Type I diabetes is caused by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic
Cell therapeutics for the Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Haekwon Kim Dept. of Biotechnology Seoul Women s University Introduction Type I diabetes is caused by the autoimmune destruction of pancreatic
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
for six pairs of mice. (b) Representative FACS analysis of absolute number of T cells (CD4 + and
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1: Peripheral lymphoid organs of SMAR1 -/- mice have an effector memory phenotype. (a) Lymphocytes collected from MLNs and Peyer s patches (PPs) of WT and SMAR1
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC
 Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Supplementary Table 1. Characterization of HNSCC PDX models established at MSKCC Supplementary Table 2. Drug content and loading efficiency estimated with F-NMR and UV- Vis Supplementary Table 3. Complete
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice
 Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Spheroid-based engineering of a human vasculature in mice Abdullah Alajati, Anna M. Laib, Holger Weber, Anja M. Boos, Arne Bartol, Kristian Ikenberg, Thomas Korff, Hanswalter Zentgraf, Cynthia Obodozie,
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and
 Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and Primary Children s Hospital, Salt Lake City, UT, both
Supplementary Methods: Omalizumab Trial This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the University of Utah Hospital and Primary Children s Hospital, Salt Lake City, UT, both
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system
 Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Preferential reduction of β cells derived from Pax6 MafB pathway in MafB deficient mice
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Developmental Biology 314 (2008) 443 456 www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Genomes & Developmental Control Preferential reduction of β cells derived from Pax6
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Developmental Biology 314 (2008) 443 456 www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Genomes & Developmental Control Preferential reduction of β cells derived from Pax6
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG

 Supplementary Figure 1 (Mu) SBP (mmhg) 2 18 16 p
Supplementary Figure 1 (Mu) SBP (mmhg) 2 18 16 p