Direct Interaction of Ligand-Receptor Pairs Specifying Stomatal Patterning
|
|
|
- Aubrey Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lee_Jin Suk 1 Direct Interaction of Ligand-Receptor Pairs Specifying Stomatal Patterning Jin Suk Lee, Takeshi Kuroha, Marketa Hnilova, Dmitriy Khatayevich, Masahiro M. Kanaoka, Jessica M. McAbee, Mehmet Sarikaya, Candan Tamerler, and Keiko U. Torii Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figures 1-12 Supplemental Tables 1, 2 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Domain structure and amino-acid sequence of EPF1, EPF2, MEPF1, and MEPF2 used for this study (A) Domain structure of EPF1 and EPF2. Nt, N-terminus; Ct, C-terminus; orange shade, signal peptide (SP); gray box, propeptide region (Pro); blue shade, predicted mature EPF (MEPF) domain with eight cysteines (black) in conserved positions. Scale bar for A-C, 10 amino acids. (B) Domain structure of EPF1 and EPF2 used for Co-IP assays. Black, 3xFLAG tag (Tag). (C) Domain structure of recombinant, E. coli-expressed MEPF1 and MEPF2 used for bioassays, QCM, and SPR. Black, single Myc and 6xHis tag (Tag). (D) Amino-acid sequence of EPF1-FLAG and EPF2-FLAG used for Co-IP assays (see B) and MEPF1 and MEPF2 sequence used for bioassays, QCM, and SPR analyses. (Top) Bold, EPF1 and EPF2 coding sequence; plain, linker and 3xFLAG sequence. (Bottom) Underline: signal sequence from pbadg vector; blue, predicted MEPF1 and MEPF2 sequence; plain, linker, cmyc tag, and 6xHis tag.
2 Lee_Jin Suk 2 Supplemental Figure 2: EPF-FLAG peptides expressed in N. benthamiana are functional Shown are confocal microscopy of liquid cultured 6-day-old abaxial cotyledons from wild type that were incubated with buffer only (mock; A), buffer with immunopurified EPF1-FLAG (B), or buffer with immunopurified EPF2-FLAG (C). Unlike mock treatment, which has no effects on stomatal differentiation (A: dots), application of EPF1-FLAG conferred arrested meristemoids (B: asterisks), a phenotype identical to induced EPF1 overexpression. Application of EPF2-FLAG conferred severe inhibition of asymmetric entry divisions (C) similar to induced EPF2 overexpression. Concentrations of EPF1-FLAG and EPF2-FLAG immunoeluates are approx. 6.2 M and 7.3 M, respectively. Images were taken under the same magnification. Scale bar, 20 m. Supplemental Figure 3: Epitope-tagged receptors expressed in N. benthamiana are predominantly detected in microsomal fractions Shown is an immunoblot of subcellular fractionations of protein extracts from N. benthamiana transiently expressing ERECTA K-GFP, ERL1 K-GFP, and TMM- GFP driven by the CaMV35S promoter. The fractionation was performed as described in the Supplemental Methods. T, total fraction; C, cytosol fraction; M, microsomal (membrane) fraction. Arrowheads indicate the size of each epitopetagged receptor. Experiments were repeated two times. Supplemental Figure 4: LURE2, an unrelated cysteine-rich peptide, does not associate with ERECTA, ERL1, or TMM Co-IP assays of epitope-tagged receptors and LURE2 expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Top two panels, input (Input). Bottom two panels, immunoprecipitated fraction using anti-gfp antibodies (IP -GFP). Immunoblots using anti-flag antibodies (WB -FLAG) detect LURE2-FLAG signals in input but not in Co-IP fraction, indicating that LURE2 does not associate with ERECTA K,
3 Lee_Jin Suk 3 ERL1 K, or TMM. Asterisks, non-specific bands. All experiments were repeated two times. Supplemental Figure 5: Expression and purification of bioactive recombinant MEPF peptides Shown are SDS-PAGE gels stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue showing expression and purification of bacterially expressed MEPF1-His (A) and MEPF2- His (B). Lanes 1, 2, 5, and 6: Bacterial lysate carrying MEPF1 (lanes 1, 2) and MEPF2 (lanes 5, 6) in the absence (lanes 1, 5) or presence (lanes 2, 6) of L- arabinose for induction. Lanes 3, 7: Eluates from Ni 2+ -NTA column containing purified MEPF1-His (lane 3) and MEPF2-His (lane 7) proteins. Lanes 4, 8: Purified, dialyzed, and refolded peptide solution (lane 4, MEPF1-His; lane 8, MEPF2-His) used for bioassays in Figs. 2, 5. The positions of molecular mass markers in kilodaltons are indicated on the left. Asterisks indicate the size of each His-tagged peptide. Supplemental Figure 6: Separation of properly folded MEPF1 by reverse phase chromatography followed by mass spectrometry and bioassays (A) HPLC chromatogram of purified MEPF1-His. Refolded MEPF1 solution was fractionated by HPLC using a C18 reverse-phase column. Each peak in the UV chromatogram (215 nm) was analyzed by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Based on molecular mass data, peak 1, 2, and 3 contain MEPF1 isoforms. The peptide in each peak was lyophilized, re-dissolved in MS medium, and subsequently analyzed using bioassays. (B) MALDI-TOF spectrum of fraction 1 from (A). A single-charged peptide corresponding to expressed MEPF1 lacking the signal peptide from pbadg vector was observed at m/z = 9,386.9 ([M+H] + ) and a double-charged at m/z = 4,695.1 ([M+2H] 2+ ). (C) Confocal images of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown 5 days in a solution with fraction 1 from (A). The epidermis is devoid of stomata, with arrested meristemoids, indicating that fraction 1 contains bioactive MEPF1 isoform. (D)
4 Lee_Jin Suk 4 MALDI-TOF spectrum of fraction 2 from (A). A single-charged peptide corresponding to expressed MEPF1 including the signal peptide from pbadg vector was observed at m/z = 11,457.7 ([M+H] + ) and a double-charged at m/z = 5,732.1 ([M+2H] 2+ ). (E) Confocal images of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown 5 days in a solution with fraction 2 from (A). Again, the epidermis is devoid of stomata with arrested meristemoids, indicating that fraction 2 contains bioactive MEPF1 isoform. (F) MALDI-TOF spectrum of fraction 3 from (A). A single-charged peptide corresponding to expressed MEPF1 including the signal peptide from pbadg vector was observed at m/z = 11,461.2 ([M+H] + ) and a double-charged at m/z = 5,734.2 ([M+2H] 2+ ). (G) Confocal images of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown 5 days in a solution with fraction 3 from (A). Stomatal differentiation (dots) is visible, indicating that fraction 3 contains only inactive, misfolded MEPF1. Supplemental Figure 7: Separation of properly-folded, bioactive MEPF2 by reverse-phase chromatography followed by mass-spectrometry and bioassays (A) HPLC chromatogram of purified, refolded MEPF2-His. Each peak in the UV chromatogram was collected and analyzed by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry as described in fig. S3. The peaks 1 and 2 were subsequently analyzed for bioassays. (B) MALDI-TOF spectrum of fraction 1 from (A). A single-charged peptide corresponding to expressed MEPF2 lacking the signal peptide from pbadg vector was observed at m/z = 9,515.9 ([M+H] + ) and a double-charged at m/z = 4,759.3 ([M+2H] 2+ ). (C) Confocal images of cotyledon epidermis from wildtype seedling grown 5 days in a solution with fraction 1. Severe inhibition of asymmetric division is observed, indicating that this fraction contains bioactive MEPF2. (D) MALDI-TOF spectrum of fraction 2 from (A). Low molecular weight contaminant was observed at m/z = 1,721.2 ([M+H] + ). (E) Confocal images of cotyledon epidermis from wild-type seedling grown 5 days in a solution with fraction 2 from (A), with visible stomatal differentiation (dots).
5 Lee_Jin Suk 5 Supplemental Figure 8: Real-time binding curves detecting direct ligandreceptor interactions by QCM Shown are representative QCM real-time binding curves for the attachment of bioactive recombinant MEPF1 (A-C) and MEPF2 (D-F) to surface-immobilized ERECTA K-GFP (A,D: ERECTA, red), ERL1 K-GFP (B, E: ERL1, green), TMM- GFP (C, F: TMM, blue), and GFP (A-F: GFP, black). Arrows indicate the time point of injection of 300 nm recombinant peptide solutions (A-C: MEPF1, D-F: MEPF2). Reduction in frequency (Hz) of quartz crystals indicates total mass shifts due to ligand-receptor interaction. See Supplemental Methods for experimental details. Supplemental Figure 9: Heat denaturation severely compromises binding of MEPF1 and MEPF2 to receptors Shown are observed SPR kinetic sensograms fitted by least square regression with Langmuir adsorption model from representative SPR binding assay upon injection (t=0) of: (A) heat-denatured MEPF1 peptide solution (300 nm); and (B) heat-denatured MEPF2 peptide solution (300 nm) to biosensor chips immobilized with ERECTA K-GFP (ERECTA, red), ERL1 K-GFP (ERL1, green), and TMM- GFP (TMM, blue). The peptide solution was heat denatured at 70 C for 30 min. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Supplemental Figure 10: Functional epitope-tagged receptors expressed in Arabidopsis are predominantly detected in microsomal fractions (A-F) Immunoblots of subcellular fractionations of protein extracts from 2-weekold seedlings of Arabidopsis wild type (WT) and transgenic lines expressing each functional epitope-tagged receptor in its respective null mutant background: proerecta::erecta-yfp in erecta (A); proerl1::erl1-yfp in erl1 (B);
6 Lee_Jin Suk 6 proerecta::erecta-flag in erecta (C); proerl1::erl1-flag in erl1 (D); protmm::tmm-yfp in tmm (E); protmm::tmm-ha in tmm (F). The fractionation was performed as described in the Supplemental Methods. T, total fraction; C, cytosol fraction; M, microsomal (membrane) fraction. Arrowheads indicate the size of each epitope-tagged receptor. Non-specific bands are detected in immunoblots using anti-ha antibody (TMM-HA) and anti-gfp antibody (TMM- YFP and ERL1-YFP). 6% (for panels A-E) or 8% (for panel F) acrylamide gels were used for SDS-PAGE. Asterisks, non-specific bands. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kilodaltons (kd). Supplemental Figure 11: Dominant-negative receptors link ERECTA and ERL1 predominantly with EPF2- and EPF1-mediated signaling, respectively (A-F) Confocal microscopy of 12-day-old abaxial cotyledons from wild type (WT; A), erecta (B), ERECTA K in erecta (C), epf2 (D), erecta erl1 erl2 (E), erl1 (F), ERL1 K in erl1 (G), and epf1 (H). Both dominant-negative ERECTA and epf2 mutation confer excessive entry asymmetric divisions (C,D; brackets). This phenotype is less notable in erecta (B; brackets). erecta erl1 erl2 exhibits massive stomatal clusters (E). erl1 exhibits no discernible phenotype (F). Both dominantnegative ERL1 and epf1 mutation confer stomatal pairing (G, H; asterisks). Scale bar, 20 m. (I-K) Quantitative analysis of 12-day-old abaxial cotyledon epidermis. (I) Stomatal density (p=0.02, one-way ANOVA). (J) Stomatal pairing density (p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA). (K) Non-stomatal epidermal cell density (p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA). Asterisk and double asterisk represent groups significantly different (p<0.01) from others by Tukey's HSD test. WT, epf1, ERL1 K erl1: n=8; epf2 and ERECTA K erecta: n=5. Total numbers of stomata and non-stomatal epidermal cells counted: WT (301, 841); epf1 (390, 940); ERL1 K erl1 (378, 708); epf2 (211, 1657); ERECTA K erecta (230, 2147). Bars, means. Error bars, s.e.m.
7 Lee_Jin Suk 7 Supplemental Figure 12: Model of ligand-receptor actions during stomatal development (A) Cartoon of stomatal development. A subset of protodermal cells (P) adopt stomatal-lineage fate and become meristemoid mother cells (MMC), undergoing asymmetric entry division. Daughter cells of an MMC are a meristemoid (M) and a stomatal-lineage ground cell (SLGC). A meristemoid reiterates asymmetric amplifying divisions, but eventually differentiates into a guard mother cell (GMC), which terminally differentiates into paired guard cells (GCs) constituting a stoma. EPF2 (purple) is secreted from MMCs and early meristemoids (Hara et al. 2009; Hunt and Gray 2009). EPF1 (cyan) is secreted from late meristemoids and GMCs (Hara et al. 2007). (B) Hypothetical cell-cell interaction between EPF2-expressing MMC early M (purple) and its neighbor cell (white). EPF2-ERECTA (red) ligandreceptor pair inhibits entry division initiating stomatal cell lineage, while TMM (black) may prevent ERECTA's inhibition in the MMC early M (purple). In addition, in nonstomatal neighbor cells TMM may fine-tune EPF2-ERECTA signaling. (C) EPF1- ERL1 (orange) ligand-receptor pair inhibits stomatal differentiation and orients asymmetric spacing divisions. In stomatal precursor cells (late Ms and GMCs) TMM associates with ERL1 to prevent ERL1 from inhibiting stomatal differentiation. In contrast, TMM cooperatively acts in SLGC to inhibit secondary asymmetric division from occurring adjacent to the pre-existing stomatal precursor (i.e. enforcing onecell-spacing rule). ERECTA is expressed high in protodermal tissues, while ERL1 and TMM are expressed in stomatal-lineage cells, in MMCs, meristemoids, and SLGCs (Nadeau and Sack 2002; Shpak et al. 2005). In (B) and (C), the presence of ERECTA-ERL1 heterodimers may contribute to signaling redundancy. (D) Excessive EPF2, either by overexpression or recombinant MEPF2 peptide application, confers ERECTA-mediated inhibition of asymmetric entry division, resulting in an epidermis solely composed of pavement cells (confocal image, cell periphery highlighted in purple). (E) Excessive EPF1, either by overexpression or recombinant MEPF1 peptide application, confers ERL1-mediated inhibition of stomatal differentiation, resulting in an epidermis devoid of stomata. While asymmetric entry and amplifying divisions (sequence of cell divisions numbered) still occur, stomatal precursors
8 Lee_Jin Suk 8 trans-differentiate into SLGC-like cells (asterisk) instead of guard cells (confocal image, cell periphery highlighted in cyan). Stoichiometry and localization of each receptor species remain uncertain. References for Supplemental Figure Legends Hara K, Kajita R, Torii KU, Bergmann DC, Kakimoto T The secretory peptide gene EPF1 enforces the stomatal one-cell-spacing rule. Genes Dev 21: Hara K, Yokoo T, Kajita R, Onishi T, Yahata S, Peterson KM, Torii KU, Kakimoto T Epidermal cell density is auto-regulated via a secretory peptide, EPIDERMAL PATTERNING FACTOR2 in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 50: Hunt L, Gray JE The signaling peptide EPF2 controls asymmetric cell divisions during stomatal development. Curr Biol 19: Nadeau JA, Sack FD Control of stomatal distribution on the Arabidopsis leaf surface. Science 296: Shpak ED, McAbee JM, Pillitteri LJ, Torii KU Stomatal patterning and differentiation by synergistic interactions of receptor kinases. Science 309:
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10962 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of AvrAC-FLAG in protoplasts. Total protein extracted from protoplasts described in Fig. 1a was subjected to anti-flag immunoblot to detect AvrAC-FLAG
doi:10.1038/nature10962 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of AvrAC-FLAG in protoplasts. Total protein extracted from protoplasts described in Fig. 1a was subjected to anti-flag immunoblot to detect AvrAC-FLAG
Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random
 S1 Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random Conical Tilt (RCT) reconstruction (left: -50,right:
S1 Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random Conical Tilt (RCT) reconstruction (left: -50,right:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Patterns of Cell Division, Cell Differentiation and Cell Elongation in Epidermis and Cortex of Arabidopsis pedicels in the Wild Type and in erecta
 Patterns of Cell Division, Cell Differentiation and Cell Elongation in Epidermis and Cortex of Arabidopsis pedicels in the Wild Type and in erecta Mark G. R. Bundy, Olivia A. Thompson, Matthew T. Sieger,
Patterns of Cell Division, Cell Differentiation and Cell Elongation in Epidermis and Cortex of Arabidopsis pedicels in the Wild Type and in erecta Mark G. R. Bundy, Olivia A. Thompson, Matthew T. Sieger,
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2013). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.112.108993 Supplemental Figure 1. 3-MA Treatment Reduces the Growth of Seedlings. Two-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana seedlings germinated on
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Crystallization-grade After D After V3 cocktail. Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s) Time (s)
 Ligand Type Name 6 Crystallization-grade After 447-52D After V3 cocktail Receptor CD4 Resonance Units 5 1 5 1 5 1 Broadly neutralizing antibodies 2G12 VRC26.9 Resonance Units Resonance Units 3 1 15 1 5
Ligand Type Name 6 Crystallization-grade After 447-52D After V3 cocktail Receptor CD4 Resonance Units 5 1 5 1 5 1 Broadly neutralizing antibodies 2G12 VRC26.9 Resonance Units Resonance Units 3 1 15 1 5
Double charge of 33kD peak A1 A2 B1 B2 M2+ M/z. ABRF Proteomics Research Group - Qualitative Proteomics Study Identifier Number 14146
 Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/471/eaah5085/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphorylation of the exocyst protein Exo84 by TBK1 promotes insulin-stimulated GLUT4 trafficking Maeran Uhm,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/471/eaah5085/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphorylation of the exocyst protein Exo84 by TBK1 promotes insulin-stimulated GLUT4 trafficking Maeran Uhm,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Predictive PP1Ca binding region in BIG3 : 1,228 1,232aa (-KAVSF-) HEK293T cells *** *** *** KPL-3C cells - E E2 treatment time (h)
 Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Figure legends of supplementary figures
 Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Figure legends of supplementary figures Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis of rice early flowering1 () plants and enhanced expression of floral identity genes in.. Leaf emergence of,, and plants with complementary
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
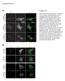 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene
 Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
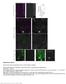 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti, Patricia Cogswell, Lewis C. Cantley, and Albert S. Baldwin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska, Sayan Gupta, Benlian Wang, Masaru Miyagi, Mark R. Chance, and Krzysztof Palczewski
 Structure, Volume Supplemental Information Conformational Dynamics of Activation for the Pentameric Complex of Dimeric G Protein-Coupled Receptor and Heterotrimeric G Protein Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska,
Structure, Volume Supplemental Information Conformational Dynamics of Activation for the Pentameric Complex of Dimeric G Protein-Coupled Receptor and Heterotrimeric G Protein Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska,
Biology Open (2014) 000, 1 10 doi: /bio
 (2014) 000, 1 10 doi:10.1242/bio.201410041 Supplementary Material Michael Brauchle et al. doi: 10.1242/bio.201410041 Fig. S1. Alignment of GFP, sfgfp, egfp, eyfp, mcherry and mruby2. Sequence-based alignment
(2014) 000, 1 10 doi:10.1242/bio.201410041 Supplementary Material Michael Brauchle et al. doi: 10.1242/bio.201410041 Fig. S1. Alignment of GFP, sfgfp, egfp, eyfp, mcherry and mruby2. Sequence-based alignment
Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70.
 Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70. peptide MH+ charge XCorr score Delta Cn score Protein ID KNAVVTVPAYFNDSQRQ 1680.83 2 2.22 0.37
Supplemental Table S1. The list of peptides identified in TAP-WPP1 LC/MS/MS analysis, corresponding to HSC70. peptide MH+ charge XCorr score Delta Cn score Protein ID KNAVVTVPAYFNDSQRQ 1680.83 2 2.22 0.37
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS
 BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems. Expressway Mini Cell-Free Expression System
 Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
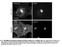 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
crossmark Ca V subunits interact with the voltage-gated calcium channel
 crossmark THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 291, NO. 39, pp. 20402 20416, September 23, 2016 Author s Choice 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in
crossmark THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 291, NO. 39, pp. 20402 20416, September 23, 2016 Author s Choice 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Design of isolated protein and RNC constructs, and homogeneity of purified RNCs. (a) Schematic depicting the design and nomenclature used for all the isolated proteins and RNCs used
Supplementary Figure 1 Design of isolated protein and RNC constructs, and homogeneity of purified RNCs. (a) Schematic depicting the design and nomenclature used for all the isolated proteins and RNCs used
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB
 Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/308/ra4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Antipsychotics Activate mtorc1-dependent Translation to Enhance Neuronal Morphological Complexity Heather Bowling, Guoan
Supporting Information
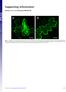 Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Supporting Information Harries et al. 1.173/pnas.9923916 A Fig. S1. Disruption of microfilaments within epidermal cells after treatment with 5 M Lat. Images of N. benthamiana cells are from plants expressing
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2919 Direct observation of the influence of cardiolipin and antibiotics on lipid II binding to MurJ Jani
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2919 Direct observation of the influence of cardiolipin and antibiotics on lipid II binding to MurJ Jani
Supplementary Figure 1
 S U P P L E M E N TA R Y I N F O R M AT I O N DOI: 10.1038/ncb2896 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sequence alignment of TERB1 homologs in vertebrates. M. musculus TERB1 was derived from
S U P P L E M E N TA R Y I N F O R M AT I O N DOI: 10.1038/ncb2896 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sequence alignment of TERB1 homologs in vertebrates. M. musculus TERB1 was derived from
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Manja Henze, Dorothee Merker and Lothar Elling. 1. Characteristics of the Recombinant β-glycosidase from Pyrococcus
 S1 of S17 Supplementary Materials: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Glycoconjugates by Transgalactosylation with Recombinant Thermostable β-glycosidase from Pyrococcus Manja Henze, Dorothee Merker and Lothar
S1 of S17 Supplementary Materials: Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Glycoconjugates by Transgalactosylation with Recombinant Thermostable β-glycosidase from Pyrococcus Manja Henze, Dorothee Merker and Lothar
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Chapter 8. Interaction between the phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase SH3 domain and a photocleavable cyclic peptide
 Interaction between the phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase SH3 domain and a photocleavable cyclic peptide 129 Abstract The interaction of the PI3K SH3 domain with a cyclic photocleavable peptide and the linear
Interaction between the phosphatidylinositol 3- kinase SH3 domain and a photocleavable cyclic peptide 129 Abstract The interaction of the PI3K SH3 domain with a cyclic photocleavable peptide and the linear
Supplementary Figure S1 (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. An orthogonal ribosome-trnas pair by the engineering of
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION An orthogonal ribosome-trnas pair by the engineering of peptidyl transferase center Naohiro Terasaka 1 *, Gosuke Hayashi 1 *, Takayuki Katoh 1, and Hiroaki Suga 1,2 1 Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION An orthogonal ribosome-trnas pair by the engineering of peptidyl transferase center Naohiro Terasaka 1 *, Gosuke Hayashi 1 *, Takayuki Katoh 1, and Hiroaki Suga 1,2 1 Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry. Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013
 The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis
 Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
Problem Set #5 4/3/ Spring 02
 Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Supplementary Table 1. Properties of lysates of E. coli strains expressing CcLpxI point mutants
 Supplementary Table 1. Properties of lysates of E. coli strains expressing CcLpxI point mutants Species UDP-2,3- diacylglucosamine hydrolase specific activity (nmol min -1 mg -1 ) Fold vectorcontrol specific
Supplementary Table 1. Properties of lysates of E. coli strains expressing CcLpxI point mutants Species UDP-2,3- diacylglucosamine hydrolase specific activity (nmol min -1 mg -1 ) Fold vectorcontrol specific
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Supplementary Figure 1. Chemical structures of activity-based probes (ABPs) and of click reagents used in this study.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Chemical structures of activity-based probes (ABPs) and of click reagents used in this study. In this study, one fluorophosphonate (FP, 1), three nitrophenol phosphonate probes
Supplementary Figure 1. Chemical structures of activity-based probes (ABPs) and of click reagents used in this study. In this study, one fluorophosphonate (FP, 1), three nitrophenol phosphonate probes
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking
 5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking In the quest of the omics sciences for holistic schemes, the identification of binding partners of proteins
5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking In the quest of the omics sciences for holistic schemes, the identification of binding partners of proteins
Supplementary Figure 1
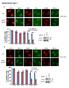 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted. residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue. Supplementary Figure 2. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant
Supplementary Figure 1. Amino acid sequences of GodA and GodA*. Inserted residues are colored red. Numbers indicate the position of each residue. Supplementary Figure 2. SDS-PAGE analysis of purified recombinant
Supplemental Data. Beck et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
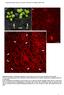 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic comparison of the rosette leaves of four-week-old mpk4 and Col-0 plants. A mpk4 vs Col-0 plants grown in soil. Note the extreme dwarfism of the mpk4 plants (white arrows)
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S2
 Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
Supplementary Figure S A) The blots shown in Figure B were qualified by using Gel-Pro analyzer software (Rockville, MD, USA). The ratio of LC3II/LC3I to actin was then calculated. The data are represented
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
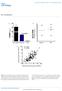 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes trna wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism Kiruthika Selvadurai, Pei Wang, Joseph Seimetz & Raven H Huang* Department of Biochemistry,
Supplementary Information Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes trna wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism Kiruthika Selvadurai, Pei Wang, Joseph Seimetz & Raven H Huang* Department of Biochemistry,
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Appendix. Table of Contents
 Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
