LPA is a highly bioactive phospholipid which acid receptor signaling axis. (Harald M.
|
|
|
- Emily Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Progress Report Description of activities: 1. mtor signaling in kidney cell with silenced HNF1B 2. Differentiation of 3T3 cells into adipose cells 3. Silencing of HNF1B gene in adipose cells and disturbing beta-catenin degradation complex within cells with silenced HNF1B gene 4. Learning of specific techniques Introduction HNF1B-MODY is rare autosomal dominant genetic diabetes syndrome with wide range of comorbidities from which polycystic kidney disease is the most typical representation. Kidney abnormalities in patients with HNF1B mutation range from renal cysts, familial hypoplastic glomerulocystic kidney disease, renal malformations (i.e. single or horseshoe kidney) to atypical nephropathy. Insulin-dependent diabetes develops in early age (median 20 years) in 29% of cases of patients with mutations (Edghill, et al. 2006). Additionally to kidney abnormalities and diabetes HNF1B-MODY syndrome is characterized by great phenotypic variability that includes: neurological features, abnormal liver function, pancreatic hypoplasia, genital tract malformation, hypomagnesaemia, hyperuricaemia, early-onset gout (Clissold, et al. 2015) or pectus excavatum (Dubois-Laforgue, et al. 2014). Considering the broad range of the affect organs. HNF1B-MODY syndrome is considered as a systematic disease rather than a single tissue abnormality. A different genetic disorder resulting in polycystic kidney disease is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Previous molecular studies showed the link between ADPKD and activation of mtor pathway which is responsible for cell proliferation. Animals study showed that mtor inhibitor has an ability to slow down disease progression (Ravichandran et al., 2015). That is why mtor inhibitor everolimus was investigated in human clinical trials as an agent which could stop/slow down further cysts formation and prevent/delay need for kidney transplant in ADPKD. Results of everolimus treatment are not impressive, but a moderate slowing of kidney volume increase and decline of egfr in ADPKD can be achieved with this treatment (Waltz et al., 2010; Serra et al., 2010). Several reports suggest that commonly used dose of everolimus may be suboptimal (Grantham et al., 2011) and that a longer follow-up needed to fully evaluate the treatment effects (Levey et al., 2011) so in the future we may expect further studies on this treatement. Thus, we wanted to check if in cell line culture of kidney cells (HEK293) with silenced HNF1B gene we could observe a dysregulation of mtor pathway suggesting that a potential treatment with everolimus may also benefit patients with HNF1B-related renal cysts. 1. mtor signaling in kidney cell with silenced HNF1B Aim: Evaluate the activation of mtor pathway in cells with disrubted function of HNF1B gene Supervisors: Justyna Janikiewicz, Agniesza Dobrzyń, Wojciech Fendler 1
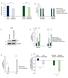
2 We silenced the expression of the HNF1B gene using two different sirnas (Figure 1). Both reagents affected the level og Hnf1b protein, however only first one decreased the level of Hnf1b protein significantly versus the scrambled RNA negative control. Figure 1 Level of Hnf1b protein in HEK293 cells with silenced of HNF1B gene with two different sirna Afterwards, we measured activation of mtor signaling pathway by assessing the level mtor protein, phosphorylated mtor protein (pmtor) and level of its down-stream effector ribosomal S6 kinase (both in total and phosphorylated form) (Figure 2). Figure 2 Levels of phospho and total mtor protein and phospho and total S6K protein. Even though, the total level of mtor and S6K protein seemed unaltered by silencing of Hnf1b, their ratios of phosphorylated form (activated) to total protein amount decreased significantly in Hnf1b-silenced samples. Those results suggest that mtor signaling pathway is not up-regulated in kidney cells with abnormal function of HNF1B gene, suggesting that mtor pathway is not a likely culprit of cyst formation in the HNF1B-MODY syndrome. However, the relatively low expression of Hn1b in HEK293 cells versus real kidney (Figure 3 A and B), necessitates further validation to exclude the role of mtor pathway completely in vivo. 2
3 Figure 3 - Expression of HNF1B gene in different cell cultures (A) and within different organs (B). Data from the Human Protein Atlas (Uhlen et al., 2015) Our research team conducted a nationwide genetic screening program for monogenic forms of diabetes in children (Malachowska, et al. 2017). Using this data, we were able to genetically confirm HNF1B-MODY syndrome in 9 families in the Polish population. This enabled us to perform microrna profiling (Fendler, et al. 2016) and metabolomics fingerprinting in order to better understand spectrum of abnormalities caused by dysfunction of HNF1B gene. In our preliminary studies we identified three forms of lysophosphatidic acid (LysoPA 18:1, LysoPA 18:2 and LysoPA 20:4) to be significantly elevated above the levels observed in healthy controls, patients with type 1 diabetes or other monogenic types. Figure 4 Autotaxin-lysophosphatidic LPA is a highly bioactive phospholipid which acid receptor signaling axis. (Harald M. serum concentration depends mostly on activity of an enzyme called autotaxin (Tanaka, et al. 2006) H. G. Albers et al. 2010) (Figure 4). In our validation cohort comprising (10 patients with HNF1B-MODY, 5 children with renal cysts and diabetes without mutation in 3
4 HNF1B gene, 11 patients with HNF1A-MODY and 17 healthy controls matched by sex and age to HNF1B-MODY group) we measured concentration of lysophosphatidic acid and autotaxin (ATX) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Even though, we were able to confirm elevated level of LPA specifically among HNF1B-MODY patients, autotaxin levels were not elevated. This indicated that a pathway independent of plasma autotaxin is responsible for elevated level of LPA observed in HNF1B-MODY patients. This urged us to investigate intracellular LPA synthesis machinery and its dependence on HNF1B-dependent regulation. As liver is the main organ responsible for metabolism of LPA (Salous, et al. 2013) and liver abnormalities are observed in HNF1B-MODY syndrome we performed experiments on HepG2 cell lines with sirna depleted HNF1B (Figure 5). Figure 5 - ENPP2 gene (autotaxin protein) expression levels in kidney (A) and liver cells (B) with silenced HNF1B gene Expression of ENPP2 gene coding autotaxin protein was significantly down-regulated in liver cells with silenced HNF1B gene. A similar pattern of change was observed within HEK293 cells however differences did not reached statistical significance. To investigate the whole ensemble of LPA-metabolizing enzymes in the intracellular milieu we checked the expression pattern of genes associated with LPA production and degradation (Figure 7). We did not observe an up-regulation of LPA producing genes in HNF1B-deficient liver cells (p=0.2202) but instead observed and up-regulation of genes associated with LPA degradation pathways (p= ). Thus, we inferred that liver was not responsible for elevated level of LPA in sera of HNF1B-MODY patients but was actively counteracting heightened concentrations of this metabolite. 4
5 Figure 8 - Enrichment map analysis of gene sets deregulated by collaboration of silencing of HNF1B and LPA stimulation Figure 7 - Gene-set enrichment analysis of genes producing (a) and degrading (B) LPA in liver cells with silenced HNF1B gene Then, in order to confirm whether the upregulated LPA-degradation pathways were indeed due to extracellular influx of LPA we evaluated the effect of LPA stimulation on the transcriptomic profile of liver cells with silenced HNF1B gene. In gene-set enrichment analysis, we noted down-regulation of: glucose transport, lipid metabolism and aminoacid metabolism. Interesting one of two up-regulated pathway was: Wnt signaling. However, we still did not found the source of elevated serum LPA among our patients. Thus, we switched to another putative tissue that could be associated with LPA production - adipose tissue (Figure 9), We planned an experiment on adipocytes usage of HNF1B sirna in order to check if disruption of Hnf1b function may cause adipose cells to produce more LPA than in normally. Figure 8 - Enrichment map analysis of gene sets deregulated by collaboration of silencing of HNF1B and LPA stimulation 5
6 Figure 9 Adipocytes and cancer cells as a source of elevated level of serum LPA (by Pages et al. 2001) 2. Differentiation of 3T3 cells into adipose cells Supervisors: Justyna Janikiewicz, Agnieszka Dobrzyń Aim: To create a stable adipose cell line for further studies on HNF1B We used below-mentioned protocol in order to differentiated 3T3-L1 cells into adipocytes. The 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cell line was grown in DMEM with 10% calf serum, 1% L-glutamine, and 1% pen/strep at 37 C in 5% CO2. For differentiation, 2-day post-confluent cells were incubated for 72 h in DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), antibiotics, and a differentiation cocktail that consisted of methylisobutylxanthine (115 μg/ml), dexamethasone (390 ng/ml), and insulin (10 μg/ml). After 72 h, the cells were maintained in DMEM with 10% FBS, L-glutamine, insulin, and antibiotics only (without dexamethasone). On day 6 of differentiation, the medium was replaced with DMEM with 10% FBS, L-glutamine, and antibiotics, and 3T3-L1 cells were further cultured for 2 days to achieve a phenotype with fully differentiated adipocytes (Figure 10). Pre-adipocytes culture After reaching Adipocytes Adipocytes Further confluence differentiation maturation culture Day -1 Day hours Day 0 to Day 4 Day 5-8 D8 Full medium DMEM z 10% Calf Serum Medium MDI DMEM + INS DMEM + 10% FBS 6
7 Figure 10-3T3-L1 cells before and after differentiation to adipocytes We measured the level of Hnf1b and autotaxin protein expression in obtained cells (Figure 10) and we found that its high enough for further silencing experiment. Figure 11 - Expression level of autotaxin and Hnf1b protein in 3t3-L1 cells differentiated into adipocytes. 7
8 3. Silencing of HNF1B gene in adipose cells and disturbing beta-catenin degradation complex within cells with silenced HNF1B gene As we found up-regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway within cells with silenced HNF1B we wondered if this could be a pathway via which dysregulation of HNF1B may lead to overproduction of LPA by adipose cells. Thus, we would like to evaluate the effect of HNF1B gene silencing on LPA production by adipose cells with and without a functional beta-catenin degradation complex (Figure 12 AB). We planned four groups: sihnf1b (pure effect of HNF1B silencing), NegSiRNA (transfection control), NegSiRNA with block of beta-catenin degradation complex (activation Wnt/beta-catenin pathway), sihnf1b with block of beta-catenin degradation complex. In order to achieve higher purity of proteins and mrna for further studies we will perform separate experiments for each isolations protocols. Those experiments are currently on-going and their results should be available in next months. 8
9 Figure 12 - Flowchart of adipose cells experiment Funding: Preliminary analysis were financed by PRELUDIUM grant from National Science Centre Poland granted to Beata Malachowska. 3T3-L1 and HEK293 cell lines experiments were financed by ISPAD Research Fellowship. Publication plans: the results are planned to be presented during ISPAD Annual Conference 2018 and ADA Congress Manuscript summarizing the results of the project is scheduled to be written at the beginning of Learning of specific techniques A. Western blot techniques B. Gene expression measurements (qpcr) technique C. Cell cultures protocols D. 3t3-L1 cell lines differentiation protocol E. Transfection protocols 9
Research Introduction
 Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Research Introduction 9.17.13 Altered metabolism in polycystic kidney disease Telomerase activity in polycystic kidney disease cells Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most common
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling through LPA1 in organ fibrosis: A pathway with pleiotropic pro-fibrotic effects. and Andrew M.
 78 Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Bases for Fibrotic Diseases Review Article Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling through LPA1 in organ fibrosis: A pathway with pleiotropic pro-fibrotic effects
78 Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Bases for Fibrotic Diseases Review Article Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling through LPA1 in organ fibrosis: A pathway with pleiotropic pro-fibrotic effects
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Production of Exosomes in a Hollow Fiber Bioreactor
 Production of Exosomes in a Hollow Fiber Bioreactor John J S Cadwell, President and CEO, FiberCell Systems Inc INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small lipid membrane vesicles (80-120 nm) of endocytic origin generated
Production of Exosomes in a Hollow Fiber Bioreactor John J S Cadwell, President and CEO, FiberCell Systems Inc INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small lipid membrane vesicles (80-120 nm) of endocytic origin generated
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Supplemental Material:
 Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
Expanded View Figures
 Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Pr oject Summar y. The Role of Fatty Acids at Enhancing Marbling Development through Bovine G-coupled Protein Receptors (GPR)
 Pr oject Summar y The Role of Fatty Acids at Enhancing Marbling Development through Bovine G-coupled Protein Receptors (GPR) Principal Investigators: S.B. Smith & B.J. Johnson, Texas A&M University & Texas
Pr oject Summar y The Role of Fatty Acids at Enhancing Marbling Development through Bovine G-coupled Protein Receptors (GPR) Principal Investigators: S.B. Smith & B.J. Johnson, Texas A&M University & Texas
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease
 microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we?
 New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
New Treatments for ADPKD how close are we? Leicester General Hospital 28 Jan 2012 Professor Albert Ong a.ong@sheffield.ac.uk The cystic degeneration of the kidneys, once it reaches the point where it can
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this study the authors analysed 18 deep penetrating nevi for oncogenic genomic changes (single nucleotide variations, insertions/deletions,
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this study the authors analysed 18 deep penetrating nevi for oncogenic genomic changes (single nucleotide variations, insertions/deletions,
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Title:Role of LPAR3, PKC and EGFR in LPA-induced cell migration in oral squamous carcinoma cells
 Author's response to reviews Title:Role of LPAR3, PKC and EGFR in LPA-induced cell migration in oral squamous carcinoma cells Authors: Ingvild J Brusevold (i.j.brusevold@medisin.uio.no) Ingun H Tveteraas
Author's response to reviews Title:Role of LPAR3, PKC and EGFR in LPA-induced cell migration in oral squamous carcinoma cells Authors: Ingvild J Brusevold (i.j.brusevold@medisin.uio.no) Ingun H Tveteraas
Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer
 Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Masur K, Thévenod F, Zänker KS (eds): Diabetes and Cancer. Epidemiological Evidence and Molecular Links. Front Diabetes. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 19, pp 97 113 Diabetes Mellitus and Breast Cancer Ido Wolf
Favorable human safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the autotaxin inhibitor GLPG1690, a potential new treatment in COPD
 Favorable human safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the autotaxin inhibitor GLPG1690, a potential new treatment in COPD Ellen M. van der Aar, PhD Galapagos, Mechelen, Belgium L. Fagard, J.
Favorable human safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the autotaxin inhibitor GLPG1690, a potential new treatment in COPD Ellen M. van der Aar, PhD Galapagos, Mechelen, Belgium L. Fagard, J.
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes
 BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
BIOL212- Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is, after heart disease and cancer, the third leading cause of death in the west. Insulin is either not secreted in sufficient
SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist. Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann
 SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann 4 th of July 2004 Database development with outcomes and safety
SUISSE ADPKD Cohort Treatment and Outcomes with Tolvaptan, first in class Vasopressin V2 Antagonist Hirslanden, 22 March 2018 Stefan Russmann 4 th of July 2004 Database development with outcomes and safety
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
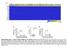 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU. PhD THESIS Summary
 ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
Project Summary. Funded by The Beef Checkoff. Regulation of Marbling Development in Beef Cattle by Specific Fatty Acids
 Project Summary Regulation of Marbling Development in Beef Cattle by Specific Fatty Acids Principal Investigators: S. Smith 1, B. Johnson 2 and M. Doumit 3 Texas A&M University 1, Texas Tech University
Project Summary Regulation of Marbling Development in Beef Cattle by Specific Fatty Acids Principal Investigators: S. Smith 1, B. Johnson 2 and M. Doumit 3 Texas A&M University 1, Texas Tech University
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease
 Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease Li Chen,, Jared J. Grantham, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2015;125(6):2399-2412. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci80467.
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease Li Chen,, Jared J. Grantham, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2015;125(6):2399-2412. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci80467.
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
Kidney Disease Research
 Thomas Weimbs Assistant Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology Kidney Disease Research The mtor pathway is regulated by polycystin 1, and its inhibition reverses renal cystogenesis
Thomas Weimbs Assistant Professor, Department of Molecular, Cellular & Developmental Biology Kidney Disease Research The mtor pathway is regulated by polycystin 1, and its inhibition reverses renal cystogenesis
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Complexity DNA. Genome RNA. Transcriptome. Protein. Proteome. Metabolites. Metabolome
 DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay
 TECHNICAL MANUAL Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay Instructions for Use of Products J1341, J1342, and J1343 Revised 2/17 TM467 Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
TECHNICAL MANUAL Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay Instructions for Use of Products J1341, J1342, and J1343 Revised 2/17 TM467 Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions
 Supplementary Information mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions Shyuichiro Matsubara 1, Qiang Ding 1, Yumi Miyazaki 1, Taisaku Kuwahata
Supplementary Information mtor plays critical roles in pancreatic cancer stem cells through specific and stemness-related functions Shyuichiro Matsubara 1, Qiang Ding 1, Yumi Miyazaki 1, Taisaku Kuwahata
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplemental Information. Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell. Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated Inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega Gene Cluster Stas Wüst,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated Inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega Gene Cluster Stas Wüst,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Maternal diet induced micrornas and mtor underlie b cell dysfunction in offspring
 Maternal diet induced micrornas and mtor underlie b cell dysfunction in offspring Emilyn U. Alejandro,, Peter Arvan, Ernesto Bernal- Mizrachi J Clin Invest. 2014;124(10):4395-4410. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci74237.
Maternal diet induced micrornas and mtor underlie b cell dysfunction in offspring Emilyn U. Alejandro,, Peter Arvan, Ernesto Bernal- Mizrachi J Clin Invest. 2014;124(10):4395-4410. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci74237.
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Egr-1 regulates RTA transcription through a cooperative involvement of transcriptional regulators
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 53), pp: 91425-91444 Egr-1 regulates RTA transcription through a cooperative involvement of transcriptional regulators Roni Sarkar 1 and Subhash C. Verma 1 1 Department of Microbiology
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 53), pp: 91425-91444 Egr-1 regulates RTA transcription through a cooperative involvement of transcriptional regulators Roni Sarkar 1 and Subhash C. Verma 1 1 Department of Microbiology
Regents of the University of Colorado Aurora, CO 80045
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0172 TITLE: Novel mtorc1 and 2 Signaling Pathways in Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Charles L. Edelstein MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Regents of
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-16-1-0172 TITLE: Novel mtorc1 and 2 Signaling Pathways in Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Charles L. Edelstein MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Regents of
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
 phosphorylated proteins on treatment with Erlotinib.This chapter describes the finding of the SILAC experiment. 4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This is the first global report of its kind using dual strategies
phosphorylated proteins on treatment with Erlotinib.This chapter describes the finding of the SILAC experiment. 4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This is the first global report of its kind using dual strategies
2013 OTS Annual Meeting Pre-clinical Development of ALN-AS1 RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Acute Intermittent Porphyria.
 2013 OTS Annual Meeting Pre-clinical Development of ALN-AS1 RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Acute Intermittent Porphyria October 8, 2013 Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) Program Unmet Need and
2013 OTS Annual Meeting Pre-clinical Development of ALN-AS1 RNAi Therapeutic for the Treatment of Acute Intermittent Porphyria October 8, 2013 Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) Program Unmet Need and
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is a heterogeneous group
 Over the years, different forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) have been identified, with mutations in a number of different genes associated with a MODY-like phenotype. Depending on the
Over the years, different forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) have been identified, with mutations in a number of different genes associated with a MODY-like phenotype. Depending on the
Basics of Signal Transduction. Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD
 Basics of Signal Transduction Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD What is signal transduction? Cell signaling The science of understanding how individual cells sense their environments and respond to stimuli... how
Basics of Signal Transduction Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD What is signal transduction? Cell signaling The science of understanding how individual cells sense their environments and respond to stimuli... how
Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (Red Fluorescence)
 Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (Red Fluorescence) Catalog Number KA4085 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the
Glucose Uptake Assay Kit (Red Fluorescence) Catalog Number KA4085 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the
Late progression of renal pathology and cyst enlargement is reduced by rapamycin in a mouse model of nephronophthisis
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 29 International Society of Nephrology Late progression of renal pathology and cyst enlargement is reduced by rapamycin in a mouse model of nephronophthisis
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 29 International Society of Nephrology Late progression of renal pathology and cyst enlargement is reduced by rapamycin in a mouse model of nephronophthisis
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/271/ra25/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Phosphoproteomic Analysis Implicates the mtorc2-foxo1 Axis in VEGF Signaling and Feedback Activation of Receptor Tyrosine
EGFR kinase activity is required for TLR4 signaling and the septic shock response
 Manuscript EMBOR-2015-40337 EGFR kinase activity is required for TLR4 signaling and the septic shock response Saurabh Chattopadhyay, Manoj Veleeparambil, Darshana Poddar, Samar Abdulkhalek, Sudip K. Bandyopadhyay,
Manuscript EMBOR-2015-40337 EGFR kinase activity is required for TLR4 signaling and the septic shock response Saurabh Chattopadhyay, Manoj Veleeparambil, Darshana Poddar, Samar Abdulkhalek, Sudip K. Bandyopadhyay,
SDC (Supplemental Digital Content) Figure S1. Percentages of Granzyme B expressing CD8 + T lymphocytes
 Figure S1. Percentages of Granzyme expressing D8 + T lymphocytes 13.5% 1.4%.6% 77% 21% 24% 76% 8 8 Granzyme + (%) 6 4 2 Granzyme + (%) 6 4 2 D8 + Tnaive Tcm Tem Temra D8 + D8 + D28 + D8 + D28 null We analyzed
Figure S1. Percentages of Granzyme expressing D8 + T lymphocytes 13.5% 1.4%.6% 77% 21% 24% 76% 8 8 Granzyme + (%) 6 4 2 Granzyme + (%) 6 4 2 D8 + Tnaive Tcm Tem Temra D8 + D8 + D28 + D8 + D28 null We analyzed
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
ab Intracellular O 2 Probe
 ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate axis: a new player for insulin-like growth factor-1- induced myoblast differentiation
 Bernacchioni et al. Skeletal Muscle, :5 http://www.skeletalmusclejournal.com/content///5 Skeletal Muscle RESEARCH Open Access Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine -phosphate axis: a new player for insulin-like
Bernacchioni et al. Skeletal Muscle, :5 http://www.skeletalmusclejournal.com/content///5 Skeletal Muscle RESEARCH Open Access Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine -phosphate axis: a new player for insulin-like
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: Is there a link?
 Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: Is there a link? Sonali Thosani, MD Assistant Professor Department of Endocrine Neoplasia & Hormonal Disorders MD Anderson Cancer Center No relevant financial disclosures Objectives
Type 2 Diabetes and Cancer: Is there a link? Sonali Thosani, MD Assistant Professor Department of Endocrine Neoplasia & Hormonal Disorders MD Anderson Cancer Center No relevant financial disclosures Objectives
JYNARQUE REMS (RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY) PATIENT GUIDE
 JYNARQUE REMS (RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY) PATIENT GUIDE Patients: Your healthcare provider will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions you may have. Keep
JYNARQUE REMS (RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY) PATIENT GUIDE Patients: Your healthcare provider will go over this patient guide with you. It is important to ask any questions you may have. Keep
Metabolic Programming. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Metabolic Programming Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD nutritional stress/stimuli organogenesis of target tissues early period critical window consequence of stress/stimuli are
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Digenic inheritance of HNF-1 and HNF-1 with MODY, polycystic thyroid and urogenital malformations. Running title: HNF-1, HNF-1, and digenic MODY
 Diabetes Care In Press, published online March 2, 2007 Digenic inheritance of HNF-1 and HNF-1 with MODY, polycystic thyroid and urogenital malformations Running title: HNF-1, HNF-1, and digenic MODY Received
Diabetes Care In Press, published online March 2, 2007 Digenic inheritance of HNF-1 and HNF-1 with MODY, polycystic thyroid and urogenital malformations Running title: HNF-1, HNF-1, and digenic MODY Received
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Shuma Hirashio 1,2, Shigehiro Doi 1 and Takao Masaki 1*
 Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD
 micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1
 Manuscript EMBOR-2014-39218 SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1 Joanne Durgan, Guangbo Tao, Matthew S. Walters, Oliver Florey, Anja Schmidt, Vanessa
Manuscript EMBOR-2014-39218 SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1 Joanne Durgan, Guangbo Tao, Matthew S. Walters, Oliver Florey, Anja Schmidt, Vanessa
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Cost-effectiveness of tolvaptan (Jinarc ) for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
 Cost-effectiveness of tolvaptan (Jinarc ) for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) The NCPE has issued a recommendation regarding the cost-effectiveness of tolvaptan (Jinarc
Cost-effectiveness of tolvaptan (Jinarc ) for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) The NCPE has issued a recommendation regarding the cost-effectiveness of tolvaptan (Jinarc
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells
 EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
EM-X Herbal Tea Inhibits Interleukin-8 Release in Alvelor Epithelial cells Okezie I. Arouma a) and Irfan Rahman b) a) Department of Neuroinflammation, Division of Neuroscience & Psychological Medicine,
Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Linda Xiaoyan Li,, Julien Sage, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2751-2764. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci90921.
Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Linda Xiaoyan Li,, Julien Sage, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2751-2764. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci90921.
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts
 Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Regulation of the Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance.
Regulation of the Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Timing and rates of cell division in different parts of an animal or plant are crucial for normal growth, development, and maintenance.
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells
 The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
The Expression and Significance of Drainderived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Its Specific Receptor Trk B in Colon Cancer Cells Yi Liu, Lunhui Zhang, Liang Xu * ABSTRACT This paper aims at analyzing the
