PHF8 is a histone H3K9me2 demethylase regulating rrna synthesis
|
|
|
- Augustine Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 npg Histone demethylase PHF8 794 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (21) 2: IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 11-62/1 $ npg PHF8 is a histone H3K9me2 demethylase regulating rrna synthesis Ziqi Zhu 1, 2, Yanru Wang 1, 2, 3, Xia Li 1, 2, Yiqin Wang 1, 2, Longyong Xu 1, 2, Xiang Wang 2, Tianliang Sun 2, Xiaobin Dong 2, Lulu Chen 2, Hailei Mao 1, 2, 3, Yi Yu 1, 2, Jingsong Li 2, 4, Pin Adele Chen 2, Charlie Degui Chen 1, 2 1 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31 Yueyang Road, Shanghai 131, China; 2 Shanghai Key laboratory of Molecular Andrology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31 Yueyang Road, Shanghai 131, China; 3 Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong 2261, China; 4 Laboratory of Molecular Cell Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 31 Yueyang Road, Shanghai 131, China Dimethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) is an important epigenetic mark associated with transcription repression. Here, we identified PHF8, a JmjC-domain-containing protein, as a histone demethylase specific for this repressing mark. Recombinant full-length wild type protein could remove methylation from H3K9me2, but mutation of a conserved histidine to alanine H247A abolished the demethylase activity. Overexpressed exogenous PHF8 was colocalized with B23 staining. Endogenous PHF8 was also colocalized with B23 and fibrillarin, two well-established nucleolus proteins, suggesting that PHF8 is localized in the nucleolus and may regulate rrna transcription. Indeed, PHF8 bound to the promoter region of the rdna gene. Knockdown of PHF8 reduced the expression of rrna, and overexpression of the gene resulted in upregulation of rrna transcript. Concomitantly, H3K9me2 level was elevated in the promoter region of the rdna gene in PHF8 knockdown cells and reduced significantly when the wild type but not the catalytically inactive H247A mutant PHF8 was overexpressed. Thus, our study identified a histone demethylase for H3K9me2 that regulates rrna transcription. Keywords: PHF8; histone demethylase; H3K9me2; rrna synthesis Cell Research (21) 2: doi:1.138/cr.21.75; published online 8 June 21 Introduction Histone methylation is a complex modification regulating transcription and chromatin dynamics [1-3]. Methylation can occur on arginine and lysine residues in histone proteins [4]. Each lysine can have three states of methylation, having one (mono), two (di), or three (tri) methyl groups covalently attached to the amine group of the lysine side chain, and arginine can be mono- or di-methylated symmetrically and asymmetrically [5]. Depending on specific residues and modification states, histone methylation can activate or repress transcription. Correspondence: Pin Adele Chen a, Charlie Degui Chen b a pinchen@sibs.ac.cn b cdchen@sibs.ac.cn Received 16 March 21; revised 3 March 21; accepted 7 April 21; published online 8 June 21 Histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) is an important epigenetic modification mainly localized within the silent regions of the euchromatin and associated with transcriptional silencing [6-9]. Three methyltransferases G9a, GLP-1 (EuHMTare), and ESET (SetDB1) have been identified to be able to catalyze the formation of H3K9me2 [8, 1-13], and G9a is a major histone methyltransferase for H3K9me2, because knockout of this gene in mice causes a 9% loss of H3K9me2 [6, 7, 9]. Histone methylation can be reversed by histone demethylases. LSD1 is the first histone demethylase identified, which can remove di- and mono-methylation from H3K4 using an amine oxidase reaction [14]. Subsequently, a JmjC-domain-containing protein was identified to possess histone demethylase activity, and the JmjC domain was shown as a demethylase signature motif [15]. This class of enzymes catalyzes demethylation by a hydroxylation reaction and requires both iron and Cell Research Vol 2 No 7 July 21
2 α-ketoglutarate as cofactors. In eukaryotes, rrna is an essential component of the ribosome and the genes are tandemly arrayed in hundreds to thousands of copies within nucleolus organizer regions [16]. The nascent rrna transcripts are synthesized in the nucleolus and the transcription is regulated at two levels: by controlling the number of rrna genes in on or off state and by regulating the transcriptional activity of the active ones. Several regulatory elements upstream of the transcript start site, including the gene promoter, the spacer promoter, and the repetitive enhancer element, play key roles in regulating the transcription of the nascent rrna. In this report, we demonstrated that PHF8, a member of the PHF2/PHF8 family, is a histone demethylase specific for H3K9me2. The protein was localized in the nucleolus and bound to the promoter region of the rdna gene. Knockdown of PHF8 reduced the expression of rrna and overexpression of the gene increased rrna Ziqi Zhu et al. npg 795 transcription. Concomitantly, H3K9me2 level was elevated in the promoter region of the rdna gene in PHF8 knockdown cells and reduced more significantly in the wild type cells compared to catalytically inactive PHF8- overexpressed cells. Thus, our study identified PHF8 as a histone demethylase for H3K9me2 that regulates rrna transcription. Results PHF8 is a histone demethylase Human PHF8 is a protein of 1 24 amino acids in length, which contains two recognizable domains: a PHD and a JmjC domain (Figure 1A). On the basis of domain structure of the full-length protein, PHF8 is closely related to the JHDM1 family [17]. We predicted that this protein would have histone demethylase activities toward H3K4 and/or H3K36, because JHDM1 proteins can reverse the methylation on these two residues. A B PHD JmjC 124 aa hphf8 hphf8 WT H247A C WT WT WT H3K4me1 H3K27me1 H3K79me1 H3K4me2 H3K4me3 H3K9me1 H3K9me2 H3K9me3 H3K27me2 H3K27me3 H3K36me1 H3K36me2 H3K36me3 H3K79me2 H3K79me3 H3 D WT H247A H3K9me2 H3 Figure 1 PHF8 is a histone demethylase for H3K9me2. (A) The domain structure of human PHF8 protein. (B) Purified Histagged recombinant wild type and mutant PHF8 were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie blue. (C) Calf thymus histone was reacted with increasing doses of PHF8 protein (, 2.5, and 5 µg) and assayed by immunoblotting. (D) Immunoblotting of in vitro demethylation assay in which calf thymus histone was reacted with the wild type and H247A mutant (H247A). Cell Research
3 npg Histone demethylase PHF8 796 To determine whether PHF8 has histone demethylase activities, we expressed and purified his-tagged protein from baculovirus-infected Tn5 cells (Figure 1B). Increasing doses of the purified protein were incubated with calf histones that contain various histone methylations in the presence of ascorbic acid, α-ketoglutarate, and Fe(II). The reaction was subjected to western blot analysis using antibodies against various lysine methylations. As shown in Figure 1C, the signal of H3K9me2 was significantly reduced. However, the levels of H3K9me3 and H3K9me1 were not affected, nor were the levels of mono-, di-, or trimethylated H3K4, H3K27, H3K36, and H3K79 (Figure 1C). These data suggest that PHF8 is a histone demethylase specific for H3K9me2. Crystal structure indicates that the JmjC domain is a jellyroll-like structure with eight β-sheets [18]. Three residues for chelating iron are required for the demethylase activity. In PHF8, these three residues are His247, Glu249, and His319. To determine whether this structure is required for the enzymatic activity, we mutated His247 to alanine (H247A). The mutant was expressed in the insect expression system and purified (Figure 1B). In vitro demethylation analysis indicates that the mutation diminished the histone demethylase activity (Figure 1D). These data suggest that PHF8 is an iron-dependent dioxygenase. PHF8 is localized in the nucleoli and binds to the promoter of the rrna gene To understand the biological function of PHF8, we examined its cellular localization using indirect immunofluorescence analysis. Overexpressed exogenous human PHF8 protein was largely localized in the nucleoli, as the overexpressed protein was colocalized with the nucleolar protein B23 in HeLa cells (Figure 2A). The nucleolar localization was also observed for the endogenous PHF8 protein in HeLa cells and 293T cells, as the protein was colocalized with the nucleolar proteins B23 in HeLa cells (Figure 2B) and fibrillarin in 293T cells (Figure 2C). These results indicate that PHF8 is localized in the nucleoli. Because the nucleolus is the transcriptional site for rrna, we examined whether PHF8 bound to the rdna gene. We performed chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays followed by quantitative real-time PCR using primer pair sets that span the entire human rdna repeat (Figure 2D). Mapping of PHF8 binding throughout the rdna locus showed that PHF8 bound mainly to the promoter and its upstream region of the rdna gene, with particular enrichment at kilobases (kb) (Figure 2E). Since this region was shown to be important for rrna transcription [19], these results indicate that PHF8 binds to the regulatory elements of the rdna gene and may regulate rrna transcription. PHF8 regulates rrna transcription through H3K9m2 demethylase activity To determine whether PHF8 regulates rrna transcription in vivo, we established short hairpin RNA (shrna)- mediated PHF8 knockdown cells by lentiviral transduction and measured the levels of the pre-ribosomal RNA (pre-rrna) by quantitative reverse transcriptasemediated PCR. Both shrna1 and shrna2 knocked down about 75-9% of PHF8 expression (Figure 3A), and silencing of PHF8 resulted in a significant decrease in the expression of the pre-rrna compared with the control (Figure 3B). Conversely, overexpression of exogenous PHF8 caused a marked increase in pre-rrna synthesis compared with mock-transfected cells (Figure 3D and 3E). In contrast, we observed slight enhancement of the transcription when the catalytically inactive H247A mutant was overexpressed, even though overexpression of the wild type and the mutant were similar (Figure 3D and 3E). These results suggest that PHF8 regulates rrna transcription and the enzymatic activity is required for the regulation. To confirm that PHF8 regulates rrna transcription through the H3K9me2 demethylase activity, we examined H3K9me2 occupancy in the promoter region of the rdna gene using ChIP assays. Consistent with its biochemical function as an H3K9me2 demethylase, enrichment of H3K9me2 in the highly enriched PHF8-bound regions from H36 to H42 was greatly increased in PHF8 knockdown cells (Figure 3C). Consistently, overexpression of the wild type resulted in a significant decrease of H3K9me2 occupancy in these regions, whereas overexpression of the catalytically inactive H247A mutant had less effect (Figure 3F). These data suggest that PHF8 directly regulates pre-rrna transcription and has H3K9me2 demethylase activity in vivo. Discussion Using biochemical approaches, we identified PHF8 as a histone demethylase specific for H3K9me2, an important repressive epigenetic modification. PHF8 belongs to a family of the JmjC-domain-containing proteins whose biochemical functions have just begun to be elucidated. This group of proteins consists of PHF2, KIAA1718, and PHF8. PHF2 was shown to be a histone demethylase specific for H3K9me1 [2]. KIAA1718 is a dual specificity histone demethylase for H3K9me2 and H3K27me2 [21, 22]. PHF8 was shown to be a histone demethylase for H3K9me2, H3K27me2, and H3K36me2 [23]. However, Cell Research Vol 2 No 7 July 21
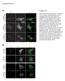
4 A Ziqi Zhu et al. npg 797 DAPI Exogenous PHF8 B23 Merge B DAPI Exogenous PHF8 B23 Merge C DAPI Exogenous PHF8 Fibrillarin Merge D 45 S 18 S 5.8 S 28 S rdna base number (kb) Non-transcribed Promoter Transcribed E Anti-PHF8 IP.3 % of input.2.1 H13 H27 H36 H39 H42 H H8 Amplicon Figure 2 PHF8 is localized in the nucleoli and binds to rdna. (A) HeLa cells transfected with Myc-PHF8 were immunofluorescently stained with a PHF8 antibody and the nucleolar marker B23. DAPI stains the nuclei. (B) HeLa cells were immunofluorescently stained with a PHF8 antibody and the nucleolar marker B23. (C) 293T cells were immunofluorescently stained with a PHF8 antibody and the nucleolar marker fibrillarin. (D) Schematic representation of a single human rdna repeat. The locations of rdna base number (kb) and the corresponding amplicons are shown below the diagram. (E) ChIP assays with anti-phf8 antibody in 293T cells. DNA binding was quantified by real-time PCR with indicated amplicons along the rdna gene in D. Cell Research
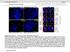
5 npg Histone demethylase PHF8 798 A shrna C 1 2 PHF8 β-actin D Flag β-actin Control hphf8 wt hphf8 mut B Relative pre-rrna level pre-rrna Control shrna1 shrna2 E Relative pre-rrna level pre-rrna Control hphf8 hphf8 mut C Anti-H3K9me2 IP.3 F Anti-H3K9me2 IP.3 Control Control % of input.2.1 PHF8 KD % of input.2.1 PHF8 wt PHF8 mut H13 H27 H36 H39 H42 H Amplicon H8 H13 H27 H36 H39 H42 H H8 Amplicon Figure 3 PHF8 regulates pre-rrna expression via its demethylase activity. (A) Western blot analyses of the control (C) and shrna-mediated knockdown cells (1 and 2) with antibodies against PHF8 and β-actin. (B) RT-PCR analysis of pre-rrna expression in control and shrna-mediated knockdown cells. (C) ChIP analysis of H3K9me2 enrichment on the rdna gene in control and shrna-mediated knockdown cells. (D) Western blot analyses of Flag-PHF8 protein levels in cells overexpressing human wild type PHF8 or H247A mutant using anti-flag antibody. (E) RT-PCR analysis of pre-rrna in cells with overexpression of wild type or the H247A mutant, compared to an empty vector (control). (F) ChIP analysis of H3K9me2 enrichment on the rdna gene in control, wild type or the H247A mutant overexpressed cells. three reports identified PHF8 as a histone demethylase specific for H3K9me2 [21, 24, 25], which are consistent with our results. According to the proposed nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes [26], PHF8 should be named as lysine demethylase 7B (KDM7B), since its close homolog KIAA1718 was named as KDM7A [22]. Our study indicates that PHF8 is localized to the nucleoli, where transcription of the pre-rrna takes place. These data suggest that PHF8 may regulate rrna transcription. Indeed, knockdown of PHF8 reduced the expression of pre-rrna, and overexpression of the gene increased the pre-rrna expression. This is consistent with a recent report that PHF8 is required for efficient Pol I transcription and regulates rrna transcription [24]. However, our data indicate that PHF8 is mostly enriched in the promoter region of the pre-rrna gene, in contrast to the widespread association of PHF8 in the entire rdna gene, with similar intensity in the published report [24]. This discrepancy may result from the use of different antibodies. We used an antibody from Novus and they raised their own antibody. Our data also show that PHF8 regulates H3K9me2 in the promoter region with high enrichment of PHF8 binding, but not other regions with no or weak PHF8 association. Consistent with our Cell Research Vol 2 No 7 July 21
6 data, Feng et al. [24] also demonstrated that PHF8 regulates H3K9me2 in the promoter region, but did not provide data whether PHF8 regulates H3K9me2 across the entire rdna gene. In contrast to other families of the JmjC-domaincontaining proteins that have similar substrate specificity, members of the PHF2/PHF8 family have different substrate selection. PHF2 demethylates H3K9me1, KIAA1718 demethylates H3K9me2 and H3K27me2, and PHF8 demethylates H3K9me2. The different substrate specificity may result from different sizes of the substrate-binding pockets. Indeed, one of the three highly conserved residues in the JmjC-domain that is required for the enzymatic activity for all of the other JmjC-domain-containing histone demethylases is tyrosine (Y321) instead of histidine in PHF2 [17]. Since tyrosine is larger than histidine, this substitution may reduce the size of the binding pocket of PHF2. This renders the protein with smaller binding pocket only for mono-methyl group. Further detailed structural analysis may explain the molecular mechanism of the different substrate selection. Materials and Methods Reagents Sources of the antibodies used are as follows: H3 monomethyl- K4 (Abcam 8895), H3 dimethy-k4 (Upstate 7-3), H3 trimethyl-k4 (Upstate 5-745), H3 monomethyl-k9 (Abcam 945), H3 dimethyl-k9 (Upstate 7-441), H3 trimethyl-k9 (Abcam 8898), H3 monomethyl-k27 (Upstate 7-448), H3 dimethyl-k27 (Upstate and Abcam 24684), H3 trimethyl-k27 (Upstate 7-449), H3 monomethyl-k36 (Abcam 948), H3 dimethyl-k36 (Upstate 7-369), H3 trimethyl-k36 (Abcam 95), H3 monomethyl-k79 (Abcam 2886), H3 dimethyl-k79 (Abcam 3594), H3 trimethyl- K79 (Abcam 2621), H3 (Abcam 1791), goat anti-rabbit IgG and goat anti-mouse IgG (Jackson), donkey anti-rabbit (Molecular Probes; Alexa 594) goat anti-mouse (Molecular Probes; Alexa 488) and anti-flag M2 affinity gel (Sigma A222). PHF8 antibody (Abcam 35471, Novus NB and from Jiemin Wong), B23 (Invitrogen 32-52), fibrillarin (Abcam ab4566). The other chemicals used are α-ketoglutaric acid disodium salt dehydrate (Sigma cat. no ), ascorbic acid (Sigma cat. no. A2218), ammonium iron (II) sulfate hexahydrate (Sigma cat. no. F1543), Ni- NTA agarose (25 ml) (Qiagen cat. no. 321). Cloning procedures Plasmid pphf8-myc-his was constructed by RT-PCR from 293T cell cdna into pcmv-myc-his vector and sequenced. The H247A mutant was generated by QuickChange (Stratagene) according to the manufacturer s instructions. The full-length wild type PHF8 cdna and H247A mutant were digested from pphf8- myc-his using NheI and XhoI and ligated to XbaI- and XhoI-digested pfastbact1 (Invitrogen) vector to engineer insect expression vector pfastbact1-his-phf8 that contains a C-terminal 6 His for affinity purification. They were also subcloned into lentiviral vectors pcsii-ires-dsred2 for overexpression experiments. Ziqi Zhu et al. npg 799 Recombinant PHF8 and H247A mutant Tn5 cells were infected with baculovirus, collected 72 h later, incubated in 2 mm Tris, 1% NP-4 with protease inhibitors in ice for 3 min, and sonicated 25 times at 2 W (sonicated for 2 s and paused for 15 s). After centrifugation, the supernatant was loaded onto Ni-NTA column and washed. The recombinant proteins were eluted by 25 mm imidazole and determined using SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. Demethylation assay Bulk histones were incubated with the purified his-phf8 in demethylation buffer (2 mm Tris-HCl (ph 7.3), 15 mm NaCl, 5 µm (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 + 6(H 2 O), 1 mm α-ketoglutarate, 2 mm ascorbic acid, and 1% glycerol) for 3 h at 37 C. A total of µg of the protein and 2.5 µg of bulk histones were reacted in a total volume of 2 µl of reaction mixture. The reaction was stopped with SDS-loading buffer and western blot analysis was performed. Chromatin immunoprecipitation Crosslinking was performed in 1% formaldehyde and sonication was carried out at 85 Hz for 1 s and paused for 3 s up to 75 cycles (Sonics Vibra Cell) to shear DNA to an average fragment size of 2-4 bp. Sonication buffer or FA lysis buffer was used for PHF8 (NB ) or H3K9me2 IP, respectively. After decrosslinking and protein digestion, DNA was precipitated and quantitative PCR was performed. Cell culture and transfection The 293T and Hela cells were grown in Iscove s DMEM containing 1% FBS. Transfection was carried out using Lipofectamine 2 (Invitrogen). To knockdown PHF8, cells were transfected with GIPZ lentiviral shrnamir (Open Biosystems) for 48 h. After 48-h transfection, GFP-positive 293T cells were sorted using FACS Aria cell sorter (BD Biosciences). Human wild type PHF8 and H247A mutant were constructed into vector pcsii- IRES-DsRed2 for overexpression in 293T cells. The DsRedpositive 293T cells were sorted using FACS Aria II cell sorter (BD Biosciences). Immunocytochemistry The 293T and Hela cells were plated on glass coverslips and transfection was carried out next day. At h after the transfection, the dish was washed with PBS and cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 1 min. The cells were washed once with cold PBS and permeabilized for 1 min with cold PBS containing.2% Triton X-1. Permeabilized cells were washed three times with blocking buffer (1% bovine serum albumin in PBS) and blocked for 3 min before incubation with primary antibodies for 1 h in a humidified chamber. After three consecutive 5-min washes with PBS, cells were incubated with secondary antibodies for 1 h, washed with PBS, and stained with 4,6-diamidino- 2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) (1:4 ) in PBS. Cells were washed twice with PBS and mounted with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories) before viewing under a fluorescence microscope. Fluorescence detection and imaging were carried out on Leica SP5 confocal microscope. Real-time PCR analysis Total RNA from 293T cells was isolated using RNArep cell Cell Research
7 npg Histone demethylase PHF8 8 Table 1 Primer sequences for RT-PCR and quantitative PCR 47s precursor RNA s TGTCAGGCGTTCTCGTCTC 47s precursor RNA a GAGAGCACGACGTCACCAC GAPDH s CGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA GAPDH a AGGGGAGATTCAGTGTGGTG H s GGTATATCTTTCGCTCCGAG H a GACGACAGGTCGCCAGAGGA H8 s AGTCGGGTTGCTTGGGAATGC H8 a CCCTTACGGTACTTGTTGACT H13 s ACCTGGCGCTAAACCATTCGT H13 a GGACAAACCCTTGTGTCGAGG H27 s CCTTCCACGAGAGTGAGAAGC H27 a TCGACCTCCCGAAATCGTAC H36 s TGCTCGGATGCCCCGAGTGA H36 a ACGTGTGTCCCGAGCTCCTGT H39 s CCCCGGGAGACAGACCCTGG H39 a CGAGGCGGAAGAGTCCACGC H42 s AGAGGGGCTGCGTTTTCGGCC H42 a CGAGACAGATCCGGCTGGCAG kit from TIANGEN (DP41). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed on the Eppendorf realplex2 using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Toyobo). Gene expressions were calculated following normalization to GAPDH levels by the comparative Ct (cycle threshold) method. Primer sequences for quantitative PCR used in this study are showed in Table 1. Acknowledgments We thank the cell biology core facility for confocal study. The PHF8 antibody was kindly provided by Dr Jiemin Wong (East China Normal University). This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (27CB9479, 21CB52975, 27CB9471), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX2-YW-R-4, KSCX2-YW-R-111), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (387538, ), Postdoctoral fellowship (294667), and the Council of Shanghai Municipal Government for Science and Technology. References 1 Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 2; 43: Bhaumik SR, Smith E, Shilatifard A. Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease pathogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 27; 14: Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 27; 128: Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. Reversing histone methylation. Nature 25; 436: Bedford MT, Richard S. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell 25; 18: Peters AH, Kubicek S, Mechtler K, et al. Partitioning and plasticity of repressive histone methylation states in mammalian chromatin. Mol Cell 23; 12: Rice JC, Briggs SD, Ueberheide B, et al. Histone methyltransferases direct different degrees of methylation to define distinct chromatin domains. Mol Cell 23; 12: Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Fukushima T, Shinkai Y. Set domain-containing protein, G9a, is a novel lysine-preferring mammalian histone methyltransferase with hyperactivity and specific selectivity to lysines 9 and 27 of histone H3. J Biol Chem 21; 276: Tachibana M, Sugimoto K, Nozaki M, et al. G9a histone methyltransferase plays a dominant role in euchromatic histone H3 lysine 9 methylation and is essential for early embryogenesis. Genes Dev 22; 16: Schultz DC, Ayyanathan K, Negorev D, Maul GG, Rauscher III FJ. SETDB1: a novel KAP-1-associated histone H3, lysine 9-specific methyltransferase that contributes to HP1-mediated silencing of euchromatic genes by KRAB zinc-finger proteins. Genes Dev 22; 16: Tachibana M, Ueda J, Fukuda M, et al. Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP form heteromeric complexes and are both crucial for methylation of euchromatin at H3-K9. Genes Dev 25; 19: Wang H, An W, Cao R, et al. mam facilitates conversion by ESET of dimethyl to trimethyl lysine 9 of histone H3 to cause transcriptional repression. Mol Cell 23; 12: Yang L, Xia L, Wu DY, et al. Molecular cloning of ESET, a novel histone H3-specific methyltransferase that interacts with ERG transcription factor. Oncogene 22; 21: Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, et al. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 24; 119: Tsukada Y, Fang J, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. Histone demethylation by a family of JmjC domain-containing proteins. Nature 26; 439: McStay B, Grummt I. The epigenetics of rrna genes: from molecular to chromosome biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28; 24: Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y. JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet 26; 7: Chen Z, Zang J, Whetstine J, et al. Structural insights into histone demethylation by JMJD2 family members. Cell 26; 125: Paalman MH, Henderson SL, Sollner-Webb B. Stimulation of the mouse rrna gene promoter by a distal spacer promoter. Mol Cell Biol 1995; 15: Wen H, Li J, Song T, et al. Recognition of histone H3K4 trimethylation by the plant homeodomain of PHF2 modulates histone demethylation. J Biol Chem 21; 285: Yue WW, Hozjan V, Ge W, et al. Crystal structure of the PHF8 Jumonji domain, an Nepsilon-methyl lysine demethylase. FEBS Lett 21; 584: Huang C, Xiang Y, Wang Y, et al. Dual-specificity histone demethylase KIAA1718 (KDM7A) regulates neural differentiation through FGF4. Cell Res 21; 2: Loenarz C, Ge W, Coleman ML, et al. PHF8, a gene associated with cleft lip/palate and mental retardation, encodes for Cell Research Vol 2 No 7 July 21
8 Ziqi Zhu et al. npg 81 an Nepsilon-dimethyl lysine demethylase. Hum Mol Genet 21; 19: Feng W, Yonezawa M, Ye J, Jenuwein T, Grummt I. PHF8 activates transcription of rrna genes through H3K4me3 binding and H3K9me1/2 demethylation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21; 17: Yu L, Wang Y, Huang S, et al. Structural insights into a novel histone demethylase PHF8. Cell Res 21; 2: Allis CD, Berger SL, Cote J, et al. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell 27; 131: Cell Research
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Lecture 8. Eukaryotic gene regulation: post translational modifications of histones
 Lecture 8 Eukaryotic gene regulation: post translational modifications of histones Recap.. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases Core promoter elements General transcription factors Enhancers and upstream activation
Lecture 8 Eukaryotic gene regulation: post translational modifications of histones Recap.. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases Core promoter elements General transcription factors Enhancers and upstream activation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases
 Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases SunHwa Hong*, Young-Wook Cho*, Li-Rong Yu, Hong Yu*, Timothy D. Veenstra, and Kai Ge* *Nuclear Receptor Biology
Identification of JmjC domain-containing UTX and JMJD3 as histone H3 lysine 27 demethylases SunHwa Hong*, Young-Wook Cho*, Li-Rong Yu, Hong Yu*, Timothy D. Veenstra, and Kai Ge* *Nuclear Receptor Biology
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
AGCGGCTGGTGTATGAGG AGCTCGAGCTGCAGGACT AAAGGTGCACTGGTAGCC AGGGCACAAGTGCATGGC CCCGCTGTGCAGAAGTAG
 Supplementary Table S1. Primer sequence information Gene Primer sequence 1 st round PCR 2 nd round PCR Accession# Dnmt3a TCAAGGAGATCATTGATG TGTTCCCACACATGAGCA AGCGGCTGGTGTATGAGG AGCAGATGGTGCAATAGGAC NM_007872.4
Supplementary Table S1. Primer sequence information Gene Primer sequence 1 st round PCR 2 nd round PCR Accession# Dnmt3a TCAAGGAGATCATTGATG TGTTCCCACACATGAGCA AGCGGCTGGTGTATGAGG AGCAGATGGTGCAATAGGAC NM_007872.4
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Eukaryotic transcription (III)
 Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Histones modifications and variants
 Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplemental information contains 7 movies and 4 supplemental Figures Movies: Movie 1. Single virus tracking of A4-mCherry-WR MV
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene
 Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Antibodies: LB1 buffer For 50 ml For 10ml For 30 ml Final 1 M HEPES, ph 2.5 ml 0.5 ml 1.5 ml 50mM. 5 M NaCl 1.4 ml 280 µl 0.
 Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
supplementary information
 Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
Supplementary Materials and Methods Reagents and antibodies was purchased from iaffin GmbH & Co KG. Cisplatin (ristol-myers Squibb Co.) and etoposide (Sandoz Pharma Ltd.) were used. Antibodies recognizing
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
(Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig. 1A). A 5.4-kb EcoRI fragment
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Supplemental Methods Generation of RyR2-S2808D Mice Murine genomic RyR2 clones were isolated from a 129/SvEvTacfBR λ-phage library (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) (Supplemental Fig.
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Cesarini et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Cesarini et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201504035 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Lamin A/C depletion generates two distinct phenotypes in
Supplemental material JCB Cesarini et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201504035 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Lamin A/C depletion generates two distinct phenotypes in
Nature Structural and Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational analysis of the SA2-Scc1 interaction in vitro and in human cells. (a) Autoradiograph (top) and Coomassie stained gel (bottom) of 35 S-labeled Myc-SA2 proteins (input)
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation
 Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation The number of mechanisms that are known to be involved in splicing regulation approximates the number of splicing decisions that have been analyzed in detail.
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
This PDF file includes: Supplementary Figures 1 to 6 Supplementary Tables 1 to 2 Supplementary Methods Supplementary References
 Structure of the catalytic core of p300 and implications for chromatin targeting and HAT regulation Manuela Delvecchio, Jonathan Gaucher, Carmen Aguilar-Gurrieri, Esther Ortega, Daniel Panne This PDF file
Structure of the catalytic core of p300 and implications for chromatin targeting and HAT regulation Manuela Delvecchio, Jonathan Gaucher, Carmen Aguilar-Gurrieri, Esther Ortega, Daniel Panne This PDF file
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data. Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016
 Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
Session 6: Integration of epigenetic data Peter J Park Department of Biomedical Informatics Harvard Medical School July 18-19, 2016 Utilizing complimentary datasets Frequent mutations in chromatin regulators
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems. Expressway Mini Cell-Free Expression System
 Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related chromatin-remodeling proteins in Arabidopsis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) :1-21. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2014) :1-21. 2014 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/14 www.nature.com/cr npg SUVR2 is involved in transcriptional gene silencing by associating with SNF2-related
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Stelter et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201105042/dc1 S1 Figure S1. Dyn2 recruitment to edid-labeled FG domain Nups.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Stelter et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201105042/dc1 S1 Figure S1. Dyn2 recruitment to edid-labeled FG domain Nups.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
doi: 10.1038/nature05473 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Association of Runx2 with mitotic chromosomes Mitotic chromosome spreads were prepared for a. Human Saos-2
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Supporting Information Palmisano et al. 10.1073/pnas.1202174109 Fig. S1. Expression of different transgenes, driven by either viral or human promoters, is up-regulated by amino acid starvation. (A) Quantification
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
 Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Linda Xiaoyan Li,, Julien Sage, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2751-2764. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci90921.
Lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 promotes cyst growth in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Linda Xiaoyan Li,, Julien Sage, Xiaogang Li J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2751-2764. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci90921.
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Discussion The cell cycle machinery and the DNA damage response network are highly interconnected and co-regulated in assuring faithful duplication and partition of genetic materials into
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2153 Figure S1 Ectopic expression of HAUSP up-regulates REST protein. (a) Immunoblotting showed that ectopic expression of HAUSP increased REST protein levels in ENStemA NPCs. (b) Immunofluorescent
2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein
![2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein](/thumbs/86/94743397.jpg) Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Epigenetics q&more 01.11
 Laurie. Knight, istockphoto.com Epigenetics 6 Bookmarks About the reading of genes in the Book of Life Prof. Dr. Manfred Jung, Julia M. Wagner, Institute for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Albert-Ludwig-University
Laurie. Knight, istockphoto.com Epigenetics 6 Bookmarks About the reading of genes in the Book of Life Prof. Dr. Manfred Jung, Julia M. Wagner, Institute for Pharmaceutical Sciences, Albert-Ludwig-University
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
