WT siz1-2 siz1-3. WT siz1-2 siz1-3. -Pi, 0.05 M IAA. -Pi, 2.5 M NPA
|
|
|
- Sheena Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A WT siz1-2 siz1-3 B WT siz1-2 siz1-3 -Pi C +Pi WT siz1-2 siz1-3 D WT siz1-2 siz1-3 E +Pi, 0.05 M IAA -Pi, 0.05 M IAA WT siz1-2 siz1-3 WT siz1-2 siz1-3 F +Pi, 2.5 M NPA -Pi, 2.5 M NPA Supplemental Figure S1. Wild-type seedlings treated with IAA in low Pi mimicked the siz1 phenotype in response to Pi deficiency, and treatment with NPA suppressed LR formation. Three-and-a-half-day-old seedlings grown on high Pi medium were transferred onto agar plates containing IAA or NPA. Photographs were taken 7 days after the transfer to the new medium. Wild-type and siz1 (siz1-2 and siz1- -Pi, 2.5 M BFA 3) seedlings were grown on agar containing 1.25 mm (A) or mm (B) KH 2 PO 4 without IAA or NPA. Seedlings grown under high Pi conditions were treated with 0.05 μm IAA (C) or 2.5 μm NPA (E). Low Pi-grown seedlings were treated with 0.05 μm IAA (D) or 2.5 μm NPA (F). Scale bar = 10 mm. +Pi, 2.5 M BFA
2 A PR growth (cm) B LR density (number/cm) Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi Col-0 siz1-2 YUCCA1 YUCCA6 +Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi +Pi -Pi Col-0 siz1-2 YUCCA1 YUCCA6 Supplemental Figure S2. Overexpression of YUCCA1 reduced PR elongation and enhanced LR density. Seedling were grown on a basal medium containing Pi for 3.5 days, then transferred onto medium containing high Pi (1.25 mm KH 2 PO 4, +Pi) or low Pi ( mm KH 2 PO 4, -Pi) and grown for 7 days. PR growth and LR density of wild-type, siz1-2, YUCCA1, and YUCCA6 seedlings were scored. All values represent the mean of 10 seedlings ±SE.
3 Supplemental Table S1. Genes with 3-hold or higher expression in siz1-2 that are also induced by NAA (Himanen et al., 2004; Vanestte et al., 2005) b c a siz1-2(+pi) siz1-2(-pi) AGI ID Gene Description WT(+Pi) WT(-Pi) At1g30760 At5g20230 At2g15480 At1g60730 At1g78110 At1g73260 At3g45140 At1g33600 At1g02850 At5g64240 At4g01630 At2g26530 At1g77120 At4g22530 At3g47540 At1g67810 At1g17170 At3g50970 At1g76680 At2g41380 At2g15490 At4g19880 At2g18210 At2g29480 At5g06860 At2g17500 FAD-linked oxidoreductase family blue copper binding protein putative glucosyltransferase auxin-induced protein, putative/ aldo/keto reductase family protein unknown protein putative trypsin inhibitor lipoxygenase AtLOX2 leucine rich repeat protein family glycosyl hydrolase family 1 latex-abundant family protein (AMC3) / caspase family protein expansin, putative (EXP17) putative yeast pheromone receptor protein AR781 alcohol dehydrogenase embryo-abundant protein-related glycosyl hydrolase family 19 (chitinase) Fe-S metabolism associated domain-containing protein glutathione transferase, putative dehydrin xero2 (XERO2) / low-temperature-induced protein LTI30 12-oxophytodienoate reductase (OPR1) putative embryo-abundant protein putative glucosyltransferase glutathione S-transferase-related unknown protein glutathione transferase, putative polygalacturonase inhibiting protein (PGIP1) auxin efflux carrier family protein a. Protein detabase AGI number. b. Fold mrna accumulation in siz1 versus wild type under phosphate sufficient condition. c. Fold mrna accumulation in siz1 versus wild type under phosphate deficient condition. d. Not applicable. Data could not be obtained because of low signal or high variation n.a. d 2.3 n.a. d
4 Supplemental Table S2. Genes 3.0 fold up-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the low-pi condition Locus Gene Description Fold a Fold a siz1(+pi) siz1(-pi) /WT(+Pi) /WT(-Pi) At4g27450 unknown protein 1.8 ± ±1.2 At1g30760 FAD-linked oxidoreductase family 1.5 ± ±1.0 At2g22860 phytosulfokines 2 (PSK2) 2.5 ± ±1.6 At5g54780 RabGAP/TBC domain-containing protein 5.8 ± ±1.1 At2g17850 senescence-associated protein 1.4 ± ±1.3 At5g50170 C2 and GRAM domain-containing protein 4.0 ± ±1.2 At3g59930 A defensin-like family protein 1.7 ± ±1.3 At5g20230 blue copper binding protein 3.2 ± ±1.4 At2g05540 putative glycine-rich protein 1.4 ± ±1.7 At2g15480 UDP-glucosyl transferase 6.0 ± ±1.1 At1g60730 putative auxin-induced aldo/keto reductase family 5.2 ± ±1.5 At2g02930 glutathione transferase, putative 3.5 ± ±1.1 At2g16005 MD-2-related lipid recognition domain-containing 2.8 ± ±1.3 At5g24780 vegetative storage protein Vsp1 4.8 ± ±1.2 At1g78110 unknown protein 1.6 ± ±1.5 At4g12850 far-red impaired responsive family protein 1.7 ± ±1.1 At1g43800 acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] desaturase, putative 1.2 ± ±1.1 At1g02920 glutathione transferase, putative 3.4 ± ±1.2 At2g16060 class 1 non-symbiotic hemoglobin (AHB1) -1.1 ± ±1.3 At1g75830 plant defensin protein, putative (PDF1.1) 1.4 ± ±1.1 At1g55240 unknown protein 3.2 ± ±1.5 At1g73260 putative trypsin inhibitor 2.4 ± ±1.1 At1g47960 invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor family 2.6 ± ±1.3 At4g33560 putative protein 1.1 ± ±1.3 At3g45140 lipoxygenase AtLOX2 2.0 ± ±1.4 At2g30770 cytochrome P450 71A ± ±1.6 At1g33600 leucine rich repeat protein family 1.5 ± ±1.6 At2g25510 expressed protein 2.1 ± ±1.3
5 At5g64240 latex-abundant family protein, caspase family protein 1.4 ±1.1 ±1.5 At3g21720 putative isocitrate lyase 1.8 ±1.2 ±1.4 At5g17650 glycine/proline-rich protein 1.3 ±1.1 ±2.0 At4g01630 expansin (EXP17) 1.3 ±1.0 ±1.4 At2g26530 putative yeast pheromone receptor protein AR ±1.1 ±1.2 At1g02850 glycosyl hydrolase family ±1.4 ±1.2 At2g33830 dormancy/auxin associated family protein 2.0 ±1.1 ±1.1 At5g37990 S-adenosyl-L-methionine:carboxyl methyltransferase 5.2 ± ±1.2 At2g47600 magnesium/proton exchanger (MHX1) 1.6 ± ±1.6 At5g58820 subtilisin-like serine protease 1.3 ± ±1.1 At4g02520 glutathione S-transferase PM ± ±2.6 b At1g33055 expressed protein 1.4 ± ±1.1 At1g14250 nucleoside phosphatase family protein/gda1 2.1 ± ±1.1 At4g22530 embryo-abundant protein-related 2.4 ± ±1.2 At3g22231 Pathogen and circadian controlled ± ±1.5 At3g47540 glycosyl hydrolase family 19 (chitinase) 2.5 ± ±1.6 At1g OG-Fe(II) oxygenase family protein 2.7 ± ±1.6 At1g33670 leucine rich repeat protein family 1.9 ± ±1.7 At4g23600 coronatine-responsive tyrosine aminotransferase 1.0 ± ±1.2 At1g71692 agamous-like MADS box protein AGL ± ±1.3 At2g '-5' exonuclease domain-containing protein 1.3 ± ±1.2 At3g21950 S-adenosyl-L-methionine:carboxyl methyltransferase 2.6 ± ±1.7 At3g59270 syntaxin-related family protein 3.1 ± ±1.3 a Mean ± SD (n = 3). b p > 0.01 (t-test).
6 Supplemental Table S3. Genes 3.0 fold up-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the high-pi condition, but < 3.0 fold up-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the low-pi condition Locus Gene Description Fold a Fold a siz1(+pi) siz1(-pi) /WT(+Pi) /WT(-Pi) At2g14610 pathogenesis-related PR-1 protein 8.4 ±1.2 n.a. b At5g26220 ChaC-like family protein 6.5 ±1.2 n.a. b At5g36140 cytochrome P450-related 6.2 ±1.1 n.a. b At4g33720 pathogenesis-related protein 1 precursor 6.1 ± ±1.3 At3g29970 germination protein-related 6.0 ±1.1 n.a. b At1g67810 Fe-S metabolism associated domain-containing 5.9 ± ±1.2 At5g48850 male sterility MS5 family protein 5.9 ±1.2 n.a. b At1g65340 cytochrome P450, putative 5.7 ±1.2 n.a. b At2g18050 histone H1 5.4 ± ±1.4 At5g52320 cytochrome P450, putative 5.0 ±1.0 n.a. b At2g39030 GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase (GNAT) family 4.6 ±1.2 n.a. b At5g59520 zinc transporter (ZIP2) 4.5 ± ±1.0 At3g54150 embryo-abundant protein -like 4.4 ±1.1 n.a. b At1g17170 glutathione transferase, putative 4.4 ± ±1.3 At2g26270 hypothetical protein 4.4 ±1.2 n.a. b At2g43590 putative endochitinase 4.3 ± ±1.1 At3g43180 zinc finger (C3HC4-type RING finger) family protein 4.2 ±1.3 n.a. b At2g18660 expansin-related protein 3 precursor 4.2 ± ±1.2 At5g13900 protease inhibitor/seed storage/lipid transfer protein 4.1 ±1.1 n.a. b At3g50970 dehydrin xero2/ low-temperature-induced protein LTI ± ±1.6 At3g08860 putative β-alanine aminotransferase 4.1 ± ±1.3 At3g32030 terpene synthase/cyclase family 4.0 ± ±1.2 At3g26740 light responsive protein-related 4.0 ±1.2 n.a. b At1g oxophytodienoate reductase (OPR1) 3.9 ± ±1.1 At2g02990 ribonuclease, RNS1 3.9 ± ±1.3 At1g oxophytodienoate reductase (OPR2) 3.8 ± ±1.3 At5g06870 polygalacturonase inhibiting protein 2 (PGIP2) 3.6 ±1.3 n.a. At5g09490 ribosomal protein S15-like 3.6 ±1.1 n.a.
7 At2g35380 peroxidase family 3.6 ± ±1.3 At2g41380 putative embryo-abundant protein 3.6 ± ±1.1 At3g12500 basic endochitinase 3.5 ± ±1.4 At5g59380 methyl-cpg-binding domain-containing protein 3.5 ± ±1.5 At1g63530 unknown protein 3.5 ±1.1 n.a. b At5g09520 surface protein PspC-related 3.5 ± ±1.1 At5g23190 cytochrome P450-like protein 3.5 ± ±1.3 At2g15490 putative glucosyltransferase 3.5 ±1.1 n.a. b At4g11650 osmotin-like protein (OSM34) 3.4 ± ±1.4 At4g19880 glutathione S-transferase-related ± ±1.2 At2g18210 unknown protein ±1.1 n.a. b At2g29480 glutathione transferase, putative ± ±1.2 At5g66170 senescence-associated protein ± ±1.2 At3g04210 disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS class), putative ± ±1.3 At5g06860 polygalacturonase inhibiting protein (PGIP1) ± ±1.2 At5g45380 sodium:solute symporter family protein ±1.3 n.a. b At1g18970 germin, putative 3.2 ± ±1.4 At2g43670 glycosyl hydrolase family ±1.3 n.a. b At2g14560 late upregulated in response to H.parastica 3.2 ± ±1.2 At3g15990 putative sulfate transporter 3.2 ± ±1.1 At2g48130 protease inhibitor/seed storage/lipid transfer protein 3.2 ± ±1.4 At2g39310 jacalin lectin family protein 3.2 ± ±1.3 At4g15610 integral membrane family protein 3.2 ± ±1.2 At1g64170 cation/hydrogen exchanger, putative (CHX16) 3.1 ±1.3 n.a. b At3g12820 myb family transcription factor (MYB10) 3.1 ±1.3 n.a. b At2g17500 auxin efflux carrier family protein 3.1 ± ±1.2 At5g24770 vegetative storage protein Vsp2 3.0 ±1.1 n.a. b a Mean ± SD (n = 3). b Not applicable. Data could not be obtained because of low signal or high variation.
8 Supplemental Table S4. Genes 3.0 fold down-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the low -Pi condition Locus Gene Description Fold a Fold a siz1(+pi) siz1(-pi) /WT(+Pi) /WT(-Pi) At1g03170 expressed protein - ± ±1.8 At1g52400 glycosyl hydrolase family 1, beta-glucosidase (BG1) -1.1 ± ±1.3 At4g22520 protease inhibitor/seed storage/lipid transfer protein -1.5 ± ±1.7 At5g02220 expressed protein -1.1 ± ±1.3 At3g28990 unknown protein n.a. b -3.1 ±1.3 At1g50320 thioredoxin, putative -2.2 ± ±1.6 At5g41440 zinc finger (C3HC4-type RING finger) family protein -1.5 ± ±1.7 At5g39760 zinc finger homeobox protein-related -2.0 ± ±1.5 a Mean ± SD (n = 3). b Not applicable. Data could not be obtained because of low signal or high variation.
9 Supplemental Table S5. Genes 3.0 fold down-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the high -Pi condition, but < 3.0 fold down-regulated in siz1-2 plants under the low-pi condi tion Locus Gene Description Fold a Fold a siz1(+pi) siz1(-pi) /WT(+Pi) /WT(-Pi) At5g20630 germin-like protein (GER3) -6.0 ± ±1.3 At3g61530 ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase family -4.8 ± ±1.7 At1g67090 ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small unit -4.6 ± ±1.4 At5g58370 putative GTP-binding protein CGPA -4.4 ± ±2.1 At2g45180 protease inhibitor/seed storage/lipid transfer -4.3 ± ±1.3 At1g18120 putative myrosinase-associated protein -4.2 ±1.2 n.a. b At3g14210 myrosinase-associated protein, putative -4.1 ± ±1.2 At1g62780 unknown protein -3.9 ± ±1.7 At3g43290 putative protein -3.8 ±1.1 n.a. b At5g14740 carbonic anhydrase ± ±1.1 At1g72610 germin-like protein -3.8 ± ±1.2 At5g34839 unknown protein -3.6 ±1.3 n.a. b At5g38940 unknown protein -3.6 ±1.2 n.a. b At5g36900 hypothetical protein -3.5 ±1.2 n.a. b At4g27520 putative protein -3.5 ± ±1.8 At3g13470 chaperonin 60 beta, putative - ± ±1.2 At4g25050 acyl carrier family protein -3.1 ±1.3 n.a. b At4g37360 cytochrome p450 family -3.1 ± ±2.0 At2g32540 cellulose synthase -3.1 ±1.3 n.a. b At5g28500 unknown protein -3.1 ± ±1.7 At5g40590 DC1 domain-containing protein -3.0 ±1.2 n.a. b At1g73600 phosphoethanolamine N-methyltransferase -3.0 ± ±1.1 At1g74970 ribosomal protein S9, putative -3.0 ± ±1.3 a Mean ± SD (n = 3). b Not applicable. Data could not be obtained because of low signal or high variation.
10 Supplemental Table S6. Primers used for quantitative RT-PCR analysis Gene name Primer sequence ACT2 (For) 5 - TAACAGGGAGAAGATGACTCAGATCA -3 ; (Rev) 5 - AAGATCAAGACGAAGGATAGCATGAG -3 EXP17 (For) 5 - CGCAATGATCTTCTCCACAA -3 ; (Rev) 5 - GGTTTCCATAACCACAAGCTC -3 GLH (For) 5 - TGGGTCTAGATTGCCAGCTT -3 (Rev) 5 - GCATATGATGGATGGTGCAG -3 UGT73B4 (For) 5 - GAATGCCTAAAATGGCTGGA -3 (Rev) 5 - GAGGACCCTCCTTCTTCCAG -3
Supplementary Tables 1
 Supplementary Tables 1 Supplementary Table 1: The 11 genes in the geneset for Case Study 1 At1g62570 At1g09350 At1g60470 At2g47180 At4g17090 At5g20830 At2g16890 At3g51240 At3g55120 At4g27560 At5g08640
Supplementary Tables 1 Supplementary Table 1: The 11 genes in the geneset for Case Study 1 At1g62570 At1g09350 At1g60470 At2g47180 At4g17090 At5g20830 At2g16890 At3g51240 At3g55120 At4g27560 At5g08640
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function
 Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Table Ia. Differentially regulated genes in the arr2 loss-of-function mutant compared to wildtype
 i ANHANG Table Ia. Differentially regulated genes in the arr2 loss-of-function mutant compared to wildtype AGI No. Putative Function Fold Change a Abscisic acid-related AT4G24960 abscisic acid-induced
i ANHANG Table Ia. Differentially regulated genes in the arr2 loss-of-function mutant compared to wildtype AGI No. Putative Function Fold Change a Abscisic acid-related AT4G24960 abscisic acid-induced
Supplemental Table S1 Up-regulated genes in irjazh plants compared to WT plants by microarray.
 Supplemental Table S1 Up-regulated genes in irjazh plants compared to WT plants by microarray. Classification Fold Change Bincode (TAIR) Annotation Probe number ACC number Cell wall. Degradation 3.29 10.6.2
Supplemental Table S1 Up-regulated genes in irjazh plants compared to WT plants by microarray. Classification Fold Change Bincode (TAIR) Annotation Probe number ACC number Cell wall. Degradation 3.29 10.6.2
The Arabidopsis mir396 mediates pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune responses against fungal pathogens
 The Arabidopsis mir396 mediates pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune responses against fungal pathogens Mauricio Soto-Suárez, Patricia Baldrich, Detlef Weigel, Ignacio Rubio-Somoza and
The Arabidopsis mir396 mediates pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immune responses against fungal pathogens Mauricio Soto-Suárez, Patricia Baldrich, Detlef Weigel, Ignacio Rubio-Somoza and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1 Sequencing quality. Sample screenshot of re-sequencing raw file quality generated by FastQC. For both the graphs, scores were based on the Illumina 1.5 quality score.
Supplementary Information Figure S1 Sequencing quality. Sample screenshot of re-sequencing raw file quality generated by FastQC. For both the graphs, scores were based on the Illumina 1.5 quality score.
The N-end rule pathway regulates pathogen responses. in plants
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The N-end rule pathway regulates pathogen responses in plants Rémi de Marchi 1,2, Maud Sorel 1, Brian Mooney 1, Isabelle Fudal 3, Kevin Goslin 1, Kamila Kwaśniewska 4, Patrick
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The N-end rule pathway regulates pathogen responses in plants Rémi de Marchi 1,2, Maud Sorel 1, Brian Mooney 1, Isabelle Fudal 3, Kevin Goslin 1, Kamila Kwaśniewska 4, Patrick
Protein Class/Name KEGG Pathways
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 4. Proteins Increased in Either Soil medium at 37 o C and 25 o C Table 4A. Proteins
Figure S3 Differentially expressed fungal and plant genes organised by catalytic activity ontology Organisation of E. festucae (A) and L.
 sak WT Number of branches 3 WT sak Figure S1 Vasculature of plants infected with the E. festucae sak mutant. Light micrographs of perennial ryegrass blade tissue showing branching between the vasculature
sak WT Number of branches 3 WT sak Figure S1 Vasculature of plants infected with the E. festucae sak mutant. Light micrographs of perennial ryegrass blade tissue showing branching between the vasculature
MG132. GRXS17:V5-His MG132 GRXS17:HA. RuBisCo. Supplemental Data. Walton et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 MG132 GRXS17:V5-His MG132 GRXS17:HA RuBisCo Supplemental Figure 1. Degradation of GRXS17 by the 26S proteasome. (A) Cell-free degradation assay. Recombinant protein GRXS17:V5-HIS was incubated with total
MG132 GRXS17:V5-His MG132 GRXS17:HA RuBisCo Supplemental Figure 1. Degradation of GRXS17 by the 26S proteasome. (A) Cell-free degradation assay. Recombinant protein GRXS17:V5-HIS was incubated with total
0.5. Normalized 95% gray value interval h
 Normalized 95% gray value interval.5.4.3.2.1 h Supplemental Figure 1: Symptom score of root samples used in the proteomics study. For each time point, the normalized 95% gray value interval is an averaged
Normalized 95% gray value interval.5.4.3.2.1 h Supplemental Figure 1: Symptom score of root samples used in the proteomics study. For each time point, the normalized 95% gray value interval is an averaged
Table S1 Differential genes repressed in copt2-1 seedlings. MIPS code Ratio gene annotation gene name -Fe-Cu/ -Fe+Cu/ +Fe+Cu -Fe-Cu/ -Fe+Cu
 Table S1. Differential genes repressed in copt2-1 seedlings. MIPS code, the microarray values under -Fe-Cu, -Fe+Cu and +Fe+Cu, gene annotation and gene name are indicated. MIPS code Ratio gene annotation
Table S1. Differential genes repressed in copt2-1 seedlings. MIPS code, the microarray values under -Fe-Cu, -Fe+Cu and +Fe+Cu, gene annotation and gene name are indicated. MIPS code Ratio gene annotation
Transcriptome analyses give insights into selenium-stress responses and selenium tolerance mechanisms in Arabidopsis
 Physiologia Plantarum 2007 Copyright ª Physiologia Plantarum 2007, ISSN 0031-9317 Transcriptome analyses give insights into selenium-stress responses and selenium tolerance mechanisms in Arabidopsis Doug
Physiologia Plantarum 2007 Copyright ª Physiologia Plantarum 2007, ISSN 0031-9317 Transcriptome analyses give insights into selenium-stress responses and selenium tolerance mechanisms in Arabidopsis Doug
Supplemental data. Uppalapati et al. (2012) Plant Cell /tpc
 PAL Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 OPR Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 CHS PR3 CHR PR5 CHI PR10 IFS IFR Supplemental Figure 1. Expression profiles for selected genes in phenylpropanoid pathway
PAL Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 OPR Control P. emaculata 0 8 24 48 8 24 48 CHS PR3 CHR PR5 CHI PR10 IFS IFR Supplemental Figure 1. Expression profiles for selected genes in phenylpropanoid pathway
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
Genome-wide association studies for understanding pathogen evolution. Samuel K. Sheppard
 Genome-wide association studies for understanding pathogen evolution Samuel K. Sheppard Pathogenic bacteria Population genomics and evolution Sheppard et al. Science 2008; 11: 237-239. Sheppard et al.
Genome-wide association studies for understanding pathogen evolution Samuel K. Sheppard Pathogenic bacteria Population genomics and evolution Sheppard et al. Science 2008; 11: 237-239. Sheppard et al.
Supplemental Information. Spatial Auxin Signaling. Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis
 Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Supporting Information Lee et al. 10.1073/pnas.0910950106 Fig. S1. Fe (A), Zn (B), Cu (C), and Mn (D) concentrations in flag leaves from WT, osnas3-1, and OsNAS3-antisense (AN-2) plants. Each measurement
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids Fatty acid biosynthesis takes place in the cytosol rather than the mitochondria and requires a different activation mechanism and different enzymes and coenzymes than fatty
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Structure and Function In Biochemistry
 University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
Supporting Information
 t t l l t l Supporting Information Zemach et al. 1.173/pnas.1969517.8 TE > 1 bp Leaf n o a Embryo h y C H H m e Endosperm Seedling root Seedling shoot -3-2 -1 1 2 3 4 3 2 1-1 -2-3 Fig. S1. Distribution
t t l l t l Supporting Information Zemach et al. 1.173/pnas.1969517.8 TE > 1 bp Leaf n o a Embryo h y C H H m e Endosperm Seedling root Seedling shoot -3-2 -1 1 2 3 4 3 2 1-1 -2-3 Fig. S1. Distribution
Phosphorus Deficiency in Potatoes. Helen Bowen, Rory Hayden & Will Spracklen
 A Molecular Diagnostic for Phosphorus Deficiency in Potatoes Philip J. White John P. Hammond, Martin R. Broadley, Helen Bowen, Rory Hayden & Will Spracklen (Warwick, Nottingham, SCRI) IPNC XVI, Sacramento,
A Molecular Diagnostic for Phosphorus Deficiency in Potatoes Philip J. White John P. Hammond, Martin R. Broadley, Helen Bowen, Rory Hayden & Will Spracklen (Warwick, Nottingham, SCRI) IPNC XVI, Sacramento,
Effects of jasmonic acid signalling on the wheat microbiome differ between
 Supplementary Information: Effects of jasmonic acid signalling on the wheat microbiome differ between body sites Hongwei Liu 1, Lilia C. Carvalhais 1, Peer M. Schenk 1, Paul G. Dennis 1* 1 School of Agriculture
Supplementary Information: Effects of jasmonic acid signalling on the wheat microbiome differ between body sites Hongwei Liu 1, Lilia C. Carvalhais 1, Peer M. Schenk 1, Paul G. Dennis 1* 1 School of Agriculture
f(x) = x R² = RPKM (M8.MXB) f(x) = x E-014 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.
 14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary igure 1. The expression level of PP4 (At4g16860) is diminished in the rpp4 mutant (SK017569). The mna was extracted to analyze the expression level of PP4 using quantitative PC (qpc). Gene
Supplementary igure 1. The expression level of PP4 (At4g16860) is diminished in the rpp4 mutant (SK017569). The mna was extracted to analyze the expression level of PP4 using quantitative PC (qpc). Gene
Emerging Allergens. Karin Hoffmann-Sommergruber Dept. of Pathophysiology & Allergy Research, Medical University of Vienna, Austria
 Emerging Allergens Karin Hoffmann-Sommergruber Dept. of Pathophysiology & Allergy Research, Medical University of Vienna, Austria Allergens Proteins Small mol mass Resistant against enzymatic digestion
Emerging Allergens Karin Hoffmann-Sommergruber Dept. of Pathophysiology & Allergy Research, Medical University of Vienna, Austria Allergens Proteins Small mol mass Resistant against enzymatic digestion
Supplementary Data AtMYB12
 Supplementary Data AtMYB12 expression in tomato leads to large scale differential modulation in transcriptome and flavonoid content in leaf and fruit tissues Ashutosh Pandey 1,$,#, Prashant Misra 1,$,#,
Supplementary Data AtMYB12 expression in tomato leads to large scale differential modulation in transcriptome and flavonoid content in leaf and fruit tissues Ashutosh Pandey 1,$,#, Prashant Misra 1,$,#,
Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold).
 Supplemental Tables Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold). PHT1;1 PHT1;2 PHT1;3 PHT1;4 PHT1;5
Supplemental Tables Table I: PHT1 transporter family comparison at the amino acid level. BLAST program was used to obtain percentage of similarity and identity (in bold). PHT1;1 PHT1;2 PHT1;3 PHT1;4 PHT1;5
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Coenzymes. Coenzymes 9/11/2018. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
Figure 1 Original Advantages of biological reactions being catalyzed by enzymes:
 Enzyme basic concepts, Enzyme Regulation I III Carmen Sato Bigbee, Ph.D. Objectives: 1) To understand the bases of enzyme catalysis and the mechanisms of enzyme regulation. 2) To understand the role of
Enzyme basic concepts, Enzyme Regulation I III Carmen Sato Bigbee, Ph.D. Objectives: 1) To understand the bases of enzyme catalysis and the mechanisms of enzyme regulation. 2) To understand the role of
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003
 CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
CH395G FINAL (3 rd ) EXAM Kitto/Hackert - Fall 2003 1. A cell in an active, catabolic state has a. a high (ATP/ADP) and a high (NADH/NAD + ) ratio b. a high (ATP/ADP) and a low (NADH/NAD + ) ratio c. a
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Lignin and the General Phenylpropanoid Pathway. Introduction and Importance:
 Lignin and the General Phenylpropanoid Pathway 13. Phenolics and Lignin p. 1 Introduction and Importance: Phenolic: a compound consisting of an aromatic ring plus at least one hydroxyl [= phenyl group],
Lignin and the General Phenylpropanoid Pathway 13. Phenolics and Lignin p. 1 Introduction and Importance: Phenolic: a compound consisting of an aromatic ring plus at least one hydroxyl [= phenyl group],
Figure S1: Abundance of Fe related proteins in oceanic Synechococcus sp. strain WH8102 in. Ferredoxin. Ferredoxin. Fe ABC transporter
 0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids
 Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Supplemental Data. Pick and Bräutgam et al. Plant Cell. (2011) /tpc Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters
 Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters Mean Adjustment FOM Number of Clusters Supplemental Figure 1. Figure of merit analysis of metabolite clustering. The algorithm tries 20 times to
Mean Adjustment FOM values (± SD) vs. Number of Clusters Mean Adjustment FOM Number of Clusters Supplemental Figure 1. Figure of merit analysis of metabolite clustering. The algorithm tries 20 times to
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis
 ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis Barkat Mustafa, David Tan, Paul WJ Taylor and Rebecca Ford Melbourne School of Land and Environment
ABA-dependant signalling of PR genes and potential involvement in the defence of lentil to Ascochyta lentis Barkat Mustafa, David Tan, Paul WJ Taylor and Rebecca Ford Melbourne School of Land and Environment
Lecture 13 (10/13/17)
 Lecture 13 (10/13/17) Reading: Ch6; 187-189, 204-205 Problems: Ch4 (text); 2, 3 NXT (after xam 2) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 5, 6, 7, 24 OUTLIN NZYMS: Binding & Catalysis
Lecture 13 (10/13/17) Reading: Ch6; 187-189, 204-205 Problems: Ch4 (text); 2, 3 NXT (after xam 2) Reading: Ch6; 190-191, 194-195, 197-198 Problems: Ch6 (text); 5, 6, 7, 24 OUTLIN NZYMS: Binding & Catalysis
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the
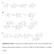 Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Supplementary Figure 1. The proposed biosynthetic pathways for the A-ring transformation of the kinamycin and lomaiviticin antibiotics. A, by Steven J. Gould; B, by Emily P. Balskus; C, by Bradley S. Moore.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle Slide 1 The Eight Steps of the Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes: 4 dehydrogenases (2 decarboxylation) 3
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge III. Metabolism The Citric Acid Cycle Slide 1 The Eight Steps of the Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes: 4 dehydrogenases (2 decarboxylation) 3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209. Petr Tůma Eva Samcová
 Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Biochemical networks related to carbon accumulation in sugarcane
 Biochemical networks related to carbon accumulation in sugarcane Marcos Buckeridge Department of Botany, Laboratory of Plant Physiological Ecology IB USP How are we approaching the sugarcane metabolic
Biochemical networks related to carbon accumulation in sugarcane Marcos Buckeridge Department of Botany, Laboratory of Plant Physiological Ecology IB USP How are we approaching the sugarcane metabolic
BOT 6516 Plant Metabolism
 BOT 6516 Plant Metabolism Lecture 19 Nitrate & Sulfur Assimilation Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bot6516/index.html Overview of Nitrate Assimilation 16.34 What does Δψ
BOT 6516 Plant Metabolism Lecture 19 Nitrate & Sulfur Assimilation Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bot6516/index.html Overview of Nitrate Assimilation 16.34 What does Δψ
Supplemental Data. Müller-Xing et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Supplemental Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental Design. A. To benchmark the performance of software parameter sets proteins were extracted from a pool of Arabidopsis
Supporting Information Supplemental Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental Design. A. To benchmark the performance of software parameter sets proteins were extracted from a pool of Arabidopsis
Lecture 16. Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III
 Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
Lecture 16 Finish lipid metabolism (Triglycerides, Isoprenoids/Steroids, Glyoxylate cycle) Amino acid metabolism (Urea cycle) Google Man III The Powertrain of Human Metabolism (verview) CARBHYDRATES PRTEINS
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
molecular function. The right hand y-axis indicates the number of annotated unigenes.
 Takemura et al. Supplementary Fig.S1 Supplementary Fig. S1. GO assignment of all unigenes. The unigenes were mapped to three main categories: iological process, cellular component and molecular function.
Takemura et al. Supplementary Fig.S1 Supplementary Fig. S1. GO assignment of all unigenes. The unigenes were mapped to three main categories: iological process, cellular component and molecular function.
NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA. Citrus responses to huanglongbing
 NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA Citrus responses to huanglongbing HLB is Vector-borne Disease! Vector psyllids Pathogen Ca. Liberibacter asiaticus. Host Citrus spp.
NABIL KILLINY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PLANT PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA Citrus responses to huanglongbing HLB is Vector-borne Disease! Vector psyllids Pathogen Ca. Liberibacter asiaticus. Host Citrus spp.
Figure legends of supplementary figures
 Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Protein Class/Name. Pathways. bat00250, bat00280, bat00410, bat00640, bat bat00270, bat00330, bat00410, bat00480
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 1. Proteins Increased in Either Soil or Laboratory media Table 1A. Proteins Increased
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 1. Proteins Increased in Either Soil or Laboratory media Table 1A. Proteins Increased
Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative
 1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
Protein Class/Name. Pathways. bat00250, bat00280, bat bat00640, bat00650 bat00270, bat00330, bat00410, bat00480 bat00270, bat00330,
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 2. Proteins Increased in Either Blood or Horizon media Table 2A. Proteins Increased
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplemental Table 2. Proteins Increased in Either Blood or Horizon media Table 2A. Proteins Increased
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
A basic helix loop helix transcription factor controls cell growth
 A basic helix loop helix transcription factor controls cell growth and size in root hairs Keke Yi 1,2, Benoît Menand 1,3, Elizabeth Bell 1, Liam Dolan 1,4 Supplementary note Low soil phosphate availability
A basic helix loop helix transcription factor controls cell growth and size in root hairs Keke Yi 1,2, Benoît Menand 1,3, Elizabeth Bell 1, Liam Dolan 1,4 Supplementary note Low soil phosphate availability
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
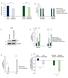 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
Arabidopsis Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Roles of Melatonin in Plant Defense Systems
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Study of Biological Complexity Publications Center for the Study of Biological Complexity 2014 Arabidopsis Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Roles
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Study of Biological Complexity Publications Center for the Study of Biological Complexity 2014 Arabidopsis Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Key Roles
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible and extremely colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains Raad Jasim, Mark A. Baker, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A comparative study of outer membrane proteome between a paired colistinsusceptible and extremely colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains Raad Jasim, Mark A. Baker, 2
Protein Name. IFLENVIR,DSVTYTEHAK,TV TALDVVYALK,KTVTALDVV YALK,TVTALDVVYALKR,IF LENVIRDSVTYTEHAK gi Histone H2B
 Table 1. A functional category list of proteins (Lentinula edodes) identified by 1-DGE and nesi-lc-ms/ms. The table lists indicated fraction numbers, matching peptides, scores, accession numbers, protein
Table 1. A functional category list of proteins (Lentinula edodes) identified by 1-DGE and nesi-lc-ms/ms. The table lists indicated fraction numbers, matching peptides, scores, accession numbers, protein
Glycogen Metabolism. BCH 340 lecture 9
 Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Glycogen Metabolism BC 340 lecture 9 Structure of glycogen Glycogen is homopolysaccharide formed of branched D-glucose units The primary glycosidic bond is 1-4-linkage Each branch is made of 6-12 glucose
Chapter 10. 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation)
 Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Genomics of plant defense against insects. Dr. Philippe Reymond, MER
 Genomics of plant defense against insects Dr. Philippe Reymond, MER Herbivorous insects are abundant on earth and cause severe damage to crops Biomass of ants compared to biomass of vertebrates (4 to 1)
Genomics of plant defense against insects Dr. Philippe Reymond, MER Herbivorous insects are abundant on earth and cause severe damage to crops Biomass of ants compared to biomass of vertebrates (4 to 1)
Metabolic Biochemistry / BIBC 102 Midterm Exam / Spring 2011
 Metabolic Biochemistry / BIBC 102 Midterm Exam / Spring 2011 I. (25 points) Fill in all of the enzyme catalyzed reactions which convert glycogen to lactate. Draw the correct structure for each intermediate
Metabolic Biochemistry / BIBC 102 Midterm Exam / Spring 2011 I. (25 points) Fill in all of the enzyme catalyzed reactions which convert glycogen to lactate. Draw the correct structure for each intermediate
Chapter 9. Biotransformation
 Chapter 9 Biotransformation Biotransformation The term biotransformation is the sum of all chemical processes of the body that modify endogenous or exogenous chemicals. Focus areas of toxicokinetics: Biotransformation
Chapter 9 Biotransformation Biotransformation The term biotransformation is the sum of all chemical processes of the body that modify endogenous or exogenous chemicals. Focus areas of toxicokinetics: Biotransformation
incorporation into fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P); 2-
 Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
NAME KEY ID # EXAM 3a BIOC 460. Wednesday April 10, Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided!
 EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
Zinc Deficiency-Inducible OsZIP8 Encodes a Plasma Membrane-Localized Zinc Transporter in Rice
 Mol. Cells 29, 551-558, June 30, 2010 DOI/10.1007/s10059-010-0069-0 Molecules and Cells 2010 KSMCB Zinc Deficiency-Inducible OsZIP8 Encodes a Plasma Membrane-Localized Zinc Transporter in Rice Sichul Lee
Mol. Cells 29, 551-558, June 30, 2010 DOI/10.1007/s10059-010-0069-0 Molecules and Cells 2010 KSMCB Zinc Deficiency-Inducible OsZIP8 Encodes a Plasma Membrane-Localized Zinc Transporter in Rice Sichul Lee
Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
 Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
De novo assembly of rubber transcriptome
 Project Title: De novo assembly of rubber transcriptome Name: Minami Matsui, Ng Kiaw Kiaw, Ong Wen Dee Laboratory at RIKEN: Synthetic Genomics Research Team, CSRS Background and Mission: Natural rubber
Project Title: De novo assembly of rubber transcriptome Name: Minami Matsui, Ng Kiaw Kiaw, Ong Wen Dee Laboratory at RIKEN: Synthetic Genomics Research Team, CSRS Background and Mission: Natural rubber
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways
 Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways Three stages of catabolism Glucose Synthesis of compounds e.g. lactose glycolipids Glucose-6-P Pentosephosphate Pathway Glycolysis Glycogenesis Acetyl-CoA
Comparison of catabolic and anabolic pathways Three stages of catabolism Glucose Synthesis of compounds e.g. lactose glycolipids Glucose-6-P Pentosephosphate Pathway Glycolysis Glycogenesis Acetyl-CoA
Energy storage in cells
 Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition
 In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
Coenzymes. Coenzymes 9/15/2014. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
9/16/2015. Coenzymes. Coenzymes. BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins. Types of cofactors
 BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
BCMB 3100 Introduction to Coenzymes & Vitamins Cofactors Essential ions Coenzymes Cosubstrates Prosthetic groups Coenzymes structure/function/active group Vitamins 1 Coenzymes Some enzymes require for
Overexpression of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWF4 in Brassica napus simultaneously increases seed yield and stress tolerance
 Overexpression of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWF4 in Brassica napus simultaneously increases seed yield and stress tolerance Authors Sangita Sahni 1+, Bishun D. Prasad 1+, Qing Liu 2, Vojislava
Overexpression of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWF4 in Brassica napus simultaneously increases seed yield and stress tolerance Authors Sangita Sahni 1+, Bishun D. Prasad 1+, Qing Liu 2, Vojislava
Quantification of Free Sterols, Sterol Esters, Sterol Glucosides and Acylated Sterol Glucosides in Plants by
 Quantification of Free Sterols, Sterol Esters, Sterol Glucosides and Acylated Sterol Glucosides in Plants by Q-TOF Mass Spectrometry Vera Wewer and Peter Dörmann Seville, Spain, July 2012 Institute of
Quantification of Free Sterols, Sterol Esters, Sterol Glucosides and Acylated Sterol Glucosides in Plants by Q-TOF Mass Spectrometry Vera Wewer and Peter Dörmann Seville, Spain, July 2012 Institute of
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil
 Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil Yuan Qin 1, Alexander R. Leydon 2, Ann Manziello 3, Ritu Pandey 3, David
Penetration of the Stigma and Style Elicits a Novel Transcriptome in Pollen Tubes, Pointing to Genes Critical for Growth in a Pistil Yuan Qin 1, Alexander R. Leydon 2, Ann Manziello 3, Ritu Pandey 3, David
A Conserved Transcript Pattern in Response to a Specialist and a Generalist Herbivore W
 This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
This article is published in The Plant Cell Online, The Plant Cell Preview Section, which publishes manuscripts accepted for publication after they have been edited and the authors have corrected proofs,
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose. Jana Novotna
 Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Metabolism of pentoses, glycogen, fructose and galactose Jana Novotna 1. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP): (hexose monophosphate or 6-phosphogluconate patway) Process that
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain. Pavla Balínová
 Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III
 BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III 1. (10 pts.) (a.) Briefly describe the purpose of the glycerol dehydrogenase phosphate shuttle. (b.) How many ATPs can be made when electrons enter the electron transport chain
BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III 1. (10 pts.) (a.) Briefly describe the purpose of the glycerol dehydrogenase phosphate shuttle. (b.) How many ATPs can be made when electrons enter the electron transport chain
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
General Detoxification and Stress Responses Are Mediated by Oxidized Lipids through TGA Transcription Factors in Arabidopsis W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 768 785, March 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists General Detoxification and Stress Responses Are Mediated by Oxidized Lipids through TGA Transcription
The Plant Cell, Vol. 20: 768 785, March 2008, www.plantcell.org ª 2008 American Society of Plant Biologists General Detoxification and Stress Responses Are Mediated by Oxidized Lipids through TGA Transcription
