Evolution of metal hyperaccumulation required cis-regulatory changes and triplication of HMA4
|
|
|
- Harry Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol My 28 doi:1.138/nture6877 LETTERS Evolution of metl hyperumultion required is-regultory hnges nd triplition of HMA4 Mr Hnikenne 1 {*, In N. Tlke 1 {*, Mihel J. Hydon 1 {, Christ Lnz 2, Andre Nolte 1 {, Ptrik Motte 3,4, Juergen Kroymnn 5, Detlef Weigel 2 & Ute Krämer 1 { Little is known out the types of muttions underlying the evolution of speies-speifi trits. The metl hyperumultor Aridopsis hlleri hs the rre ility to olonize hevy-metlpolluted soils, nd, s n extremophile sister speies of Aridopsis thlin, it is powerful model for reserh on dpttion 1 3. A. hlleri nturlly umultes nd tolertes lef onentrtions s high s 2.2% zin nd.28% dmium in dry iomss 4.On the sis of trnsriptomis studies, metl hyperumultion in A. hlleri hs een ssoited with more thn 3 ndidte genes tht re expressed t higher levels in A. hlleri thn in A. thlin 4 6. Some of these genes hve een genetilly mpped to rod hromosoml segments of etween 4 nd 24 M o-segregting with Zn nd Cd hypertolerne 7 9. However, the in plnt loss-of-funtion pprohes required to demonstrte the ontriution of given ndidte gene to metl hyperumultion or hypertolerne hve not een pursued to dte. Using RNA interferene to downregulte HMA4 (HEAVY METAL ATPASE 4) expression, we show here tht Zn hyperumultion nd full hypertolerne to Cd nd Zn in A. hlleri depend on the metl pump HMA4. Contrry to postulted glol trns regultory ftor governing high expression of numerous metl hyperumultion genes, we demonstrte tht enhned expression of HMA4 in A. hlleri is ttriutle to omintion of modified is-regultory sequenes nd opy numer expnsion, in omprison to A. thlin. Trnsfer of n A. hlleri HMA4 gene to A. thlin repitultes Zn prtitioning into xylem vessels nd the onstitutive trnsriptionl upregultion of Zn defiieny response genes hrteristi of Zn hyperumultors. Our results demonstrte the importne of is-regultory muttions nd gene opy numer expnsion in the evolution of omplex nturlly seleted extreme trit 1. The eluidtion of nturl strtegy for metl hyperumultion enles the rtionl design of tehnologies for the len-up of metl-ontminted soils nd for io-fortifition. HMA4 (ref. 4) is mong lrge numer of genes more highly expressed in A. hlleri thn in A. thlin 5,6 nd enodes plsm memrne protein of the 1 B fmily of trnsition metl pumps in the P-type ATPse superfmily 8,11. To investigte whether A. hlleri HMA4 (HMA4) funtions in metl hyperumultion or hypertolerne of A. hlleri, we redued the expression of HMA4 y RNA interferene (RNAi) 12 (Supplementry Fig. 1). For this, we developed geneti trnsformtion system, whih hs not so fr een ville for hyperumultor speies. HMA4 trnsript levels were deresed to etween 45% nd 1% of wild-type levels in different RNAi lines (Fig. 1, Supplementry Fig. 2), whih ppered morphologilly norml. After ultivtion of HMA4 RNAi lines in hydroponi solutions, their shoots ontined only 12 35% of the Zn onentrtions found in wild-type A. hlleri (Fig. 1, Supplementry Fig. 3). These levels were similr to shoot Zn onentrtions in A. thlin s representtive non-umultor 4. In roots of wildtype A. hlleri, metl onentrtions re low, refleting high root-toshoot metl fluxes 4,13,14. By omprison, roots of HMA4 RNAi lines umulted 49- to 134-fold higher Zn onentrtions, gin similr to the non-umultor A. thlin (Fig. 1). Prtitioning nd umultion of metls other thn Zn nd Cd (Supplementry Fig. 4) were not onsistently hnged in HMA4 RNAi lines. Together these results demonstrte tht high HMA4 trnsript levels re required for highly effiient root-to-shoot Zn flux nd for Zn hyperumultion in the shoots of A. hlleri. This is distint from the funtion of A. thlin HMA4 (AtHMA4) in root-to-shoot trnslotion of Zn for the mintenne of Zn-dependent proesses in the shoot 15,16. We next exmined how HMA4 lters the distriution of Zn within the roots of A. hlleri, y imging with the fluoresent Zn inditor Zinpyr In the wild type, fluoresene ws most intense in the xylem vessels loted inwrds from the periyle ell lyer of the root vsulture (Fig. 1d, Supplementry Fig. 5). By ontrst, in the HMA4 RNAi lines signl intensity ws mximl in the periyle ell lyer, qulittively similr to the hnge in Zn loliztion reported for the A. thlin hm4 mutnt ompred to the wild type 15. This indites tht silening of HMA4 impirs the relese of Zn from the root symplsm into the poplsti xylem vessels, whih provide the primry pthwy for the movement of solutes from the root to the shoot with the trnspirtion strem 17. These results re in greement with the deresed Zn prtitioning into the shoots in HMA4 RNAi lines. If inresed HMA4 tivity is primry event in hevy metl hyperumultion, we would expet tht this ffets other ndidte genes for hyperumultion known to e highly expressed in A. hlleri 4. We therefore nlysed RNA from plnts ultivted in 5 mm Zn solution y rel-time RT PCR. Expression of Zn defiieny response genes 4,18 ws speifilly deresed in roots of the HMA4 RNAi lines. For exmple, reltive trnsript levels of IRT3 (Fig. 1e) nd ZIP4 (Fig. 1f) were orrelted with HMA4 trnsript levels ross ll genotypes (r 5.99 nd.98, respetively). The memrne trnsporters enoded y IRT3 nd ZIP4 re oth memers of the sme fmily of proteins implited in the ellulr uptke of Zn (ref. 18). Thus, the high expression of these genes in roots of wild-type A. hlleri 4 ppers to e seondry onsequene of inresed HMA4 tivity, nd is likely to further enhne shoot metl umultion. 1 Mx Plnk Institute of Moleulr Plnt Physiology, D Potsdm, Germny. 2 Mx Plnk Institute for Developmentl Biology, D-7276 Tüingen, Germny. 3 Plnt Cell Biology, Deprtment of Life Sienes, 4 Center for Assistne in Tehnology of Mirosopy, Deprtment of Chemistry, University of Liège, B-4 Liège, Belgium. 5 Mx Plnk Institute for Chemil Eology, D-7745 Jen, Germny. {Present ddresses: Plnt Cell Biology, Deprtment of Life Sienes, University of Liège, B-4 Liège, Belgium (M.H.); Deprtment of Thori, Crdi nd Vsulr Surgery, University of Tüingen, D-7276 Tüingen, Germny (A.N.); BIOQUANT Center, Heidelerg Institute of Plnt Sienes, University of Heidelerg, D-6912 Heidelerg, Germny (I.N.T., M.J.H., U.K.). *These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. 28 Nture Pulishing Group 391
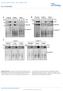
2 LETTERS NATURE Vol My 28 Heterologous expression of HMA4 in ells of the udding yest Shromyes erevisie ws reported to onfer metl tolerne 4 nd metl hypersensitivity 8. Reently, three respetive mjor QTL (quntittive trit loi) for Zn nd Cd hypertolerne were mpped in progeny from ross etween A. hlleri nd its metl-sensitive non-umultor reltive Aridopsis lyrt 8,9. Notly, mjor QTL for oth Zn nd Cd hypertolerne ontined HMA4, ut omprised severl entimorgns nd thus t lest severl hundred genes. To exmine whether HMA4 funtions not only in metl hyperumultion of A. hlleri, ut lso in hypertolerne, we determined the effets of toxi metl onentrtions on root growth of plnts in hydroponi solutions 19,2. In the presene of 3 mm Cd or 1.5 mm Zn, root elongtion in wild-type A. hlleri plnts ws still out 68% nd 6% of the elongtion under ontrol onditions, respetively. In ontrst, roots of HMA4 RNAi lines exhiited only 3 15% nd 12 37% of the elongtion under ontrol onditions, respetively (Fig. 1g, h). These dt demonstrte tht HMA4 mkes sustntil ontriution to Cd nd Zn hypertolerne in A. hlleri. Our results indite tht HMA4 hs key role in severl spets of the omplex metl hyperumultor phenotype. We therefore ddressed the moleulr sis for elevted HMA4 expression in A. hlleri ompred to the non-umultor A. thlin. Erlier, Southern lot sreening provided irumstntil evidene tht there my e more thn single HMA4 gene opy in the genome of A. hlleri 4. However, informtion on the numer of gene opies, their respetive sequenes, expression nd funtionlity hs een unville. To exmine this, two overlpping A. hlleri genomi BAC (teril rtifiil hromosome) lones were sequened. Compred to the synteni segment in A. thlin, there is omplex triplition of region tht inludes HMA4 (orresponding to At2g1911 in A. thlin) nd the two downstrem genes (At2g1912 nd At2g1913) (Fig. 2). In ddition to prtil deletions nd inversions of At2g1912 nd At2g1913 orthologues, severl trnsposon nd retrotrnsposon insertions re evident. The flnking sequenes re lrgely synteni with A. thlin. Within oding sequenes, the three HMA4 gene opies re on verge 99% identil to eh other, ut shre only 88% sequene identity with AtHMA4, suggesting tht the triplition my hve ourred reltively reently in the A. hlleri linege (Supplementry Tle 1). After reverse trnsription we speifilly quntified either the HMA4-1 omplementry DNA lone or oth the lmost identil HMA4-2 nd HMA4-3 DNAs y rel-time PCR (Supplementry Fig. 6). The results re onsistent with similr expression levels of ll three HMA4 gene opies (Fig. 2). Thus, oth n inrese in opy numer nd elevted expression of individul gene opies ontriute to the high trnsript levels of HMA4 in A. hlleri in omprison with A. thlin. Sequene divergene from A. thlin is most pronouned in the 59-flnking regions of HMA4 genes (Supplementry Tle 1) 21, suggesting possile regultory innovtions in A. hlleri. To determine experimentlly whether the inresed expression of individul HMA4 gene opies is due to is-regultory hnges, we generted fusions of the promoters of AtHMA4 nd of the three HMA4 gene opies to the -gluuronidse (GUS) reporter for the trnsformtion of oth A. hlleri nd A. thlin. Reporter tivity direted y the A. hlleri Reltive trnsript level HMA4 1, 2, 3, 4, S P -GUS HMA4 RNAi lines d A. hlleri Shoot Zn onentrtion (mg kg 1 DW) Root Zn onentrtion (mg kg 1 DW) , 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, HMA4 RNAi lines HMA4 RNAi lines At At Men root elongtion (% of ontrol) Figure 1 Chrteriztion of A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi lines., HMA4 trnsript levels reltive to EF1 in roots of A. hlleri wild type () nd 35S P -GUS trnsformnt ontrols, nd four HMA4 RNAi lines.,, Zin onentrtions in shoots () nd roots () of A. hlleri () genotypes nd A. thlin Col (At), ultivted in hydroponi solution ontining 5 mm Zn for 3 weeks (DW, dry weight). d, Zn loliztion in A. hlleri roots. Confol imges show fluoresent Zn signls (green) nd ell wlls (red). 392 g e RTL IRT3 in roots HMA4 RNAi ** ** ** HMA4 RNAi lines * RTL ZIP4 in roots A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi A. hlleri 5 A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi A. hlleri A. thlin A. thlin 1,5 3, 4,5 6, 1,5 3, 4,5 6, RTL HMA4 in roots RTL HMA4 in roots h 8 3 µm CdSO mm ZnSO 4 28 Nture Pulishing Group f Men root elongtion (% of ontrol) ** ** HMA4 RNAi lines Sle rs, 5 mm;, periyle; rrowheds highlight fluoresent Zn signls in xylem vessels. e, f, Reltive trnsript levels (RTL) of IRT3 (e) nd ZIP4 (f) plotted ginst reltive HMA4 trnsript levels, ll normlized to EF1, in different genotypes. g, Cdmium tolerne, nd h, zin tolerne of A. hlleri genotypes. Vlues re men 6 s.e.m., n 5 4 to 6 nd 12 to 18 individuls for RNAi lines nd wild type, respetively (,, g, h), n 5 3to4(), n 5 6to8 (e, f). *P,.5, **P,.1, P,.1. *
3 NATURE Vol My 28 LETTERS A. hlleri BAC 17L A. hlleri BAC 7C17 HMA4-1 HMA4-2 HMA4-3 At2g191 At2g193 At2g194 Copi At2g195 At2g196 At2g197 At2g198 At2g At2g At2g Copi 1 At2g At2g At2g () Copi At2g At2g At2g At2g At2g1915 At2g1916 At2g At2g () 2 At2g () HMA4-1 HMA4-2 + HMA4-3 Trnsript level reltive to EF1 5 1, 1,5 2, 2,5 >85% identity with A. thlin ~88% identity with A. thlin 1 k Asent from synteni region of A. thlin hromosome 2 Clss I LTR retrotrnsposon elements (- nd Copi-like) (HMA ) >9% identity with A. thlin Clss I non LTR retrotrnsposon reverse trnsriptse HMA4 AtHMA4 95% identity with A. thlin Clss II trnsposon elements (En/Spm sulss) Figure 2 Genomi orgniztion nd expression of HMA4 genes in A. hlleri., Digrm showing two overlpping A. hlleri genomi BACs. Genes re represented y oxes nd nmed y A. thlin Genome Identifier odes (lue text, regions synteni with A. thlin; green, triplited genes). Tringles indite the diretion of trnsription (filled, intt genes; open, AtHMA4 promoter (AtHMA4 P ) ws muh lower thn tht direted y ny of the three HMA4 promoters (HMA4-1 P, HMA4-2 P, HMA4-3 P ), whih were s effetive s the strong onstitutive trunted or pseudogenes). Three frgments of one At2g1912 orthologue re denoted (), () nd (); LTR, long terminl repet., Reltive trnsript levels of HMA4 gene opies in A. hlleri roots, nd of AtHMA4 in A. thlin roots for omprison (men 6 s.e.m., n 5 6). uliflower mosi virus (CMV) 35S promoter, 35S P (Fig. 3 d). Sptil ptterns of reporter tivity for ll three HMA4 P onstruts were highly similr in oth A. hlleri nd A. thlin (Fig. 3e, g, A. hlleri A. thlin AtHMA4 P HMA4-1 P HMA4-2 P HMA4-3 P AtHMA4 P HMA4-1P HMA4-2 P HMA4-3 P Speifi reporter tivity (mmol MU mg 1 h 1 ) Shoot Root d Speifi reporter tivity (mmol MU mg 1 h 1 ) Shoot Root AtHMA4 P HMA4-1 P HMA4-2 P HMA4-3 P 35S P AtHMA4 P HMA4-1 P HMA4-2 P HMA4-3 P 35S P e f g h xp xp HMA4-2 P HMA4-2 P Figure 3 Levels nd ell speifiity of HMA4 promoter tivity in A. hlleri nd A. thlin.,, e, f, A. hlleri (left);, d, g, h, A. thlin (right).,, Histohemil detetion of GUS tivity (lue), direted y the A. thlin or A. hlleri HMA4 promoters, in leves of 5-week-old plnts., d, Speifi GUS tivity in protein extrts (men 6 s.e.m., n 5 4to7 independent lines; MU, 4-methylumelliferone). Vlues for the CMV 35S promoter re shown for omprison. e h, Reporter tivity in whole mounts 28 Nture Pulishing Group (e, g) nd trnsverse setions (f, h) of root tips from HMA4-2 P -GUS trnsformnts representtive of ll HMA4 promoters (Supplementry Figs 7, 8 nd 1). Tissues were stined for 18 h (, ) or.5 h (e to h). The inset (f) shows lose-up of the vsulr ylinder. Sle rs:,, 5 mm; e, g, 1 mm; f, 25mm; nd h, 15mm., periyle; xp, xylem prenhym. Root ntomy differs slightly etween A. thlin nd A. hlleri. 393
4 LETTERS NATURE Vol My 28 Supplementry Figs 7 1). Qulittively, tivity ptterns were lso similr for promoters originting from oth speies (Supplementry Figs 7, 8) 15. The HMA4 expression pttern ws onfirmed y in situ hyridiztion in wild-type A. hlleri (Supplementry Figs 9, 1). This reveled speifi messenger RNA umultion in the root periyle nd xylem prenhym (Fig. 3f, h, Supplementry Fig. 1), supporting funtion for HMA4 in xylem loding of Zn (see Fig. 1d). Expression in the xylem prenhym nd the mium of leves (Supplementry Fig. 9) is onsistent with possile role of HMA4 in metl distriution within the lef lde nd the exlusion of metls from speifi ell types. Together, our dt onfirm tht high HMA4 trnsript levels in A. hlleri re the result of gene opy numer triplition omined with the enhned expression of ll three A. hlleri HMA4 genes speified in is. Finlly, we determined whether inresed HMA4 tivity is not only neessry ut lso suffiient for ltered hevy metl umultion nd tolerne. To this end, we trnsformed A. thlin with n HMA4 mini-gene, onsisting of n HMA4 DNA linked to the HMA4-1 promoter. Primry trnsformnts ontined modertely elevted HMA4 trnsript levels ( nd fold in roots nd shoots, respetively, ompred to wild type, men 6 s.e.m., ZIP4 IRT3 A. thlin HMA4 P -HMA4 Trnsript level reltive to EF A. thlin HMA4 P -HMA4 n 5 6; Supplementry Fig. 9m o), t the lower end of the rnge expeted sed on previous omprisons etween A. hlleri nd A. thlin 4. Zinpyr-1 imging showed high levels of Zn in xylem tissues of roots of trnsgeni plnts (Fig. 4), mimiking the distriution of Zn in wild-type A. hlleri (see Fig. 1d). By ontrst, in non-trnsgeni A. thlin Zn levels were highest in the root periyle ell lyer (Fig. 4), resemling the loliztion in A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi lines (see Fig. 1d). Thus, trnsformtion of A. thlin with HMA4 is suffiient to repitulte Zn distriution typil of A. hlleri in the roots of the non-hyperumultor A. thlin. Roots of HMA4- trnsformed A. thlin lso ontined inresed trnsript levels of the Zn defiieny response genes ZIP4 nd IRT3 (Fig. 4), in nlogy with wild-type A. hlleri (see Fig. 1e, f). These results further support the model tht in roots of A. hlleri, the high HMA4-dependent Zn flux into the xylem depletes symplsti Zn pools, therey triggering the upregultion of Zn defiieny response genes in the roots 4. A. thlin HMA4 trnsformnts grown in medi supplemented with toxi onentrtions of 15 mmznor4mm Cd developed enhned lef hlorosis nd smller rosettes, whih re signs of Zn nd Cd hypersensitivity of the shoots (Fig. 4, Supplementry Fig. 11). When ultivted in 5 mm Zn, HMA4 trnsformnts were helthy nd umulted slightly higher Zn onentrtions thn non-trnsgeni plnts ( fold, men 6 s.e.m., n 5 4 independent experiments, P,.5; dt not shown). These results suggest more effiient trnsfer of metls from roots to leves in HMA4 trnsformnts ompred to non-trnsgeni A. thlin. The metl sensitivity of shoots of A. thlin expressing HMA4 indites tht dditionl genes re required for metl detoxifition in order to ommodte the high HMA4-dependent metl flux into the shoots of A. hlleri 7,9,22. In summry, using series of funtionl riteri 23, we hve demonstrted mjor role for HMA4 in nturlly seleted Zn hyperumultion nd ssoited Cd nd Zn hypertolerne in A. hlleri. High HMA4 expression in A. hlleri is speified in is nd mplified y gene opy numer expnsion. Inresed expression of HMA4 in A. hlleri supports the enhned Zn flux from the root symplsm into the xylem vessels neessry for shoot Zn hyperumultion, nd ts s physiologil mster swith to upregulte Zn defiieny response gene expression in roots (Supplementry Fig. 1). These findings re of entrl importne for the development of phytoremedition nd io-fortifition strtegies. Tken together, our results provide evidene for previously proposed roles of is regultory diversifition 24 nd opy numer expnsion 25,26 in eukryoti dpttion µm ZnSO 4 15 µm ZnSO 4 µm CdSO 4 4 µm CdSO 4 A. thlin HMA4 P -HMA4 Figure 4 Chrteriztion of A. thlin expressing HMA4.,Zn loliztion in roots of 1-dy-old seedlings. Confol imges show fluoresent Zn signls (green) nd ell wlls (red). Sle rs, 25 mm;, periyle; rrowheds highlight fluoresent Zn signls in xylem vessels., Reltive trnsript levels of ZIP4 nd IRT3 in roots of hydroponilly ultivted 5.5-week-old plnts (men 6 s.e.m., n 5 6)., Zn nd Cd toxiity in shoots of 17-dy-old HMA4 trnsformnts seven dys fter trnsfer to ontrol medium (5 mm Zn, no Cd) or medium supplemented with 15 mm Zn or 4 mm Cd Nture Pulishing Group METHODS SUMMARY Plnt mteril. A. hlleri (L.) O Kne nd Al-Shehz ssp. hlleri (ession Lngelsheim) or A. thlin L. Heynhold (ession Columi) were used in ll experiments. Plnts were ultivted hydroponilly 4,5 or on solid medium ontining the hydroponi solution (HD pltes) in plsti Petri dishes 28 (Methods). Plnt trnsformtions. Construts were generted y loning of PCR produts into GATEWAY-omptile inry vetors (Methods; Supplementry Methods for primer sequenes). A. thlin ws trnsformed y florl dip 29. Agroterium tumefiens-medited stle trnsformtion of A. hlleri ws performed using tissue-ulture sed proedure 3 (Supplementry Methods). Genomi DNA nd RNA gel lot nlyses were performed for the primry hrteriztion of A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi trnsformnts (Supplementry Methods). Physiologil hrteriztion of plnts. For the determintion of zin umultion nd trnsript levels, plnts were ultivted hydroponilly t 5 mm ZnSO 4 in ontrolled growth hmer for 3 weeks (Supplementry Methods). The Zn inditor Zinpyr-1 (Sigm) ws used for onfol fluoresene imging of Zn in roots of A. hlleri nd A. thlin plnts 16. For the determintion of metl tolerne, sequentil root elongtion ssys nd growth ssys were performed in metl-supplemented hydroponi solutions nd on HD pltes, respetively (Methods). BAC nlysis nd sequening. Two A. hlleri BACs (7C17, 17L7) overing the region orthologous to the HMA4 region of the A. thlin genome nd ontining totl of three genomi HMA4 opies of A. hlleri, were isolted nd ompletely sequened (Methods). Gene nd trnsposle element nnottions were
5 NATURE Vol My 28 LETTERS mde on the sis of similrity serhes performed using the BLASTN nd BLASTX progrms ginst the TAIR dtse ( nd the non-redundnt dtse (nr, Expression nlyses. Reltive trnsript levels were determined y rel-time RT PCR 4. Histohemil GUS stining, fluorimetri quntittive GUS tivity ssys nd in situ hyridiztions were rried out ording to stndrd proedures (Supplementry Methods). Full Methods nd ny ssoited referenes re ville in the online version of the pper t Reeived 2 Deemer 27; epted 28 Ferury 28. Pulished online 2 April Mithell-Olds, T. Aridopsis thlin nd its wild reltives. Trends Eol. Evol. 16, (21). 2. Koornneef, M., Alonso-Blno, C. & Vreugdenhil, D. Nturlly ourring geneti vrition in Aridopsis thlin. Annu. Rev. Plnt Biol. 55, (24). 3. Bker, A. J. M., MGrth, S. P., Reeves, R. D. & Smith, J. A. C. in Phytoremedition of Contminted Soil nd Wter (eds Terry, N. & Bñuelos, G. S.) (CRC Press LLC, Bo Rton, Florid, 1999). 4. Tlke, I. N., Hnikenne, M. & Krämer, U. Zin-dependent glol trnsriptionl ontrol, trnsriptionl deregultion, nd higher gene opy numer for genes in metl homeostsis of the hyperumultor Aridopsis hlleri. Plnt Physiol. 142, (26). 5. Beher, M., Tlke, I. N., Krll, L. & Krämer, U. Cross-speies mirorry trnsript profiling revels high onstitutive expression of metl homeostsis genes in shoots of the zin hyperumultor Aridopsis hlleri. Plnt J. 37, (24). 6. Weer, M. et l. Comprtive mirorry nlysis of Aridopsis thlin nd Aridopsis hlleri roots identifies niotinmine synthse, ZIP trnsporter nd other genes s potentil metl hyperumultion ftors. Plnt J. 37, (24). 7. Dräger, D. B. et l. Two genes enoding Aridopsis hlleri MTP1 metl trnsport proteins o-segregte with zin tolerne nd ount for high MTP1 trnsript levels. Plnt J. 39, (24). 8. Courot, M. et l. A mjor QTL for Cd tolerne in Aridopsis hlleri o-lolizes with HMA4, gene enoding hevy metl ATPse. Plnt Physiol. 144, (27). 9. Willems, G. et l. The geneti sis of zin tolerne in the metllophyte Aridopsis hlleri ssp. hlleri (Brssiee): An nlysis of quntittive trit loi. Genetis 176, (27). 1. Hoekstr, H. E. & Coyne, J. A. The lous of evolution: evo devo nd the genetis of dpttion. Evolution Int. J. Org. Evolution 61, (27). 11. Axelsen, K. B. & Plmgren, M. G. Inventory of the superfmily of P-type ion pumps in Aridopsis. Plnt Physiol. 126, (21). 12. Smith, N. A. et l. Totl silening y intron-splied hirpin RNAs. Nture 47, (2). 13. Krämer, U. et l. Free histidine s metl heltor in plnts tht hyperumulte nikel. Nture 379, (1996). 14. Lst, M. M. et l. Moleulr physiology of zin trnsport in the Zn hyperumultor Thlspi erulesens. J. Exp. Bot. 51, (2). 15. Hussin, D. et l. P-type ATPse hevy metl trnsporters with roles in essentil zin homeostsis in Aridopsis. Plnt Cell 16, (24). 16. Sinlir, S. A. et l. The use of the zin-fluorophore, Zinpyr-1, in the study of zin homeostsis in Aridopsis roots. New Phytol. 174, (27). 17. Clemens, S., Plmgren, M. G. & Krämer, U. A long wy hed: understnding nd engineering plnt metl umultion. Trends Plnt Si. 7, (22). 18. Grotz, N. et l. Identifition of fmily of zin trnsporter genes from Aridopsis tht respond to zin defiieny. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 95, (1998). 19. Bert, V. et l. Geneti sis of Cd tolerne nd hyperumultion in Aridopsis hlleri. Plnt Soil 249, 9 18 (23). 2. MNir, M. R. et l. Zin tolerne nd hyperumultion re genetilly independent hrters. Pro. R. So. Lond. B 266, (1999). 21. Windsor, A. J. et l. Prtil shotgun sequening of the Boeher strit genome revels extensive mirosynteny nd promoter onservtion with Aridopsis. Plnt Physiol. 14, (26). 22. Küpper, H., Lomi, E., Zho, F. J. & MGrth, S. P. Cellulr omprtmenttion of dmium nd zin in reltion to other elements in the hyperumultor Aridopsis hlleri. Plnt 212, (2). 23. Weigel, D. & Nordorg, M. Nturl vrition in Aridopsis. How do we find the usl genes? Plnt Physiol. 138, (25). 24. Clrk, R. M., Wgler, T. N., Quijd, P. & Doeley, J. A distnt upstrem enhner t the mize domestition gene t1 hs pleiotropi effets on plnt nd infloresent rhiteture. Nture Genet. 38, (26). 25. Bekmnn, J. S., Estivill, X. & Antonrkis, S. E. Copy numer vrints nd geneti trits: loser to the resolution of phenotypi to genotypi vriility. Nture Rev. Genet. 8, (27). 26. Sugino, R. P. & Innn, H. Seletion for more of the sme produt s fore to enhne onerted evolution of duplited genes. Trends Genet. 22, (26). 27. Zhong, S., Khodursky, A., Dykhuizen, D. E. & Den, A. M. Evolutionry genomis of eologil speiliztion. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 11, (24). 28. Arrivult, S., Senger, T. & Krämer, U. The Aridopsis metl tolerne protein AtMTP3 mintins metl homeostsis y mediting Zn exlusion from the shoot under Fe defiieny nd Zn oversupply. Plnt J. 46, (26). 29. Clough, S. J. & Bent, A. F. Florl dip: simplified method for Agroteriummedited trnsformtion of Aridopsis thlin. Plnt J. 16, (1998). 3. Chteu, S., Sngwn, R. S. & Sngwn-Norreel, B. S. Competene of Aridopsis thlin genotypes nd mutnts for Agroterium tumefiens-medited gene trnsfer: role of phytohormones. J. Exp. Bot. 51, (2). Supplementry Informtion is linked to the online version of the pper t Aknowledgements We thnk D. Burin, D. Wlther, C. Glnte, T. Werner nd the grdeners of the Mx Plnk Institute of Moleulr Plnt Physiology for ssistne, R. Shmidt for A. thlin 35S P -GUS lines, I. Somssih for pjawohl8, nd S. Thomine for omments on the mnusript. This work ws funded y: Germn Reserh Foundtion Kr1967/3-1, Heisenerg Fellowship Kr1967/4-1; Germn Federl Ministry of Edution nd Reserh Biofuture nd GABI-ADVANCIS 31537A; Europen Union RTN METALHOME HPRN CT , InP PHIME FOOD-CT (U.K.). Further funding ws from Fonds spéiux pour l Reherhe, University of Liège, Belgium (M.H., P.M.), Fonds de l Reherhe Sientifique FNRS, Belgium (M.H.), nd the Mx Plnk Soiety (D.W.). Author Contriutions I.N.T., M.H., M.J.H., A.N., U.K., P.M. nd J.K. performed experiments, C.L. the BAC sequening nd ssemly, M.H. ssemly nd BAC nnottion; D.W. nd J.K. provided the BAC lirry nd filters; U.K., M.H. nd I.N.T. jointly designed experiments; D.W. gve experimentl dvie nd edited the mnusript; U.K. oneived of the study nd direted the reserh; U.K., M.H. nd I.N.T. wrote nd edited the mnusript; ll uthors ommented on the mnusript. Author Informtion Reprints nd permissions informtion is ville t BAC sequenes re ville online (Gennk ession numers EU38272, EU38273). Correspondene nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to U.K. (ute.kremer@ioqunt.uni-heidelerg.de). 28 Nture Pulishing Group 395
6 doi:1.138/nture6877 METHODS Plnt ultivtion. Plnts were ultivted in limte-ontrolled glsshouse t 21 uc dy/17 uc night, onstnt humidity of 5%, with supplementry lighting from equl mounts of HPIT nd Son-T Agro lmps (Philips) providing photoperiod of 16 h, or in growth hmer t 2 uc dy/18 uc night, humidity of 6% dy/75% night, nd photoperiod of 11 h t photon flux density 145 mmol m 22 s 21. Genertion of onstruts. All HMA4 sequenes were PCR-mplified using proofreding polymerse (Pfu Turo, Strtgene), nd verified y sequening fter diretionl loning into pentr/d TOPO (Invitrogen) nd gin fter sitedireted reomintion into the respetive GATEWAY-omptile inry vetor efore plnt trnsformtion, unless indited otherwise. To generte the HMA4 RNAi onstrut for trnsformtion of A. hlleri, frgment orresponding to p 2,541 2,997 of the open reding frme of HMA4 ws mplified from A. hlleri DNA nd suloned into the inry vetor pjawohl8 (GenBnk ession AF48413), generting n intronsplied hirpin onstrut with ntisense HMA4 frgment intron sense HMA4 frgment onfigurtion downstrem of the CMV 35S promoter 12. To generte promoter-reporter onstruts for the trnsformtion of A. thlin nd A. hlleri, n AtHMA4 promoter frgment of 2,625 p ws mplified from genomi DNA of A. thlin. The HMA4-1, HMA-2 nd HMA4-3 promoter frgments of 2,326, 1,311 nd 1,82 p, respetively, were mplified from A. hlleri genomi DNA. All promoter frgments, whih inlude promoter nd 59-UTR regions nd end fter the first 3 p of the respetive HMA4 oding sequene, were suloned into the pmdc163 inry vetor 31. The HMA4 P -HMA4 onstrut for trnsformtion of A. thlin ws generted y inserting oth the HMA4-1 promoter frgment nd the full-length HMA4 oding sequene into promoter-less vrint of the pmdc32 vetor 31 (Supplementry Methods). Physiologil hrteriztion of plnts. A. hlleri plnts were mintined in hydroponi ulture 4,5 in limte-ontrolled glsshouse. A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi lines nd wild type ontrol individuls were propgted vegettively vi rooting of shoot uttings on snd for 5 weeks nd susequently ultivted in hydroponis for 4 5 weeks efore inititing experimentl tretments. Results for wild type ontrols were verged from the following A. hlleri individuls: (1) untrnsformed, (2) regenerted from tissue ulture following mok trnsformtion nd (3) trnsformed with uliflower mosi virus (CMV) 35S promoter-gus- Intron onstrut 32. A. thlin plnts were grown from seeds in hydroponi ulture 4,5 for 6 weeks efore experimentl tretments were initited. Metl tolerne of A. hlleri genotypes ws determined in limte-ontrolled glsshouse y mesuring root elongtion in slightly modified hydroponi ontrol solution (5 mm Zn, no dded Cd,.14 mm KH 2 PO 4 to void preipittion t high metl onentrtions), nd susequently in the presene of sequentilly inresed metl onentrtions, in 5-dy intervls (Zn: 8 mm, 1.5 mm; Cd: 1 mm, 3 mm) 2. Two experiments were performed for eh metl. For metl tolerne ssys in A. thlin HMA4 trnsformnts (T1 genertion), 1-dy-old hygromyin-resistnt seedlings were trnsferred onto HD pltes ontining 5 mm ZnSO 4 (ontrol), 15 mm ZnSO 4,or4mM CdSO 4 (nd 5 mm ZnSO 4 ) nd mintined in limte-ontrolled growth hmer. Photogrphs of representtive individuls were tken one week fter trnsfer. The experiment ws repeted three times, with three pltes per genotype nd 1 replite seedlings per plte in eh experiment. For Zn imging, segments of newly formed distl roots were used of A. hlleri plnts grown in hydroponi medium ontining 1 mm ZnSO 4. For A. thlin, seedlings (T3 genertion) were grown for 1 dys on HD pltes in limte-ontrolled growth hmer nd inuted in hydroponi solution with 25 mm ZnSO 4 for 2.5 h efore stining. Fluoresene of the Zn-Zinpyr-1 helte ws oserved using onfol lser snning mirosopy (Lei SP2) with 488 nm exittion using FITC nd Texs Red filters. For A. thlin, two trnsgeni HMA4 lines showing inresed HMA4 trnsript levels were nlysed. For A. hlleri, HMA4 RNAi lines 4.2.1, nd were nlysed (4.2.1 is shown in Fig. 1d). Imges shown re representtive of the results from t lest 6 wild type plnts nd 6 trnsgeni plnts. Rel-time RT PCR nlysis. Preprtion of totl DNse-treted RNA, synthesis of DNA, primer design nd sequenes, qulity ontrol nd dt nlysis were s desried 4. Vlues shown in Fig. 1 re verges from three to four independent iologil experiments, vlues shown in Figs 1e, f, 2 nd 4 re verges from six to eight tehnil replites from one experiment representtive of totl of three independent iologil experiments. BAC nlysis nd sequening. A BAC lirry ws onstruted in the pindigobac-536 vetor using HindIII-digested totl genomi DNA of 8 individuls from A. hlleri ssp. hlleri, essions Roderherrunn nd Stutenkmm (Germny) (Keygene), nd sreened with n HMA4 proe 4 s desried 33. A totl of 18 positive BAC lones were otined. A omintion of Southern lots nd restrition pttern nlyses, together with BAC end sequening, demonstrted tht two BACs (7C17, 17L7) overed ll of totl of three genomi HMA4 opies of A. hlleri, nd the region orthologous to the HMA4 region of the A. thlin genome. For omplete sequening, BAC 7C17 nd 17L7 sulone lirries were prepred with n verge insert size of 5 1 k, nd totl of 1,152 positive lones for eh BAC were end-sequened to 13-fold overge s desried 34. Sequene reds were se-lled using the LifeTre softwre 35 nd ssemled into ontigs with the PHRAP nd CONSED softwre pkges ( 36. Remining gps nd miguously ssemled regions were losed nd polished y primer wlking nd PCR with oligonuleotides designed sed on the flnking sequenes. Comprtive genomi sequene nlyses were done with the GenomeVISTA softwre ( 37,38 to identify synteni regions. Sttistis. All dt evlution nd sttistis were done using Mirosoft Exel. Sttistil nlysis of dt from A. hlleri HMA4 RNAi lines ws performed y multiple omprisons sed on ANOVA. 31. Curtis, M. D. & Grossniklus, U. A gtewy loning vetor set for high-throughput funtionl nlysis of genes in plnt. Plnt Physiol. 133, (23). 32. Vnnneyt, G. et l. Constrution of n intron-ontining mrker gene: spliing of the intron in trnsgeni plnts nd its use in monitoring erly events in Agroterium-medited plnt trnsformtion. Mol. Gen. Genet. 22, (199). 33. Benderoth, M. et l. Positive seletion driving diversifition in plnt seondry metolism. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 13, (26). 34. Eppinger, M. et l. Who te whom? Adptive Helioter genomi hnges tht ompnied host jump from erly humns to lrge felines. PLoS Genet. 2, e12 (26). 35. Wlther, D., Brth, G. & Morris, M. Bselling with LifeTre. Genome Res. 11, (21). 36. Gordon, D., Ajin, C. & Green, P. Consed: grphil tool for sequene finishing. Genome Res. 8, (1998). 37. Bry, N., Duhk, I. & Phter, L. AVID: A glol lignment progrm. Genome Res. 13, (23). 38. Couronne, O. et l. Strtegies nd tools for whole-genome lignments. Genome Res. 13, 73 8 (23). 28 Nture Pulishing Group
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on February 21, 2017, as DOI: /pp
 Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Gibberellins regulate iron deficiency-response by influencing iron transport and translocation in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa)
 nnls of otny 119: 95 956, 17 doi:1.19/o/mw5, ville online t www.o.oxfordjournls.org Gierellins regulte iron defiieny-response y influening iron trnsport nd trnslotion in rie seedlings (Oryz stiv) oln Wng
nnls of otny 119: 95 956, 17 doi:1.19/o/mw5, ville online t www.o.oxfordjournls.org Gierellins regulte iron defiieny-response y influening iron trnsport nd trnslotion in rie seedlings (Oryz stiv) oln Wng
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Chemically assisted phytoextraction of heavy metal contaminated soils using three plant species
 Plnt nd Soil (25) 276:153 162 Ó Springer 25 DOI 1.17/s1114-5-391- Chemilly ssisted phytoextrtion of hevy metl ontminted soils using three plnt speies P. Zhung, Z.H. Ye, C.Y. Ln, Z.W. Xie & W.S. Shu 1 Shool
Plnt nd Soil (25) 276:153 162 Ó Springer 25 DOI 1.17/s1114-5-391- Chemilly ssisted phytoextrtion of hevy metl ontminted soils using three plnt speies P. Zhung, Z.H. Ye, C.Y. Ln, Z.W. Xie & W.S. Shu 1 Shool
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
CHROMIUM ACCUMULATION BY PHYTOREMEDIATION WITH MONOCOT WEED PLANT SPECIES AND A HYDROPONIC SAND CULTURE SYSTEM
 Journl of Environmentl Reserh And Development Vol. 4 No. 3, Jnury-Mrh 21 CHROMIUM ACCUMULATION BY PHYTOREMEDIATION WITH MONOCOT WEED PLANT SPECIES AND A HYDROPONIC SAND CULTURE SYSTEM Pntwt Smpnpnish *1,2,
Journl of Environmentl Reserh And Development Vol. 4 No. 3, Jnury-Mrh 21 CHROMIUM ACCUMULATION BY PHYTOREMEDIATION WITH MONOCOT WEED PLANT SPECIES AND A HYDROPONIC SAND CULTURE SYSTEM Pntwt Smpnpnish *1,2,
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES
 CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
The effect of manure, zeolite and soil ageing in the dynamics of hexavalent chromium in Cichorium spinosum
 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 1 11 1 13 14 1 16 17 18 19 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 3 31 3 33 34 3 The effet of mnure, zeolite nd soil geing in the dynmis of hexvlent hromium in Cihorium spinosum V. Antonidis, T. Polyzois, S. Petropoulos,
1 3 4 6 7 8 9 1 11 1 13 14 1 16 17 18 19 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 3 31 3 33 34 3 The effet of mnure, zeolite nd soil geing in the dynmis of hexvlent hromium in Cihorium spinosum V. Antonidis, T. Polyzois, S. Petropoulos,
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Chemosphere 84 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Chemosphere. journal homepage:
 Chemosphere 84 (211) 63 69 Contents lists ville t SieneDiret Chemosphere journl homepge: www.elsevier.om/lote/hemosphere Clium protets roots of Sedum lfredii H. ginst dmium-indued oxidtive stress Shengke
Chemosphere 84 (211) 63 69 Contents lists ville t SieneDiret Chemosphere journl homepge: www.elsevier.om/lote/hemosphere Clium protets roots of Sedum lfredii H. ginst dmium-indued oxidtive stress Shengke
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on cadmium toxicity and antioxidative system in perennial ryegrass
 Journl of Soil Siene nd Plnt Nutrition, 218, 18 (1), 129-143 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effets of exogenous nitri oxide on dmium toxiity nd ntioxidtive system in perennil ryegrss Chen, Weifeng 1, Dong, Yunjie 1*,
Journl of Soil Siene nd Plnt Nutrition, 218, 18 (1), 129-143 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effets of exogenous nitri oxide on dmium toxiity nd ntioxidtive system in perennil ryegrss Chen, Weifeng 1, Dong, Yunjie 1*,
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
DHRS3, a retinal reductase, is differentially regulated by retinoic acid and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in THP-1 cells and rat liver
 Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation of Notch-dependent monociliated choroid plexus tumour cells
 Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
RESEARCH ARTICLE Transport of selenium across the plasma membrane of primary hepatocytes and enterocytes of rainbow trout
 191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Inoculation of selenium hyperaccumulator Stanleya pinnata and related non-accumulator Stanleya elata
 Physiologi Plntrum 13 13 Sndinvin Plnt Physiology Soiety, ISSN 31-9317 Inoultion of selenium hyperumultor Stnley pinnt nd relted non-umultor Stnley elt with hyperumultor rhizosphere fungi investigtion
Physiologi Plntrum 13 13 Sndinvin Plnt Physiology Soiety, ISSN 31-9317 Inoultion of selenium hyperumultor Stnley pinnt nd relted non-umultor Stnley elt with hyperumultor rhizosphere fungi investigtion
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
FRAMEstar. 2-Component PCR Plates
 FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
Interaction between dietary calcium supplementation and chronic waterborne zinc exposure in juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss
 Comprtive Biohemistry nd Physiology, Prt C 143 (26) 94 12 www.elsevier.om/lote/p Intertion etween dietry lium supplementtion nd hroni wterorne zin exposure in juvenile rinow trout, Onorhynhus mykiss S.
Comprtive Biohemistry nd Physiology, Prt C 143 (26) 94 12 www.elsevier.om/lote/p Intertion etween dietry lium supplementtion nd hroni wterorne zin exposure in juvenile rinow trout, Onorhynhus mykiss S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
 nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
nestin ironetin p75 s1 CNS SKPs Dermo-1 +ve SKPs CNS H2O SCGs Skin Di. SKPs TH SHOX2 GAPDH NCAM D H Figure S1, Immunoytohemil nlysis o SKP spheres ulture rom neontl mouse (nestin, ironetin, S-1) or rt
Lysine enhances methionine content by modulating the expression of S-adenosylmethionine synthase
 The Plnt Journl (7) 5, 85 86 doi:./j.365-33x.7.384.x ine enhnes methionine ontent y modulting the expression of S-denosylmethionine synthse Yel Hhm,, Luhu Song, Gdi Shuster nd Rhel Amir,3, Lortory of Plnt
The Plnt Journl (7) 5, 85 86 doi:./j.365-33x.7.384.x ine enhnes methionine ontent y modulting the expression of S-denosylmethionine synthse Yel Hhm,, Luhu Song, Gdi Shuster nd Rhel Amir,3, Lortory of Plnt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on uptake of Zn and P by two contrasting rice genotypes
 Influene of rusulr myorrhizl fungi on uptke of Zn nd P y two ontrsting rie genotypes R. Hjiolnd 1, 3, N. Alisghrzd, R. Brzeghr 1 1 Plnt Siene Deprtment, University of Triz, Triz, Irn Soil Siene Deprtment,
Influene of rusulr myorrhizl fungi on uptke of Zn nd P y two ontrsting rie genotypes R. Hjiolnd 1, 3, N. Alisghrzd, R. Brzeghr 1 1 Plnt Siene Deprtment, University of Triz, Triz, Irn Soil Siene Deprtment,
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Ethylene treatment improves diosgenin accumulation in in vitro cultures of Dioscorea zingiberensis via up-regulation of CAS and HMGR gene expression
 Eletroni Journl of Biotehnology ISSN: 0717-3458 http://www.ejiotehnology.info DOI: 10.2225/vol16-issue5-fulltext-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ethylene tretment improves diosgenin umultion in in vitro ultures of
Eletroni Journl of Biotehnology ISSN: 0717-3458 http://www.ejiotehnology.info DOI: 10.2225/vol16-issue5-fulltext-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ethylene tretment improves diosgenin umultion in in vitro ultures of
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant
 Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. Interactions Between MTHFR C677T - A1298C Variants and Folic Acid Deficiency Affect Breast Cancer Risk in a Chinese Population
 OI:http://dx.doi.org/1.71/PJP.2.1.5.21 Intertions etween MTHFR 77T - nd Foli id efiieny in rest ners in hin RSRH OMMUNITION Intertions etween MTHFR 77T - Vrints nd Foli id efiieny ffet rest ner Risk in
OI:http://dx.doi.org/1.71/PJP.2.1.5.21 Intertions etween MTHFR 77T - nd Foli id efiieny in rest ners in hin RSRH OMMUNITION Intertions etween MTHFR 77T - Vrints nd Foli id efiieny ffet rest ner Risk in
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
