Role of oxytocin in energy metabolism
|
|
|
- Ilene Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Role of oxytocin in energy metabolism Peptides 45 (2013) Valéria Ernestânia Chaves Federal University of São João Del Rei Brazil
2 Oxytocin First peptide hormone whose structure was determined and the first to be chemically synthesized in its biologically active form. Du Vigneaud V, Ressler C, Trippett S. The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin. J Biol Chem 1953; 205:
3 Functions of Oxytocin OT affects: 1. Myometrium, stimulating uterine contraction and 2. Myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland, stimulating the milk ejection. Dale HH. On some physiological actions of ergot. J Physiol(Lond) 1906; 34: Ott J, Scott JC. The galactogogue action of the thymus and corpus luteum. Proc Soc Exp Biol 1910; 8:49.
4 Functions of Oxytocin OT exerts several central influences, from modulating neuroendocrine reflexes to establishing the complex social behaviors related to reproduction and the care of offspring as well as learning and memory. Feldman R, Weller A, Zagoory-Sharon O, Levine A. Evidence for a neuroen-docrinological foundation of human affiliation: plasma oxytocin levels across pregnancy and the post partum period predict mother-infant bonding. PsycholSci 2007;18: Guastella AJ, Mitchell PB, Dadds MR. Oxytocin increases gaze to the eye regionof human faces. Biol Psychiatry 2008;63:3 5. Insel TR, Young L, Wang Z. Central oxytocin and reproductive behaviours. RevReprod 1997;2: Kosfeld M, Heinrichs M, Zak PJ, Fischbacher U, Fehr E. Oxytocin increases trustin humans. Nature 2005;435: Ross HE, Young LJ. Oxytocin and the neural mechanisms regulating social cognition and affiliative behavior. Front Neuroendocrinol 2009;30:
5 Functions of Oxytocin The physiological importance of OT in metabolic homeostasis has also been reported. Camerino C. Low sympathetic tone and obese phenotype in oxytocin-deficientmice. Obesity 2009;7: Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport2008;19: Zhang G, Cai D. Circadian intervention of obesity development via resting-stagefeeding manipulation or oxytocin treatment. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab2011;301:E
6 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008; 19:951 5.
7 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008; 19:951 5.
8 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008; 19:951 5.
9 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008; 19:951 5.
10 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K.Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008; 19:951 5.
11 Mice deficient in OT receptor develop lateonset obesity despite normal food intake and motor activity Takayanagy Y, Kasahara Y, Onaka T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Nishimori K. Oxytocin receptor-deficient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 2008;19:951 5.
12 Mice deficient in OT also increase the body weight accompanied by a 40% increase in abdominal fat pads Figure 1 Body weight and fat mass. Body weight curves of Oxt / (n = 10) and Oxt+/+ (n = 10) male and female mice. No body weight difference between control and knockout mice until 2nd month of age has been observed. Differences in the body weight between Oxt / and wild-type mice were observed at 3rd month of age. No differences between gender were observed within Oxt / or Oxt+/+ mice. *Significantly different with respect to Oxt+/+ with P < (a). Weight of abdominal fat pad in 6 months old Oxt / and Oxt+/+ males and females mice. *Significantly different with respect to Oxt+/+withP<0.05(b). Camerino C. Low sympathetic tone and obese phenotype in oxytocin-deficient mice. Obesity 2009;7:980 4.
13 Mice deficient in OT develop obesity with normal food intake and increase in leptin levels 4th month of age Figure 2 Food intake and leptin plasma levels. Food intake per day in Oxt+/+ (n = 5) and Oxt / (n = 5) male mice (a). The numbers indicate the four consecutive days of measurements. The histogram referred to a food measurement performed at 4th month of age. However, the same results have been obtained at each time. Plasma leptin concentration in male Oxt+/+ (n = 8) and Oxt / (n = 8) mice and in female Oxt+/+ (n = 5) and Oxt / (n = 5) mice at 6 months of age. *Significantly different with respect to Oxt+/+ with P < 0.05(c). Camerino C. Low sympathetic tone and obese phenotype in oxytocin-deficient mice. Obesity 2009;7:980 4.
14 Central OT infusion causes a lower body weight gain in diet-induced obese rats. > 50% Figure 1. Central OT infusion causes body weight loss independently from changes in food intake. The measurements were performed over a 14-day experimental period(weeks 5 through 7 of a high fat diet): (A) Cumulative body weight changes; (B) cumulative food intake. Filled bars: i.c.v. saline infused controls; open bars: i.c.v. OT-infused rats (1.6 nmol/d). Values aremean6semof6to7rats/group.*p,0.05comparedtocontrols. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
15 OT modulates the peripheral metabolism Lipid Metabolism
16 The continuous ICV infusion of OT (1.6 nmol/day for 14 days) caused a body weight loss independently of the changes in food intake and induced an increase in the plasma glycerol levels, which was accompanied by a decrease in the plasma triacylglycerol levels without changes in the plasma insulin, leptin, and glucose levels Table. Effects of i.c.v. oxytocin (1.6 nmol/d) infusion on plasma glucose, insulin, leptin, FFA, glycerol, TG, oleoylethanolamide (OEA), palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), anandamide (AEA) and 2- arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) levels. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
17 The continuous ICV infusion of OT (1.6 nmol/day for 14 days) also induced an increase in the expression and content of hormone-sensitive lipase in adipose tissue, suggesting higher lipolytic activity in this tissue. Figure. Central OT infusion stimulates lipid metabolism. The following analyses were performed on epididymal white adipose tissue (ewat) of i.c.v. saline infused controls (filled bars) and i.c.v. OTinfused rats (1.6 nmol/d; open bars): (A) mrna expression of enzymes related to lipid metabolism; and (B) Western blot analysis of HSL standardized to actin expression; Values are mean ± SEM of 6 to 7 rats/group. *P>0.05, **P>0.01 compared to controls. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
18 Central OT infusion induces hypothalamic OT synthesis and release into the bloodstream Figure 4. Central OT infusion induces hypothalamic OT synthesis and release into the bloodstream. The following parameters were measured at the end of 14-day treatments with two doses of i.c.v. OT infusion: (A) Oxytocin expression (Oxt) in rat hypothalamus; (B) plasma OT levels in saline infused controls (filled bars) and OT-infused rats (1.6 nmol/d, open bars). Values are mean 6 SEM of 6 to 7 rats/group. *P<0.05 compared to controls. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
19 Incubating epididymal adipose tissue with OT (10 nm for 4 h) increased the glycerol content in the incubation medium. Figure 5. OT directly affects lipid metabolism(b C) Epididymal fat pads from lean Wistar rats were incubated at 37ºC in the presence of Krebs-Ringer-Hepes buffer containing 2% FA-free BSA and 0.1% glucose. After 4 h of incubation in the presenceofeithersalineorot(10nm),the amount of (B) glycerol and (C) free fatty acid released in the medium was measured. Values are mean 6 SEM of three independent experiments. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
20 A peripheral and continuous OT treatment (3.6 mg/100 g 1 body weight perdayfor14days)ofwistarratsfedwithacommercialdietdecreased the diameter of the adipocytes without changing adipose tissue mass. Eckertova M, Ondrejcakova M, Krskova K, Zorad S, Jezova D. Subchronic treatment of rats with oxytocin results in improved adipocyte differentiation andincreased gene expression of factors involved in adipogenesis. Br J Pharmacol 2011;162:
21 OT treatment increased number of small adipocytes and the expression of the PPAR-gamma gene, an important transcriptional factor involved in adipogenesis, in epididimal adipose tissue. Eckertova M, Ondrejcakova M, Krskova K, Zorad S, Jezova D. Subchronic treatment of rats with oxytocin results in improved adipocyte differentiation andincreased gene expression of factors involved in adipogenesis. Br J Pharmacol 2011;162:
22 Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor(ppar)-alpha may mediate the body weight gain control, because a peripheral administration of OT (50 nmol for 3 days) did not affect the body weight gain in PPAR-alpha knockout mice but did decrease this parameter in wild-type mice. Figure 7. PPAR-alpha mediates peripheral OT effects. (A) Cumulative body weight gain after 3 days of s.c. saline or OT treatment in PPARalpha KO and wild-type (WT) mice. Values are mean ± SEM of 5 animals/group. *P < 0.05 compared to controls. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
23 The peripheral OT treatment of obese mice fed a high-fat diet induced a decrease in the respiratory quotient, specifically during the light phase, without significantly altering the energy expenditure or the locomotor activity, suggestingthatotpromotestheuseoffatasanenergysubstrate. Figure 4. Chronic Oxt infusion promotes use of fat. (A, B) Effect of chronic Oxt infusion on (A) time course of respiratory quotient (RQ) (B)averageRQinthelightanddarkphases (C) time course of energy expenditure (EE) (D) average values for the light and dark phases (E) time course of cumulative locomotor activity every 0.5 hr (F) average values in the light and dark phases.n=5ineachgroup. *p<0.05,**p<0.01. Maejima Y, Iwasaki Y, Yamahara Y, Kodaira M, Sedbazar U, Yada T. Peripheral oxytocin treatment ameliorates obesity by reducing food intake and visceral fat mass. Aging (Albany, NY) 2011;3:
24 OT modulates the peripheral metabolism Glucose Metabolism
25 Thepresenceofoxytocinintheincubationmedium(1 mol/lfor20min) induced an increase in the rate of glucose 1-14 C oxidation to CO 2 in adipocytes. 40% Fain JN, Gokmen-Polar Y, Bahouth SW. Wortmannin converts insulin but not oxytocin from an antilipolytic to a lipolytic agent in the presence of forskolin. Metabolism 1997;46:62 6.
26 OT was shown to stimulate the glucose oxidation and lipogenesis in adipocytes Hanif K, Goren HJ, Hollenberg MD, Lederis K. Oxytocin action: mechanisms forinsulin like activity in isolated rat adipocytes. Mol Pharmacol 1982;22:381 8.
27 Whether infused centrally or peripherally, chronic OT infusion improved the insulin sensitivity of diet-induced obese rats. Figure. Central OT infusion protects against high fat diet-induced insulin resistance. I.c.v. saline- (black circles) or OT - (1.6 nmol/d; white diamonds) infused rats received: glucose tolerance tests (1.5 g/kg) before (black triangles, dashed line; 3 weeks of HFD; n = 16 rats) or after infusions (7 weeks of HFD; 14-day i.c.v. infusions; n = 6 for each treatment group): (A) delta glucose and (B) delta insulin; One-way ANOVA: *P<0.05 compared to black triangles; {P,0.05 compared to black circles. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
28 Mice deficient in OT have an insulin-resistant state and a lower capability to counteract the glycemia increase following a glucose bolus Figure. Glucose metabolism. Insulin tolerance test (ITT) (a). Representative plots of glucose disposal curves for each experimental condition. (b). Representative plots of glucose disposal curves for each experimental condition. The data are the mean ± ES of blood glucose values from three wild-type and three Oxt / mice normalized on the starting glucose values at time 0 for each mice. *Significantly different with respect to Oxt+/+ with P < Camerino C. Low sympathetic tone and obese phenotype in oxytocin-deficient mice. Obesity 2009;7:980 4.
29 Peripheral OT increased the GLUT-4 (an insulin-dependent glucose transporter) expression in the epididymal adipose tissue. Eckertova M, Ondrejcakova M, Krskova K, Zorad S, Jezova D. Subchronic treatment of rats with oxytocin results in improved adipocyte differentiation andincreased gene expression of factors involved in adipogenesis. Br J Pharmacol 2011;162:
30 OT directly stimulated the insulin release from mice islets via phosphoinositide turnover and protein kinase C activation Effects of various concentrations of OT on release of insulin from mouse islets. Gao ZY, Drews G, Henquin JC. Mechanism of the stimulation of insulin release by oxytocin in normal mouse islets. Biochem J 1991;276:
31 However, the continuous ICV administration of OT to high-fat diet-fed rats did not affect the plasma levels of insulin Table. Effects of i.c.v. oxytocin (1.6 nmol/d) infusion on plasma glucose, insulin, leptin, FFA, glycerol, TG, oleoylethanolamide (OEA), palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), anandamide (AEA) and 2- arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) levels. Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e25565.
32 Deblon N, Veyrat-Durebex C, Bourgoin L, Caillon A, Bussier AL, Petrosino S, et al. Mechanisms of the anti-obesity effects of oxytocin in diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2011;6(9):e Summary of the metabolic effects of oxytocin. Upon chronic central (i.c.v.) or peripheral (s.c.) infusion into diet-induced obese rats, oxytocin (OT) increases triglyceride (TG) uptake, lipolysis, and fatty acid b-oxidation in adipose tissue. OT activates stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 (Scd1) to produce the endocannabinoid oleoylethanolamide (OEA), a known ligand of PPAR-alpha. The action of OT on fatty acid b- oxidation is thus exerted by direct activation of PPAR-alpha target genes via the production of OEA. Red arrows indicate the direction (up or down) of regulation.
33
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Peripheral oxytocin treatment ameliorates obesity by reducing food intake and visceral fat mass
 Δ www.impactaging.com AGING, December 2011, Vol 3 N 12 Research Paper Peripheral oxytocin treatment ameliorates obesity by reducing food intake and visceral fat mass Yuko Maejima 1, Yusaku Iwasaki 1, Yui
Δ www.impactaging.com AGING, December 2011, Vol 3 N 12 Research Paper Peripheral oxytocin treatment ameliorates obesity by reducing food intake and visceral fat mass Yuko Maejima 1, Yusaku Iwasaki 1, Yui
1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]
![1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h] 1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]](/thumbs/87/97258189.jpg) 7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice
 Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity
 ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
In The Name Of God. In The Name Of. EMRI Modeling Group
 In The Name Of God In The Name Of God EMRI Modeling Group Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: Epithelial lining and covering Connective support Muscle movement
In The Name Of God In The Name Of God EMRI Modeling Group Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: Epithelial lining and covering Connective support Muscle movement
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at
 Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution
 Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Obesity in aging: Hormonal contribution Hormonal issues in obesity and aging Hormonal role in regulation of energy balance Genetic component in hormonal regulation Life style contribution to hormonal changes
Activités scientifiques
 Prof. Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud Activités scientifiques I. A role for adipose tissue de novo lipogenesis in glucose homeostasis during catch-up growth: A Randle cycle favoring fat storage Catch-up growth
Prof. Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud Activités scientifiques I. A role for adipose tissue de novo lipogenesis in glucose homeostasis during catch-up growth: A Randle cycle favoring fat storage Catch-up growth
1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1. EE/g lean mass 0,8 0,6 0,4 0,2. Ambulatory locomotor activity. (beam brakes/48h) V MCH MCHpf 0,86 0,85 0,84 0,83 0,82 0,81 0,8
 Supplementary figure 1 vehicle A -pf Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/48h) 25 2 15 1 5 V pf EE/g lean mass 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,8,6,4,2 Total locomotor activity (beam brakes/48h) C D E 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 V pf Ambulatory
Supplementary figure 1 vehicle A -pf Energy expenditure (kcal/kg/48h) 25 2 15 1 5 V pf EE/g lean mass 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,8,6,4,2 Total locomotor activity (beam brakes/48h) C D E 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 V pf Ambulatory
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4171
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1 a b c PF %Change - -4-6 Body weight Lean mass Body fat Tissue weight (g).4.3.2.1. PF GC iwat awat BAT PF d e f g week 2 week 3 NEFA (mmol/l) 1..5. PF phsl (Ser565)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1 a b c PF %Change - -4-6 Body weight Lean mass Body fat Tissue weight (g).4.3.2.1. PF GC iwat awat BAT PF d e f g week 2 week 3 NEFA (mmol/l) 1..5. PF phsl (Ser565)
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]
![TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1] TBP (H) CACAGTGAATCTTGGTTGTAAACTTGA AAACCGCTTGGGATTATATTCG ANGPTL8 (H) CTGGGCCCTGCCTACCGAGA CCGATGCTGCTGTGCCACCA [1]](/thumbs/89/99233308.jpg) ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
ESM Table 1. Immunoblot antibodies. Primary Supplier Dilution Antibody Akt Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology Phosphorylated Cell Signaling 1:1000 Akt (Ser 473) Technology PKCε Cell Signaling 1:1000 Technology
WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH
 MENOPAUSE WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? The cessation of the menstrual cycle for one year. WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH Jan Schroeder, Ph.D. Chair of The Department of Kinesiology California State
MENOPAUSE WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? The cessation of the menstrual cycle for one year. WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH Jan Schroeder, Ph.D. Chair of The Department of Kinesiology California State
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The authors provide an interesting data set concerning the effects of an ATGL inhibitor on energy balance and indices of insulin action in mice fed a high fat diet.
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The authors provide an interesting data set concerning the effects of an ATGL inhibitor on energy balance and indices of insulin action in mice fed a high fat diet.
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Supplementary Table 1. Primer Sequences Used for Quantitative Real-Time PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse Primer (5-3 ) cadl CTTGGGGGCGCGTCT CTGTTCTTTTGTGCCGTTTCG cyl-coenzyme Dehydrogenase, very
Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism
 Research article The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism Ruben Nogueiras, 1,2 Petra Wiedmer, 2 Diego Perez-Tilve, 1 Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, 3 Julia M. Keogh, 4
Research article The central melanocortin system directly controls peripheral lipid metabolism Ruben Nogueiras, 1,2 Petra Wiedmer, 2 Diego Perez-Tilve, 1 Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, 3 Julia M. Keogh, 4
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr
 Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used in qpcr Gene forward primer (5'-3') reverse primer (5'-3') β-actin AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT Hif-p4h-2 CTGGGCAACTACAGGATAAAC GCGTCCCAGTCTTTATTTAGATA
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM IN ADIPOSE TISSUE. Key Points
 December 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 3, pages 31-35) THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM IN ADIPOSE TISSUE By Uberto Pagotto, MD, PhD Endocrinology Unit and Center of Applied Biomedical Research (C.R.B.A.), Department
December 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 3, pages 31-35) THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM IN ADIPOSE TISSUE By Uberto Pagotto, MD, PhD Endocrinology Unit and Center of Applied Biomedical Research (C.R.B.A.), Department
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
University of California, San Diego La Jolla CA 92093
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
Streptozotocin Induces Lipolysis in Rat Adipocytes in Vitro
 Physiol. Res. 51: 255-259, 2002 Streptozotocin Induces Lipolysis in Rat Adipocytes in Vitro T. SZKUDELSKI, K. SZKUDELSKA Department of Animal Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Poznań,
Physiol. Res. 51: 255-259, 2002 Streptozotocin Induces Lipolysis in Rat Adipocytes in Vitro T. SZKUDELSKI, K. SZKUDELSKA Department of Animal Physiology and Biochemistry, University of Agriculture, Poznań,
IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO. IL-6Rα f/f bp. f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp. 500 bp
 STD H 2 O WT KO IL-6Rα f/f IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO 1000 bp 500 bp f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation of T-cell IL-6Rα deficiency. (a) Representative histograms and (b) quantification
STD H 2 O WT KO IL-6Rα f/f IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO 1000 bp 500 bp f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation of T-cell IL-6Rα deficiency. (a) Representative histograms and (b) quantification
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table 1. Tph1+/+ Tph1 / Analyte Supplementary Table 2. Tissue Vehicle LP value
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Mobilisation des lipides du tissu adipeux et insulinorésistance. Dominique Langin
 Obesity Research Laboratory Institut Universitaire de France Franco-Czech Laboratory for Clinical Research on Obesity Mobilisation des lipides du tissu adipeux et insulinorésistance Dominique Langin Séminaire
Obesity Research Laboratory Institut Universitaire de France Franco-Czech Laboratory for Clinical Research on Obesity Mobilisation des lipides du tissu adipeux et insulinorésistance Dominique Langin Séminaire
Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasma measurements Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were determined using ELISA kits according
Supplemental Data Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasma measurements Mouse Glu-OC (undercarboxylated osteocalcin) and Gla-OC (carboxylated osteocalcin) levels were determined using ELISA kits according
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets. James M. Ntambi Ph.D
 Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism
 Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents
 Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
Supplementary Figure S1
 Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin
 Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Leptin Intro/Signaling. ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph
 Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
Leptin Intro/Signaling ATeamP: Angelo, Anthony, Charlie, Gabby, Joseph Overview Intro to Leptin Definition & Sources Physiology Bound vs. Free Receptors Signaling JAK/STAT MAPK PI3K ACC Experimental findings
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
AMPK. Tomáš Kučera.
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation
 Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out
Overall Energy metabolism: Integration and Regulation We have discussed various fuels which are oxidized via different catabolic pathways to generate ATP, or reducing equivalents required to carry out
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice.
 Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Figure S1. Body composition, energy homeostasis and substrate utilization in LRH-1 hep+/+ (white bars) and LRH-1 hep-/- (black bars) mice. (A) Lean and fat masses, determined by EchoMRI. (B) Food and water
Expanded View Figures
 Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
AMPK. Tomáš Kuc era. Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze
 AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
AMPK (AMP- ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE ) Tomáš Kuc era Ústav lékar ské chemie a klinické biochemie 2. lékar ská fakulta, Univerzita Karlova v Praze 2013 AMPK AMP-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE present in all eukaryotic
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO. Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu ABSTRACT
 Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1
 Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1 Authors: Georgios K. Paschos, Salam Ibrahim, Wen-Liang Song, Takeshige Kunieda, Gregory Grant, Teresa M. Reyes, Christopher
Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1 Authors: Georgios K. Paschos, Salam Ibrahim, Wen-Liang Song, Takeshige Kunieda, Gregory Grant, Teresa M. Reyes, Christopher
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids?
 Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING
 HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
Oxytocin reduces caloric intake in men
 Oxytocin reduces caloric intake in men The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
Oxytocin reduces caloric intake in men The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed Citable
change of free fatty acids during incubation was
 EFFECT OF GLUCOSE AND INSULIN ON THE ESTERIFICATION OF FATTY ACIDS BY ISOLATED ADIPOSE TISSUE* By M. S. RABEN AND C. H. HOLLENBERG t (Fromn the Ziskind Research Laboratories, New Englantd Centter Hospital,
EFFECT OF GLUCOSE AND INSULIN ON THE ESTERIFICATION OF FATTY ACIDS BY ISOLATED ADIPOSE TISSUE* By M. S. RABEN AND C. H. HOLLENBERG t (Fromn the Ziskind Research Laboratories, New Englantd Centter Hospital,
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland
 Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in ap2-hif1ako and ap2-hif2ako mice under control and high fat diets.
 Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in Hif1aKO and Hif2aKO mice under control and high fat diets. Hif1a (n=6) Hif1aK O (n=6) Hif2a Hif2aK O Hif1a (n=5) Hif1aKO (n=5) Hif2a Hif2aK
Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in Hif1aKO and Hif2aKO mice under control and high fat diets. Hif1a (n=6) Hif1aK O (n=6) Hif2a Hif2aK O Hif1a (n=5) Hif1aKO (n=5) Hif2a Hif2aK
Supplemental Information. FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating. Antibody Act on the Nervous System. to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC. Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC
 Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Metabolic Programming. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 25 Metabolism and Nutrition Metabolic Reactions Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions taking place in the body. Reactions that break
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis
 A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
Hypothalamus. Small, central, & essential.
 Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
JNJ : selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor. Central and Peripheral PK/PD
 JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
JNJ-42165279: selective and slowly reversible FAAH inhibitor Central and Peripheral PK/PD The Endocannabinoid System Research initiated by efforts to elucidate the active substance of Cannabis (THC in
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS. Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008
 EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
EAT TO LIVE: THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Felicia V. Nowak, M.D., Ph.D. Ohio University COM 22 January, 2008 THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS Exocrine pancreas Endocrine pancreas THE ROLE OF THE PANCREAS EXOCRINE
DOWNLOAD PDF ADIPOSE TISSUE AND ADIPOKINES IN HEALTH AND DISEASE (NUTRITION AND HEALTH)
 Chapter 1 : Adiposity, Adipokines, and Adiposopathy - Sick Fat Explained Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Health and Disease, Second Edition is a useful resource for physicians interested in adipose tissue
Chapter 1 : Adiposity, Adipokines, and Adiposopathy - Sick Fat Explained Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Health and Disease, Second Edition is a useful resource for physicians interested in adipose tissue
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Week 3 The Pancreas: Pancreatic ph buffering:
 Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Week 3 The Pancreas: A gland with both endocrine (secretion of substances into the bloodstream) & exocrine (secretion of substances to the outside of the body or another surface within the body) functions
Food Intake Regulation & the Clock. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Food Intake Regulation & the Clock Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Circadian disruption affect multiple organ systems: The diagram provides examples of how circadian disruption
Food Intake Regulation & the Clock Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Circadian disruption affect multiple organ systems: The diagram provides examples of how circadian disruption
Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice
 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284: R87 R100, 2003; 10.1152/ajpregu.00431.2002. Method of leptin dosing, strain, and group housing influence leptin sensitivity in high-fat-fed weanling mice HEATHER
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11):
 902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary legends
 Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Preface Acknowledgments Introduction Introductory Concepts Definitions and Context Chronological Age and Age Groups Why Study These Phenomena?
 Preface Acknowledgments Introduction Introductory Concepts Definitions and Context Chronological Age and Age Groups Why Study These Phenomena? Types of Studies Principles of Measurement and Observation
Preface Acknowledgments Introduction Introductory Concepts Definitions and Context Chronological Age and Age Groups Why Study These Phenomena? Types of Studies Principles of Measurement and Observation
Supplementary Information. Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose. neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
 Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only CAMPUS GROSSHADERN CAMPUS INNENSTADT BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH Maria Grunewald, Hans Demmelmair, Berthold Koletzko AGENDA Breast Milk
Note: for non-commercial purposes only CAMPUS GROSSHADERN CAMPUS INNENSTADT BREAST MILK COMPONENTS AND POTENTIAL INFLUENCE ON GROWTH Maria Grunewald, Hans Demmelmair, Berthold Koletzko AGENDA Breast Milk
The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome
 UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
Male 30. Female. Body weight (g) Age (weeks) Age (weeks) Atg7 f/f Atg7 ΔCD11c
 ody weight (g) ody weight (g) 34 3 Male 3 27 Female 26 24 22 18 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 21 18 15 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 Age (weeks) Age (weeks) Supplementary Figure 1. Lean phenotypes in mice regardless
ody weight (g) ody weight (g) 34 3 Male 3 27 Female 26 24 22 18 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 21 18 15 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 Age (weeks) Age (weeks) Supplementary Figure 1. Lean phenotypes in mice regardless
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
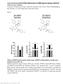 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent
 Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R115 R132, 2001. Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent RUTH B. S. HARRIS, TIFFANY D. MITCHELL, XIAOLANG YAN, JACOB
Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R115 R132, 2001. Metabolic responses to leptin in obese db/db mice are strain dependent RUTH B. S. HARRIS, TIFFANY D. MITCHELL, XIAOLANG YAN, JACOB
Introduction. Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet
 Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
Leptin secretion after a high-fat meal in normal-weight rats: strong predictor of long-term body fat accrual on a high-fat diet - Diet - Activity - Genetics etc. Introduction Obesity - Cardiovascular disease
Nutritional and metabolic mechanisms. in the ovarian follicle
 Nutritional and metabolic mechanisms in the ovarian follicle Joëlle Dupont Team Leader : «Interaction Metabolism and Reproduction» Unit of Physiology of Reproduction and Behaviors UMR 6175 INRA/CNRS/Université
Nutritional and metabolic mechanisms in the ovarian follicle Joëlle Dupont Team Leader : «Interaction Metabolism and Reproduction» Unit of Physiology of Reproduction and Behaviors UMR 6175 INRA/CNRS/Université
Supplementary Figure 1.
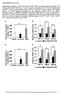 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
