Supplemental Data. Feiz et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc /- raf1-1
|
|
|
- Charlotte Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1/ WT 1/5 1 -/- raf1-1 +/+ -/- raf1-1 +/+ bsd2 BSD2 actin Supplemental Figure 1. Accumulation of the BSD2 transcript in raf1. RT- PCR was performed using primers ZmBSD2-SQF and ZmBSD2-SQR (Supplemental Table 3). Actin was used as the control gene amplified using primers ZmActin1-SQF and ZmActin1- SQR. Samples with genotype +/+ are siblings of the parents of raf1-1 homozygous (-/-) mutants. bsd2 mutant was used as a negative control. 1
2 A MW -/- raf1-1 +/+ WT cousins B ZmRAF1-FOR1 and ZmRAF1-REV1 (386 bp) RAF1 WT 1/ 1/5 1 -/- raf1-1 -/- raf1-1 +/+ +/+ Mu primers and ZmRAF1-REV1 (~2 bp) actin Supplemental Figure 2. Validation of RAF1 gene identification. (A) Gene-specific PCR validating RAF1 identification. The higher and lower molecular weight products appear to result from mis-priming by the ZMRAF1-FOR1 primer. (B) Accumulation of RAF1 transcripts in raf1-1. RT-PCR was performed using ZmRAF1-FOR1 and ZmRAF1-REV1 primers. Actin was used as the control gene. MW -/- raf1-1 -/- raf1-2 -/- raf bp 700 bp 600 bp 500 bp 400 bp Supplemental Figure 3. Gene-specific PCR validating the locations of the three RAF1 insertions. The primers Mu and ZmRAF1-REV2 amplified the region between each insertion and 23 bp upstream of the stop codon. 2
3 Supplemental Data. Feiz et al. (2012). Plant Cell.15/tpc raf1-1-1 raf1-1-2 raf1-1-2 raf1-1-3 raf1-2-1 raf1-2-2 raf1-2-4 raf1-2-5 raf1-2-6 raf1-3-1 raf1-3-2 raf1-3-3 raf1-3-5 raf1-3-2 raf1-2-1 raf1-2-1 raf1-2-3 raf1-3-6 raf1-1-1 raf1-1-3 raf1-1-3 raf1-1-1 raf1-1-2 raf1-1-2 raf1-1-1 raf1-1-3 raf1-1-1 raf1-2-4 C B Ear ID A B C D cross female male LF4.7 LF3.4 4DT LS segregating P pale green F1 value D segregating green F C1 C2 D1 Ear female parent(+) male parent(+) A188 A1 A2 B1 B2 A α-ls raf1 alleles α-raf1 α -PetA Supplemental Figure 4. Complementation crosses confirm that raf1 encodes the regulator of Rubisco accumulation. (A) Genetic analysis of crosses between heterozygotes carrying the indicated alleles. The P-value was derived from a Chi-squared test, based on the phenotypic segregation patterns of F1 progeny. (B) Crosses used for the immunoblot analysis in panel (C). (C) Immunoblot analysis of representative complementation cross progeny as given in panel (B). 3
4 A Supplemental Figure 5. Alignment of RAF1 homologues. Page 1 of 2; see legend on page 2. 4
5 Supplemental Figure 5. Alignment of RAF1 homologues. Alignments were performed using the ClustalW option of the MEGA4 program, after deletion of the predicted chloroplast transit peptide from the plant proteins. Amino acids are color coded as hydrophobic, yellow; polar, green; acidic, red; basic, blue; tyrosine, light green; glycine, pink; proline, blue; cysteine, brown; and histidine, light blue. The first 35 amino acids of a 60 amino acid domain identified by MGD as having homology to Docking domain A of the erythromycin polyketide synthase are highlighted with a black bar, whereas the last 21 amino acids, highlighted is gray, are conserved only in monocots and are absent from cyanobacterial proteins. 5
6 (A) kd WT 1/ 1/50 1/0 raf1-1 (1X) raf1-1 (5X) (B) WT 1X WT 1/X WT 1/50X WT 1/0X raf1-1x raf1-5x LS C Rb Supplemental Figure 6. Analysis of LS from total soluble protein. (A) Native gel analysis. Total soluble leaf proteins of -day-old WT and raf1-1 seedlings were extracted from equal surface areas and separated in a 3-12% native gel, which was analyzed by immunoblotting for LS. LS C marks the migration of the putative LS-chaperone complex, and Rb the position of Rubisco holoenzyme. (B) Denaturing gel analysis of the same protein samples. 6
7 A RAF1 260 nm absorbance Ovalbumin 44 kd γ-globulin, 157 kd Min B Charge envelope of the Raf monomer Deconvoluted data to find monomer mass Supplemental Figure 7. Analysis of recombinant RAF1. (A) Purified γ-globulin, ovalbumin and RAF1 were separated in parallel by size exclusion chromatography. The smaller peaks observed for ovalbumin and γ-globulin are dimers. X-axis, time in min. QTof-MS was used to assess the purity of the three RAF1 peaks. Both the trimeric and monomeric peaks yielded a monomermic mass as 47,601.1 Da, corresponding to rraf1. The peak migrating near 75 min, however, contained a mixture of proteins and thus cannot be confirmed as a RAF1 complex. (B) QTOF mass spectrometry of the ~150 kda peak of rraf to determine the components of the higher molecular complex. 7
8 Tagged Protein / Vector His-LS/pET RAF1/pRSF His-BSD2/pRSF Cpn60β1-S/pCDF His-Cpn60α1/ pacyc Cpn20-2-S/pACYC + + Cpn20-3-S/pACYC + His-RBCX/pCDF + + SS/pCDF + His-LS α-ls RAF1 α-raf1 Soluble Cpn60β1-S Cpn20-2/3-S α-s His-Cpn60α1 α-his His-LS α-ls Insoluble Supplemental Figure 8. Co-expression of LS and Rubisco biogenesis factors in E. coli. The RAF1 requirement for the solubility of maize LS was assessed in E. coli cells with coexpression of RAF1 and other Rubisco biogenesis factors, including BSD2 (GRMZM2G062788), Cpn60α1, Cpn60β1, Cpn20-2 (GRMZM2G127609), Cpn20-3 (GRMZM2G399284), RBCX (GRMZM2G115476) and SS (GRMZM2G098520). Extracted lysate from untransformed E. coli Bl21DE3 was used as negative control (lane 1). Methods: Expression from Duet vectors (Novagen) was induced by 1 mm IPTG in Bl21(DE3) cells grown to OD of 0.5, for two hr at 28 C. Equivalent amounts of cells were lysed by sonication and fractioned into soluble and insoluble fractions by centrifugation (15,000xg, 30 min at 4 C). Fractions were analyzed by 13% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with LS (Agrisera), RAF1, S-tag (GenScript) and His-tag (Sigma) antibodies. 8
9 Species Locus 1 Zea mays GRMZM2G Oryza sativa NM_ Sorghum bicolor XM_ Triticum aestivum AK Glycine max AK Arabidopsis thaliana-1 AT5G Arabidopsis thaliana-2 AT3G Brassica rapa AC Vitis vinifera XM_ Ricinus communis XM_ Populus trichocarpa XM_ Coffea canephora ABZ Medicago truncatula AC Selaginella moellendorffii XM_ Physcomitrella patens XM_ Picea glauca BT Ostreococcus tauri XM_ Micromonas sp. XM_ Nostoc azollae CP Anabaena variabilis CP Acaryochloris marina CP Synechococcus sp. CP Cyanothece sp. CP Gloeobacter violaceus BA Trichodesmium erythraeum CP Microcystis aeruginosa AM Supplemental Table 1. Accession numbers of RAF1 sequences from green species. The maize accession number was obtained from The raf1 loci from other species were obtained from Genbank, except the Setaria viridis sequence, which was kindly provided by Dr. Katrien Devos, Univ. Georgia. The protein sequence for Selaginella moellendorffii present in the database is incorrect. 9
10 Data from WT sample Accession number Annotation Curated Loc. Score Match GRMZM2G385622_P01 (GRMZM2G062854_P01) CF1 beta subunit (atpb) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side GRMZM2G360821_P01 Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large subunit plastid stroma NP_ CF1α alpha subunit (atpa) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side GRMZM2G083841_P01 Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase 1 (PEPCase 1) cytosol GRMZM2G113033_P01 Rubisco small subunit-4 (RBCS-4) -1 plastid stroma GRMZM2G085019_P01 NADP-malic enzyme 4-1&2 (NADP-ME4) plastid stroma GRMZM2G098520_P01 Rubisco small subunit-4 (RBCS-4) -2 plastid stroma GRMZM2G011507_P01 pyruvate phosphate dikinase-1 (PPDK-1) M (C4) plastid stroma GRMZM2G337113_P02 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase A-2 (GAPA-2) plastid stroma GRMZM2G048907_P01 CF1 γ subunit (atpc) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side GRMZM2G083716_P01 Cpn60-beta-1 plastid stroma AC _FGP005 Cpn60-alpha-1 plastid stroma GRMZM2G064096_P01 germin-like protein (GER3) 111 GRMZM2G046284_P01 fructose-bisphosphate aldolase-2 (SFBA-2) plastid stroma 2 7 GRMZM2G007263_P01 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase B ( M-enriched) plastid stroma 80 8 GRMZM2G6061_P01 elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu-1), plastid plastid stroma 60 8 GRMZM2G001696_P01 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mitochondria 52 2 GRMZM2G041275_P01 ATP synthase beta subunit mitochondria 48 4 GRMZM2G083016_P01 phosphoglycerate kinase 2 (PGK-2) BS-enriched plastid stroma 43 6 GRMZM2G089136_P01 phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK-1) M-enriched plastid stroma 43 8 GRMZM2G018197_P01 Ribosomal protein L4/L1 family chloroplast/cytosol 42 6 GRMZM2G098290_P01 glutamate-ammonia ligase (GS2), chloroplast plastid stroma 41 5 GRMZM2G079668_P01 cphsp70-1 (DnaK homologue) plastid stroma 41 3 NP_ ribosomal protein S18 chloroplast 38 2 GRMZM2G084465_P01 40S ribosomal protein S GRMZM2G007695_P01 Ribosomal protein L4/L1 family chloroplast/cytosol 35 4 GRMZM2G015419_P02 lipoxygenase 2.3 chloroplast 35 5 GRMZM2G1689_P01 U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein PRP4-like protein-like 35 4 GRMZM2G3533_P01 40S ribosomal protein S GRMZM2G016232_P01 Histone H4 nucleus 33 2 GRMZM2G360021_P01 50S ribosomal protein L12-C plastid ribosome 32 6 Data from raf1 sample GRMZM2G083841_P01 Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase 1 (PEPCase 1) cytosol GRMZM2G011507_P01 pyruvate phosphate dikinase-1 (PPDK-1) M (C4) plastid stroma GRMZM2G085019_P01 NADP-malic enzyme 4-1&2 (NADP-ME4) plastid stroma GRMZM2G385622_P01 (GRMZM2G062854_P01) CF1 beta subunit (atpb) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side NP_ CF1a alpha subunit (atpa) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side GRMZM2G064096_P01 germin-like protein (GER3) GRMZM2G097457_P01 C3-type pyruvate phosphate dikinase-2 plastid stroma GRMZM2G6061_P01 elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu-1), plastid plastid stroma GRMZM2G158394_P01 extracellular ribonuclease LE precursor GRMZM2G007263_P01 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase B (M-enriched) plastid stroma GRMZM2G121878_P01 carbonic anhydrase chloroplastic-like chloroplast GRMZM2G337113_P02 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase A-2 (GAPA-2) plastid stroma 124 GRMZM2G046284_P01 fructose-bisphosphate aldolase-2 (SFBA-2) plastid stroma GRMZM2G089136_P01 phosphoglycerate kinase 7 20 GRMZM2G083716_P01 Cpn60-beta-1 plastid stroma 1 11 GRMZM2G079668_P01 cphsp70-1 (DnaK homologue) plastid stroma 66 3 GRMZM2G047028_P01 phosphoglycerate kinase 56 4 GRMZM2G154218_P01 elongation factor 1 alpha 53 5 GRMZM2G048907_P01 CF1 gamma subunit (atpc) thylakoid-peripheral-stromal-side 49 2 GRMZM2G134797_P02 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 48 8 NP_ ribosomal protein S18 chloroplast 45 4 GRMZM2G057535_P01 elongation factor 1-alpha 45 3 GRMZM2G172369_P03 lysosomal alpha-mannosidase-like 43 1 GRMZM2G008247_P01 beta-d-glucosidase precursor 40 8 AC _FGP005 Cpn60-alpha-1 plastid stroma 40 7 GRMZM2G119169_P01 60S ribosomal protein L GRMZM2G129246_P01 peroxisomal (S)-2-hydroxy-acid oxidase GLO1-like 39 2 GRMZM2G134264_P01 hypothetical protein 39 4 GRMZM2G024354_P01 60S ribosomal protein L GRMZM2G013478_P01 nucleoside diphosphate kinase GRMZM2G360021_P01 50S ribosomal protein L12-1 plastid ribosome 30 2 GRMZM2G137868_P01 serine--glyoxylate aminotransferase 29 2 GRMZM2G084465_P01 40S ribosomal protein S Supplemental Table 2. Protein data obtained from gel slices corresponding to the position of LS C. Accession numbers are from Gramene. Curated Loc. indicates the annotated subcellular location. Score, the sum of the highest ion score for each protein; Match, the number of MS/MS spectra that were matched to each protein. The cells highlighted in yellow indicate proteins identifed in both genotypes; cells highlighted in green indicate the chaperonins discussed in the main text.
11 Primer name Sequence 1 ZmBSD2-SQF CGTCTCCCGCCACTGCAAGA 2 ZmBSD2-SQR TTCATCGAAAGTGCTAAACCGATGAC 3 ZmActin1-SQF TACGAGCGCTGAGCGGGAGA 4 ZmActin1-SQR GCTGCTAGGAGCCAGGGACG 5 ZmrbcL-Cod1 TTGCCGCGACAACGGCCTAC 6 ZmrbcL-Rev1 TCGCGCCCTTCGTTACGAGC 7 ZmRBCS2-Cod1 GGCCTACGGCAACAAGAAGTT 8 ZmRBCS2-Rev1 CAAGAATCGACAGTCGTTGC 9 ZmPsbA-5 CTTCTTCTTGCCCGAATCTG ZmPsbA-3 TATCGCATTCATTGCTGCTC 11 EoMu1 GCCTCCATTTCGTCGAAT CCC 12 EoMu2 GCCTCTATTTCGTCGAATCCG 13 ZmRAF1-FOR1 AGCTCTACC AGCCGTTCCAC 14 ZmRAF1-REV1 CTCGAGCCTGTAGCCGATG ZmRAF1-FOR2 GGTCCTGTACGAGCTCCGCT 15 ZmRAF1-REV2 CATGTCGTCCTCGTCCTTGG 16 Zmqactin-1F GTG ACA ATGGCACTGGAATG 17 Zmqactin-1R CCA TGCTCAATCGGGTACTT 18 ZmqLS-1F AAGGGGAACGCGAAATAACT 19 ZmqLS-123R AGGCTTCTAAAGCCACACGA 20 ZmqSS-9F GTTCGTGTACCGCGAGAACT 21 ZmqSS-9R GTCGATCTAGCCACGGTCTC 22 ZmqME-1F TGGCAGAGCAGACGTATTTG 23 ZmqME-1R TGAAGGGAGCCTTTACGAGA 24 ZmqMDH-1F TCACCTGCTGTTCAA ACTCG 25 ZmqMDH-1R GGATACAGCGAGTCCTCCAG Supplemental Table 3. Primers used in this work. 11
Supplementary Information. thylakoid membrane
 Supplementary Information ALB3 insertase mediates cytochrome b6 co-translational import into the thylakoid membrane Jarosław Króliczewski 1, Małgorzata Piskozub 2,3, Rafał Bartoszewski 3, Bożena Króliczewska
Supplementary Information ALB3 insertase mediates cytochrome b6 co-translational import into the thylakoid membrane Jarosław Króliczewski 1, Małgorzata Piskozub 2,3, Rafał Bartoszewski 3, Bożena Króliczewska
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Supplemental Data. Pick and Bräutgam et al. Plant Cell. (2011) /tpc Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters
 Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters Mean Adjustment FOM Number of Clusters Supplemental Figure 1. Figure of merit analysis of metabolite clustering. The algorithm tries 20 times to
Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters Mean Adjustment FOM Number of Clusters Supplemental Figure 1. Figure of merit analysis of metabolite clustering. The algorithm tries 20 times to
WT siz1-2 siz1-3. WT siz1-2 siz1-3. -Pi, 0.05 M IAA. -Pi, 2.5 M NPA
 A WT siz1-2 siz1-3 B WT siz1-2 siz1-3 -Pi C +Pi WT siz1-2 siz1-3 D WT siz1-2 siz1-3 E +Pi, 0.05 M IAA -Pi, 0.05 M IAA WT siz1-2 siz1-3 WT siz1-2 siz1-3 F +Pi, 2.5 M NPA -Pi, 2.5 M NPA Supplemental Figure
A WT siz1-2 siz1-3 B WT siz1-2 siz1-3 -Pi C +Pi WT siz1-2 siz1-3 D WT siz1-2 siz1-3 E +Pi, 0.05 M IAA -Pi, 0.05 M IAA WT siz1-2 siz1-3 WT siz1-2 siz1-3 F +Pi, 2.5 M NPA -Pi, 2.5 M NPA Supplemental Figure
Electron Transport and Carbon Fixation in Chloroplasts
 Module 0210101: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of the Cell Lecture 17 Electron Transport and Carbon Fixation in Chloroplasts Dale Sanders 10 March 2009 Objectives By the end of the lecture you should
Module 0210101: Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of the Cell Lecture 17 Electron Transport and Carbon Fixation in Chloroplasts Dale Sanders 10 March 2009 Objectives By the end of the lecture you should
Supplementary data Characterization of terpene synthase gene family in Artemisia annua L
 POJ 7(5):373-381 (2014) ISSN:1836-3644 Supplementary data Characterization of terpene synthase gene family in Artemisia annua L Weizhang Jia, Ying Wang *, Xuesong Yu, Ling Zhang, Shunhui Liu, Zebo Huang
POJ 7(5):373-381 (2014) ISSN:1836-3644 Supplementary data Characterization of terpene synthase gene family in Artemisia annua L Weizhang Jia, Ying Wang *, Xuesong Yu, Ling Zhang, Shunhui Liu, Zebo Huang
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
s -1 (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in WT, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by
 A 250-2 s -1 B 250-2 s -1 Supplemental Figure 1. The NPQ Phenotype in riq Mutants Was Complemented by Introduction of RIQ Genes. (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by the RIQ1
A 250-2 s -1 B 250-2 s -1 Supplemental Figure 1. The NPQ Phenotype in riq Mutants Was Complemented by Introduction of RIQ Genes. (A) and (B) 2 s 1 in, riq1, and the riq1 mutant complemented by the RIQ1
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB
 Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Supplemental Data. Candat et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc Cytosol. Nucleus. Mitochondria. Plastid. Peroxisome. Endomembrane system
 Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
Cytosol Nucleus 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 PSORT MultiLoc YLoc SubLoc BaCelLo WoLF PSORT
ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis
 ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis Barkat Mustafa, David Tan, Paul WJ Taylor and Rebecca Ford Melbourne School of Land and Environment
ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis Barkat Mustafa, David Tan, Paul WJ Taylor and Rebecca Ford Melbourne School of Land and Environment
Problem Set #5 4/3/ Spring 02
 Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Regulation of Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism Prof. Louise E. Anderson
 Regulation of Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism Louise E. Anderson University of Illinois-Chicago 1 The black dots are gold particles; The smaller particles mark the thylakoid-bound ATP synthase; The larger
Regulation of Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism Louise E. Anderson University of Illinois-Chicago 1 The black dots are gold particles; The smaller particles mark the thylakoid-bound ATP synthase; The larger
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1: Components of Arabidopsis tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Schematic summary of the TCA cycle and the enzymes related to the reactions. The large text and
Journal of Cell Science Supplementary information. Arl8b +/- Arl8b -/- Inset B. electron density. genotype
 J. Cell Sci. : doi:.4/jcs.59: Supplementary information E9. A Arl8b /- Arl8b -/- Arl8b Arl8b non-specific band Gapdh Tbp E7.5 HE Inset B D Control al am hf C E Arl8b -/- al am hf E8.5 F low middle high
J. Cell Sci. : doi:.4/jcs.59: Supplementary information E9. A Arl8b /- Arl8b -/- Arl8b Arl8b non-specific band Gapdh Tbp E7.5 HE Inset B D Control al am hf C E Arl8b -/- al am hf E8.5 F low middle high
Student name ID # 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron acceptor in respiration? In photosynthesis?
 1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron acceptor
1. Membrane transport. A. (4 pts) What ion couples primary and secondary active transport in animal cells? What ion serves the same function in plant cells? 2. (4 pts) What is the terminal electron acceptor
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Biological processes. Mitochondrion Metabolic process Catalytic activity Oxidoreductase
 Full name Glyceraldehyde3 phosphate dehydrogenase Succinatesemialdehyde Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] 2',3'cyclicnucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase Dihydropyrimidinaserelated 2
Full name Glyceraldehyde3 phosphate dehydrogenase Succinatesemialdehyde Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP+] 2',3'cyclicnucleotide 3' phosphodiesterase Dihydropyrimidinaserelated 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10250 Pyruvate uptakes into plastids of C 3 plants Plastids of primary endosymbiotic origin (i.e., plastids of the Archaeplastida 30 ) are bounded by two concentric envelope membranes
doi:10.1038/nature10250 Pyruvate uptakes into plastids of C 3 plants Plastids of primary endosymbiotic origin (i.e., plastids of the Archaeplastida 30 ) are bounded by two concentric envelope membranes
Slide 1. Institute of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science
 Proteome analysis and ph sensitive ratio imaging: Tools to explore the decline in leaf growth under salinity K. H. Mühling, B. Pitann, T. Kranz, C. M. Geilfus and C. Zörb ph MW Slide 1 Plant growth under
Proteome analysis and ph sensitive ratio imaging: Tools to explore the decline in leaf growth under salinity K. H. Mühling, B. Pitann, T. Kranz, C. M. Geilfus and C. Zörb ph MW Slide 1 Plant growth under
Transient Ribosomal Attenuation Coordinates Protein Synthesis and Co-translational Folding
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Transient Ribosomal Attenuation Coordinates Protein Synthesis and Co-translational Folding Gong Zhang 1,2, Magdalena Hubalewska 1 & Zoya Ignatova 1,2 1 Department of Cellular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Transient Ribosomal Attenuation Coordinates Protein Synthesis and Co-translational Folding Gong Zhang 1,2, Magdalena Hubalewska 1 & Zoya Ignatova 1,2 1 Department of Cellular
f(x) = x R² = RPKM (M8.MXB) f(x) = x E-014 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.
 14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
Progenesis QI: complex data processing in plant metabolomics. Introducing an extra gear for. Geert Goeminne
 Progenesis QI: Introducing an extra gear for complex data processing in plant metabolomics. Geert Goeminne gegoe@psb.vib-ugent.be Why Plants? EM Rubin Nature 454, 841-845 (2008) doi:10.1038/nature07190
Progenesis QI: Introducing an extra gear for complex data processing in plant metabolomics. Geert Goeminne gegoe@psb.vib-ugent.be Why Plants? EM Rubin Nature 454, 841-845 (2008) doi:10.1038/nature07190
Mock Exam All of the following are oxidizing agents EXCEPT a. NADP+ b. NADH c. FAD d. e. cytochromes
 Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
Role of GABA Shunt Pathway in Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance
 Role of GABA Shunt Pathway in Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance Dr. Nisreen A. AL-Quraan Jordan University of Science and Technology JORDAN What is GABA? GABA : Gamma-aminobutyric Acid Four carbon non-protein
Role of GABA Shunt Pathway in Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance Dr. Nisreen A. AL-Quraan Jordan University of Science and Technology JORDAN What is GABA? GABA : Gamma-aminobutyric Acid Four carbon non-protein
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration
 AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
AP Bio Photosynthesis & Respiration Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Scantron Instructions
 BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
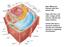 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Identification of lysine succinylation as a new post-translational
 Supplementary Information Identification of lysine succinylation as a new post-translational modification Zhihong Zhang 1,2, Minjia Tan 1,2, Zhongyu Xie 1, Lunzhi Dai 1, Yue Chen 1, Yingming Zhao 1* 1.
Supplementary Information Identification of lysine succinylation as a new post-translational modification Zhihong Zhang 1,2, Minjia Tan 1,2, Zhongyu Xie 1, Lunzhi Dai 1, Yue Chen 1, Yingming Zhao 1* 1.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. AtMYB12 antibody detects both Arabidopsis and tomato MYB12 protein. (a) AtMYB12 antibody detects both SlMYB12 and AtMYB12 in tomato fruit. Both WT and AtMYB12
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. AtMYB12 antibody detects both Arabidopsis and tomato MYB12 protein. (a) AtMYB12 antibody detects both SlMYB12 and AtMYB12 in tomato fruit. Both WT and AtMYB12
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002
 RECITATION TA: NAME: 7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002 This is an open book exam and you are allowed access to books, notes, and calculators. Please limit your answers to the spaces allotted after
RECITATION TA: NAME: 7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002 This is an open book exam and you are allowed access to books, notes, and calculators. Please limit your answers to the spaces allotted after
MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam ANSWER KEY
 MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam ANSWER KEY NAMES: MIT Invitational Tournament 2015 Cell Biology ANSWER KEY ANSWER KEY TEAM ID SCHOOL: 1/2 pt for each row fully correct. Part Plant Animal
MIT Invitational Tournament Cell Biology Exam ANSWER KEY NAMES: MIT Invitational Tournament 2015 Cell Biology ANSWER KEY ANSWER KEY TEAM ID SCHOOL: 1/2 pt for each row fully correct. Part Plant Animal
NAME KEY ID # EXAM 3a BIOC 460. Wednesday April 10, Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided!
 EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
incorporation into fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P); 2-
 Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Cloning and Expression of a Bacterial CGTase and Impacts on Phytoremediation. Sarah J. MacDonald Assistant Professor Missouri Valley College
 Cloning and Expression of a Bacterial CGTase and Impacts on Phytoremediation Sarah J. MacDonald Assistant Professor Missouri Valley College Phytoremediation of Organic Compounds Phytodegradation: Plants
Cloning and Expression of a Bacterial CGTase and Impacts on Phytoremediation Sarah J. MacDonald Assistant Professor Missouri Valley College Phytoremediation of Organic Compounds Phytodegradation: Plants
Chapter 20 - The Calvin Cycle and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway. - Recall the relationship between the light and dark reactions of photosynthesis:
 hapter 20 - The alvin ycle and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway Pages: 550-555 + notes, 563-566, 568, 571-572. Dark Reactions - The alvin ycle - Recall the relationship between the light and dark reactions
hapter 20 - The alvin ycle and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway Pages: 550-555 + notes, 563-566, 568, 571-572. Dark Reactions - The alvin ycle - Recall the relationship between the light and dark reactions
BIOINFORMATICS. Cambridge, MA USA, 3 Department of Plant Biology, University of Florence, Via La Pira, Florence, Italy,
 BIOINFORMATICS Vol. no. Pages Robust and Pareto-Efficient Enzyme Partitions for the Optimisation of CO Uptake and Nitrogen Consumption in C Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism Supplementary information G.
BIOINFORMATICS Vol. no. Pages Robust and Pareto-Efficient Enzyme Partitions for the Optimisation of CO Uptake and Nitrogen Consumption in C Photosynthetic Carbon Metabolism Supplementary information G.
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM LAB SECTION
 BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis
 JOURNAL OF PROTEOMICS 74 (2011) 431 441 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/jprot N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis Masahiro Kamita
JOURNAL OF PROTEOMICS 74 (2011) 431 441 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/jprot N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis Masahiro Kamita
Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold).
 Supplemental Tables Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold). PHT1;1 PHT1;2 PHT1;3 PHT1;4 PHT1;5
Supplemental Tables Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold). PHT1;1 PHT1;2 PHT1;3 PHT1;4 PHT1;5
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1 Sequencing quality. Sample screenshot of re-sequencing raw file quality generated by FastQC. For both the graphs, scores were based on the Illumina 1.5 quality score.
Supplementary Information Figure S1 Sequencing quality. Sample screenshot of re-sequencing raw file quality generated by FastQC. For both the graphs, scores were based on the Illumina 1.5 quality score.
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism
 Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Direct Interaction of Ligand-Receptor Pairs Specifying Stomatal Patterning
 Lee_Jin Suk 1 Direct Interaction of Ligand-Receptor Pairs Specifying Stomatal Patterning Jin Suk Lee, Takeshi Kuroha, Marketa Hnilova, Dmitriy Khatayevich, Masahiro M. Kanaoka, Jessica M. McAbee, Mehmet
Lee_Jin Suk 1 Direct Interaction of Ligand-Receptor Pairs Specifying Stomatal Patterning Jin Suk Lee, Takeshi Kuroha, Marketa Hnilova, Dmitriy Khatayevich, Masahiro M. Kanaoka, Jessica M. McAbee, Mehmet
Cell Biology (2020), First Midterm, Spring (5 pts) 2. (4 pts) 3. (2 pts) 4. (6 pts) 5. (6 pts) 6. (2.5pts) 7. (8 pts) 8. (5 pts) 9.
 Cell Biology (2020), First Midterm, Spring 2004 1. (5 pts) 2. (4 pts) 3. (2 pts) 4. (6 pts) 5. (6 pts) 6. (2.5pts) 7. (8 pts) 8. (5 pts) 9. (4 pts) 10. (2pts) 11. (4pts) 12. (3 pts) 13. (8 pts) 14. (4
Cell Biology (2020), First Midterm, Spring 2004 1. (5 pts) 2. (4 pts) 3. (2 pts) 4. (6 pts) 5. (6 pts) 6. (2.5pts) 7. (8 pts) 8. (5 pts) 9. (4 pts) 10. (2pts) 11. (4pts) 12. (3 pts) 13. (8 pts) 14. (4
Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli
 Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli Hye Soon Won Dept. of Chem. Eng. Chungnam National University INTRODUCTION Human interleukin-2(hil-2) - known as T Cell Growth
Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli Hye Soon Won Dept. of Chem. Eng. Chungnam National University INTRODUCTION Human interleukin-2(hil-2) - known as T Cell Growth
Sequence Coverage (%) Profilin-1 P UD 2
 Protein Name Accession Number (Swissprot) Sequence Coverage (%) No. of MS/MS Queries Mascot Score 1 Reference Cytoskeletal proteins Beta-actin P60709 37 14 298 Alpha-actin P68032 33 10 141 20 Beta-actin-like
Protein Name Accession Number (Swissprot) Sequence Coverage (%) No. of MS/MS Queries Mascot Score 1 Reference Cytoskeletal proteins Beta-actin P60709 37 14 298 Alpha-actin P68032 33 10 141 20 Beta-actin-like
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Main Functions maintain homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics
 Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Metabolism III. Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis
 Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
Predictive PP1Ca binding region in BIG3 : 1,228 1,232aa (-KAVSF-) HEK293T cells *** *** *** KPL-3C cells - E E2 treatment time (h)
 Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
 Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Phillips and Milo 10.1073/pnas.0907732106 Table S1. Database vital statistics Number of entries Number of distinct references Number of organisms Unique visitors per day Searches
Supporting Information Phillips and Milo 10.1073/pnas.0907732106 Table S1. Database vital statistics Number of entries Number of distinct references Number of organisms Unique visitors per day Searches
Supplemental Figure S1.
 53 kda- WT TPS29.2 (ethanol) TPS29.2 (water) Supplemental Figure S1. Inducible expression of E. coli otsa (TPS) in Arabidopsis. Immunoblot of leaf proteins (20 µg per lane) extracted from: (i) WT Col-0,
53 kda- WT TPS29.2 (ethanol) TPS29.2 (water) Supplemental Figure S1. Inducible expression of E. coli otsa (TPS) in Arabidopsis. Immunoblot of leaf proteins (20 µg per lane) extracted from: (i) WT Col-0,
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions. Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU
 Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
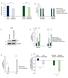 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
Fatty Acid Desaturation
 Fatty Acid Desaturation Objectives: 1. Isolation of desaturase mutants 2. Substrates for fatty acid desaturation 3. ellular localization of desaturases References: Buchanan et al. 2000. Biochemistry and
Fatty Acid Desaturation Objectives: 1. Isolation of desaturase mutants 2. Substrates for fatty acid desaturation 3. ellular localization of desaturases References: Buchanan et al. 2000. Biochemistry and
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene
 Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
 Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
Very-Long Chain Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Objectives: 1. Review information on the isolation of mutants deficient in VLCFA biosynthesis 2. Generate hypotheses to explain the absence of mutants with lesions
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is
 AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
AP Biology Book Notes Chapter 4: Cells v Cell theory implications Ø Studying cell biology is in some sense the same as studying life Ø Life is continuous v Small cell size is becoming more necessary as
Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers.
 Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Page 1 of 13 IMPORTANT INFORMATION Hand in the Test Sheets (with the checked multiple choice answers) and your Sheets with written answers. THE exam has an 'A' and 'B' section SECTION A (based on Dykyy's
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues.
 Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
Supplemental Figure 1. Small RNA size distribution from different soybean tissues. The size of small RNAs was plotted versus frequency (percentage) among total sequences (A, C, E and G) or distinct sequences
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1500980/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The crystal structure of human dopamine -hydroxylase at 2.9 Å resolution Trine V. Vendelboe, Pernille Harris, Yuguang
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1500980/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The crystal structure of human dopamine -hydroxylase at 2.9 Å resolution Trine V. Vendelboe, Pernille Harris, Yuguang
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of Toc159 co-suppression lines nts
 Supplemental Data. ischof et al. Plant Cell (211)..1/tpc.111.92882 Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of Toc19 co-suppression lines nts () Phenotype of rabiopsis plants co-suppressing attoc19. Images
Supplemental Data. ischof et al. Plant Cell (211)..1/tpc.111.92882 Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of Toc19 co-suppression lines nts () Phenotype of rabiopsis plants co-suppressing attoc19. Images
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core Candidates answer on the Question
Centre Number Candidate Number Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Structured Questions A2 Core Candidates answer on the Question
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism . Anabolism
 If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative
 1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10962 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of AvrAC-FLAG in protoplasts. Total protein extracted from protoplasts described in Fig. 1a was subjected to anti-flag immunoblot to detect AvrAC-FLAG
doi:10.1038/nature10962 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of AvrAC-FLAG in protoplasts. Total protein extracted from protoplasts described in Fig. 1a was subjected to anti-flag immunoblot to detect AvrAC-FLAG
Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Cytochrome C (10 M) Z-VAD-fmk. Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Z-VAD-fmk
 A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
sesquiterpenes monoterpenes mg gfw -1 fruit skin peel seed whole fruit
 mg gfw -1 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 sesquiterpenes monoterpenes fruit skin peel seed whole fruit Supplementary Figure S1. Terpene amount in fruit skin, seeds, and whole fruits of Japanese pepper. Monoterpenes (β-phellandrene,
mg gfw -1 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 sesquiterpenes monoterpenes fruit skin peel seed whole fruit Supplementary Figure S1. Terpene amount in fruit skin, seeds, and whole fruits of Japanese pepper. Monoterpenes (β-phellandrene,
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes. Enzyme Engineering
 Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
Figure legends of supplementary figures
 Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
