Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy
|
|
|
- Oswin Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 10 Arne Fischmann and Christopher D.J. Sinclair 10.1 Introduction The aim of this chapter is to provide a topographical guideline for identifying muscles involved in neuromuscular disorders. The scope of the volume cannot include a complete anatomical description of all structures visible on the images. We have therefore decided not to label bones, vessels, nerves and internal organs if they appear on the imaging slices. All imaging was performed on a clinical 3T scanner with variable spine array and body array coils, depending on the region scanned, as well as peripheral angiography coils for the legs. The subject for this atlas was a healthy 40-year-old male with a moderately obese constitution and a mainly sedentary lifestyle. Axial T1-weighted images were acquired for all body regions as these are currently the standard for neuromuscular imaging. When evaluating neuromuscular images and especially when assessing fatty replacement/ degeneration in muscles, the reader should always be aware of the great variability between muscles in healthy adults. In addition, imaging parameters A. Fischmann, M.D. (*) Department of Radiology, University of Basel Hospital, 4031 Basel, Switzerland arne.fischmann@unibas.ch C.D.J. Sinclair MRC Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, UK such as the slice thickness and resolution can in fl uence the appearance of fatty streaks in the slice (Fig ) Neck and Cervical Spine Imaging of the neck is challenging due to the high variability of the anatomy. Exact reproduction of slice positioning is essential, especially for follow-up studies, otherwise even large muscles like the trapezius can change from the muscle bulk to a small linear con fi guration in the image. In most clinical routine MRI examinations, it is dif fi cult to separate the different components of the spinal muscles from each other. As these form a functional unit, it is common to refer to them collectively as the erector spinae muscles. It is also important to realise that degenerative diseases of the spine e.g. herniated discs and immobility can cause localized atrophy of the paraspinal muscles without clinical symptoms (Figs. 10.2, 10.3, and 10.4 ) Shoulder, Upper Arm and Thoracic Wall Muscle volume in the shoulder girdle and upper arm is especially variable depending on training state and lifestyle. In addition, degenerative disease, especially in elderly patients, can lead to atrophy and fatty replacement which might M.P. Wattjes and D. Fischer (eds.), Neuromuscular Imaging, DOI / _10, Springer Science+Business Media New York
2 82 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Images of the calf with a slice thickness of 3 mm ( a ) and with a reduced slice thickness of 1 mm ( b ). The extent of fatty replacement in b appears to be higher. There is also deformation and compression of the calf in ( b ) due to the use of a knee coil Fig Neck muscles at the level of C1/C2. DG digastric muscle, LC longus colli muscle, LsC longissimus colli, LPt lateral pterygoid muscle, MA masticator muscle, OCI obliquus capitis inferior muscle, RCP rectus capitis posterior muscle, SCM sternocleidomastoid muscle, SP splenius capitis, SS semispinalis capitis and cervicis, TR trapezius muscle
3 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 83 Fig Neck muscles at the level of the hyoid (C3). AS anterior scalenus muscle, DG digastric muscle; IS interspinosus muscle, LC longus colli muscle, LSc levator scapulae muscle, MF multifidus muscle, SCM sternocleidomastoid muscle, SP splenius capitis, SS semispinalis cervicis, TR trapezius muscle Fig Neck muscles at the level of C6/C7. AS anterior scalenus muscle, IS interspinosus muscle, LC longus colli muscle, LSc levator scapulae muscle, MF multifidus muscle, MS middle scalenus muscle, PS posterior scalenus muscle, SCM sternocleidomastoid muscle, SH sternohyoid muscle, SP splenius capitis/cervicis muscle, SSp supraspinatus muscle, TR trapezius muscle
4 84 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair be misinterpreted as neuromuscular disease involvement. Muscles especially prone to degenerative atrophy are the supraspinatus and the subscapularis. The deltoid muscle will usually present with multiple small T1-hyperintensities which should not be misinterpreted as fatty replacement/degeneration (Figs. 10.5, 10.6, 10.7, 10.8, 10.9, 10.10, and ) Forearm When imaging and evaluating the muscles of the forearm, special attention should be given to the amount of pronation or supination as these will not only in fl uence anatomy but also muscle tension and therefore cross sectional area. In most scanners, optimal positioning of the arm in the Fig Shoulder muscles at the level Th2. CB coracobrachialis muscle, DE deltoid muscle, IS infraspinatus muscle, LSc levator scapulae muscle, PMa pectoralis major muscle, PMi pectoralis minor muscle, RH rhomboideus muscle, SA serratus anterior muscle, SSc subscapularis muscle, TMi teres minor muscle, TR trapezius muscle Fig Shoulder muscles at the level Th4. CB coracobrachialis muscle, DE deltoid muscle, IC iliocostalis lumborum muscle, IS infraspinatus muscle, LD latissimus dorsi muscle, LSc levator scapulae muscle, LT longissimus thoracis muscle, MF multifidus muscle, PMa pectoralis major muscle, PMi pectoralis minor muscle, RH rhomboideus muscle, SA serratus anterior muscle, SSc subscapularis muscle, TMi teres minor muscle, TR trapezius muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle
5 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 85 Fig Shoulder muscles at the level Th6. BH biceps humeri muscle, CB coracobrachialis muscle, DE deltoid muscle, IC iliocostalis lumborum muscle, IS infraspinatus muscle, LD latissimus dorsi muscle, LT longissimus thoracis muscle, PMa pectoralis major muscle, PMi pectoralis minor muscle, RH rhomboideus muscle, SA serratus anterior muscle, SP serratus posterior muscle, SSc subscapularis muscle, TR trapezius muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle Fig Muscles of the upper arm and thoracic wall. BH biceps humeri muscle, CB coracobrachialis muscle, DE deltoid muscle, IC iliocostalis lumborum muscle, IS infraspinatus muscle, LD latissimus dorsi muscle, LT longissimus thoracis muscle, PMa pectoralis major muscle, PMi pectoralis minor muscle, RH rhomboideus muscle, SA serratus anterior muscle, SP serratus posterior muscle, SSc subscapularis muscle, TR trapezius muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle
6 86 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the upper arm. BH biceps humeri muscle, Bra brachialis muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle Fig Muscles of the distal upper arm. BH biceps humeri muscle, BR brachioradial muscle, Bra brachialis muscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle Fig Muscles of the distal upper arm above the elbow. BH biceps humeri muscle, BR brachioradial muscle, Bra brachialis muscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, TrH triceps humeri muscle
7 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 87 Fig Muscles of the proximal forearm. AN anconeus muscle, BR brachioradial uscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, ECU extensor carpi ulnaris muscle, ED extensor digitorum muscle, EDM extensor digiti minimi muscle, FCR fl exor carpi radialis muscle, FCU flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, FDP fl exor digitorum profundus muscle, FDS flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, PL palmaris longus muscle, PT pronator teres muscle, SU supinator muscle Fig Muscles of the proximal forearm. AN anconeus muscle, APL abductor pollicis longus muscle, BR brachioradial muscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, ECU extensor carpi ulnaris muscle, ED extensor digitorum muscle, EDM extensor digiti minimi muscle, FCR flexor carpi radialis muscle, FCU fl exor carpi ulnaris muscle, FDP flexor digitorum profundus muscle, FDS flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, PL palmaris longus muscle, PT pronator teres muscle centre of the bore requires either a supine position with the arm elevated over the head, or a position with the arm along the body and the patient moved outside the centre of the magnet. As both positioning methods are uncomfortable for the patient, imaging of the forearm is usually restricted to those cases with predominant forearm involvement. Apart from some smaller muscles like the pronator quadratus, most muscles of the forearm run parallel to the bones and small variations in positioning will have less in fl uence than in the neck or the pelvis. However, the distal third of the forearm mainly contains tendons. Imaging can therefore be limited to the proximal parts (Figs , 10.13, 10.14, and ).
8 88 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the forearm. APL abductor pollicis longus muscle, BR brachioradial muscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, ECU extensor carpi ulnaris muscle, ED extensor digitorum muscle, EDM extensor digiti minimi muscle, EPL extensor pollicis longus muscle, FCR fl exor carpi radialis muscle, FCU flexor carpi ulnaris muscle, FDP fl exor digitorum profundus muscle, FDS flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, FPL flexor pollicis longus muscle, PL palmaris longus muscle, PT pronator teres muscle Fig Muscles of the distal forearm. APL abductor pollicis longus muscle, ECR extensor carpi radialis muscle, ECU extensor carpi ulnaris muscle, ED extensor digitorum muscle, EDM, extensor digiti minimi muscle, EPL, extensor pollicis longus muscle, FCR fl exor carpi radialis muscle, FCU fl exor carpi ulnaris muscle, FDP flexor digitorum profundus muscle, FDS flexor digitorum superficialis muscle, FPL fl exor pollicis longus muscle, PT pronator teres muscle 10.5 Lower Abdomen and Pelvis Muscles of the pelvis and the hip often take a horizontal course and therefore appear highly variable depending on slice positioning in the axial plane. It might therefore be useful to acquire coronal images in selected patients depending on the clinical purpose. As with the thigh, several muscles of the pelvis will display greater amounts of intramuscular fat even in slim healthy adults. These include the gluteus maximus and the tensor fascia lata muscles especially. The gluteus
9 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 89 Fig Muscles of the abdominal wall and lumbar spine. ICL iliocostalis lumborum muscle, LT longissimus thoracis muscle, MF multifidus muscle, OAE obliquus abdominis externus muscle, OAI obliquus abdominis internus muscle, PS psoas muscle, QL quadratus lumborum muscle, RA rectus abdominis muscle, TrA transversus abdominis muscle minimus and medius might also display regional fatty atrophy due to degenerative changes of the hip joint. Currently there are only few reports of muscular involvement of the pelvis in neuromuscular disease. However, with increasing use of whole body MRI scans, we can expect further patterns to be described in the near future (Figs , 10.17, 10.18, 10.19, 10.20, and ) Thigh When evaluating muscles of the thigh, it is especially important to compare any fatty replacement with observations in healthy volunteers as there can be a great variation in the appearance of fatty streaks in speci fi c thigh muscles: e.g. the amount of fat that can be seen in a healthy glutaeus maximus would be abnormal in the quadriceps.
10 90 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the abdominal wall and pelvis. GMa glutaeus maximus muscle; GMe glutaeus medius muscle; GMm glutaeus minimus muscle; IL iliacus muscle; LT longissimus thoracis muscle; MF multifidus muscle; OAM obliquus abdominis externus, internus and transversus abdominis muscles; PS psoas muscle; RA rectus abdominis muscle
11 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 91 Fig Muscles of the pelvis. GMa glutaeus maximus muscle; GMe glutaeus medius muscle; GMm glutaeus minimus muscle; IL iliacus muscle; LT longissimus thoracis muscle; OAM obliquus abdominis externus, internus and transversus abdominis muscles; PI piriformis muscle; PS psoas muscle; RA rectus abdominis muscle; SA sartorius muscle; TFL tensor fasciae latae
12 92 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the pelvis. GMa glutaeus maximus muscle, IL iliacus muscle, OI obturator internus muscle, PE pectineus muscle, PS psoas muscle, QF quadratus femoris, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, TFL tensor fasciae latae, VL vastus lateralis muscle
13 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 93 Fig Muscles of the pelvis. AB adductor brevis muscle, AL adductor longus muscle, AM adductor magnus muscle, GMa glutaeus maximus muscle, IL iliacus muscle, PE pectineus muscle, QF quadratus femoris, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, TFL tensor fasciae latae, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle
14 94 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the pelvis. AB adductor brevis muscle, AL adductor longus muscle, AM adductor magnus muscle, GMa glutaeus maximus muscle, GR gracilis muscle, HS hamstring muscles, IL iliacus muscle, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle The separation of the adductor muscles, especially the adductor magnus from the adductor longus often proves dif fi cult to visualise, as does the separation of the adductor muscles from the proximal semimembranosus. It is also often dif fi cult to exactly separate the three vasti muscles from each other, although separation might be facilitated by prominent fascia. As many diseases have different involvement of the short and long head of the biceps femoris muscle, these two muscles should usually be evaluated separately (Figs , 10.23, 10.24, 10.25, 10.26, and ) Lower Leg, Calf Most muscles of the calf display a relatively homogeneous amount of fat and comparison between muscles in one leg might therefore be helpful in order to assess disease involvement. Usually there are three to fi ve larger fatty streaks in the medial gastrocnemius muscle and several small fatty streaks in the soleus. The extensor digitorum and hallucis muscles are often dif fi cult to separate from the anterior tibial muscle, especially in patients
15 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 95 Fig Muscles of the proximal thigh. AB adductor brevis muscle, AL adductor longus muscle, AM adductor magnus muscle, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GMa glutaeus maximus muscle, GR gracilis muscle, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, Hamstrings in blue, Adductors in yellow, Glutaeus muscles are in shades of purple Fig Muscles of the thigh. AL adductor longus muscle, AM adductor magnus muscle, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GR gracilis muscle, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, hamstrings in blue, adductors in yellow with little subcutaneous fat. In those cases, these muscles might be treated as one unit. In addition, several smaller muscles (e.g. fl exor hallucis longus or peroneus brevis) will only be discernible in distal slices even when they are present in more proximal regions of the calf as tendinous structures (Figs , 10.29, 10.30, and ).
16 96 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the thigh. AL adductor longus muscle, AM adductor magnus muscle, BB biceps femoris muscle short head, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GR gracilis muscle, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, hamstrings in blue, adductors in yellow Fig Muscles of the thigh. AM adductor magnus muscle, BB biceps femoris muscle short head, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GR gracilis muscle, RF rectus femoris muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, hamstrings in blue, adductors in yellow
17 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 97 Fig Muscles of the distal thigh. AM adductor magnus muscle, BB biceps femoris muscle short head, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GR gracilis muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, hamstrings in blue, adductors in yellow Fig Muscles of the distal thigh. AM adductor magnus muscle, BB biceps femoris muscle short head, BL biceps femoris muscle long head, GR gracilis muscle, SA sartorius muscle, SM semimembranosus muscle, ST semitendinosus muscle, VI vastus intermedius muscle, VL vastus lateralis muscle, VM vastus medialis muscle. Quadriceps muscle in shades of red, hamstrings in blue, adductors in yellow
18 98 A. Fischmann and C.D.J. Sinclair Fig Muscles of the proximal calf. EDL extensor digitorum longus, GM medial gastrocnemius muscle, GL lateral gastrocnemius muscle, PB peroneus brevis muscle, PL peroneus longus muscle, PLa plantaris muscle, POP popliteus muscle, TA tibialis anterior muscle, TP tibialis posterior muscle. Triceps surae in shades of blue Fig Muscles of the calf. EDL extensor digitorum longus, FDL fl exor digitorum longus muscle, FHL fl exor hallucis longus muscle, GM medial gastrocnemius muscle, GL lateral gastrocnemius muscle, PB peroneus brevis muscle, PL peroneus longus muscle, TA tibialis anterior muscle, TP tibialis posterior muscle. Triceps surae in shades of blue
19 10 Atlas of Topographical Muscle Anatomy 99 Fig Muscles of the calf. EDL extensor digitorum longus, FDL fl exor digitorum longus muscle, FHL flexor hallucis longus muscle, GM medial gastrocnemius muscle, GL lateral gastrocnemius muscle, PB peroneus brevis muscle, PL peroneus longus muscle, TA tibialis anterior muscle, TP tibialis posterior muscle. Triceps surae in shades of blue Fig Muscles of the calf. EDL extensor digitorum longus, FDL fl exor digitorum longus muscle, FHL flexor hallucis longus muscle, GM medial gastrocnemius muscle, PB peroneus brevis muscle, PL peroneus longus muscle, TA tibialis anterior muscle, TP tibialis posterior muscle. Triceps surae in shades of blue
20 本文献由 学霸图书馆 - 文献云下载 收集自网络, 仅供学习交流使用 学霸图书馆 ( 是一个 整合众多图书馆数据库资源, 提供一站式文献检索和下载服务 的 24 小时在线不限 IP 图书馆 图书馆致力于便利 促进学习与科研, 提供最强文献下载服务 图书馆导航 : 图书馆首页文献云下载图书馆入口外文数据库大全疑难文献辅助工具
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number
 Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Head & Neck The muscle names are followed by the chapter number. Splenius capitis (9) 2. Occipitalis (2) Temporalis () 3. Temporalis () 4. Semispinalis capitis (9) Facial / Scalp (2) 5. Temporalis () Facial
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Manual Muscle Testing, MMT
 Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Muscle Testing, MMT Manual This is the official list of names of all manual neuromuscular tests within Manual Muscle Testing MMT as used in Manual Kinesiology at the Swedish School of Kinesiology and the
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Cat Muscles Flashcards Mt SAC
 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 2. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 3. MUSCLES OF THE ARM AD CHEST
Supporting Information. Electrochemiluminescence for Electric-Driven Antibacterial. Therapeutics
 Supporting Information Electrochemiluminescence for Electric-Driven Antibacterial Therapeutics Shanshan Liu, a,b Huanxiang Yuan, a Haotian Bai, a Pengbo Zhang, a Fengting Lv, a Libing Liu, a Zhihui Dai,
Supporting Information Electrochemiluminescence for Electric-Driven Antibacterial Therapeutics Shanshan Liu, a,b Huanxiang Yuan, a Haotian Bai, a Pengbo Zhang, a Fengting Lv, a Libing Liu, a Zhihui Dai,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement Includes: breathing,
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
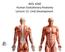 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
8546d_c01_1-42 6/21/02 1:34 PM Page 4 mac62 mac62:1253_ge: 4 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 1: SKELETAL MUSCLES Many skeletal muscles of the cat are similar to human muscles. This dissection will reinforce
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER
 ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER ANATOMICAL GUIDE FOR THE ELECTROMYOGRAPHER The Limbs and Trunk By EDWARD F. DELAGI, M.D. JOHN IAZZETTI, M.D. ALDO O. PEROTTO, M.D. DANIEL MORRISON, M.D. Fourth
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Coloring Book Muscolino, Joseph E. ISBN-13: 9780323057219 Table of Contents Introduction â How to Use This Book 1. The Skeletal System Bones of the Head â Anterior View Bones of
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44
 Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-44 Temporalis Frontalis Orbicularis Occuli Orbicularis Oris Masseter Sternocleidomastoid Orbicularis Occuli Human Muscles (Anterior View) Model 3-65 Temporalis Masseter
Racial disparities in the management of acne: evidence from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey,
 Journal of Dermatological Treatment ISSN: 0954-6634 (Print) 1471-1753 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ijdt20 Racial disparities in the management of acne: evidence from the National
Journal of Dermatological Treatment ISSN: 0954-6634 (Print) 1471-1753 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ijdt20 Racial disparities in the management of acne: evidence from the National
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System
 Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
Exercise Science Section 3: The Muscular System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Major Functions of Muscles Movement v Includes: breathing,
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Chiropractic Technician Class
 Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Chiropractic Technician Class Presentation By: Dr. Kay Miller. The Role of Exercise as it Relates to Our Musculoskeletal System Introduction to the topic and Preliminary Physical exam Musculoskeletal anatomy:
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association
 C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
C.F.A. Christian Fitness Association Personal Trainer/Advanced Personal Trainer/ Master Trainer/ Sports Nutritionist/ Martial Arts Strength Trainer/Step & Kickbox Aerobics Instructor/ Health Club Manager/
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Optimization of Processing Parameters of Stabilizers After Enzymes Hydrolysis for Cloudy Ginkgo Juice
 Optimization of Processing Parameters of Stabilizers After Enzymes Hydrolysis for Cloudy Ginkgo Juice Haifeng Yu, Junyan Liu and Jingxi Yang 1 Introduction Ginkgo biloba, dating back 300 million years,
Optimization of Processing Parameters of Stabilizers After Enzymes Hydrolysis for Cloudy Ginkgo Juice Haifeng Yu, Junyan Liu and Jingxi Yang 1 Introduction Ginkgo biloba, dating back 300 million years,
Chapter 5 Trimalleolar Ankle Fracture: Posterior Plate for Posterior Malleolus Fractures
 Chapter 5 Trimalleolar Ankle Fracture: Posterior Plate for Posterior Malleolus Fractures Roy I. Davidovitch and Alexander M. Crespo Introduction Trimalleolar ankle fractures with a posterior malleolus
Chapter 5 Trimalleolar Ankle Fracture: Posterior Plate for Posterior Malleolus Fractures Roy I. Davidovitch and Alexander M. Crespo Introduction Trimalleolar ankle fractures with a posterior malleolus
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8
 Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biol 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2017 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
The Muscular System. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
11 The Muscular System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Muscular System The Muscular System Consists only of skeletal muscles
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Lowe w r e r B ody Resistance Training
 Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
Lower Body Resistance Training Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Proneus Tertius AROM 25-40 degrees Extensor active-insufficiency Flexion & Eversion (Pronation) Flexion
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model
 MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
MicroAnatomy Muscle Fiber Model Muscle fiber whole model (but model is only a fraction of a fiber) Sarcolemma 14 Myofibril 1 Nucleus 8 Mitochondria 2 Triad 16 Sarcoplasmic reticulum 17 T tubule 15 Thin
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Preface ORGANIZATION AND CONTENT
 Preface Today s massage, bodywork, and fitness professionals are increasingly becoming members of the healthcare team. These professionals collaborate with physicians, physical therapists, occupational
Preface Today s massage, bodywork, and fitness professionals are increasingly becoming members of the healthcare team. These professionals collaborate with physicians, physical therapists, occupational
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Lab 11 Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross skeletal
The Muscular System. Part A
 The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
The Muscular System Part A 10 The Muscular System Part A 10 Hold onto your glutes, this is a big one. 10 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym!
 Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
Take your baby to the gym. Which gym? BabyGym! The word FOMO (short for fear of missing out) crops up everywhere, even in the nursery where parents and caregivers race from the one stimulation class to
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
CHAPTER 11 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The muscular system specifically concerns skeletal muscles and associated connective tissue that make individual muscle organs. B. This chapter discusses how
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8
 Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
Biology 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam III Fall 2016 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then
200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley,
 Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Butterfly is one of four competitive strokes in swimming. Usually it is raced, in a 100 or 200 meter or yard event. However, it is also the lead off event in the individual medley, meaning it is part of
Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body
 Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 11 Department of Myotherapy Lumbar Plexus Iliohypogastric nerve (T12-L1) Motor: Transverse abdominis and internal obliques Sensory:
Peripheral Nervous System: Lower Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 11 Department of Myotherapy Lumbar Plexus Iliohypogastric nerve (T12-L1) Motor: Transverse abdominis and internal obliques Sensory:
What you should do in labs 11 & 12
 Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
Bio 101 Laboratories 11 & 12 Muscle Histology Gross Human Skeletal Muscle Cat Muscle Dissection 1 What you should do in labs 11 & 12 Today (Lab 11) Muscle Histology (skeletal, smooth, cardiac) Human gross
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
Accepted Manuscript. Hemorrhagic cystitis associated with gefitinib treatment: a case report. Peng Zhang, Jinjing Tu, Tieding Chen, Rubing Li
 Accepted Manuscript Hemorrhagic cystitis associated with gefitinib treatment: a case report Peng Zhang, Jinjing Tu, Tieding Chen, Rubing Li PII: S0090-4295(18)30555-7 DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2018.05.035
Accepted Manuscript Hemorrhagic cystitis associated with gefitinib treatment: a case report Peng Zhang, Jinjing Tu, Tieding Chen, Rubing Li PII: S0090-4295(18)30555-7 DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2018.05.035
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Anatomy Module Study Guide
 Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Anatomy Module Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come in for the face-to-face Anatomy tutorial.
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
STRETCHING. Benefits of stretching
 STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
STRETCHING Benefits of stretching Most individuals and athletes, never take stretching seriously. They have what we refer to as a weight lifting mentality. The misconception is that if you do not feel
3/27/2012. Muscle Classification: Functional Groups. Interactions of Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles. Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
Interactions of Skeletal Muscles Skeletal muscles work together or in opposition Muscles only pull (never push) As muscles shorten, the insertion generally moves toward the origin Whatever a muscle (or
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST
 ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
ANATOMY COURSE STUDY GUIDE & CHECKLIST 1 Anatomy Course Study Guide Please use this step-by-step study guide and checklist to ensure that you have covered all that you need to learn by the time you come
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Fetal Response to Intramuscular Epinephrine for Anaphylaxis during Maternal Penicillin Desensitization for Secondary Syphilis
 The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine ISSN: 1476-7058 (Print) 1476-4954 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ijmf20 Fetal Response to Intramuscular Epinephrine for Anaphylaxis
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine ISSN: 1476-7058 (Print) 1476-4954 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/ijmf20 Fetal Response to Intramuscular Epinephrine for Anaphylaxis
Chapter 10. An Overview of the Muscle System
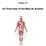 Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Chapter 10 An Overview of the Muscle System The Muscular System Superficial Deep Deep Superficial Frontalis Platysma Deltoid Pectoralis major Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Flexor carpi radialis External
Accepted Manuscript. Robotics in Orthopedics: A Brave New World. Brian S. Parsley, MD, Associate Professor
 Accepted Manuscript Robotics in Orthopedics: A Brave New World Brian S. Parsley, MD, Associate Professor PII: S0883-5403(18)30163-3 DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.032 Reference: YARTH 56428 To appear in:
Accepted Manuscript Robotics in Orthopedics: A Brave New World Brian S. Parsley, MD, Associate Professor PII: S0883-5403(18)30163-3 DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.032 Reference: YARTH 56428 To appear in:
Thinking & Reasoning Publication details, including instructions for authors and subscription information:
 This article was downloaded by: [Umeå University Library] On: 07 October 2013, At: 11:46 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Umeå University Library] On: 07 October 2013, At: 11:46 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
Muscular System. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
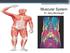 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh The Muscular System. Superficial Deep Structural and functional organization of muscles Platysma Frontalis Orbicularis oculi Zygomaticus major Masseter Orbicularis oris
PAB Test Manual. Introduction
 PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially
 NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially designed to stimulate the body-mind complex to resolve injury, stress, and pain. Unlike other therapeutic
NellroKil1!!ticTilerapy presents manual muscle testing used with a specific protocol specially designed to stimulate the body-mind complex to resolve injury, stress, and pain. Unlike other therapeutic
Compiled and Designed by: Sport Dimensions - 2 -
 SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
SOCCER TRAINING While all reasonable care has been taken during the preparation of this edition, neither the publisher, nor the authors can accept responsibility for any consequences arising from the use
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
ACCEPTED ARTICLE PREVIEW. Accepted manuscript
 First in Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor in Heart Failure Orly Vardeny, PharmD, MS, Travis Tacheny, Scott D. Solomon, MD Cite this article as: Orly Vardeny, PharmD, MS, Travis Tacheny,
First in Class Angiotensin Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitor in Heart Failure Orly Vardeny, PharmD, MS, Travis Tacheny, Scott D. Solomon, MD Cite this article as: Orly Vardeny, PharmD, MS, Travis Tacheny,
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
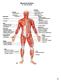 Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Muscular System Dr. Gary Mumaugh 1 Organization of Muscles about 600 human skeletal muscles constitute about half of our body weight three kinds of muscle tissue o skeletal, cardiac, smooth specialized
Naming Skeletal Muscles
 Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Naming Skeletal Muscles Direction of Muscle Fibers Action Location Origin & Insertion Skeletal Muscle Size Shape Number Of Origins Direction of Muscle Fibers Relative to the Midline RECTUS = parallel to
Muscle stations Answers
 Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
Muscle Unit Muscle stations Answers A: What #is: C = 3 F = 5 E = 6 D = 1 B =4 A =2 B 5. superior 6. Inferior 4. anterior C: 1. What # is a,b,c,d 2. What muscle group #1? Quads 3. What muscle is #5? Gastrocnemius
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Name Phone ( ) DOB. Address City State Zip. Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( Occupation Male Female Physician
 Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
Client Information Name Phone ( ) DOB Address City State Zip E-mail: Referred by: Phone ( In case of emergency: Phone ( ) ) Occupation Male Female Physician Health Insurance Carrier Please take a moment
uncorrected proof version
 Galley Proof 8/02/2017; 9:17 File: jcm 1-jcm708.tex; BOKCTP/ljl p. 1 Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering -1 (2017) 1 10 1 DOI 10.3233/JCM-170708 IOS Press 1 2 3 Comparison of sliding
Galley Proof 8/02/2017; 9:17 File: jcm 1-jcm708.tex; BOKCTP/ljl p. 1 Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering -1 (2017) 1 10 1 DOI 10.3233/JCM-170708 IOS Press 1 2 3 Comparison of sliding
Effects of idebenone on electroencephalograms of patients with cerebrovascular disorders
 Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr., 8 (1989) 355-366 355 Elsevier AGG 00266 Effects of idebenone on electroencephalograms of patients with cerebrovascular disorders Takashi Nakano a Matu6 Miyasaka a, Katsumi Mori
Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr., 8 (1989) 355-366 355 Elsevier AGG 00266 Effects of idebenone on electroencephalograms of patients with cerebrovascular disorders Takashi Nakano a Matu6 Miyasaka a, Katsumi Mori
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Journal of Chromatography A 819 (1998)
 Journal of Chromatography A 89 (998) 33 42 Investigation of potential degradation products of a newly synthesised b-lactam antibiotic by multi-stage liquid chromatography electrospray mass spectrometry
Journal of Chromatography A 89 (998) 33 42 Investigation of potential degradation products of a newly synthesised b-lactam antibiotic by multi-stage liquid chromatography electrospray mass spectrometry
Accepted Manuscript. Red yeast rice preparations: are they suitable substitutions for statins?
 Accepted Manuscript Red yeast rice preparations: are they suitable substitutions for statins? Carlos A. Dujovne, MD, Fellow NLA, Certified Clinical Lipidologist PII: S0002-9343(17)30591-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.05.013
Accepted Manuscript Red yeast rice preparations: are they suitable substitutions for statins? Carlos A. Dujovne, MD, Fellow NLA, Certified Clinical Lipidologist PII: S0002-9343(17)30591-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.05.013
Chapter 10. The Muscular System. AP1-Lecture Goodwin College. Introduction. In this chapter we will cover: 4/27/2015
 Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Chapter 10 The Muscular System AP1-Lecture Goodwin College Introduction In this chapter we will cover: Structural and functional organization of muscles Muscles of the head and neck Muscles of the trunk
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Integumentary system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED READINGS o Principles of anatomy and
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. 1) Skeletal 2) Smooth 3) Cardiac 2 Walls of blood vessels. 2 Walls of digestive tract
 S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
S T U D Y G U I D E. Types of Muscle Tissues Match the types of muscle tissues with the words and phrases. ) Skeletal ) Smooth ) Cardiac, Striated Walls of blood vessels, Single nucleus Heart muscle, Involuntary
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
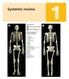 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology POSTURE & GAIT ASSESSMENT MSAK201-I Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of session 4, the student
