ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT. Single Cell RNA-Sequencing Identifies Diverse Roles of Epithelial Cells in. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
|
|
|
- Rosemary Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT Single Cell RNA-Sequencing Identifies Diverse Roles of Epithelial Cells in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Yan Xu Takako Mizuno Anusha Sridharan Yina Du Minzhe Guo Jie Tang Kathryn A. Wikenheiser-Brokamp Anne-Karina T. Perl Vincent Funari Jason J. Gokey Barry R. Stripp Jeffrey A. Whitsett (JAW-111) 1 10/17/16
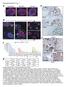
2 SUPPLEMENTAL LEGENDS AND FIGURES Figure S1: Histologic features of usual interstitial pneumonia in lung biopsies from IPF patients. Lung tissue were stained with H&E for pathological evaluation: A) Normal lung parenchyma consisting of a bronchiole with surrounding alveoli separated by thin alveolar septae in tissue from a normal donor (CC019-14). B) Patchy interstitial fibrosis adjacent to areas of preserved lung parenchyma with thin alveolar septae was characteristic of IPF (IPF001-14). C) Fibroblastic foci at the interface between fibrotic and preserved lung parenchyma (IPF001-14). D) Honeycomb fibrosis with dense collagen scars, loss of lung architecture and cysts containing intraluminal mucin (IPF 185). E) Normal uniformly thin alveolar septae in donor lung (CC019-14). F) Alveolar septae expanded by fibrosis and chronic inflammatory infiltrates in lesions lined by hyperplastic AT2 cells (IPF 180). G) IPF cysts lined by cuboidal and squamous alveolar type epithelium contiguous to mucinous cells showing distinct demarcations between the different cell types (IPF 171). H) Cysts lined by mucinous, flattened alveolar and squamous epithelium (IPF 185). I) Normal bronchiole in biopsy from donor lung (CC019-14). J) Bronchiolar-like epithelial hyperplasia lining cysts in a fibrotic area (IPF 185). K) Cyst in a honeycomb lesion with sharply demarcated ciliated and cuboidal alveolar type epithelial cells (IPF 180). L) Cyst in honeycomb lung with sharply demarcated squamous metaplastic and squamous alveolar-like epithelial cells (IPF 180). Short scale bar=50 µm, Long scale bar=250 µm. Figure S2. RNAs expression profiles from CD326/HTII-280 FACS sorted IPF and control epithelial cells were analyzed using Ingenuity Pathways Analysis to generate a biological association network. A) Predicted key regulators that were activated in IPF epithelial cells are shown in bold and larger font. Target genes are represented by nodes, and the regulatory relationships between key regulators and their predicted targets are identified through literature (JAW-111) 2 10/17/16
3 mining using the Ingenuity knowledge base represented by an edge (line). A solid line predicts direct interaction; a dashed line, indirect interaction. Color range indicates the relative induction of genes in IPF condition (the darker the red color, the larger induction of gene expression in IPF vs control). Signaling and transcriptional pathways, including TP53/63, TGFB1, NFKB, CTNNB1, and ETS family members are predicted to serve as important regulatory hubs in the network. B) EZH2 is predicted to be an epigenetic regulator of genes involved in IPF related bioprocesses. Figure S3. Selected cytokines and growth factors induced in IPF Epithelial Cells. A) Heatmap represents predicted induction of genes related to" response to cytokines." B). Heatmap represents the induction of genes responding to growth factors in IPF samples. C). Predicted biological network of cytokines, growth factors and associated bio-processes in IPF. Circled nodes represent growth factors; diamond nodes represent cytokines; pink represents genes induced in IPF; yellow represents bioprocesses activated by growth factors and cytokines. Samples were CD326/HTII-280 FACS sorted epithelial cells from IPF and normal peripheral lung. Figure S4. Heterogeneity and variation of the distribution of four major epithelial cell types. Pie charts show the % detection of the four major epithelial cell types identified by single cell RNA-Seq of normal and IPF single cells from cells from IPF (n=6) and normal adult (n=3) lungs. Distinct cell types are color-coded as indicated. Figure S5. Single cell RNA analysis supports the activation of epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition in basal and indeterminate cells. Signaling via TGFBR1, Wnt/β-catenin, EGFR, and PI3K/AKT, and transcription factors ZEB1, SNAl2, SMAD2/3, and ESRP1, an RNA splicing factor, were selectively induced in C3 basal cells. E-Cadherin (CDH1) was suppressed in C3 basal cells. Mesenchymal markers included MMPs, vimentin, N-cadherin (CHD12), and fibronectin (FN1) (JAW-111) 3 10/17/16
4 are selectively induced basal (pink) or indeterminate cells (blue), supporting the potential role of basal cells as progenitors of the "indeterminate" cell type. The network analysis was performed using IPA (Ingenuity Pathway Analysis). The regulatory relationships (lines with arrows) connecting gene nodes are identified through literature mining using the Ingenuity knowledge base. A solid line predicts direct interaction; a dashed line, indirect interaction. Figure S6A. Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy identifies atypical epithelial cell coexpressing E-cadherin and Vimentin in IPF. Vimentin staining, restricted to non-epithelial cells in normal tissues, was detected in many pan-cytokeratin and E-cadherin positive epithelial cells in IPF, indicating a partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Images were obtained at 10X magnification [scale bar=200 µm]. Insets in yellow and blue boxes are at 60X magnification. Figure S6B. Phosphohistone H-3 staining of control and IPF lung tissue. Cell proliferation was estimated by immunofluorescence staining for Phosphohistone H-3 (PHH3). Few cells stained in either IPF or control tissue. Images represent n=3 of control and IPF lung. Shown are examples of images co-stained with ABCA3 (AT2 cell marker, white), p63 (basal cell marker, green), and PHH3 (red). Yellow indicates co-localization. Most PHH3 stained cells in IPF were non-epithelial. Images were obtained at 10X magnification [scale bar=200 µm]. Insets in yellow boxes are at 20X magnification with a Nyquist zoom of Figure S7. Immunofluorescence staining of control and IPF tissue for SP-B (surfactant protein, red), MUC5B (green), and tubulin (TUBA4A). MUC5B and TUBA4A are exclusively expressed in goblet or ciliated cells in conducting airways, respectively. SP-B and MUC5B were co-expressed in IPF epithelial cells. Yellow indicates overlapping expression.. Images were obtained at 10X magnification [scale bar=200 µm]. Insets in yellow boxes are at 40X (JAW-111) 4 10/17/16
5 magnification. Insets in pink boxes were obtained at 100X magnification with high-resolution confocal imaging by oversampling in x, y, z and deconvolved by Landweber 3D. Figure S8A-D: Representative gating strategy for isolating EpCAM + epithelial cells from both control and IPF samples for single-cell C1 capture and RNA-sequencing experiments. Lungs cells were stained with 7AAD for viability (not shown); A and B) CD45/31-PE-Cy7 for hematopoetic and endothelial cell exclusion and C and D) CD326-APC for epithelial cells. Figure S8E and F: Relative abundance of basal versus AT2 cells in human distal lung tissue. Representative FACS analysis of CD271-PE and HTII-280-FITC for basal and AT2 cells, respectively, within CD326+ cells. Figure S8G: Quantification of relative cell abundance in control and IPF tissue sampled for epithelia cell isolation. Representative cell abundance of CD271+ basal cells compared to HTII AT2 cells in control (n=7) and IPF (n=7) and determined by FACS. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (JAW-111) 5 10/17/16
6 Table S1. List of 40 RNAs most increased in IPF compared to control epithelial cells Gene p-value Fold Change (IPF vs. Control) KRT E E+02 PCDH7 3.33E E+02 PXDN 1.48E E+02 IGFBP3 4.79E E+02 KCNN4 1.10E E+02 MMP E E+02 ANXA8L2 1.50E E+02 ANXA8L1 1.53E E+02 TP E E+02 ANXA8 2.34E E+02 GJB3 8.60E E+02 GPR E E+02 PKP1 1.41E E+02 LGR4 2.57E E+02 CXCL6 6.02E E+02 SERPINB5 5.60E E+02 UGT1A6 1.46E E+02 IL36G 5.63E E+02 ALDH1A3 3.24E E+02 KRT6A 1.70E E+02 TIMP3 1.02E E+02 ITGB4 1.34E E+02 CXCR7 1.43E E+01 TIAM1 4.45E E+01 MUC5B 4.50E E+01 CARD E E+01 CYP24A1 1.97E E+01 SNAI2 6.27E E+01 IGFBP5 3.35E E+01 FAM83A 3.64E E+01 CX3CL1 2.53E E+01 KRTAP E E+01 PROM1 7.22E E+01 PLAU 8.17E E+01 BPIFB1 3.37E E+01 DUSP4 5.40E E+01 SRPX2 6.36E E+01 PAX9 7.68E E+01 SULT2B1 1.83E E+01 GALNT E E+01 Note: EPCAM (CD326) and HTII-280 sorted epithelial cells from control and IPF donors were isolated from peripheral lung tissue by FACS. RNA-seq analysis identified differentially expressed genes in IPF vs. control samples. (JAW-111) 6 10/17/16
7 Table S2. List of 40 RNAs most decreased in IPF compared to control epithelial cells Gene p-value Fold Change (IPF vs. Control) EDNRB 4.39E E+01 CHI3L2 2.33E E+01 C8A 1.69E E+01 NECAB1 6.89E E+01 RMST 2.65E E+01 SLC10A4 2.46E E+00 MUC E E+00 NAP1L2 1.09E E+00 ACPP 1.32E E+00 HSPA6 3.55E E+00 ASRGL1 4.34E E+00 FAM46C 4.80E E+00 TNIP3 3.66E E+00 GUCY1B3 4.51E E+00 GPR E E+00 PEG3 9.34E E+00 CHIAP2 4.62E E+00 DAAM2 3.97E E+00 DGKG 2.37E E+00 ACSS3 3.29E E+00 FTLP3 6.13E E+00 EDIL3 4.22E E+00 ARHGAP E E+00 ZNF E E+00 NRGN 4.98E E+00 TMOD1 3.06E E+00 CA8 3.68E E+00 CES1 3.23E E+00 FZD7 2.29E E+00 SLC7A8 4.70E E+00 BEX1 8.44E E+00 PRKD1 3.86E E+00 SDC2 1.77E E+00 GEM 2.09E E+00 CDKL2 3.28E E+00 LRRK2 8.97E E+00 FAM49A 4.33E E+00 ACADL 2.52E E+00 PLAG1 8.50E E+00 FNIP2 1.93E E+00 Note: EPCAM (CD326) and HTII-280 positive epithelial cells from control and IPF donors were isolated from peripheral lung tissue by FACS. RNA-seq analysis identified differentially expressed genes in IPF vs. control samples. (JAW-111) 7 10/17/16
8 Table S3. Expression of vimentin in IPF and normal epithelial single cells. Statistics Average Expression T-test p-value Control Cells ( n = 215 ) Relative Normal IPF Cells ( n = 9 ) IPF Cells ( n = 316 ) C1: AT2 (n=217) C2: Indeterminate (n=91) C3: Basal (n=131) C4: Goblet (n=101) 8.55 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± Fold change Note: Average expression of VIM in control, IPF cells clustering with C1 and other IPF cells is shown in the left panel, average expression of VIM in four predicted cell types is shown in the right panel. P values were determined by one-tailed Welch's t-test. Vimentin expression was significantly induced in basal and indeterminate cells in IPF, with highest expression in the relatively normal IPF AT2-like cells. (JAW-111) 8 10/17/16
9 Table S4. Antisera and antibodies used for immunofluorescence microscopy. Antibody Dilution Source Catalog No. Antigen Retrieval 1 ABCA3 1:100 Seven Hills Bioreagents GP-984 Citrate 2 ACTA2 1:400? Sigma Citrate 3 Acetylated- 1:3000 Sigma T TUBA4A 4 CD326 (323/A3) 1:100 Thermo Scientific Pierce MA Do not 5 CDH1 (24E10) 1:200 Cell Signaling 3195 Tris-EDTA 6 HOPX 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology SC Citrate 7 HTII-280 1:200 Gift from Dr. Leland Dobbs -- Citrate 8 KRT14 1:100 Abcam ab7800 Citrate 9 KRT8 1:100? DHSB TROMA-I Tris-EDTA 10 MUC5B 1:300 Santa Cruz Biotechnology SC Citrate 11 P63 1:100 Biocare Medical CM163A Citrate 12 pan-cytokeratin 1:100 Sigma C2931 Tris-EDTA 13 SMA 1:2000 Sigma A Vimentin 1:50 Santa Cruz Biotechnology sc-7557 Tris-EDTA (JAW-111) 9 10/17/16
10 Figure S1 (JAW-111) 10 10/17/16
11 Figure S2 (JAW-111) 11 10/17/16
12 Figure S3 (JAW-111) 12 10/17/16
13 Figure S4 (JAW-111) 13 10/17/16
14 Figure S5 (JAW-111) 14 10/17/16
15 A B Figure S6 (JAW-111) 15 10/17/16
16 Figure S7 (JAW-111) 16 10/17/16
17 Figure S8 (JAW-111) 17 10/17/16
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Yan Xu,, Barry R. Stripp, Jeffrey A. Whitsett JCI Insight. 2017;1(20):e90558. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90558.
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Yan Xu,, Barry R. Stripp, Jeffrey A. Whitsett JCI Insight. 2017;1(20):e90558. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.90558.
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Yan Xu, 1 Takako Mizuno, 2 Anusha Sridharan, 1 Yina Du, 1 Minzhe Guo, 1 Jie Tang, 2 Kathryn A. Wikenheiser-Brokamp,
Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies diverse roles of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Yan Xu, 1 Takako Mizuno, 2 Anusha Sridharan, 1 Yina Du, 1 Minzhe Guo, 1 Jie Tang, 2 Kathryn A. Wikenheiser-Brokamp,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Supporting Information Rock et al. 10.1073/pnas.1117988108 Fig. S1. Heterogeneity of stromal cells in normal and fibrotic mouse lungs. Sections of normal mouse lungs (A and D) and fibrotic lungs collected
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Nitra and the Gangs.
 Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
Usual Interstitial pneumonia and Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia Nitra and the Gangs. บทน ำและบทท ๓, ๑๐, ๑๒, ๑๓, ๑๔, ๑๕, ๑๗ Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) Most common & basic pathologic pattern
stomach p63/krt5 CDH17 CEACAM5 CEACAM7 ANXA13 ANXA10 CLDN18 VSIG1 TFF2 VIL1 GDA
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a esophagus Barrett s e FABP1 Ecad stomach TFF3 b p63/krt5 CDH17 REG4 CDH17 f c signal intensity p63/krt5 EsoSC 5000 4000 3000 2000 CDH17 1500 1000 Barrett s KRT14 KRT6A KRT13 KRT5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a esophagus Barrett s e FABP1 Ecad stomach TFF3 b p63/krt5 CDH17 REG4 CDH17 f c signal intensity p63/krt5 EsoSC 5000 4000 3000 2000 CDH17 1500 1000 Barrett s KRT14 KRT6A KRT13 KRT5
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1700521/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Functional vascularized lung grafts for lung bioengineering N. Valerio Dorrello, Brandon A. Guenthart, John D. O Neill,
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes
 Supplemental Tables Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 Basal Immune Luminal AR Mesenchymal Stem Like WT 27 (87%) 24 (100%) 4 (66%)
Supplemental Tables Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 Basal Immune Luminal AR Mesenchymal Stem Like WT 27 (87%) 24 (100%) 4 (66%)
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Phenotype of regenerative epithelium in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias
 J Med Dent Sci 2003; 50: 213 224 Original Article Phenotype of regenerative epithelium in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Nae Hinata 1,2, Tamiko Takemura 2, Soichiro Ikushima 3, Takashi Yanagawa 3,
J Med Dent Sci 2003; 50: 213 224 Original Article Phenotype of regenerative epithelium in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias Nae Hinata 1,2, Tamiko Takemura 2, Soichiro Ikushima 3, Takashi Yanagawa 3,
Supplemental Information. High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the. Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells
 Cell Systems, Volume 5 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells Eric Lin, Lianette Rivera-Báez, Shamileh Fouladdel, Hyeun
Cell Systems, Volume 5 Supplemental Information High-Throughput Microfluidic Labyrinth for the Label-free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells Eric Lin, Lianette Rivera-Báez, Shamileh Fouladdel, Hyeun
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Restrictive lung diseases
 Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Restrictive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases are diseases that affect the interstitium of the lung. Interstitium of the lung is the very thin walls surrounding the alveoli, it s formed of epithelium
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II
 Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
Pathobasic Non-neoplastic Lung Disease II Spasenija Savic Prince Pathology Program Systematic approach to surgical lung biopsies with ILD Examples (chronic ILD): Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: UIP,
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figures for
 Supplementary Figures for SOX2 suppresses CDKN1A to sustain growth of lung squamous cell carcinoma Takuya Fukazawa 1, Minzhe Guo 4, 5, Naomasa Ishida 1, Tomoki Yamatsuji 1, Munenori Takaoka 1, Etsuko Yokota
Supplementary Figures for SOX2 suppresses CDKN1A to sustain growth of lung squamous cell carcinoma Takuya Fukazawa 1, Minzhe Guo 4, 5, Naomasa Ishida 1, Tomoki Yamatsuji 1, Munenori Takaoka 1, Etsuko Yokota
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress. Presented at: of new drugs for respiratory diseases. Barcelona, Spain, September 7-11, 2013 Page 1
 PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
PBI-4050, a novel first-in-class anti-fibrotic compound, reduces lung fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model: a comparative study with pirfenidone Presented at: Thematic Poster Session:
Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical
 Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia/epithelial hyperplasia (AAH/EH),
Supplementary Figure 1. Lkb1-deficient lung ADC progressively transdifferentiates into SCC. (a) A scheme showing the progression pattern of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia/epithelial hyperplasia (AAH/EH),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Title: Single Cell Dual Adherent-Suspension Co-Culture Micro-Environment for Studying Tumor- Stromal Interactions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Title: Single Cell Dual Adherent-Suspension Co-Culture Micro-Environment for Studying Tumor-
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Title: Single Cell Dual Adherent-Suspension Co-Culture Micro-Environment for Studying Tumor-
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
7/12/2012. Respiratory system. Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course.
 Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
Ninth Industrial Toxicology and Pathology Short Course 23 27 July, 2012 Contemporary Concepts in Target Organ Toxicologic Pathology Respiratory system Respiratory Response to Toxic Injury (Lung) Eric Wheeldon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
doi:10.1038/nature15260 Supplementary Data 1: Gene expression in individual basal/stem, luminal, and luminal progenitor cells. Box plots show expression levels for each gene from the 49-gene differentiation
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology
 Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
IPF: PATHOGENESIS. Marco Chilosi University of Verona, Italy Anatomic Pathology, Professor & Chief
 IPF: PATHOGENESIS Marco Chilosi University of Verona, Italy Anatomic Pathology, Professor & Chief ILD classification and pathogenesis Molecular advances Genetic analysis Gene expression profiling Molecular
IPF: PATHOGENESIS Marco Chilosi University of Verona, Italy Anatomic Pathology, Professor & Chief ILD classification and pathogenesis Molecular advances Genetic analysis Gene expression profiling Molecular
Case 4 History. 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar
 Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
Case 4 History 58 yo man presented with prox IP joint swelling 2 months later pain and swelling in multiple joints Chest radiograph: bi-basilar basilar infiltrates suggestive of pulmonary fibrosis Open
B220 CD4 CD8. Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN
 B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
Mitosis. Single Nano Micro Milli Macro. Primary. PCNA expression
 a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
Conditional Depletion of Airway Progenitor Cells Induces Peribronchiolar Fibrosis
 Conditional Depletion of Airway Progenitor Cells Induces Peribronchiolar Fibrosis Anne-Karina T. Perl 1, Dieter Riethmacher 2, and Jeffrey A. Whitsett 1 1 Division of Pulmonary Biology, Perinatal Institute,
Conditional Depletion of Airway Progenitor Cells Induces Peribronchiolar Fibrosis Anne-Karina T. Perl 1, Dieter Riethmacher 2, and Jeffrey A. Whitsett 1 1 Division of Pulmonary Biology, Perinatal Institute,
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
PBZ FT01_PBZ FT01_TZ FT01_NZ. interface zone (I) tumor zone (TZ) necrotic zone (NZ)
 Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ SUPPLEMENTRY FLES ndividuals factor map (P) FT_ FT_ FT_ Dim (.%) Dim (.%) >% peripheral brain zone () around % interface zone () FT
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo. SI Figures and Legend
 Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Macrophages form functional vascular mimicry channels in vivo Authors: *Faith H. Barnett, *Mauricio Rosenfeld, Malcolm Wood, William Kiosses, Yoshihiko Usui, Valentina Marchetti, Edith Aguilar, and Martin
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Immunological Lung Diseases
 Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells. (a) Bright-field images showing cellular morphology of MES-type (691-MES, 700-MES, 717-MES) and ADRN-type (691-ADRN, 700-
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells. (a) Bright-field images showing cellular morphology of MES-type (691-MES, 700-MES, 717-MES) and ADRN-type (691-ADRN, 700-
Supplementary Data for:
 Supplementary Data for: Tumour sampling method can significantly influence gene expression profiles derived from neoadjuvant window studies Dominic A. Pearce 1, Laura M. Arthur 1, Arran K. Turnbull 1,
Supplementary Data for: Tumour sampling method can significantly influence gene expression profiles derived from neoadjuvant window studies Dominic A. Pearce 1, Laura M. Arthur 1, Arran K. Turnbull 1,
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease
 Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Why? Much of interstitial lung disease biopsies
Histopathologic Approach to Interstitial Lung Disease Kirk D. Jones, MD UCSF Dept of Pathology kirk.jones@ucsf.edu Disclosures I have nothing to disclose 1 Why? Much of interstitial lung disease biopsies
Foxm1 Transcription Factor is Required for Lung Fibrosis and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition.
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-82682 Foxm1 Transcription Factor is Required for Lung Fibrosis and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. David Balli, Vladimir Ustiyan, Yufang Zhang, I-Ching Wang, Alex J. Masino,
Manuscript EMBO-2012-82682 Foxm1 Transcription Factor is Required for Lung Fibrosis and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. David Balli, Vladimir Ustiyan, Yufang Zhang, I-Ching Wang, Alex J. Masino,
Virginia A. Folcik, Ph.D. and Gerard J. Nuovo, M.D. The Ohio State University at Marion, and Phylogeny, Inc.
 As close as you can get to finding the cause of disease with Agent-Based Modeling Virginia A. Folcik, Ph.D. and Gerard J. Nuovo, M.D. The Ohio State University at Marion, and Phylogeny, Inc. Koch s Postulates
As close as you can get to finding the cause of disease with Agent-Based Modeling Virginia A. Folcik, Ph.D. and Gerard J. Nuovo, M.D. The Ohio State University at Marion, and Phylogeny, Inc. Koch s Postulates
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results
 Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
B16F1 B16F10 Supplemental Figure S1
 B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
B16F1 B16F1 Supplemental Figure S1 Representative microangiography images of B16F1 and B16F1 tumors grown in the cranial windows. FITC-dextran (2 million MW) was injected systemically to visualize blood
3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank
 @QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
@QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is
 Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Supplemental Figure 1: Lrig1-Apple expression in small intestine. Lrig1-Apple is observed at the crypt base and in insterstial cells of Cajal, but is not co-expressed in DCLK1-positive tuft cells. Scale
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק
 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3200 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression analysis of stomach markers in gutlike structure. (a) Differentiation scheme of gut-like structure formation from embryonic stem cells. (b) RT-PCR
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3200 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression analysis of stomach markers in gutlike structure. (a) Differentiation scheme of gut-like structure formation from embryonic stem cells. (b) RT-PCR
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Supporting Information Chan et al. 1.173/pnas.9654916 A Patient B Xenograft C * remaining feature of normal lymph node * * * D lymphocytes Infiltrating transitional carcinoma cells E Enlarged axillary
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9
 Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung
 Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung Christina E. Barkauskas,, Paul W. Noble, Brigid L.M. Hogan J Clin Invest. 2013;123(7):3025-3036. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci68782. Research Article Pulmonology
Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung Christina E. Barkauskas,, Paul W. Noble, Brigid L.M. Hogan J Clin Invest. 2013;123(7):3025-3036. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci68782. Research Article Pulmonology
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY HISTO-PHYSIOLOGY. 09-Mar-15. Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Lec-1 Dr. Muhammad Tariq Javed Professor Department of Pathology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. Email: mtjaved@uaf.edu.pk Web: http://www.geocities.ws/mtjaved 1 2 Conducting
Supplement Results, Figures and Tables
 Supplement Results, Figures and Tables Results PET imaging The SUV was significantly higher in tumours of the parental HSC-3 cell line than tumours of the EV and the MMP-8 overexpressing cell lines (Figure
Supplement Results, Figures and Tables Results PET imaging The SUV was significantly higher in tumours of the parental HSC-3 cell line than tumours of the EV and the MMP-8 overexpressing cell lines (Figure
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Ganesh Raghu, MD. Professor of Medicine and Laboratory Medicine (Adjunct) University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA
 Ganesh Raghu, MD. Professor of Medicine and Laboratory Medicine (Adjunct) University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA Director, Interstitial Lung Disease, Sarcoid and Pulmonary Fibrosis Program Medical
Ganesh Raghu, MD. Professor of Medicine and Laboratory Medicine (Adjunct) University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA Director, Interstitial Lung Disease, Sarcoid and Pulmonary Fibrosis Program Medical
Layered-IHC (L-IHC): A novel and robust approach to multiplexed immunohistochemistry So many markers and so little tissue
 Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TMA-BERN COHORT-2
 Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through. Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
 Masuda et al. Supplementary information for ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through enhancing CXCR4 signaling Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
Masuda et al. Supplementary information for ANGPTL2 increases bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through enhancing CXCR4 signaling Tetsuro Masuda, Motoyoshi Endo, Yutaka Yamamoto, Haruki Odagiri, Tsuyoshi
Lung Physiology. Jamie Havrilak, PhD Postdoctoral Research Associate Layden Lab October 26th, 2018
 Lung Physiology Jamie Havrilak, PhD Postdoctoral Research Associate Layden Lab October 26th, 2018 Nkx2.1- Lung epithelium Endomucin- Vasculature Alveoli/Capillaries: Site of Gas Exchange in the Lung
Lung Physiology Jamie Havrilak, PhD Postdoctoral Research Associate Layden Lab October 26th, 2018 Nkx2.1- Lung epithelium Endomucin- Vasculature Alveoli/Capillaries: Site of Gas Exchange in the Lung
Supplementary Figure 1 The ability to regenerate an ear hole is discontinuous with wound healing. Ear-hole closure at D85 for each sex within each
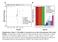 Supplementary Figure 1 The ability to regenerate an ear hole is discontinuous with wound healing. Ear-hole closure at D85 for each sex within each species observed. Data show a binary response to a 4 mm
Supplementary Figure 1 The ability to regenerate an ear hole is discontinuous with wound healing. Ear-hole closure at D85 for each sex within each species observed. Data show a binary response to a 4 mm
(JPC ) Caprine lungs
 2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
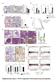 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
