Qualifying Examination (Part I)
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Student Edition Qualifying Exam December 2015 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15, 2015 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Time Student Name Tuesday, December 15 th 9:00 am 11:00 am (EXAM #1) 1:00 pm 3:00 pm (EXAM #2) 3:00 pm 3:30 pm (Committee Meets to determine results) 3:30 pm (Results given to students Pharm South Conf. Rm.) Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not necessary, you may prepare written answers, overhead figures, or any type of materials that you think might be useful in the presentation of your answers. You may bring such preparation materials with you to the examination. The oral examination itself will not extend beyond two hours. If you have any questions regarding the examination, please contact Christine Konradi at: (office) (cell) (home)
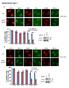
2 Infusion number # of lever presses Student Edition Question 1 Qualifying Exam December 2015 The long-term treatment with opioid drugs is used to control chronic pain. Therefore, it is important to understand how pain affects the rewarding effect of opioids and hence risk of prescription opioid misuse and abuse. In this study, the rat model of morphine self-administration (MSA) was used to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the impact of pain on morphine seeking before and after morphine withdrawal. Chronic pain was induced by injection of complete Freund s adjuvant (CFA) into the left hindpaw. Figure 1. Time courses for the two dimensions of pain. A, The sensory dimension (hyperalgesia) of pain was measured by pawwithdrawal latencies (thermal stimulus) in rats after injection of CFA or saline on day 0 (arrow). B, The affective dimension of pain measured by conditioned place aversion (CPA) in conditioned rats after the same injection of CFA or saline on day 0 (arrow; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p <0.001; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). The data are shown as the CPA score (the difference in the time spent in the compartment before and after its pairing with the indicated drug). Figure 2. Persistent pain maintains morphine-seeking behavior after withdrawal from self-administered morphine. A, The number of daily infusions of morphine in saline- and CFA injected rats before and after withdrawal from morphine dose. CFA or saline was injected on day 0 (arrow), saline or morphine self-administration started on day 2 and morphine withdrawal (morphine substituted with saline) started on day12 (withdrawal day1). B, Number of presses of active and inactive levers for data shown in A during morphine withdrawal (** - p<0.01; *** - p<0.001 active lever presses the CFA versus saline group; ###<p0.001 active vs inactive lever presses in the CFA group).
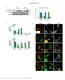
3 Student Edition Question 1 Qualifying Exam December 2015 GluA1 subunits of glutamate receptors play a critical role in synaptic plasticity involved in drug reward and in promoting behavioral responses to drugs of abuse and pain. The study next examined the expression of GluR1 in the central nucleus of amygdala, the structure critical for the emotional aspects of pain and generally for the processing of negative emotions. Tubulin Figure 3. The level of the GluA1 protein in CeA after morphine withdrawal. Normalized protein levels of GluA1 and GluA2 in the central nucleus of amygdala (CeA), a limbic structure critically involved in the affective dimension of pain, in saline- and CFA-injected rats withdrawn from self-administered morphine for 13 d. B, Western blots data for GluA1 in CeA in saline- and in CFA-injected rats that did not undergo morphine self-administration at 3 and 24 d after CFA-injection (Student's t test and one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). MeCP2 is a global transcriptional regulator, and genome-wide expression analysis indicates that MeCP2 can activate or repress transcription of many target genes. MeCP2 is increasingly implicated in the epigenetic mechanisms of several neurological diseases including drug addiction and chronic pain. Thus, the study next examined the expression of MeCP2 in the CeA following morphine withdrawal in rats with or without chronic pain.
4 Student Edition Question 1 Qualifying Exam December 2015 Tubulin Tubulin Figure 4. The expression level of MeCP2 after morphine withdrawal. A, B, Western blots data of GluA1 and MeCP2 proteins in the CeA of saline-injected SSA rats (n = 4) and MSA rats injected with saline (n = 4) or CFA (n = 4) on morphine withdrawal day 1 (n = 4, A) and day 13 (n = 4, B; one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). Questions: 1. Briefly describe the behavioral tests used in the study to measure sensory and emotional aspects of pain and the rewarding effect of morphine (and what exactly is measured in each test). What conclusion can you draw based on the data presented in Figs. 1 and 2 about the effect of the chronic pain on the characteristics of pain perception? 2. What conclusions can you reach based on the data presented in Figs. 3 and 4 as to the molecular mechanism of the effect of chronic pain on morphine craving during withdrawal? 3. Propose a simple model regarding the molecular mechanisms of opioid reward explored in this study. Propose experiments to test the model.
5 Student Edition Question 2 Qualifying Exam December 2015 Drug N under development for hypertension is tested for the first time in vivo in an animal model. You obtain the following data: Questions: 1. Interpret these data and provide both in vivo and in vitro experimental strategies to establish the main factors responsible for the differences observed. 2. Illustrate the expected profiles if the same results were plotted using log plasma concentrations versus time.
6 Student Edition Question 3 Qualifying Exam December 2015 You have recently identified a family in which multiple family members have two copies of a mutant thyroglobulin gene containing the C886T transition indicated below: The presence of this premature stop codon results in the production of a 32 kilodalton thyroglobulin protein rather than the wild-type 330 kd isoform normally produced by the thyroid gland. Blood samples from affected siblings were assessed for total T4, total T3, and TSH levels and the results from such measurements are presented in the table below: Patient # T4 (nm) T3 (nm) TSH (mu/l) Normal Range <4.5 Questions: 1) Based upon your knowledge of thyroid hormone biosynthesis, how would you explain the levels of T4, T3 and TSH in these individuals? 2) All three patients had a diffusely enlarged thyroid gland. Explain this observation. 3) Patients 2 and 3 developed compressive symptoms (e.g., difficulty in breathing and swallowing) due to thyroid enlargement. Suggest an appropriate course of treatment for these individuals.
7 Student Edition Question 4 Qualifying Exam December 2015 Administration of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) that block the biosynthesis of prostaglandins has beneficial effects for reducing the occurrence of colon cancer. Further studies indicate that prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ) promotes the growth of colonic polyps in the gastrointestinal tracts of mice. Importantly, EGFR is critical for the proliferation of the intestinal mucosa,, and its expression is up-regulated in colon cancer. To explore the mechanism by which the activity of EGFR may be modulated by PGE 2, several experiments were carried out in human colon cancer cells (Caco-2), and experimental results are shown in Figures 1 and 2. Figure 1: Effects of PGE 2 on the phosphorylation of EGFR (left panel). Cells were treated with PGE 2 or/and EGFR inhibitors (PD and AG1478) as indicated below. The levels of EGFR and phosphorylated EGFR were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting (top, left panel). The ratios between phosphorylated EGFR and EGFR were quantified and shown in a histogram (bottom, left panel). PGE 2 activates ERK2/MAPK activity (right panel). The ERK2 activity was analyzed by in vitro kinase assay following immunoprecipitation from cell lysates using MBP (myosin basic protein) as a substrate in the presence of 32 P-ATP (top, right panel). Phosphorylation of MBP and ERK2 under different experimental conditions was analyzed by autoradiogram and quantified (bottom, right panel). *, p <0.05, versus control; **, p< 0.001, versus PGE 2. PY, phosphotyrosine Figure 2: The effect of PGE 2 on the phosphorylation of EGFR (top) and ERK (bottom) in the presence of neutralizing antibodies (against EGFR, TGF-, EGF and HB-EGF, respectively) (left panel) and metalloprotease inhibitor, GM6001 (right panel). Ct, control. TGF-, EGF and HB-EGF are ligands for EGFR.
8 Student Edition Question 4 Qualifying Exam December 2015 QUESTIONS: 1. Explain the experiments and results in Figures 1 and Based on these results, propose a hypothesis that links PGE 2 to the phosphorylation of EGFR and ERK (include a diagram). 3. There are four EGF receptors, EGFR1-4. These EGFRs usually form heterodimers. What will be your experimental strategies to identify the critical EGFR for the PGE 2 mediated proliferation in Caco cells.
9 Student Edition Question 5 Qualifying Exam December 2015 Calmodulin (CaM) is an essential Ca binding protein that transduces Ca signals in a wide range of biological processes. CaM binds to larger proteins and functions as a Ca sensor for decoding Ca signals into downstream responses. In the heart, CaM regulates many ion channels such as the L-type Ca channel (Ca-dependent inhibition), Ca-activated K channels (Ca-dependent activation) and the RyR2 sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca release channel (Ca-independent inhibition). Humans have 3 CaM genes CALM1, CALM2, CALM3 encoding the identical amino acid sequence that are all expressed in the heart muscle. Genetic studies have identified CaM missense mutations in humans with severe ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death susceptibility, albeit with distinct clinical presentations: A mutation in CALM1 (N54I) was associated with stress-induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia reminiscent of catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT-CaMs), whereas three other mutations in either CALM1 or CALM2 (D96V, D130G and F142L) led to recurrent cardiac arrest in infancy associated with severe QT prolongation reminiscent of a long QT syndrome (LQTS-CaMs). A fifth mutation (F90L) was found in a family with idiopathic ventricular fibrillation and mild QT prolongation. CPVT is commonly caused by mutations in sarcoplasmic reticulum genes that increase diastolic Ca leakage through the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) channels. LQTS is usually caused by dysfunctional plasma membrane ion channels that prolong the ventricular action potential. The mechanism underlying idiopathic ventricular fibrillation (IVF) is not known. Using recombinant mutant CaM protein, the following experiments were performed to elucidate how mutant CaM-F90L causes IVF: Fig. 1. Measurement of Ca sparks and SR Ca release. Representative confocal line scans (A,E) and average data (B-D, F-G) from permeabilized mouse ventricular myocytes after 30 min incubation with either WT or mutant CaMs (100nM, physiological free [CaM]). After permeabilization, myocytes were incubated in internal solution containing 50 nm free [Ca], and 25 M Fluo. Bars represent mean+se. WT values on each experimental day. WT (n=45), F90L (n=33), N54I (n=35). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs WT CaM. AIP Auto-inhibitory peptide (1 µm), a selective inhibitor of Ca- Calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII).
10 Student Edition Question 5 Qualifying Exam December 2015 QUESTIONS: 1. Describe the results of the Ca release measurements in Fig. 1. Formulate a hypothesis on how mutant CaM F90L regulate RyR2 channels and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca release and design experiments that will test your hypothesis. 2. How is F90L different from N54I? What other targets in the cardiomyocytes could be affected?
11 Student Edition Question 6 Qualifying Exam December 2015 P2Y 12 receptor (P2Y 12 -R) signaling is mediated through Gi, ultimately reducing cellular camp levels. Because camp is a central modulator of arginine vasopressin (AVP)-induced water transport in the renal collecting duct (CD), you want to determine if P2Y 12 -R may play a role in renal handling of water in health and in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. The most common acquired nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by chronic lithium (Li) administration for the treatment of bipolar disorder, which affects 2% of the general population of the United States. You perform the following experiment using clopidogrel, an irreversible inhibitor of P2Y 12 -R: Figure: Effect of clopidogrel administration on Li-induced polyuria and decrease in AQP2 protein abundance in rats. (A) Water intake;(b) urine output; (C) urine osmolality. Questions: 1) Describe the pathway of the regulation of water reabsorption in the collecting duct. 2) Describe the difference between nephrogenic and central diabetes insipidus. 3) Describe the data. Why does water intake increase concomitantly with urine output? What effect does clopidogrel (CLPD) have on lithium-induced changes in water intake and urine output? 4) Why would P2Y 12 receptor blockade blunt lithium induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus based on how the P2Y 12 receptor signals and the pathway of water regulation in the collecting duct?
12 Gi activation (% of control) Gi activation (% of control) Student Edition Question 7 Qualifying Exam December 2015 MAPKs are activated in response to G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) stimulation and play essential roles in regulating cellular processes downstream of these receptors. However, very little is known about the reciprocal effect of MAPK activation on GPCRs. To investigate possible crosstalk between MAPK and GPCRs, a group of investigators performed the following experiments. FIGURE 1. HEK293T cells stably expressing HA-tagged CXCR4 (HA-CXCR4; a Gi-coupled GPCR) were transfected with empty vector (Control), constitutively active Ras (Ras CA), dominant-negative Ras (Ras DN), constitutively active MEK (MEK CA), or dominant-negative MEK (MEK DN). Gi activation was measured 3 min after the addition of CXCL12 (the native agonist for CXCR4) and expressed as a % of the control condition, which was set at 100%. Expression of total ERK1/2, active ERK1/2 [(p)erk1/2], and the CA and DN forms of Ras and MEK were assessed by Western analysis. **, P < 0.01; NS, not significant. FIGURE 2. CXCR4-YFP localization was assessed by fluorescence confocal microscopy in unstimulated HeLa cells co-transfected with CXCR4-YFP and empty vector (Control) or the indicated Ras and MEK mutants. Intensity plots derived from 20 confocal fluorescence microscopy images obtained in three independent experiments were analyzed to quantify CXCR4 localization at the plasma membrane and inside the cell. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM of the 20 images and were normalized to the total fluorescence intensity (plasma membrane + intracellular compartment) set to 100% in each condition.
13 mol [ 32 P]/mol barr2 Student Edition Question 7 Qualifying Exam December 2015 A Autorad: barr2 Coom: barr2 Autorad: GST Coom: GST B C FIGURE 3. (A) Phosphorylation of βarr2 was performed with recombinant bovine βarr2 (or GST) as a substrate and recombinant active ERK1 in the presence of [γ 32 P]-ATP for 15 min. The reaction mixtures were subjected to SDS- PAGE. The gel was stained with Coomassie (Coom) and analyzed by autoradiography (Autorad); 32 P incorporation was quantified using a PhosphorImager (Left) or during kinetics using scintillation counting (Right). The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (B and C) CXCR4 cell-surface expression was assessed in unstimulated βarr1/2-ko MEFs transiently transfected with HA-CXCR4-YFP, βarr2 WT, or the indicated βarr2 mutants, with or without Ras CA. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments and were normalized to the control condition (100%). Expression of βarr2 WT and mutants were assayed by immunoblotting. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant. QUESTIONS: A) What major conclusion can be drawn from the data in Fig. 1? Fig. 2? Fig. 3? B) Develop a hypothesis that might explain the the information provided and the collective data shown in Figs Describe how the results support your hypothesis. C) Design a pharmacological experiment that would allow you to further test your hypothesis in non-transfected cells.
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 STUDENT VERSION Qualifying Exam July 2013 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 15-19, 2013 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Tuesday, July 16 th
STUDENT VERSION Qualifying Exam July 2013 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 15-19, 2013 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Tuesday, July 16 th
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 11 & 12, 2003 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3218
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous EGFR trafficking and responses depend on biased ligands. (a) Lysates from HeLa cells stimulated for 2 min. with increasing concentration of ligands were immunoblotted
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/278/rs11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for In Vivo Phosphoproteomics Analysis Reveals the Cardiac Targets of β-adrenergic Receptor Signaling Alicia Lundby,* Martin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 12 & 13, 2006 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic depiction of the tandem Fc GDF15. Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 2 Gfral mrna levels in the brains of both wild-type and knockout Gfral
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Chapter 11 Guided Reading: Cell Communication
 Name Chapter 11 Guided Reading: Cell Communication The special challenge in Chapter 11 is not that the material is so difficult, but that most of the material will be completely new to you. Cell communication
Name Chapter 11 Guided Reading: Cell Communication The special challenge in Chapter 11 is not that the material is so difficult, but that most of the material will be completely new to you. Cell communication
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplemental material Jewell et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201007176/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. IR Munc18c association is independent of IRS-1. (A and
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 14 & 15, 2010 Committee Members: Eugenia Gurevich Vsevolod Gurevich Tina Iverson Heidi Hamm Joey Barnett, for retakes Exam Schedule:
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Fig. S1. High K+ increases intracellular calcium level.
 Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Receptors and Drug Action. Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil
 Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Receptors and Drug Action Dr. Subasini Pharmacology Department Ishik University, Erbil Receptors and Drug Action Receptor Receptor is defined as a macromolecule or binding site located on the surface or
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2
 ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Muraski et al. 10.1073/pnas.0709135105 SI Text Generation of Transgenic Animals. Pim-WT and Pim-DN cdnas were subcloned NheI/SmaI from pegfp-c1 Pim-1 and pegfp-c1 Pim-DN plasmids
Supporting Information Muraski et al. 10.1073/pnas.0709135105 SI Text Generation of Transgenic Animals. Pim-WT and Pim-DN cdnas were subcloned NheI/SmaI from pegfp-c1 Pim-1 and pegfp-c1 Pim-DN plasmids
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 11 Cell Communication BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 210, and for Concept 11.1, read from the first full paragraph on p. 212. Read all of Concept 11.2. Pay
Incorporation of photo-caged lysine (pc-lys) at K273 of human LCK allows specific control of the enzyme activity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Incorporation of photo-caged lysine (pc-lys) at K273 of human LCK allows specific control of the enzyme activity. (a) Modeling of the kinase domain of LCK with ATP (left) or pc-lys
Supplementary Figure 1 Incorporation of photo-caged lysine (pc-lys) at K273 of human LCK allows specific control of the enzyme activity. (a) Modeling of the kinase domain of LCK with ATP (left) or pc-lys
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) July 31 August 3, 2007 Please remember that this is a closed-book examination. You must be prepared to answer 4 of the 7 questions. Although not
Chapter 11: Cell Communication
 Name Period Chapter 11: Cell Communication The special challenge in Chapter 11 is not that the material is so difficult, but that most of the material will be completely new to you. Cell communication
Name Period Chapter 11: Cell Communication The special challenge in Chapter 11 is not that the material is so difficult, but that most of the material will be completely new to you. Cell communication
G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Structure and Function
 PCTH 400 G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Structure and Function Dr. Rishi Somvanshi 2405 Wesbrook Mall rishiks@mail.ubc.ca 604-827-3672 Learning Objectives 1. GPCR? Structure and Synthesis 2. Function? Receptor
PCTH 400 G-Protein Coupled Receptors: Structure and Function Dr. Rishi Somvanshi 2405 Wesbrook Mall rishiks@mail.ubc.ca 604-827-3672 Learning Objectives 1. GPCR? Structure and Synthesis 2. Function? Receptor
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists
 Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists of: (i) the YPet domain (an enhanced YFP); (ii) the
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures for p38 activity imaging in living cells. (a) Schematic model of the p38 activity reporter. The reporter consists of: (i) the YPet domain (an enhanced YFP); (ii) the
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15 & 17, 2009 Examination Committee: 1. Ron Emeson 2. Eugenia Gurevich 3. Tina Iverson 4. Brian Wadzinski Tuesday, December 15 Thursday,
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter. pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its
 Supplementary Information Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its implications in gastric carcinogenesis Lisa Nagase, Takeru Hayashi,
Supplementary Information Dramatic increase in SHP2 binding activity of Helicobacter pylori Western CagA by EPIYA-C duplication: its implications in gastric carcinogenesis Lisa Nagase, Takeru Hayashi,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes
 1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras
 Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Cell Signaling (part 1)
 15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4078
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Principal Investigator: Project title:
 Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2. The Phosphoinositide Cascade
 Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2 The Phosphoinositide Cascade Calcium ion as a second messenger Tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization scribd.com Faisal Khatib JU The Phosphoinositide Cascade Used by
Signal-Transduction Cascades - 2 The Phosphoinositide Cascade Calcium ion as a second messenger Tyrosine kinase and receptor dimerization scribd.com Faisal Khatib JU The Phosphoinositide Cascade Used by
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis
 Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY FEBRUARY 16, PAGE
 STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
STEIN IN-TERM EXAM -- BIOLOGY 3058 -- FEBRUARY 16, 2017 -- PAGE 1 of 9 There are 25 questions in this Biology 3058 exam. All questions are "A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H" questions worth one point each. There
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering
 nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
nature methods Organelle-specific, rapid induction of molecular activities and membrane tethering Toru Komatsu, Igor Kukelyansky, J Michael McCaffery, Tasuku Ueno, Lidenys C Varela & Takanari Inoue Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
Life Science 1A Final Exam. January 19, 2006
 ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
