Negative feedback-defective PRPS1 mutants drive thiopurine. resistance in relapsed childhood ALL
|
|
|
- Horace Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Negative feedback-defective PRPS1 mutants drive thiopurine resistance in relapsed childhood ALL Benshang Li 1,5,, Hui Li 1,5,, Yun Bai 2,, Renate Kirschner-Schwabe 3,10, Jun J Yang 4, Yao Chen 1,5, Gang Lu 2, Gannie Tzoneva 6, Xiaotu Ma 4, Tongmin Wu 1,5,7, Wenjing Li 8, Haisong Lu 9, Lixia Ding 1,5, Huanhuan Liang 1, Xiaohang Huang 1, Minjun Yang 2, Lei Jin 2, Hui Kang 2, Shuting Chen 2, Alicia Du 9, Shuhong Shen 1,5, Jianping Ding 8, Hongzhuan Chen 7,11, Jing Chen 1, Arend von Stackelberg 3, Longjun Gu 1*, Jinghui Zhang 4, Adolfo Ferrando 6,*, Jingyan Tang 1,*, Shengyue Wang 2,11* & Bin-Bing S. Zhou 1,5,7,11* 1
2 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 CIRCOS plot of genetic alterations identified through whole-exome sequencing of 15 matched triad diagnosis-remission-relapse childhood ALL samples. The inner pink, green, and pale blue circles represent the diagnosis-specific, diagnosis and relapse shared, and relapse-specific mutations, respectively. Interchromosomal translocations are indicated by different curves across the center of CIRCOS plot. 2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 From top to bottom, clinical characteristics, substitution frequency, single nucleotide variants (SNV) and copy number alterations (CNA) in 15 individuals at diagnosis (D) and relapse (R). 3
4 Supplementary Figure 3 Mutations at diagnosis (D) and relapse (R). Mutant Allele Fraction (MAF) identified by intensity of red (SNV) and blue (indel). CNAs (including deletion and amplification) are shown in grey. Cases with oncogenic fusions involving BCR-ABL, TEL-AML1, MLL-AF4 and MLL-rearrangement are marked at the top along with immunophenotype. 4
5 V e ct W T S 1 0 S 1 0 N 1 4 K 1 7 D 1 8 A 1 9 L 1 9 T 3 0 D 1 8 A 1 9 His-PRPS1 Actin V e ct W T S 1 0 N 1 1 G 1 7 V 5 3 I7 2 V C 7 7 D 1 3 Y 3 1 Supplementary Figure 4 The comparable expression levels of wild-type and mutant PRPS1 in lentivirus infected Reh cells. The same cell numbers were used for making cell lysates, and actin was shown as a loading control. Supplementary Figure 5 Viability of Reh cells expressing wild-type PRPS1, relapse-specific PRPS1 mutated alleles or vector only (GV303), treated with increasing concentrations of 6-MP or 6-TG. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 5
6 Supplementary Figure 6 Viability of Reh cells expressing wild-type NT5C2, relapse-specific R238W mutant or vector treated with increasing concentration of 6-MP or 6-TG. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 7 Viability of cells expressing wild-type PRPS1 and various PRPS1 mutants including activating and reduced-function mutants. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 6
7 Supplementary Figure 8 All relapse-specific mutation residues of PRPS1 mapped on the crystal structure of human PRPS1 dimer showing one subunit in beige and the other in tan. Docked ATP and GDP are shown as yellow and red stick, respectively. Cα atoms of mutant residues are shown as spheres. Drug-resistant mutations reported in this work are colored in green, while mutations with unknown function colored in magenta. 7
8 Supplementary Figure 9 Viability of Reh cells expressing control or PRPS1 shrnas were treated with increasing concentration of 6-MP and 6-TG. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 10 Viability of Jurkat cells expressing wild-type PRPS1, relapse-specific PRPS1 mutant alleles or vector treated with increasing concentrations of 6-MP. Values were shown as IC 50. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 8
9 Supplementary Figure 11 Viability of Reh cells expressing wild-type PRPS1 or mutants treated with increasing concentrations of methotrexate (MTX), cytosine arabinoside (AraC), daunorubicin (DNR) or L-asparaginase (L-ASP). Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Re h Ve cto r W T 8h A1 90 T S1 03 T Ve cto r W T 24h A1 90 T S1 03 T Ve cto r W48h T A1 90 T S1 03 T H2AX (S139) H2AX Chk2(T68) Chk2 Actin Supplementary Figure 12 DNA damage response and apoptosis biomarkers in western blot analysis of Reh cells with the indicated PRPS1 mutations. Reh cells were treated with 1 g/ml 6-MP for indicated time and lysed for immunoblot with different antibodies. 9
10 Supplementary Figure 13 Intracellular TGMP measured by LC-MS in Reh cells expressing various PRPS1 mutants treated with 10 M 6-MP for 4 hr. Values are relative concentrations estimated based on standard curves of pure compounds without correcting for the cell matrix s effect, data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 14 Identification of 6-MP metabolite derivatives in Reh cells expressing different PRPS1 variants by LC-MS. Upon de-phosphorylation treatment with phosphatase, r-mp and r-mmp were surrogates for TIMP, r-tg was surrogate for TGMP, respectively. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 10
11 Supplementary Figure 15 Measurement of PRPS1 cellular activity by [ 13 C 5 ]-PRPP in Reh cells. Values were direct reading from LC-MS. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 16 IMP synthesis (flux) through the de novo purine synthesis pathway was measured by [ 13 C 2, 15 N] incorporation into cells. IMP and HX were measured directly by LC-MS. The HX cellular concentration was estimated by a standard curve using isotope-labeled HX with cell matrix effect corrected. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 11
12 Supplementary Figure 17 Identification of IMP in Reh cells by LC-MS. Total IMP concentration=the concentration of unlabeled plus labeled IMP. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 18 Western blot analysis of PRPS1 protein purified from E.coli. 12
13 Supplementary Figure 19 Viability of Reh cells at increasing concentrations of 6-MP in the presence of IMP. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 20 Cell viability for Reh cells treated with increasing concentrations of 6-TG in the presence of hypoxanthine (HX) and IMP, respectively. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 13
14 Supplementary Figure 21 DNA damage response and apoptosis biomarkers in western blot analysis of Reh cells with indicated treatment. Reh cells were mock treated, treated with 6-MP or 6-TG in the presence of IMP or hypoxanthine (HX), and lysed for immunoblot analysis of H2AX (S139), pchk2 (T68), cleaved PARP and their corresponding native forms. Supplementary Figure 22 Reh cells were treated with 10 M 6-MP in the presence of different nucleotides, then intracellular TGMP was measured by LC-MS. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 14
15 Supplementary Figure 23 The HPRT1-catalyzed 6-MP conversion into TIMP and [ 13 C 5, 15 N 4 ]-HX into [ 13 C 5, 15 N 4 ]-IMP were measured simultaneously in Reh cells by following different peaks using LC-MS and were shown as normalized activity. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 24 IMP inhibition of HPRT1 enzymatic activity showing the titration curve with increasing IMP concentration. 15
16 Supplementary Figure 25 De novo pathway blockage by gene knock down is sufficient to reverse the drug resistance and HX increase caused by PRPS1 mutants. Cell viability of Reh cells expressing wild-type or drug resistant A190T and S103T PRPS1 treated with increasing amount of 6-MP with or without ATIC or GART knock-down by CRISPR-CAS9. The concentrations of HX from the same set of samples were measured by LC-MS. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. Supplementary Figure 26 Viability of Reh cells with or without 5 ng/ml GART inhibitor lometrexol. HX and TGMP were measured in the same sample set by LC-MS. Data are shown as the means ± s.d. 16
17 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of 16 cases of children with relapsed ALL in Chinese cohort Patient ID Age at diagnosis (year) Sex WBC ( 10 9 ) Cytogenetics Immunoph enotype BM Blast at diagnosis (%) & BM Blast at Time interval relapse (%) & (Month) ALL Male 1.9 Hyperdiploid (54~55) B 86.4% 58.4% 40.6 ALL Male Normal B 86.4% 62.0% 11.4 ALL Male 20.9 Normal B 90.0% 75.2% 9.1 ALL Male 57.1 Normal B 93.6% 67.2% 10.9 ALL Male Normal T 91.2% 90.0% 10.6 ALL Female Normal B 94.0% 93.6% 17.2 ALL Female t(4;11) B 99.2% 82.8% 6.5 ALL Male Normal T 95.2% 97.2% 18.3 ALL Female t(9;22) B 96.4% 83.0% 7.4 ALL Female Normal T 94.4% 88.8% 11.0 ALL Male 15.5 t(12;21) B 90.4% 96.0% 46.3 ALL Male der(21); t(9,21) T 91.2% 72.8% 10.8 ALL Male 55.6 del(9)(q22) B 87.4% 44.6% 13.0 ALL Male der(11); t(11;14); T 87.2% 65.2% 10.9 del(14)(q12) ALL Male 16.6 t(9;22) B 90.0% 84.0% 4.3 ALL Male 2.9 t(9;22) B 86.4% 97.2% 32.9 & BM blast ratio at diagnosis and relapse were identified by bone marrow morphology observe, samples were separated by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation before cryopreserved. Months elapsed from diagnosis to relapse. 17
18 Supplementary Table 2. All non-silence variants identified in the 15 trios of diagnosis, remission, and relapse samples Sample ID Gene Name Position (in hg19) Mutated type Ref Allele Var Allele Ref Reads in Diagnosis Var Reads in Diagnosis Ref Reads in Remission Var Reads in Remission Ref Reads in Relapse Var Reads in Relapse Var Distribution Predicted amino acid change SIFT PolyPhen SNV ALL-004 NEK2 chr1: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.p269t ALL-004 MYH11 chr16: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.v264m ALL-004 ASB15 chr7: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.p419h 0 1 ALL-004 RPL7A chr9: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v143i ALL-004 PAX5 chr9: DRSV C A stopgain p.e205x ALL-004 ARHGAP40 chr20: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.g301s ALL-004 MKRN2 chr3: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.c343y ALL-004 AFP chr4: DSV C A nonsynonymous p.a544e ALL-004 SPTA1 chr1: RSV C T splicing - ALL-004 RET chr10: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r969w 0 1 ALL-004 CTR9 chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a700t ALL-004 PTPN11 chr12: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.s502l 0 1 ALL-004 FBXO31 chr16: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v162m ALL-004 HOXB3 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.p36l ALL-004 HDAC2 chr6: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.d100g ALL-004 FBXO30 chr6: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r104w ALL-004 SYNE1 chr6: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a1649v ALL-023 NUP210L chr1: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.a976t ALL-023 HMCN1 chr1: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.s928l ALL-023 OR6T1 chr11: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r261c 0 1 ALL-023 OR5A1 chr11: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.g155d 0 1 ALL-023 XRRA1 chr11: DRSV A G splicing ALL-023 FZD10 chr12: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.p563s ALL-023 SPATA13 chr13: DRSV A G nonsynonymous p.q230r ALL-023 CDC42BPB chr14: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r1203k ALL-023 BNIP2 chr15: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.a379v
19 ALL-023 SLC25A11 chr17: DRSV G C nonsynonymous p.p186a ALL-023 SETBP1 chr18: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r54h ALL-023 ACP5 chr19: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.d177n ALL-023 ACP5 chr19: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.r174m ALL-023 RASGRP4 chr19: DRSV G C nonsynonymous p.c469w ALL-023 TGFBRAP1 chr2: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.l817f ALL-023 IL1RN chr2: DRSV G A splicing - ALL-023 XDH chr2: DRSV C T stopgain p.w994x ALL-023 AFTPH chr2: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r242k ALL-023 BPIFB3 chr20: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v228m ALL-023 ODAM chr4: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.p55a ALL-023 P4HA2 chr5: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.r448s 0 1 ALL-023 C5orf64 chr5: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.p124l ALL-023 SOGA3 chr6: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r422h ALL-023 WNT16 chr7: DRSV T G nonsynonymous p.c71g ALL-023 MLL3 chr7: DRSV C A splicing - ALL-023 CCDC129 chr7: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.t872m ALL-023 BBS9 chr7: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.g47e 0 1 ALL-023 SEMA3E chr7: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.r208p ALL-023 DOCK5 chr8: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.e1387k ALL-023 DFNB31 chr9: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.a440t ALL-023 MTOR chr1: DSV A G nonsynonymous p.w1449r 0 1 ALL-023 NRAS chr1: DSV C A nonsynonymous p.g12c ALL-023 ANO5 chr11: DSV G T nonsynonymous p.l609f ALL-023 KRTAP4-11 chr17: DSV G C nonsynonymous p.l161v 1 0 ALL-023 PAX5 chr9: DSV A C nonsynonymous p.v26g 0 1 ALL-023 C1orf173 chr1: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.a795p ALL-023 COL24A1 chr1: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.g1393a - 1 ALL-023 ZNF644 chr1: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.f953l ALL-023 SORCS1 chr10: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.r1078p
20 ALL-023 TAS2R14 chr12: RSV A C nonsynonymous p.s117a ALL-023 MLL2 chr12: RSV T A nonsynonymous p.d5279v - 0 ALL-023 C14orf79 chr14: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r313c ALL-023 FAM71D chr14: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.n195d ALL-023 SPTBN4 chr19: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a382v ALL-023 FPR1 chr19: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a117v ALL-023 PLEKHA3 chr2: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.p253a ALL-023 ZDBF2 chr2: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.s370c ALL-023 ZNF167 chr3: RSV T G nonsynonymous p.y354d ALL-023 ZNF167 chr3: RSV T G stopgain p.y354x ALL-023 MITF chr3: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.r22m ALL-023 ZNF518B chr4: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.d629y ALL-023 QRFPR chr4: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v317m ALL-023 AKD1 chr6: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.m481i ALL-024 RRN3 chr16: DRSV G A splicing ALL-024 FAHD2B chr2: DRSV T C nonsynonymous p.i309v ALL-024 PNPLA3 chr22: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.a279e 1 0 ALL-024 CNTN6 chr3: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.s381y ALL-024 CMYA5 chr5: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.a444e 0 0 ALL-024 DHX32 chr10: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.t732m ALL-024 BZRAP1 chr17: DSV C A nonsynonymous p.r1705l ALL-024 EIF3A chr10: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.s1263i ALL-024 KATNAL1 chr13: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r445h ALL-024 KIF23 chr15: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r631h ALL-024 TTN chr2: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.d5177e ALL-039 CEP350 chr1: DRSV A C nonsynonymous p.d1617a ALL-039 CPN1 chr10: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.s100l ALL-039 UBTD1 chr10: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.s187l ALL-039 B3GNT4 chr12: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.p6a ALL-039 MASP1 chr3: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r127h
21 ALL-039 SLC22A2 chr6: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.g82d ALL-039 PXDNL chr8: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.g923c 0 1 ALL-039 ASTN2 chr9: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r285w ALL-039 JAK1 chr1: DSV C G nonsynonymous p.s703t ALL-039 AHNAK2 chr14: DSV C T nonsynonymous p.r5502q ALL-039 PLCH1 chr3: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.t1658m ALL-039 PTPRO chr12: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.p632q 0 1 ALL-039 PNMA1 chr14: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.e154d ALL-039 MLL3 chr7: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.d2024y ALL-039 NBN chr8: RSV A C nonsynonymous p.i41s ALL-057 IL15RA chr10: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.p212l ALL-057 OR10H3 chr19: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.t281s ALL-057 SMPD4 chr2: DRSV G A stopgain p.r507x ALL-057 SCN11A chr3: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.a1335s ALL-057 GABRP chr5: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.a369s ALL-057 NOTCH1 chr9: DRSV A G nonsynonymous p.l1678p 0 1 ALL-057 LIN28A chr1: DSV C T nonsynonymous p.a10v ALL-057 PIK3CD chr1: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.e1021k 0 1 ALL-057 PLXNA1 chr3: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.e775k ALL-057 GLTPD1 chr1: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.v177m ALL-057 ATP1B1 chr1: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r91h ALL-057 GPR3 chr1: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.l253f ALL-057 FGR chr1: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r185w ALL-057 ZNF691 chr1: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.s206n ALL-057 ST3GAL3 chr1: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r105w ALL-057 AKR1A1 chr1: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.t143i ALL-057 FUBP1 chr1: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.l254s ALL-057 ABCA4 chr1: RSV C T splicing - ALL-057 SLC25A28 chr10: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a221v ALL-057 UBXN1 chr11: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r233q
22 ALL-057 SF1 chr11: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.m36i ALL-057 C11orf85 chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.p116l ALL-057 GSTP1 chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.v145m ALL-057 B3GNT4 chr12: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a8t ALL-057 SLC16A7 chr12: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a412t ALL-057 MDM2 chr12: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.k191r ALL-057 GNB3 chr12: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.s122p ALL-057 SHISA2 chr13: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a292t ALL-057 IPO4 chr14: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r264h 0 1 ALL-057 KIAA1737 chr14: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a263t ALL-057 BUB1B chr15: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.i878t 0 1 ALL-057 TLN2 chr15: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.r281m ALL-057 TRIP4 chr15: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a319t ALL-057 TXNDC11 chr16: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.e372k ALL-057 TUFM chr16: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a254t ALL-057 SRCAP chr16: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.r2070p ALL-057 C16orf80 chr16: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r101h ALL-057 SPG7 chr16: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.m757i ALL-057 TRPV2 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r515h 0 1 ALL-057 SLFN13 chr17: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.g57r 0 1 ALL-057 IKZF3 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.t190m ALL-057 ATXN7L3 chr17: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r229k ALL-057 GJC1 chr17: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.y65h 0 1 ALL-057 FMNL1 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a81t 1 0 ALL-057 KIF2B chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a112t ALL-057 POLG2 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.s19f ALL-057 NOTUM chr17: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v452i ALL-057 DUS1L chr17: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v144i ALL-057 CEP192 chr18: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a2400t ALL-057 TSHZ1 chr18: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r227h
23 ALL-057 KRI1 chr19: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v137i ALL-057 ZNF653 chr19: RSV C T nonsynonymous G344S ALL-057 RFX1 chr19: RSV G A stopgain p.q627x ALL-057 ZNF555 chr19: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.s321g ALL-057 KDM4B chr19: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a211v ALL-057 KCNH7 chr2: RSV G A stopgain p.q672x ALL-057 GAL3ST2 chr2: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.l140p ALL-057 PCGF1 chr2: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r102w ALL-057 SMYD1 chr2: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r76h ALL-057 SNRNP200 chr2: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r598h 0 1 ALL-057 TRPM2 chr21: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.s152n ALL-057 SF3A1 chr22: RSV C T nonsynonymous V142M ALL-057 POLR3H chr22: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a94v ALL-057 CX3CR1 chr3: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.s156n ALL-057 USP19 chr3: RSV C T nonsynonymous V616M ALL-057 RHOA chr3: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.c16y 0 1 ALL-057 BSN chr3: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.h3219y - 0 ALL-057 IQCF1 chr3: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r103w ALL-057 MAGI1 chr3: RSV G A stopgain p.r1451x ALL-057 INTU chr4: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a452t ALL-057 CCDC158 chr4: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r406q ALL-057 GNPDA1 chr5: RSV C T splicing - ALL-057 ITK chr5: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.m438t ALL-057 DDX41 chr5: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r255c ALL-057 TFAP2A chr6: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.p313h ALL-057 DSE chr6: RSV A C nonsynonymous p.y816s ALL-057 ARHGAP18 chr6: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r636c ALL-057 PRRC2A chr6: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r503w ALL-057 CYP39A1 chr6: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r103h ALL-057 MUT chr6: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.d165g
24 ALL-057 HTR1E chr6: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a140v ALL-057 ZFAT chr8: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r766w ALL-057 LGI3 chr8: RSV G A stopgain p.r133x ALL-057 PRSS3 chr9: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a147v ALL-057 CTSL1 chr9: RSV T A nonsynonymous p.v129e ALL-057 BCORL1 chrx: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.v265m 0 0 ALL-057 MECP2 chrx: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.t158m 0 1 ALL-057 EMD chrx: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.h166y ALL-058 FAM55D chr11: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.t69m ALL-058 MRC2 chr17: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.d773n ALL-058 C3 chr19: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.p292t ALL-058 OSM chr22: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.g2r ALL-058 MUC17 chr7: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.e4270k - 0 ALL-058 IKZF1 chr7: DRSV G C nonsynonymous p.g226a 0 1 ALL-058 MACF1 chr1: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.v3109i ALL-058 PLA2G7 chr6: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.r82c 0 1 ALL-058 CDC42BPA chr1: RSV A T nonsynonymous p.f337l 0 1 ALL-058 TARBP1 chr1: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.f1180l ALL-058 PEX16 chr11: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v310i ALL-058 ACP2 chr11: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.v206l ALL-058 KRAS chr12: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.g12a ALL-058 MAP4K5 chr14: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.v739i ALL-058 TMEM8A chr16: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.r304m ALL-058 TBC1D26 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.g14e ALL-058 NLRP2 chr19: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.s947n ALL-058 AAK1 chr2: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.a663v ALL-058 ZNF512B chr20: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r864q ALL-058 PLSCR2 chr3: RSV A C nonsynonymous p.i123s ALL-058 TRIM73 chr7: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.r221l ALL-058 ASAP1 chr8: RSV G C splicing
25 ALL-058 PRPS1 chrx: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.s103t ALL-058 KIF4A chrx: RSV A C splicing - ALL-059 NRAS chr1: DRSV T A nonsynonymous p.q61l ALL-059 CDH18 chr5: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.a156v ALL-059 VPS13B chr8: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v2389m ALL-059 CHM chrx: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.d585n ALL-059 DAB1 chr1: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.a144s ALL-061 TPCN1 chr12: DRSV C G nonsynonymous p.q746e ALL-061 NEDD4L chr18: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v517m ALL-061 RHPN2 chr19: DRSV G A stopgain p.q378x ALL-061 TNC chr9: DRSV A C nonsynonymous p.l1664r ALL-061 IL1RAPL1 chrx: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.d399n ALL-061 OR5AS1 chr11: RSV T G nonsynonymous p.l250v ALL-061 OR52E6 chr11: RSV C T stopgain p.w133x ALL-061 FRY chr13: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.d2654h ALL-061 FBN1 chr15: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.e963k ALL-061 MYO9A chr15: RSV T A nonsynonymous p.q622h ALL-062 SH3PXD2A chr10: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r1031h ALL-062 ARMC4 chr10: DRSV T C nonsynonymous p.n724s ALL-062 SUGT1 chr13: DRSV A G nonsynonymous p.e92g ALL-062 BCL11B chr14: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.s394l ALL-062 FBXW7 chr4: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r385h 0 1 ALL-062 CTNND2 chr5: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.g985s ALL-062 ZDHHC11 chr5: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.v193i ALL-062 CSPG4 chr15: DSV T C nonsynonymous p.n2034s ALL-062 FABP3 chr1: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.l95m ALL-062 FAM71C chr12: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r65h ALL-062 PTPLAD1 chr15: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.d182n ALL-062 ELMO3 chr16: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r687h ALL-062 TAF15 chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r525q
26 ALL-062 PRKACA chr19: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.d213n 0 1 ALL-062 LBP chr20: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.p347l 0 1 ALL-062 MED12L chr3: RSV A T nonsynonymous p.n1003i ALL-062 MLL3 chr7: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r4789q ALL-062 MAGEC3 chrx: RSV G C stoploss p.x347y ALL-063 MYOM3 chr1: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.t1269m ALL-063 DRD2 chr11: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.v154i ALL-063 NAV3 chr12: DRSV T A nonsynonymous p.y1915n ALL-063 KIAA0564 chr13: DRSV T A nonsynonymous p.q262h 0 1 ALL-063 UBA2 chr19: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r122q 0 1 ALL-063 TRIOBP chr22: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.e1372d ALL-063 SLITRK3 chr3: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r777c ALL-063 XIRP1 chr3: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.a1486t ALL-063 FAT4 chr4: DSV A T nonsynonymous p.k3971n ALL-063 C1orf173 chr1: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.e900k ALL-063 MINPP1 chr10: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.l280f ALL-063 ARHGAP32 chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.p878s ALL-063 PCF11 chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.g883s ALL-063 OVCH1 chr12: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r301q ALL-063 EIF4A1 chr17: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.r319l ALL-063 ZNF257 chr19: RSV T A nonsynonymous p.c203s ALL-063 NLRC4 chr2: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.t460m ALL-063 OSTalpha chr3: RSV A T splicing - ALL-063 ALB chr4: RSV C A stopgain p.s294x ALL-063 FBN2 chr5: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.r414l ALL-063 CMYA5 chr5: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.e3484k ALL-063 ALDH8A1 chr6: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.t335m ALL-063 MBOAT1 chr6: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.m289i ALL-063 POT1 chr7: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.e194q ALL-063 CRISPLD1 chr8: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.p130l
27 ALL-064 NFASC chr1: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r83q ALL-064 WNT3A chr1: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.r173q ALL-064 ARID1A chr1: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.s2202i ALL-064 KNDC1 chr10: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.a1399t ALL-064 CYP2C8 chr10: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.h316n ALL-064 ASPHD1 chr16: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v294i ALL-064 ZNRF4 chr19: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.c348f 0 1 ALL-064 TPO chr2: DRSV A C nonsynonymous p.t725p 1 0 ALL-064 TMPRSS15 chr21: DRSV C A splicing - ALL-064 CAND2 chr3: DRSV A T nonsynonymous p.s364c ALL-064 CTBP1 chr4: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.a73v ALL-064 FAT4 chr4: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v4258i 1 0 ALL-064 USO1 chr4: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.s301n ALL-064 NRXN1 chr2: DSV C T nonsynonymous p.a165t ALL-064 OMP chr11: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.v158m ALL-064 PSPC1 chr13: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.q253e ALL-064 KDM6B chr17: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r669q ALL-064 ABCB11 chr2: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.l81f ALL-064 POLQ chr3: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.h1405d ALL-064 CXorf26 chrx: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.e168d ALL-065 MTF2 chr1: DRSV G T startgain - ALL-065 RECQL5 chr17: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.e573k ALL-065 NCBP2 chr3: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.r112h ALL-065 MAP3K4 chr6: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.g1316r ALL-065 PAX5 chr9: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.l58f ALL-065 DNAH9 chr17: RSV A T nonsynonymous p.n627i ALL-065 ZIM2 chr19: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r402c ALL-066 CDC73 chr1: DRSV T A nonsynonymous p.i182n 0 1 ALL-066 PCDH15 chr10: DRSV G C splicing - ALL-066 OTOF chr2: DRSV C A nonsynonymous p.c24f
28 ALL-066 TBCK chr4: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.a622e 0 1 ALL-066 PIK3R1 chr5: DRSV A G splicing - ALL-066 LRRN3 chr7: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.d28y ALL-066 H2BFWT chrx: DRSV C T nonsynonymous p.e155k ALL-066 MUC5B chr11: DSV G A nonsynonymous p.r108h - 0 ALL-066 C10orf90 chr10: RSV T C nonsynonymous p.i49v ALL-066 RGR chr10: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.g30s ALL-066 TCP11L2 chr12: RSV C T stopgain p.r102x ALL-066 LTBP2 chr14: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.g1081r ALL-066 SLC6A2 chr16: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.g20e - 0 ALL-066 KRT34 chr17: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.q306h ALL-066 TTN chr2: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.r12650p ALL-066 ZNF804A chr2: RSV T C nonsynonymous F952S ALL-066 EP300 chr22: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.c1385y 0 1 ALL-066 SEMA5A chr5: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.q500h ALL-066 CSMD1 chr8: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.a181t ALL-066 C9orf93 chr9: RSV A G nonsynonymous K369E ALL-066 TLE4 chr9: RSV G A splicing - ALL-067 ANKRD33 chr12: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.v261i ALL-067 HOXD4 chr2: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.g83d ALL-067 AQP12B chr2: DRSV A C nonsynonymous p.f51c 1 0 ALL-067 WDR36 chr5: DRSV A C nonsynonymous p.i657l ALL-067 BRD9 chr5: DRSV T A nonsynonymous p.m406l ALL-067 MXRA5 chrx: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.t2430m ALL-067 KIAA1804 chr1: DSV C A nonsynonymous p.a450d ALL-067 GUCY1A2 chr11: RSV C A nonsynonymous D362Y ALL-067 ABL1 chr9: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.t315i 0 1 ALL-076 PAMR1 chr11: DRSV G A nonsynonymous p.p67l 0 1 ALL-076 DCHS1 chr11: DRSV G T nonsynonymous p.a2095e ALL-076 TNPO1 chr5: DRSV T G stopgain p.l57x 28
29 ALL-076 RHPN2 chr19: DSV T C nonsynonymous p.q384r ALL-076 SPEF2 chr5: DSV G C splicing - ALL-076 MARK1 chr1: RSV C T stopgain p.q618x ALL-076 C10orf91 chr10: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.p39t ALL-076 KBTBD4 chr11: RSV C A nonsynonymous p.a139s ALL-076 GCN1L1 chr12: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.d225h ALL-076 CHD8 chr14: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.l614v ALL-076 LOC81691 chr16: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.l187f ALL-076 SRSF1 chr17: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.e60d ALL-076 KIAA1755 chr20: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.r34c ALL-076 PTPRG chr3: RSV G A nonsynonymous p.v237i ALL-076 FAM149A chr4: RSV G T nonsynonymous p.r410l ALL-076 SCD5 chr4: RSV C T nonsynonymous p.r247h - 0 ALL-076 KCNK5 chr6: RSV C G nonsynonymous p.e48q ALL-076 KIFC2 chr8: RSV G C nonsynonymous p.r415p 0 1 ALL-076 PRPS1 chrx: RSV A G nonsynonymous p.n144s Indels ALL-004 TTN chr2: RSV GAGA G Coden deletion p.s ALL-023 SMC3 chr10: DRSV G GTAGC Frame shift - ALL-023 MAML2 chr11: DSV CTGT C Coden deletion p.qq607q ALL-023 PELP1 chr17: DSV CTCT C Coden deletion p.ee900e ALL-024 MYT1 chr20: RSV GGAA G Coden deletion p.e284- ALL-024 TPRKB chr2: RSV GATTT G Frame shift - ALL-024 NIPBL chr5: RSV AG A Frame shift - ALL-057 DNAH5 chr5: DRSV A AG Frame shift - ALL-057 PKN3 chr9: DSV - G Frame shift ALL-057 NCOA3 chr20: RSV GCAA G Coden deletion p.q ALL-057 ZNF649 chr19: RSV AAC Coden deletion p.v306del ALL-057 SEC24B chr4: RSV G GA Frame shift - ALL-057 VRTN chr14: RSV GC G Frame shift - 29
30 ALL-057 C19orf51 chr19: RSV C Frame shift - ALL-057 KIF6 chr6: RSV A Frame shift - ALL-057 TEAD2 chr19: RSV TG T Frame shift - ALL-058 KRT1 chr12: DRSV ALL-058 TMEM163 chr2: RSV ALL-059 NCOA3 chr20: DRSV ALL-061 TCHH chr1: RSV T CACCTCCG GAGCCGT AGCTGCT GAGTCATG CTTGAACA CTT GCAGCAG CAGCAGC AGCAA C Coden deletion G Coden deletion G Coden deletion TTGCTG CTCGCG CCTCTCC Codon insertion ALL-062 NBEAL1 chr2: DRSV T TGA Frame shift - p.ssygs GGG557G p.evfkh DS241A p.qqqqq QQ1244Q p.q506rr GASSK ALL-062 NR3C1 chr5: RSV T TC Frame shift - ALL-062 SFRS15 chr21: RSV CTGTCGTG Frame shift - ALL-063 ZNF236 chr18: DRSV A AGCC Codon insertion p.h763qp ALL-063 MGA chr15: DRSV T TC Frame shift - ALL-063 YPEL5 chr2: RSV CT C Frame shift - ALL-064 DIDO1 chr20: DRSV C CT Frame shift - ALL-064 RPL5 chr1: RSV T TA Frame shift - ALL-066 NOTCH1 chr9: DRSV TGGCG GCTGCAGG Frame shift - ALL-076 SETD2 chr3: DSV T TC Frame shift - ALL-076 ATXN1 chr6: RSV ATGC A Coden deletion p.qh208h Abbreviation: DSV, diagnosis-specific variant; DRSV, diagnosis and relapse shared variant; RSV, relapse-specific variant. 30
31 Supplementary Table 3. samples Summary of somatic mutations in the 15 paired diagnosis and relapse Mutations DSV DRSV RSV Total Missense/Gene 26/25 103/ / /301 Nonsense/Gene 0/0 6/6 10/10 16/16 Splice site/gene 1/1 7/7 7/7 15/15 Indels Frame shift/gene 2/2 6/6 11/11 19/19 Coden Insertion & deletion/gene 2/2 3/3 7/7 12/11 Total/Gene 31/30 125/ / /356 Abbreviation: DSV, diagnosis-specific variant; DRSV, diagnosis and relapse shared variant; RSV, relapse-specific variant. 31
32 Supplementary Table 4. SNVs correlation between whole-exome sequencing and microarray array Sample ID Total Affy SNP number in capture region Detected in Affy 6.0 Array Detected in Seq. (depth>1) Consistent with Chip (depth>1) Percentage (depth>1) Detected in Seq. Depth >8 Consisten t with Chip (depth>8 ) Percentage (depth>8) ALL-058-D 9,959 9,689 9,620 9, % 8,575 8, % ALL-058-CR 9,959 9,247 9,224 7, % 8,844 7, % ALL-058-R 9,959 9,602 9,544 9, % 8,423 8, % ALL-059-D 9,959 9,808 9,715 9, % 8,455 8, % ALL-059-CR 9,959 9,790 9,750 9, % 8,892 8, % ALL-059-R 9,959 9,612 9,570 9, % 8,551 8, % ALL-061-D 9,959 9,870 9,377 8, % 6,776 6, % ALL-061-CR 9,959 9,450 9,421 8, % 8,821 8, % ALL-061-R 9,959 9,601 9,592 9, % 9,472 9, % ALL-063-D 9,959 9,876 9,859 9, % 9,351 9, % ALL-063-CR 9,959 9,887 9,861 9, % 9,282 9, % ALL-063-R 9,959 9,700 9,673 9, % 9,127 9, % ALL-057-D 9,959 9,864 9,850 9, % 9,494 9, % ALL-057-CR ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ALL-057-R 9,959 9,836 9,824 9, % 9,509 9, % ALL-062-D 9,959 9,843 9,823 9, % 9,409 9, % ALL-062-CR 9,959 9,534 9,517 8, % 9,275 8, % ALL-062-R 9,959 9,745 9,722 9, % 9,257 9, % ALL-076-D 13,439 13,244 13,210 13, % 12,748 12, % ALL-076-CR 13,439 13,370 13,329 13, % 12,612 12, % ALL-076-R 13,439 13,273 13,241 13, % 12,653 12, % ALL-024-D 13,439 13,313 13,275 13, % 12,838 12, % ALL-024-CR 13,439 13,330 13,272 13, % 12,534 12, % ALL-024-R 13,439 12,912 12,865 12, % 12,097 11, % ALL-065-D 13,439 13,226 13,190 13, % 12,537 12, % ALL-065-CR 13,439 13,360 13,325 13, % 12,651 12, % ALL-065-R 13,439 13,204 13,179 13, % 12,670 12, % ALL-023-D 13,439 13,277 13,193 12, % 11,636 11, % ALL-023-CR 13,439 13,355 13,274 13, % 11,811 11, % ALL-023-R 13,439 12,951 12,856 12, % 11,361 11, % ALL-004-D 13,439 13,289 13,243 13, % 12,454 12, % ALL-004-CR 13,439 13,289 13,260 13, % 12,777 12, % ALL-004-R 13,439 13,075 13,021 12, % 12,247 12, % ALL-039-D 13,439 13,305 13,276 13, % 12,778 12, % ALL-039-CR 13,439 13,181 13,123 12, % 12,158 12, % ALL-039-R 13,439 13,145 13,113 12, % 12,620 12, % ALL-067-D 13,439 13,274 13,230 13, % 12,555 12, % ALL-067-CR 13,439 13,303 13,206 12, % 11,596 11, % ALL-067-R 13,439 12,957 12,922 12, % 12,450 12, % ALL-064-D 13,439 13,265 13,188 12, % 11,727 11, % 32
33 ALL-064-CR 13,439 13,338 13,295 13, % 12,587 12, % ALL-064-R 13,439 13,195 13,148 12, % 12,333 12, % ALL-066-D 13,439 13,311 13,236 13, % 12,176 12, % ALL-066-CR 13,439 13,339 13,282 13, % 12,299 12, % ALL-066-R 13,439 13,164 13,135 12, % 12,746 12, % Abbreviation: ND, No data. * Captured by using SureSelect Human All Exon 38Mb kit. Others using 50Mb kit. 33
34 Supplementary Table 5. Somatic copy number alterations Sample ID Chromosome Start* End* Copy Number CytoBand Diagnosis Relapse ALL-004 chr q21.2-q ALL-004 chr q21.2-q ALL-004 chr p15.33-q ALL-004 chr p25.3-q ALL-004 chr p ALL-004 chr p15.3-q ALL-004 chr p15.5-q ALL-004 chr q22.1-q ALL-004 chr p11.32-q ALL-004 chr q11.2-q ALL-004 chr q11.1-q ALL-023 chr p ALL-023 chr q13-q ALL-023 chr p24.3-p ALL-023 chr p ALL-023 chr p21.3-p ALL-023 chr p13.33-p ALL-023 chr p12.3-p ALL-023 chr p13.3-p ALL-023 chr p11.2-q ALL-023 chr q ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr q21.1-q ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr q21.2-q ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr q23.3-q ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr q ALL-024 chr q26-q ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p23-p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p22.2-p ALL-024 chr p21.1-p ALL-024 chr p22.1-p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p
35 ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p21.3-p ALL-024 chr p21.2-p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p ALL-024 chr p21.1-p ALL-024 chr q ALL-039 chr p ALL-039 chr p ALL-039 chr q ALL-039 chr p22.1-p ALL-039 chr p22.1-p ALL-039 chr p ALL-039 chr p ALL-039 chr q ALL-039 chr q ALL-039 chr q ALL-039 chr q22.2-q ALL-039 chr p11.32-p ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr q31.2-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q33.3-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q35.2-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr p15.3-p ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr p14.1-7p ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q11.22-q ALL-058 chr q11.23-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q22.1-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q32.1-q ALL-058 chr q32.2-q ALL-058 chr q33-q
36 ALL-058 chr q34-q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q36.2-q ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr p ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q ALL-058 chr q13.12-q ALL-058 chr q11.2-q ALL-061 chr q ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr p ALL-061 chr q ALL-061 chr q ALL-062 chr p ALL-062 chr p24.3-p ALL-062 chr p15.3-q ALL-062 chr q ALL-062 chr q ALL-062 chr q ALL-062 chr p ALL-062 chr p11.31-p ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr p ALL-063 chr p ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr p ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q31.33-q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q35-q ALL-063 chr p ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q ALL-063 chr q
37 ALL-064 chr p24.3-p ALL-064 chr q21.11-q ALL-064 chr q21.11-q ALL-064 chr q22.31-q ALL-064 chr q23.2-q ALL-064 chr q ALL-064 chr q ALL-064 chr q24.1-q ALL-064 chr q ALL-064 chr q ALL-065 chr p ALL-065 chr q ALL-065 chr p ALL-065 chr p ALL-065 chr p22.1-p ALL-065 chr p22.1-p ALL-065 chr p ALL-065 chr p21.3-p ALL-066 chr p24.3-p ALL-066 chr p ALL-066 chr p21.3-p ALL-066 chr q ALL-067 chr p ALL-067 chr p22.3-p ALL-067 chr p ALL-067 chr p14.1-q ALL-067 chr q ALL-076 chr q ALL-076 chr p24.3-p ALL-076 chr q ALL-076 chr q34.12-q ALL-076 chr q ALL-076 chr q11.2-q ALL-076 chr q11.1-q *Based on hg 19 Copy number > 2 represents amplification, < 2 deletion. 37
Supplementary Table 2. Identified causative mutations and/or mutation candidates.
 Supplementary Table 2. Identified causative mutations and/or mutation candidates. Nonsense mutations base change aa change Average depth Result of next generation in 432 patient Hereditary form of the
Supplementary Table 2. Identified causative mutations and/or mutation candidates. Nonsense mutations base change aa change Average depth Result of next generation in 432 patient Hereditary form of the
Supporting Information
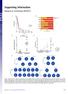 Supporting Information Rampal et al. 10.1073/pnas.1407792111 Fig. S1. Genetic events in leukemic transformation of chronic-phase MPNs. (A) Survival of post-mpn AML patients according to mutational status
Supporting Information Rampal et al. 10.1073/pnas.1407792111 Fig. S1. Genetic events in leukemic transformation of chronic-phase MPNs. (A) Survival of post-mpn AML patients according to mutational status
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. TCGA data set on HNSCCs reanalyzed in this study.
 Supplementary Figure 1 TCGA data set on HNSCCs reanalyzed in this study. Summary of the TCGA dataset on HNSCCs re-analyzed in this study and the respective numbers of samples available within each. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 TCGA data set on HNSCCs reanalyzed in this study. Summary of the TCGA dataset on HNSCCs re-analyzed in this study and the respective numbers of samples available within each. Supplementary
Whole Exome Sequenced Characteristics
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Patient characteristics of 45 whole exome sequenced HNSCC tumors Whole Exome Sequenced Characteristics Tumors (n=45) Age, years Median (range) 61.0 (19-90) Sex,
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Patient characteristics of 45 whole exome sequenced HNSCC tumors Whole Exome Sequenced Characteristics Tumors (n=45) Age, years Median (range) 61.0 (19-90) Sex,
Spectrum of somatically acquired mutations identified by combining WES and genome-wide DNA array analysis in the discovery cohort of 30 JMML cases.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Spectrum of somatically acquired mutations identified by combining WES and genome-wide DNA array analysis in the discovery cohort of 30 JMML cases. A total of 85 somatically acquired
Supplementary Figure 1 Spectrum of somatically acquired mutations identified by combining WES and genome-wide DNA array analysis in the discovery cohort of 30 JMML cases. A total of 85 somatically acquired
Supplementary Information. Exome sequencing identifies distinct mutational patterns in liver fluke related and noninfection-related
 Supplementary Information Exome sequencing identifies distinct mutational patterns in liver fluke related and noninfection-related bile duct cancers Waraporn Chan-on 1,2,3*, Maarja-Liisa Nairismägi 1,2*,
Supplementary Information Exome sequencing identifies distinct mutational patterns in liver fluke related and noninfection-related bile duct cancers Waraporn Chan-on 1,2,3*, Maarja-Liisa Nairismägi 1,2*,
July 2015 Assay ID Assay Name Gene COSMIC ID Amino acid change Nucleotide change Wild type allele (VIC label) Mutant allele (FAM label)
 July 2015 Assay ID Assay Name Gene COSMIC ID Amino acid change Nucleotide change Wild type allele (VIC label) Mutant allele (FAM label) p AHLJ090 AKT1_33765 AKT1 33765 p.e17k c.49g>a C T 2 AHBKFRM BRAF_473
July 2015 Assay ID Assay Name Gene COSMIC ID Amino acid change Nucleotide change Wild type allele (VIC label) Mutant allele (FAM label) p AHLJ090 AKT1_33765 AKT1 33765 p.e17k c.49g>a C T 2 AHBKFRM BRAF_473
Clinical presentation. Duration (Month)
 Supplementary information, Table S1A: Clinical information for 125 PAs. No. Subtype Gender (M/F) Age at diagnosis (year) Clinical presentation Duration (Month) Maximal adenoma diameter(cm) Tumor invasion*
Supplementary information, Table S1A: Clinical information for 125 PAs. No. Subtype Gender (M/F) Age at diagnosis (year) Clinical presentation Duration (Month) Maximal adenoma diameter(cm) Tumor invasion*
p.r623c p.p976l p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r2922w p.r2370h p.c1201y p.a868v p.s952* RING_C BP PHD Cbp HAT_KAT11
 ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
ARID2 p.r623c KMT2D p.v650fs p.p976l p.r2922w p.l1212r p.d1400h DNA binding RFX DNA binding Zinc finger KMT2C p.a51s p.d372v p.c1103* p.d2847fs p.t2671 p.d2847fs p.r4586h PHD/ RING DHHC/ PHD PHD FYR N
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Cytoscape bioinformatics toolset was used to create the network of protein-protein interactions between the product of each mutated gene and the panel of 125 cancer-driving genes
Supplementary Table 1. Information on the 174 single nucleotide variants identified by whole-exome sequencing
 Supplementary Table 1. Information on the 174 single nucleotide s identified by whole-exome sequencing Chr Position Type AF exomes Database 1 10163148 A/G UBE4B missense 0.000326 1534 2 98 1 4.44 Damaging
Supplementary Table 1. Information on the 174 single nucleotide s identified by whole-exome sequencing Chr Position Type AF exomes Database 1 10163148 A/G UBE4B missense 0.000326 1534 2 98 1 4.44 Damaging
Laboratory, Division of Medical Sciences, National Cancer Centre, Singapore
 Supplementary Information Exome sequencing of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma Choon Kiat Ong 1,2*, Chutima Subimerb 1,2,3*, Chawalit Pairojkul 3, Sopit Wongkham 3, Ioana Cutcutache 4, Willie
Supplementary Information Exome sequencing of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma Choon Kiat Ong 1,2*, Chutima Subimerb 1,2,3*, Chawalit Pairojkul 3, Sopit Wongkham 3, Ioana Cutcutache 4, Willie
Spectrum and Classification of ATP7B Variants in a Large Cohort of Chinese Patients with Wilson s Disease Guides Genetic Diagnosis
 Ivyspring International Publisher 638 Theranostics Research Paper 2016; 6(5): 638-649. doi: 10.7150/thno.14596 Spectrum and Classification of ATP7B Variants in a Large Cohort of Chinese Patients with Wilson
Ivyspring International Publisher 638 Theranostics Research Paper 2016; 6(5): 638-649. doi: 10.7150/thno.14596 Spectrum and Classification of ATP7B Variants in a Large Cohort of Chinese Patients with Wilson
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Pearlman R, Frankel WL, Swanson B, et al. Prevalence and spectrum of germline cancer susceptibility gene mutations among patients with early-onset colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol.
Supplementary Online Content Pearlman R, Frankel WL, Swanson B, et al. Prevalence and spectrum of germline cancer susceptibility gene mutations among patients with early-onset colorectal cancer. JAMA Oncol.
Supplementary Figures. Supplementary Figure 1. Dinucleotide variant proportions. These are described and quantitated. for each lesion type.
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Dinucleotide variant proportions. These are described and quantitated for each lesion type. a b Supplementary Figure 2. Non-negative matrix factorization-derived
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Dinucleotide variant proportions. These are described and quantitated for each lesion type. a b Supplementary Figure 2. Non-negative matrix factorization-derived
Supplementary Figure 1
 Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
Count Count Supplementary Figure 1 Coverage per amplicon for error-corrected sequencing experiments. Errorcorrected consensus sequence (ECCS) coverage was calculated for each of the 568 amplicons in the
Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR) is an inheritable
 Genetics Spectrum of Variants in 389 Chinese Probands With Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy Jia-Kai Li, 1 Yian Li, 1 Xiang Zhang, 1 Chun-Li Chen, 2 Yu-Qing Rao, 1 Ping Fei, 1 Qi Zhang, 1 Peiquan Zhao,
Genetics Spectrum of Variants in 389 Chinese Probands With Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy Jia-Kai Li, 1 Yian Li, 1 Xiang Zhang, 1 Chun-Li Chen, 2 Yu-Qing Rao, 1 Ping Fei, 1 Qi Zhang, 1 Peiquan Zhao,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Generation of cetuximab-resistant cells and analysis of singlecell clones. Cetuximab-sensitive cells (LIM1215 and OXCO-2) were chronically treated with cetuximab
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Generation of cetuximab-resistant cells and analysis of singlecell clones. Cetuximab-sensitive cells (LIM1215 and OXCO-2) were chronically treated with cetuximab
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information JAK1 truncating mutations in gynecologic cancer define new role of cancerassociated protein tyrosine kinase aberrations Yuan Ren, Yonghong Zhang, Richard Z. Liu, David A. Fenstermacher,
Supplementary Information JAK1 truncating mutations in gynecologic cancer define new role of cancerassociated protein tyrosine kinase aberrations Yuan Ren, Yonghong Zhang, Richard Z. Liu, David A. Fenstermacher,
DNA Analysis in Glycogen storage disease
 DNA Analysis in Glycogen storage disease Nick Beauchamp PhD Sheffield, Sheffield Children s NHS Foundation Trust 14th October 2010 Glycogen Synthase Type 0 Glycogen Synthesis and Breakdown Type IV UDPGlucose
DNA Analysis in Glycogen storage disease Nick Beauchamp PhD Sheffield, Sheffield Children s NHS Foundation Trust 14th October 2010 Glycogen Synthase Type 0 Glycogen Synthesis and Breakdown Type IV UDPGlucose
DYSREGULATION OF WT1 (-KTS) IS ASSOCIATED WITH THE KIDNEY-SPECIFIC EFFECTS OF THE LMX1B R246Q MUTATION
 DYSREGULATION OF WT1 (-KTS) IS ASSOCIATED WITH THE KIDNEY-SPECIFIC EFFECTS OF THE LMX1B R246Q MUTATION Gentzon Hall 1,2#, Brandon Lane 1,3#, Megan Chryst-Ladd 1,3, Guanghong Wu 1,3, Jen-Jar Lin 4, XueJun
DYSREGULATION OF WT1 (-KTS) IS ASSOCIATED WITH THE KIDNEY-SPECIFIC EFFECTS OF THE LMX1B R246Q MUTATION Gentzon Hall 1,2#, Brandon Lane 1,3#, Megan Chryst-Ladd 1,3, Guanghong Wu 1,3, Jen-Jar Lin 4, XueJun
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Alternative splicing events in the 5K panel.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Alternative splicing events in the 5K panel. The majority of cryptic splicing occurred by creation of an AG or GT (Type I). While some other mutations increased the usage of a nearby
Supplementary Figure 1 Alternative splicing events in the 5K panel. The majority of cryptic splicing occurred by creation of an AG or GT (Type I). While some other mutations increased the usage of a nearby
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B HEC1A PTEN +/+ HEC1A PTEN -/- 16 HEC1A PTEN -/- 22 PTEN RAD51 % Cells with RAD51 foci 40 -IR +IR 30 20 10 * *! TUBULIN 0 HEC1A PTEN+/+ HEC1A PTEN-/- 16 HEC1A PTEN-/- 22 C D 1.0
Supplementary Figure 1 A B HEC1A PTEN +/+ HEC1A PTEN -/- 16 HEC1A PTEN -/- 22 PTEN RAD51 % Cells with RAD51 foci 40 -IR +IR 30 20 10 * *! TUBULIN 0 HEC1A PTEN+/+ HEC1A PTEN-/- 16 HEC1A PTEN-/- 22 C D 1.0
Table S4. List of point mutations found by WES in SMZL patients. * DNA extracted from frozen tissue *Method of detection: Variant detected using
 Table S4. List of point mutations found by WES in SMZL patients. * DNA extracted from frozen tissue *Method of detection: Variant detected using RAMSES (R) or CNAG method (C) or both (R/C) **Validation
Table S4. List of point mutations found by WES in SMZL patients. * DNA extracted from frozen tissue *Method of detection: Variant detected using RAMSES (R) or CNAG method (C) or both (R/C) **Validation
Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations
 Article Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations Jingrui Jiang 1, *, Alexei Protopopov 2, Ruobai
Article Genomic Profiling on an Unselected Solid Tumor Population Reveals a Highly Mutated Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Associated with Oncogenic EGFR Mutations Jingrui Jiang 1, *, Alexei Protopopov 2, Ruobai
Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Tumor Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients
 Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients Chang Eun Yoo 1,2#, Jong-Myeon Park 3#, Hui-Sung Moon 1,2, Je-Gun Joung 2, Dae-Soon Son
Vertical Magnetic Separation of Circulating Cells and Somatic Genomic-Alteration Analysis in Lung Cancer Patients Chang Eun Yoo 1,2#, Jong-Myeon Park 3#, Hui-Sung Moon 1,2, Je-Gun Joung 2, Dae-Soon Son
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. TNFAIP3-associated haplotypes in family 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1 TNFAIP3-associated haplotypes in family 1. The p.leu227* mutation (shown as a star) arose de novo in the first affected member of the family (P1). Red haplotypes carry the TNFAIP3
Supplementary Figure 1 TNFAIP3-associated haplotypes in family 1. The p.leu227* mutation (shown as a star) arose de novo in the first affected member of the family (P1). Red haplotypes carry the TNFAIP3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
Supplemental Tables and Figures
 Supplemental Tables and Figures Post-zygotic de novo changes in glutamate and dopamine pathways may explain discordance of monozygotic twins for schizophrenia Castellani, CA., Melka, MG., Gui, JL., Gallo,
Supplemental Tables and Figures Post-zygotic de novo changes in glutamate and dopamine pathways may explain discordance of monozygotic twins for schizophrenia Castellani, CA., Melka, MG., Gui, JL., Gallo,
Belgian study into von Willebrand Disease (B-Will): First results
 Belgian study into von Willebrand Disease (B-Will): First results Inge Vangenechten VWD Research Unit, Antwerp University Hospital Supported by CSL Behring Chair in von Willebrand Disease, Antwerp University
Belgian study into von Willebrand Disease (B-Will): First results Inge Vangenechten VWD Research Unit, Antwerp University Hospital Supported by CSL Behring Chair in von Willebrand Disease, Antwerp University
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information! Recurrent activating mutation in PRKACA in cortisol-producing adrenal tumors Gerald Goh, Ute I. Scholl, James M. Healy, Murim Choi, Manju L. Prasad, Carol Nelson- Williams, John
Supplementary information! Recurrent activating mutation in PRKACA in cortisol-producing adrenal tumors Gerald Goh, Ute I. Scholl, James M. Healy, Murim Choi, Manju L. Prasad, Carol Nelson- Williams, John
Frequency(%) KRAS G12 KRAS G13 KRAS A146 KRAS Q61 KRAS K117N PIK3CA H1047 PIK3CA E545 PIK3CA E542K PIK3CA Q546. EGFR exon19 NFS-indel EGFR L858R
 Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Spectrum of mutations in monogenic diabetes genes identified from high-throughput DNA sequencing of 6888 individuals
 Bansal et al. BMC Medicine (2017) 15:213 DOI 10.1186/s12916-017-0977-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Spectrum of mutations in monogenic diabetes genes identified from high-throughput DNA sequencing of 6888 individuals
Bansal et al. BMC Medicine (2017) 15:213 DOI 10.1186/s12916-017-0977-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Spectrum of mutations in monogenic diabetes genes identified from high-throughput DNA sequencing of 6888 individuals
Genomic sequencing of meningiomas identifies oncogenic SMO and AKT1 mutations
 Genomic sequencing of meningiomas identifies oncogenic SMO and AKT mutations Priscilla K. Brastianos*; Peleg M. Horowitz*; Sandro Santagata; Robert T. Jones; Aaron McKenna; Gad Getz; Keith L. Ligon; Emanuele
Genomic sequencing of meningiomas identifies oncogenic SMO and AKT mutations Priscilla K. Brastianos*; Peleg M. Horowitz*; Sandro Santagata; Robert T. Jones; Aaron McKenna; Gad Getz; Keith L. Ligon; Emanuele
POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
 POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Andrew J. Ramsay, Víctor Quesada, Miguel Foronda, Laura Conde, Alejandra Martínez-Trillos, Neus Villamor, David Rodríguez, Agnieszka
POT1 mutations cause telomere dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Andrew J. Ramsay, Víctor Quesada, Miguel Foronda, Laura Conde, Alejandra Martínez-Trillos, Neus Villamor, David Rodríguez, Agnieszka
Activating mutations in the NT5C2 nucleotidase gene drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed ALL Supplementary Figure 1. TP53 , RPL11 and BANP
 Activating mutations in the NT5C2 nucleotidase gene drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed ALL Gannie Tzoneva, Arianne Perez Garcia, Zachary Carpenter, Hossein Khiabanian, Valeria Tosello, Maddalena
Activating mutations in the NT5C2 nucleotidase gene drive chemotherapy resistance in relapsed ALL Gannie Tzoneva, Arianne Perez Garcia, Zachary Carpenter, Hossein Khiabanian, Valeria Tosello, Maddalena
TCF3 breakpoints of TCF3-PBX1 (patients 1a 5a) and TCF3-HLF (patients 6a 9a and11a) translocations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 TCF3 breakpoints of TCF3-PBX1 (patients 1a 5a) and TCF3-HLF (patients 6a 9a and11a) translocations. The CpG motifs closest to the breakpoints are highlighted in red boxes and the
Supplementary Figure 1 TCF3 breakpoints of TCF3-PBX1 (patients 1a 5a) and TCF3-HLF (patients 6a 9a and11a) translocations. The CpG motifs closest to the breakpoints are highlighted in red boxes and the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10860 Supplementary Discussion It remains unclear why H3K9 demethylation appeared to be more sensitive to suppression than at least some other histone methylation marks as a result of
doi:10.1038/nature10860 Supplementary Discussion It remains unclear why H3K9 demethylation appeared to be more sensitive to suppression than at least some other histone methylation marks as a result of
Characterisation of structural variation in breast. cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on. the Illumina Genome Analyser
 Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Whole exome sequencing as a first line test: Is there even a role for metabolic biochemists in the future?
 Whole exome sequencing as a first line test: Is there even a role for metabolic biochemists in the future? Tony Marinakii Purine Research Laboratory Biochemical Sciences Whole exome sequencing No doubt
Whole exome sequencing as a first line test: Is there even a role for metabolic biochemists in the future? Tony Marinakii Purine Research Laboratory Biochemical Sciences Whole exome sequencing No doubt
MSI positive MSI negative
 Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
IPATIMUP Translational Research Unit Matching IPATIMUP s Expertise with Company s Research/Clinical Strategy
 IPATIMUP Translational Research Unit Matching IPATIMUP s Expertise with Company s Research/Clinical Strategy Innovative Projects Questions & Needs André Albergaria INDUSTRY Pharma R&D Clinical Research
IPATIMUP Translational Research Unit Matching IPATIMUP s Expertise with Company s Research/Clinical Strategy Innovative Projects Questions & Needs André Albergaria INDUSTRY Pharma R&D Clinical Research
X-exome Sequencing of 405 Unresolved Families Identifies Seven Novel Intellectual Disability Genes
 X-exome Sequencing of 405 Unresolved Families Identifies Seven Novel Intellectual Disability Genes Hao Hu, 1,41 Stefan A. Haas, 2,41 Jamel Chelly, 3,4 Hilde Van Esch, 5 Martine Raynaud, 6,7,8 Arjan P.M.
X-exome Sequencing of 405 Unresolved Families Identifies Seven Novel Intellectual Disability Genes Hao Hu, 1,41 Stefan A. Haas, 2,41 Jamel Chelly, 3,4 Hilde Van Esch, 5 Martine Raynaud, 6,7,8 Arjan P.M.
Supplementary information to:
 Supplementary information to: Digital Sorting of Pure Cell Populations Enables Unambiguous Genetic Analysis of Heterogeneous Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tumors by Next Generation Sequencing Authors
Supplementary information to: Digital Sorting of Pure Cell Populations Enables Unambiguous Genetic Analysis of Heterogeneous Formalin-Fixed Paraffin Embedded Tumors by Next Generation Sequencing Authors
Exomes and Beyond Addressing the Genome with OneSeq. Madhuri Hegde, PhD, FACMG Emory University Emory Genetics Laboratory Atlanta, GA
 Exomes and Beyond Addressing the Genome with OneSeq Madhuri Hegde, PhD, FACMG Emory University Emory Genetics Laboratory Atlanta, GA Technologies to Detect Various Types of Mutations RESOLUTION Targeted
Exomes and Beyond Addressing the Genome with OneSeq Madhuri Hegde, PhD, FACMG Emory University Emory Genetics Laboratory Atlanta, GA Technologies to Detect Various Types of Mutations RESOLUTION Targeted
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Clinical timeline for the discovery WES cases.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Clinical timeline for the discovery WES cases. This illustrates the timeline of the disease events during the clinical course of each patient s disease, further indicating the available
Supplementary Figure 1 Clinical timeline for the discovery WES cases. This illustrates the timeline of the disease events during the clinical course of each patient s disease, further indicating the available
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Round Table: Tissue Biopsy versus Liquid Biopsy. César A. Rodríguez Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL
 Round Table: Tissue Biopsy versus Liquid Biopsy César A. Rodríguez Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL Introduction Classic Advantages of liquid biopsy collection over standard biopsy Standard biopsy
Round Table: Tissue Biopsy versus Liquid Biopsy César A. Rodríguez Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL Introduction Classic Advantages of liquid biopsy collection over standard biopsy Standard biopsy
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
Illumina Trusight Myeloid Panel validation A R FHAN R A FIQ
 Illumina Trusight Myeloid Panel validation A R FHAN R A FIQ G E NETIC T E CHNOLOGIST MEDICAL G E NETICS, CARDIFF To Cover Background to the project Choice of panel Validation process Genes on panel, Protocol
Illumina Trusight Myeloid Panel validation A R FHAN R A FIQ G E NETIC T E CHNOLOGIST MEDICAL G E NETICS, CARDIFF To Cover Background to the project Choice of panel Validation process Genes on panel, Protocol
Circulating tumour DNA in breast cancer. Kathleen Burke, PhD Bioinformatics Postdoctoral Fellow Laboratory of Dr. Jorge Reis-Filho
 Circulating tumour DNA in breast cancer Kathleen Burke, PhD Bioinformatics Postdoctoral Fellow Laboratory of Dr. Jorge Reis-Filho Conflicts of Interest I have no financial relationships to disclose I will
Circulating tumour DNA in breast cancer Kathleen Burke, PhD Bioinformatics Postdoctoral Fellow Laboratory of Dr. Jorge Reis-Filho Conflicts of Interest I have no financial relationships to disclose I will
BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome. Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space
 Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Wells JM, Farris RF, Gosdin TA, et al. Pulmonary
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Wells JM, Farris RF, Gosdin TA, et al. Pulmonary
Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer.
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content
 Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
Supplementary Figure 1. Estimation of tumour content a, Approach used to estimate the tumour content in S13T1/T2, S6T1/T2, S3T1/T2 and S12T1/T2. Tissue and tumour areas were evaluated by two independent
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma
 Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Supplemental Information For: The genetics of splicing in neuroblastoma Justin Chen, Christopher S. Hackett, Shile Zhang, Young K. Song, Robert J.A. Bell, Annette M. Molinaro, David A. Quigley, Allan Balmain,
Published Ahead of Print on March 6, 2015, as doi: /haematol Copyright 2015 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
 Published Ahead of Print on March 6, 2015, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2015.123612. Copyright 2015 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Somatic mutations of cell-free circulating DNA detected by Next Generation Sequencing
Published Ahead of Print on March 6, 2015, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2015.123612. Copyright 2015 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Somatic mutations of cell-free circulating DNA detected by Next Generation Sequencing
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Supplementary Figure 1 HOX fusions enhance self-renewal capacity. Mouse bone marrow was transduced with a retrovirus carrying one of three HOX fusion genes or the empty mcherry reporter construct as described
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ellingford JM, Sergouniotis PI, Lennon R, et
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ellingford JM, Sergouniotis PI, Lennon R, et
Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic
 Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic Davide Rossi, M.D., Ph.D. Hematology IOSI - Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland IOR - Institute of Oncology Reserach Bellinzona - Switzerland
Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic Davide Rossi, M.D., Ph.D. Hematology IOSI - Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland IOR - Institute of Oncology Reserach Bellinzona - Switzerland
BCR ABL1 like ALL: molekuliniai mechanizmai ir klinikinė reikšmė. IKAROS delecija: molekulinė biologija, prognostinė reikšmė. ASH 2015 naujienos
 BCR ABL1 like ALL: molekuliniai mechanizmai ir klinikinė reikšmė. IKAROS delecija: molekulinė biologija, prognostinė reikšmė. ASH 2015 naujienos Ph like ALL BCR ABL1 like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
BCR ABL1 like ALL: molekuliniai mechanizmai ir klinikinė reikšmė. IKAROS delecija: molekulinė biologija, prognostinė reikšmė. ASH 2015 naujienos Ph like ALL BCR ABL1 like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
Case 1. Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX
 Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
Mutational and phenotypical spectrum of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Denmark
 Clin Genet 2016: 90: 247 251 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12692 Mutational and
Clin Genet 2016: 90: 247 251 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Short Report 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd CLINICAL GENETICS doi: 10.1111/cge.12692 Mutational and
Next Generation Sequencing in Haematological Malignancy: A European Perspective. Wolfgang Kern, Munich Leukemia Laboratory
 Next Generation Sequencing in Haematological Malignancy: A European Perspective Wolfgang Kern, Munich Leukemia Laboratory Diagnostic Methods Cytomorphology Cytogenetics Immunophenotype Histology FISH Molecular
Next Generation Sequencing in Haematological Malignancy: A European Perspective Wolfgang Kern, Munich Leukemia Laboratory Diagnostic Methods Cytomorphology Cytogenetics Immunophenotype Histology FISH Molecular
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples
 A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
Acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes
 11/01/2012 Post-ASH meeting 1 Acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes Peter Vandenberghe Centrum Menselijke Erfelijkheid & Afdeling Hematologie, UZ Leuven 11/01/2012 Post-ASH meeting 2 1. Acute myeloid
11/01/2012 Post-ASH meeting 1 Acute leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes Peter Vandenberghe Centrum Menselijke Erfelijkheid & Afdeling Hematologie, UZ Leuven 11/01/2012 Post-ASH meeting 2 1. Acute myeloid
Recent advances in the molecular pathology of lung cancer: role of EGFR and KRAS mutation testing in treatment selection
 ASIP 2009 USCAP Companion Meeting Molecular Pathology for the Practicing Pathologist Recent advances in the molecular pathology of lung cancer: role of EGFR and KRAS mutation testing in treatment selection
ASIP 2009 USCAP Companion Meeting Molecular Pathology for the Practicing Pathologist Recent advances in the molecular pathology of lung cancer: role of EGFR and KRAS mutation testing in treatment selection
Jennifer Hauenstein Oncology Cytogenetics Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA
 Comparison of Genomic Coverage using Affymetrix OncoScan Array and Illumina TruSight Tumor 170 NGS Panel for Detection of Copy Number Abnormalities in Clinical GBM Specimens Jennifer Hauenstein Oncology
Comparison of Genomic Coverage using Affymetrix OncoScan Array and Illumina TruSight Tumor 170 NGS Panel for Detection of Copy Number Abnormalities in Clinical GBM Specimens Jennifer Hauenstein Oncology
Effects of Obesity Related Genetic Variations on Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Distribution in a Chinese Population
 Effects of Obesity Related Genetic Variations on Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Distribution in a Chinese Population Tao Wang #, Xiaojing Ma #, Danfeng Peng, Rong Zhang, Xue Sun, Miao Chen, Jing Yan, Shiyun
Effects of Obesity Related Genetic Variations on Visceral and Subcutaneous Fat Distribution in a Chinese Population Tao Wang #, Xiaojing Ma #, Danfeng Peng, Rong Zhang, Xue Sun, Miao Chen, Jing Yan, Shiyun
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Clinical Genetics. Functional validation in a diagnostic context. Robert Hofstra. Leading the way in genetic issues
 Clinical Genetics Leading the way in genetic issues Functional validation in a diagnostic context Robert Hofstra Clinical Genetics Leading the way in genetic issues Future application of exome sequencing
Clinical Genetics Leading the way in genetic issues Functional validation in a diagnostic context Robert Hofstra Clinical Genetics Leading the way in genetic issues Future application of exome sequencing
A genome-wide association study identifies vitiligo
 A genome-wide association study identifies vitiligo susceptibility loci at MHC and 6q27 Supplementary Materials Index Supplementary Figure 1 The principal components analysis (PCA) of 2,546 GWAS samples
A genome-wide association study identifies vitiligo susceptibility loci at MHC and 6q27 Supplementary Materials Index Supplementary Figure 1 The principal components analysis (PCA) of 2,546 GWAS samples
The Amazing Brain Webinar Series: Select Topics in Neuroscience and Child Development for the Clinician
 The Amazing Brain Webinar Series: Select Topics in Neuroscience and Child Development for the Clinician Part VII Recent Advances in the Genetics of Autism Spectrum Disorders Abha R. Gupta, MD, PhD Jointly
The Amazing Brain Webinar Series: Select Topics in Neuroscience and Child Development for the Clinician Part VII Recent Advances in the Genetics of Autism Spectrum Disorders Abha R. Gupta, MD, PhD Jointly
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
UW359 Ovary 3c 3 Serous Recurrent 68 BRCA1 816delGT BRCA1 del exon 1-2. UW417 Ovary 3c 3 Serous Primary 38 BRCA1 1675delA
 Supplementary Table 1. Cases with deleterious germline mutations, somatic HR mutations, and somatic PTEN mutations. ID Site Stage Grade Histology Tumor Age Germline mutation(s) a Somatic HR mutation(s)
Supplementary Table 1. Cases with deleterious germline mutations, somatic HR mutations, and somatic PTEN mutations. ID Site Stage Grade Histology Tumor Age Germline mutation(s) a Somatic HR mutation(s)
The Personalized Cancer Medicine Initiative at Vanderbilt
 The Personalized Cancer Medicine Initiative at Vanderbilt October 26, 2009 William Pao, MD, PhD Assistant Director, Personalized Cancer Medicine Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Cancer in the United States,
The Personalized Cancer Medicine Initiative at Vanderbilt October 26, 2009 William Pao, MD, PhD Assistant Director, Personalized Cancer Medicine Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Cancer in the United States,
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
devseek (Sequence(Analysis(Panel(for(Neurodevelopmental(Disorders
 ACSL4 Mental/retardation,/XBlinked/63 XLBR ADSL Adenylosuccinase/Deficiency AR AFF2 Mental/retardation,/XBlinked,/FRAXE/type XLBR ALG6 Congenital/disorder/of/glycosylation/type/Ic AR ANK3 Mental/retardation,/autosomal/recessive/37
ACSL4 Mental/retardation,/XBlinked/63 XLBR ADSL Adenylosuccinase/Deficiency AR AFF2 Mental/retardation,/XBlinked,/FRAXE/type XLBR ALG6 Congenital/disorder/of/glycosylation/type/Ic AR ANK3 Mental/retardation,/autosomal/recessive/37
Sample Metrics. Allele Frequency (%) Read Depth Ploidy. Gene CDS Effect Protein Effect. LN Metastasis Tumor Purity Computational Pathology 80% 60%
 Supplemental Table 1: Estimated tumor purity, allele frequency, and independent read depth for all gene mutations classified as either potentially pathogenic or VUS in the metatastic and primary tumor
Supplemental Table 1: Estimated tumor purity, allele frequency, and independent read depth for all gene mutations classified as either potentially pathogenic or VUS in the metatastic and primary tumor
Clonal Evolution of saml. Johnnie J. Orozco Hematology Fellows Conference May 11, 2012
 Clonal Evolution of saml Johnnie J. Orozco Hematology Fellows Conference May 11, 2012 CML: *bcr-abl and imatinib Melanoma: *braf and vemurafenib CRC: *k-ras and cetuximab Esophageal/Gastric: *Her-2/neu
Clonal Evolution of saml Johnnie J. Orozco Hematology Fellows Conference May 11, 2012 CML: *bcr-abl and imatinib Melanoma: *braf and vemurafenib CRC: *k-ras and cetuximab Esophageal/Gastric: *Her-2/neu
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Patel JP, Gönen M, Figueroa ME, et al. Prognostic relevance
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Patel JP, Gönen M, Figueroa ME, et al. Prognostic relevance
GALAFOLD (migalastat) capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GALAFOLD safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GALAFOLD. GALAFOLD (migalastat)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GALAFOLD safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GALAFOLD. GALAFOLD (migalastat)
Novel Insights into Breast Cancer Genetic Variance through RNA Sequencing
 Insights into Breast Cancer Genetic Variance through RNA Sequencing SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Anelia Horvath, 1,2* Suresh Babu Pakala, 2* Prakriti Mudvari, 1* Sirigiri Divijendra Natha Reddy, 2 Kazufumi Ohshiro,
Insights into Breast Cancer Genetic Variance through RNA Sequencing SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Anelia Horvath, 1,2* Suresh Babu Pakala, 2* Prakriti Mudvari, 1* Sirigiri Divijendra Natha Reddy, 2 Kazufumi Ohshiro,
Supplementary Information to
 Supplementary Information to Exome sequencing to identify de novo mutations in sporadic ALS trios Alessandra Chesi 1,11, Brett T. Staahl 2, Ana Jovicic 1, Julien Couthouis 1, Maria Fasolino 3, Alya R.
Supplementary Information to Exome sequencing to identify de novo mutations in sporadic ALS trios Alessandra Chesi 1,11, Brett T. Staahl 2, Ana Jovicic 1, Julien Couthouis 1, Maria Fasolino 3, Alya R.
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia
 Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia Feng-Ming Tien, Hsin-An Hou, Jih-Luh Tang, Yuan-Yeh Kuo, Chien-Yuan Chen, Cheng-Hong Tsai, Ming Yao, Chi-Cheng
Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia Feng-Ming Tien, Hsin-An Hou, Jih-Luh Tang, Yuan-Yeh Kuo, Chien-Yuan Chen, Cheng-Hong Tsai, Ming Yao, Chi-Cheng
Supplementary Figure 1
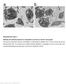 Supplementary Figure 1 Platelets from affected patients are comparable to controls on electron micrograph. Thin-section transmission electron micrographs of representative platelets from a normal control
Supplementary Figure 1 Platelets from affected patients are comparable to controls on electron micrograph. Thin-section transmission electron micrographs of representative platelets from a normal control
Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos 3, Hui Yang 1, and Guillermo Garcia-Manero 1
 Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
6/12/2018. Disclosures. Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective. Outline. COH HopeSeq Heme Panels
 Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
Clinical Genomics The CLIA Lab Perspective Disclosures Raju K. Pillai, M.D. Hematopathologist / Molecular Pathologist Director, Pathology Bioinformatics City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays
 SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
SureSelect Cancer All-In-One Custom and Catalog NGS Assays Detect all cancer-relevant variants in a single SureSelect assay SNV Indel TL SNV Indel TL Single DNA input Single AIO assay Single data analysis
Please Silence Your Cell Phones. Thank You
 Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You Utility of NGS and Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Hematopathology Practice Maria E. Arcila M.D. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Disclosure
Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You Utility of NGS and Comprehensive Genomic Profiling in Hematopathology Practice Maria E. Arcila M.D. Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Disclosure
underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Patient cohorts and study design. To define and interrogate the genetic alterations underlying metastasis and recurrence in HNSCC, we analyzed two groups of patients. The
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH )
 Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH2017-0314) Habibe Kurt, Joseph D. Khoury, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, Guilin Tang, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, and
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH2017-0314) Habibe Kurt, Joseph D. Khoury, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, Guilin Tang, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, and
DNA-seq Bioinformatics Analysis: Copy Number Variation
 DNA-seq Bioinformatics Analysis: Copy Number Variation Elodie Girard elodie.girard@curie.fr U900 institut Curie, INSERM, Mines ParisTech, PSL Research University Paris, France NGS Applications 5C HiC DNA-seq
DNA-seq Bioinformatics Analysis: Copy Number Variation Elodie Girard elodie.girard@curie.fr U900 institut Curie, INSERM, Mines ParisTech, PSL Research University Paris, France NGS Applications 5C HiC DNA-seq
Next generation sequencing analysis - A UK perspective. Nicholas Lea
 Next generation sequencing analysis - A UK perspective Nicholas Lea King s HMDC LMH is part of an integrated pathology service at King s Haematological Malignancy Diagnostic Centre (HMDC) HMDC serves population
Next generation sequencing analysis - A UK perspective Nicholas Lea King s HMDC LMH is part of an integrated pathology service at King s Haematological Malignancy Diagnostic Centre (HMDC) HMDC serves population
EXAMPLE. - Potentially responsive to PI3K/mTOR and MEK combination therapy or mtor/mek and PKC combination therapy. ratio (%)
 Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
NeoTYPE Cancer Profiles
 NeoTYPE Cancer Profiles Multimethod Analysis of 25+ Hematologic Diseases and Solid Tumors Anatomic Pathology FISH Molecular The next generation of diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic assessment NeoTYPE
NeoTYPE Cancer Profiles Multimethod Analysis of 25+ Hematologic Diseases and Solid Tumors Anatomic Pathology FISH Molecular The next generation of diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic assessment NeoTYPE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Somatic ERCC2 Mutations Are Associated with a Distinct Genomic Signature in Urothelial Tumors Jaegil Kim, Kent W Mouw, Paz Polak, Lior Z Braunstein, Atanas Kamburov, Grace Tiao, David J Kwiatkowski, Jonathan
Somatic ERCC2 Mutations Are Associated with a Distinct Genomic Signature in Urothelial Tumors Jaegil Kim, Kent W Mouw, Paz Polak, Lior Z Braunstein, Atanas Kamburov, Grace Tiao, David J Kwiatkowski, Jonathan
