Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems
|
|
|
- Millicent Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems eacher s Guide Middle School Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Graphics: Dean Ladago red hodal Lyndsey Canfi eld Reviewers: Andrew P. Zak, MD Visual Learning Company Union Street Brandon, Vermont
2 Use and Copyright he purchase of this video program entitles the user the right to reproduce or duplicate, in whole or in part, this teacher s guide and the blackline master handouts for the purpose of teaching in conjunction with this video, Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems. he right is restricted only for use with this video program. Any reproduction or duplication, in whole or in part, of this guide and student masters for any purpose other than for use with this video program is prohibited. he video and this teacher s guide are the exclusive property of the copyright holder. Copying, transmitting or reproducing in any form, or by any means, without prior written permission from the copyright holder is prohibited (itle 17, U.S. Code Sections 501 and 506). Copyright 2008 ISBN Visual Learning Company
3 able of Contents A Message rom Our Company National Standards Correlations Student Learning Objectives Assessment Introducing the Video Video Viewing Suggestions Video Script Student Assessments and Activities Answers to Student Assessments Answers to Student Activities Assessment and Student Activity Masters Page Visual Learning Company
4 Viewing Clearances he video and accompanying teacher s guide are for instructional use only. In showing these programs, no admission charges are to be incurred. he programs are to be utilized in face-to-face classroom instructional settings, library settings, or similar instructional settings. Duplication rights are available, but must be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. elevision, cable or satellite rights are also available, but must be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. Closed circuit rights are available, and are defi ned as the use of the program beyond a single classroom but within a single campus. Institutions wishing to utilize the program in multiple campuses must purchase the multiple campus version of the program, available at a slightly higher fee. Video streaming rights are available and must be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. Discounts may be granted to institutions interested in purchasing programs in large quantities. hese discounts may be negotiated with the Visual Learning Company. Visual Learning Company
5 A Message from our Company... Dear Educator: hank you for your interest in the educational videos produced by the Visual Learning Company. We are a Vermont-based, family owned and operated business specializing in the production of quality educational science videos and materials. We have a long family tradition of education. Our grandmothers graduated from normal school in the 1920 s to become teachers. Brian s mother was an elementary teacher and guidance counselor, and his father was a high school teacher and superintendent. his family tradition inspired Brian to become a science teacher, and to earn a Ph.D. in education, and led Stephanie to work on science educational programs at NASA. In developing this video, accompanying teacher s guide, and student activities, our goal is to provide educators with the highest quality materials, thus enabling students to be successful. In this era of more demanding standards and assessment requirements, supplementary materials need to be curricular and standards based - this is what we do! Our videos and accompanying materials focus on the key concepts and vocabulary required by national and state standards and goals. It is our mission to help students meet these goals and standards, while experiencing the joy and thrill of science. Sincerely, Brian and Stephanie Jerome Visual Learning Company
6 National Standards Correlations National Science Education Standards (Content standards: 5-8, National Academy of Sciences) Life Science - Content Standard C: As a result of their activities in grades 5-8, all students should understand that: Specialized cells perform specialized functions in multicellular organisms. Groups of specialized cells cooperate to form a tissue, such as a muscle. Different tissues are in turn grouped together to form larger functional units, called organs. Each type of cell, tissue, and organ has a distinct structure and set of functions that serve the organism as a whole. he human organism has systems for digestion, respiration, reproduction, circulation, excretion, movement, control, and coordination, and for protection from disease. hese systems interact with one another. Science in Personal and Social Perspectives (Content Standard - Personal Health) Regular exercise is important to the maintenance and improvement of health. he benefi ts of physical fi tness include maintaining healthy weight, having energy and strength for routine activities, good muscle tone, bone strength, strong heart/lung systems, and improved mental health. Personal exercise, especially developing cardiovascular endurance, is the foundation of physical fi tness. Benchmarks for Science Literacy (Project 2061 AAAS) he Human Organism - Human Identity (6A), Physical Health (6E). By the end of 8th grade, students should know that : Like other animals, human beings have body systems for obtaining and providing energy, defense, reproduction, and the coordination of body functions. he amount of food energy (calories) a person requires varies with body weight, age, sex, activity level, and natural body effi ciency. Regular exercise is important to maintain a healthy heart/lung system, good muscle tone, and bone strength. Visual Learning Company
7 Student Learning Objectives Upon viewing the video and completing the enclosed student activities, students will be able to do the following: Understand that bone is the principle structural material of the skeletal system, and a tough, hard, living material. State some of the functions of the skeletal system: provides structure for the body, protects vital organs, and produces red blood cells. Provide examples of common joints in the body such as the knee, elbow, and wrist. Explain the role ligaments play in connecting bones together at joints. Understand the importance of eating a balanced diet in helping to maintain a healthy skeletal system. Describe muscles as tissues in the body made up of special muscle cells or muscle fibers. Differentiate and compare skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Provide an example of structures in the body made up of the different kinds of muscle. Understand the importance of regular exercise in maintaining a healthy muscular system. Comprehend the dangers of using illegal muscle-enhancing products such as steroids and other chemicals. Understand that these could cause long lasting, serious health problems. Describe some of the common problems which may occur with the muscular system such as contusions, muscle strains, and muscle cramps Visual Learning Company
8 Assessment Preliminary Assessment: he Preliminary Assessment, provided in the Student Masters section, is an assessment tool designed to gain an understanding of students pre-existing knowledge. It can also be used as a benchmark upon which to assess student progress based on the objectives stated on the previous pages. Video Review: he Video Review, provided in the Student Masters section, can be used as an assessment tool or as a student activity. here are two main parts. he fi rst part contains questions that can be answered during the video. he second series of ten questions consists of a video quiz to be answered at the conclusion of the video. Post Assessment: he Post Assessment, provided in the Student Masters section, can be utilized as an assessment tool following completion of the video and student activities. he results of the Post Assessment can be compared against the results of the Preliminary Assessment to evaluate student progress. Visual Learning Company
9 Introducing the Video Before showing students the video program ask them to roll their fi ngers into a fi st and then straighten them out. Next, instruct them to bend their arm back and forth at the elbow. inally, tell students to rotate their feet at the ankles. Now ask students what structures in the body enabled them to make these movements. Explain to the class that bones make up the skeletal system. he skeleton provides a framework for the body, similar to a house that is built on a framework of wood. Explain to students that muscles are tissues which are attached to the skeleton. Muscles enable us to move. here are hundreds of different bones and muscles in the body enabling us to do amazing things. ell students to pay close attention to the program to learn more about the fascinating characteristics and features of the skeletal and muscular systems. ollowing the video discuss some of the characteristics and functions of the skeletal and muscular systems. Also discuss some of the common problems which may occur in these systems. Video Viewing Suggestions he student Master Video Review is provided for distribution to students. You may choose to have your students complete this Master while viewing the program or to do so upon its conclusion. he program is approximately twenty minutes in length and includes a ten question video quiz. Answers are not provided to the Video Quiz on the video, but are included in this teacher s guide. You may choose to grade student quizzes as an assessment tool or to review the answers in class. he video is content-rich with numerous vocabulary words. or this reason you may want to periodically stop the video to review and discuss new terminology and concepts Visual Learning Company
10 Video Script: Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Blink your eyes. 2. Move your thumb. 3. Bend your leg. 4. hese very simple actions involve movements of the muscular and skeletal systems. 5. Nearly everything we do from throwing a ball, or playing an instrument, to writing, involves the skeletal and muscular systems. 8. Without these systems we couldn t move, talk, or carry out our daily lives. 9. How do these systems work? 10. What problems can occur with these systems? 11. And what are some of the things we should do to take care of these systems? 12. During the next few minutes we are going to take a look at these questions and others as we explore the health of the skeletal and muscular systems. 14. Graphic ransition Your Skeletal System 15. Make a fi st and lightly tap your head. 16. You Observe! Describe how your head feels. 17. It feels hard nearly as hard as a rock. 18. Why? his is because your skull, which lies under a thin layer of skin, is made up of a hard material called bone. 19. Bone is the principle structural material of the skeletal system. It is a tough, hard material made up of a variety of elements including minerals. 20. When you observe the dried bone of an animal, you tend to think of bone as nonliving. 21. But bones are actually living tissue made of cells. 22. he cells in bones use energy and oxygen for growth and repair. 23. Another material called cartilage is also found in the skeletal system. 24. Cartilage is a soft connective tissue which is found at the end of bones, between your vertebrae in your backbone, and in your nose and ears. 25. he skeletal system performs many important functions. 26. It is often referred to as the framework of the body because it provides structure for the body. 27. Without the skeletal system we would be shapeless. Visual Learning Company
11 Script (cont.) 28. he skeletal system also enables the human body to move. 29. Certain parts of the skeletal system also protect vital organs. 30. he breastbone and ribs, for example, protect the lungs and heart. 31. In addition, some bones in the skeletal system carry out the important job of producing red blood cells. 32. Graphic ransition he Skeletal System in Action 33. It is remarkable to think about all that a skeletal system does in a single day. 34. One of the most important functions of the skeletal system is movement. 35. he skeleton is uniquely designed for movement through the use of joints. 36. he knee, elbow, wrist, and ankle are all examples of joints. 37. A joint is a place where two or more bones come together. 38. Place your hand on your elbow and bend your arm back and forth. 39. You Observe! Describe what you feel. 40. As you bend your arm you can actually feel where the bones come together at the joint. 41. Most joints allow for movement, and there are many different types of joints. 42. Cartilage, the connective tissue we mentioned earlier, is present at the ends of bones at joints. Cartilage enables the ends of bones to move smoothly against each other. 43. Strong cord-like elastic tissues called ligaments connect bones at joints, holding the bones in place. 44. Graphic ransition Caring for Your Skeletal System 45. You probably don t think about taking care of your skeleton that often because it is hidden inside the body. 46. But there are several things you should do everyday to take care of this body system. 47. One of the most important things you can do for bone strengthening and growth is to eat a healthy balanced diet. 48. Bones need a wide variety of vitamins as well as minerals such as calcium. 49. Milk products, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain these valuable nutrients. 50. As adolescents it is very important to eat a balanced diet, to provide your bones with the ingredients they need for growth and development. 51. In addition to eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular exercise is also important. 52. But, sometimes people experience bone and skeletal injuries while exercising Visual Learning Company
12 Script (cont.) 53. Many of these injuries could have been prevented through the proper use of safety equipment. 54. Wearing a helmet while bicycling, skateboarding, skiing, and snowboarding helps protect the skull and the brain in the event of an accident, reducing your chance of a severe injury. 57. Wearing other protective equipment and padding protects other parts of the body from injury. 58. Graphic ransition Problems of the Skeletal System 59. his is an x-ray of a bone. 60. You Decide! What is wrong with this bone? 61. hat s right, it is broken. 62. Bones are hard, however, they can occasionally break. 63. A fracture is a break in a bone, usually caused by an accident or an injury. 64. Sometimes fractures require a cast or surgery. 65. Because bones are living tissue, a fracture can repair itself over time. 66. Perhaps you have sprained your ankle while running or walking. 67. Or maybe you sprained a fi nger while catching a ball. 68. A sprain occurs when ligaments at a joint are stretched or torn. 69. Usually a sprain involves pain and swelling. 70. Another type of skeletal problem called osteoporosis is a disease in which bone density decreases. 71. his causes bones to become weak and more prone to fractures. 72. Osteoporosis tends to be more common in older women. It is minimized through exercise, diet along with appropriate minerals such as calcium and vitamins. 73. Graphic ransition Your Muscular System 74. You may think this person has a lot of muscles. 75. But actually, each of us has the same number of muscles. It s just that some people have bigger and stronger muscles. 76. What exactly is muscle? 77. Muscle is tissue in the body made up of special muscle cells or muscle fi bers. Muscle fi bers contract and relax to cause movement. 78. Your heart is made of a special type of muscle called cardiac muscle. 79. You Decide! Does your stomach contain muscle? 80. Yes, the stomach and intestines contain another type of muscle called smooth muscle. Visual Learning Company
13 Script (cont.) 81. A third type of muscle called skeletal muscle is attached to bones. Skeletal muscles enable us to move. 82. ough tissues called tendons attach muscles to bones. 83. While the skeleton provides the framework the attached muscles allow it to move. So as you can see the muscular system and the skeletal system work in tandem. 84. or this reason the skeletal and muscular systems are sometimes referred to as the musculo-skeletal system. 85. Graphic ransition Caring for Your Muscles 86. Eating a well balanced diet is very important in caring for your muscles. 87. Muscle growth and maintenance require adequate protein, carbohydrates, and a wide array of minerals and vitamins. 88. It is also important to rest tired or overly exerted muscles. 89. o keep muscles fi t, regular exercise is essential. 90. A wide range of exercises utilizing a variety of muscle groups is critical. 91. Aerobic exercise in which the body utilizes higher amounts of oxygen is not only good for skeletal muscle but for cardiac muscle as well. 92. Stay away from products that promise to increase your muscle mass and strength. 93. And never use illegal drugs such as steroids or other muscle enhancing chemicals. hese could cause long lasting, serious health problems. 94. Graphic ransition Problems of the Muscular System 95. If you have ever bumped into something or gotten hit hard you have probably gotten a black and blue mark called a contusion or bruise. 97. A contusion occurs when muscle tissue is injured and blood vessels are broken, causing a discoloration under the skin. 98. Contusions usually heal after a few days. 99. Sometimes when muscles are overworked or over stretched they become strained Rest, cold packs, and later pain-free gentle stretching exercises are recommended for the treatment of a muscle strain A more serious injury than a strained muscle is a torn muscle In a torn muscle the muscle is actually torn apart or torn from the bone Rest or even surgery is sometimes required to treat a torn muscle Have you ever felt a terrible pain in your leg muscles during or after exercise? Visual Learning Company
14 Script (cont.) 105. his may be a cramp, sometimes called a charley horse. A cramp is a painful, involuntary muscle contraction A person can get a muscle cramp to subside by stretching and applying ice packs Sometimes a problem arises not with muscles but with tendons. endonitis involves the infl ammation of the tendon usually caused by excessive exercise endonitis is commonly treated with rest, and sometimes with medication Graphic ransition Summing Up 110. During the past few minutes we have explored some of the fascinating features of the skeletal and muscular systems, and the health of these systems We began by investigating living tissue called bones the basis of the skeletal system We also discussed some of the functions of this system. How it provides a framework for the body, how it protects vital organs, facilitates movement, and how it produces red blood cells We also discussed the role joints and ligaments play in the process of movement Some essential things you should do to take care of your skeletal system were also described such as eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and using safety equipment while doing certain activities Problems may sometimes arise with the skeletal system such as bone fractures We took a look at the muscular system as well, which works with the skeletal system to produce movement Eating a balanced diet, regular aerobic exercise, and rest are all things you can do to maintain a healthy muscular system inally, we briefl y explored some of the problems which may effect muscles including contusions, strains, cramps, and torn muscles or tendons So, the next time you take a walk do some work, or play a sport, think about some of the things we discussed during the past few minutes You just might think about the health of your skeletal and muscular systems a little differently. Visual Learning Company
15 Script (cont.) 123. Graphic ransition Video Assessment ill in the correct word to complete the sentence. Good luck and let s get going! 1. he is the framework of the body. 2. is the structural material of the skeletal system. 3. Bone is actually tissue made of cells. 4. A is a place where two or more bones come together. 5. When bicycling, snowboarding, and skateboarding always wear a. 6. A is a break in a bone. 7. A may occur when ligaments are stretched at a joint. 8. fi bers expand and contract to cause movement. 9. Regular aerobic is important in keeping muscles fi t. 10. A muscle can be caused by over stretching or overuse of muscles. Answers can be found on page Visual Learning Company
16 Student Assessments and Activities Assessment Masters: Preliminary Assessment Video Review Post Assessment Student Activity Masters: Muscles in the Body Joints and Joint Problems Bruises and Strains Vocabulary of Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Visual Learning Company
17 Answers to Student Assessments Preliminary Assessment (pgs ) 1. skeletal 2. bone 3. joint 4. fracture 5. helmet 6. muscles 7. tendons 8. exercise 9. contusion 10. balanced 11. true 12. true 13. false 14. true 15. false 16. true 17. false 18. false 19. true 20. true Video Review (p. 22) 1. Your head feels hard because your skull, which lies under a thin layer of skin, is made up of a hard material called bone. 2. When you place your hand on your elbow and bend your arm back and forth, you can actually feel where the bones come together at the joint. 3. he bone is broken or fractured which is usually caused by an accident or injury. 4. Yes, the stomach contains a type of muscle called smooth muscle. Video Quiz (p. 22) 1. skeleton 2. bone 3. living 4. joint 5. helmet 6. fracture 7. sprain 8. muscle 9. exercise 10. strain Post Assessment (pgs ) 1. contusion 2. tendons 3. helmet 4. joint 5. skeletal 6. balanced 7. exercise 8. muscles 9. fracture 10. bone 11. true 12. false 13. false 14. false 15. true 16. true 17. false 18. true 19. true 20. true Visual Learning Company
18 Answers to Student Activities Muscles in the Body (p. 26) A. 1. stomach - smooth muscle 2. digests food 3. indigestion, acid refl ux, ulcer 4. eat a balanced diet B. 1. heart - cardiac muscle 2. pumps blood throughout body 3. coronary arteries may block leading to heart attack 4. regular aerobic exercise, low fat diet, regular physical examination C. 1. triceps and biceps - skeletal muscle 2. help the arm move 3. strain, sprain 4. regular exercise, eat a well balanced diet Joints and Joint Problems (p ) Hinge Joint 1. he hinge joint bends mainly in one plane, back and forth. 2. An advantage of a hinge joint is that it allows for a wide range of movement in one plane. 3. he fi ngers are another example of a hinge joint. 4. A hinge joint can be hyperextended; can also be dislocated. Gliding Joint 1. his joint moves laterally (side to side). No, the knee cannot do this. 2. A gliding joint allows side to side movement. 3. Another example of gliding joints are the joints between vertebrae. 4. An injury might occur in a gliding joint. he bones can be fractured or the surfaces may be injured. Ball and Socket Joint 1. A ball and socket joint allows movement in all directions (360 ) 2. An advantage of a ball and socket joint is that it allows a great deal of movement in all directions. 3. Another example of a ball and socket joint is the hip. 4. An injury that might occur in a ball and socket joint is it can be dislocated. Athritus in the hip is also relatively common in older people. Bruises and Sprains (p. 29) fracture contusion tendinitis bursitus strain cramp Vocabulary of Healthy Skeletal and Muscular Systems (p. 30) 1. h - skeletal system 2. j - bone 3. a - joint 4. d - calcium 5. b - fracture 6. g - osteoporosis 7. c - tendons 8. f - ligaments 9. i - contusion 10. e - tendonitis Description reatment C 6 A E D B Visual Learning Company
19 Assessment and Student Activity Masters
20 Name Preliminary Assessment Directions: ill in the blank with the correct word. A list of possible answers is provided at the bottom of the page. 1. he system is the framework of the human body. 2. is the main structural material of the skeletal system. 3. A is where two or more bones come together. 4. A is a break in a bone. 5. When bicycling or skateboarding always wear a to prevent head injuries. 6. are tissues which help the body move. 7. ough tissues called attach muscles to bones. 8. o keep muscles fi t, regular is essential. 9. A black and blue mark on the skin resulting from an injury to a muscle is called a. 10. It is very important to eat a diet to care for the skeletal and muscular systems. tendons joint balanced helmet skeletal contusion bone muscles exercise fracture
21 Name Preliminary Assessment Directions: Decide whether the statement is true () or false (). 11. Bones in the body are actually living tissue. 12. Cartilage is a material located in your ears and nose. 13. he skeletal system does not play a role in movement. 14. Ligaments connect bones to bones. 15. A sprain involves a fracture in a bone. 16. Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone density decreases. 17. he body has just one type of muscle. 18. Aerobic exercise involves the body using small amounts of oxygen. 19. A strain may occur when muscles are overworked or overstretched. 20. Muscle fi bers expand and contract to cause movement
22 Video Review Name Directions: During the course of the program, answer the questions as they are presented in the video. At the end of the video, answer the Video Quiz questions. You Observe! 1. Describe how your head feels. You Observe! 2. Describe what you feel. You Decide! 3. What is wrong with this bone? You Decide! 4. Does your stomach contain muscle? Video Quiz: ill in the correct word to complete the sentence. 1. he is the framework of the body. 2. is the structural material of the skeletal system. 3. Bone is actually tissue made of cells. 4. A is a place where two or more bones come together. 5. When bicycling, snowboarding, and skateboarding always wear a. 6. A is a break in a bone. 7. A may occur when ligaments are stretched at a joint. 8. fi bers expand and contract to cause movement. 9. Regular aerobic is important in keeping muscles fi t. 10. A muscle can be caused by over stretching or overuse of muscles
23 Post Assessment Name Directions: ill in the blank with the correct word. A list of possible answers is provided at the bottom of the page. 1. A black and blue mark on the skin resulting from an injury to a muscle is called a. 2. ough tissues called attach muscles to bones. 3. When bicycling or skateboarding always wear a to prevent head injuries. 4. A is where two or more bones come together. 5. he system is the framework of the human body. 6. It is very important to eat a diet to care for the skeletal and muscular systems. 7. o keep muscles fi t, regular is essential. 8. are tissues which help the body move. 9. A is a break in a bone. 10. is the main structural material of the skeletal system. fracture exercise contusion helmet bone muscles tendons skeletal balanced joint
24 Post Assessment Name Directions: Decide whether the statement is true () or false (). 11. A strain may occur when muscles are overworked or overstretched. 12. he body has just one type of muscle. 13. A sprain involves a fracture in a bone. 14. he skeletal system does not play a role in movement. 15. Bones in the body are actually living tissue. 16. Muscle fi bers expand and contract to cause movement. 17. Aerobic exercise involves the body using small amounts of oxygen. 18. Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone density decreases. 19. Ligaments connect bones to bones. 20. Cartilage is a material located in your ears and nose
25 Name Muscles in the Body Background: Have you ever woken up and felt sore after playing basketball or running the previous day? he soreness is most likely the result of overusing your muscles. Muscles are very important tissues in the body that perform a wide range of functions. Without muscles, we wouldn t be able to walk, run, or move. he contraction and relaxation of muscle cells produces movement. Humans and other vertebrate animals have three different kinds of muscle: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. he relaxing and contracting of skeletal muscles enable us to move. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone. Cardiac muscle, another type of muscle, is sometimes referred to as heart muscle Cardiac muscle in the heart pumps blood throughout the body. he third type of muscle, smooth muscle, is found in a variety of organs including the stomach, intestines, the uterus in females, and in blood vessels. We depend on our muscles to carry out a wide range of activities from digesting food, to pumping blood, to helping us get out of bed in the morning. Muscles therefore are extremely important to our existence. Unfortunately there are problems that may arise with our muscles. or example, skeletal muscles can be bruised, strained, sprained, or torn. Cardiac muscles can be damaged during a heart attack. And smooth muscle can be attacked by diseases such as cancer. here are many things you can do to care for your muscles. Eating a well balanced diet is very important. Muscle growth and maintenance requires adequate protein, carbohydrates, and a number of vitamins and minerals. It is also important to rest tired or overly exerted muscles. o keep muscles fi t, regular exercise is essential! Aerobic exercise, in which muscle tissue consumes high amounts of oxygen, is good for skeletal and cardiac muscles. It is also very important to stay away from substances that have a negative effect on the body such as drugs, alcohol, unhealthy foods, and muscle enhancing chemicals such as steroids. Having a regular physical examination by a medical professional is also vital in maintaining healthy muscles and a healthy body
26 Name Muscles in the Body cont. Directions: Below are three images representing the three different types of muscle. Write the correct answer next to each structure. 1. Identify the structure and state the type of muscle of which it consists. 2. Describe the main function the muscle carries out in the body. 3. Explain a problem which may occur with this type of muscle. 4. Describe some of the things you should do to care for this structure/type of muscle. A B C
27 Name Joints and Joint Problems Background: A joint is the place where two or more bones come together. Your elbows and knees are examples of joints you may commonly think about because you use them often. But there are other joints in the body including joints in the skull, feet, neck, and shoulder to name just a few. here are several different types of joints in the human body. In this activity you will learn about the following types of joints: hinge joint, ball and socket joint, and a gliding joint. Activity: Hinge Joint: 1. Bend your knee back and forth. his is an example of a hinge joint. Describe the motion in a hinge joint. 2. What is the advantage or benefi t of a hinge joint? 3. List another example of a hinge joint in your body. 4. Describe an example of an injury that might occur in a hinge joint
28 Name Joints and Joint Problems cont. Gliding Joint: 1. Slide your hand from side to side as if you were waving goodbye. Describe the motion at this joint. Can you do this with your knee? 2. What is the advantage or benefi t of a gliding joint? 3. List another example of a gliding joint in the body. 4. Describe an example of an injury that might occur in a gliding joint. Ball and Socket Joint: 1. Move your arm around in a circle over your head. Describe the motion of the joint in your shoulder. 2. What is the advantage or benefi t of a ball and socket joint? 3. List another example of a ball and socket joint in the body. 4. Describe an example of an injury that might occur in a ball and socket joint
29 Name Bruises and Strains Background: here are many different injuries which may occur to the skeletal and muscular systems. Hopefully, such injuries are not serious, and can heal quickly. It is a good idea to be aware of various problems which may occur with these body systems and to know how to prevent injuries. Directions: Using textbooks, medical reference books, the internet, and this video program research the problem in the left column. hen match it to its description. inally match the common treatment to the injury. fracture contusion tendinitis bursitis strain cramp Description reatment Description of Problem A. An injury to soft tissue such as muscle. Often caused by a blow. Sometimes referred to as a bruise. B. Slight pain or muscle stiffness resulting from muscles being overworked or overstreched. C. A break in a bone. D. Pain and swelling in area of elbow, hip, knee, shoulder or other joint. E. An infl ammation of tendon.. Somtimes called a charley horse. A painful involuntary muscle contraction. Possible reatments 1. Rest is essential. Ice and elevating sometimes recommended. Medical examination sometimes recommended. 2. Relieve pain by stretching and apply cold packs. 3. Rest and anti-infl ammatory medicine such as asprin. 4. Rest of involved joint, cold packs, and later pain-free gentle stretching exercises. 5. Cold packs help reduce swelling. If serious see a doctor. 6. See a doctor immediately. Immobilization through a cast or splint is necessary. Serious fractures may require surgery
30 Name Vocabulary of Skeletal and Muscular Systems Directions: Unscramble the vocabulary words in the fi rst column. Match the words to the defi nitions in the second column. 1. eellksat ytmsse 2. oenb 3. ijton 4. ccuimla 5. rtafecur 6. ersostioposo 7. edntsno 8. gesimtlna 9. cnuinosot a. Place where two or more bones meet b. a break in a bone c. tough tissues which connect muscles to bones d. an important mineral needed by bones e. infl ammation of a tendon f. strong cord-like elastic tissues which connect bones to bones g. a disease in which bone density decreases h. provides a framework for the body and performs many important functions i. occurs when muscle tissue is injured; often results in discoloration under the skin j. living tissue which serves as main structural material of skeletal system 10. osneittdin
food chains teacher s guide Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Josh Hummel Graphics: Fred Thodal
 www.visuallearningsys.com 1 800 43 8481 Union Street, Brandon, VT 0733 food chains teacher s guide Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Josh Hummel Graphics:
www.visuallearningsys.com 1 800 43 8481 Union Street, Brandon, VT 0733 food chains teacher s guide Editors: Brian A. Jerome Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Josh Hummel Graphics:
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Strength, any two: curl-ups/crunches, push-ups, step-ups; heart and lung endurance, any two:
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
To meet the expectations of this unit, students should already be able to describe the skeleton s role in movement, support and protection.
 GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body.
 II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
II. Skeletal System A. Structure - Your skeletal system is your basic framework in your body. 1. 206 bones - Comprise the adult human body. 2. "os-", "osteo-" Both of these roots mean bone. What is an
Structure and Movement
 Name Structure and Movement How do bones, muscles, and skin help maintain the body s homeostasis? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record three things
Name Structure and Movement How do bones, muscles, and skin help maintain the body s homeostasis? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record three things
SU228R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY
 Hayes SU228R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY Fast Facts & Dazzling Data The Human Body This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc., Grand
Hayes SU228R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY Fast Facts & Dazzling Data The Human Body This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc., Grand
A Healthy Body. Teacher s Guide Middle School. Visual Learning Company Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome
 eacher s Guide Middle School Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Hannah jeld Graphics: Dean Ladago red hodal Lyndsey Canfi eld Visual Learning Company
eacher s Guide Middle School Editors: Brian A. Jerome, Ph.D. Stephanie Zak Jerome Assistant Editors: Louise Marrier Hannah jeld Graphics: Dean Ladago red hodal Lyndsey Canfi eld Visual Learning Company
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
Muscles: A Lot of Work!
 Move Your Muscles! By Sharon Guynup Muscles keep you on the go. Here s how they work and why you need to keep them in tip-top shape. Picture this: You re out shooting hoops with your friends. As you take
Move Your Muscles! By Sharon Guynup Muscles keep you on the go. Here s how they work and why you need to keep them in tip-top shape. Picture this: You re out shooting hoops with your friends. As you take
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
Related KidsHealth Links
 K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
K to Grade 2 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This guide
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY
 UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
UNIT 1 : THE HUMAN BODY 1.1.- KNOWING YOUR BODY The first thing we need to do before starting the P.E. class, it s to make sure that we really now our own body. But not only its parts, but also how does
Life Science. Packet: Body Organization 2. OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be able to DO NOW
 Life Science Unit: Body Organization Packet: Body Organization 2 Name: Date: Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be able to SWBAT list 5 functions of the skeletal system. SWBAT describe
Life Science Unit: Body Organization Packet: Body Organization 2 Name: Date: Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be able to SWBAT list 5 functions of the skeletal system. SWBAT describe
Muscular System. Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person?
 Muscular System Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person? 2. What are the three types of muscles? 1. 2. 3. 3. Smooth muscles make up what? _ 4. What do you
Muscular System Muscular System Video 1. Does a muscular person have more muscles than a smaller person? 2. What are the three types of muscles? 1. 2. 3. 3. Smooth muscles make up what? _ 4. What do you
April 20, Living Organisms: The Skeletal System
 Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
Living Organisms: The Skeletal System Day 1 April 20, 2018 The skeleton is a structural framework that supports and protects the human body.. April 20, 2018 Estimate- How many bones you have in your body?
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Section 13.1 The Importance of Physical Activity
 Objectives Explain some of the physical, psychological, and social benefits of physical activity. Define the five components of fitness. Describe five types of physical activity. Slide 1 of 24 The Benefits
Objectives Explain some of the physical, psychological, and social benefits of physical activity. Define the five components of fitness. Describe five types of physical activity. Slide 1 of 24 The Benefits
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION OF MUSCLES
 FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System
 BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
BIO 2 GO! 3213b Movement in Animals-Skeletal Muscular System All multicellular animals that can move to escape harm or to capture food have an advantage over those animals that cannot move. After the successful
Muscles. Grade Level: 4-6
 Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
Muscles Grade Level: 4-6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 6 Activity Page pages 7 Practice Page page 8-9 Homework Page page 10 Answer Key page 11-13 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
What type of tissue is this
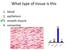 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness? Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness vs. Exercise Physical Fitness is the ability
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness? Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness vs. Exercise Physical Fitness is the ability
Bones are made up of bone cells and tissues Hard, dense and smooth outer materials, which are made of calcium, give bones there shape and strength.
 1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Bone myths
 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
F.8.1 Understand the structure and function of cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, and whole organisms
 Subject area: Science Teacher: David Klang Title of Lesson: Skeletal System Grade Level: 8 Time Needed: 2 days of 43 minutes State Core Objective: F.8.1 Understand the structure and function of cells,
Subject area: Science Teacher: David Klang Title of Lesson: Skeletal System Grade Level: 8 Time Needed: 2 days of 43 minutes State Core Objective: F.8.1 Understand the structure and function of cells,
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
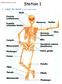 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy
 Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
What Are Shoulder Problems?
 What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
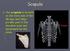 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry. After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to:
 Chapter 2 Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry Learning outcomes: After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to: Describe the anatomical structure
Chapter 2 Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry Learning outcomes: After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to: Describe the anatomical structure
The Chiropractic Neck Book
 The Chiropractic Neck Book A Painful Neck Problem Many people have neck pain at some point in their lives. Pain is often the result of injuries or other problems that cause the spine to be misaligned.
The Chiropractic Neck Book A Painful Neck Problem Many people have neck pain at some point in their lives. Pain is often the result of injuries or other problems that cause the spine to be misaligned.
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. :
 1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
Body Organization and Structure
 CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
CHAPTER 19 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Body Organization and Structure As you read Chapter 19, which begins on page 462 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 462)
The Muscular System. The Muscular System: Moving your Body
 The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
The Muscular System: Moving your Body The Muscular System So, which systems have Which systems will we learned about sowe far? learn about next? Can you sit totally still without moving a muscle? Ø Try
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1
 Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
B) Sprains cause swelling in the injured area, but strains do not have a tendency to swell
 Lesson U4C2L4 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L4:F1) How many times have you broken a bone? A) none B) one C) two D) more than two 2. (U4C2L4:F2) How many times have you sprained an arm, leg, or other body part?
Lesson U4C2L4 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L4:F1) How many times have you broken a bone? A) none B) one C) two D) more than two 2. (U4C2L4:F2) How many times have you sprained an arm, leg, or other body part?
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
The Hard Stuff! All About Bones
 The Hard Stuff! All About Bones A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 1,353 LEVELED BOOK R The Hard Stuff! All About Bones R U X Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands
The Hard Stuff! All About Bones A Reading A Z Level R Leveled Book Word Count: 1,353 LEVELED BOOK R The Hard Stuff! All About Bones R U X Written by Lisa Trumbauer Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands
Muscular Strength and Endurance:
 PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 45-1 The Human Body Plan Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank 1. Nervous tissue contains specialized cells called a. Transmitters. b. neurons c. messenger
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan
 1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY
 THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
Related KidsHealth Links
 Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Grades 3 to 5 Human Body Series KidsHealth.org/classroom Teacher s Guide This guide includes: Standards Related Links Discussion Questions Activities for Students Reproducible Materials Standards This
Physical Fitness. Chapter 4
 Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness is the ability to do everyday activities without becoming short of breath, sore, or tired. There are four
Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness is the ability to do everyday activities without becoming short of breath, sore, or tired. There are four
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Unscramble THE HUMAN BODY. aehtr. taryre. vreil. hmsotac. crathea. Riddle: Why didn t the teddy bear tell the doll the bad news? Answer: He didn t.
 Unscramble Name Date Directions: To answer the riddle, unscramble each word and write it in the squares. Then write the circled letters in order on the numbered spaces below. 1 3 taryre 5 9 11 a blood
Unscramble Name Date Directions: To answer the riddle, unscramble each word and write it in the squares. Then write the circled letters in order on the numbered spaces below. 1 3 taryre 5 9 11 a blood
**************CLASS COPY DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5. Muscular System
 **************CLASS COPY ------ DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5 Muscular System INSTRUCTIONS: Complete a Quick Notes for paragraphs 1-10 on the next few pages. Answer all other questions on
**************CLASS COPY ------ DO NOT WRITE ON************** Body Packet 5 Muscular System INSTRUCTIONS: Complete a Quick Notes for paragraphs 1-10 on the next few pages. Answer all other questions on
Musculoskeletal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma
 Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
What is the skeletal system?
 .^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
.^ ^)\ Djn' ^ /r n_'i & 1^ MW What is the skeletal system? W?c"';'Wi?''l''. 'C'tW;«
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE IN FEMUR
 Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Strong, Healthy Muscles
 Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Strong, Healthy Muscles Objective: Students will be able to: Review prior knowledge of body systems, especially the muscular system. Identify positive ways that a person can keep (or
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Strong, Healthy Muscles Objective: Students will be able to: Review prior knowledge of body systems, especially the muscular system. Identify positive ways that a person can keep (or
PE Improvement Targets
 PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
Chapter 9 The body and its movement
 Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Chapter: Structure and Movement
 Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
Table of Contents Chapter: Structure and Movement Section 1: The Skeletal System Section 2: The Muscular System Section 3: The Skin 1 Living Bones The Skeletal System The bones in your body are very much
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? How Are Shoulder Problems Treated? What Are the Most Common Shoulder Problems? What Are Shoulder Problems?
 How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend
 Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 36
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
