LKB1 and AMPK regulate synaptic remodeling in old age
|
|
|
- Jasper McCoy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LKB1 nd AMPK regulte synpti remodeling in old ge Melnie A Smuel 1,8, P Emnuel Voinesu 1,8, Brendn N Lilley 1, Rf de Co 2, Mr Foretz 3 5, Benoit Viollet 3 5, Bsil Pwlyk, Mihel A Snderg, Demetrios G Vvvs 7 & Joshu R Snes Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Age-relted dereses in neurl funtion result in prt from ltertions in synpses. To identify moleulr defets tht led to suh hnges, we foused on the outer retin, in whih synpses re mrkedly ltered in old rodents nd humns. We found tht the serine/threonine kinse LKB1 nd one of its sustrtes, AMPK, regulte this proess. In old mie, synpti remodeling ws ompnied y speifi dereses in the levels of totl LKB1 nd tive (phosphorylted) AMPK. In the sene of either kinse, young dult mie developed retinl defets similr to those tht ourred in old wild-type nimls. LKB1 nd AMPK funtion in rod photoreeptors where their loss leds to errnt xonl retrtion, the extension of postsynpti dendrites nd the formtion of etopi synpses. Conversely, inresing AMPK tivity genetilly or phrmologilly ttenutes nd my reverse ge-relted synpti ltertions. Together, these results identify moleulr determinnts of ge-relted synpti remodeling nd suggest strtegies for ttenuting these hnges. The nervous system hnges in mny wys s we ge: sensory, motor nd ognitive funtions derese, nd the risk of neurodegenertive disese inreses 1. Although multiple ftors likely ontriute to gessoited hnges in the nervous system, severl lines of evidene suggest tht defets in synpses hve entrl role 2. Synpses re espeilly vulnerle to dmge s result of their distne from the ell ody, high omplexity nd extensive regultion. In ddition, ge-relted synpti dysfuntion is thought to preipitte neurologil degenertion in ge-relted diseses 3,4. However, the moleulr ltertions tht underlie ge-relted synpti hnges remin unknown 2. A mjor diffiulty in deiphering these moleulr uses is tht most doumented ge-relted ltertions in synpti struture, funtion nd numer re sutle or diffiult to quntify 1,2. To irumvent this prolem, we foused on synpses in the outer retin, whih re prtiulrly lrge nd undergo mrked ge-relted ltertions in rodents nd humns 5 8. In the outer retin, two types of photoreeptors, rods nd ones, form synpses with two types of interneurons, ipolr nd horizontl ells 9,1. In young dults, these synpses lolize to nrrow nd known s the outer plexiform lyer (OPL), where photoreeptor nd interneuron proesses terminte (Fig. 1). In old retin, errnt horizontl nd ipolr neuron proesses sprout fr eyond the OPL into the photoreeptor nuler lyer, where they form numerous etopi synpses. These hnges provide roust struturl iomrker tht we used to ssy ndidte meditors of synpti ging. One promising ndidte is the serine/theonine kinse LKB1 (lso known s Stk11). LKB1 is multifuntionl enzyme tht regultes ellulr energy homeostsis, ell prolifertion, polrity nd xon outgrowth y tivting kinses of the AMPK sufmily, inluding AMPK itself In ddition, LKB1 nd AMPK hve een shown to modulte longevity nd hve een implited in ge-relted diseses, inluding Alzheimer s disese nd ner 18,19. We found tht LKB1 nd AMPK ontriute to the regultion of synpti ging. ge speifilly deresed the tivity of the LKB1-AMPK xis in retin. Intivting either LKB1 or AMPK elerted synpti ging, wheres tivting this signling pthwy genetilly or phrmologilly suppressed the pthologil hnges in old nimls. Finlly, we used single neuron visuliztion pprohes to unover the ellulr sis of synpti ging nd found tht rod xon retrtion is key driver. Together, these results identify the LKB1-AMPK pthwy s moleulr determinnt of ge-relted synpti remodeling nd suggest pprohes for ttenuting this proess. RESULTS Deletion of LKB1 indues ge-relted hnges in young mie Given tht Lk1 null mie die during emryogenesis, we used onditionl llele (Lk1 F/F ) 2 tht is speifilly deleted from retinl progenitors when pired with Six3-Cre, Chx1-Cre or Px-Cre; the resulting mie re referred to s. dult mie ore numerous horizontl nd ipolr ell sprouts tht resemled those of old (24 28 month old) wild-type nimls (Fig. 1 d). Bsed on this similrity, we ompred old wild-type nd young mie in detil. retins developed normlly, ut, y 1 month of ge, sprouts in mie were similr in struture, numer nd length to those in old wild-type mie. (Fig. 1e,f nd Supplementry Fig. 1). Moreover, in oth old wild-type nd young mie, horizontl nd ipolr ell sprouts ofsiulted (Supplementry Fig. 2,) 1 Deprtment of Moleulr nd Cellulr Biology nd Center for Brin Siene, Hrvrd University, Cmridge, Msshusetts, USA. 2 Lortory of Experimentl Gerontology, Trnsltionl Gerontology Brnh, Intrmurl Reserh Progrm, Ntionl Institute on Aging, Bltimore, Mrylnd, USA. 3 Inserm, U11, Institut Cohin, Pris, Frne. 4 CNRS, UMR814, Pris, Frne. 5 Université Pris Desrtes, Soronne Pris Cité, Pris, Frne. The Bermn-Gund Lortory for the Study of Retinl Degenertions, Deprtment of Ophthlmology, Msshusetts Eye nd Er Infirmry, Hrvrd Medil Shool, Boston, Msshusetts, USA. 7 Retin Servie, Angiogenesis Lortory, Msshusetts Eye nd Er Infirmry, Deprtment of Ophthlmology, Hrvrd Medil Shool, Boston, Msshusetts, USA. 8 These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to J.R.S. (snesj@m.hrvrd.edu). Reeived 5 April; epted 1 July; pulished online 3 August 214; doi:1.138/nn.3772 nture NEUROSCIENCE dvne online pulition
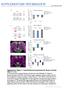
2 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Figure 1 LKB1 deletion indues ge-relted hnges in young mie. () Shemti of retinl struture. A, mrine ell; B, ipolr ell; GCL, gnglion ell lyer; H, horizontl ell; INL, inner nuler lyer; IPL, inner plexiform lyer; ONL, outer nuler lyer; OPL, outer plexiform lyer; RGC, retinl gnglion ell. ( d) Lower power (top row, sle rs represent 25 µm) nd higher power (middle nd ottom rows, sle rs represent 15 µm) imges of rod ipolr nd horizontl ell etopi proesses (rrows) in young nd old wild-type nd young Lk1- defiient dult retins. The dotted line indites the OPL/ONL order. (e,f) Numer nd length of etopi rod ipolr ell dendrites. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 45, 81 nd 51 (e) nd 53, 83 nd 58 (f) mesurements from five young ontrol, old nd mie, respetively. (g) The OPL thinned to similr extent in oth nd old mie reltive to young ontrols. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 55, 428 nd 22 mesurements from four young ontrol, old nd mie, respetively. (h) Mislolized synpses (, green) formed long etopi ipolr proesses (PKCα, red). Sle r represents 15 µm. (i) Synpses in the ONL of nd old mie resemled rod spherule synpses in the OPL of young ontrols y eletron mirosopy. ^ indites ipolr terminl, # indites horizontl terminl. Sle rs represent 25 nm. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P <.1. nd the OPL thinned nd ontined displed nulei (Fig. 1g nd Supplementry Fig. 2,d). Stining with synpti mrkers reveled tht sprouts in nd old nimls were dotted with numerous etopi synpses ering oth pre- nd postsynpti proteins (Fig. 1h nd Supplementry Fig. 3). Eletron mirosopy reveled tht the etopi synpses displyed the trid struture nd rion typil of rod spherule synpses in the OPL of young nimls (Fig. 1i). Although the numer of etopi synpses inresed ~4-fold (see elow), the remodeling involved more thn shift in synpti position, s the totl numer of synpses deresed y ~2% in oth old nd outer retin (3.7 ± 4.4 synpses per 1 µm in young ontrols versus 28.4 ± 4.3 nd 3.9 ± 4.3 in nd old mie, respetively; men ± s.d., P <.1). Control (Lk1 F/F ) retins exhiited proper retinl orgniztion (Fig. 1), s did heterozygotes (Lk1 F/+ ; Six3-Cre nd Lk1 F/+ ; Chx1-Cre), whih retined norml levels of LKB1 despite hving only single opy of Lk1 (Supplementry Fig. 4). We lso reorded eletroretinogrms (ERGs) to determine whether young LKB1-defiient nimls exhiit ltertions in retinl funtion similr to those tht hve een reported for old wild-type mie 21. The ERG -wve represents eletril tivity in photoreeptors, wheres the -wve is derived from summed synpti responses in oth inner nd outer retin. Responses in drk- nd light-dpted retins represent sotopi (rod-dominnt) nd photopi (oneisolted) signls, respetively. Drk-dpted - nd -wve mplitudes were signifintly lower in nimls thn in ontrols (48% nd % redution, respetively; P.4), inditing defet in rodmedited signling. Light-dpted (one) ERG -wves were lso redued (Tle 1 nd Supplementry Fig. 5). Both defets resemle those oserved in old mie 21 (B.P., unpulished dt). e f ONL OPL INL IPL GCL A Numer of sprouts per 1 µm Sprout length (µm) Rods 4 2 B H RGC A Cones B RGC Control 15 Control 18 g OPL thikness (µm) 1 5 Control h ontrol i ontrol ontrol # LKB1 is required in rods to mintin outer retin synpses We next investigted the ellulr sis of these struturl ltertions. In mie, rods omprise the mjority of photoreeptors (97%) nd hve high demnd for energy s result of the iohemistry tht underlies visul trnsdution 22. These fetures mke them good ndidtes for driving LKB1-dependent remodeling. We seletively deleted Lk1 from rod photoreeptors using trnsgeni line tht expresses Cre only in these ells 23. Deletion of Lk1 in rods lone (Lk1 rod ) indued sprouting of oth rod ipolr nd horizontl ells similr to tht oserved in whole retin deletion (Fig. 2). Moreover, Lk1 rod mie developed similr numers of etopi synpses s nd ged nimls (1.7 ±.2 versus 1.2 ±.3 etopi synpses per 1 µm in Lk1 rod nd, respetively; Fig. 2). However, sprouting ws delyed in Lk1 rod retins y pproximtely 1 month ompred with retins (dt not shown), suggesting tht, lthough rods re the primry driver of remodeling, other ells my ontriute. We next sought to distinguish the funtion of LKB1 in development from its roles in synpti mintenne. To this end, we # d Tle 1 Full-field ERG mplitudes in ontrol nd mie Control mie, n = men ± s.e.m. (geometri men) LKB1 mutnts, n = 8 men ± s.e.m. (geometri men) P vlue Rod A-wve (log e µv) 5.18 ±.15 (178 µv) 4.52 ±.7 (92 µv).44 Rod B-wve (log e µv).35 ±.11 (572 µv) 5.42 ±.1 (22 µv) <.1 Cone B-wve (log e µv) 3.8 ±.9 (47 µv) 2.85 ±.11 (17 µv) <.1 Comined dt from equl numers of Lk1 F/F Chx1-Cre nd LKB1 F/F Six3-Cre mie. Clulted for the differene in mens y repeted-mesures regression with the eye s the unit of nlysis using PROC MIXED of SAS llowing for unequl vrines. # dvne online pulition nture NEUROSCIENCE
3 Figure 2 Rods require LKB1 to mintin synpses in the outer retin. () Lk1 deletion in rods lone (Lk1 rod ) indued ge-relted remodeling of rod ipolr nd horizontl ells. Sle r represents 25 µm. () The numer of etopi synpses in Lk1 rod nimls is similr to tht in nd old mie. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 218, 71, 25 nd 183 mesurements in young,, Lk1 rod nd old mie, respetively, from eight young ontrol nd knokout nimls nd four old nimls per group. () Lk1 deletion in young dult retin using AAV-Cre indues neurite remodeling. The dshed line indites the OPL/ONL order. Sle r represents 25 µm. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P <.1. ontrol Lk1 F/F AAV-Cre Lk1 rod Cre synpses per 1 µm 18 Control Lk1 rod Merge 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. used deno-ssoited virus (AAV) 2/5 expressing Cre to delete Lk1 in dults. This serotype infeted photoreeptors seletively (Supplementry Fig. ), llowing for trgeted gene mnipultion. Deletion of Lk1 from dult photoreeptors used sprouting similr to tht oserved in Lk1 rod retins (Fig. 2), inditing tht LKB1 is required for mintenne of norml synpti rhiteture in the OPL. LKB1 funtions through AMPK to regulte synpti ging In view of the prllels etween ged nd nimls, we next sked whether defets in LKB1 signling might led to ge-relted ltertions. We onsidered three possiilities. First, LKB1 levels might deline in ged retin. Immunolotting reveled tht LKB1 levels deresed y ~2% in whole retin nd isolted photoreeptors of old mie (Fig. 3,). This derese ws signifint (P.4) nd might ontriute to ge-relted synpti ltertions, ut seems unlikely to LKB1 retin LKB1 PRs GAPDH Control GAPDH e pmark psad pampk AMPK pacc GAPDH Control CAC- NA1f GAPDH Reltive density d 1.2 f Reltive density g Reltive density Reltive density Control ount for them ompletely. Seond, in the sene of LKB1, ritil synpti omponents might e downregulted or mislolized. This possiility ws suggested y reports tht mutnt mie lking the photoreeptor nerve terminl proteins CACNA1f nd show OPL remodeling tht is similr in some respets to tht in old retin However, no signifint hnge ws oserved in the level or synpti loliztion of these or other synpti proteins y immunolotting or stining (P.7; Figs. 1h nd 3,d, nd Supplementry Fig. 3). Finlly, downstrem omponents of the LKB1 signling pthwy might e ompromised in ged retin. LKB1 phosphoryltes 14 relted serine/threonine kinses t ritil site in n tivtion loop; unless this site is phosphorylted, the kinses re tlytilly intive 11. Of these kinses, t lest eight re good ndidte meditors of the LKB1 effet: SAD-A nd SAD-B, MARK1 4, nd AMPKα1/α2. All of these proteins regulte Totl retin Photoreeptors CACNA1f Control psad pmark pampk AMPK pacc psad pmark pampk AMPK pacc Figure 3 LKB1-AMPK signling is disrupted in old ge. (,) Levels of LKB1 were redued in whole retin nd in photoreeptors from oth nd old mie s ssyed y immunolot nlysis. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. from 18, 17 nd 4 ontrol, old (P =.4) nd (P <.1) nimls per group, respetively, for whole retin, nd 1, 1 nd 4 ontrol, old (P =.5) nd (P =.1) nimls per group, respetively, for photoreeptors. (,d) The levels of nd CACNA1f were not signifintly ltered in old ge. Protein levels in whole retin were ssyed y immunolot nlysis (, quntified in d). Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. from 4 (, P =.783) nd 7 (CACNA1f, P =.73) nimls per group. (e g) Levels of tive phosphorylted SAD- A/SAD-B (psad), MARK1 4 (pmark), AMPK (pampk) nd ACC (pacc) were redued in retin, s determined y immunolot nlysis (e, quntified in f), wheres only pampk nd its trget pacc deresed in old retin (g). Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. from the following sets of ontrol,, young nd old nimls, respetively: psad (n =,, 4, 4; P <.1), pmark (n =, 4, 4, 4; P =.5), pampk (n =, 4, 9, 8; P =. for nd P <.1 old nimls), AMPK (n =, 4, 4, ); pacc (n = 4, 4, 4, 4; P <.1 for nd P =.8 for old nimls). Full-length lots re presented in Supplementry Figure 11. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P <.1. nture NEUROSCIENCE dvne online pulition
4 Ampkα1α2 F/F /AAV-Cre Ampkα1α2 F/F AAVCre + AAVCre synpses per 1 µm Cre Cre d Lk1 rod CA-AMPK CA-AMPK + e synpses per 1 µm Control- Ampkα1α2 F/F AAV2/5-Cre Lk1 rod Lk1 rod +CA-AMPK 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Figure 4 AMPK ts downstrem of LKB1 to mintin retinl synpses. () Deletion of Ampkα1 nd Ampkα2 from photoreeptors (Ampkα1α2/AAV2/5-Cre) indued remodeling (rrows) of rod ipolr nd horizontl ells. Sle r represents 25 µm. (,) Similr levels of etopi synpse formtion (, green) were oserved in Ampkα1α2/AAV2/5 mie s in old nd nimls (, quntified in ). Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 2 nd 28 fields from 4 nimls per group. Sle r represents 25 µm. (d,e) CA-AMPK ttenuted neurl remodeling. Lk1 rod nimls were infeted with AAV2/5 enoding CA-AMPK t P1, nd etopi synpses (, green) were quntified (d, sle r represents 25 µm). CA-AMPK signifintly deresed remodeling in infeted regions (e, dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 241 nd 8 fields from 8 nd 4 Lk1 rod nd Lk1 rod + CA-AMPK nimls, respetively). Dshed lines indite the OPL/ONL order. Nulei, lue. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P <.1. neuronl polrity nd xon outgrowth,14,28 31, nd AMPK is the primry trget through whih LKB1 regultes energy homeostsis 32. Sd, Mrk, Ampk nd Lk1 re ll expressed in retin (Supplementry Fig. 7 nd dt not shown). We proed Lk1-defiient nd old retins with ntiodies speifi for the phosphorylted tivtion loops of SAD, MARK or AMPK proteins. Deletion of Lk1 led to ~75% derese in the levels of phosphorylted SAD, MARK nd AMPK (Fig. 3e,f). In old retin, however, the tivtion levels of ll LKB1 trgets were norml, with the exeption of AMPK. ge indued n ~8% derese in AMPK phosphoryltion (ssyed with n ntiody tht reognizes oth AMPKα1 nd α2), lthough totl AMPK protein levels were unhnged (Fig. 3e,g). Consistent with deresed levels of AMPK tivity, the levels of phosphorylted etyl-coa roxylse (pacc), n AMPK sustrte 32 signifintly delined in oth old nd LKB1-defiient retin (P.8, Fig. 3e g). The derese in phosphorylted AMPK (pampk) in oth LKB1-defient nd old retins suggests tht LKB1 ts through AMPK to mintin retinl synpses nd tht loss of pampk my underlie ge-relted synpti remodeling. Bsed on these results, we sked whether AMPK is required to mintin outer retinl synpses. To irumvent possile developmentl ffets, we used AAV2/5-Cre to intivte oth AMPK suunits in photoreeptors of dult Ampkα1 nd Ampkα2 (lso known Figure 5 Synpti remodeling is ompnied y rod terminl retrtion nd postsynpti sprouting. () Rod xons retrted in LKB1 mutnts, Ampkα1α2/AAV2/5-Cre nimls nd old mie, s visulized y sprse infetion with AAV2/5GFP. Sle r represents 5 µm. Rods (GFP), green; nulei, lue. () Retrted terminls were ontted y etopi rod ipolr ell sprouts. Sle r represents 5 µm. Rods (GFP), green; rod ipolr ells (PKCα), red. (,d) Sprse Lk1 () or Ampkα1α2 (d) deletion in dult retin using AAV-Cre indued single horizontl nd rod ipolr ell sprouts diretly eneth defiient neurons (rrows). Sle rs represent 25 µm. (e) Horizontl ell xons, ut not dendrites, mrkedly remodeled in old nd LKB1 mutnt mie. Sle r represents 5 µm. 4 8 nimls were exmined for eh group. Dshed lines indite the OPL/ONL order. s Prk1 nd Prk2) onditionl doule mutnts (Ampkα1α2 F/F ). AMPK intivtion indued sprouting of rod ipolr nd horizontl ells nd formtion of etopi synpses (Ampkα1α2 F/F /AAV-Cre) t levels similr to those oserved in LKB1 mutnts nd old nimls (Fig. 4 ). These results indite tht similr to LKB1, AMPK is required to prevent ge-relted outer retin remodeling. We then sked whether AMPK funtions downstrem of LKB1. To this end, we generted AAV2/5 enoding onstitutively tive form of AMPK (CA-AMPK) 33 nd used it to infet photoreeptors in Lk1 rod mie shortly fter irth, efore sprouts develop. CA-AMPK redued etopi synpse formtion in infeted regions y ~35% (Fig. 4d,e). This vlue likely underestimtes the effiy of CA-AMPK, s not ll photoreeptors were infeted. Thus, restoring d Control Lk1 F/F low titer AAV Cre Ampk F/F low titer AAV Cre e ontrol Dendrite Ampkα1α2 Ampkα1α2 rod Lk1 AAV2/5-Cre Control rod Lk1 AAV2/5-Cre Axon dvne online pulition nture NEUROSCIENCE
5 Figure Rods drive outer retin synpti remodeling. () Rod terminls retrted frequently in nd old mie, s visulized y infetion with AAV2/5 GFP nd o-stining with the rod terminl mrker PSD95. Rods (GFP), PSD95, red; nulei, lue. Sle r represents 25 µm. White rrows indite terminls in the OPL; mgent rrows indite terminls ove the OPL. Dshed lines indite the OPL/ONL order. (,) The levels of rod retrtion nd etopi synpse formtion were similr. The perentge of retrted terminls () ws quntified on the sis of single neuron terminl morphology (GFP), PSD95 nd nulei o-stining, wheres the perentge of etopi synpses () ws quntified following stining with. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 31, 5 nd 52 () nd 23, 4 nd 53 () mesurements from 3 young ontrol, old nd mie, respetively. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P <.1. AAV-GFP AAV-GFP/PSD95 Merge/Nulei ontrol 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. AMPK funtion in the sene of LKB1 n prevent ge-relted synpti remodeling. Finlly, we tested the speifiity of the LKB1-AMPK pthwy in mintining outer retin synpses using nimls defiient for lterntive signling proteins. Given tht SAD-A nd SAD-B re required for xon formtion in ortex downstrem of LKB1 (ref. ), we tested their role in outer retin using onditionl SAD-A/SAD-B knokouts. Retinl development proeeded normlly in these nimls, nd no etopi synpses were oserved (Supplementry Fig. 8 ). We lso sked whether n lterntive AMPK-tivting kinse, TAK1, might e involved in ge-relted synpti remodeling. Animls defiient in retinl TAK1 showed no evidene of defets or ltertions in outer retin orgniztion (Supplementry Fig. 8d f). Tken together, these results indite tht the LKB1-AMPK pthwy speifilly mintins synpti loliztion. Rod photoreeptor retrtion drives synpti remodeling How might ltertions in the LKB1-AMPK pthwy in rods led to ltertions in horizontl nd ipolr ells? To ddress this issue, we leled individul photoreeptors using AAV2/5-GFP t low titer. We found tht rod xons frequently retrted in young dult, Lk1 rod nd Ampkα1α2 F/F /AAV-Cre mutnts nd in old wild-type mie, ut not in young dult wild-type ontrols (Fig. 5 nd Supplementry Fig. 9). Rod ipolr nd horizontl ells sprouted ner the tips of these xons (Fig. 5 nd dt not shown). To estlish n ssoition etween individul retrted rods nd etopi sprouts, we deleted either Lk1 or Ampk from isolted photoreeptors using AAV2/5-Cre t low titer. Sprouts formed diretly elow Lk1- nd Ampk-defiient ells (Fig. 5,d). Moreover, sprouting ws lrgely restrited to the postsynpti prtners of rods. re polrized, with dendrites ontting ones nd xons ontting rods, nd these omprtments re redily distinguished y their morphology 34 (Fig. 1). In Lk1 mutnts nd old nimls, xons of horizontl ells sprouted fr more thn dendrites (Fig. 5e), onsistent with rod-driven remodeling. Likewise, lthough rod ipolrs sprouted extensively, ipolr sutypes tht seletively ontt ones 35 sprouted rrely (Supplementry Fig. 1). To determine whether rod retrtion ould ount for the level of etopi synpse formtion tht we oserved in young LKB1-defiient nd old wild-type nimls, we leled photoreeptors more densely using AAV2/5-GFP (Fig. ). Setions were o-stined either with PSD-95 to mrk rod spherule synpti terminls 3 or with to mrk ll photoreeptor synpses 37. Quntifition of OPL-restrited nd etopi GFP/PSD95 doule-positive rod spherules reveled tht ~5% of rod terminls were retrted in young LKB1-defiient nd old wild-type nimls (Fig. ). Similr results were otined following Perent retrted terminls 4 2 Control stining nd quntifition for totl etopi synpse formtion (~48%; Fig. ). Thus, rod terminls retrt frequently, nd the perentge of retrted rods terminls is onsistent with the perentge of etopi synpses. In mouse outer retin, rods outnumer ones 5:1. As result, hnges in lrge numers of rods terminls might osure one synpse remodeling. To sk whether one photoreeptors retrt, we leled these neurons nd their pedile synpses with mouse one rrestin. Retrtion ws rre (Supplementry Fig. 1). We did oserve sutle ltertions in one terminl struture in oth old wildtype nd young retins (Supplementry Fig. 1), lthough detiled nlyses of these hnges ws eyond the resolution limit of onfol mirosopy. This ellulr speifiity further emphsizes the prllel etween ge-relted nd LKB1/AMPK-dependent ltertions nd supports the ide tht LKB1-AMPK medited retrtion of mture rods lolly drives ge-relted synpti remodeling. Ative AMPK ttenutes synpti ging The ourrene of ge-relted hnges in young AMPK-defiient mie, together with the mrked derese in AMPK tivtion in old wildtype nimls, suggests tht this signling pthwy my provide trget for suppressing synpti hnges in old nimls. To test this ide, we sked whether retinl ltertions n e reversed in old wild-type nd young dult nd Lk1 rod nimls y diretly enhning AMPK tivity. We infeted photoreeptors with AAV2/5 CA-AMPK fter synpti remodeling hd developed nd quntified the numer of etopi synpses 3 months lter. CA-AMPK deresed synpti Perent etopi synpses 4 2 Control nture NEUROSCIENCE dvne online pulition
6 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Figure 7 Therpeuti ttenution of ge-relted synpti hnges. ( d) CA-AMPK reversed synpti remodeling. Adult LKB1 mutnts (,) nd old (24 months) wild-type mie (,d) were infeted with oth AAV2/5 CA-AMPK nd AAV2/5 GFP (s trer, red). Etopi synpses were quntified 2 months lter. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 153, 14 nd 191 mesurements from 5 young ontrol, nd Lk1 rod nimls, respetively (, P =.2 for nd P =.4 for Lk1 rod ); nd 4 nd 34 fields from 3 young nd old nimls, respetively (d, P =.2). (e,f) The numer of etopi synpses ws quntified in ontrol untreted nd metformin-treted old nimls. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 223, nd 198 fields from 4, 3 nd 4 young, old untreted nd old metformin-treted nimls per group, respetively (f, P <.1). (g,h) Mie were either lorilly restrited (CR) or fed high-ft (HF) diet. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. of 15, 132 nd 55 fields from, 8 nd 3 young, old CR nd old d liitum (AL) nimls per group, respetively (h, P <.1). Sle rs represent 25 µm in,, e nd g. (i,j) Retin from young wild-type (WT) nd old (24M) AL nd CR ontrols were exmined y immunolot for the levels of tivted AMPK (pampk, i). Clori restrition signifintly inresed AMPK tivtion reltive to old AL nimls. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. from nimls per group (j, P =.2 for young ontrol nd P =.3 for old CR versus old AL). Full-length lots re presented in Supplementry Figure 11. Dshed lines indite the OPL/ONL order. Dt were evluted using n unpired, two-tiled Student s t test. P.1, P <.1. remodeling y 17 25% in, Lk1 rod nd old mie (Fig. 7 d). Thus, tive AMPK n diretly redue ge-relted remodeling. We next sked whether ltering the tivity of the LKB1-AMPK xis through dietry or therpeuti interventions ould ffet synpti ging. We tested three regimens known to modulte this signling pthwy: metformin 38, lori restrition nd high-ft diet 39. Quntifition of synpti remodeling showed tht metformin tretment redued etopti synpse remodeling y ~2% reltive to ged ontrol nimls (Fig. 7e,f). In prllel, seprte ohorts of nimls were sujeted to lorilly restrited or high-ft diets. Clori restrition redued the formtion of etopi synpses in outer retins of old mie y 5% reltive to ge-mthed ontrols fed d liitum (Fig. 7g,h) nd restored pampk levels (Fig. 7i,j). Conversely, highft diet inresed synpti misloliztion y 7% (Fig. 7h). Thus, modulting energy homeostsis either genetilly or phrmologilly n help to restore pproprite synpti loliztion in old ge. DISCUSSION Our results suggest tht LKB1 nd its sustrte AMPK re involved in ge-relted remodeling of retinl synpses. In support of this onlusion, we found tht levels of LKB1 nd tive (phosphorylted) AMPK were redued in old retin (Fig. 3), deletion of LKB1 or AMPK led to hnges resemling those in old retin oth qulittively nd quntittively (Figs. 1 nd 4, nd Supplementry Figs. 1 3), expression of onstitutively tive AMPK in old retin ttenuted ge-relted synpti ltertions (Fig. 7 d), nd tretments known to inrese AMPK tivity (metformin nd lori restrition) lso ttenuted these ltertions (Fig. 7e,h). Comining geneti nd imging methods, we found tht LKB1 nd AMPK ted primrily in rod photoreeptors to initite multiellulr sde leding to xon retrtion nd synpti reorgniztion (Figs. 2, 5 nd ). Together, these results provide insights into oth the moleulr nd ellulr ses for synpti ging nd suggest strtegies tht ould e used to ttenute these ltertions. The LKB1-AMPK xis regultes synpti ging Deletion of either LKB1 or AMPK resulted in synpti remodeling tht quntittively nd qulittively mirrored the hnges tht we /Nulei /Nulei e /Nulei g /Nulei CA-AMPK CA-AMPK + 18 CA-AMPK Metformin AL CR CA-AMPK + Metformin + i CR AL pampk GAPDH CA-AMPK synpses per 1 µm doumented in old ge. These prllels inlude photoreeptor xon retrtion, sprouting of horizontl nd ipolr ell proesses, ofsiultion of horizontl nd ipolr ell sprouts, formtion of ultrstruturlly nd moleulrly differentited etopi synpses in the outer nuler lyer, involvement of rods nd their synpti prtners, ut not ones nd their synpti prtners, deresed OPL thikness, nd funtionl defiits s mesured y ERGs. Moreover, the numers of interneuronl sprouts nd etopi synpses nd the length of these sprouts re similr in old nd mutnt retins. Thus, lthough other genes ertinly prtiipte in ge-relted synpti remodeling, our dt suggest tht the LKB1-AMPK xis represents mjor outer retin synpse mintenne pthwy. These kinses re known to regulte lifespn in worms nd flies 15,1, ut they hve not een onsidered to e synpti mintenne regultors in ny speies. Our results lso ddress whether the roles of AMPK nd LKB1 re speifi. Phosphoryltion of AMPK y LKB1 is essentil for AMPK tivity. However, LKB1 phosphoryltes nd tivtes 13 dditionl AMPK-relted kinses 11,4, nd lthough AMPK is mjor sustrte of LKB1, its tivity is regulted through vriety of LKB1- independent pthwys. Two lines of evidene suggest tht AMPK is the d f h synpses per 1 µm synpses per 1 µm synpses per 1 µm j 1.2 Reltive density.8.4 CA-AMPK + ontrol CA-AMPK CA-AMPK + ontrol ontrol AL ontrol CR CR Lk1 rod metformin HF AL dvne online pulition nture NEUROSCIENCE
7 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. mjor LKB1 trget required for synpti mintenne in old ge. First, wheres tivtion of AMPK, MARK nd SAD kinses (MARK1 4, SAD-A nd SAD-B) ll gretly deresed in LKB1 mutnts, only AMPK exhiited deresed tivtion (T loop phosphoryltion) in old retin. Seond, no retinl defets were pprent in SAD-A nd SAD-B doule mutnts, even though they disply sustntil defets in neuronl polriztion nd xonl roriztion in other prts of the nervous system,3,41. Notly, this speifiity is unlikely to reflet restrited expression ptterns, s we nd others hve shown tht SAD kinses nd other LKB1 trgets re rodly expressed,41. In ontrst, it seems unlikely tht the mrked ge-relted deline in AMPK tivity is ompletely result of the modest derese in LKB1 levels. One possiility is tht the ility of LKB1 to tivte AMPK is deresed more thn expeted from the redution in LKB1 protein levels. For exmple, LKB1 might e mislolized or hindered in its ility to intert with its oligte oftors, STRAD nd MO25 (ref. 11). Alterntively, ltertions in the levels of metolites might ffet the ility of AMPK to serve s sustrte for LKB1. Inresed rtios of AMP to ATP result in n AMP-medited struturl shift tht exposes the T-loop tivtion site in the AMPKα suunit, the phosphoryltion of whih is required for AMPK tlyti tivity. Yet nother possiility is tht other kinses tht n phosphorylte the AMPK T-loop, suh s TAK1 nd CAMKK, re ffeted in old retin. However, onditionl TAK1 deletion did not result in ge-relted synpti hnges, nd we found no derese in CAMKKα/β levels in old retin (dt not shown). In ddition, the deresed phosphoryltion of AMPK in LKB1 mutnt retin indites tht in this tissue, s in mny others, LKB1 is the mjor AMPK-tivting kinse. Together, these results suggest tht deresed tivtion of AMPK y LKB1 is mjor driver of synpti remodeling in old retin, ut tht the deresed tivtion results not only from loss of LKB1, ut lso from derese in the ility of AMPK to serve s n LKB1 sustrte. Rods retrtion drives synpti remodeling Synpti remodeling in old outer retin involves ltertions in three neuronl types: photoreeptors, horizontl ells nd ipolr ells. Beuse the photoreeptor synpse is exeptionlly lrge, we were le to nlyze ll three of the synpti prtners using light mirosopy with level of detil tht would not e possile t most rin synpses. This nlysis reveled, unexpetedly, tht mjor ellulr feture of ge-relted remodeling is the retrtion of rod photoreeptor terminls. We provide severl lines of evidene suggesting tht this proess leds seondrily to postsynpti remodeling. First, in old nd LKB1 mutnt retins, rod photoreeptor terminls retrted, ut one photoreeptor terminls did not. Seond, deletion of LKB1 or AMPK from rods lone phenoopied the entire spetrum of ltertions seen in old retin. Third, the level of interneuronl sprouting ould e quntittively ounted for y the inidene of rod retrtion. Fourth, when LKB1 or AMPK ws deleted from only few rods, it ws pprent tht horizontl nd ipolr ell proesses sprout in diret pposition to the retrted rod terminls. Finlly, synpti prtners of rods, rod ipolrs nd horizontl ell xons, sprouted in old retin, wheres synpti prtners of ones, one ipolrs nd horizontl ell dendrites, did not. Thus, onsistent with their role in xon formtion during development,28,29, LKB1 nd AMPK re needed to mintin xonl integrity in old ge. Although our dt indite tht ipolr nd horizontl ells respond to LKB1/AMPK-indued ltertions in rods, it remins unler how ltertions in rods led to interneuron sprouting. One simple possiility is tht interneuronl proesses remin dhesive to retrting photoreeptor terminls nd re therey pulled into the outer nuler lyer; one there, they might mke en pssnt synpses on nery photoreeptor xons. A seond possiility is tht retrting rods relese sprouting ftor, s hs een postulted for the skeletl neuromusulr juntion 42. A third possiility is tht presynpti ltertions my led to dereses in neurotrnsmitter relese tht re sensed y postsynpti prtners nd led to their sprouting. Consistent with this model, muttion of severl genes implited in photoreeptor synpti trnsmission, inluding nd Cn1f, lso led to sprouting of ipolr nd horizontl ells 24 27,43,44. Thus, lthough loss or deloliztion of nd other struturl omponents of synpses re not detetle in old retin, we speulte tht deresed AMPK tivity my t in prt y deresing synpti trnsmission from rods to their trgets. Indeed, synpti trnsmission from rods dereses in old ge 21 nd AMPK ffets neuron exitility nd firing rtes 45. Moreover, the similrity of hnges in nd CACNA1f mutnts to those in old nimls suggests tht rod retrtion my represent ommon mehnism on whih these pthwys onverge. In preliminry single neuron leling studies, we hve oserved xon retrtion in rods lking (S. Srin nd J.R.S., unpulished dt). Implitions for preventing nd reversing synpti ging Three methods of inresing AMPK tivity ttenuted synpti ltertions in old retin: expression of CA-AMPK, dministrtion of metformin nd lori restrition. Among these, lori restrition ws the most effetive, leding to ~5% derese in etopi synpse formtion. This ould imply tht other ftors in ddition to AMPK re involved, ut my merely reflet the ft tht lori restrition ffets ll rods, wheres only smll frtion of the photoreeptors were trnsdued y tive AMPK in our experiments. We lso found tht CA-AMPK n derese synpti remodeling even in ses in whih etopi synpses hve lredy formed, inditing tht onnetivity etween rods nd their postsynpti prtners remins flexile one miswiring develops. Thus, tivtion of AMPK my e le to slow nd even reverse ge-relted synpti deline. Identifition of the LKB1-AMPK pthwy s regultor of synpti ging ws filitted y our use of photoreeptor synpses: these onnetions re prtiulrly lrge, essile nd well hrterized, nd speifi lels re ville tht mrk ll of the synpti prtners. An ovious question is whether this pthwy lso underlies ge-relted ltertions in the smller nd less essile synpses in other prts of the CNS. Although more hllenging, newer higher resolution mirosopy tehniques ould e rought to er on this question. Fvoring this possiility, lori restrition, whih ts in prt through AMPK 4, ttenutes ge-relted ognitive deline in rodents nd humns 47 s well s ge-relted struturl ltertions t peripherl neuromusulr juntion synpses 48. If further nlysis supports this ide, the LKB1-AMPK pthwy ould e n ttrtive trget for interventions imed t mitigting ge-relted synpti deline. Methods Methods nd ny ssoited referenes re ville in the online version of the pper. Note: Any Supplementry Informtion nd Soure Dt files re ville in the online version of the pper. Aknowledgments We thnk memers of our lortory for sientifi disussions nd dvie, nd A. Thnos for help with the AMPK nimls. This work ws funded y the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (AG32322 to J.R.S. nd 5K99AG44444 to nture NEUROSCIENCE dvne online pulition
8 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. M.A. Smuel), the Dmon Runyon Cner Reserh Foundtion (M.A. Smuel), Reserh to Prevent Blindness (J.R.S. nd D.G.V.), the Foundtion Fighting Blindness (B.P.), nd the Intrmurl Reserh Progrm of the Ntionl Institute on Aging (R.d.C.). AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS M.A. Smuel, P.E.V. nd J.R.S. designed the experiments, nd M.A. Smuel nd P.E.V. exeuted them. M.A. Smuel hrterized the LKB1 mutnt nimls, onduted the ging studies, performed the onfol imging nd the quntifition nd nlysis, nd generted ll of the figures. P.E.V. provided the first desription of the LKB1 mutnt niml phenotype nd generted the CA-AMPK AAV. B.N.L. helped with initil oservtions in the LKB mutnts nd provided the SAD onditionl knokouts used in this study. R.d.C. provided the ohorts of ged, treted mie. M.F. nd B.V. generted the AMPK onditionl nimls. B.P. nd M.A. Snderg onduted the ERG experiments. D.G.V. provided guidne on AMPK nd AMPK mutnts nd edited the mnusript. M.A. Smuel nd J.R.S wrote the mnusript. COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS The uthors delre no ompeting finnil interests. Reprints nd permissions informtion is ville online t reprints/index.html. 1. Burke, S.N. & Brnes, C.A. Neurl plstiity in the geing rin. Nt. Rev. Neurosi. 7, 3 4 (2). 2. Morrison, J.H. & Bxter, M.G. The geing ortil synpse: hllmrks nd implitions for ognitive deline. Nt. Rev. Neurosi. 13, (2). 3. Sheff, S.W. & Prie, D.A. Synpti pthology in Alzheimer s disese: review of ultrstruturl studies. Neuroiol. Aging 24, 9 14 (23). 4. Sheff, S.W., Prie, D.A., Shmitt, F.A., DeKosky, S.T. & Mufson, E.J. Synpti ltertions in CA1 in mild Alzheimer disese nd mild ognitive impirment. Neurology 8, (27). 5. Smuel, M.A., Zhng, Y., Meister, M. & Snes, J.R. Age-relted ltertions in neurons of the mouse retin. J. Neurosi. 31, (211).. Liets, L.C., Elisieh, K., vn der List, D.A. & Chlup, L.M. Dendrites of rod ipolr ells sprout in norml ging retin. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 13, 15 1 (2). 7. Elisieh, K., Liets, L.C. & Chlup, L.M. Cellulr reorgniztion in the humn retin during norml ging. Invest. Ophthlmol. Vis. Si. 48, (27). 8. Terzisi, E. et l. Age-dependnt remodeling of retinl iruitry. Neuroiol. Aging 3, (29). 9. Snes, J.R. & Zipursky, S.L. Design priniples of inset nd verterte visul systems. Neuron, 15 3 (21). 1. Mslnd, R.H. The fundmentl pln of the retin. Nt. Neurosi. 4, (21). 11. Alessi, D.R., Skmoto, K. & Byss, J.R. LKB1-dependent signling pthwys. Annu. Rev. Biohem. 75, (2).. Brnes, A.P. et l. LKB1 nd SAD kinses define pthwy required for the polriztion of ortil neurons. Cell 9, (27). 13. Shelly, M., Cnedd, L., Heilshorn, S., Sumre, G. & Poo, M.M. LKB1/STRAD promotes xon initition during neuronl polriztion. Cell 9, (27). 14. Mirouse, V. & Billud, M. The LKB1/AMPK polrity pthwy. FEBS Lett. 585, (211). 15. Funkoshi, M. et l. A gin-of-funtion sreen identifies wd nd lk1 s lifespnextending genes in Drosophil. Biohem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 45, 7 72 (211). 1. Nronne, P. & Roy, R. Cenorhditis elegns duers need LKB1/AMPK to rtion lipid reserves nd ensure long-term survivl. Nture 457, (29). 17. Houtkooper, R.H., Willims, R.W. & Auwerx, J. Metoli networks of longevity. Cell 142, 9 14 (21). 18. Ci, Z., Yn, L.J., Li, K., Quzi, S.H. & Zho, B. Roles of AMP-tivted protein kinse in Alzheimer s disese. Neuromoleulr Med. 14, 1 14 (2). 19. Ollil, S. & Mäkelä, T.P. The tumor suppressor kinse LKB1: lessons from mouse models. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 3, (211). 2. Brdeesy, N. et l. Loss of the Lk1 tumour suppressor provokes intestinl polyposis ut resistne to trnsformtion. Nture 419, (22). 21. Kolesnikov, A.V., Fn, J., Crouh, R.K. & Keflov, V.J. Age-relted deteriorition of rod vision in mie. J. Neurosi. 3, (21). 22. Plzewski, K. Chemistry nd iology of vision. J. Biol. Chem. 287, (2). 23. Li, S. et l. Rhodopsin-iCre trnsgeni mouse line for Cre-medited rod-speifi gene trgeting. Genesis 41, 73 8 (25). 24. Dik, O. et l. The presynpti tive zone protein ssoon is essentil for photoreeptor rion synpse formtion in the retin. Neuron 37, (23). 25. Mnsergh, F. et l. Muttion of the lium hnnel gene Cn1f disrupts lium signling, synpti trnsmission nd ellulr orgniztion in mouse retin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, (25). 2. Chng, B. et l. The no2 mouse, null muttion in Cn1f: ntomil nd funtionl normlities in the outer retin nd their onsequenes on gnglion ell visul responses. Vis. Neurosi. 23, (2). 27. Speht, D. et l. Struturl nd funtionl remodeling in the retin of mouse with photoreeptor synptopthy: plstiity in the rod nd degenertion in the one system. Eur. J. Neurosi. 2, (27). 28. Amto, S. et l. AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes neuronl polriztion y interfering with PI3-kinse loliztion. Siene 332, (211). 29. Willims, T., Courhet, J., Viollet, B., Brenmn, J.E. & Polleux, F. AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) tivity is not required for neuronl development ut regultes xogenesis during metoli stress. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 18, (211). 3. Kishi, M., Pn, Y.A., Crump, J.G. & Snes, J.R. Mmmlin SAD kinses re required for neuronl polriztion. Siene 37, (25). 31. Biernt, J. et l. Protein kinse MARK/PAR-1 is required for neurite outgrowth nd estlishment of neuronl polrity. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, (22). 32. Hrdie, D.G., Ross, F.A. & Hwley, S.A. AMPK: nutrient nd energy sensor tht mintins energy homeostsis. Nt. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, (2). 33. Woods, A. et l. Identifition of phosphoryltion sites in AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) for upstrem AMPK kinses nd study of their roles y site-direted mutgenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 278, (23). 34. Kol, H. The onnetions etween horizontl ells nd photoreeptors in the retin of the t: eletron mirosopy of Golgi preprtions. J. Comp. Neurol. 155, 1 14 (1974). 35. Wässle, H., Puller, C., Müller, F. & Hverkmp, S. Cone ontts, mosis, nd territories of ipolr ells in the mouse retin. J. Neurosi. 29, (29). 3. Koulen, P., Flether, E.L., Crven, S.E., Bredt, D.S. & Wässle, H. Immunoytohemil loliztion of the postsynpti density protein PSD-95 in the mmmlin retin. J. Neurosi. 18, (1998). 37. Brndstätter, J.H., Flether, E.L., Grner, C.C., Gundelfinger, E.D. & Wässle, H. Differentil expression of the presynpti ytomtrix protein ssoon mong rion synpses in the mmmlin retin. Eur. J. Neurosi. 11, (1999). 38. Shw, R.J. et l. The kinse LKB1 medites gluose homeostsis in liver nd therpeuti effets of metformin. Siene 31, (25). 39. Dgon, Y. et l. Nutritionl sttus, ognition nd survivl: new role for leptin nd AMP kinse. J. Biol. Chem. 28, (25). 4. Lizno, J.M. et l. LKB1 is mster kinse tht tivtes 13 kinses of the AMPK sufmily, inluding MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J. 23, (24). 41. Lilley, B.N., Pn, Y.A. & Snes, J.R. SAD kinses sulpt xonl rors of sensory neurons through long- nd short-term responses to neurotrophin signls. Neuron 79, (213). 42. Brown, M.C., Hollnd, R.L. & Hopkins, W.G. Motor nerve sprouting. Annu. Rev. Neurosi. 4, (1981). 43. tom Diek, S. et l. Deletion of the presynpti sffold CAST redues tive zone size in rod photoreeptors nd impirs visul proessing. J. Neurosi. 32, (2). 44. Heseleer, F. et l. Essentil role of C 2+ -inding protein 4, Cv1.4 hnnel regultor, in photoreeptor synpti funtion. Nt. Neurosi. 7, (24). 45. Ikemtsu, N. et l. Phosphoryltion of the voltge-gted potssium hnnel Kv2.1 y AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes memrne exitility. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 18, (211). 4. Stenesen, D. et l. Adenosine nuleotide iosynthesis nd AMPK regulte dult life spn nd medite the longevity enefit of lori restrition in flies. Cell Met. 17, 11 1 (213). 47. Joseph, J., Cole, G., Hed, E. & Ingrm, D. Nutrition, rin ging nd neurodegenertion. J. Neurosi. 29, (29). 48. Vldez, G. et l. Attenution of ge-relted hnges in mouse neuromusulr synpses y lori restrition nd exerise. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 17, (21). dvne online pulition nture NEUROSCIENCE
9 214 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. ONLINE METHODS Mouse strins. (24 3 months) nd young dult (3 5 months) C57BL/J wild-type mie were red in our vivrium or otined from the Ntionl Institute on Aging or the Jkson Lortory. The Lk1 onditionl null mutnt (Lk1 F/F ) hs een desried previously 2 (provided y R. DePinho, Dn-Frer Cner Reserh Institute). In this niml, loxp sequenes flnk exons 2, resulting in trnsltionl frmeshift nd omplete loss of LKB1 funtion. To rodly delete Lk1 in the retin, Lk1 F/F mie were rossed to Six3-Cre 49 (provided y W. Kline, Anderson Cner Center), Chx1-Cre 5 (provided y C. Cepko, Hrvrd University) or Px-Cre 51 (provided y P. Gruss, Mx Plnk Institute) mie to generte nimls generlly referred to here s mie. Similr remodeling phenotypes were oserved in ll LKB1-defiient rosses. All imging nd quntittive histologil nlysis ws performed with Lk1 F/F Chx1-re nimls. RdpsCre 23 mie were rossed to Lk1 F/F nimls to delete Lk1 in rod photoreeptors. Mie rrying the loxp-flnked llele of Tk1 (Tk1 F/F ), nother AMPK phosphorylting kinse 52, hve een desried previously 53 (provided y M. Shneider, Imperil College London) nd were rossed to Nestin-Cre nimls 54 (provided y A. MMhon, Hrvrd University) to rodly delete Tk1 in the retin. Conditionl SAD-A/B nimls were generted y in our lortory 41 nd were rossed to Chx1-Cre nimls to generte Sd-A/B defiient retins for nlysis. The Ampk1 F/F Ampk2 F/F doule onditionl null mutnts (Ampk F/F ) were generted y rossing Ampkα1 F/F nd Ampkα2 F/F nimls (provided y M. Foretz nd B. Viollet, Université Pris Desrtes). In the Ampkα1 line, loxp sequenes flnk exons 4 nd 5, whih inlude the tlyti domin (M. Foretz, unpulished dt), wheres, in the Ampk2 line, loxp sequenes flnk exon C, whih enodes the tlyti domin of AMPKα2 (ref. 55). Experiments were rried out in ordne with protools pproved y the Hrvrd University Stnding Committee on the Use of Animls in Reserh nd Tehing. Tissue preprtion nd immunohistohemistry. Mie were nesthetized with Nemutl nd either enuleted diretly or perfused with phosphte-uffered sline (PBS) followed y 4% prformldehyde (wt/vol) in PBS. Eyes were olleted nd fixed for 3 min in prformldehyde on ie nd then rinsed with PBS. Cryosetions nd whole-mount retins were prepred s desried 5. Briefly, setions were inuted in loking solution (3% norml donkey serum nd.3% Triton X-1 (vol/vol) in PBS), followed y inution with primry nd seondry ntiodies (Invitrogen or Jkson ImmunoReserh). Following wshing, setions were mounted in Vetshield (Vetorls). Retins from 3 9 mie were nlyzed in eh experimentl group. The primry ntiodies in this study reognized the following moleules: lindin (1:2,5, CB38, Swnt), GFP (1:1,, AB191, Chemion), protein kinse Cα (PKCα, 1:5, 31, ACm), potssium/sodium hyperpolriztiontivted yli nuleotide-gted hnnel 4 (HCN4, 1:5, 75-15, Neuroms), lsenilin (KChip, 1:1, 75-5, Neuroms), re (1:5, MMS-1P, Covne), mouse one rrestin (mcar, 1:1,, provided y C. Crft, University of Southern Cliforni 5 ), reoverin (1:4,, AB5585, Millipore), protein kinse A, regultory suunit IIβ (PKARII, 1:1,5, 125, BD Biosienes), PSD-95 (1:2, MA1-4, Thermo Sientifi), RIBEYE (1:5, 192 3, Synpti Systems), (1:5, VAM-PS3, Enzo Life Sienes), Piolo (1:5, 142 3, Synpti Systems), dystrophin (1:2, NCL-DYS2, Novstr), nd dihydropyridine-sensitive lium hnnel α1 suunit (CACNA1, 1:2,, MAB427, Millipore. TO-PRO-3 (Invitrogen) ws used to visulize nulei. Imges were quired on n Olympus FluoView FV1 onfol mirosope nd proessed using ImgeJ. ERG reording. ERGs were reorded from dult (8 9 months old) ontrol Lk1 F/F mie (n = ), Lk1 F/F Chx1-Cre mie (n = 4), nd Lk1 F/F Six3-Cre mie (n = 4). Mie were drk-dpted overnight nd nesthetized with sodium pentoritl injeted intrperitonelly efore testing. Both pupils of eh niml were topilly dilted with phenylephrine hydrohloride nd ylopentolte hydrohloride, nd mie were then pled on heted pltform. Rod dominted responses were eliited in the drk with 1-µs flshes of white light ( d m 2 ) presented t intervls of 1 min in Gnzfeld dome. Light-dpted one responses were eliited with the sme flshes presented t 1 Hz in the presene of 41 d m 2 rod-desensitizing white kground. ERGs were monitored from oth eyes simultneously with silver wire loop eletrode in ontt with eh orne topilly nesthetized with proprine hydrohloride nd wetted with Goniosol nd with sline-soked otton wik in the mouth s the referene; n eletrilly shielded hmer served s ground. All responses were differentilly mplified t gin of 1, ( 3 d t 2 Hz nd 3 Hz; AM52, Tektronix Instruments), digitized t 1-it resolution with n djustle pek-to-pek input mplitude (PCI-251, Ntionl Instruments), nd displyed on personl omputer using ustom softwre (Lview, version 8.2, Ntionl Instruments). Independently for eh eye, one responses were onditioned y -Hz noth filter nd n djustle rtift-rejet window nd were summed (n = 4 2). Eletron mirosopy. Eyeups were fixed suessively in 4% prformldehyde, 2% glutrldehyde for 2 h, in 2% prformldehyde, 4% glutrldehyde for 1 h, nd in 4% glutrldehyde overnight (wt/vol). All solutions were prepred in.1 M odylte uffer. Smples were rinsed in.1 M odylte uffer nd then osmited in 2% OsO 4 (wt/vol) overnight. Ultrthin setions were ut on Lei EMS ultrmirotome to thikness of 5 nm using Ditome 45 degree Ultrut dimond knife nd were olleted on 1 2 mm slotted grids oted with formvr nd ron. The setions were llowed to dry nd were then stined with 2% urnyl ette (wt/vol) for 15 min. They were wshed three times, stined with stilized Reynold s led itrte solution for 1 min nd wshed gin three times. Setions were imged using n FEI Teni G2 Spirit trnsmission eletron mirosope equipped with Gtn mer. AAV-medited neuron leling nd single ell deletion. For AAV-medited neuron leling, young dult ontrol, Lk ret, Lk1 rod (3 5 months) nd old (24 28 months) mie were nesthetized y intrperitonel injetion of ketmine/xylene (1.7 mg per 2 g of ody weight). To lel individul horizontl ells, the suretinl spe ws inoulted with AAV2/2-YC3. (virl stoks generted y the Hrvrd Gene Therpy Institute). YC3. is lium sensor tht omines YFP nd CFP 57, ut in this study ws used only for leling 58. To lel individul photoreeptors, the suretinl spe ws inoulted with AAV2/5-GFP (prepred t the Hrvrd Gene Therpy Institute). Mie were infeted s previously desried 59 using virus diluted to n experimentlly determined optiml titer for single ell leling (1 9 to 1 1 virl genome prtiles per ml). To delete LKB1 from individul photoreeptors, young dult Lk1 F/F, Ampk1 F/F Ampk2 F/F or ontrol nimls (2 months) were infeted with AAV2/5-Cre (Vetor BioLs) to indue either sprse (~1 1 virl genome prtiles per ml) or dense (undiluted) deletion. All nimls were killed 5 8 weeks fter infetion. No remodeling ws oserved in ontrol experiments. Histologil quntifition. All quntifition ws performed using retinl setions prepred from young ontrol,, Lk1 rod, or Ampk1 F/F Ampk2 F/F nimls (3 5 months) nd old mie (24 28 months). To quntify the thikness of the OPL, imges were quired t equivlent retinl eentriities from the opti nerve hed. Lyer width ws mesured using ImgeJ in 5 1 non-onseutive single optil plnes per imge, from t lest four imge stks per retin nd from four nimls per group. To determine the numer of totl nd etopilly lolized -positive punt, retinl setions were stined using ntiody to nd the nuler mrker TO-PRO-3 nd imged t high resolution t equivlent retinl eentriities. An etopi synpse ws defined s positive punt lolized t lest one nuleus ove the OPL. The numer of totl nd etopti punt were determined in single optil setions using ImgeJ. Dt were olleted from 4 8 mie per group. Four imges per retin were nlyzed, nd punt were quntified from 5 1 non-suessive optil setions per imge stk. To quntify the numer nd length of neurite sprouts, retinl setions were stined for rod ipolr ells using PKCα together with TO-PRO-3. The numer nd length of neurite sprouts were determined in 5 8 single optil plnes t lest 3 µm prt. 3 4 imges per retin were nlyzed from five mie per group. To quntify the perentge of retrted rods, rod terminls were visulized using AAV2/5 to lel single neurons together with stining for the nuler mrker TO-PRO-3 nd the rod terminl mrker PSD95. The totl numer of leled terminls nd the numer of those retrted within the ONL were quntified in 5 8 single optil plnes t lest 2 µm prt. Three to four imges per retin were nlyzed from three mie per group. All dt were nlyzed using Prism Grphpd. Quntifition results re represented s r grphs where error rs represent the s.e.m. doi:1.138/nn.3772 nture NEUROSCIENCE
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Stimulation of the insulin/mtor pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
 Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
 Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation of Notch-dependent monociliated choroid plexus tumour cells
 Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Braf V600E cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma
 Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Insulin regulation of heart function in aging fruit flies
 4 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Insulin regultion of hert funtion in ging fruit flies Roert J Wessells, Erin Fitzgerld, Jmes R Cypser, Mr Ttr & Rolf Bodmer Insulin-IGF reeptor
4 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Insulin regultion of hert funtion in ging fruit flies Roert J Wessells, Erin Fitzgerld, Jmes R Cypser, Mr Ttr & Rolf Bodmer Insulin-IGF reeptor
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therapeutic for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant
 Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Systemic Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Reverses Hypoalgesia and Improves Mobility in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Progestin effects on cell proliferation pathways in the postmenopausal mammary gland
 Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
A. B. C. Succiniclasticum. Paraprevotella. Control DPA EPA DHA Control DPA EPA DHA a b. a a. b c.
 389 Session 2: Miroil eosystem nd herivore nutrition Effet of dietry ddition of EPA, DPA nd DHA on rumen teril ommunity in ows nd ewes. An in vitro pproh Dvid Crreño 1, Álvro Belenguer 1, Eri Pinlohe 2,
389 Session 2: Miroil eosystem nd herivore nutrition Effet of dietry ddition of EPA, DPA nd DHA on rumen teril ommunity in ows nd ewes. An in vitro pproh Dvid Crreño 1, Álvro Belenguer 1, Eri Pinlohe 2,
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Epiphyseal growth plate growth hormone receptor signaling is decreased in chronic kidney disease related growth retardation
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
