POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
|
|
- Anne Beverley Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Andrew J. Ramsay, Víctor Quesada, Miguel Foronda, Laura Conde, Alejandra Martínez-Trillos, Neus Villamor, David Rodríguez, Agnieszka Kwarciak, Cecilia Garabaya, Mercedes Gallardo, Mónica López-Guerra, Armando López-Guillermo, Xose S. Puente, María A. Blasco, Elías Campo and Carlos López-Otín Supplementary Material Supplementary Tables 1-6 Supplementary Figures 1-4 1
2 Supplementary Table 1. Somatic mutations in POT1-mutated samples Case Gene Chr Position Reference Found Mut 006 AC C M T185N 006 APH1B C Y T27I 006 ATM C G L2033V 006 BOD1L G R G1895E 006 C12orf C M A613E 006 C3orf A M splicing-site 006 COL4A T Y C1551R 006 CTNNA A R K855E 006 CTSO G R S249N 006 DDAH G R G270R 006 DOCK G R E1608K 006 GJB G R R32H 006 GNAI C Y A101V 006 HHLA A R I14V 006 NLRP G R V239M 006 OR10C G R V115M 006 PCDHA C M L409M 006 POT A R Y223C 006 RELN G R D368N 006 RIMS C M P889T 006 RRBP C Y A688V 006 SF3B A W N626Y 006 SI G S R91T 006 TMEM194A G R S152N 013 ABHD G R G392S 013 ADAM A W E181D 013 ADAMTS T W W669R 013 ARHGAP C Y T715I 013 DTNA G S E753Q 013 GBP C Y splicing-site 013 GRM G R A184T 013 IKZF T K L162R 013 NPBWR C Y T78M 013 ODZ C M S543* 013 PCDH G K M4I 013 POT T W Y36N 013 POU3F4 X C Y R279C 013 TEAD * -GC P144fs 013 USP G R S356N 044 BIRC T K L3687R 044 DNAH C Y A2694V 044 ECE G R S672N 2
3 044 KIAA C Y R1188W 044 OR4C C Y R231W 044 PCDHA G K D376Y 044 PENK C Y R229W 044 POT T W splicing-site 044 ROBO C M Q569K 044 SECISBP A R K15R 044 TMEM C S S1256C 044 UGT2B A R I331V 157 ABCA C Y P1342L 157 ABCD A R E374G 157 CBS G K E104D 157 COG G K V689F 157 CORO1C C S T485R 157 GFRA C M Q227K 157 HMCN C Y R394* 157 IRF C M S114R 157 MUC G S R2782T 157 OR2A T W V60D 157 PCSK G R R111Q 157 POT T K Y66* 157 TBPL A M S73R 157 USH2A C Y T2310M 184 AK G R R257H 184 AKT A M K172Q 184 C1orf C Y R386C 184 CFH G R V72I 184 HCN C Y T820M 184 KCTD T Y L202P 184 LRIG G R V811M 184 LRP C Y A65V 184 LRRC T T splicing-site 184 NOTCH * -CT P2515Rfs*4 184 POT A W M1L 184 QSER C Y Q161* 184 RAB5A A R D53G 184 RNF G R E292K 184 SLC38A T W L418H 3
4 Supplementary Table 2. Main clinical characteristics of the 341 patients with CLL Variable Category Gender Male /Female 206/135 Age, median (range) 57 (21-93) years Binet stage A 279 (82%) B 49 (14%) C 12 (4%) Rai stage (56%) I-II 134 (39%) III-IV 16 (5%) Lymphocytes (x10 9 /L), median (range) 12.4 ( ) Hemoglobin (g/l), median (range) 139 (63-175) Platelets (x10 9 /L), median (range) 197 (19-470) LDH >UNL 28/315 (9%) β 2- microglobulin >UNL 106/341 (36%) LDT < 1 year 48/275 (18%) CD38 High 105/290 (36%) ZAP-70 High 99/290 (34%) IGHV Unmutated 98/204 (48%) Genetic abnormality del(13)(q14.3) 89/208 (42%) del(11)(q22.3) 36/207(17%) /210 (15%) del(17)(p13.1) 7/209 (3%) SF3B1 Mutated 22/269 (9%) NOTCH1 Mutated 25/322 (7%) 10-year TTT (95% CI) Binet stage A 58% (50-66) 10-year OS (95% CI) All 66% (59-73) Follow-up, median (range) All 7.3 (0.6-26) years UNL: upper normal level; LDT: lymphocyte doubling time; CD38 high: >30% of positive CLL cells; ZAP-70 high: 20% of positive CLL cells; IGHV unmutated: 98% identity with germline; TTT: Time to treatment; OS: overall survival 4
5 Supplementary Table 3. Characteristics of CLL patients and tumor cells included in the experimental study of chromosomal alterations Age Sex POT1 IGHV ZAP- 70 CD38 17p deletion 11q deletion 13q deletion trisomy F Mutated Unmutated Normal 21% 92% Normal 59 M Mutated Unmutated Normal Normal 90% Normal 70 F Mutated Unmutated Normal Normal Normal Normal 56 M Mutated Unmutated Normal Normal Normal Normal 45 M Mutated Unmutated Normal Normal 34% Normal 75 M Mutated Unmutated 70 3 Normal Normal 44% Normal 68 F Unmutated Unmutated 63 1 Normal Normal Normal Normal 76 M Unmutated Unmutated 3 2 Normal Normal 22% Normal 48 M Unmutated Unmutated Normal Normal Normal Normal 79 M Unmutated Unmutated Normal Normal Normal Normal 74 M Unmutated Unmutated 14 1 Normal Normal 85% Normal 67 M Unmutated Unmutated 11 1 Normal 90% Normal Normal 5
6 Supplementary Table 4. Main clinical characteristics and outcome of the 341 patients with CLL according to their POT1 mutational status Parameter Category POT1 POT1 unmutated mutated P (n=329)* (n=12)* Gender Male (%) 197 (59%) 9 (75%) ns Age (years), median (range) 57 (21-93) 58 (33-80) ns Binet stage A 272 (83%) 7 (58%) B 44 (13%) 5 (42%) 0.02 C 12 (4%) 0 (0%) Rai stage (56%) 4 (52%) I-II 128 (39%) 6 (40%) ns III-IV 15 (5%) 1 (8%) Lymphocytes (x10 9 /L), median (range) 12.4 ( ) 17.4 (4.8-69) ns Hemoglobin (g/l), median (range) 139 (63-175) 126 ( ) ns Platelets (x10 9 /L), median (range) 198 (19-451) 171 ( ) ns LDH >UNL 26/304 (9%) 2/11 (18%) ns β 2 -microglobulin >UNL 100/280 (36%) 5/10 (50%) ns LDT < 1 year 35/187 (19%) 3/9 (34%) ns ZAP-70 >UNL 90/280 (31%) 9/10 (75%) IGHV Unmutated 89/195 (46%) 9/9 (100%) SF3B1 mutated 18/259 (7%) 4/10 (40%) NOTCH1 mutated 23/311 (7%) 2/11 (18%) ns 10-year TTT (95% CI) Binet stage A 57% (49-65) 100% ns 10-year OS (95% CI) All 67% (60-74) 40% (15-75) ns UNL: upper normal level; LDT: lymphocyte doubling time; TTT: time to treatment; OS: overall survival. 95% CI: 95% interval of confidence. * For several clinical correlates some patient data were unavailable. 6
7 Supplementary Table 5. POT1 oligonucleotide sequences used in Sanger sequencing validation Exon Primer 1 Primer 2 5 CAGCAGATATTCCAGACAACAGA AAGCATGTAATCACATTGGAGG 6 AATATGCATCAGTGTTGTTTGGC AGCTAAGCTGTGTGCATTGCC 7 AAAGCAGTGGTTTGTTCAAATG TTTGCAGTGTGTATTGAAAGCC 8 GCATGAATATTGAGGCTCGTC TTGGTTCGTAGGTTGTGCATC 9 TTGCTCTAACCCATTAAGTTTATCTTT AGTGCCAATATTCAGAGGCAT 10 ATTTGATTTGTTTCATTTGGCTC TTTCCTGACTGGTCAGTGCC 11 TTTGGCATAGGCCACAGAT AAATCTGATGAAAGCAATAGATCCTT 12 GCCAACAAGACACGGTAGAAG AGTTTCTCTCAGCAACGCTCC 13 TGAAAACGTTTGTTTTATTATGGAA TGGTTCAGGAGGATGCATGT 14 AGACAATCAGCTTAGCATTGACA GAAATCTTCACGCTTACACCAAA 15 TGCCTAATGCAGGTGACG ACCTCACACGTTATTTAATAGGACTG 16 TGCCTGCTTGAAGAAATACAGAC TTGTGAAACAAACAAGCACATTAC 17 GGGAATGACTCTTTAAATCCCTG ACCTGGAGATAATGCCAAGTTT 18 TTGGAAGCAAAGCTTTCAGAC ACAATCTTGATAGAGGGAAACTGTC 19 TTCTAATCCCATACCCATGCTAAC AATGTTAAATTTGGAAGGGACG 7
8 Supplementary Table 6. Sequences of the oligonucelotides used for mutagenesis of POT1 coding regions Mutation Y36N Forward Y36N Reverse Y223C Forward Y223C Reverse Oligonucelotide Sequence (5' to 3') GTTCTTTAAGCCCCCAAATCTAAGCAAAGGAAC GTTCCTTTGCTTAGATTTGGGGGCTTAAAGAAC GACAATAGACATTTTAGTCTGCGATAACCATGTTCATGTGGC GCCACATGAACATGGTTATCGCAGACTAAAATGTCTATTGTC 8
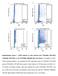
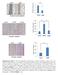
9 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1. Biological properties of wild-type POT1 and Y36N and Y223C POT1 mutants. (a) SDS-PAGE gel of 35 S-labeled wild-type and mutant POT1 proteins generated by in vitro translation. Vector refers to an empty vector reaction. (b) Representative immunoblot of HT1080 cells transiently infected with retroviral constructs encoding vector only, myc-tagged wild-type POT1, myc-tagged Y36N POT1 and myc-tagged Y223C POT1 proteins cultured for 45 population doublings. (c) Representative images of relative telomere signal intensities observed in metaphase nuclei by telomere FISH staining (red=ttaggg, blue=dapi) of HT1080 cells transiently infected with retroviral constructs encoding vector only, myc-tagged wild-type POT1, myc-tagged Y36N POT1 and myc-tagged Y223C POT1 proteins at 5 (top row) and 45 (bottom row) population doublings after selection. (d) Telomerase activity in HT1080 cells expressing wild-type and mutant POT1 proteins. A representative telomere restriction fragment (TRF) blot of HT1080 cells infected with retroviruses encoding vector only, wild-type POT1, Y223C POT1 or Y36N POT1 performed at the population doublings 5 and 45. The molecular size in kilobases is shown on the left. (e) Representative telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) assay in 5 µg and 1 µg of cell extract from the respective cell lines. Cell extracts (5 µg) treated with RNase (+) were used as negative controls. (f) Quantification of the TRAP assays shown in panel e. Bars depict means calculated from two technical replicates ± SEM. 9
10 Supplementary Fig. 2 Supplementary Fig. 2. Chromosomal aberrations in HT1080 cells expressing wild-type and mutant POT1 proteins. (a-e) Quantitation of sister chromatid fusions, multitelomeric signals, chromosomal breaks, chromosome fusions and signal-free ends per metaphase in HT1080 cells infected with retroviruses encoding vector only, wild-type POT1, Y36N POT1 or Y223C POT1 at population doublings 5, 15 and 45 by telomere FISH staining. Hatched fill indicates analysis of the respective cell type at population doubling 15 when treated with 0.5 µm aphidicolin. Bars depict means of event per metaphase calculated from two independently derived cell lines ± SEM. Two-tailed Student s t test was performed for comparisons, P values are indicated. For comparative purposes, the red dashed line marks the mean value for HT1080 cells expressing wild-type POT1 at population doubling 5. 10
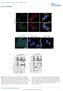
11 Supplementary Fig. 3 Supplementary Fig. 3. POT1-mutated CLL cells display unchanged telomere lengths and rates of telomere-deficient fusion. (a) Mean telomere length in kilobases (Kb), as estimated by QFISH of metaphase spreads, in purified B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations in comparison to age-matched IGHV-unmutated samples (control). Bars depict means calculated from the cells of 4 control patients and 6 POT1-mutated patients ± SEM (a total of 25 metaphases were analyzed for each group), two-tailed Student s t test was performed, P values are indicated. (b) Telomerase activity in POT1-unmutated and POT111
12 mutated CLL patient cells. Bars depict patient means calculated from 3 controls and 6 POT1- mutated CLL samples ± SEM. Two-tailed Student s t test was performed for comparisons, P values are indicated. (c) Quantification of chromosome-type end-to-end fusions with no detectable TTAGGG signal. Top, representative image of a fusion with no detectable TTAGGG signal. (d) Quantification of the number of signal-free ends (SFEs) per metaphase on CLL samples by telomere FISH staining (red=ttaggg, blue=dapi). Top, representative image of a SFE. For graphs in c and d, bars depict per patient means calculated from 4 controls and 6 POT1-mutated CLL samples ± SEM. Two-tailed Student s t test was performed for comparisons, P values are indicated. POT1 mutations result in unresolved mitotic structures. (e) Right, representative image of a DNA bridge observed in interphase nuclei from POT1-mutated CLL cells. Yellow arrows indicate TTAGGG signals within DNA bridges. Left, quantification of DNA bridges using telomere FISH on interphase nuclei (red=ttaggg-cy3; blue=dapi) of B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations (31/5692 interphase nuclei) in comparison to control cells (4/5951 interphase nuclei). (f) Right, representative image of a micronucleus (yellow arrow) in a POT1-mutated CLL cell. Left, quantification of micronuclei using telomere FISH on interphase nuclei (red=ttaggg- Cy3; blue=dapi) of B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations (87/5692 interphase nuclei) in comparison to control cells (27/5951 interphase nuclei). (g) Right, representative image of a multilobulated nucleus (yellow arrow) in a POT1-mutated CLL cell. Left, quantification of multilobulated nuclei using telomere FISH on interphase nuclei (red=ttaggg-cy3; blue=dapi) of B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations (83/5692 interphase nuclei) in comparison to control cells (33/5951 interphase nuclei). For the graphs in e, f and g, depicted are the total number of cellular events observed. χ 2 test with Yates correction was used for comparisons; P values are indicated on top of each comparison. 12
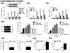
13 Supplementary Fig. 4 Supplementary Fig. 4. POT1-mutation does not induced telomeric DNA damage. (a) Somatic mutations in POT1, other frequently mutated genes in CLL patients (NOTCH1, SF3B1, CHD2 and SI) and components of the p53 pathway (TP53, ATM, BCL2, APAF1, BAX, MDM2 and RB1). Red= detection of a somatic mutation in the respective patient; Grey= no somatic mutation found in the respective patient. (b) Unchanged levels of telomeredysfunction-induced foci (TIF) in POT1-mutated CLL cells. Representative immunofluorescence images of TIFs in B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations (POT1 mutated) in comparison to control cells (control). Cells were fixed and costained with 53BP1 (green) and anti-trf1 (red) antibodies and the nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue). White arrowheads mark TIFs, characterized by co-localisation of 53BP1 with telomeres (TRF1). (c) Quantification of TIFs present in B-cells from CLL patients displaying POT1 mutations (n=5) in comparison to control cells (n=6). Bars depict means ± SEM. (d) Quantification of TIFs present in three independently derived HT1080 cells infected with retroviruses encoding vector only, wild-type POT1, Y36N POT1 or Y223C POT1 at population doubling 45. Bars depict means ± SEM. No activation of the ATR pathway in HT1080 cells expressing mutant POT1 proteins. (e) Representative immunoblot of phosphorylated CHK1, myc and β-actin in HT1080 cells transiently infected with retroviral constructs encoding vector only, myc-tagged wild-type POT1, myc-tagged Y36N POT1 and myc-tagged Y223C POT1 proteins at 45 population doublings. 13
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples
 A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E,
 Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of cells infected with TY93/H5N1 GFP-627E, TY93/H5N1 GFP-627K, or the TY93/H5N1 PB2(588-759) virus library. To establish our GFP- FACS screening platform, we compared
Supplementary Figure 1
 Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
Short Telomeres Predict Poor Prognosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
 Short Telomeres Predict Poor Prognosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia L. Yang Internal Medicine Resident University of Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. J. Johnston Prognostic factors Clinical course is unpredictable
Short Telomeres Predict Poor Prognosis in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia L. Yang Internal Medicine Resident University of Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. J. Johnston Prognostic factors Clinical course is unpredictable
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
CLL Biology and Initial Management. Gordon D. Ginder, MD Director, Massey Cancer Center Lipman Chair in Oncology
 CLL Biology and Initial Management Gordon D. Ginder, MD Director, Massey Cancer Center Lipman Chair in Oncology CLL- Epidemiology Most common adult leukemia 25-30% in western world Incidence in US 4.5
CLL Biology and Initial Management Gordon D. Ginder, MD Director, Massey Cancer Center Lipman Chair in Oncology CLL- Epidemiology Most common adult leukemia 25-30% in western world Incidence in US 4.5
1. What to test. 2. When to test
 Biomarkers: the triad of questions 1. What to test 2. When to test 3. Who to test Biomarkers: the triad of questions 1. What to test 2. When to test 3. Who to test Impact of CLL biological features on
Biomarkers: the triad of questions 1. What to test 2. When to test 3. Who to test Biomarkers: the triad of questions 1. What to test 2. When to test 3. Who to test Impact of CLL biological features on
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure 1
 Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
modified dye uptake assay including formazan test EC 90 not tested plaque reduction assay
 Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
PROGNOSTICATION IN CLL: PRESENT AND FUTURE
 PROGNOSTICATION IN CLL: PRESENT AND FUTURE Gianluca Gaidano, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Hematology Department of Translational Medicine Amedeo Avogadro University of Eastern Piedmont Novara-Italy CLL: Homogeneous
PROGNOSTICATION IN CLL: PRESENT AND FUTURE Gianluca Gaidano, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Hematology Department of Translational Medicine Amedeo Avogadro University of Eastern Piedmont Novara-Italy CLL: Homogeneous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication
 Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication Oscar Blanch-Lombarte Rome, 7-9 June, 2017 European
Virological failure to Protease inhibitors in Monotherapy is linked to the presence of signature mutations in Gag without changes in HIV-1 replication Oscar Blanch-Lombarte Rome, 7-9 June, 2017 European
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
SLX4 + MUS81 SLX4 + GEN1 SLX4 CONTROL SLX4
 GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN C LM MUS8 XPF (loading control) D H2AX Frequency of -positive bridges (% of anaphase cells) 6 4 2 p =.8 x -4 GM855 p =.27 PSNF5 E H2AX Figure S. Analysis of anaphase
GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN MUS8 GEN C LM MUS8 XPF (loading control) D H2AX Frequency of -positive bridges (% of anaphase cells) 6 4 2 p =.8 x -4 GM855 p =.27 PSNF5 E H2AX Figure S. Analysis of anaphase
EGFR shrna A: CCGGCGCAAGTGTAAGAAGTGCGAACTCGAGTTCGCACTTCTTACACTTGCG TTTTTG. EGFR shrna B: CCGGAGAATGTGGAATACCTAAGGCTCGAGCCTTAGGTATTCCACATTCTCTT TTTG
 Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
Supplementary Methods Sequence of oligonucleotides used for shrna targeting EGFR EGFR shrna were obtained from the Harvard RNAi consortium. The following oligonucleotides (forward primer) were used to
DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51. Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R. pubera. a) The
 a % 10 Number of crossover per bivalent b 0 1 c DAPI/telomere 80 1 60 40 1 2 20 d 0 0 1 2 >=3 DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 e DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51 Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R.
a % 10 Number of crossover per bivalent b 0 1 c DAPI/telomere 80 1 60 40 1 2 20 d 0 0 1 2 >=3 DAPI ASY1 DAPI/ASY1 e DAPI RAD51 DAPI/RAD51 Supplementary Figure 1. Additional information on meiosis in R.
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
Sample Metrics. Allele Frequency (%) Read Depth Ploidy. Gene CDS Effect Protein Effect. LN Metastasis Tumor Purity Computational Pathology 80% 60%
 Supplemental Table 1: Estimated tumor purity, allele frequency, and independent read depth for all gene mutations classified as either potentially pathogenic or VUS in the metatastic and primary tumor
Supplemental Table 1: Estimated tumor purity, allele frequency, and independent read depth for all gene mutations classified as either potentially pathogenic or VUS in the metatastic and primary tumor
The genetic landscape of high-risk CLL
 The genetic landscape of high-risk CLL Jonathan Strefford PhD Reader in Molecular Haematology Cancer Genomics Treatment development 2010 Further development of Small molecules for Stratified CLL treatment
The genetic landscape of high-risk CLL Jonathan Strefford PhD Reader in Molecular Haematology Cancer Genomics Treatment development 2010 Further development of Small molecules for Stratified CLL treatment
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy
 Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Figure 6: TERT regulates MYC half-life and ubiquitination.
 TERT or IgG as indicated. For the western blots, representative images of n= independent experiments are shown. Student s t-test was used, and * indicates p
TERT or IgG as indicated. For the western blots, representative images of n= independent experiments are shown. Student s t-test was used, and * indicates p
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first
 Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Supplementary Figure 1: Features of IGLL5 Mutations in CLL: a) Representative IGV screenshot of first intron IGLL5 mutation depicting biallelic mutations. Red arrows highlight the presence of out of phase
Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis
 Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Supplementary Figure 1 Weight and body temperature of ferrets inoculated with
 Supplementary Figure 1 Weight and body temperature of ferrets inoculated with A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) influenza virus. (a) Body temperature and (b) weight change of ferrets after intranasal inoculation with
Supplementary Figure 1 Weight and body temperature of ferrets inoculated with A/Anhui/1/2013 (H7N9) influenza virus. (a) Body temperature and (b) weight change of ferrets after intranasal inoculation with
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary Information. Preferential associations between co-regulated genes reveal a. transcriptional interactome in erythroid cells
 Supplementary Information Preferential associations between co-regulated genes reveal a transcriptional interactome in erythroid cells Stefan Schoenfelder, * Tom Sexton, * Lyubomira Chakalova, * Nathan
Supplementary Information Preferential associations between co-regulated genes reveal a transcriptional interactome in erythroid cells Stefan Schoenfelder, * Tom Sexton, * Lyubomira Chakalova, * Nathan
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
202002, India Author affiliations
 Copy number variation and microdeletions of the Y chromosome linked genes and loci across different categories of Indian infertile males Anju Kumari 1, Sandeep Kumar Yadav 1, M.M. Misro 2, Jamal Ahmad
Copy number variation and microdeletions of the Y chromosome linked genes and loci across different categories of Indian infertile males Anju Kumari 1, Sandeep Kumar Yadav 1, M.M. Misro 2, Jamal Ahmad
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10860 Supplementary Discussion It remains unclear why H3K9 demethylation appeared to be more sensitive to suppression than at least some other histone methylation marks as a result of
doi:10.1038/nature10860 Supplementary Discussion It remains unclear why H3K9 demethylation appeared to be more sensitive to suppression than at least some other histone methylation marks as a result of
NOTCH1 mutations in CLL associated with trisomy 12
 Blood First Edition Paper, prepublished online November 15, 2011; DOI 10.1182/blood-2011-10-386144 NOTCH1 mutations in CLL associated with trisomy 12 Veronica Balatti 1,*, Arianna Bottoni 1,*, Alexey Palamarchuk
Blood First Edition Paper, prepublished online November 15, 2011; DOI 10.1182/blood-2011-10-386144 NOTCH1 mutations in CLL associated with trisomy 12 Veronica Balatti 1,*, Arianna Bottoni 1,*, Alexey Palamarchuk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation Weizhen Ji, Jia Nee Foo, Brian J. O Roak, Hongyu Zhao, Martin G. Larson, David B.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Phenotype Prediction Analyses In order to assess the phylogenetic properties of nssnvs, sequence conservation analysis was conducted using
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Phenotype Prediction Analyses In order to assess the phylogenetic properties of nssnvs, sequence conservation analysis was conducted using
mock! A3AC106S! A3BE255Q! 86.7! 90.1! 88.0! 89.8! 89.0!
 a A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Bwh A3Blan mock V5 DAPI merge 5 µm b edited A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Blan A3Bwh A3BF38L A3BW359L mock A3AC16S A3BE255Q 79.5 79.7 8.4 81.3 82.5 83.9 85.3 86.7 88. 89. 89.8 9.1 HBV 3DPCR Td/
a A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Bwh A3Blan mock V5 DAPI merge 5 µm b edited A3A A3Bi7 A3Btok A3Blan A3Bwh A3BF38L A3BW359L mock A3AC16S A3BE255Q 79.5 79.7 8.4 81.3 82.5 83.9 85.3 86.7 88. 89. 89.8 9.1 HBV 3DPCR Td/
TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group.
 TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group. Fanny Baran-Marszak Hopital Avicenne Bobigny France 2nd ERIC workshop on TP53 analysis in CLL, Stresa 2017 TP53 abnormalities :
TP53 mutational profile in CLL : A retrospective study of the FILO group. Fanny Baran-Marszak Hopital Avicenne Bobigny France 2nd ERIC workshop on TP53 analysis in CLL, Stresa 2017 TP53 abnormalities :
CLL what do I need to know as an Internist in Taimur Sher MD Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic
 CLL what do I need to know as an Internist in 218 Taimur Sher MD Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Case 1 7 y/o white male for yearly medical evaluation Doing well and healthy Past medical history
CLL what do I need to know as an Internist in 218 Taimur Sher MD Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Case 1 7 y/o white male for yearly medical evaluation Doing well and healthy Past medical history
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rampal et al. 10.1073/pnas.1407792111 Fig. S1. Genetic events in leukemic transformation of chronic-phase MPNs. (A) Survival of post-mpn AML patients according to mutational status
Supporting Information Rampal et al. 10.1073/pnas.1407792111 Fig. S1. Genetic events in leukemic transformation of chronic-phase MPNs. (A) Survival of post-mpn AML patients according to mutational status
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Relative SOD1 activity. Relative SOD2 activity. Relative SOD activity (Infected:Mock) + CP + DDC
 Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Supplementary Figure 1. SOD1 activity is significantly increased relative to SOD1 levels. SOD1 and SOD2 activities in the infected mork13 cells are shown normalised to their corresponding levels and relative
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
Efficacy of Bendamustine and rituximab in a real-world patient population
 Efficacy of Bendamustine and rituximab in a real-world patient population Median follow-up 37,1 months Efficacy of bendamustine and rituximab as first salvage treatment in CLL and indirect comparison with
Efficacy of Bendamustine and rituximab in a real-world patient population Median follow-up 37,1 months Efficacy of bendamustine and rituximab as first salvage treatment in CLL and indirect comparison with
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary table 1
 Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
Supplementary table 1 S. pombe strain list Fig. 1A JX38 h + ade6-m216 nda3-km311 PX476 PW775 PX545 PX546 h- ade6-m216 sgo2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h 9 mad2::ura4 + nda3-km311 h + ade6-m21 nda3-km311 rad21 +
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
The role of cytogenomics in the diagnostic work-up of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
 The role of cytogenomics in the diagnostic work-up of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Adrian Zordan, Meaghan Wall, Ruth MacKinnon, Pina D Achille & Lynda Campbell Victorian Cancer Cytogenetics Service (VCCS)
The role of cytogenomics in the diagnostic work-up of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Adrian Zordan, Meaghan Wall, Ruth MacKinnon, Pina D Achille & Lynda Campbell Victorian Cancer Cytogenetics Service (VCCS)
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Risikoprofil-gesteuerte, individualisierte Therapiestrategien bei der CLL. Michael Hallek University of Cologne
 Risikoprofil-gesteuerte, individualisierte Therapiestrategien bei der CLL Michael Hallek University of Cologne 100 90 80 70 60 Substantial progress in CLL therapy in one decade 50 40 complete remissions
Risikoprofil-gesteuerte, individualisierte Therapiestrategien bei der CLL Michael Hallek University of Cologne 100 90 80 70 60 Substantial progress in CLL therapy in one decade 50 40 complete remissions
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo
 Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was
 Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was performed on a total of 85 SS patients. Data filtration
Supplementary Figure 1. Experimental paradigm. A combination of genome and exome sequencing coupled with array-comparative genome hybridization was performed on a total of 85 SS patients. Data filtration
CLL Complete SM Report
 Reported: 02/01/2012 Σ CGI ID No:5 Client:r Client Address: CLINICAL DATA: Lymphoma No CBC results provided. CLL Complete SM Report FINAL DIAGNOSIS: CD19+ B cell lymphoma, ZAP-70 + (44%), with borderline
Reported: 02/01/2012 Σ CGI ID No:5 Client:r Client Address: CLINICAL DATA: Lymphoma No CBC results provided. CLL Complete SM Report FINAL DIAGNOSIS: CD19+ B cell lymphoma, ZAP-70 + (44%), with borderline
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
CLL Ireland Information Day Presentation
 CLL Ireland Information Day Presentation 5 May 2018 Professor Patrick Thornton Consultant Haematologist, Senior Lecturer RCSI, and Clinical Director Hermitage Medical Clinic Laboratory Chronic Lymphocytic
CLL Ireland Information Day Presentation 5 May 2018 Professor Patrick Thornton Consultant Haematologist, Senior Lecturer RCSI, and Clinical Director Hermitage Medical Clinic Laboratory Chronic Lymphocytic
Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. One µg/ml recombinant human (rh) apo-e
Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. One µg/ml recombinant human (rh) apo-e
Background. Approved by FDA and EMEA for CLL and allows for treatment without chemotherapy in all lines of therapy
 Updated Efficacy and Safety From the Phase 3 RESONATE-2 Study: Ibrutinib As First-Line Treatment Option in Patients 65 Years and Older With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Abstract
Updated Efficacy and Safety From the Phase 3 RESONATE-2 Study: Ibrutinib As First-Line Treatment Option in Patients 65 Years and Older With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma Abstract
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Refresher Course for Hematologists Ekarat Rattarittamrong, MD
 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Refresher Course for Hematologists Ekarat Rattarittamrong, MD Division of Hematology Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Chiang-Mai University Outline
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Refresher Course for Hematologists Ekarat Rattarittamrong, MD Division of Hematology Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Chiang-Mai University Outline
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors
 Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors Ka-Cheuk Liu, Gunter Leuckx, Daisuke Sakano, Philip A. Seymour, Charlotte L. Mattsson, Linn Rautio, Willem Staels, Yannick Verdonck,
Inhibition of Cdk5 Promotes β-cell Differentiation from Ductal Progenitors Ka-Cheuk Liu, Gunter Leuckx, Daisuke Sakano, Philip A. Seymour, Charlotte L. Mattsson, Linn Rautio, Willem Staels, Yannick Verdonck,
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Characterisation of structural variation in breast. cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on. the Illumina Genome Analyser
 Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/385/ra70/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The interaction of heparan sulfate proteoglycans with endothelial transglutaminase-2 limits VEGF 165 -induced angiogenesis
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/385/ra70/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The interaction of heparan sulfate proteoglycans with endothelial transglutaminase-2 limits VEGF 165 -induced angiogenesis
Genomic complexity and arrays in CLL. Gian Matteo Rigolin, MD, PhD St. Anna University Hospital Ferrara, Italy
 Genomic complexity and arrays in CLL Gian Matteo Rigolin, MD, PhD St. Anna University Hospital Ferrara, Italy Clinical relevance of genomic complexity (GC) in CLL GC has been identified as a critical negative
Genomic complexity and arrays in CLL Gian Matteo Rigolin, MD, PhD St. Anna University Hospital Ferrara, Italy Clinical relevance of genomic complexity (GC) in CLL GC has been identified as a critical negative
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4078
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
