Preface ORGANIZATION AND CONTENT
|
|
|
- Letitia Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preface Today s massage, bodywork, and fitness professionals are increasingly becoming members of the healthcare team. These professionals collaborate with physicians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, chiropractors, nurse care managers, attorneys, insurance companies, and other healthcare providers. Professionals must have a clear understanding of muscle and joint function beyond simple actions. This allows them to communicate clearly, maintain credibility, and obtain reimbursement for therapeutic work. The emerging requirement for outcome-based justification of treatments further supports the need for a thorough understanding of the body in motion. Functional Anatomy was written to help students of human movement and bodywork understand how anatomical structures work together to create motion. Developing an understanding of the body in all of its complex synchronicity is critical for students of massage and bodywork. These careers require the therapist to create concise and effective treatment plans. Fitness and sports professionals are routinely called upon to analyze complex movement patterns in order to maximize the athlete s performance and prevent injury. Beyond these pragmatic benefits, an understanding of functional anatomy develops heightened intellectual and artistic appreciation of the human body in motion. With a deep understanding of structure function relationships, we begin to see the client s body as a living, breathing, moving marvel. Functional Anatomy: Musculoskeletal Anatomy, Kinesiology, and Palpation for Manual Therapists can assist you in exploring the structures and anatomical relationships responsible for movements such as walking, running, lifting, and throwing. You will be guided through activities that involve inspecting, touching, and moving these structures, enabling you to create a solid, three-dimensional image of the human body and its movement potential. ORGANIZATION AND CONTENT The chapters in Functional Anatomy are organized to build anatomical regions from the ground up. This means deeper structures are identified first, and then structural layers are added. This organization helps readers understand the relationship between static structures such as bones, ligaments, and joint capsules and dynamic functions of muscles. Muscles are presented from superficial to deep to develop systematic palpation skills. Functional Anatomy also groups muscles together functionally. For example, the latissimus dorsi and teres major are located next to each other in the body, have a common insertion, and perform the same actions. Because of this, they are considered sequentially in Chapter 4. The first three chapters in the book describe how the body is put together and how it achieves movement. In Chapter 1, the basic structures and systems of the body, the text s organization of the layers of the human body, and the language of anatomy and movement are discussed and explored. Chapter 2 provides an in-depth investigation of bones and joints, including their basic structure, various shapes and functions, classification, and location of the different types in the body. Chapter 3 delves into skeletal muscles, including their functions, properties, fiber directions and types, the different types of contractions they create, and how they are regulated. After studying these introductory chapters, you should understand the basic structures of the body and methods for creating movement. You will also have developed a language for discussing these concepts. Each of the remaining six chapters explores a specific region of the body. These chapters follow a consistent template, with the same type of information occurring at the same place in each chapter. This predictability will help you locate any topic within a given chapter quickly and easily. The recurring elements in the first half of each chapter include, in order: competency-based objectives overview of the region surface anatomy skeletal structures bony landmark palpation muscle attachment sites joints and ligaments superficial muscles of the region deep muscles of the region special structures located in the region (other than bones, ligaments, and muscles) movements allowed by the region s joints passive and resisted range of motion techniques This opening section is followed by a set of one- or twopage profiles of each muscle pertinent to that region. Profiles include an illustration of the muscle showing its origin, insertion, and fiber arrangement and direction. Text descriptions of the muscle attachments, actions, and innervations are located next to this image. The profile also includes a description of the muscle s functional anatomy; that is, the relationships it has with other muscles, how it works in the body beyond its actions, and common imbalances or dysfunctions associated with it. Finally, the profile explains in simple, easy-to-follow steps how to palpate and fire the muscle against resistance. A photograph shows proper positioning of the practitioner and client, as well as the pertinent bony landmarks and muscle features. The simple, consistent design of each muscle profile
2 ensures ease of use in the classroom or lab, as well as for studying and quick reference. A section discussing the functional aspects of the body region follows the muscle profiles. This section includes information on synergist and antagonist relationships and a photo essay called Putting It in Motion, which explores the structure function relationships involved during activities of daily living and sport. Every chapter of the book closes with a concise summary, review questions, and study activities. The latter includes specific exercises aimed at kinesthetically engaging the covered material. FEATURES Functional Anatomy will guide you to a deeper understanding of the structure and function of the human body by engaging not only your mind, but also your other senses. Features include dynamic, colorful visuals, kinesthetic exercises to enhance your palpatory skills, and individual and group activities. Each region of the body is explored from the inside out to enhance understanding of structural relationships and movement possibilities. Simple, easy-to-follow instructions for palpation of bony landmarks and each muscle profiled are provided. Functional Anatomy recognizes that you may be experiencing the challenges of learning a new language. To help you in acquiring this new language, we include within each muscle profile a guide to correct pronunciation of the muscle name. The student CD also includes an auditory guide to pronunciation, so you can hear proper pronunciation of each muscle profiled. A Synergist/Antagonist table is included in each regional chapter. A photograph of a specific body motion, such as flexion or extension, is accompanied by a list of all muscles that contribute to that motion. Each motion is paired with its opposite in order to help you appreciate balanced muscle relationships. Each regional chapter also discusses and illustrates passive and resisted range of motion procedures for assessing normal joint function. This is included to help you physically access the specific structures identified in this text. As mentioned earlier, each regional chapter contains a section called Putting It in Motion, which identifies and explains specific actions that contribute to motions we use in daily activity or in sports. The photographs of these movements are enhanced to show the pertinent muscle groups driving the action. This feature is linked to the animations on the student resource site, which further explore some of these movements. The Try This activity located at the end of each chapter includes a simple, kinesthetic activity that engages one or more key concepts identified in the chapter. Easy-to-follow steps are listed, as well as any special equipment that may be needed. For example, the Try This in Chapter 1 instructs viii readers to verbally position or move a partner in ways described on cards they create. This activity engages multiple senses and encourages correct use of anatomical terms and concepts. The student resource site for this text has been developed alongside this manuscript in order to ensure strong connections between the special features of the book, student study materials, and teacher resources. Although the text is a stand-alone product, it can be greatly enhanced when used in conjunction with the companion student resource site at thepoint.lww.com/cael. Features of the resource site include animated videos that correspond with the Putting It in Motion segment in each regional chapter. These animations sequentially reveal muscle functions during common activities such as walking, jogging, standing, and throwing. Other features include video footage of palpation, study questions for self-assessment, unlabeled illustrations of regions of the skeleton, a Stedman s audio glossary of the muscles profiled, and searchable full text online. You can use these to label bones and bony landmarks, and/or to add your own drawings of soft-tissue structures such as ligaments, muscles, and special structures. The inside front cover of the text contains more details including the passcode you will need to gain access to the Web site. In addition to the student resources, instructors will also have access to lesson plans, Power Point presentations, and Brownstone Test Generator. DESIGN The design of Functional Anatomy creates a user-friendly, predictable, and interactive experience for readers. The text and art are arranged to allow quick-reference for study as well as maximum usability during classroom activities such as guided palpation exercises. Specific icons identify where these activities are located and when they are linked to the ancillary materials. All of these features will help you develop competency in the key skills identified in each of the chapter objectives. FINAL NOTE I hope that Functional Anatomy helps you discover new and exciting things about the human body. It is intended to enhance your personal and classroom experience and engage you in exploring how the body works. I encourage you to try as many of the activities as possible, utilize the learning tools provided, and embark upon your educational journey with wonder and curiosity. Please contact me at functionalbook@hotmail.com with any comments or suggestions about this book. My students have always been both an inspiration and my toughest critics, and I wish for that to continue. Your perceptions, responses, and experiences with this text are valuable and I am interested in what you have to share. In the meantime, thank you and enjoy. Christy Cael
3 Contents Reviewers Preface vii vi Acknowledgments Chapter 1 ix Introduction to the Human Body Communicating About the Body 2 Regional Terms 2 Anatomical Position 2 Directional Terms 3 Planes of Movement 3 Axes 4 Joint Movements 4 Structures of the Human Body 6 Tissue Types in the Body 6 Epithelial 6 Connective Tissue 7 Muscle Tissue 8 Nervous Tissue 8 Body Structures Involved in Human Movement 8 Bone 8 Shapes of Bones 9 Palpating Bone 9 Ligament 10 Structure of Ligaments 10 Palpating Ligaments 11 Muscle 11 Types of Muscle 11 Palpating Muscle 12 Tendon 12 Shapes of Tendons 13 Palpating Tendons 13 Fascia 13 Structure of Fascia 13 Fascia Layers 14 Palpating Fascia 14 Special Structures 15 Skin 15 Structure of the Skin 15 Palpating Skin 16 Blood Vessels 16 Lymphatic Vessels and Nodes 18 Nerves 18 Cartilage 20 Bursae 20 Chapter 2 Osteology and Arthrology Bones of the Human Skeleton 27 Functions of Bone 27 Support and Protection 27 Movement 27 Hematopoiesis 27 Storage 27 Bone Tissue 27 Spongy Bone 27 Compact Bone 28 The Human Skeleton 28 Shapes of Bones 30 Long Bones 30 Short Bones 32 Flat Bones 32 Irregular Bones 32 Wormian Bones 32 Bony Landmarks 32 Depressions and Openings 32 Projections That Form Joints 32 Attachment Sites 32 Joints of the Human Skeleton 39 Naming Joints 39 Joint Structure 39 Fibrous Joints 39 Cartilaginous Joints 40 Synovial Joints 40 Joint Function 40 Synarthrotic Joints 40 Amphiarthrotic Joints 41 Diarthrotic Joints 41 Structure and Function of Synovial Joints 41 Synovial Joint Anatomy 41 Synovial Joint Types 41 Accessory Motions 43 Roll 43 Glide 44 Spin 45 Chapter 3 Myology Types of Muscle Tissue 50 Smooth Muscle 50 Cardiac Muscle 50 Skeletal Muscle 50
4 Skeletal Muscle Functions 51 Motion 51 Posture 51 Protection 51 Thermogenesis 51 Vascular Pump 51 Fiber Direction and Naming Muscles 51 Parallel Arrangements 51 Fusiform Muscles 51 Circular Muscles 51 Triangular Muscles 51 Pennate Arrangements 53 Unipennate Muscles 53 Bipennate Muscles 53 Multipennate Muscles 53 Naming Muscles 53 Fiber Direction 53 Location 53 Action 53 Size 53 Shape 53 Number of Heads 54 Skeletal Muscle Properties 54 Extensibility 54 Elasticity 54 Excitability 54 Conductivity 54 Contractility 54 Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Tissue 55 Macroscopic Anatomy 55 Microscopic Anatomy 55 Physiology of Muscle Contraction 55 Events at the Neuromuscular Junction 55 Sliding Filament Theory 57 Factors Affecting Force Production 59 Motor Unit Recruitment 59 Cross-Sectional Area 60 Fiber Arrangement 60 Muscle Length 60 Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types 60 Slow Twitch Fibers 60 Fast Twitch Fibers 60 Intermediate Fibers 61 Distribution of Fiber Types 61 Types of Muscle Contractions 61 Isometric Contractions 61 Isotonic Contractions 61 Concentric Contractions 61 Eccentric Contractions 61 Integrating Contraction Types in Human Movement 62 Muscle Relationships 62 Agonists 62 Synergists 62 Antagonists 62 Muscles of the Human Body 63 Levers in the Human Body 65 Components of a Lever 65 Types of Levers 65 First-Class Levers 65 Second-Class Levers 65 Third-Class Levers 65 Proprioception 65 Muscle Spindles 66 Golgi Tendon Organs 68 Other Proprioceptors 68 Vestibular Apparatus 68 Mechanoreceptors 68 Range of Motion 68 Active Range of Motion 68 Passive Range of Motion 69 Resisted Range of Motion 70 Chapter 4 Shoulder and Upper Arm Overview of the Region 75 Surface Anatomy 76 Skeletal Structures 78 Bony Landmarks 80 Muscle Attachment Sites 84 Joints and Ligaments 86 Superficial Muscles 88 Deep Muscles 89 Special Structures 90 Movements Available: Scapula 91 Movements Available: Shoulder 92 Passive Range of Motion 93 Resisted Range of Motion 95 Scapula 95 Shoulder 96 Individual Muscle Profiles 98 Deltoid 98 Pectoralis Major 100 Coracobrachialis 102 Biceps Brachii 103 Pectoralis Minor 104 Subclavius 105 xi
5 Trapezius 106 Levator Scapula 108 Rhomboid Major and Minor 109 Latissimus Dorsi 110 Teres Major 112 Serratus Anterior 113 Supraspinatus 114 Infraspinatus 115 Teres Minor 116 Subscapularis 117 Triceps Brachii 118 Synergists/Antagonists: Scapula 119 Synergists/Antagonists: Shoulder 120 Putting It in Motion 121 Chapter 5 Elbow, Forearm, Wrist, and Hand Overview of the Region 125 Surface Anatomy 126 Skeletal Structures 129 Bony Landmarks 131 Humerus 131 Radius/Ulna 132 Hand 133 Muscle Attachment Sites 136 Joints and Ligaments 138 Superficial Muscles 141 Deep Muscles 143 Special Structures 144 Movements Available: Elbow and Wrist 147 Movements Available: Hand 148 Passive Range of Motion 150 Resisted Range of Motion 153 Individual Muscle Profiles 157 Brachialis 157 Brachioradialis 158 Flexor Carpi Radialis 159 Palmaris Longus 160 Flexor Carpi Ulnaris 161 Flexor Digitorum Superficialis 162 Flexor Digitorum Profundus 163 Flexor Pollicis Longus 164 Pronator Teres 165 Pronator Quadratus 166 Supinator 167 Anconeus 168 Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus 169 Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis 170 Extensor Carpi Ulnaris 171 Extensor Digitorum 172 Extensor Indicis 173 Extensor Digiti Minimi 174 Abductor Pollicis Longus 175 xii Extensor Pollicis Brevis 176 Extensor Pollicis Longus 177 Intrinsic Hand Muscles 178 Synergists/Antagonists: Elbow and Wrist 180 Synergists/Antagonists: Hand 181 Putting It in Motion 182 Chapter 6 Head, Neck, and Face Overview of the Region 187 Surface Anatomy 188 Skeletal Structures 190 Bony Landmarks 194 Muscle Attachment Sites 197 Joints and Ligaments 200 Superficial Muscles 204 Intermediate Muscles 205 Deep Muscles 206 Muscles of the Face 207 Special Structures 208 Posture of the Head and Neck 212 Movements Available: Neck 213 Movements Available: Jaw 214 Facial Expression 215 Passive Range of Motion 216 Resisted Range of Motion 218 Individual Muscle Profile 220 Sternocleidomastoid 220 Scalenes 221 Platysma 222 Longus Colli 223 Longus Capitis 224 Suprahyoids 225 Digastric 226 Infrahyoids 227 Splenius Capitis 228 Splenius Cervicis 229 Semispinalis 230 Rectus Capitis Posterior Major 231 Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor 232 Obliquus Capitus Superior 233 Obliquus Capitis Inferior 234 Rectus Capitis Anterior 235 Rectus Capitis Lateralis 236 Temporalis 237 Masseter 238 Medial Pterygoid 239 Lateral Pterygoid 240 Synergists/Antagonists: Head and Neck 241 Synergists/Antagonists: Jaw 242 Putting It in Motion 243
6 Chapter 7 Trunk Overview of the Region 247 Surface Anatomy 248 Skeletal Structures 250 Bony Landmarks 256 Muscle Attachment Sites 260 Joints and Ligaments 262 Superficial Muscles 264 Intermediate Muscles 265 Deep Muscles 266 Special Structures 268 Posture of the Trunk 274 Movements Available: Trunk 276 Movements Available: Breathing 277 Resisted Range of Motion 278 Individual Muscle Profiles 280 Rectus Abdominus 280 External Oblique 281 Internal Oblique 282 Transverse Abdominus 283 Diaphragm 284 External Intercostals 285 Internal Intercostals 286 Iliocostalis 287 Longissimus 288 Spinalis 289 Quadratus Lumborum 290 Serratus Posterior Superior 292 Serratus Posterior Inferior 293 Semispinalis 294 Multifidi 295 Rotatores 296 Interspinalis 297 Intertransversarii 298 Other Muscles Involved in Breathing 299 Synergists/Antagonists: Trunk 300 Synergists/Antagonists: Breathing 301 Putting It in Motion 302 Chapter 8 Pelvis, Thigh, and Knee Overview of the Region 307 Surface Anatomy 308 Skeletal Structures 310 Bony Landmarks of Skeletal Structures 312 Muscle Attachment Sites 317 Joints and Ligaments 318 Superficial Muscles 320 Deep Muscles 322 Special Structures 324 Posture of the Hip and Knee 326 Movements Available: Hip 327 Movements Available: Knee 328 Passive Range of Motion 329 Resisted Range of Motion 332 Individual Muscle Profiles 335 Psoas 335 Iliacus 336 Sartorius 338 Tensor Fascia Latae 340 Rectus Femoris Vastus Lateralis 342 Vastus Medialis 343 Vastus Intermedius 344 Pectineus 346 Adductor Brevis 347 Adductor Longus 348 Gracilis 349 Adductor Magnus 350 Gluteus Maximus 351 Gluteus Medius 352 Gluteus Minimus 353 Piriformis 354 Superior Gemellus 355 Inferior Gemellus 356 Obturator Internus 357 Obturator Externus 358 Quadratus Femorus 359 Biceps Femoris 360 Semimembranosis 361 Semitendinosis 362 Popliteus 363 Synergists/Antagonists: Hip 364 Synergists/Antagonists: Knee 365 Putting It in Motion 366 Chapter 9 Leg, Ankle, and Foot Overview of the Region 371 Surface Anatomy 372 Skeletal Structures 374 Bony Landmarks of Skeletal Structures 376 Muscle Attachment Sites 380 Joints and Ligaments 382 Superficial Muscles 384 Deep Muscles 386 Special Structures 388 Posture of the Ankle and Foot 390 Movements Available: Ankle 391 Movements Available: Foot 392 Gait Cycle 394 Passive Range of Motion 396 xiii
7 Resisted Range of Motion 399 Individual Muscle Profiles 402 Tibialis Anterior 402 Extensor Digitorum Longus 403 Extensor Hallucis Longus 404 Peroneus Longus 405 Peroneus Brevis 406 Peroneus Tertius 407 Gastrocnemius 408 Soleus 409 Plantaris 410 Tibialis Posterior 411 Flexor Digitorum Longus 412 Flexor Hallucis Longus 413 Foot Intrinsic Muscles 414 Synergists/Antagonists: Ankle and Foot 417 Putting It in Motion 418 Appendix: Answers to chapter Review Questions 422 Glossary of Terms 425 Bibliography 431 Index 433 xiv
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
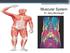
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association
 C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley,
 Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
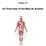 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Name Phone ( ) DOB. Address City State Zip. Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( Occupation Male Female Physician
 Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
PAB Test Manual. Introduction
 PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
STRETCHING. Benefits of stretching
 STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk
 The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The muscular system I Muscles of the head neck and trunk Dr. Nabil Khouri Dr. Nabil Khouri MD MSc, PhD Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Muscle. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8
 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
5 Specification Content
 5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
5 Specification Content These specifications are set out in the form of teaching modules. Each teaching module is assessed by its associated unit of assessment. 5.1 Module 2562: The Application of Physiological
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft organs
Human Anatomy Unit 2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft organs
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Anatomy Module Study Guide
 Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Muscular System. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
2/4/2018. Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue. Ch.7 Review. Sternocleidomastoid.
 Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Ch.7 Review Identify the two reasons why muscle cells may go through muscle fatigue Temporalis Depressor anguli oris Sternocleidomastoid Tibialis anterior 1 Gluteus medius Deltoid Adducts & rotates scapula
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1 Fall 2015 1. Muscle cells exhibit the greatest ability to shrink -- this quality of all protoplasm is: a. voluntary b. involuntary c. fusiform d. contractility e. conductivity
Muscle Lecture Test Questions Set 1 Fall 2015 1. Muscle cells exhibit the greatest ability to shrink -- this quality of all protoplasm is: a. voluntary b. involuntary c. fusiform d. contractility e. conductivity
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST
 ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Lowe w r e r B ody Resistance Training
 Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
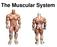 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
A-LEVEL PE SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 A-LEVEL PE - 2018 SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Physiological factors affecting performance is one of the units you will study in A Level Physical Education. Physiological factors affecting performance,
A-LEVEL PE - 2018 SUMMER HOMEWORK ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Physiological factors affecting performance is one of the units you will study in A Level Physical Education. Physiological factors affecting performance,
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
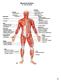 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Pain Assessment. Dana Calhoun, LMT Updated 2/2/2018
 Pain Assessment Dana Calhoun, LMT Updated 2/2/2018 What is Pain? The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defines pain as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with
Pain Assessment Dana Calhoun, LMT Updated 2/2/2018 What is Pain? The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defines pain as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially
 NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially designed to stimulate the body-mind complex to resolve injury, stress, and pain. Unlike other therapeutic
NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially designed to stimulate the body-mind complex to resolve injury, stress, and pain. Unlike other therapeutic
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
