Qualifying Examination (Part I)
|
|
|
- Miles Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 29 August 1, 2008 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary, you may prepare written answers, overhead figures, or any type of materials that you think might be useful in the presentation of your answers. You may bring such preparation materials with you to the examination. The oral examination itself will not extend beyond two hours. If you have any questions regarding the examination, please contact Joey Barnett at: (w) (h) (c) BEST WISHES FOR YOUR SUCCESSFUL COMPLETION OF THE EXAMINATION!
2 Question 1 Oolong tea (OT) is widely consumed as a health drink in Japan and China. Recent studies have provided evidence that OT exerts a variety of physiological effects. Lipton, et.al. examined the effects of intraduodenal (ID) injection of OT on renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) and blood pressure (BP) in urethaneanesthetized rats. Figure 1 depicts the effects of OT and decaffeinated oolong tea (DOT) on RSNA, mean arterial pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) after ID injection of water, OT, or DOT. In Figure 2 injection of artificial cerebral spinal fluid (acsf) or the histamine antagonist thioperamide into the intracerebral ventricle (ICV) preceded the ID injection of water or OT by 15 minutes. The effects on RSNA, MAP, and HR are depicted. Please provide a hypothesis as to the mechanism by which Oolong tea decreases blood pressure. Fig. 1. Effects of ID injection of OT or decaffeinated oolong tea (DOT) on RSNA and BP. Time changes of RSNA (A), MAP (C), and heart rate (HR) (E) after intraduodenal (ID) injection of water, OT, or DOT are expressed as means ± SEM of the percentage of the value at 0 minute (RSNA) or of absolute value change from the value at 0 minute (MAP and HR). Bars show RSNA (B), MAP (D), and HR (F) change values 60 minutes after injection of water, 2 doses (1/10 and 1) of OT, and DOT. The numbers of animals used are shown in parentheses. The significant difference between values after water and OT injections was analyzed as a group by ANOVA (P <.05). Fig. 2. Effects of thioperamide, a histamine antagonist, on changes in RSNA and MAP after ID injection of OT. Time changes of RSNA (A), MAP (B), and HR (C) after ID injection of OT are expressed as means ± SEM of percentage of their values at 0 minute (RSNA) or of absolute value change from the value at 0 minute (MAP and HR). An injection of acsf or thioperamide was given into the intracerebral ventricle (ICV) 15 minutes before ID injection of OT. The significance of the difference between the values after water and OT from 5 to 60 minutes was analyzed as a group by ANOVA (P <.05). Thiop indicates thioperamide. Your colleague at MakeMPay Pharmaceuticals isolated a single compound from OT that, when administered to urethane-anesthetized rats, yields data similar to that in Figures 1 & 2. With this compound in hand, propose experiments to test or refine your hypothesis.
3 Question 2 The thiazolidinedione antidiabetic drug pioglitazone was administered to healthy subjects as follows: In a randomized, two-phase crossover study, ten healthy subjects ingested either 600 mg rifampicin or placebo once daily for 6 days. On the last day, they received a single oral dose of 30 mg pioglitazone. The plasma concentrations and cumulative excretion of pioglitazone and its active metabolite M-IV into urine were measured up to 48 h. 1. Explain the pharmacokinetics of pioglitazone and its main metabolite based on the data given in Figures 1 and 2, and Table How do you explain the effects of rifampicin? Present in vitro and/or in vivo experiments that would test your hypothesis. Figure 1 Mean ±SEM plasma concentration-time curves for pioglitazone in ten healthy subjects after a single oral dose of 30 mg pioglitazone on the last day of a 6-day treatment with placebo ( ) or 600 mg rifampicin ( ) once daily. The inset depicts the same data on a semilogarithmic scale.
4 Question 2 Figure 2 Mean ±SEM plasma concentration-time curves for metabolite M-IV in ten healthy volunteers after a single oral dose of 30 mg pioglitazone on the last day of a 6-day treatment placebo ( ) or 600 mg rifampicin ( ) once daily. Table 1 Pharmacokinetic data for pioglitazone in ten healthy subjects after a single oral dose of 30 mg pioglitazone on the last day of a 6-day treatment with 600 mg rifampicin or placebo given once daily Variable Placebo Rifampicin Rifampicin phase P-value (control) treatment percentage of control (range) Pioglitazone Cmax (ng ml 1) 932 ± ± (52 167) tmax (h) 1 (1 3) 1.5 (1 2) t1/2 (h) 4.9 ± ± (29 110) AUC0 (mg L 1 h) 8.61 ± ± (34 80) Clrenal (ml h 1) 0.12 ± ± (49 143) Metabolite-IV kf (h 1) 0.19 ± ± ( ) Cmax (U ml 1) 0.87 ± ± (63 219) tmax (h) 12 (9 24) 8 (3 12) t1/2 (h) 32 ± ± 3 50 (32 95) AUC0 (U ml 1 h) 48.2 ± ± (49 155) Values shown as mean ± SD unless otherwise indicated, tmax data as median (range). Cmax, observed peak plasma concentration; tmax, time to reach Cmax ; t1/2, terminal elimination half-life; AUC0, area under the concentration versus time curve to infinity; kf, apparent formation rate constant; U, arbitrary units (relative to the ratio of the peak height of the metabolite to the peak height of the internal standard).
5 Question 3 Background. You are the director of a Research Division and you get a phone call from an epidemiologist in Ireland that has a perplexing mystery. A small fishing village on the Irish coast has been afflicted with some disorder and they have been baffled as to the cause. They suspect the constellation of symptoms is related to a red tide ("harmful algal bloom") that first appeared a few months ago and all of those experiencing symptoms are consumers of shellfish (e.g., clams, oysters, and scallops). Residents that ate a lot of shellfish generally appear to have worse symptoms than those that ate little. No residents that does not eat shellfish has shown any symptoms. The red tide was analyzed after it first occurred and none of the usual toxins, such as Alexandrium toxin (saxitoxin), were detected in levels that should be harmful. The disorder is unusual in part because of the wide variety of symptoms that have been reported. The most common finding is acute gastic ulceration. A subset of afflicted females reported having less discomfort than usual during their menstruation. There are assorted vascular and pulmonary symptoms, but some report problems associated with vasoconstriction, while others appear to have problems more related to vasodilation. Within the last few days (well after the symptoms began) an influenza outbreak occurred in the region affecting the fishing village as well as a much wider area. This particular strain of influenza was associated with high fevers. Those residents that had eaten shellfish (referred to as the afflicted group) had less fever than other residents, but otherwise felt the effects of the viral infection. The epidemiologist commented that this is a fairly isolated community composed of interconnected, extended families who generally refrain from taking medications. Initial Findings. You agree to assist your colleague and utilize your own expertise in pharmacology, including your Synthetic and Analytical Chemistry Facility. You obtain blood samples from the afflicted group as well as other locals that have not eaten shellfish. (1) In your initial finding you note that platelets from the afflicted group fail to aggregate normally. The control population platelets aggregated at a normal rate. Exposure to influenza alone had no systematic effect on platelets. However, you note that the platelet aggregation abnormality is linearly correlated with the amount of shellfish residents reported consuming. Interestingly, you observe that those residents that stopped eating shellfish more than a week ago had platelet aggregation rates that were approaching normal. They also reported slight improvements in gastric symptoms. (2) The leukocytes fraction of the blood samples allowed access to a fairly pure preparation of macrophages. One of your routine measurements is an ELISA for measuring Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNFα). You observe that the affected population has significantly highly levels of TNFα than the unaffected population. (3) A brilliant graduate student in your group has an idea and in the dark of night expresses oncogenic RAS GTPase in the two groups of macrophages. The macrophages from the afflicted group produce high levels of TNFα, whereas the normal macrophages show the anticipated decrease in TNFα levels. You decide to have the analytical lab measure a number of parameters in their routine screens: Detailed Analytical Measurements- (a) Genomic array analysis will take several weeks to give you specific information, but the technician tells you a number of genes products are not expressed in the afflicted group as compared to the normal group. (b) Proteomics analysis was somewhat indeterminant. There may be minor differences in individual proteins, but there are certainly no wide spread alterations in the levels of well characterized proteins. (c) Metabolomics- you have a number of extraction protocols that separate different types of metabolites. The standard metabolic parameters were normal, but your newly hired chemist notes that
6 Question 3 one of the extraction profiles that specifically isolates linear hydrocarbon compounds showed a difference in profiles after separation on a reverse phase hplc column as well as subsequent analysis by mass spectrometry. Your new chemist is not trained in biology, but her analytical skills are extraordinary. You looked for evidence of differences in phagocytosis (while looking for evidence of an unknown pathogenic organism) by challenging macrophages with lipopolysaccaride (LPS) + ATP. The induced phagocytosis between the afflicted and nonafflicted (normal) groups was the same. Your chemist analyzed these samples using hplc and LC-MS mass spectrometry and results are shown below in Figs 1 and 2. See Figs 1 and 2, next page Question #1. Your chemist isolated quantities of a previously unknown small molecule that is concentrated in the shellfish from the afflicted area. She notes that this molecule has functional groups that may allow it to form a covalent bond with a protein or protein(s). The details are not important except her comment that the molecule would need to have a high affinity for binding to the protein before it formed the covalent bond (i.e., it would need a high affinity for said protein). From the information given identify the most likely molecular target that could cause this affliction (a target that can potentially explain the constellation of symptoms described). Give the most parsimonious hypothesis to explain the symptoms. Justify your hypothesis by outlining the relevant pathways and explicitly detail how these symptoms can all be related to a single molecular target. A complete answer will include explicitly explaining how you selected the correct target and not closely related targets that fit some (but not all) of the data. Question #2. Explain the relevance of the finding on Ras GTPase expression. Does this assist you in identifying the molecular target? Question #3. Based on your conclusion what needs to be done for the afflicted residents? Why?
7 Question 3 Fig.1 Fig 2 Reverse Phase HPLC LC-MS of individual species within the hplc peaks Table A m/z Normal, unstim Internal Standard D Integrated Peak Intensity ion count ion count IS Time (mins) Table B Internal Standard E m/z Integrated Peak Intensity Integrated Peak Intensity Normal, stim Afflicted, stim Time (mins) Table C 7 9 Time (mins) Internal Standard ion count IS Fig.1. A specialized organic phase extractions was performed on macrophages and extracts chromatographed by reverse phase hplc. The peaks come off in order of hydrocarbon chain length (i.e., shorter followed by longer hydrocarbon chains). All compounds were shown to be linear hydrocarbons that were non-cyclized (i.e., contains no rings). The time of elution is indicated on the x-axis and the peak intensity is shown on the y-axis. Table A is the chromatogram from unstimulated normal subjects (unaffected), Table B is after a short stimulation with 20 um LPS and 5 mm ATP of normal subjects. Table C is the same stimulation procedure (as B) but in macrophages from the afflicted residents. Fig 2 shows the ESI-MS negative mode spectra. The major molecular species from each of the indicated peaks (corresponds to the peaks shown on the hplc trace) is indicated in bold (1-227 m/z, 14:0; 3-255m/z, 16:0; 5-283, 18:0; 7-281m/z, 18:1; IS- internal standard; m/z, 20:4; and m/z, 22:6) The next number ( ) indicates the mass/charge (m/z) and numbers following the comma indicate the molecular species (number of carbons, 14-22: number of double bonds, 0-6). The spectra shown above in panel D are from the corresponding peaks from the hplc trace in Table A. This spectra was absolutely identical to the spectra of hplc Table C (data not shown). The spectra shown in panel E is from the hplc peaks shown in Table B. Notes: (1) Any unidentified spectral lines in panels D and E may be ignored as background. (2) Hplc traces and ESI-MS spectra from unstimulated samples from afflicted macrophages looked exactly the same as those in hplc trace Table A and panel D (not shown). (3) Differences between the peak heights in the hplc can be directly compared but are not quantitative (i.e., a 2X difference in peak height may be much more than twice as much difference), whereas the differences in the MS peak heights are quantitative.
8 Question 4 The "club drug" 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA; also known as ecstasy) is a psychostimulant drug of abuse that induces hyperlocomotion in animals. A recent study shows that pharmacological inhibition and genetic ablation of 5-HT2B receptors abolishes the psychostimulatory effect of MDMA (Figure 1). Figure 1. Effect of 5-HT2B receptor inhibition on MDMAinduced hyperlocomotion. a, MDMA-induced locomotion in WT mice. WT mice were injected (i.p.) with either MDMA (10 mg/kg; squares) or saline solution (triangles) (arrow) after 1 h of habituation. b, RS (selective inhibitor of 5-HT2B receptors) abolishes MDMAinduced locomotion in WT mice. WT mice were injected with RS [0.5 mg/kg (dark squares), 0.1 mg/kg (light gray squares), or 0.05 mg/kg (white squares)] solution 1 h before MDMA (10 mg/kg) injection (arrow). c, MDMA-induced locomotion failed in 5-HT2B / mice. MDMA (10 mg/kg) or saline solutions were injected after 1 h of habituation (arrow). A. Describe the molecular mechanism of the MDMA action in the brain. Describe classes of 5-HT receptors. Describe the nuclei that produce serotonin and their location in the brain. Describe the distribution of serotonergic innervation in the brain and main recipient structures. B. Propose two alternative models of the role of the 5-HT2B receptor in the psychostimulant action of MDMA assuming that 5-HT2B receptors are either pre- or postsynaptic. Propose critical experiments to discriminate between these two models. C. Describe potential therapeutic uses or compounds targeting the 5-HT2B receptors based on your models.
9 Question 5 Researchers at the University of Copenhagen recently created a genetically engineered mouse in which a gene (Kicr1) encoding a probable kidney-specific ion channel regulator was deleted. Homozygous knockout mice (Kicr1-/-) exhibited significantly increased urinary excretion of water, sodium and potassium as compared with wildtype and heterozygous littermates. In addition, whole kidney glomerular filtration rate was significantly decreased by approximately 50% in Kicr1-/- mice as compared with wildtype and heterozygous littermates. Body weight, blood pressure, and plasma concentrations of sodium and potassium were not statistically different between wildtype and Kicr1-/- mice, but heart rate was significantly higher in the knockout animals. Specific measurements are illustrated in Fig. 1. Fig 1 Baseline renal studies in wildtype (Kicr1+/+, filled bars) and knockout (Kicr1-/-, open bars) mice determined for a 6 hour period. Data are mean ± SEM. The p values compare knockout to wildtype mice. To identify the location of the renal defect, the investigators used diuretic pharmacotyping, a strategy examining the effect of specific diuretic agents on the renal phenotype of the animals. Fig. 2 illustrates their findings. ** Fig 2 Effect of diuretics on renal excretion. Drugs were given intravenously at the end of the control period, then urine was collected for 6 hours. Furo, furosemide (loop diuretic); HCTZ, a thiazide diuretic. Statistical significance is indicated by *, p<0.05 compared with control period for same genotype; and **, p<0.05 compared with wildtype (panel B only). Questions: 1. Describe the renal phenotype of Kicr1 knockout mice. 2. Formulate hypotheses to explain the renal phenotype and explain how to test your ideas. 3. Predict the impact of Kicr1 knockout on tubuloglomerular feedback.
10 Question 6 A recently formed pharmaceutical company, Chubby R Us, initially focused its research efforts upon the growing problem of human obesity by attempting to identify new compounds that can modulate the central regulation of feeding behavior. Unfortunately, oral administration of one of their newest test compounds significantly increased food intake in rodents. Not deterred by this minor setback, Chubby R Us changed it research direction to focus upon that small percentage of Americans that are chronically underweight and have difficulty in maintaining their body mass. Additional dose response analyses of their new drug revealed that when administered at levels five fold higher than those shown to affect food uptake, experimental animals demonstrated weakness, sluggishness and eventually died within about 6 weeks. A more detailed analysis of these mice revealed the fasted, mean blood values indicated below: 1. Based upon all of these observations, develop a hypothesis regarding the physiological changes in response to your compound and propose a mechanism for its action. 2. Describe a series of experiments by which to confirm your proposed mechanism of action.
11 Question 7 Arrestin3 regulates signaling via the α 2 -adrenergic receptor (AR). A recent report identified spinophilin as another α 2 -adrenergic receptor (AR) interacting partner. To elucidate the roles that spinophilin (Sp) and arrestin3 (Arr3) play in the control AR function, a group of investigators performed the following experiments. Shown in Figure 1, CosM6 cells were cotransfected with HAtagged AR and either empty vector, spinophilin, or arrestin3. Cells were incubated with 100 µm epinephrine + 1 µm propranolol (to block βar) to stimulate the AR. HA immunoprecipitations were performed from the cell lysates and the resulting immune complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting using a GRK2 antibody. Depicted in Figure 2, mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) harvested from wildtype, Arr3 null, or Sp null embryos were transfected with HA-AR, labeled with 32Pi, and then stimulated with 100 µm epinephrine + 1 µm propranolol for 0, 5, and 20 minutes. HA immunoprecipitations were performed from the cell lysates and the resulting immune complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiographic analysis (32P-HA-AR). Fold change of GRK2 in IP complex Fig. 1. (A) CosM6 cells cotransfected with HA-AR AR and the indicated cdnas (empty vector, spinophilin, or arrestin3) were stimulated with an AR-agonist (100 µm epinephrine + 1 µm propranolol to block βar). HA immunoprecipitations were performed from the cell lysates and the resulting immune complexes were analyzed by immunoblotting using a GRK2 antibody. Aliquots of the corresponding membrane fractions were also immunoblotted with the GRK2 antibody. Bar graphs represent quantitative data from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, comparing the fold change of GRK2 protein detected in the HA-AR immune complex after agonist stimulation versus no agonist (the latter defined as control, or 1.0-fold). Western blot analysis confirmed comparable amounts of HA-AR in immunoprecipitated complexes and comparable amounts of each protein in total lysates for each of the lanes shown (not shown). 32 P-HA-AR Total HA-AR AR on Fold change of phosphorylatio Sp +/+, Arr3 +/+ Sp +/+, Arr3 -/- Sp +/+, Arr3 +/+ Sp -/-, Arr3 +/+ Fig. 2. MEFs with the indicated genotypes were transduced with HA-AR, labeled with 32 Pi, and then stimulated with an AR-agonist (100 µm epinephrine + 1 µm propranolol) for the indicated times. HA immunoprecipitations were performed from the cell lysates and the resulting immune complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE and autoradiographic analysis ( 32 P-HA-AR). AR) Also shown is awestern blot of total HA-AR in each immune complex (Total HA- AR). Bar graphs represent quantitative data from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, comparing the fold change of HA-AR phosphorylation (HA-AR phosphorylation in WT MEFs, with no agonist defined as 1.0-fold). A) Develop a hypothesis to explain these data. Describe how these results support your hypothesis. Remember that the level of receptor phosphorylation depends on GRK activity and the rate of dephosphorylation. B) Design two independent experiments to test your hypothesis.
12 Question 7 Stimulation of the AR is known to induce sedation in animal models. To study the in vivo relevance of spinophilin and arrestin3 in AR-elicited sedation, the group of investigators examined the ability of α2- agonists it to evoke AR-mediated ditdsedation dti in spinophilin null mice (Sp-/-), arrestin3 null mice (Arr3-/-), and corresponding wild type mice (WT). Sedation was assessed via rotarod latency, which is defined as the time the mice were able to stay on the rotarod treadmill (decreased rotarod latency = increased sedation). Fig. 3. Sedation in response to a specific AR agonist (UK14,304) was assessed via rotarod latency after administration of increasing doses of UK 14,304. The EC50 values for sedation in Arr3 / and corresponding WT littermates (n = 5 for each genotype) are 2.1 and 1.1 mg/kg, respectively, and the EC50 values for sedation in Sp / and corresponding WT mice (n = 11 for each genotype) are 0.4 and 1.2 mg/kg, respectively. *P < 0.01; **P < C) Based on the results of the experiments depicted in Figs. 1 and 2, as well as your knowledge of arrestin s pleiotropic roles in GPCR signaling, how would you explain the results of the experiment depicted in Fig. 3? D) Other GPCRs, including A1 adenosine receptors, are known to evoke sedation in wild type mice. Design an in vivo experiment to test whether spinophilin p and arrestin3 are involved in A1 adenosine receptor-elicited sedation.
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 11-14, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 11-14, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
LPS LPS P6 - + Supplementary Fig. 1.
 P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table 1. Tph1+/+ Tph1 / Analyte Supplementary Table 2. Tissue Vehicle LP value
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from WT and Adcy1 KO mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody.
 ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
Concentration of drug [A]
![Concentration of drug [A] Concentration of drug [A]](/thumbs/74/70683906.jpg) Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS 1 Receptor occupancy - mass action The interaction of a drug with a receptor is reversible due to interactions via weak bonds (not covalent). [A] +
Pharmacology Semester 1 page 1 of 5 PHARMACODYNAMICS 1 Receptor occupancy - mass action The interaction of a drug with a receptor is reversible due to interactions via weak bonds (not covalent). [A] +
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 19-22, 2011 Committee Members: Heidi Hamm Craig Lindsley Chang Chung Seva Gurevich Tuesday, July 19 Exam 9:00 11:00 Sara Savage Exam 11:00
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 19-22, 2011 Committee Members: Heidi Hamm Craig Lindsley Chang Chung Seva Gurevich Tuesday, July 19 Exam 9:00 11:00 Sara Savage Exam 11:00
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0463 TITLE: The Ketogenic Diet and Potassium Channel Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Geoffrey Murphy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0463 TITLE: The Ketogenic Diet and Potassium Channel Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Geoffrey Murphy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109
chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists.
 chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
chapter 1 - fig. 1 The -omics subdisciplines. chapter 1 - fig. 2 Mechanism of transcriptional control by ppar agonists. 201 figures chapter 1 chapter 2 - fig. 1 Schematic overview of the different steps
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 20 24, 2009 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 20 24, 2009 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
Supporting Information. Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in. Mouse Rod Cells
 Supporting Information Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in Mouse Rod Cells David Salom,, Benlian Wang,, Zhiqian Dong, Wenyu Sun, Pius Padayatti, Steven
Supporting Information Post translational Modifications of Serotonin Type 4 Receptor Heterologously Expressed in Mouse Rod Cells David Salom,, Benlian Wang,, Zhiqian Dong, Wenyu Sun, Pius Padayatti, Steven
NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON TOXICOKINETICS: THE ASSESSMENT OF SYSTEMIC EXPOSURE IN TOXICITY STUDIES S3A
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON TOXICOKINETICS: THE ASSESSMENT
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON HARMONISATION OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR REGISTRATION OF PHARMACEUTICALS FOR HUMAN USE ICH HARMONISED TRIPARTITE GUIDELINE NOTE FOR GUIDANCE ON TOXICOKINETICS: THE ASSESSMENT
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
DEFINITIONS. Pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics. The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body
 PHARMACOLOGY BASICS DEFINITIONS Pharmacokinetics The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body Pharmacodynamics The interactions of a drug and the receptors
PHARMACOLOGY BASICS DEFINITIONS Pharmacokinetics The process by which a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and eliminated by the body Pharmacodynamics The interactions of a drug and the receptors
Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome Yang Xu 1, Colin K.L. Phoon 2, Bob Berno 5, Kenneth D Souza 6, Esthelle Hoedt 4, Guoan Zhang 4, Thomas
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Loss of protein association causes cardiolipin degradation in Barth syndrome Yang Xu 1, Colin K.L. Phoon 2, Bob Berno 5, Kenneth D Souza 6, Esthelle Hoedt 4, Guoan Zhang 4, Thomas
Supplemental Figures:
 Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
Supplemental Figures: Figure 1: Intracellular distribution of VWF by electron microscopy in human endothelial cells. a) Immunogold labeling of LC3 demonstrating an LC3-positive autophagosome (white arrow)
OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4
![OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4](/thumbs/90/104143670.jpg) Opioid MCQ OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP02 [Mar96] Which factor does NOT predispose to bradycardia with
Opioid MCQ OP01 [Mar96] With regards to pethidine s physical properties: A. It has an octanol coefficient of 10 B. It has a pka of 8.4 OP02 [Mar96] Which factor does NOT predispose to bradycardia with
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR-2B cells untreated (-) or stimulated (+) for 45 min
 Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m.
 20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except Drs.
20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except Drs.
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Analysis of Common Sweeteners and Additives in Beverages with the PerkinElmer Flexar FX-15 System Equipped with a PDA Detector
 application Note Liquid Chromatography Author Njies Pedjie PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT 06484 USA Analysis of Common Sweeteners and Additives in Beverages with the PerkinElmer Flexar FX-15 System Equipped
application Note Liquid Chromatography Author Njies Pedjie PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT 06484 USA Analysis of Common Sweeteners and Additives in Beverages with the PerkinElmer Flexar FX-15 System Equipped
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
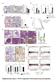 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection
 ## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
The Opportunity: c-ibs and pain relief with confidence YKP10811
 The Opportunity: c-ibs and pain relief with confidence YKP10811 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Profile Summary Clinical Data Mode of Action Pharmacologic Profile Safety and Toxicity Profile ADME Overview vs. Competitors
The Opportunity: c-ibs and pain relief with confidence YKP10811 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Profile Summary Clinical Data Mode of Action Pharmacologic Profile Safety and Toxicity Profile ADME Overview vs. Competitors
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
Furosemide: Properties, Alternatives, and the Medication Approval Process. Heather Brown EMS 209-Advanced Pharmacology Don Knox
 Furosemide: Properties, Alternatives, and the Medication Approval Process Heather Brown EMS 209-Advanced Pharmacology Don Knox Pre-hospital treatment of critical patients is a key factor in determining
Furosemide: Properties, Alternatives, and the Medication Approval Process Heather Brown EMS 209-Advanced Pharmacology Don Knox Pre-hospital treatment of critical patients is a key factor in determining
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Principal Investigator: Project title:
 Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 16, 2013, at 1:30 p.m. Due: October 21, 2013, at 10:00 a.m.
 20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 16, 2013, at 1:30 p.m. Due: October 21, 2013, at 10:00 a.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except:
20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 16, 2013, at 1:30 p.m. Due: October 21, 2013, at 10:00 a.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except:
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
DiscovIR-LC. Application Note 026 May 2008 READING TEA LEAVES SUMMARY INTRODUCTION
 TM DiscovIR-LC Deposition and Detection System Application Note 026 May 2008 READING TEA LEAVES The DiscovIR-LC is a powerful new tool for materials analysis. When connected to the outlet of an LC column,
TM DiscovIR-LC Deposition and Detection System Application Note 026 May 2008 READING TEA LEAVES The DiscovIR-LC is a powerful new tool for materials analysis. When connected to the outlet of an LC column,
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE. Definitions. Pharmacology: the study of the interaction of drugs within living systems
 Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
Lecture 1 and 2 ONE 1. Explain what pharmacology encompasses and how it relates to other disciplines 2. Discuss the types of drug target and the factors that influence the binding of drugs to these targets
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether
 Supplemental Material Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether species by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry James G. Bollinger *, Hiromi Ii*, Martin
Supplemental Material Improved method for the quantification of lysophospholipids including enol ether species by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry James G. Bollinger *, Hiromi Ii*, Martin
Myelin suppresses axon regeneration by PIR-B/SHPmediated inhibition of Trk activity
 Manuscript EMBO-2010-76298 Myelin suppresses axon regeneration by PIR-B/SHPmediated inhibition of Trk activity Yuki Fujita, Shota Endo, Toshiyuki Takai and Toshihide Yamashita Corresponding author: Toshihide
Manuscript EMBO-2010-76298 Myelin suppresses axon regeneration by PIR-B/SHPmediated inhibition of Trk activity Yuki Fujita, Shota Endo, Toshiyuki Takai and Toshihide Yamashita Corresponding author: Toshihide
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Proteomics of body liquids as a source for potential methods for medical diagnostics Prof. Dr. Evgeny Nikolaev
 Proteomics of body liquids as a source for potential methods for medical diagnostics Prof. Dr. Evgeny Nikolaev Institute for Biochemical Physics, Rus. Acad. Sci., Moscow, Russia. Institute for Energy Problems
Proteomics of body liquids as a source for potential methods for medical diagnostics Prof. Dr. Evgeny Nikolaev Institute for Biochemical Physics, Rus. Acad. Sci., Moscow, Russia. Institute for Energy Problems
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were
 Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were compared in SS rats fed 1% salt diet (black circles) and WKY
Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were compared in SS rats fed 1% salt diet (black circles) and WKY
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture
 Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture Nanna Goldman *, Michael Chen *, Takumi Fujita *, Qiwu Xu, Weiguo Peng, Wei Liu, Tina K. Jensen, Yong Pei, Fushun Wang, Xiaoning
Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture Nanna Goldman *, Michael Chen *, Takumi Fujita *, Qiwu Xu, Weiguo Peng, Wei Liu, Tina K. Jensen, Yong Pei, Fushun Wang, Xiaoning
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches
 Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response.
 Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System
 Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System Keywords Introduction Application Note PHA0413 High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
Automated Purification and Analytical Reinjection of a Small Molecule Drug, Probenecid, on a Gilson LC/MS Dual Function System Keywords Introduction Application Note PHA0413 High Pressure Liquid Chromatography
Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra
 Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra Jeevan K. Prasain, PhD Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, UAB jprasain@uab.edu utline Introduction Putative
Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra Jeevan K. Prasain, PhD Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, UAB jprasain@uab.edu utline Introduction Putative
Supplementary material page 1/10
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metoprolol administration during ongoing AMI reduces MVO in STEMI patients (a, b) Complete representative CMR exams (short-axis covering the entire left ventricle (LV) from base
Supplementary Figure 1. Metoprolol administration during ongoing AMI reduces MVO in STEMI patients (a, b) Complete representative CMR exams (short-axis covering the entire left ventricle (LV) from base
Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Metlin Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra
 Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Metlin Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra Jeevan K. Prasain, PhD Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, UAB jprasain@uab.edu Outline Introduction
Metabolite identification in metabolomics: Metlin Database and interpretation of MSMS spectra Jeevan K. Prasain, PhD Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, UAB jprasain@uab.edu Outline Introduction
Pharmacology for CHEMISTS
 Pharmacology for CHEMISTS JOSEPH G. CANNON ACS Professional Reference Book AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Washington D.C. New York Oxford 1999 CONTENTS I Chemical and Biological Bases
Pharmacology for CHEMISTS JOSEPH G. CANNON ACS Professional Reference Book AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Washington D.C. New York Oxford 1999 CONTENTS I Chemical and Biological Bases
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Quantification of PtdInsP 3 molecular species in cells and tissues by mass spectrometry
 Nature Methods Quantification of PtdInsP 3 molecular species in cells and tissues by mass spectrometry Jonathan Clark, Karen E Anderson, Veronique Juvin, Trevor S Smith, Fredrik Karpe, Michael J Wakelam,
Nature Methods Quantification of PtdInsP 3 molecular species in cells and tissues by mass spectrometry Jonathan Clark, Karen E Anderson, Veronique Juvin, Trevor S Smith, Fredrik Karpe, Michael J Wakelam,
TITLE: Proteomic Mapping of the Immune Response to Gluten in Children with Autism
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0293 TITLE: Proteomic Mapping of the Immune Response to Gluten in Children with Autism PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Armin Alaedini, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Trustees of Columbia
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0293 TITLE: Proteomic Mapping of the Immune Response to Gluten in Children with Autism PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Armin Alaedini, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Trustees of Columbia
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
Analysis of Pesticides (II) Metribuzin & their metabolites in Rice Jun Yonekubo, Nihon Waters, JAPAN
 Waters Alliance LC/MS System Analytical Conditions Chromatograms Mass Spectra Calibration Quantitation Analysis of Pesticides (II) Metribuzin & their metabolites in Rice Jun Yonekubo,, JAPAN Key Words
Waters Alliance LC/MS System Analytical Conditions Chromatograms Mass Spectra Calibration Quantitation Analysis of Pesticides (II) Metribuzin & their metabolites in Rice Jun Yonekubo,, JAPAN Key Words
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Screening of Antihistamine Agents (Diphenhydramine) with Blood and Urine Samples by REMEDi-HS System
 Screening of Antihistamine Agents (Diphenhydramine) with Blood and Urine Samples by REMEDi-HS System Ohtsuji M, Ohshima T, Takayasu T, Nishigami J, Kondo T, Lin Z, Minamino T Department of Legal Medicine,
Screening of Antihistamine Agents (Diphenhydramine) with Blood and Urine Samples by REMEDi-HS System Ohtsuji M, Ohshima T, Takayasu T, Nishigami J, Kondo T, Lin Z, Minamino T Department of Legal Medicine,
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products)
 Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Analytical Method for 2, 4, 5-T (Targeted to Agricultural, Animal and Fishery Products) The target compound to be determined is 2, 4, 5-T. 1. Instrument Liquid Chromatograph-tandem mass spectrometer (LC-MS/MS)
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic
![Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic](/thumbs/90/103241154.jpg) Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
 Metabolomica Analisi di biofluidi mediante spettroscopia NMR Michael Assfalg Università di Verona Terminology Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
Metabolomica Analisi di biofluidi mediante spettroscopia NMR Michael Assfalg Università di Verona Terminology Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
a 10 4 Link et al. Supplementary Figure 1 Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.1842 Cells per mouse ( 10 5 ) TRPV2KO anti-gr1 anti-gr anti-f4/80
 a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
Sample Preparation is Key
 PLOS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117232 February 6, 2015 Presented by Katie Gibbs Sample Preparation is Key Sample extraction and instrumental analysis methods are well documented in metabolomics. Understanding
PLOS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117232 February 6, 2015 Presented by Katie Gibbs Sample Preparation is Key Sample extraction and instrumental analysis methods are well documented in metabolomics. Understanding
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
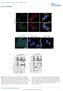 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Sample Concentration and Analysis of Human Hormones in Drinking Water
 Sample Concentration and Analysis of Human Hormones in Drinking Water Carl Fisher Applications Chemist Ion Chromatography/Sample Preparation Thermo Fisher Scientific March 1, 215 1 The world leader in
Sample Concentration and Analysis of Human Hormones in Drinking Water Carl Fisher Applications Chemist Ion Chromatography/Sample Preparation Thermo Fisher Scientific March 1, 215 1 The world leader in
Food Intake Regulation & the Clock. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Food Intake Regulation & the Clock Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Circadian disruption affect multiple organ systems: The diagram provides examples of how circadian disruption
Food Intake Regulation & the Clock Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Circadian disruption affect multiple organ systems: The diagram provides examples of how circadian disruption
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for New Journal of Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
