Critical role of c-kit in beta cell function: increased insulin secretion and protection against diabetes in a mouse model
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 DOI 1.17/s ARTICLE Criticl role of c-kit in et cell function: incresed insulin secretion nd protection ginst dietes in mouse model Z. C. Feng & J. Li & B. A. Turco & M. Riopel & S. P. Yee & R. Wng Received: 5 Ferury 1 /Accepted: 3 Mrch 1 /Pulished online: 14 My 1 # Springer-Verlg 1 Astrct Aims/hypothesis The receptor tyrosine kinse, c-kit, nd its lignd, stem cell fctor, control vriety of cellulr processes, including pncretic et cell survivl nd differentition s reveled in c-kit Wv mice, which hve point muttion in the c-kit llele leding to loss of kinse ctivity nd develop dietes. The present study further investigted the intrinsic role of c-kit in et cells, especilly the underlying mechnisms tht influence et cell function. Methods We generted novel trnsgenic mouse model with c-kit overexpression specificlly in et cells () to Z. C. Feng nd J. Li contriuted eqully to this work. Electronic supplementry mteril The online version of this rticle (doi:1.17/s ) contins peer-reviewed ut unedited supplementry mteril, which is ville to uthorised users. Z. C. Feng : J. Li : B. A. Turco : M. Riopel : R. Wng () Victori Reserch Lortories, Room A5-14, 8 Commissioners Rod Est, London, ON, Cnd NC V5 e-mil: rwng@uwo.c Z. C. Feng : J. Li : B. A. Turco : R. Wng Deprtments of Physiology nd Phrmcology, University of Western Ontrio, London, ON, Cnd R. Wng Deprtment of Medicine, University of Western Ontrio, London, ON, Cnd M. Riopel Deprtment of Pthology, University of Western Ontrio, London, ON, Cnd S. P. Yee Deprtment of Genetics nd Developmentl Biology, University of Connecticut Helth Center, Frmington, CT, USA further exmine the physiologicl nd functionl roles of c-kit in et cells. Isolted islets from these mice were used to investigte the underlying moleculr pthwy of c-kit in et cells. We lso chrcterised the ility of c-kit to protect nimls from high-ft-diet-induced dietes, s well s to rescue c-kit Wv mice from erly onset of dietes. Results mice exhiited improved et cell function, with significntly improved insulin secretion, nd incresed et cell mss nd prolifertion in response to high-ft-dietinduced dietes. islets exhiited upregultion of: (1) insulin receptor nd IRSs; () Akt nd glycogen synthse kinse 3β phosphoryltion; nd (3) trnscription fctors importnt for islet function. c-kit overexpression in et cells lso rescued dietes oserved in c-kit Wv mice. Conclusions/interprettion These findings demonstrte tht c-kit plys direct protective role in et cells, y regulting glucose metolism nd et cell function. c-kit my therefore represent novel trget for treting dietes. Keywords Bet cell function. Bet cell-specific c-kit trnsgenic mice. c-kit Wv muttion. High-ft-diet-induced dietes. Insulin secretion Arevitions mice Trnsgenic mouse model with c-kit overexpression specificlly in et cells egfp Enhnced green fluorescent protein GSIS Glucose-stimulted insulin secretion GSK3β Glycogen synthse kinse 3β HFD High-ft diet IPGTT Intrperitonel glucose tolernce test IPITT Intrperitonel insulin tolernce test MAFA v-mf musculoponeurotic firosrcom oncogene fmily, protein A (vin) PDX1 Pncretic nd duodenl homeoox 1
2 Dietologi (1) 55: PI3K RIP SCF Introduction Phosphoinositide-3-kinse Rt insulin promoter Stem cell fctor present study, we descrie novel trnsgenic mouse model with c-kit overexpression specificlly in et cells (), which we used to investigte the underlying mechnism of c-kit ctivity in et cells, nd to further delinete the physiologicl nd functionl role of c-kit in norml, high-ft diet (HFD)-induced dietic nd c-kit Wv mice. Therpeutic strtegies imed t repopulting insulinproducing cells show gret potentil for restoring glycemi in dietes. Extensive studies hve focused on wys to fcilitte the differentition of progenitor cells into et cells [1 3], nd to mintin their viility nd function [4, 5]. It hs een shown tht the hemtopoietic stem cell mrker c-kit is importnt in the development nd function of islets of Lngerhns, especilly in support of et cell prolifertion, mturtion nd survivl [ 1]. Upon inding to the stem cell fctor (SCF), c-kit undergoes dimeristion nd utophosphoryltion, followed y the recruitment of downstrem signlling molecules to induce susequent cell prolifertion, differentition, survivl nd migrtion [13, 14]. c-kit is found in fetl nd dult rodent pncretic islets [ 8, 1]. We hve demonstrted tht humn nd rt fetl pncretic ductl epithelil cells producing c-kit disply high prolifertion nd level of SCF [11, 1, 15]. After pncretic duct ligtion in the rt, c-kit is ctivted in ductl cells during islet cell neogenesis, long with n increse of pncretic nd duodenl homeoox 1 (PDX1) levels [1]. Incresed c-kit nd PDX1 undnce is lso oserved in islets from pncreses of streptozotocin-induced dietic rts, suggesting tht c-kit is involved in et cell regenertion [17]. Mnipultion of rt islets in cell culture hs further reveled tht c-kit-enriched cells cn give rise to new et cells tht secrete insulin in glucose-responsive fshion [18]. Fetl rt islets treted with SCF hd significnt increse in insulin levels nd DNA content [7]. Furthermore, INS-1 cells responded to SCF with incresed cell prolifertion [1]. Downregultion of c-kit (lso known s KIT) expression in humn islet epithelil clusters using smll interfering RNA leds to significntly reduced mrna nd protein levels of PDX1 nd insulin in conjunction with decresed cell prolifertion, s well s incresed cell deth [1]. These studies revel remrkle correltion etween the functions of c-kit nd enhnced et cell development nd function. Homozygous c-kit-null (c-kit W/W ) mutnt mice, disply reltively norml islet morphology, ut die shortly fter irth nd re not ville for further functionl studies [19]. We hve previously chrcterised c-kit Wv mice, which hve point muttion in the c-kit llele, disrupting receptor function. These mice exhiit loss of et cell mss nd prolifertion, resulting in erly onset of dietes []. In the Methods Genertion nd mintennce of mice Humn c-kit cdna (.9 k pirs) followed y the IRES-enhnced green fluorescence protein (egfp) (Clontech, Plo Alto, CA, USA) sequence ws inserted into the pks/rt insulin promoter (RIP) plsmid [1] to generte the trnsgene. Trnsgenic mice () were generted using C57BL/J emryos nd identified y PCR [] using the primers gloin 5 nd c-kit, nd further confirmed y second set of primers, egfp3 nd gloin 3 (Electronic supplementry mteril [ESM] Tle 1). Five RIP c-kit trnsgenic founders were otined nd red with C57BL/J mice (Jckson Lortory, Br Hror, ME, USA) to estlish independent mouse lines. Initil chrcteristion reveled tht the mice displyed similr, if not identicl, ptterns of trnsgene expression nd phenotype tht eliminte ny positionl effect due to the loction of trnsgene integrtion. We therefore used offspring from two independent trnsgenic lines for susequent detiled nlyses. All mice hd free ccess to stndrd diet. The protocol used ws pproved y the University of Western Ontrio Animl User Sucommittee in ccordnce with the guidelines of the Cndin Council of Animl Cre. Body weight, food intke nd in vivo metolic studies Body weight, lood glucose levels, intrperitonel glucose tolernce tests (IPGTT) nd intrperitonel insulin tolernce tests (IPITT) were performed using mice nd their wildtype littermtes from 4 to 4 weeks of ge s descried previously [, 3]. Food intke ws monitored t weeks of ge for week period. Blood glucose levels were exmined under non-fsting, nd fter 4 h nd overnight fsting (1 h) with free ccess to wter. For the IPGTT nd IPITT, n intrperitonel injection of glucose (D-(+)-glucose; dextrose; Sigm, St Louis, MO, USA) t dosge of mg/g ody weight or of humn insulin (Humlin; Eli Lilly, Toronto, ON, Cnd) t 1 U/kg ody weight ws dministered nd lood glucose levels were exmined. The AUC ws used to quntify responsiveness [, 3]. Genertion of HFD-induced dietes nd :Wv mouse models The HFD study ws initited t weeks of ge, with nd wild-type mle mice receiving HFD
3 1 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 chow (D149; Reserch Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) for 4 weeks, followed y in vivo metolic studies [4, 5]. Breeding with c-kit Wv mice yielded four different mouse genotypes: (1) wild-type; () ; (3) c-kit Wv nd (4) :Wv. Presence of the c-kit Wv llele ws identified y the niml s chrcteristic fur pigmenttion []; the llele ws identified y PCR. In vivo metolic studies were performed on mle mice groups t 8 weeks of ge. INS-1 cell culture INS-1 (83/13) cells were cultured in RPMI 14 contining 1% FBS vol./vol., s descried previously []. For the exogenous SCF study, INS-1 cells were cultured in RPMI 14 plus 1% (wt/vol.) BSA, nd treted for 4 h with SCF (5 ng/ml; ID Lortory, London, ON, Cnd), SCF plus wortmnnin (1 nmol/l; Sigm) or non-scf (control) [15]. Cells were collected for immunofluorescence stining nd protein extrction. Cell prolifertion ws exmined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthizol--yl)-,5- diphenyltetrzolium romide (MTT) ssy nd Ki7 stining [15]. Three different cell pssges were used for ech set of experiments, representing n3. In vivo nd ex vivo glucose-stimulted insulin secretion ssy nd insulin ELISA For the in vivo glucose-stimulted insulin secretion (GSIS) ssy, lood smples were collected following 4 h of fsting ( min), nd t 5 nd 35 min fter glucose loding [, 3]. For the ex vivo GSIS ssy, freshly isolted islets from mice were hnd-picked nd incuted for 1 h with RPMI 14 plus.5% (wt/vol.) BSA contining. or mmol/l glucose []. Insulin secretion ws mesured using n ultrsensitive (mouse) insulin ELISA (Alpco, Slem, NH, USA). A sttic GSIS index ws clculted [, ]. The insulin content of isolted islets ws mesured nd expressed s nnogrms per microgrm DNA. Immunofluorescence nd morphometric nlyses Pncreses were fixed in 4% (wt/vol.) prformldehyde, nd sections prepred from the entire length of the pncres nd stined with primry ntiodies of dilutions s listed (ESM Tle ). Quntittive evlutions of lph cell nd et cell mss were performed using Openl imge softwre (Improvision, Lexington, MA, USA) [, 3]. Bet cell prolifertion nd levels of different trnscription fctors were determined y doule immunofluorescence stining nd quntifiction from t lest 1 rndom islets per pncretic section [, 3]. RNA extrction nd rel-time RT-PCR RNA ws extrcted from isolted islets of nd wild-type mice with or without HFD using kit (mirnesy; Qigen, Germntown, MD, USA) [3]. Sequences of PCR primers re listed in ESM Tle 3. Rel-time PCR nlyses were performed using kit (iq SYBR Green Supermix; Bio-Rd Lortories, Mississug, ON, Cnd). Reltive levels of gene expression were clculted nd normlised to the internl gene, 18S rrna, with t lest four repets per ge per experimentl group [, 3]. Protein extrction nd Western lot nlysis Islet proteins from nd wild-type pncreses were extrcted in NP-4 lysis uffer [, ]. An equl mount of protein from ech group ws frctionted y 1% (wt/vol.) SDS- PAGE, trnsferred on to nitrocellulose memrne (Bio- Rd) nd incuted with primry ntiodies s listed (ESM Tle ). Proteins were detected using western lot detection regents (ECL-Plus; Perkin Elmer, Wellesley, MA, USA) nd imged using Versdoc Imging System (Bio-Rd). Bnds were densitometriclly quntified y Imge l softwre (Bio-Rd). Sttisticl nlysis Dt re expressed s mens±sem. Sttisticl significnce ws determined y unpired Student s t test or ANOVA followed y Fisher s lest significnt differences post-hoc test. Differences were considered to e sttisticlly significnt t p<.5. Results Genertion of mouse model We generted mice on C57BL/J ckground using the RIP to direct overexpression of humn c-kit specificlly in et cells; humn c-kit ws lso linked with n IRES-eGFP to fcilitte monitoring of trnsgene expression. Immunolot nlysis of egfp in pncres, liver, muscle, rin nd isolted islet protein lystes showed positive signls in the pncres nd islets of mice (Fig. 1). The RIP did not led to ny errnt trnsgene expression. Fluorescence microscopy showed tht egfp ws present in islets freshly isolted from, ut not in those from wildtype littermtes (Fig. 1). This ws further confirmed y immunofluorescence stining for egfp nd insulin (Fig. 1). Humn c-kit mrna ws only detected in mouse islets (Fig. 1c), finding corroorted y elevted islet c-kit levels (Fig. 1d) nd c-kit immunofluorescence stining (Fig. 1e). We lso exmined the undnce of SCF, lignd of c-kit, in mouse islets (ESM Fig. 1). A significnt increse of Scf (lso known s Kitl) mrna ws noted in islets compred with wild-type islets (ESM Fig. 1); however, protein levels of SCF were not sttisticlly different etween nd wild-type islets (ESM Fig. 1). Tken together, these results indicte tht overexpression of humn c-kit under the trnscriptionl control of the RIP in mice is specific to et cells.
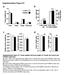
4 Dietologi (1) 55: Fig. 1 Genertion of C57BL/J trnsgenic mice with c-kit overexpression specificlly in et cells. Western lot nlysis of egfp undnce in tissues s indicted nd isolted islets (representtive lots shown). Aundnce of egfp on freshly isolted islets nd pncretic sections of 4-weekold mle wild-type () nd mice y doule immunofluorescence stining for egfp (green) with insulin (red). c RT-PCR nlysis of humn c-kit mrna in isolted islets of wild-type nd mice t 4 weeks of ge. d Western lot nlysis of c-kit levels in isolted islets of wild-type nd mice t 8 weeks of ge; vlues re men±sem; n3; p<.1 vs wild-type. e Immunofluorescence stining for c-kit (green) on pncretic sections from 4-week-old wild-type nd mle mice. Nuclei were stined with DAPI (lue). Representtive imges re shown. Scle rs (, e), 5 μm d Reltive c-kit protein level (normlised to clnexin) c-kit Clnexin c c-kit e egfp β-actin c-kit egfp expression in freshly isolted islets c-kit βtg Insulin c-kit βtg egfp/insulin/dapi c-kit/insulin/dapi Improved glucose tolernce nd insulin secretion in mice There were no significnt differences in ody weight during the 4 weeks of oservtion, with no chnges in food intke, etween nd wild-type mice (ESM Fig. ). No significnt differences in 4 h fsting plsm insulin nd lood glucose levels (Fig.,, ESM Fig. 3, ) were detected etween nd wild-type mice t 8 weeks of ge; however, the overnight fsting lood glucose levels were significntly lower in mice thn in wild-type littermtes (Fig., ESM Fig. 3). The IPGTT showed reltively similr response cpcity in nd wild-type mle mice t 4 weeks (ESM Fig. 4). However, significntly improved glucose tolernce ws oserved in mle mice t 8 nd weeks of ge, long with significnt decreses in the AUC during the IPGTT (Fig. c, ESM Fig. 4); no significnt chnge ws oserved in femle mice (ESM Fig. 3c, ESM Fig. 4). No chnges were oserved in insulin tolernce etween the experimentl groups (Fig. d, ESM Fig. 3d). Furthermore, the effect of c-kit overexpression on et cell insulin secretion ws significnt, with isolted islets from mle nd femle mice relesing significntly more insulin thn wild-type controls in response to mmol/ l glucose (Fig. e, ESM Fig. 3e). This ws ssocited with higher insulin content in islets (Fig. f). Since femle mice did not exhiit significnt ltertion in the IPGTT, we focused on mle mice for detiled chrcteristion. Incresed islet trnscription fctors, et cell mss nd prolifertion in mice To further chrcterise the functionl role of c-kit in et cells, we exmined levels of trnscription fctors essentil for islet growth, function nd morphology in nd wild-type mice. At 8 weeks of ge, we oserved slightly incresed islet numer (Fig. 3), with significnt increse in the numer of smll (<5 μm ) nd lrge islets (>1, μm ; Fig. 3) in the pncres of mice. No significnt ltertions in lph cell mss were detected etween wild-type nd mice (Fig. 3c). However, et cell mss in
5 18 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 Fig. Glucose tolernce nd insulin secretion in 8-week-old mle mice. Fsting plsm insulin () nd lood glucose () in wild-type (, white rs) nd (lck rs) mice. c IPGTT nd (d) IPITT in wild-type (lck circles) nd (lck squres) mice. The glucose responsiveness of the corresponding experimentl groups is shown s the AUC of the IPGTT (c, insert) or IPITT (d, insert) grphs, with units of (mmol/l x min). Dt ( d) re expressed s men±sem; n5 18; p<.5 nd p<.1 vs wild-type mice. e Insulin secretion of isolted islets from wild-type nd mice in response to mmol/l glucose chllenge; dt re expressed s fold chnge normlised to sl (. mmol/l glucose) secretion; n3 4. f Insulin content in isolted islets; dt re normlised to DNA content; n7; p<.5 nd p<.1 vs wild-type mice c 3 1 Fsting plsm insulin (pmol/l) e GSIS in isolted islets (fold chnge normlised to sl) AUC (mmol/l min) non-fbg 4h-FBG ON-FBG,5, 1,5 1, Time fter glucose i.p. injection (min).5 8 d f Insulin content (ng/µg DNA) Time fter insulin i.p. injection (min) 3 1 AUC (mmol/l min) 8 4 mice ws incresed y 1.-fold compred with wild-type (Fig. 3d). Incresed et cell mss ws ssocited with n increse in et cell prolifertion in mice (Fig. 3e, ESM Fig. 5). Quntittive rel-time RT-PCR nlysis of Pdx1, Neurod1, Mf, Px, Nkx- nd Nkx-1 showed significntly incresed mrna levels in mice (Fig. 3f), with elevted intensity of the corresponding signls in the islets of mice (ESM Fig. ). The expression of Glut (lso known s Slc), Ins1 nd Ins, Gcg nd Glp1r mrna in isolted islets ws lso significntly incresed (Fig. 3g) with reltively enhnced Glut nd glucgon-like peptide 1 receptor (Glp1R) stining (ESM Fig. ). Incresed undnce of insulin receptor, phosphorylted IRS1/ nd their downstrem signlling molecules in the islets of mice Our previous study showed tht the c-kit Wv muttion cused et cell dysfunction [] nd tht this muttion ws ssocited with downregultion of the Akt glycogen synthse kinse 3β (GSK3β) cyclin D1 pthwy [7]. We therefore exmined whether signlling molecules up- nd downstrem of the phosphoinositide-3- kinse (PI3K) Akt pthwy or cell survivl signls re ltered in islets. Interestingly, significnt upregultion of Insr nd Irs1 mrna ws oserved in islets (Fig. 4), with n increse of insulin receptor nd phosphorylted IRS1/ protein levels (Fig. 4, c) compred with wild-type mice. Protein levels of phospho-akt (Fig. 4d), phospho-gsk3β (Fig. 4e), cyclin D1 (Fig. 4f) nd PDX1 (Fig. 4g) were lso significntly incresed in islets compred with islets isolted from wildtype littermtes. This oservtion ws further chrcterised using the INS-1 cell line. When treted with exogenous SCF, INS-1 cells exhiited significntly incresed cell prolifertion (ESM Fig. 7, ), with upregultion of the phospho-akt GSK3β pthwy (ESM Fig. 7c), together with incresed insulin receptor nd phosphorylted IRS1/ protein levels (ESM Fig. 7d). The increse in insulin receptor nd phospho-irs1/ protein levels ws regulted y the PI3K Akt signlling pthwy.
6 Dietologi (1) 55: Fig. 3 Islet morphology in mle mice. Morphometric nlysis of islet numer (), islet size (), lph cell mss (c), et cell mss (d) nd the percentge of Ki7 + in et cells (e) in wild-type (, white rs) nd (lck rs) mice t 8 weeks of ge. f Trnscription fctor nd (g) islet gene expression in nd wild-type mice t 8 weeks of ge, s nlysed y quntittive RT-PCR. Dt re expressed s mens±sem; n4 8; p<.5, p<.1 nd p<.1 vs wild-type mice f c Alph cell mss (mg) Reltive mrna expression (normlised to 18S) Islet numer per mm Bet cell mss (mg) Islet size/totl islets (%) <5 µm 1. 5-,5 µm,5-1, µm >1, µm.. d Pdx1 Neurod1 Mf Px4 Px Nkx- Nkx-1 Glut Ins Gcg Glp1r g Reltive mrna expression (normlised to 18S) e Ki7 + /Insulin + cells (%) mice tolerted HFD-induced dietes To investigte how et cell-specific c-kit overexpression would ffect glucose homeostsis of mice under dietic conditions, mle nd wild-type littermtes were sujected to HFD. Similr food intke nd ody weight gins were oserved in oth experimentl groups (Fig. 5). Interestingly, fter 4 weeks of HFD, the ft pd mss ws significntly smller (Fig. 5) nd the 4 h fsting glucose level ws lower in HFD mice thn in wild-type HFD mice (Fig. 5c). Glucose intolernce ws noted in wildtype HFD littermtes, ut ws significntly improved in c- KitβTg HFD mice (Fig. 5d), with similr results for insulin response in wild-type HFD s determined y the IPITT (Fig. 5e). In vivo GSIS ssys reveled slightly higher sl nd 5 min plsm insulin levels in HFD mice (Fig. 5f); moreover, t 35 min fter glucose stimultion, the plsm insulin relese ws significntly reduced in wildtype HFD compred with HFD mice (Fig. 5f). GSIS on isolted islets further demonstrted tht HFD islet insulin secretion ws significntly incresed in response to mmol/l glucose compred with wild-type HFD islets (Fig. 5g). The insulin content ws lso significntly incresed in HFD islets (Fig. 5h). Improvements in glucose tolernce in HFD mice were ssocited with significntly incresed Pdx1, Mf, Ins, Insr nd Irs1 mrna, s well s phospho-irs1/ levels in HFD islets (Fig. ). The improved metolic phenotype of HFD mice ws ssocited with significnt increse in the numer of pncretic islets nd et cell mss compred with wild-type HFD mice (Fig., d). A slightly incresed lph cell mss ws oserved in HFD mice; however, the increse ws not sttisticlly significnt (Fig. c). Nevertheless, significnt increse in et cell mss ws detected, with incresed et cell prolifertion in HFD mice compred with the wild-type HFD group (Fig. e). c-kit Wv mice with specific overexpression of c-kit in et cells displyed norml glucose metolism c-kit Wv mice were red with mice to determine whether c-kit overexpression in et cells could rescue nimls with the c-kit Wv muttion from erly onset of dietes. Wild-type, nd :Wv mice exhiited similr fsting lood glucose levels, with significnt improvement in fsting lood glucose levels eing noted in :Wv compred with c-kit Wv mice (Fig. 7). :Wv mice lso hd similr glucose tolernce cpcity to tht of the wild-type nd groups, nd lso displyed significnt decreses in the AUC (Fig. 7). The IPITT reveled no differences etween the experimentl groups (Fig. 7c).
7 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 Reltive mrna expression (normlised to18s) c Insr Irs1 Irs Reltive insulin receptor (normlised to β-ctin)..4.. InsR β-actin Significntly improved GSIS ws oserved t 5 nd 35 min in :Wv mice compred with c-kit Wv mice (Fig. 7d). To further confirm islet function, n ex vivo GSIS study ws conducted, in which insulin secretion in response to mmol/l glucose chllenge in :Wv islets ws similr to tht in wild-type nd islets (Fig. 7e), ut significntly higher thn tht of c-kit Wv islets (Fig. 7e). Insulincontentinisolted:Wv islets ws lso higher thn in c-kit Wv islets, ut significntly lower thn in controls (Fig. 7f). These results indicte tht the c-kit point muttion is directly responsile for defective et cell function in c-kit Wv mice nd tht c-kit overexpression ws le to preserve et cell function in c-kit Wv mice. Discussion Reltive phospho-akt S473 (normlised to totl Akt) Reltive cyclin D1 protein (normlised to β-ctin) d f pirs1/ pakt takt Insulin pirs1//insulin/dapi e Cyclin D1 β-actin Reltive phospho-gsk3β S9 (normlised to totl GSK3β) Reltive PDX1 protein (normlised to β-ctin) g pgsk3β tgsk3β PDX1 β-actin Fig. 4 Levels of phosphorylted Akt/GSK3β signlling nd downstrem signlling molecules in mle mice. Quntittive RT- PCR nlysis of Insr, Irs1 nd Irs in isolted islets of wild-type (, white rs) nd (lck rs) mice t 8 weeks of ge. Dt re expressed s men±sem; n3 4. Western lot nlysis for insulin receptor (InsR) nd (c) doule immunofluorescence stining for phospho-irs1/ (green) nd insulin (red) in pncretic sections from 8-week-old wild-type nd mice. Nuclei were stined y DAPI (lue); representtive imges shown; scle rs 5 μm. d Western lot nlysis of phosphorylted (p) nd totl (t) Akt, (e) pgsk3β nd tgsk3β, (f) cyclin D1 nd (g) PDX-1 undnce in isolted islets of wild-type nd mice t 8 weeks of ge. Representtive lots re shown. Dt re normlised to totl protein or loding control nd expressed s mens±sem; n4 5. p<.5, p<.1 nd p<.1 vs wild-type mice Here, we demonstrted tht c-kit overexpression in et cells confers improved glucose metolism y enhncing insulin secretion, nd incresing et cell mss nd prolifertion, proly through ctivtion of the PI3K Akt signlling pthwy. When mice were sujected to HFD, they displyed resistnce to HFD-induced glucose intolernce nd preserved et cell function reltive to wild-type littermtes. Moreover, mice were protected ginst erly onset of dietes. These results clerly indicte tht c-kit is intrinsic to et cell function nd prolifertion. This effect is medited y the regultion of key et cell trnscription fctors (e.g. PDX1 nd v-mf musculoponeurotic firosrcom oncogene fmily, protein A (vin) [MAFA]) nd possily through interction with the insulin receptor to ctivte downstrem PI3K Akt signlling. Compred with wild-type mice, mice hd significntly lower overnight fsting lood glucose levels, improved glucose tolernce nd enhnced GSIS. The improvement in glucose metolism of mice ws ssocited with n increse in et cell mss nd prolifertion, s well s in Glut nd Glp1r expression. These results corroorte our previous finding of glucose intolernce in c-kit Wv mice []. We monitored the mice up to 4 weeks of ge nd did not detect ny norml cell growth or islet tumours, indicting tht et cell-specific c-kit overexpression does not led to mlignncy. We detected significnt increse in Scf mrna, ut only modest increse in the corresponding protein. This is likely to e due to our western lotting technique, which could only detect memrne-ssocited, not solule, SCF. Nevertheless, the concentrtion of SCF my e in excess nd is sufficient to interct with the incresed numer of c-kit receptors ( 5%) to trnsduce mrkedly enhnced intrcellulr signls in mice. Our dt indicte tht c-kit overundnce in et cells enhnces glucose tolernce nd et
8 Dietologi (1) 55: c Weight gined/food intke (g) HFD -HFD Ft pd/ody weight (%) 4 -HFD -HFD HFD -HFD d 3 1 AUC (mmol/l min),5, 1,5 1, Time fter glucose i.p. injection (min) -HFD -HFD e Percentge of seline lood glucose AUC (mmol/l min) Time fter insulin i.p. injection (min) -HFD -HFD f. 3 g h Insulin relese (ng/ml) Time fter i.p. glucose injection (min) GSIS in isolted islets (fold chnge normlised to sl) HFD -HFD Insulin content (ng/μg DNA) HFD -HFD Fig. 5 Effect of HFD on mice. Weight gined per food intke, () ft pd per ody weight nd (c) 4 h fsting lood glucose levels in HFD nd wild-type () HFD mice. d IPGTTs nd (e) IPITTs were performed on wild-type HFD (lck circles) nd HFD (lck squres) mice. The glucose responsiveness of the corresponding experimentl groups is shown s the AUC of the IPGTT (d, insert) or IPITT (e, insert) grphs, with units of (mmol/l x min). Dt ( e) re expressed s mens±sem; n7 8. f In vivo GSIS of wild-type HFD nd HFD mice (n). Lighted rs, - HFD insulin; drked rs, HFD insulin; lck circles, - HFD glucose; lck squres, HFD glucose. g GSIS is improved in isolted islets from HFD mice in response to mmol/l glucose chllenge; dt re expressed s fold chnge normlised to sl (. mmol/l glucose) secretion (n5). h Insulin content in isolted islets. Dt re normlised to DNA content (n1). p<.5, p<.1, p<.1 nd p<.5 vs wild-type HFD mice cell function in mles, while the effect is less significnt in femle mice. These sex-relted differences in glucose metolism re consistent with our previous results using c-kit Wv mice nd conditionl β1 integrin knockout mice [, 3], nd hve lso een descried in other mouse models [8, 9]. We oserved tht isolted islets from femle mice hd significntly enhnced insulin secretion in response to high glucose chllenge compred with wild-type femles, indicting tht the sex-relted differences my involve other pthwys, such s the contriution of oestrogen to glucose homeostsis in femle rodents. Significntly incresed Pdx1 mrna nd protein undnce ws oserved in mice. We previously reported tht SCF-stimulted c-kit receptor ctivity leds to incresed PDX1 mrna expression in humn fetl islet epithelil clusters [15], while c-kit Wv mice showed significnt reduction in Pdx1 expression in islets []. It is well documented tht PDX1 is integrl to norml pncres development nd et cell function [3]. In ddition to et cell prolifertion [31], Pdx1 expression is lso required for modultion of insulin gene expression nd glucose metolism [3]. Our results showed tht islets exhiited high PDX1 levels nd hd incresed et cell prolifertion nd mss, confirming correltion etween PDX1 nd islet et cell repliction. Indeed, the enhnced islet insulin secretion in response to high glucose chllenge nd the improved glucose tolernce oserved in mice my lso e due to incresed islet PDX1 undnce. Interestingly, significnt upregultion of
9 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 Islet numers per mm d Bet cell mss (mg) Reltive mrna expression (normlised to 18S) HFD -HFD Pdx1 Mf Ins Insr Irs1 Irs c-kit βtg-hfd c-kit βtg-hfd Mf mrna ws oserved in oth sexes of mice. MAFA inds to the C1 element of the insulin gene to modulte insulin gene trnscription nd enhnce et cell mturtion [33]. Mf-null mice hd defect only in dult islet rchitecture nd et cell ctivity, while MAFA overproduction enhnced et cell insulin iosynthesis nd secretion through upregultion of importnt et cell genes, including Pdx1, Neurod1, Nkx-1 nd Glp1r [34]. Moreover, overexpression of MAFA in neontl rt et cells led to enhnced glucose-responsive insulin secretion nd et cell mturtion [35]. Thus, improved glucose metolism nd insulin secretion in mice my e due to incresed c-kit receptor stimultion of islet Pdx1 nd Mf expression. The moleculr mechnisms ssocited with the phenotypic chnges oserved in mice include significnt c Alph cell mss (mg) e Ki7 + /insulin + cells (%) HFD -HFD c-kit βtg-hfd c-kit βtg-hfd Fig. Effect of HFD on islet morphology of mice. Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of genes s indicted on isolted islets of wild-type HFD (light rs) nd HFD (drk rs) mice. Dt re expressed s mens±sem; n3. Morphometric nlysis of islet numer, (c) lph cell mss, (d) et cell mss nd (e) percentge of Ki7 + in et cells from wild-type HFD nd HFD mice. Dt re expressed s mens±sem; n 7. e p<.5 nd p<.1 vs wild-type HFD mice upregultion of phospho-akt nd phospho-gsk3β in et cells. Our previous in vitro study on humn fetl islet epithelil clusters demonstrted tht incresed c-kit SCF interctions resulted in upregultion of PI3K Akt, ut not of mitogen-ctivted protein kinse (MAPK) extrcellulr signl-regulted kinse (ERK) pthwy signlling [15]. In the current study, we lso oserved significnt increses in insulin receptor nd phospho-irs1/ levels, in ddition to the increse in Akt nd GSK3β phosphoryltion together with upregultion of cyclin D1 in islets isolted from mice. These results suggest the following possile mechnisms, wherey c-kit might stimulte et cell function nd prolifertion: (1) vi direct ctivtion of the Akt GSK3β cyclin D1 pthwys [15, 3]; () vi direct or indirect interction etween c-kit nd the insulin receptor nd IRSs to estlish cross-tlk; nd/or (3) y positive feedck of the insulin receptor vi PI3K Akt signlling in ssocition with PDX1- nd Mf-induced insulin secretion. Islets of et cell-specific Gsk3β lted mice hd incresed et cell mss with lower fsting lood glucose, long with improved glucose tolernce nd GSIS [37]. Furthermore, et cell-specific Gsk3β knockout mice hd incresed islet IRS-1 nd - levels with significntly improved et cell function [37], which is in greement with our oservtions. It hs een reported tht insulin secreted y pncretic et cells positively regultes its own iosynthesis y enhncing insulin gene trnscription in n utocrine mnner vi the et cell insulin receptor nd downstrem signlling pthwys [38, 39]. Specific knockout of Insr in pncretic et cells results in defective insulin secretion, similr to tht oserved in type dietes [4]. Tken together, these results suggest tht Akt GSK3β cyclin D1 signlling downstrem of c-kit is essentil for et cell function. HFD tretment is detrimentl to et cell function nd insulin sensitivity in mice [4, 41], nd leds to impired glucose tolernce due to insulin resistnce nd insufficient et cell insulin secretion [4, 41 43]. While nd wild-type mice mintined on HFD showed similr food intke nd weight gin, significntly less ft pd formtion ws oserved in the former fter 4 weeks on the HFD. Importntly, HFD mice exhiited significntly improved glucose tolernce nd GSIS, supporting the notion tht c-kit hs direct effect on et cell function. Islets of HFD mice lso showed significntly incresed levels of insulin receptor nd insulin signls, suggesting possile secondry mechnism, wherey c-kit stimultes et cell function y cross-tlking to the insulin receptor vi PI3K Akt signlling. Therefore, overundnce of c-kit in et cells plys primry role y incresing et cell mss nd prolifertion, s well s secondry role y incresing insulin secretion vi upregultion of the insulin receptor through the PI3K Akt signlling pthwy, which enles HFD mice to tolerte HFD-induced dietes.
10 Dietologi (1) 55: Blood glucose level (mmol/l) c-kit βtg c-kitwv c-kit βtg:wv AUC (mmol/l min),5, 1,5 1, Time fter glucose i.p. injection (min) c-kit βtg c-kitwv c-kit βtg:wv c Percentge of seline lood glucose AUC (mmol/l min) 3 Time fter insulin i.p. injection (min) c-kit βtg c-kitwv c-kit βtg:wv d Insulin relese (ng/ml) Time (min) 35 e GSIS in isolted islets (Fold chnge normlised to sl) f Insulin content (ng/μg DNA) 1.. c-kit βtg c-kitwv c-kit βtg:wv c-kit βtg c-kitwv.5..5 c-kit βtg:wv Fig. 7 Glucose tolernce nd insulin secretion in :Wv mice. Fsting lood glucose levels, () IPGTT nd (c) IPITT vlues in mle wild-type (),, c-kitwv nd :Wv mice t 8 weeks of ge. The glucose responsiveness of the corresponding experimentl groups is shown s the AUC of the (, insert) IPGTT or (c, insert) IPITT grphs with units of (mmol/l x min). Dt ( c) re expressed s mens±sem; n7 8. d In vivo GSIS of wild-type (white rs), c- KitβTg (lck rs), c-kitwv (grey rs) nd :Wv (dotted rs) mice (n3 4). e GSIS of isolted islets from :Wv mice is improved in response to mmol/l glucose chllenge; dt re expressed s fold chnge normlised to sl (. mmol/l glucose) secretion; n3. f Insulin content in isolted islets; dt re normlised to DNA content; n 8. p<.5, p<.1 nd p<.1 Finlly, we red with c-kit Wv mice to determine whether c-kit overexpression could prevent et cell dysfunction in c-kit Wv mice. Our results showed tht : Wv mice displyed norml fsting glycemi nd glucose tolernce, s well s enhnced glucose-induced insulin secretion. This mrked improvement in glucose metolism in :Wv mice provides direct evidence of primry effect of the c-kit receptor on et cell function. In summry, we showed tht c-kit overexpression in et cells led to improved et cell prolifertion nd function, nd protected mice from HFD-induced dietes. Furthermore, et cell-specific overexpression of c-kit ws le to prevent et cell defects in c-kit Wv mice. This study provides direct evidence to support the notion tht c-kit plys primry physiologicl role in et cells, nd thus my help efforts to develop gene nd cell therpeutic schemes for ptients with dietes. Funding This work ws supported y grnts from the Cndin Institutes of Helth Reserch (CIHR, grnt numer MOP 898). Dulity of interest The uthors declre tht there is no dulity of interest ssocited with this mnuscript.
11 4 Dietologi (1) 55:14 5 Contriution sttement ZCF nd JL contriuted to the cquisition of dt, dt nlysis nd interprettion, mnuscript drfting nd finl pprovl of the mnuscript. BAT contriuted to the dt nlysis nd interprettion, mnuscript drfting nd finl pprovl of the mnuscript. MR contriuted to nlysis nd interprettion of dt, revising the rticle, nd finl pprovl of the mnuscript. SPY contriuted to the design of the trnsgenic model, nlysis nd interprettion of dt, the provision of study mterils, nd the criticl revision nd finl pprovl of the mnuscript. RW contriuted to the conception nd design of the study, the collection nd ssemly of dt, dt nlysis nd interprettion, mnuscript writing nd finl pprovl of the mnuscript. References 1. Meier JJ, Bhushn A, Butler PC () The potentil for stem cell therpy in dietes. Peditr Res 59:5R 73R. Ho E, Tyrerg B, Itkin-Ansri P et l () Bet-cell differentition from nonendocrine epithelil cells of the dult humn pncres. Nt Med 1: Jing J, Au M, Lu K et l (7) Genertion of insulin-producing islet-like clusters from humn emryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 5: Bonner-Weir S, Shrm A () Pncretic stem cells. J Pthol 197: Heit JJ, Kim SK (4) Emryonic stem cells nd islet replcement in dietes mellitus. Peditr Dietes 5(Suppl ):S5 S15. Oerg C, Wltenerger J, Clesson-Welsh L, Welsh M (1994) Expression of protein tyrosine kinses in islet cells: possile role of the flk-1 receptor for et-cell mturtion from duct cells. Growth Fctors 1: Oerg-Welsh C, Welsh M (199) Effects of certin growth fctors on in vitro mturtion of rt fetl islet-like structures. Pncres 1: LeBrs S, Czernichow P, Schrfmnn R (1998) A serch for tyrosine kinse receptors expressed in the rt emryonic pncres. Dietologi 41: Welsh M, Anneren C, Lindholm C, Kriz V, Oerg-Welsh C () Role of tyrosine kinse signling for et-cell repliction nd survivl. Ups J Med Sci 15: Rchdi L, El Ghzi L, Bernex F, Pnthier JJ, Czernichow P, Schrfmnn R (1) Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinse KIT in mture et-cells nd in the pncres in development. Dietes 5: Yshpl NK, Li J, Wng R (4) Chrcteriztion of c-kit nd nestin expression during islet cell development in the prentl nd postntl rt pncres. Dev Dyn 9: Li J, Quirt J, Do HQ et l (7) Expression of c-kit receptor tyrosine kinse nd effect on et-cell development in the humn fetl pncres. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 93:E475 E Ashmn LK (1999) The iology of stem cell fctor nd its receptor C-kit. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31: Linnekin D (1993) Erly signling pthwys ctivted y c-kit in hemtopoietic cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31: Li J, Goodyer CG, Fellows F, Wng R () Stem cell fctor/c-kit interctions regulte humn islet-epithelil cluster prolifertion nd differentition. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38: Peters K, Pnienk R, Li J, Kloppel G, Wng R (5) Expression of stem cell mrkers nd trnscription fctors during the remodeling of the rt pncres fter duct ligtion. Virchows Arch 44: Tiemnn K, Pnienk R, Kloppel G (7) Expression of trnscription fctors nd precursor cell mrkers during regenertion of et cells in pncret of rts treted with streptozotocin. Virchows Arch 45:1 18. Wng R, Li J, Yshpl N (4) Phenotypic nlysis of c-kit expression in epithelil monolyers derived from postntl rt pncretic islets. J Endocrinol 18: Bernex F, de Sepulved P, Kress C, Elz C, Delouis C, Pnthier J (199) Sptil nd temporl ptterns of c-kit expressing cells in WlcZ/+ nd WlcZ/WlcZ mouse emryos. Development 1: Krishnmurthy M, Ayzi F, Li J et l (7) c-kit in erly onset of dietes: morphologicl nd functionl nlysis of pncretic et-cells in c-kit W-v mutnt mice. Endocrinology 148: Vler A, Solnes G, Fernández-Alvrez J et l (1994) Expression of GLUT- ntisense RNA in et cells of trnsgenic mice leds to dietes. J Biol Chem 9: Ngy A, Gertsenstein M, Vintersten K, Behringer R (3) Mnipulting the mouse emryo: lortory mnul, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Hror Lortory Press, New York 3. Riopel M, Krishnmurthy M, Li J, Liu S, Lesk A, Wng R (11) Conditionl et1-integrin-deficient mice disply impired pncretic et cell function. J Pthol 4: Qiu L, List EO, Kopchick JJ (5) Differentilly expressed proteins in the pncres of diet-induced dietic mice. Mol Cell Proteomics 4: Collins SC, Hopp MB, Wlker JN et l (1) Progression of diet-induced dietes in C57BLJ mice involves functionl dissocition of C + chnnels from secretory vesicles. Dietes 59: Krishnmurthy M, Li J, Fellows GF, Rosenerg L, Goodyer CG, Wng R (11) Integrin α3, ut not β1, regultes islet cell survivl nd function vi PI3K/Akt signling pthwys. Endocrinology 15: Feng ZC, Donnelly L, Li J, Krishnmurthy M, Riopel M, Wng R (1) Inhiition of GSK3β ctivity improves et-cell function in c-kit Wv/+ mle mice. L Invest 9: Liu S, Muvis-Jrvis F (1) Minireview: estrogenic protection of et-cell filure in metolic diseses. Endocrinology 151: Geisler JG, Zwlich W, Zwlich K et l () Estrogen cn prevent or reverse oesity nd dietes in mice expressing humn islet myloid polypeptide. Dietes 51: Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Jonsson L, Simu K, Edlund H (1998) Betcell-specific inctivtion of the mouse Ipf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the et-cell phenotype nd mturity onset dietes. Genes Dev 1: Dutt S, Gnnon M, Peers B, Wright C, Bonner-Weir S, Montminy M (1) PDX:PBX complexes re required for norml prolifertion of pncretic cells during development. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A 98: Brissov M, Shiot M, Nicholson WE et l () Reduction in pncretic trnscription fctor PDX-1 impirs glucose-stimulted insulin secretion. J Biol Chem 77: Nishimur W, Bonner-Weir S, Shrm A (9) Expression of MfA in pncretic progenitors is detrimentl for pncretic development. Dev Biol 333: Wng H, Brun T, Ktok K, Shrm AJ, Wollheim CB (7) MAFA controls genes implicted in insulin iosynthesis nd secretion. Dietologi 5: Aguyo-Mzzucto C, Koh A, El Khtti I et l (11) Mf expression enhnces glucose-responsive insulin secretion in neontl rt et cells. Dietologi 54: Kushner JA, Ciemerych MA, Sicinsk E et l (5) Cyclins D nd D1 re essentil for postntl pncretic et-cell growth. Mol Cell Biol 5: Liu Y, Tne K, Bronnier D et l (1) Conditionl ltion of gsk-3et in islet et cells results in expnded mss nd resistnce to ft feeding-induced dietes in mice. Dietologi 53: 1
12 Dietologi (1) 55: Leiiger IB, Leiiger B, Moede T, Berggren PO (1998) Exocytosis of insulin promotes insulin gene trnscription vi the insulin receptor/pi-3 kinse/p7 s kinse nd CM kinse pthwys. Mol Cell 1: Xu GG, Rothenerg PL (1998) Insulin receptor signling in the etcell influences insulin gene expression nd insulin content: evidence for utocrine et-cell regultion. Dietes 47: Kulkrni RN, Bruning JC, Winny JN, Postic C, Mgnuson MA, Khn CR (1999) Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pncretic et cells cretes n insulin secretory defect similr to tht in type dietes. Cell 9: Lewis GF, Crpentier A, Adeli K, Gicc A () Disordered ft storge nd moiliztion in the pthogenesis of insulin resistnce nd type dietes. Endocr Rev 3: Ahren B, Simonsson E, Scheurink AJ, Mulder H, Myrsen U, Sundler F (1997) Dissocited insulinotropic sensitivity to glucose nd crchol in high-ft diet-induced insulin resistnce in C57BL/J mice. Metolism 4: Ahren B, Pcini G () Insufficient islet compenstion to insulin resistnce vs. reduced glucose effectiveness in glucoseintolernt mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 83:E738 E744
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
ARTICLE. J. E. Bowe & A. Chander & B. Liu & S. J. Persaud & P. M. Jones
 Dietologi (23) 56:783 79 DOI.7/s25-2-2828-2 ARTICLE The permissive effects of glucose on receptor-operted potentition of insulin secretion from mouse islets: role for ERK/2 ctivtion nd cytoskeletl remodelling
Dietologi (23) 56:783 79 DOI.7/s25-2-2828-2 ARTICLE The permissive effects of glucose on receptor-operted potentition of insulin secretion from mouse islets: role for ERK/2 ctivtion nd cytoskeletl remodelling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Reciprocal modulation of adult beta cell maturity by activin A and follistatin
 Dietologi (21) 53:168 1689 DOI 1.17/s125-1-1758- ARTICLE Reciprocl modultion of dult et cell mturity y ctivin A nd follisttin M. Szt & J. D. Johnson & J. M. Piret Received: 31 Jnury 21 /Accepted: 22 Mrch
Dietologi (21) 53:168 1689 DOI 1.17/s125-1-1758- ARTICLE Reciprocl modultion of dult et cell mturity y ctivin A nd follisttin M. Szt & J. D. Johnson & J. M. Piret Received: 31 Jnury 21 /Accepted: 22 Mrch
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
Deletion of Fas protects islet beta cells from cytotoxic effects of human islet amyloid polypeptide
 Dietologi (212) 55:135 147 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2451-2 ARTICLE Deletion of Fs protects islet et cells from cytotoxic effects of humn islet myloid polypeptide Y. J. Prk & S. Lee & T. J. Kieffer & G. L. Wrnock
Dietologi (212) 55:135 147 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2451-2 ARTICLE Deletion of Fs protects islet et cells from cytotoxic effects of humn islet myloid polypeptide Y. J. Prk & S. Lee & T. J. Kieffer & G. L. Wrnock
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 d MAP2 GFAP e MAP2 GFAP GFAP c f Clindin GFAP Supplementry Figure S1. Neuronl deth nd ltered strocytes in the rin of n ffected child. Neuron specific MAP2 ntiody stining in the hippocmpus
Supplementry Figure S1 d MAP2 GFAP e MAP2 GFAP GFAP c f Clindin GFAP Supplementry Figure S1. Neuronl deth nd ltered strocytes in the rin of n ffected child. Neuron specific MAP2 ntiody stining in the hippocmpus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementary Information Titles
 Supplementry Informtion Titles Journl: Nture Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Modelling colorectl cncer using CRISPR-Cs9-medited engineering of humn intestinl orgnoids Toshiro Sto Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Titles Journl: Nture Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Modelling colorectl cncer using CRISPR-Cs9-medited engineering of humn intestinl orgnoids Toshiro Sto Supplementry
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
ESM Table 1. Characterisation of the human non-diabetic cohort used for MRIbased assessment of pancreatic fat and insulin secretion via OGTT.
 ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Protein kinase Cδ regulates nuclear export of FOXO1 through phosphorylation of the chaperone ζ
 Dietologi (215) 58:2819 2831 DOI 1.17/s125-15-44-z ARTICLE Protein kinse Cδ regultes nucler export of through phosphoryltion of the chperone Felici Gerst 1,2 & Griele Kiser 1,2 & Mdhur Pnse 1 & Tin Srtorius
Dietologi (215) 58:2819 2831 DOI 1.17/s125-15-44-z ARTICLE Protein kinse Cδ regultes nucler export of through phosphoryltion of the chperone Felici Gerst 1,2 & Griele Kiser 1,2 & Mdhur Pnse 1 & Tin Srtorius
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Effects of Recombinant Bovine Somatotropin Administration at Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus and Subsequent Offspring Performance of Beef Cattle
 Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
Effects of Recominnt Bovine Somtotropin Administrtion t Breeding on the Cow, Conceptus nd Susequent Offspring Performnce of Beef Cttle V. R. G. Mercdnte 1, F. M. Cirico 1, D. D. Henry 1, P. L. P. Fontes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Unique roles of the unfolded protein response pathway in fungal. development and differentiation. Kwang Woo Jung, Yee Seul So, & Yong Sun Bahn *
 Supplementry Informtion Unique roles of the unfolded protein response pthwy in fungl development nd differentition Kwng Woo Jung, Yee Seul So, & Yong Sun Bhn * Contents Supplementry Figure S1 Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Unique roles of the unfolded protein response pthwy in fungl development nd differentition Kwng Woo Jung, Yee Seul So, & Yong Sun Bhn * Contents Supplementry Figure S1 Supplementry
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
AMPK maintains energy homeostasis and survival in cancer cells via. regulating p38/pgc-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
Arachidonic acid induces ERK activation via Src SH2 domain association with the epidermal growth factor receptor
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 6 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Archidonic cid induces ERK ctivtion vi Src SH2 domin ssocition with the epiderml growth fctor receptor LD Alexnder
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 6 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Archidonic cid induces ERK ctivtion vi Src SH2 domin ssocition with the epiderml growth fctor receptor LD Alexnder
Platelet-derived growth factor-a receptor activation is required for human cytomegalovirus infection
 Vol 455 18 Septemer 28 doi:1.138/nture729 LETTERS Pltelet-derived growth fctor- receptor ctivtion is required for humn cytomeglovirus infection Lilin Sorocenu 1, Armin Akhvn 1 & Chrles S. Cos 1,2 Humn
Vol 455 18 Septemer 28 doi:1.138/nture729 LETTERS Pltelet-derived growth fctor- receptor ctivtion is required for humn cytomeglovirus infection Lilin Sorocenu 1, Armin Akhvn 1 & Chrles S. Cos 1,2 Humn
Keywords ATP. GK rat. Na + /K + -ATPase. Pancreatic islet. ROS. Src
 Dietologi (28) 51:1226 1235 DOI 1.17/s125-8-18-x ARTICLE ctivtion genertes rective oxygen species nd impirs metolism secretion coupling in dietic Goto Kkizki nd ouin-treted rt pncretic islets R. Kominto
Dietologi (28) 51:1226 1235 DOI 1.17/s125-8-18-x ARTICLE ctivtion genertes rective oxygen species nd impirs metolism secretion coupling in dietic Goto Kkizki nd ouin-treted rt pncretic islets R. Kominto
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
The activating receptor NKp46 is essential for the development of type 1 diabetes
 A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
Common genetic variation in the melatonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) is associated with decreased early-phase insulin response
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1537 1542 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1392-x ARTICLE Common genetic vrition in the meltonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) is ssocited with decresed erly-phse insulin response C. Lngenerg & L.
Dietologi (2009) 52:1537 1542 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1392-x ARTICLE Common genetic vrition in the meltonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) is ssocited with decresed erly-phse insulin response C. Lngenerg & L.
GLUT4 in the Endocrine Pancreas Indicating an Impact in Pancreatic Islet Cell Physiology?
 442 Originl Bsic in the Endocrine Pncres Indicting n Impct in Pncretic Islet Cell Physiology? Authors I. Bähr 1, I. Bzwinsky-Wutschke 1, S. Wolgst 2, K. Hofmnn 1, S. Streck 1, E. Mühluer 2, D. Wedekind
442 Originl Bsic in the Endocrine Pncres Indicting n Impct in Pncretic Islet Cell Physiology? Authors I. Bähr 1, I. Bzwinsky-Wutschke 1, S. Wolgst 2, K. Hofmnn 1, S. Streck 1, E. Mühluer 2, D. Wedekind
R-α-Lipoic acid and acetyl-l-carnitine complementarily promote mitochondrial biogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 adipocytes
 Dietologi (28) 51:165 174 DOI 1.17/s125-7-852-4 ARTICLE R-α-Lipoic cid nd cetyl-l-crnitine complementrily promote mitochondril iogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 dipocytes W. Shen & K. Liu & C. Tin & L. Yng &
Dietologi (28) 51:165 174 DOI 1.17/s125-7-852-4 ARTICLE R-α-Lipoic cid nd cetyl-l-crnitine complementrily promote mitochondril iogenesis in murine 3T3-L1 dipocytes W. Shen & K. Liu & C. Tin & L. Yng &
CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4 + T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator
 CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
VEGFR-3 controls tip to stalk conversion at vessel fusion sites by reinforcing Notch signalling
 R T I C L E S EGFR-3 controls tip to stlk conversion t vessel fusion sites y reinforcing Notch signlling Tuoms Tmmel 1,9, Georgi Zrkd 1,9, Hrri Nurmi 1, Lrs Jkosson 2,10, Krist Heinolinen 1, Denis Tvorogov
R T I C L E S EGFR-3 controls tip to stlk conversion t vessel fusion sites y reinforcing Notch signlling Tuoms Tmmel 1,9, Georgi Zrkd 1,9, Hrri Nurmi 1, Lrs Jkosson 2,10, Krist Heinolinen 1, Denis Tvorogov
Signals for death and differentiation: a two-step mechanism for in vitro transformation of adult islets of Langerhans to duct epithelial structures
 (23) 1, 987 996 & 23 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 135-947/3 $25. www.nture.com/cdd Signls for deth nd differentition: two-step mechnism for in vitro trnsformtion of dult islets of Lngerhns
(23) 1, 987 996 & 23 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 135-947/3 $25. www.nture.com/cdd Signls for deth nd differentition: two-step mechnism for in vitro trnsformtion of dult islets of Lngerhns
Overcoming EGFR T790M-based Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance with an Allele-specific DNAzyme
 Cittion: Moleculr Therpy Nucleic Acids (214) 3, e15; doi:1.138/mtn.214.3 214 The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy All rights reserved 2162-2531/14 www.nture.com/mtn Overcoming T79M-sed Tyrosine Kinse
Cittion: Moleculr Therpy Nucleic Acids (214) 3, e15; doi:1.138/mtn.214.3 214 The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy All rights reserved 2162-2531/14 www.nture.com/mtn Overcoming T79M-sed Tyrosine Kinse
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Supplemental Materials
 Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
