Novel Physiological Role of Caveolin-1 in Aging and Aging-related Diseases. Sang Chul Park Gachon University Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute
|
|
|
- Janice Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Novel Physiological Role of Caveolin-1 in Aging and Aging-related Diseases Sang Chul Park Gachon University Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute
2 Primarily I asked questions on biological issues on aging Parenchymal loss Functional loss Morphological alteration
3 Question 1 Apoptosis for parenchymal loss
4 Young UV Old DNA Fragmentation by UV-irradiation UV-Induced Activation of SAPK/JNK UV Young M Old M (J/m 2 ) UV (J / m 2 ) Young Old
5 Suh et al.naturemedicine,2002,8,3 Young MMS? Old.. Absence of Apoptotic Response to MMS in vivo 0 Hrs 2 Hrs Young Old No.of apoptotic cells/ 50,000 cells young old Time (Hrs) after MMS tx.
6 DAPI p-p38 MERGE O +Stau Control Y +Stau Control A 노화에따른세포사멸신호핵내이동차단 B DAPI p-jnk MERGE 2+ H 2O O Control 2+ H 2O Y Control Tx : stau 50nM for 60 min Tx : H 2 O 2 100uM for 60 min
7 Nuclear Barrier Hypothesis of Aging Membrane Membrane Cytosol Cytosol Nucleus Nucleus
8 노화현상의 비가역성과불가피성의 생물학적근거 텔로미어단축 노화색소축적 생체분자의손상
9 C D Y O O R Y O O R Hela O on Y-ECM /5.0/ /3.5 htert (183bp) Hela Y O (day) ITAS GAPDH
10 DNA damage repair in restoration A Y O O R B Y TTAGGG-FISH ƔH2AX Merge Enlarged O Tail moment Tail moment ** Y O O R O R TIF positive cells (%) ** Y O O R
11 노화현상의 비가역성과불가피성의 생물학적근거 : 부정되고있음 텔로미어단축 : 제어가능 노화색소축적 : 제어가능 생체분자의손상 : 제어가능
12 Aging phenotype is an adaptive response for Survival toward environmental stress through resistance to apoptotic stress Possibility of Restore Principle Instead of Replace Principle
13 Question 2 Loss of Functional Efficiency
14 Senescence-associated cellular responses 1. Metabolic response stability essential 2. Stress response unstable response 3. Mitogenic response No response or low response Major source of irreversibility nature of aging
15 Aging effect on Caveolin expression Cav-1 Cortex Mid Br Hippo Cbll Heart Lung Liver Kidney Spleen Y O Y O Y O Y O Y O Y O Y O Y O Y O Cav-2 Coomassie stain Park et al JBC 2000
16 Up-regulation of caveolin attenuates epidermal growth factor signaling in senescent cells. Park, et al. (2000 ) J Biol Chem. 275, Park et al(2001) Ann NYAcad Sc, 2001,928,79 In young cells EGF Park et al(2002)ann NYAcad Sc, 2002,959,45 EGF In old cells EGFR -P EGFR Caveolin-1 ` Aging ` Erk-1/2 -P Erk-1/2
17 Senescent phenotype can be reversed by reduction of caveolin status In old cells Cho et al. (2003) J Biol Chem. 278(30):27789 Park (2002) Mech.Age.Dev, 123,917 EGF In old cells EGFR EGF Caveolin-1 - caveolin EGFR -P Erk-1/2 -P Erk-1/2 p53 Elk -P p21 Cell cycle progression
18 Question 3 Morphological alteration
19 ECM Integrin Cav-1 Rac P- FAK Pax -P Cdc42 F-actin Disruption of focal adhesion by down-regulation of caveolin?
20 Morphological adjustment of senescent cells sirna of cav-1 O-GL O-Cav O-GL FAK p-fak Cav-1 Actin O-CAV Cho et al., J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(40):42270 Focal adhesion Actin stress fiber Nucleus
21 Morphological adjustment of the senescent cells can be induced by simple modulation of the caveolin status Structural restoration of the senescent cells by crosstalk between determinants of function and morphology
22 Caveolin in signal regulation, intracellular trafficking, polarity, migration, endocytosis and More!!
23 Question 4 Organ pathology level Diabetes Stem cell differentiation Cancer cell differentiation, Wound healing Exercise
24 Caveolin-1 and Aging-related Diseases Cancer Caveolin-1 as a negative regulator of the Ras-p42/44 MAP Kinase Cascade Alzheimer disease APP in caveolae Cav-1 promote secretase cleavage Caveolin-1 Diabetes Key roles in activation of insulin RTK and GLUT4 translocation Vascular disease Direct interaction with e-nos Activity inhibition of e-nos
25 Prevalence of Diabetes
26 Control of blood glucose levels Type 1 Diabetes Type 2 Diabetes β Cell Insulin x Liver Glucose Muscle Glucose α Cell Glucagon Fat Glucose Digestive System
27 Type II Diabetes - NIDDM (non-insulin dependent) 90-95% of DM Obese type and Lean type (65 %) - Insulin resistance - Mainly occurs in adults Is Ageing itself related with Type II DM? Why no adequate Age dependent lean type DM model?
28 Type II D.M Animal models GK OLETF ob/ob ZDF Ageing independent obese Few studies on obesity independent or age dependent lean type D.M
29 Roles of Caveolin-1 in Muscle Tissues?
30 Caveolae Small vesicular organelles of cell membrane Signaling molecules enriched in caveolae; G-protein subunits, EGFR and related receptor tyrosine kinases Caveolin, marker protein of caveolae Ubiquitous Cav-1 N TM C Cav-2 Muscle specific Cav-3
31 Caveolin & insulin sensitivity in adipocytes Relationship of caveolin with insulin signaling Insulin Glucose IR TC10 P Caveolin-1 IRS-1/2 GLUT-4 Erk-1/2 P PI3-K P Akt P
32 Can caveolins regulate the insulin signaling in skeletal muscle cells as in adipocytes?
33 Expression of caveolins during differentiation A Pan Liv Adi Mus Lu He Br Tes B Undi Di Cav-1 Cav-1 Cav-2 Cav-2 Cav-3 Cav-3 Tubulin IR Akt C Undifferentiated Differentiated GLUT4 Myogenin -actin D Insulin (-) Insulin (+)
34 Caveolins and GLUT-4 A Cav-1 GLUT-4 Nuclei Merged B Top Bottom Cav-1 - insulin - insulin Cav-3 GLUT-4 + insulin Top Bottom Cav-1 + insulin Cav-3 GLUT-4
35 Role of caveolins in glucose uptake A B Insulin (-) Insulin (+) Insulin (-) Insulin (+) GL sirna DeGlu uptake (relative basal) Cav-1 sirna Cav-1 sirna 0.5 sirna: 0 GL C1 C3 Cav-3 sirna Cav-1 Cav-3
36 Caveolin-1 in Muscle Aging?
37 Aging Effect on Caveolin-1 Status in Muscle and Fat Tissues Muscle Fat Lung Insulin (μiu/ml) Y O Y O Y O IR 20 GLUT-4 Cav Cav-3 0 Y O Common nature of muscle and fat tissue would be the insulin-sensitivity
38 NEW ASSUMPTION AGE DEPENDENT LOSS OF CAVEOLIN-1 IN MUSCLE AND FAT TISSUE WOULD BE CAUSATIVE FOR NON-OBESE TYPE II DIABETES? Caveolin-1 and Diabetes type II
39 JYD animal model Collaboration with University of Calgary (Dr. Ji-Won Yoon & Hee-Sook Jun) F M DBA X C57BL/6 Age dependent phenotype Sex dependent diabetic phenotype
40 Blood glucose levels, incidence of diabetes, and body weight in male JYD mice A B C Blood glucose (mg/dl) 300 JYD B6 250 DBA * ** ** ** Incidence of diabetes (%) JYD B6 DBA Body weight (g) JYD B6 DBA ** ** Age (wks) Age (wks) Age (wks)
41 Glucose and insulin tolerance tests in male JYD mice 10 Blood glucose (mg/dl) JYD B6 DBA * * * * weeks 30 Time (min) Time (min) Blood glucose (mg/dl) 600 JYD B6 500 DBA * * * weeks % of initial blood glucose JYD B6 DBA * * * % of initial blood glucose JYD B6 DBA * * * * Time (min) Time (min)
42 Whole-body 18 F-FDG PET images in JYD mice C57BL/6 ob/ob JYD M %ID/g 4.0 Harderian gland Brain Brown fat Heart Paraspinal muscle lung Liver Bowel Bladder 0.0
43 Expression of caveolins in skeletal muscle and other insulin responsive tissues A B Mus Adi Pan DBA/2 C57BL/6 JYD (wks) Cav-1 Cav-3 Tubulin Cav-1 Tubulin DBA/2 B6 JYD Can Caveolins regulate the insulin resistance in JYD model? Cav-1 C Tubulin Fold change * * D-M ND-F ND-M 3 wks 10 wks 30 wks * Liv Cav-1 Tubulin Cav-1 Cav-3 tubulin
44 Down-regulation of caveolin-1 by shlenti-cav-1 viral vector A shlenti-gfp ; CMV GFP U6 loop shlenti-cav-1 ; CMV GFP U6 Cav-1 B C Cav-1 actin shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 D E shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 Cav-1 Flotillin Cav-1 Flotillin shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1
45 Impairment of glucose and insulin tolerance in shlenti-cav-1-injected C57BL/6 mice A B Blood glucose (mg/dl) shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 * * * Body weight (g) shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 C (Day) D (weeks) Blood glucose (mg/dl) * shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav-1 % of initial blood glucose * * shlenti-gfp shlenti-cav Time (min) Time (min)
46 Overexpression of caveolin-1 by adenovirus-cav-1 viral vector A Ade-GFP ; CMV CMV EGFP Ade-cav-1 ; CMV Cav-1 CMV EGFP B C Cav-1 actin Ade-GFP Ade-cav-1 Ade-GFP Ade-cav-1-GFP D E Mus CON 3 DAYS IV IM GFP Ade-GFP Ade-cav-1 Cav-1 Flotillin Cav-1 Flotillin Adi Liv Tubulin GFP Tubulin GFP Tubulin
47 Improvement of glucose uptake and insulin tolerance in Ade-cav-1 injected JYD mice A Blood glucose (mg/dl) * * * Ade-GFP Ade-cav-1 C p/sec/cm 2 /sr x B % of initial blood glucose * Time (min) * Ade-GFP Ade-cav D Ade-GFP Ade-cav-1 80 Time (min)
48 Caveolin-1 status of the skeletal muscle might influence insulin sensitivity in the aged organism and might contribute to prevent or delay the appearance of type 2 diabetes
49 Exercise and Caveolin-1 Status?
50 Can in vivo expression of caveolin-1 be increased by exercise training?
51 Exercised C57BL/6 Y (6-8 wks), O (68-75 wks), O-ex (68-75 wks) Mus Liv Y O OE Y O OE IR GLUT-4 Cav-1 Cav-3 tubulin
52 Expression of caveolins and insulin related proteins in EDL muscle during resistance exercise B A CON RE AE IRβ GLUT-4 Percent of CON (%) * * * CON RE AE * IRβ GLUT-4 Cav-1 Cav-3 CAV-1 CAV-3 C CON RE AE TUBULIN SOL EDL
53 Effect of exercise on caveolin-1 status in Human study Exercise type : 100m and 1500 m swimming Participants : 14 male penthlon athletes Samplings : Deltoid muscle and Vastus lateralis muscle biopsy before and after the exercise Purpose : modulation of glucose utilization
54 Kim et al., Eur J Appl Physiol (2009) 106:
55 Caveolin-1 and Hormone Sensitivity? 1. Sex hormone effects
56 Glucose and insulin tolerance test of male and female JYD mice Body weight (g) male female 10 0 JYD Male JYD Female Age (weeks) C Blood glucose (mg/dl) * * * JYD male JYD female * % of initial blood glucose * ** * JYD male JYD female * * Time (min) Time (min)
57 Expression level of insulin signaling molecules and caveolin in male and female JYD mice A IRβ ADI MUS LIV PAN M F M F M F M F B 1.2 IRβ C 1.2 AKT/PKB AKT/PKB 1 1 GLUT-4 Cav-1 Cav-3 Tubulin Fold change ADI MUS LIV PAN Fold change ADI MUS LIV PAN Fold change D E F GLUT-4 Fold change Cav-1 Fold change Cav-3 ADI MUS LIV PAN ADI MUS LIV PAN 0 ADI MUS LIV PAN
58 FDG-PET of whole body glucose uptake M MG F %ID/g 4 0 Oh et al (2011) Modulation of Insulin Sensitivity and Caveolin-1 Expression by Orchidectomy. Molecular Medicine. 17(1-2):4-11.
59 Caveolin-1 and Hormone Sensitivity? 2. Growth Hormone Effects
60 Aging dependent growth hormone sensitivity Growth hormone & Insulin sensitivity TYPE 2 DM Sarcopenia P GHR /IGF-IR P JAK IRS IR P TYPE 2 DM STAT IRS P P SHC STAT N Transcription of target genes PI3K AKT GSK GLUT translocation MAPK Proliferation / Differentiation
61 Growth hormone responses in skeletal muscle % of CON CON GH treated IR G4 C1 C3 * * P-STAT GHR bcl tubulin 200 Cav-1 0 CON Ex G.H Ex+G.H
62 Caveolin-1 and Hormone Sensitivity? 3. Glucocorticoid hormone effects
63 Dexamethasone inhibits caveolin-1 in C2C12 myotubes A B C
64 Caveolin-1 status in muscle tissues is sensitive to hormonal status and might be responsible for muscle differentiation and age dependent muscle loss
65 Summary Q1. A1. Can Regulation caveolins of insulin regulate response the insulin signaling in in skeletal skeletal muscle muscle cells as by in caveolin adipocytes? status Q2. A2. Why Development we can not and develop Characterization lean type non of obese ageing dependent type 2 diabetic JYD animal DM model? Q3. A3. Can Potential caveolins role for regulate skeletal the muscle insulin caveolin-1 resistance in ageing dependent type 2 diabetic in JYD JYD model? Q4. A4. Is Exercise in vivo expression type and muscle of caveolin fiber specific increased induction of caveolin-1 expression for by insulin exercise sensitivity training? Q5. A5. Can Modulation sex hormone of Insulin modulate Sensitivity insulin and sensitivitiy Caveolin-1 of Expression by Gonadectomy in Non-Obese Type 2 JYD Diabetes mice?
66 Further Questions Caveolin-1 in Stem Cell Differentiation Cancer Development Longevity
67 Inhibitory effect of caveolin-1 on adipogenic differentiation in young hmsc Ad /GFP Ad / Cav-1 MOI adipogenesis Adipogenesis (%) Park et al (2005) Mechanism of Aging and Development 0 MOI Mock Cav-1
68 Caveolin-1 as an index of wound healing Rhim et al (2010). Molecular Medicine 16:
69 Modulation of wound healing by caveolin-1 status in human corneal epithelium after excimer laser photoablation surgery Ji-Heon Rhim 1, Jae Hoon Kim 2, Jae Chan Kim 2* and Sang Chul Park 1
70
71
72 Summary of Variations detected in caveolin -1 Exon Locus Amino acid change Normal(=62) Frequency Centenarian(=65) intron exon exon % 0.00% - Val->Ile 4.84% 0.00% 1.61% 0.00%
73 Caveolin and aging Cellular aging mechanism 1. Mitogenic response 2. Intracellular trafficking 3. Polarity 4. Metabolic response by hormone sensitivity 5. Microbial infection 6. Structural determination Age related diseases 1. Stem cell differentiation 2. Cancer cell differentiation 3. Wound healing 4. Diabetes 5. Dementia 6. Vascular tone 7. Infectious diseases 8. Muscle aging
74 Collaborators Sung Chun Cho (Gachon Univ) Sung Jin Ryu (NIH) Yoon Sin Oh (Gachon Univ) Jeong Soo Park (Dangook Univ) Kyung A Cho (Chonnam Univ) Young Hoon Son (SNU) Hee Sook Jun (Gachon Univ) Ji Won Yoon (Chicago Univ *) Chang Geun Kim (SSU)
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
E3 ligase TRIM72 negatively regulates myogenesis by IRS-1 ubiquitination
 E3 ligase negatively regulates myogenesis by IRS-1 ubiquitination Young-Gyu Ko College of Life Science and Biotechnology Korea University MyHC immunofluorescence Lipid rafts are plasma membrane compartments
E3 ligase negatively regulates myogenesis by IRS-1 ubiquitination Young-Gyu Ko College of Life Science and Biotechnology Korea University MyHC immunofluorescence Lipid rafts are plasma membrane compartments
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes.
 What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
FH- FH+ DM. 52 Volunteers. Oral & IV Glucose Tolerance Test Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemic Clamp in Non-DM Subjects ACADSB MYSM1. Mouse Skeletal Muscle
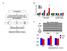 A 52 Volunteers B 6 5 4 3 2 FH- FH+ DM 1 Oral & IV Glucose Tolerance Test Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemic Clamp in Non-DM Subjects ZYX EGR2 NR4A1 SRF target TPM1 ACADSB MYSM1 Non SRF target FH- FH+ DM2 C SRF
A 52 Volunteers B 6 5 4 3 2 FH- FH+ DM 1 Oral & IV Glucose Tolerance Test Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemic Clamp in Non-DM Subjects ZYX EGR2 NR4A1 SRF target TPM1 ACADSB MYSM1 Non SRF target FH- FH+ DM2 C SRF
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
GFP Assays
 GFP Assays 2009-07-03 GFP Assays Akt1 SMAD2 STAT3 NFAT-C1 MAPKAP-k2 Rac-1 PLCδ PH domain FYVE G2M CCPM Cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, insulin response pathways TGF-beta signalling, growth, differentiation,
GFP Assays 2009-07-03 GFP Assays Akt1 SMAD2 STAT3 NFAT-C1 MAPKAP-k2 Rac-1 PLCδ PH domain FYVE G2M CCPM Cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, insulin response pathways TGF-beta signalling, growth, differentiation,
Prediction of invasiveness of hepatic tumor cells
 Prediction of invasiveness of hepatic tumor cells (Overexpression of Romo1 Promotes Production of Reactive Oxygen Species and Invasiveness of Hepatic Tumor Cells) (Romo1 : Reactive Oxygen Species Modulator
Prediction of invasiveness of hepatic tumor cells (Overexpression of Romo1 Promotes Production of Reactive Oxygen Species and Invasiveness of Hepatic Tumor Cells) (Romo1 : Reactive Oxygen Species Modulator
Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors
 Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors Seo-Yoon Chang, Jae Min Cho, Yang-Hyeok Jo, Myung-Jun Kim Departments of Physiology, College of Medicine, The
Exendin-4-mediated cell proliferation in beta-cells: focusing on the transcription factors Seo-Yoon Chang, Jae Min Cho, Yang-Hyeok Jo, Myung-Jun Kim Departments of Physiology, College of Medicine, The
Revision. camp pathway
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision camp pathway camp pathway Revision camp pathway Adenylate cyclase Adenylate Cyclase enzyme Adenylate cyclase catalyses the formation of camp from ATP. Stimulation or inhibition
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision camp pathway camp pathway Revision camp pathway Adenylate cyclase Adenylate Cyclase enzyme Adenylate cyclase catalyses the formation of camp from ATP. Stimulation or inhibition
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat. day, cells were transduced with adenoviruses expressing GFP, MKP-3 or shgfp,
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Curriculum Vitae. Dissertation Title M.S. Thesis: Regulation of Notch1 signaling by Runx2 during osteoblast differentiation.
 Curriculum Vitae Name: Eun-Jung Ann Education Mar.2009 : Ph.D. in Graduate School of Biological Sciences and Technology, Chonnam National University Mar.2007 Feb. 2009: M.S. in Graduate School of Biological
Curriculum Vitae Name: Eun-Jung Ann Education Mar.2009 : Ph.D. in Graduate School of Biological Sciences and Technology, Chonnam National University Mar.2007 Feb. 2009: M.S. in Graduate School of Biological
In vivo prediction of anti-tumor effect of 3- bromopyruvate in Hepatocellular Carcinoma using Tc-99m labeled annexin-v imaging
 In vivo prediction of anti-tumor effect of 3- bromopyruvate in Hepatocellular Carcinoma using Tc-99m labeled annexin-v imaging Won Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon*, Gi Jeong Cheon, Tae Sup Lee, Chung Yong Kim Department
In vivo prediction of anti-tumor effect of 3- bromopyruvate in Hepatocellular Carcinoma using Tc-99m labeled annexin-v imaging Won Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon*, Gi Jeong Cheon, Tae Sup Lee, Chung Yong Kim Department
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Therapeutic Resistance to HER2 Targeted Therapies. Neil Spector, M.D Duke Cancer Institute Duke University Medical Center
 Therapeutic Resistance to HER2 Targeted Therapies Neil Spector, M.D Duke Cancer Institute Duke University Medical Center Relevant Financial Disclosures Millennium/Takeda Pharmaceuticals (consultant, sponsored
Therapeutic Resistance to HER2 Targeted Therapies Neil Spector, M.D Duke Cancer Institute Duke University Medical Center Relevant Financial Disclosures Millennium/Takeda Pharmaceuticals (consultant, sponsored
Body Mass Index Chart = overweight; = obese; >40= extreme obesity
 Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 26 February 2007 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 5'4" Weight
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 26 February 2007 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 5'4" Weight
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents:
 Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR
 Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR Treatment of early stage, HER2 positive breast cancer Treatment of early stage,
Kevin R. Fox, MD Rena Rowan Breast Center Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of MedicineR Treatment of early stage, HER2 positive breast cancer Treatment of early stage,
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK. Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous
 Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin by Gema FRUHBECK Presentation by Amnesiacs Anonymous Introduction to Leptin By Ahrial Young Why is Leptin important? Pleiotropic = it controls the
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.
![Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9. Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.](/thumbs/90/103696086.jpg) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
Angiostasis and Angiogenesis Regulated by Angiopoietin1-Tie2 Receptor System
 Japan-Mexico Workshop on Pharmacology and Nanobiology Feb. 25, 2009; Universidad Nacional Autönoma de Mëxico, Mexico City Angiostasis and Angiogenesis Regulated by Angiopoietin1-Tie2 Receptor System Shigetomo
Japan-Mexico Workshop on Pharmacology and Nanobiology Feb. 25, 2009; Universidad Nacional Autönoma de Mëxico, Mexico City Angiostasis and Angiogenesis Regulated by Angiopoietin1-Tie2 Receptor System Shigetomo
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of therapeutic strategies
 Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat
 A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
Figure S1, Beyer et al.
 Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
Figure S1, eyer et al. Pax7 Myogenin si sitrl Hoechst T = 72h 14 1.8.6.4.2 12 1 8 6 4 2 24h 48h 96h diff. sitrl siset1 212 72h diff. b1 td r t Se km MyH Vinculin Myogenin β-ctin Vinculin MW b1 ka td r
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Final Review Sessions. 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office Hours
 Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Enhancement of C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by diarylheptanoid form Curcuma comosa Roxb.
 Enhancement of C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by diarylheptanoid form Curcuma comosa Roxb. Curcuma comosa Roxb. Mr. Chittipong Tipbunjong Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand Muscle regeneration
Enhancement of C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation by diarylheptanoid form Curcuma comosa Roxb. Curcuma comosa Roxb. Mr. Chittipong Tipbunjong Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand Muscle regeneration
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
Master class Biomolecular Sciences Molecular Cell Biology.
 Master class Biomolecular Sciences Molecular Cell Biology. 04-09-08: Paul van Bergen en Henegouwen. Clathrin-indep Endocytosis 11-09-08: Willem Stoorvogel. Endocytosis and MHC classii 18-09-08: X-track
Master class Biomolecular Sciences Molecular Cell Biology. 04-09-08: Paul van Bergen en Henegouwen. Clathrin-indep Endocytosis 11-09-08: Willem Stoorvogel. Endocytosis and MHC classii 18-09-08: X-track
Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets
 Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets Bernd Helms Article Brand Recter Hendrik Mertens 1 The Basics I: FAs The Basics II: FA Activation 2 Basics III: TG-FA Interplay. Why? Adipocytes 3 Foam cells
Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets Bernd Helms Article Brand Recter Hendrik Mertens 1 The Basics I: FAs The Basics II: FA Activation 2 Basics III: TG-FA Interplay. Why? Adipocytes 3 Foam cells
Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways
 Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways John DiGiovanni, Ph.D. Professor and Coulter R. Sublett Endowed
Mechanisms Associated with Dietary Energy Balance Effects on Tumor Development: Alterations in Growth Factor and Energy Sensing Pathways John DiGiovanni, Ph.D. Professor and Coulter R. Sublett Endowed
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells
 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment blocks inflammatory pathways and promotes survival and proliferation of pancreatic beta cells Gérald J. Prud homme, MD, FRCPC Keenan Research Centre for Biomedical
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3922
 Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Phospholipase C γ Prof. Graham Carpenter
 Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Graham Carpenter, h.d. rofessor of Biochemistry Cornelia Crooke Department of Biochemistry Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN 1 Receptor Tyrosine Kinases GF Extracellular M Intracellular
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting
 Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Title: Cytosolic DNA-mediated, STING-dependent pro-inflammatory gene. Fig. S1. STING ligands-mediated signaling response in MEFs. (A) Primary MEFs (1
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Title: Cytosolic DNA-mediated, STING-dependent pro-inflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-κB activation through TBK1 5 6 Authors: Abe et al. 7 8 9 Supporting
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Title: Cytosolic DNA-mediated, STING-dependent pro-inflammatory gene induction necessitates canonical NF-κB activation through TBK1 5 6 Authors: Abe et al. 7 8 9 Supporting
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
 Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
NASH Bench to Bedside
 NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
Body Mass Index Chart = overweight; = obese; >40= extreme obesity
 Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 25 February 2008 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" Weight (lbs)
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 25 February 2008 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" Weight (lbs)
Hormones. Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6
 Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination
 AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl
 Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Journal Club WS 2012/13 Stefanie Nickl Background Mesenchymal Stem Cells First isolation from bone marrow 30 ys ago Isolation from: spleen, heart, skeletal muscle, synovium, amniotic fluid, dental pulp,
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010
 Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= 39.9 obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 52
Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus R. Leibel Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center 19 March 2010 Body Mass Index Chart 25-29.9 29.9 = overweight; 30-39.9= 39.9 obese; >40= extreme obesity 5'0" 5'2" 52
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells
 Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells Sandrine Ruchaud E12.5! Acridine Orange! Role of apoptosis in sculpting the mouse paw E13.5! E14.5! gift of William Wood & Paul Martin! University College, London! Normal
Studying apoptosis in DT40 cells Sandrine Ruchaud E12.5! Acridine Orange! Role of apoptosis in sculpting the mouse paw E13.5! E14.5! gift of William Wood & Paul Martin! University College, London! Normal
New Drug Development for Hepatic Insulin Resistance
 New Drug Development for Hepatic Insulin Resistance Innovative Drug Research Center for Metabolic and Inflammatory Disease College of Pharmacy Sang Geon Kim AMPK as an energy sensor, (A novel drug target
New Drug Development for Hepatic Insulin Resistance Innovative Drug Research Center for Metabolic and Inflammatory Disease College of Pharmacy Sang Geon Kim AMPK as an energy sensor, (A novel drug target
Thomas Jefferson University Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 Thomas Jefferson University Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Thomas Jefferson University received $3,455,597 in formula
Thomas Jefferson University Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Thomas Jefferson University received $3,455,597 in formula
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 72. 139 ~ 144, 1 ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY FENG XU, SATOKO ITO, MICHINARI HAMAGUCHI and TAKESHI
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 72. 139 ~ 144, 1 ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY FENG XU, SATOKO ITO, MICHINARI HAMAGUCHI and TAKESHI
EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes
 1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1
 Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Defects in glucose utilization & GLP-1 Song, Dae-Kyu Department of Physiology & Chronic Disease Research Center Keimyung University School of Medicine 2800 dalgubeol-daero, Dalseo-gu, Daegu, 704-701, Korea
Endothelial PGC 1 - α 1 mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes
 Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
STARS. Mini-Symposium. Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease. Gain Without Pain
 STARS Mini-Symposium Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease Gain Without Pain Rhonda Bassel-Duby, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Molecular Biology Diagram of Skeletal Muscle Myoglobin Immunohistochemistry
STARS Mini-Symposium Skeletal Muscle: Development, Adaptation & Disease Gain Without Pain Rhonda Bassel-Duby, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Molecular Biology Diagram of Skeletal Muscle Myoglobin Immunohistochemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. 2 3 4 DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4893 EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices Mayur Saxena 1,*, Shuaimin Liu 2,*, Bo Yang 3, Cynthia Hajal
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. 2 3 4 DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4893 EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices Mayur Saxena 1,*, Shuaimin Liu 2,*, Bo Yang 3, Cynthia Hajal
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM 1 web 2017 József Mandl Strategy of metabolism 1 Strategy of metabolism to extract energy ( hydrogen ) from the environment to store the energy excess to store hydrogen CH 3 O 2
