DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS: LIVER, PANCREAS, STOMACH
|
|
|
- Hilary Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEAD AND BRAIN HEAD DISSECTION - life size Size: 18x25x23 cm g - 4 parts SENSE ORGANS: EYE AND EAR EAR SIZES 33x23x21 cm 33x23x21 cm These models show the external, middle and inner ear. The eardrum with malleus, incus and stapes are removable. Also cochlea and labyrinth with vestibular and cochlear nerves and 2 bones sections (40042 only) that define the middle and inner ear are removable. Kg Mag 3X 3X 3x life size, the model shows a medial section of the nasal cavity. The nasal septum and part of the olfactory epithelium are removable to show deep internal structures NASAL CAVITY Size: 15x20x30 cm - 1 kg - 3 parts - 3X Mounted on base with stand LIVER SECTION WITH GALLBLADDER Size: 28x27x14 cm g - 1 part - 1.5X Life size Can be divided into 9 parts showing the temporal and occipital lobes, the frontal and parietal lobes, the cerebellum, the brain stem and basilary artery BRAIN WITH ARTERIES Size: 16x18x16 cm - 1 kg - 9 parts Disassembled Accurate representation of the pancreas, spleen and duodenum. The pancreas is open to show the entire pancreatic duct. The duodenum is partially dissected to expose its internal structure Assembled A life size reproduction of the complete human respiratory system. It is composed of 7 parts showing the larynx (dissected along the sagittal plane), the lungs (dissected along the frontal plane) and a 2-part heart RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Size: 26x40x12 cm kg - 7 parts life size DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS: LIVER, PANCREAS, STOMACH PANCREAS, DUODENUM AND SPLEEN Size: 16x15x23 cm g - 1 part Models show the eye ball with optic nerves and muscles in its natural position in the bony orbit EYE WITH ORBIT SIZES 15x17x27 cm 42x30x31 cm 42x30x31 cm RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: NASAL CAVITY, LARYNX This model, 1.5x life size, shows the liver and gallbladder in open section with the complex network of vessels and bile ducts, displayed in different colours to clarity and ease of examination. Cornea, iris, lens and vitreous body can be removed REGIONAL BRAIN Size: 20x17x15 cm kg - 2 parts Kg STOMACH Size: 16x14.5x5 cm g - 2 parts - 1.5X Mag 6X 5X 5X LARYNX Size: 18x11x8 cm g - 5 parts - 2X Longitudinally sectioned to reveal inner details of internal structure including hyoid bone, vessels, ligaments, cartilages, muscles, nerves and thyroid gland Can be opened to show the internal structure of the stomach, including the mucosa, the pylorus, and a section of the gastric wall. Superficial dissection exposes the longitudinal, circular and oblique muscle layers, with nerves and vascular structures Life size brain with distinct colour for: frontal lobe, pariental lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, motor cortex, somatosensory cortex, limbic cortex, cerebellum, brain stem 40088
2 HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Life size in 2 parts. The anterior heart wall can be removed to show the left and right ventricles and atria as well as the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral and aortic valves. Show internal structures including the cardiac valves and the comparative morphology of the right and left ventricles. The right atrium is also removable A general view of the human circulation. It includes the heart (2 parts), lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys and relevant connections with the pulmonary and systematic circulatory pathways. Assembled Disassembled Enlarged 2000 times, this model shows the various types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells (lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils) and blood platelets PELVIS - FEMALE AND MALE HEART - mounted on base GIANT HEART - mounted on base BLOOD CELLS - mounted on board CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - mounted on board This life size model, composed of 4 parts, presents an open view through a median sagittal section of the pelvis. Internal structures of the male urogenital system are represented in fine detail. The removable parts include a half penis divided into medial and transverse sections, and half of the male reproductive system with an open dissection of a testis showing details of the internal structure. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Size cm 11x7x10 24x25x28 58x38x7 90x32x11 URINARY SYSTEM: MALE BLADDER, KIDNEY MALE URINARY BLADDER WITH PROSTATE Size: 27x20x15 cm - 1,2 kg - 2 parts - 3X This model, enlarged 3 times, shows the male urinary bladder with the prostate gland surrounding the urethra. The model is dissected medially to expose both internal and external structures of the bladder and prostate, including the ureteric and urethral orifices, ductus deferens, seminal gland, ejaculatory duct KIDNEY WITH ADRENAL GLAND+RENAL CORPUSCLE Size: 40x15x8 cm - 1,2 kg - 1 part - 3X This model shows a frontal section of the human kidney enlarged 3 times. The kidney is shown with the renal capsule. Additional structures include: the cortex, medulla, pyramids with papillae, partially dissected renal pelvis, renal calices, ureter, blood vessels, suprarenal gland with cortex and medulla. A schematic representation of the renal corpuscle with the system of collecting tubules is included kg PREGNANCY PELVIS This life size model depicts the female human pelvis in median section with a fetus in the 40th week of pregnancy. The fetus is in the normal position prior to birth, showing the anatomical relationship between various structures of the maternal pelvis and the fetus. Fetus is detachable for closer examination Magnif. 3X 2000X 0.5X This life size model, composed of 3 parts, shows an open dissection through the median sagittal section of the pelvis. Internal structures of the female urogenital system are portrayed in great detail. Removable parts include half of the female reproductive system with the uterus opened to reveal medial and transverse sectional views. SKIN SKIN MODEL - 30X Size: 20x15x15.5 cm kg Mounted on base All the skin layers can be easily identified and the main structures such as hair follicle, sensitive corpuscles, sebaceous and sweat glands, are numbered and referred on the accompanying k-card PELVIS Sex Kg size cm 30x20x27 fem x20x27 male Mag SKIN MODEL - 70X Size: 25x18x28 cm kg 2 parts - 70X Mounted on base Anatomical structures are shown in details including the hair follicles, sebaceous, glands, sweat glands, erector muscles, Pacinian corpuscles, nerves and blood vessels. The different layers of the skin are clearly defined. A portion of a hair shaft can be removed to show internal details PREGNANCY PELVIS WITH MATURE FETUS Size: 40x26x34 cm kg - 2 part - 372
3 HUMAN TORSOS WITH CD AND MUSCULAR FIGURES MINI TORSO MINI TORSO - african TORSO UNI SEX * TORSO DUAL SEX* TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK* MUSCULAR TORSO DUAL SEX OPENBACK* MUSCULAR FIGURE Some of the detachable parts of human torsos ( ): HUMAN TORSOS *SUPPLIED WITH CD ROM GUIDE Size 20x15xh45 cm 20x15xh45 cm 30x33xh87 cm Removable structures, of s , include the following: - eye with optic nerve and extraocular muscles - half of the brain - trachea - descending thoracic aorta and esophagus - right and left lungs (two parts each)- liver with gallbladder - half of one kidney - two part heart - stomach dissected in two parts (not for 40005) - pancreas, duodenum and spleen - small and large intestines - male and female urogenital systems (4 parts each), (on female system is in 3 parts and provided of detachable fetus) - thoracic vertebra (T12) with spinal cord ( and only). 2.1 kg 2.1 kg 9 kg 9.3 kg 9.3 kg 10 kg 5.3 kg Detachable parts of human muscular figure 40019: This CD-ROM Guide greatly extends the educational value of the anatomical torsos by identifying hundreds of structures that are not included on the printed key. High-resolution digital images of torso components show the finest anatomical details of all body systems from various angles HEAD/NECK MUSCULATURE Size: 37x23x46 cm kg - 1 part - life size Superficial and deep musculature are well represented as are the pathways of the subclavian and carotid arteries 373 HEAD MUSCULATURE MUSCLES: SHOULDER, ARM, LEG SHOULDER MUSCLE Size: 23x19x11 cm g 1 part - Mounted on a base with stand This model illustrates in great details the muscles, ligaments and bones of the shoulder. Through different muscles section it is possible to observe the deep musculature to the bone ARM MUSCLE Size: 74x20x12 cm kg - 7 parts This 7-part life size model shows, in great detail, the anatomical structure of the arm, complete with superficial and deeper muscles, vascular structures, nerves and ligaments. The hand and the shoulder are also well represented. The following parts are removable: - deltoid muscle - biceps muscle - triceps muscle - long palmar muscle with radial flexor muscle of wrist - brachioradial muscle - radial extensor muscle of wrist - palmar aponeurosis LEG MUSCLE Size: 110x19x14.5 cm kg 13 parts Mounted on a base with stand This 13-part model shows, in great detail, the anatomical structure of the leg, complete with superficial and deeper muscles, vascular structures, nerves and ligaments. The following parts are removable: - sartorius - long head of biceps - gluteus maximus - soleus - gastrocnemius - gluteus medius - gracilis - semitendinosus and semimembranous - rectus femoris - extensor digitorum longus - sole of foot - tensor fasciae latae 40018
4 40120 SKELETONS VERTEBRAL COLUMNS MINI SKELETON Height: 80 cm : 1.5 kg. This 1/2 life size model shows the anatomy of the human skeleton in high detail. The skull can be disassembled into 3 parts: skullcap, base of skull and mandible. All the main joints are articulated. Arms and legs can be removed easily. Mounted on a stand for hanging HUMAN SKELETON Height: 170 cm. : approx 10 kg. This model is a replica of a life size human skeleton and shows all the skeleton parts in high detail. It's hand-assembled to provide intricate details and long-lasting durability. The main joints are articulated; the upper and lower limbs can be removed easily. The following parts are detachable: Calvarium, Skull, Jaw, Arms, Legs. Supplied with 5-caster roller stand MUSCULAR HUMAN SKELETON Same as but with the left side of the skeleton showing the point of origin (red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles KNEE AND SHOULDER SHOULDER JOINT Size: 29x12x12cm - 560g - 1 part - Mounted on stand KNEE JOINT Size: 12x12x31cm - 440g - 1 part - The life size model represents a functional model of knee joint with lateral ligaments, meniscus and patellar ligament SKELETAL SYSTEM Advanced osteoporosis model. Shows 3 vertebrae: one healthy vertebra, one vertebra with pathological changes at first stage, one vertebra with pathological changes at advanced stage FLEXIBLE VERTEBRAL COLUMNS Fully flexible life size vertebral columns consisting of the occipital plate, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, complete pelvis with symphysis, removable femur heads (only 40130,31,32). All models also feature representation of the vertebral arteries, spinal nerve branches, and a prolapsed L3-L4 intervertebral disc. On the left side of the skeleton shows the points of origin (red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles. On and the sacral crest and coccyx are removable to show the sacral section of the spinal cord and associated nerve branches. On the various regions of the spinal column are colour d for easy identification FLEXIBLE VERTEBRAL COLUMNS VERTEBRAL COLUMN with femur heads VERTEBRAL COL with femur + muscle VERTEBRAL COL with femur + open sacrum SPINAL COL with colour d regions Size cm 95x20x20 95x20x20 95x20x20 98x23x23 Magnif. 3 kg 3 kg 3 kg 970 g Cervical spinal column consists of 7 cervical vertebrae with intervertebral discs, occipital plate, cervical nerves, vertebral arteries, spinal cord and brain stem Thoracic spinal Lumbar spinal column consists of 12 thoracic vertebrae with intervertebral discs, thoracic nerves and spinal cord. SKELETAL SYSTEM CERVICAL SPINAL COLUMN THORACIC SPINAL COLUMN LUMBAR SPINAL COLUMN HERNIA PATHOLOGY ADVANCED OSTEOPOROSIS column with sacral and coccyx bones. It consists of 5 lumbar vertebrae with intervertebral discs, lumbar nerves and spinal cord. The sacral crest and coccyx are removable. Size cm 12x12x22 12x12x40 12x12x x12x26 12x12x15 3 lumbar vertebrae with hernia and prolapsed intervertebral disc. Shows 3 lumbar vertebrae with spinal nerves, dura mater and 2 intervertebral discs affected by lateral and medial hernia. 350 g 600 g 800 g 300 g 200 g Magnif. 374
5 HUMAN SKULLS - 3 PARTS Numbered skull (40161) Significant structures are numerated Coloured skull (40162) All the bones are depicted in different colours, making this model a useful tool to study the correct position and relationship of all the structures. Muscular skull (40163) The left side of the skull shows the points of origin(red) and the point of insertion (blue) of the muscles. MINI SKULL (40165) ½ adult natural size It depicts all structural details of the skull. It can be disassembled into skullcap and base of skull. Articulated mandible. DENTAL MODELS DECIDUOUS TEETH Size: 9x9x10 cm - weight: 85 g. Mounted on base with stand. This life size model shows the upper and lower jaw of a 5 year old child. The lower jaw is movable to reproduce the natural chew. The model exposes the arrangement of the young teeth. Life size human skull reproduction with all details, made in PVC. Removable skull cap and articulated mandible. HUMAN SKULLS Size cm g Magnif HUMAN SKULL 22x14x HUMAN SKULL - numerated 22x14x HUMAN SKULL - coloured 19.5x17x HUMAN SKULL - muscular 18x17x MINI SKULL 11x11x X PERMANENT TEETH Size: 11x11x12 cm - weight: 170 g. Mounted on base with stand. This life size model shows the upper and lower jaw of an adult. The lower jaw is movable to reproduce the natural chew. The model exposes the complete set of permanent teeth with roots and nerves fibres LOWER JAW Size: 35x18x31 cm - weight: 1130 g Mounted on base with stand. This 3X life size model is divisible into 6 parts to show all the characteristics of an adult half mandible. A portion of the jaw can be removed to show the roots of the teeth and the internal structure of the bone. Canine and molar teeth can be removed and dissected longitudinally to observe the tooth roots, pulp and nerves DENTAL PATHOLOGY MODEL Size: 6x4.5x11 cm - weight: approx. 100 g This 4X life size model shows the process of dental caries in its progressive stages. The tissues forming the tooth (enamel, dentine and pulp) are shown, along with the way in which they are affected by the caries process ORAL HYGIENE Size: 12x16x22 cm - weight: 1 kg Mounted on base. A 3X life size model useful to teach the correct way to brush teeth. A giant toothbrush is included SET 3 TEETH: INCISOR, CANINE, MOLAR Size: 33x33x11 cm - weight: 700 g 5-part model includes representations (10X life size) of human incisor, canine and molar teeth. The canine and molar can be divided into 2 parts each, showing internal features (dentine, enamel, cement and pulp) LOWER MOLAR WITH CARIES Size: 11x11x19.5 cm - weight: approx. 250 g Mounted on base with stand. This 1-piece model is approximately 10X life size; it shows the most important dental pathologies, including dental caries, pulpitis, gingivitis and periapical periodontitis DENTAL CARIES Size: 12x6x6 cm - weight: approx. 300 g This model, composed of 7 parts, is 4X life size. It consists of 3 teeth, seated in their sockets, showing the progressive deterioration of tooth structure by dental caries. The first tooth shows the caries in the enamel. In the second tooth, the caries spreads through the dentine. In the third tooth, the pathology affects the pulp, jeopardizing the vitality of the tooth.
6 VALUE HUMAN ANATOMY MODELS HUMAN SKULLS - 3 parts A detailed reproduction of a life size human skull with all structural details. The mandible is articulated, the skullcap is removable to show internal details. All of the joints, sutures, fissures, foramina and processes are portrayed with utmost accuracy. HUMAN ANATOMY - MODELS HUMAN SKULL - 3 parts HUMAN SKULL NUMERATED - 3 parts Giant toothbrush is included Life size human skeletons show all the skeleton parts in high detail. The main joints are articulated; the upper and lower limbs can be easily removed. The following parts are detachable: Calvarium, Skull, Jaw, Arms, Legs. Supplied with 5-caster roller stand Height: 180 cm : approx 10 kg HUMAN SKULL COLOURED - 3 parts Fully flexible life size vertebral columns consisting of the occipital plate, cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx, complete pelvis with symphysis, removable femur heads ORAL HYGIENE MODEL - 3X A functional model of knee joint with lateral ligaments, meniscus and patellar ligament HUMAN SKELETON HUMAN MUSCULAR SKELETON Life size in 2 parts. The anterior heart wall can be removed to show the left and right ventricles and atria as well as the tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral and aortic valves FLEXIBLE VERTEBRAL COLUMN with femur heads SHOULDER JOINT HEART - 2 parts KNEE JOINT Assembled EYE 6X - 6 parts Disassembled Cornea, iris, lens and vitreous body can be removed HEART 3X - 3 parts Shows internal structures including the cardiac valves and the comparative morphology of the right and left ventricles. These models show the external, middle and inner ear. The eardrum with malleus, incus and stapes are removable. Also cochlea and labyrinth with vestibular and cochlear nerves and 2 bones sections (40039 only) that define the middle and inner ear are removable EAR 3X - 3 parts EAR 3X - 5 parts 376
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE. X Biology II
 Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Unit 2-5, Animal Biology & Organ Systems, FETAL PIG DISSECTION MANUAL X Biology II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE X Biology II
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
A. Incorrect! The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull, inner ear, chest and spinal column.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Pricelist Human Models HUMAN MODELS FUNCTIONAL MODELS ACUPUNCTURE MODELS ANATOMY MODELS DENTAL - MODELS
 Pricelist Human Models HUMAN MODELS FUNCTIONAL MODELS ACUPUNCTURE MODELS ANATOMY MODELS DENTAL - MODELS HUMAN FUNCTIONAL MODELS...3 HUMAN ACUPUNCTURE MODELS...5 HUMAN ANATOMY MODELS...7 Skeleton Models...7
Pricelist Human Models HUMAN MODELS FUNCTIONAL MODELS ACUPUNCTURE MODELS ANATOMY MODELS DENTAL - MODELS HUMAN FUNCTIONAL MODELS...3 HUMAN ACUPUNCTURE MODELS...5 HUMAN ANATOMY MODELS...7 Skeleton Models...7
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System. A list of the first 3 digits - 72 terms
 1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
2. Be able to define and give examples of each of the following planes:
 Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Descriptive Histology
 Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
Atlas of Descriptive Histology Michael H. Ross University of Florida College of Medicine Gainesville, Florida Wojciech Pawlina Mayo Medical School College of Medicine, Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
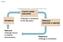 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY. MCQs: Marks SEQs: Marks. Segment MCQs SEQs
 M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY MCQs: 150 150 Marks SEQs: 15 150 Marks Segment MCQs SEQs Gross Anatomy 35% 35% Microanatomy (Histology) 25% 25% Neuroanatomy 20% 20% Embryology 20% 20% GROSS ANATOMY Table of specification
M. PHIL ANATOMY SUMMARY MCQs: 150 150 Marks SEQs: 15 150 Marks Segment MCQs SEQs Gross Anatomy 35% 35% Microanatomy (Histology) 25% 25% Neuroanatomy 20% 20% Embryology 20% 20% GROSS ANATOMY Table of specification
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology. ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations
 Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets
 HARRY BROOKES ALLEN MUSEUM OF ANATOMY AND PATHOLOGY PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets PHOTOGRAPHY & FILMING IN THE MUSEUM ARE STRICTLY PROHIBITED Real people have generously donated their bodies so that
HARRY BROOKES ALLEN MUSEUM OF ANATOMY AND PATHOLOGY PHYS. ED. VCE student worksheets PHOTOGRAPHY & FILMING IN THE MUSEUM ARE STRICTLY PROHIBITED Real people have generously donated their bodies so that
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
BIOLOGY 2325 HUMAN ANATOMY
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Score Please do not write in these spaces. BIOLOGY 2325 HUMAN ANATOMY 75 Points Possible FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION AUTUMN SEMESTER 2017 Name Last First (Please print clearly) DIRECTIONS:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Score Please do not write in these spaces. BIOLOGY 2325 HUMAN ANATOMY 75 Points Possible FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION AUTUMN SEMESTER 2017 Name Last First (Please print clearly) DIRECTIONS:
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Practical #1 Checklist Spring 2010
 External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul)
 TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
Introduction and Terminology
 Introduction and Terminology Histology - study of tissues (histo = tissues). Tissue Epithelial Tissue Covers and protects exposed surfaces. Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.
Introduction and Terminology Histology - study of tissues (histo = tissues). Tissue Epithelial Tissue Covers and protects exposed surfaces. Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax
 Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones
Jikishin Ju Jitsu Association
 A written examination is set for Dan Gradings from information contained within the text of these pages. Note also that the anatomical diagrams do NOT form part of the examination there is NO requirement
A written examination is set for Dan Gradings from information contained within the text of these pages. Note also that the anatomical diagrams do NOT form part of the examination there is NO requirement
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Kidney Model (Model 3-13)
 Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Kidney Model (Model 3-13) Kidney Model Blood Vessels (Model 3-29) Segmental Artery Interlobar Artery Renal Artery Renal Vein Interlobular Artery Interlobular Vein Arcuate Artery Interlobar Vein Arcuate
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body
 1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Chapter 2. Organization of the Body. Copyright 2012, 2009, 2005, 2003, 1999, 1991 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 2 Organization of the Body 1 Learning Objectives Name the body systems and their functions. Identify body cavities and specific organs within them. List the divisions of the back. Identify three
Chapter 2 Organization of the Body 1 Learning Objectives Name the body systems and their functions. Identify body cavities and specific organs within them. List the divisions of the back. Identify three
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
ANATOMY - II. FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX
 ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Course: Human Body Systems Year: Teacher: Meghann Redman
 Course: Human Body Systems Year: 2015 2016 Teacher: Meghann Redman Unit 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Approximate Time Frame: 2 Weeks The human body has its own set of medical terminology. What terms
Course: Human Body Systems Year: 2015 2016 Teacher: Meghann Redman Unit 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Approximate Time Frame: 2 Weeks The human body has its own set of medical terminology. What terms
