Atlas A. Lecture Outline A-1. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
|
|
|
- Gabriel Barnard Potter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atlas A Lecture Outline Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. A-1
2 Atlas A (Orientation to Anatomy) Anatomical position Anatomical planes Directional terms Body regions Body cavities and membranes Organ systems Visual survey of the body Thyroid cartilage of larynx Thyroid gland Brachial nerve plexus Superior vena cava Coracobrachialis m. Humerus Lobes of lung Small intestine Cecum Appendix Tensor fasciae latae m. Pectineus m. Adductor longus m. Gracilis m. Adductor magnus m. Brachiocephalic v. Subclavian v. Subclavian a. Aortic arch Axillary v. Axillary a. Cephalic v. Brachial v. Brachial a. Heart Spleen Stomach Large intestine Penis (cut) Ductus deferens Epididymis T estis Scrotum Rectus femoris m. Figure A.14 A-2
3 Anatomical Position Person stands erect Feet flat on floor Arms at sides Palms, face & eyes facing forward Standard frame of reference for anatomical descriptions & dissection McGraw-Hill Companies/Joe DeGrandis, photographer Figure A.1 A-3
4 Forearm Positions When supinated palms face forward or upward radius & ulna are parallel When pronated palms face rearward or downward radius & ulna are crossed Figure A.2 A-4
5 Anatomical Planes and Sections Transverse plane McGraw-Hill Companies/Joe DeGrandis, photographer Figure A.3 Frontal plane Sagittal plane Section implies actual cut or slice to reveal internal anatomy Plane implies an imaginary flat surface passing through the body Sagittal plane divides body into right and left regions median (midsagittal) plane divides body or organ into equal halves Frontal (coronal) plane divides body into anterior (front) & posterior (back) portions Transverse (horizontal) plane divides the body into superior (upper) & inferior (lower) portions A-5
6 Anatomical Sections (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Sagittal Frontal Transverse Figure A.4 A-6
7 Directional Terms Ventral / Dorsal Superior / Inferior Medial / Lateral Anterior /Posterior Proximal / Distal Superficial / Deep Cephalic Rostral Caudal Intermediate directions - often given as combinations of these terms (ex. dorsolateral) Different meanings for humans and four-legged animals anterior = ventral surface of human front of chest & abdomen anterior (cranial) in a four-legged animal is head end posterior = dorsal surface of human last in locomotion back side posterior (caudal) in a four-legged animal is tail end A-7
8 Body Regions Axial region = head, neck, & trunk thoracic region = trunk above diaphragm abdominal region = trunk below diaphragm divided into quadrants divided into nine regions by tic-tac-toe grid Appendicular region = upper & lower limbs upper limb arm (brachial region), forearm (antebrachial region), wrist (carpal region), hand (manual region), fingers (digits) lower limb thigh (femoral region), leg (crural region), ankle (tarsal region), foot (pedal region), toes (digits) A-8
9 Abdominal Quadrants and Regions Quadrants Regions Right upper quadrant Left upper quadrant Hypochondriac region Subcostal line Epigastric region Lumbar region Umbilical region Right lower quadrant Left lower quadrant Intertubercular line Inguinal region Midclavicular line Hypogastric region (a) (c) Figure A.6 A-9
10 Anatomical Terminology (ventral) Cephalic r. (head) Facial r. (face) Upper limb: Acromial r. (shoulder) Axillary r. (armpit) Brachial r. (arm) Cubital r. (elbow) Antebrachial r. (forearm) Carpal r. (wrist) Palmar r. (palm) Lower limb: Coxal r. (hip) Patellar r. (knee) Cervical r. (neck) Thoracic r. (chest): Sternal r. Pectoral r. Umbilical r. Abdominal r. Inguinal r. (groin) Pubic r.: Mons pubis External genitalia: Penis Scrotum Testes Lower limb: Femoral r. (thigh) (a) Anterior (ventral) Crural r. (leg) Tarsal r. (ankle) Pedal r. (foot): Dorsum Plantar surface (sole) McGraw-Hill Companies/Joe DeGrandis, photographer Figure A.5 (b) Anterior (ventral) A-10
11 Anatomical Terminology (dorsal) Cranial r. Nuchal r. (back of neck) Interscapular r. Scapular r. Vertebral r. Lumbar r. Sacral r. Gluteal r. (buttock) Dorsum of hand Perineal r. Femoral r. Popliteal r. Crural r. (c) Posterior (dorsal) Tarsal r. Calcaneal r. (heel) McGraw-Hill Companies/Joe DeGrandis, photographer Figure A.5 (d) Posterior (dorsal) A-11
12 Body Cavities and Membranes Thoracic cavity Diaphragm Abdominal cavity Pelvic cavity Cranial cavity Vertebral canal Major body cavities cranial cavity vertebral canal meninges thoracic cavity abdominopelvic cavity abdominal cavity pelvic cavity Lined by serous membranes (a) Left lateral view Figure A.7 Filled with viscera A-12
13 Cranial Cavity & Vertebral Canal Cranial cavity Thoracic cavity Diaphragm Abdominal cavity Vertebral canal cranial cavity contains brain lined with meninges vertebral canal contains the spinal cord lined with meninges Pelvic cavity (a) Left lateral view Figure A.7 A-13
14 Thoracic Cavity Mediastinum - region between lungs heart, major blood vessels, esophagus, trachea, & thymus Pericardium around heart visceral pericardium parietal pericardium pericardial cavity pericardial fluid Diaphragm Thoracic cavity: Pleural cavity Mediastinum Pericardial cavity Abdominopelvic cavity: Abdominal cavity Pleura around lungs visceral pleura parietal pleura pericardial cavity pericardial fluid (b) Anterior view Figure A.7 Pelvic cavity A-14
15 Pericardial Membranes Parietal pericardium Pericardial cavity Visceral pericardium Heart Diaphragm (a) Pericardium Figure A.8a A-15
16 Pleural Membranes Parietal pleura Pleural cavity Visceral pleura Lung Diaphragm (b) Pleurae Figure A.8b A-16
17 Abdominopelvic Cavity Thoracic cavity: Pleural cavity Mediastinum Pericardial cavity Diaphragm Abdominopelvic cavity: Abdominal cavity (b) Anterior view Pelvic cavity Pelvic brim separates abdominal & pelvic cavities Figure A.7 abdominal cavity contains most digestive organs, kidneys & ureters pelvic cavity contains rectum, urinary bladder, urethra & reproductive organs Peritoneum - Serous Membranes of Abdominopelvic cavity visceral peritoneum - peritoneal cavity parietal peritoneum - peritoneal fluid A-17
18 Retroperitoneal Organs Posterior 2nd lumbar vertebra Back muscles Kidney Liver Renal vein and artery Inferior vena cava Aorta Intestine Anterior Spinal cord Fat Dorsal mesentery Parietal peritoneum Visceral peritoneum (serosa) Peritoneal cavity Omentum or other ventral mesentery Kidneys, Ureters, Adrenal Glands, most of Pancreas, Abdominal portions of Aorta and Inferior Vena Cava Figure A.9 A-18
19 Intraperitoneal Organs organs encircled by peritoneum and connected to posterior body wall by peritoneal sheets dorsal mesentery suspends intestines from posterior abdominal wall mesocolon dorsal mesentery of large intestine ventral mesentery suspends viscera from anterior abdominal wall greater omentum inferolateral border of stomach overlies intestines - fatty apron lesser omentum superomedial border of stomach to liver serosa outer layer of an organ formed when the visceral peritoneum divides and wraps around the organ A-19
20 Membranes of Abdominal Cavity Diaphragm Liver Serosae Stomach Greater omentum Large intestine Lesser omentum Pancreas Duodenum Dorsal mesentery Small intestine Parietal peritoneum Peritoneal cavity Urinary bladder Visceral peritoneum Rectum Figure A.10 A-20
21 Potential Spaces Found between two membranes normally pressed firmly together not physically attached, may separate, and fill with fluid in unusual situations Examples pleural cavity air or fluid can accumulate between parietal and visceral pleura forming a space uterus in a nonpregnant uterus, mucous membranes of walls are in contact A-21
22 11 Organ Systems Protection, Support, and Movement Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Internal Communications & Integration Nervous System Endocrine System Fluid Transport Circulatory System Lymphatic System Defense Immune (Lymphatic System) Input and Output Respiratory System Urinary System Digestive System Reproduction Reproductive System A-22
23 Organ Systems (1) Principal organs: Skin, hair, nails, cutaneous glands Principal functions: Protection, water retention, thermoregulation, vitamin D synthesis, cutaneous sensation, nonverbal communication Principal organs: Bones, cartilages, ligaments Principal functions: Support, movement, protective enclosure of viscera, blood formation, electrolyte and acid base balance Principal organs: Skeletal muscles Principal functions: Movement, stability, communication, control of body openings, heat production Principal organs: Lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, thymus, spleen, tonsils Principal functions: Recovery of excess tissue fluid, detection of pathogens, production of immune cells, defense against disease Integumentary system Skeletal system Muscular system Lymphatic system Figure A.11 A-23
24 Organ Systems (2) Principal organs: Nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs Principal functions: Absorption of oxygen, discharge of carbon dioxide, acid base balance, speech Principal organs: Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra Principal functions: Elimination of wastes; regulation of blood volume and pressure; stimulation of red blood cell formation; control of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance; detoxification Principal organs: Brain, spinal cord, nerves, ganglia Principal functions: Rapid internal communication, coordination, motor control and sensation Principal organs: Pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, testes, ovaries Principal functions: Hormone production ; internal chemical communication and coordination Respiratory system Urinary system Nervous system Endocrine system Figure A.11 A-24
25 Organ Systems (3) Principal organs: Heart, blood vessels Principal functions: Distribution of nutrients, oxygen, wastes, hormones, electrolytes, heat, immune cells, and antibodies; fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance Principal organs: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas Principal functions: Nutrient breakdown and absorption. Liver functions include metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals; synthesis of plasma proteins; disposal of drugs, toxins, and hormones; and cleansing of blood. Principal organs: Testes, epididymides, spermatic ducts, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands, penis Principal functions: Production and delivery of sperm; secretion of sex hormones Principal organs: Ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, mammary glands Principal functions: Production of eggs; site of fertilization and fetal development; fetal nourishment; birth; lactation; secretion of sex hormones( Circulatory system Digestive system Male reproductive system Female reproductive system Figure A.11 A-25
26 Superficial Anatomy (female) Platysma Trapezius m. Clavicle Deltoid m. Pectoralis major m. Cephalic v. Breast Biceps brachii m. External abdominal oblique m. Sheath of rectus abdominis m. Umbilicus Inguinal ligament Tensor fasciae latae m. Sartorius m. Femoral vein Great saphenous vein Anterior superior spine of ilium Mons pubis Adductor longus m. Gracilis m. Vastus lateralis m. Rectus femoris m. Figure A.12 A-26
27 Visceral Anatomy (male) 1 Internal jugular v. External jugular v. Omohyoid m. Clavicle Internal intercostal mm. External intercostal mm. Costal cartilages Liver Gallbladder External abdominal oblique m. Internal abdominal oblique m. Transverse abdominal m. Greater omentum Common carotid a. Sternum Subscapularis m. Coracobrachialis m. Lung Pericardium Pleura Diaphragm Stomach Large intestine Urinary bladder Penis Scrotum Femoral n. Femoral a. Femoral v. Figure A.13 A-27
28 Visceral Anatomy (male) 2 Thyroid cartilage of larynx Thyroid gland Brachial nerve plexus Superior vena cava Coracobrachialis m. Humerus Lobes of lung Brachiocephalic v. Subclavian v. Subclavian a. Aortic arch Axillary v. Axillary a. Cephalic v. Brachial v. Brachial a. Heart Spleen Stomach Large intestine Small intestine Cecum Appendix Tensor fasciae latae m. Pectineus m. Adductor longus m. Gracilis m. Adductor magnus m. Rectus femoris m. Penis (cut) Ductus deferens Epididymis T estis Scrotum Figure A.14 A-28
29 Retroperitoneal Anatomy (female) Superior vena cava Trachea Bronchus Esophagus Pleural cavity Lung (sectioned) Thoracic aorta Hepatic vv. Inferior vena cava Splenic a. Duodenum Superior mesenteric v. Abdominal aorta Common iliac a. Ureter Ovary Uterine tube Uterus Urinary bladder Pectineus m. Gracilis m. Adductor longus m. Spleen Adrenal gland Pancreas Kidney Superior mesenteric a. Inferior mesenteric a. Tensor fasciae latae m. (cut) Sartorius m. (cut) Rectus femoris m. (cut) Adductor brevis m. Vastus intermedius m. Adductor longus m. (cut) Vastus lateralis m. Vastus medialis m. Figure A.15 A-29
30 Dorsal Body Wall (female) Right common carotid a. Right subclavian a. Brachiocephalic trunk External intercostal m. Ribs Internal intercostal m. Left common carotid a. Left subclavian a. Thoracic aorta Esophagus Diaphragm Abdominal aorta Quadratus lumborum m. Psoas major m. Iliacus m. Gluteus medius m. Rectum Vagina Urethra Femur Gracilis m. Adductor longus m. Intervertebral disc Lumbar vertebra Iliac crest Ilium Sacrum Anterior superior spine of ilium Brim of pelvis Adductor magnus m. Adductor brevis m. Figure A.16 A-30
31 Median Section of the Head Scalp Cranium Cerebrum Frontal sinus Nasal cavity Brainstem Palate Oral cavity Tongue Cerebellum Foramen magnum of skull Epiglottis Pharynx Spinal cord Vertebral column Vocal cord Larynx Trachea Intervertebral discs Esophagus McGraw-Hill Companies/Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections Figure A.17 A-31
32 Dissection of Thoracic Cavity Internal jugular v. Subclavian v. Nerves Lungs Ribs Heart Diaphragm Figure A.18 McGraw-Hill Companies A-32
33 Transverse Section of Thorax Anterior Pectoralis major m. Ventricles of heart Fat of breast Sternum Ribs Pericardial cavity Atria of heart Left lung Pleural cavity Right lung Esophagus Aorta Vertebra Spinal cord Posterior McGraw-Hill Companies/Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections Figure A.19 A-33
34 Dissection of Abdomen Lung Diaphragm Transverse colon Gallbladder Small intestine Mesenteric arteries and veins Mesentery Descending colon Cecum Figure A.20 Sigmoid colon McGraw-Hill Companies/Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections A-34
35 Transverse Section of Abdomen Duodenum Stomach Large intestine Pancreas Kidney Anterior Subcutaneous fat Rectus abdominis m. Superior mesenteric artery and vein Inferior vena cava Liver Peritoneal cavity Perirenal fat of kidney Erector spinae m. Peritoneum Aorta Vertebra Posterior Spinal cord McGraw-Hill Companies/Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections Figure A.21 A-35
36 Median Section of Male Pelvic Region Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Sigmoid colon Seminal vesicle Prostate gland Penis: Root Bulb Rectum Shaft: Corpus cavernosum Anal canal Anus Corpus spongiosum Epididymis Figure A.22 Glans (a) Male The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Dennis Strete, photographer Scrotum Testis A-36
37 Median Section of Female Pelvic Region Vertebra Red bone marrow Mesentery Small intestine Intervertebral disc Sacrum Sigmoid colon Uterus Cervix Urinary bladder Pubic symphysis Urethra Vagina Labium minus Prepuce Labium majus Rectum Anal canal Anus Figure A.22 (b) Female McGraw-Hill Companies/Rebecca Gray, photographer/don Kincaid, dissections A-37
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
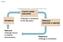 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Lab Activity 1. Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
8/27/2017. The Human Body: An Orientation. Homeostasis BODY SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER TO MAINTIN HOMEOSTASIS. Chapter 1 Part B
 Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Date Lab Pd. Lecture Notes (57)
 Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Name SECTION OBJECTIVES Describe the locations of the major body cavities List the organs located in each major body cavity Name the membranes associated with the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Name
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
NOSE GOES. What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent?
 1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
1 The Human Body An Orientation What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? Anatomy & Physiology anatomy - study
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Classification of Living
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: ext. 6049
 Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Human Anatomy and Physiology (ANAT 5) Mrs. Fulton Phone: 645-1300 ext. 6049 Please, read your green sheets. 1 Lecture #1 A. Definitions: anatomy, physiology B. Requirements of an Organism C. Homeostasis
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology
 Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Unit I: Introduction to Anatomy & Physiology Written Response #1: Read the passage and explain what happened to Kati at the London Marathon. In 2007, Kati Mori took part in the London Marathon her fourth,
Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization 1. Anatomy and physiology is the relationship of the structure and function of the human body. a. Architect Louis Henry Sullivan coined the phrase Form follows function.
Chapter 1 Introduction and Organization 1. Anatomy and physiology is the relationship of the structure and function of the human body. a. Architect Louis Henry Sullivan coined the phrase Form follows function.
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
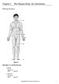 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Practical #1 Checklist Spring 2010
 External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
