Qualifying Examination (Part I)
|
|
|
- Erick King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 19-22, 2011 Committee Members: Heidi Hamm Craig Lindsley Chang Chung Seva Gurevich Tuesday, July 19 Exam 9:00 11:00 Sara Savage Exam 11:00 1:00 Lisa Murphy Exam 2:00 4:00 Cierra Spencer Exam 4:00 6:00 Greg Sliwoski Wednesday, July 20 Exam 11:00 1:00 Ryan Ceddia Exam 2:00 4:00 Zack Zurawski Exam 4:00 6:00 Jamille Robinson Thursday, July 21 Exam 9:00 11:00 Rene Raphemot Exam 11:00 1:00 David Stevens Exam 2:00 4:00 Alex Nackenoff Friday, July 22 Exam 9:00 11:00 Tu Mai Exam 11:00 1:00 Craig Goodwin Exam 2:00 4:00 Jing Wu 5:00 pm Results to Students (in Pharm South, 449 PRB) Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary, you may prepare written answers, overhead figures, or any type of materials that you think might be useful in the presentation of your answers. You may bring such preparation materials with you to the examination. The oral examination itself will not extend beyond two hours. If you have any questions regarding the examination, please contact Seva Gurevich at: (w) (c)
2 Question 1 Cocaine is an abused psychostimulant that interacts with monoamine (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin) transporters blocking the reuptake of these neurotransmitters. Neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens (NAC), a central component of the mesolimbic dopamine (DA) system, has been implicated in the development of cocaine induced psychomotor sensitization and relapse to cocaine seeking. Administration of mglur agonists induces long term depression (LTD), i.e. persistent reduction in the evoked synaptic currents, in NAC neurons. Experiments were conducted to investigate the effect of withdrawal from chronic cocaine on mglurdependent LTD. Some of the results are presented in Figures 1 and 2 below. LTD recording were conducted in brain slices prepared from animals chronically treated with saline, cocaine, or cocaine in combination with other drugs as indicated in the legends to Figures. Figure 1. Effect of cocaine withdrawal on the induction of LTD by a non selective group I mglur agonist DHPG in NAC. Example (C) LTD in NAC and summary (E) of normalized EPSC (excitatory postsynaptic current) amplitude before and after brief application of DHPG (100 μm) for 5 min in saline (SAL) or cocaine (COC) treated mice on withdrawal day 14. The magnitude of LTD was measured 30 min after washout of DHPG. Horizontal bar denotes the period of delivery of DHPG. Dashed line indicates baseline level. *p < 0.05 compared with SAL control, unpaired Student's t test.
3 Question 1 Figure 2. mglur mediated the LTD in NAC. Graphs show normalized EPSC amplitude before and after brief application of DHPG (100 μm) for 5 min in the NAC. Drugs were applied 10 min prior the application of DHPG. Summary of experiments showing the effects of mglur1 antagonists, CPCCOEt (A) or LY (B), on DHPG LTD induction in the NAC in slices from saline (SAL) or cocaine (COC) treated mice examined on withdrawal day 14. Summary of experiments showing the effect of mglur5 antagonist MPEP on DHPG LTD induction in the NAC in slices from SAL or COC treated mice (C). Summary of experiments showing the effect of M1 muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist pirenzepine on DHPG LTD induction (D). Summary of experiments showing the effects of different mglur antagonists on DHPG LTD induction for data in A D (E). #p < 0.05 compared with SAL control; *p < 0.05 compared with SAL drug alone, unpaired Student's t test.
4 Question 1 Figure 3. The role of dopamine receptors in LTD in NAC. Summary of experiments showing the induction of DHPG LTD in the NAC in slices from mice receiving D1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH min before saline (SAL) or cocaine (COC) injections for 5 d and then examined on withdrawal day 14 (A). Summary of experiments showing the induction of DHPG LTD in the NAC in slices from mice receiving D2 receptor antagonist raclopride before SAL or COC injections (B). Summary of experiments showing the induction of DHPG LTD in the NAC in slices from mice receiving a specific 5 HT2C receptor antagonist RS before SAL or COC injections (C). Summary of experiments showing the effects of different antagonist pretreatment on the development of cocaine induced impairment of DHPG LTD for data in A C (D). *p < 0.05 compared with SAL drug alone, unpaired Student's t test. 1. Describe the study as you see it from the figures presented. Describe the main objective of the study and the steps. Provide the rationale for each step and for the use of the specific drugs. 2. Based on the data presented, do you think the objective has been achieved? If not, propose additional experiments to obtain necessary information and propose a model to account for all findings.
5 Question 2 An exploratory compound, VUXY (MW = 300 g/mol) displayed an in vitro IC 50 of 200 nm in antagonizing a receptor expressed in a rodent cell line. VUXY was subsequently evaluated in vivo (single oral dose of 10 mg/kg) and found to be ineffective in a rodent pharmacological model that is sensitive to antagonism of the receptor. It is well established that efficacy associated with this particular rat pharmacological model correlates with a Cmax obtained that is equal to, or exceeds the in vitro IC 50. An in vitro DMPK appraisal indicated that VUXY was highly protein bound in rat plasma producing a fraction unbound (F u ) of 0.03 and was metabolized in rat liver microsomes with a predicted hepatic clearance (CL HEP ) of 35 ml/min/kg (Figure 1). The metabolism of VUXY in rat microsomes is NADPH dependent. Displayed in Table 1 are the resulting pharmacokinetic parameters of VUXY calculated from data obtained following an IV and PO dose of the test article in rats. Figure 1. Metabolism of VUXY in rat liver microsomes employing substrate depletion approach. Nonlinear Regression Analysis Linear Regression Analysis Table 1. VUXY PK in Sprague-Dawley Rats Data compiled from a 1 mg/kg IV and 10 mg/kg PO study PK parameters Cl (ml/min/kg) 34 Vss (L/kg) 5.6 T ½ (min) 114 AUC (I.V., 1 mg/kg) (ng.hr/ml) 485 Cmax, systemic (ng/ml) 1410 Cmax, portal vein (ng/ml) 2310 Tmax (hr) 1.5 AUC (PO, 10 mg/kg) (ng.hr/ml) 2625
6 Question 2 1. Interpret the PK data from Figure 2 & Table 1, indicating how the Clearance and Volume of distribution values were obtained. Estimate the bioavailability of VUXY in rats. Please include in your discussion a definition of the statement that half life is a dependent PK parameter. Discuss the basic design of an in vivo PK experiment, quantitative analysis of compound levels in blood, plasma or serum and the basics of PK analysis. 2. Davies and Morris (Pharmaceutical Research 1993, 10(7), ) report the blood flow to the liver (Q H ) of male rats is 55 ml/min/kg. Using pertinent data from the in vitro DMPK assessment, calculate the predicted hepatic extraction ratio (ER) of VUXY in rat? Is the relationship between Cmax systemic and Cmax portal vein consistent with your calculated ER for VUXY? Please explain. 3. Using the information available to you, how do you account for the lack of efficacy in the rodent model described? 4. Based on the in vitro pharmacology facts associated with VUXYand the corresponding in vitro and in vivo DMPK properties of the compound, propose an experiment that would enable the investigator to test the efficacy of VUXY in the rat pharmacological model.
7 Question 3 You have a new job at a pharmaceutical company. They ask you do design an oral contraceptive pill for women. 1. Other than the ovary, what tissues or organs contribute to regulation of the female reproductive cycle? 2. Starting at the hypothalamus, describe hormones made by this axis that control the reproductive cycle use a drawing to help 3. What is the difference between the first half of the menstrual cycle and the second half? How do hormone changes result in ovulation of a single oocyte? 4. With this hypothalamic pituitary ovarian axis in mind, what hormones would you include in an oral contraceptive pill, and how would you expect this to prevent ovulation?
8 Question 4 c-kit is a member of platelet derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) family (Figure 1), and is activated by stem cell factor (SCF) that regulates hematopoiesis. Mutations in c-kit have been found in human mastocytosis, which is characterized by increased mast cells. In adult sporadic mastocytosis, three types of mutations, D816V, D816Y, and D816F were detected in c-kit. Mutations such as E839K also were found in patients with anemia with reduced red blood cells. To understand how these mutations lead to mastocytosis and anemia, each mutation was introduced into full-length c-kit cdna, and mutant cdna was transfected into COS cells for functional characterization. Results are shown in Figures 2 and 3. Figure 1. A schematic diagram depicting structure of c-kit and mutations found in patients with mastocytosis and anemia. Figure 2. Wild-type and mutant c-kit phosphorylation in COS cells. Shown is the Western blotting (top, anti-phosphotyrosine, bottom, anti-kit antibodies) of immunoprecipitates using anti-kit antibodies. Figure 3. Phosphorylation of c-kit (E839K) and c-kit (E839K, D816V) in COS cells. 1. Explain the experimental details and results as shown in Figures 2 and 3. Speculate how each mutation (D816V, D816Y, D816F, and E839K) affects the normal activity of c-kit. 2. Based on your understanding regarding how c-kit is regulated, design additional experiments to support your hypothesis in relation to how mutant c-kit functions to cause mastocytosis and anemia. 3. What are known downstream targets following c-kit activation? Which pathway is most likely to cause the observed mastocytosis phenotype? Design at least two independent experiments to support your hypothesis.
9 Question 5 The genes encoding the β1 adrenergic receptor (β1ar) and Gαs have been targeted in the mouse. Both heterozygous null mice are viable and have no significant difference in cardiac contractility as measured by echocardiography. Wild type and heterozygous null cardiac myocytes were analyzed below. Figure 1. β1ar, Gαs levels of Gαs+/- and β1ar+/- mice. (a d) β1ar mice (a, c) and Gαs mice (b, d) protein levels were measured by immunoblotting in heart muscle extracts of Gαs +/- (n=5, b, d) and β1ar+/- (n=6, a, c) mice and expressed as percentages of the levels found in the myocytes of their wild-type littermates (n=5 6). Student's t-test: * p<0.05, *** p< Figure 2, below. Contractility in isolated myocytes from wildtype and β1ar+/- or wildtype and Gαs+/- mice. Left panel Myocytes isolated from 3 month old littermates. N=5 for each genotype. Right panel Myocytes isolated from 3 month old littermates. N=5 for each genotype. 1. Diagram the pathway whereby the β1 adrenergic receptor regulates cardiac contractility. 2. How do you explain the above data? Present hypotheses for data in Figure 2, left and right panels, with experiments to test them. 3. How do you explain the lack of altered contractility in intact heterozygous null animals?
10 Question 6 Several factors mediate the regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) such as angiotensin II and tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF). Recently, investigators at the Panamanian Institute for Glomerular Science (PIGS) have uncovered a novel mechanism of GFR regulation involving feedback from the connecting tubule (CNT) a short segment of the distal nephron locating between the end of the distal convoluted tubule and the cortical collecting duct. Changes in tubular fluid flow rate or solute delivery to the CNT evoke changes in GFR analogous to TGF, but in the opposite direction. Specifically, a high rate of fluid delivery to the CNT evokes vasodilation of the afferent arteriole and a rise in GFR (see Figure 1). This CNT glomerular feedback (CTGF) requires a functional amiloride sensitive sodium channel (ENaC) in the CNT. The investigators have now tested the hypothesis that CTGF can modulate the magnitude of TGF by performing the experiments illustrated in Figure 2. Specifically, stop flow pressure (surrogate for GFR) was measured in superficial rat cortical nephrons while changes in the rate of perfusion of the adjacent thick ascending limb were made. Benzamil, a more selective and more potent derivative of amiloride was used in one set of experiments. 80 Fig 1 Effect of perfusing CNT with low or high NaCl concentration. *, p < 0.05, high vs low NaCl. Fig 2 TGF measurements in rat cortical nephrons. (A) Stop-flow pressure (P SF ) in response to changes in thick ascending limb perfusion rate in the presence or absence of benzamil (Bzl). (B) Change (delta) in P SF calculated for each perfusion rate relative to 0 nl/min. ***, p< Propose at least one hypothesis or model to explain the behavior of P SF under the control condition, especially at the highest perfusion rates. Explain the effect of benzamil with your model. 2. Predict how the behavior of P SF under control conditions might change if the experimental animals were pretreated for 1 week with a supra physiological dose of aldosterone. 3. Predict how the behavior of P SF under control conditions might change if the experimental animals were pretreated with a selective adenosine 1A receptor antagonist.
11 Question 7 β1 and β2 adrenergic receptors (βars) are highly homologous and both activate Gs, but they play distinct roles in cardiac physiology and pathology. Myocyte contraction, for instance, is stimulated by β1ar but not β2ar signaling, and chronic stimulation of the two receptors has opposing effects on myocyte survival. Differences in the assembly of macromolecular signaling complexes could explain the distinct biological effects elicited via activation of these receptors. Although prior studies have demonstrated that agonist occupancy of the β2ar initiates recruitment of a preformed complex consisting of β arrestin and a camp specific phosphodiesterase (PDE4D5), no data are available on the potential interaction of PDEs with the β1ar. To address this question, a group of investigators performed the experiments described below. Figure 1. A) Mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes were infected with control adenovirus (Mock) or an adenovirus encoding Flag tagged β1ar. Flag immunoprecipitations were performed from the cell extracts and assayed for PDE activity. Non PDE4 activity represents the activity measured in the presence of a PDE4 specific inhibitor. B) Flag immune complexes from wild type (WT) and PDE4A, PDE4B, and PDE4D deficient mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes infected with control adenovirus (Mock) or Flag β1ar adenovirus were assayed for PDE activity. Figure 2. A) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts derived from mice deficient in β arrestin 1 and 2 (βarr1/2ko) or from wild type controls (WT MEF) were infected with Myc PDE4D8 adenovirus together with (+) or without ( ) Flagβ1AR adenovirus. The cell lysates (Input) and Flag immune complexes (IP:M1) were subjected to SDS PAGE and immunoblotted (IB) with the indicated antibodies. B) PDE4D8, Flag β1ar, and Flag β2ar were purified after expression in baculovirus. Purified PDE4D8 was incubated in the absence ( ) or presence (+) of the indicated purified βar, and the receptor was immunoprecipitated using anti Flag resin and subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis.
12 Question 7 Figure 3. Neonatal cardiac myocytes derived from β2ar null mice (A) and β1ar null mice (B) were treated for 3 min with (+) or without ( ) 10 µm isoproterenol (ISO). At the end of the incubation, PDE4D5, PDE4D8, and PDE4D9 were immunopurified from the cell lysates with isoform specific antibodies and assayed for PDE activity. C) The indicated PDE4D splice variant was immunopurified from extracts of wild type neonatal cardiac myocytes treated with (+) or without ( ) forskolin and subsequently assayed for PDE activity. Data shown are expressed as the means +/ s.e.m. of at least three experiments. NS (P>0.05); * (P<0.05); ** (P<0.005); *** (P<0.0005). 1. What do the data in Figs. 1 and 2 tell you about the interaction of PDE4Ds with the β1ar? 2. How would you interpret the data shown in Fig. 3? To assess the role of PDE4D in β1ar function in a more physiological context, the investigators monitored changes in the heart rate of mice following β adrenergic stimulation, as it is known that in vivo contraction rate is primarily controlled by β1ar. Wild type mice (4DWT) and PDE4D null mice (4DKO), matched by age, sex, and genetic background, were sedated using isoflurane. While their heart rate was continuously measured, the mice were injected with a submaximal dose of isoproterenol (ISO). Wild type mice and PDE4D null mice showed no significant differences in either basal heart rate (4DWT = 410+/ 52 and 4DKO = 400+/ 45 beats/min) or maximal heart rate after the ISO injection (4DWT = 540+/ 25 and 4DKO = 550+/ 20 beats/min). However, when the investigators monitored the decline in heart rates of 4DWT and 4DKO mice as a function of time after ISO injection, they observed the following results.
13 Question 7 3. What conclusions can be drawn from the above data about the role of PDE4D in the control of heart rate? 4. Based on the data shown in Figs. 1 4, propose a reasonable hypothesis that might explain the molecular events underlying PDE4D regulation of β1ar signaling/function. Design an experiment that would allow you to further test your hypothesis.
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 17-19, 2012 All Exams take place in the Bass Conference Room (436 RRB) Tuesday, July 17 th 10:00 am 12:00 pm (Exam #1) 12:00 pm 1:00 pm Lunch
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 17-19, 2012 All Exams take place in the Bass Conference Room (436 RRB) Tuesday, July 17 th 10:00 am 12:00 pm (Exam #1) 12:00 pm 1:00 pm Lunch
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 STUDENT VERSION Qualifying Exam July 2013 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 15-19, 2013 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Tuesday, July 16 th
STUDENT VERSION Qualifying Exam July 2013 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 15-19, 2013 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Tuesday, July 16 th
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 11-14, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 11-14, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 19 23, 2010 Examination Schedule: Tuesday, 10:00 AM 12:00 PM EXAM Lyndsey Anderson July 20 th 12:00 PM 1:00 PM Lunch for Examination Committee
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 19 23, 2010 Examination Schedule: Tuesday, 10:00 AM 12:00 PM EXAM Lyndsey Anderson July 20 th 12:00 PM 1:00 PM Lunch for Examination Committee
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Development of the camp biosensor targeted to the SERCA2a microdomain.
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Development of the camp biosensor targeted to the SERCA2a microdomain. A B C (A) Schematic representation of the new constructs designed for local camp imaging.
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Development of the camp biosensor targeted to the SERCA2a microdomain. A B C (A) Schematic representation of the new constructs designed for local camp imaging.
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
Biology 153/155. Equivalency Exam 60 QUESTIONS 18 PAGES
 Biology 153/155 Equivalency Exam 60 QUESTIONS 18 PAGES Student name: Student number: Signature: READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. The mark value for each question is posted in the margin. Good luck! 3 1) On
Biology 153/155 Equivalency Exam 60 QUESTIONS 18 PAGES Student name: Student number: Signature: READ EACH QUESTION CAREFULLY. The mark value for each question is posted in the margin. Good luck! 3 1) On
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
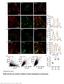 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 20 24, 2009 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 20 24, 2009 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary,
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response.
 Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: % of grade in class
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) During exercise, plasma levels of Renin increase moderately. Why should Renin levels be elevated during
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 Exam # 2 October 25, 2013 Total POINTS: 100 20% of grade in class 1) During exercise, plasma levels of Renin increase moderately. Why should Renin levels be elevated during
Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m.
 20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except Drs.
20.201 Take-Home Exam Distributed: October 19, 2012, at 2:30 p.m. Due: October 24, 2012, at 1:30 p.m. Directions: This take-home exam is to be completed without help from any other individual except Drs.
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: immunoprecipitation with anti-casr antibody The Casr protein was expressed in transiently transfected HEK cells. Cell lysates from HEK cells were subjected
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Student Edition Qualifying Exam December 2015 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15, 2015 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Time Student Name
Student Edition Qualifying Exam December 2015 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15, 2015 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Time Student Name
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms
 Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from WT and Adcy1 KO mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody.
 ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function. NS201c
 Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, and Function NS201c Human Basal Ganglia Anatomy Basal Ganglia Circuits: The Classical Model of Direct and Indirect Pathway Function Motor Cortex Premotor Cortex + Glutamate
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
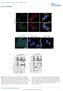 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain -
 - Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
- Neurotransmitters Of The Brain - INTRODUCTION Synapsis: a specialized connection between two neurons that permits the transmission of signals in a one-way fashion (presynaptic postsynaptic). Types of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Pharmacology. Biomedical Sciences. Dynamics Kinetics Genetics. School of. Dr Lindsey Ferrie
 Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Pharmacology Dynamics Kinetics Genetics Dr Lindsey Ferrie lindsey.ferrie@ncl.ac.uk MRCPsych Neuroscience and Psychopharmacology School of Biomedical Sciences Dynamics What the drug does to the body What
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Supplementary legends
 Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 29 August 1, 2008 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 29 August 1, 2008 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA3 output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity
 Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
Synaptic Communication. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
Synaptic Communication Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News The first exam is next week on Friday! Be sure to checkout the sample exam on the course website. 2
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
 Article Addendum Channels 5:3, 205-209; May/June 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Article Addendum Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
Article Addendum Channels 5:3, 205-209; May/June 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Article Addendum Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure 2 George D. Ford, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the Central Nervous System Ischemic Response. 2. Describe chemical sensitivities of arterial and cardiopulmonary chemoreceptors,
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels. Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker
 Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
Enhancement of synaptic transmission by cyclic AMP modulation of presynaptic I h channels Vahri Beaumont and Robert S. Zucker Background I h channels discovered in 1976 (Noma A. and Irisawa H.) Voltage-gated
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Pharmacodynamics. Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology
 Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
Pharmacodynamics Prof. Dr. Öner Süzer Cerrahpaşa Medical Faculty Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology www.onersuzer.com Last updated: 13.05.2010 English Pharmacology Textbooks 2 2 1 3 3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
MBG301. Class IV. Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish)
 MBG301 Class IV Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish) 1. Adenylcyclase activation by GPCRs 2. Ion channel regulation by GPCRs 3. Phospholipase C (PLC) activation
MBG301 Class IV Classification of GPCRs according to their effector function (according to Lodish) 1. Adenylcyclase activation by GPCRs 2. Ion channel regulation by GPCRs 3. Phospholipase C (PLC) activation
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Supplementary Figure 1
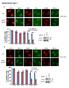 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions
 Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
