Biomarkers in Lung Diseases: from Pathogenesis to Prediction. to New Therapies CALL FOR PAPERS
|
|
|
- Dwayne Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 309: L333 L347, First published May 29, 2015; doi: /ajplung CALL FOR PAPERS to New Therapies Biomarkers in Lung Diseases: from Pathogenesis to Prediction The reversal of pulmonary vascular remodeling through inhibition of p38 MAPK-alpha: a potential novel anti-inflammatory strategy in pulmonary hypertension Alistair C. Church, 1 Damien H. Martin, 1 Roger Wadsworth, 2 Gareth Bryson, 3 Andrew J. Fisher, 4 David J. Welsh, 1 * and Andrew J. Peacock 1 * 1 Scottish Pulmonary Vascular Unit, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom; 2 Department of Cardiovascular Biology, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, United Kingdom; 3 Department of Pathology, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, United Kingdom; and 4 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom Submitted 30 January 2015; accepted in final form 26 May 2015 Church AC, Martin DH, Wadsworth R, Bryson G, Fisher AJ, Welsh DJ, Peacock AJ. The reversal of pulmonary vascular remodeling through inhibition of p38 MAPK-alpha: a potential novel antiinflammatory strategy in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 309: L333 L347, First published May 29, 2015; doi: /ajplung The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) system is increasingly recognized as an important inflammatory pathway in systemic vascular disease but its role in pulmonary vascular disease is unclear. Previous in vitro studies suggest p38 MAPK is critical in the proliferation of pulmonary artery fibroblasts, an important step in the pathogenesis of pulmonary vascular remodeling (PVremod). In this study the role of the p38 MAPK pathway was investigated in both in vitro and in vivo models of pulmonary hypertension and human disease. Pharmacological inhibition of p38 MAPK in both chronic hypoxic and monocrotaline rodent models of pulmonary hypertension prevented and reversed the pulmonary hypertensive phenotype. Furthermore, with the use of a novel and clinically available p38 MAPK antagonist, reversal of pulmonary hypertension was obtained in both experimental models. Increased expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and p38 MAPK was observed in the pulmonary vasculature from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension, suggesting a role for activation of this pathway in the PVremod A reduction of IL-6 levels in serum and lung tissue was found in the drug-treated animals, suggesting a potential mechanism for this reversal in PVremod. This study suggests that the p38 MAPK and the -isoform plays a pathogenic role in both human disease and rodent models of pulmonary hypertension potentially mediated through IL-6. Selective inhibition of this pathway may provide a novel therapeutic approach that targets both remodeling and inflammatory pathways in pulmonary vascular disease. pulmonary hypertension; p38 MAPK PULMONARY HYPERTENSION continues to be a cause of significant morbidity and mortality and there remains a need for novel approaches in tackling the underlying pulmonary vascular remodeling (PVremod). This remodeling is characterized by * D. J. Welsh and A. J. Peacock contributed equally to this work. Address for reprint requests and other correspondence: A. C. Church, Scottish Pulmonary Vascular Unit, Golden Jubilee Hospital, Clydebank G81 4HX, United Kingdom ( colinchurch@nhs.net). increased proliferation of vascular cells, increased extracellular matrix and collagen deposition, recruitment of bone marrowderived cells to the vascular wall, and increased inflammatory responses (4). Although inflammation in driving this process is now recognized, with, for example, interleukin-6 (IL-6) being shown to have an important pathogenic role, the exact link between inflammation and pulmonary vascular remodeling remains unclear (2, 15). Although both smooth muscle and endothelial cells are vital to the pathology of pulmonary hypertension, the fibroblast plays a critical role in PVremod by undergoing proliferation in response to many stimuli, for example, hypoxia, and driving smooth muscle proliferation (13). In addition, it has been established by our own group and others that the adventitial fibroblast can contribute significantly to inflammatory processes and is a source of cytokines and chemokines, which can recruit key inflammatory cells such as monocytes/macrophages to the sites of PVremod (7, 17, 20). Previous work from our group has demonstrated in vitro that activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is essential to fibroblast proliferation in the hypoxic model and that its inhibition can block the hypoxic proliferative response (11, 21). In addition, p38 MAPK is well established in other inflammatory pathological states as being a key intermediary pathway and plays an important role in mediating cellular responses to proinflammatory cytokines. Phosphorylation and activation of the alpha ( )-isoform of p38 MAPK have been implicated in both driving the hypoxic proliferation of the adventitial fibroblast (9) and release of mitogens from the fibroblast that stimulate adjacent smooth muscle cell proliferation and recruit proinflammatory cells (13, 21). Fibroblast proliferation is an important mechanism underpinning PVremod and at least in hypoxia is p38 MAPK dependent (14). This contrasts with the systemic vascular fibroblast, which does not proliferate nor does it upregulate the p38 MAPK pathway in hypoxia, offering the possibility of selectively targeting the abnormal pulmonary vascular tree in pulmonary hypertension with minimal effect on systemic vessels (12). In addition p38 MAPK has been implicated in the development of pulmonary hypertension in other animal models, although no clear mechanism has been suggested. Although both inflammation and Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution CC-BY 3.0: the American Physiological Society. ISSN L333
2 L334 p38 MAPK have been implicated in PVremod a possible link between the two in pulmonary hypertension has not previously been suggested. This study sought to investigate the hypothesis that p38 MAPK, and the -isoform in particular, mediates PVremod and pulmonary hypertension through an inflammatory process by employing both prevention and reversal inhibitor strategies in vivo and exploring p38 MAPK expression in human disease.
3 L335 METHODS Primary Cell Culture Fibroblasts from adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were obtained from freshly excised vessels using a modified explant technique, as previously described (10). Briefly, vessels were dissected free and opened into a flat sheet and muscular tissue and endothelial cell layers were removed by gentle abrasion. The remaining tissue (adventitia) was then dissected into 1-mm 3 portions, 25 of which were evenly distributed over the base of a 25-cm 2 culture flask containing 2 ml of DMEM with 20% fetal calf serum (FCS), penicillin/streptomycin (400 IU/ml and 400 mg/ml), amphotericin B (5 mg/ml), and L-glutamine (27 mg/ml). Explants were incubated in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO 2 in air at 37.0 C. Although there are no specific fibroblast markers, we have previously shown using cell morphology and the absence of smooth muscle actin that this technique produces a pure culture of fibroblasts (21). To further characterize the cell population, vimentin staining was also used. Cells were subsequently maintained in DMEM containing 10% FCS, supplemented with antibiotics and L-glutamine as before, and used between passage 3 and 10. All chemicals were obtained from Invitrogen (Paisley) unless otherwise stated. Growth of Cells in a Hypoxic Environment Maintenance of cells in a nitrogen-supplemented, humidified, temperature-controlled incubator (Galaxy R; Wolf Laboratories, York, UK) allowed control of internal chamber oxygen levels at 5%, while CO 2 level was maintained at 5%. This achieved a tissue culture supernatant PO 2 of 35 mmhg for the hypoxic conditions (10). Animal Models Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing g, were used in all experiments. All experiments were approved by the University of Strathclyde Ethics Committee and were performed under authorization of the Animals (Scientific procedures) Act Chronic hypoxic model. Animals were maintained in a hypobaric chamber at ambient pressure of 550 mmhg for up to 4 wk, equivalent to an oxygen concentration of 10%. The chamber was depressurized initially over 2 days. To allow daily injections the chamber was brought back to atmospheric pressure over a 1-h period and injections performed and then the chamber was depressurized again with gradual reductions over 1 h. The chamber was unsealed for a maximum of 30 min/day. Age and weight matched normoxic animals were housed in an adjacent perspex container but without depressurization. Animals received food and water ad libitum. Animals body weights were measured twice weekly. Monocrotaline model. Monocrotaline (MCT) was dissolved in 1 M HCl and then neutralized with a similar volume of 1 M sodium hydroxide. Animals were then injected with 60 mg/kg MCT subcutaneously in the scruff of the neck. Control animals received a similar volume of saline injected subcutaneously. The animals body weights were measured three times a week. The agents used were SB and PH Both are p38 MAPK -specific but the PH has been shown to be more specific and tolerated in humans. The animal groups were divided up into: 1) a prevention study for chronic hypoxia where the p38 MAPK antagonists were administered at the start of the animals being exposed to the hypobaric chamber; 2) a reversal study for chronic hypoxia where the animals were allowed to develop pulmonary hypertension for 2 wk and were then treated with SB203580, a p38 MAPK antagonist; 3) a reversal study for the MCT-treated animals with the p38 MAPK antagonist SB as above; 4) a reversal study with the p38 MAPK antagonist PH for the chronic hypoxic animals; and 5) a reversal study with the p38 MAPK antagonist PH for the MCT animals. Measurement of Hemodynamics and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Rats were anesthetized using subcutaneous administration of a 50:50 mixture of midazolam (Hypnovel) and fentanyl/flunisone (Hypnorm) at a dose of 0.15 ml per 100 g body wt. The animals underwent tracheotomy and were established on a ventilator. Then a midline thoracotomy was performed and the heart was exposed. The right ventricular (RV) pressure was obtained by advancing a 21-G needle attached to a pressure transducer into the RV. The pressures were recorded using a Powerlab data acquisition system (AD Instruments) and analyzed using LabChart software. Placement of the catheter in the RV was established by direct visualization and afterwards by postmortem examination. The tracings were allowed to stabilize for 3 min. Fig. 1. Proproliferative fibroblast phenotype and paracrine smooth muscle proliferation mediated by p38 MAPK in fibroblasts from experimental models of pulmonary hypertension (PH). A: cells were isolated from the 2nd order division of the pulmonary artery and grown in normoxic culture. The effect of serum stimulation was observed on these cells. At baseline with no serum stimulation, the chronic hypoxic (CH) and monocrotaline (MCT) pulmonary artery fibroblast (PAF) had an increased proliferative rate compared with the PAF derived from normoxic wild-type rats. This was also seen with low dose 1% serum stimulation. The effect was lost at 5% serum stimulation, which may reflect cell contact inhibition. The thymidine incorporation assay was used to assess the proliferation of the cells, and the results presented are representative of 3 experiments with triplicate values in each experiment. Values are means SE. ***P B: this immunoblot shows that under normoxic conditions the PAFs derived from both CH and MCT animals show a constitutive activation of p38 MAPK with increased levels of p-p38 detected. Cells were from passage 3 and were quiescesed in serum free medium for 24 h before harvest. Immunoblot for phospho-p38 and total p38 MAPK was performed and representative of 3 experiments. C: PAFs derived from MCT animals were isolated and then quiescesed for 24 h in serum free media. After 24 h, cells were stimulated with either 1% serum or some remained in serum free media SB (p38 inhib). The conditioned media were aspirated from the wells after 24 h and passed through a cell sieve to give conditioned media from serum free cells SB (SF cond med, SF cond med p38 inhib) and 1% stimulated cells SB (1% cond med, 1% cond med p38 inhib). The conditioned media were added to smooth muscle cells for 48 h before a proliferation assay was performed. Both SF cond med and 1% cond med resulted in increased proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) while this effect was lost in the conditioned media from the PAFs, which had been coincubated with SB There was no effect of SB directly on the PASMCs. Values are means SE. Data shown from 3 experiments. **P D: PAFs derived from CH animals were isolated and then quiescesed for 24 h in serum free media. After 24 h, cells were stimulated with either 1% serum or some remained in serum free media SB (p38 inhib). The conditioned media were aspirated from the wells after 24 h and passed through a cell sieve to give conditioned media from serum free cells SB (SF cond med, SF cond med p38 inhib) and 1% stimulated cells SB (1% cond med, 1% cond med p38 inhib). The conditioned media were added to normal PASMCs for 48 h before a proliferation assay was performed. Both SF cond med and 1% cond med resulted in increased proliferation of PASMCs while this effect was lost in the conditioned media from the PAF, which had been coincubated with SB There was no effect of SB directly on the PASMCs. Values are means SE. Data shown from 3 experiments. *P 0.05; **P E: PAF from normal animals were exposed to 48 h normoxia or hypoxia SB The supernatant was collected and analyzed using cytokine array. The above are representative of triplicate samples from 3 different animals. Exposure times for each blot was the same. The results for IL-6 are shown and are presented as a relative density plot vs. the positive control blots. ***P F: PASMCs are quiescesed and then incubated with conditioned media derived from normoxic or hypoxic PAF. The hypoxic conditioned media induced PASMC proliferation. When both the conditioned media and anti-il-6 were added to the PASMCs, there was an inhibition in the proliferative stimulus. Results are means SE from 3 replicates from 3 different animals. ***P
4 L336 Systemic blood pressure. This was measured by noninvasive tailcuff methods as previously outlined (26). Assessment of right ventricular hypertrophy. The RV was separated from the left ventricle (LV) and septum (S) using a dissecting microscope. The ventricles were blotted and then weighed. The degree of RV hypertrophy (RVH) was determined by the ratio of the weight of the RV to the LV S. Thymidine proliferation assay. Rat pulmonary artery fibroblasts (RPAFs) were grown in normoxic conditions to 60% confluency in 24-well plates and then quiesced for 24 h in serum free medium. Cells were then cultured under conditions of normoxia or hypoxia, in the presence or absence of serum and experimental mediators, for a further 24 h. Increased proliferation of RPAFs to hypoxia is seen with concentrations of serum 0.1% 10%. For these experiments, 1% serum was selected as this maximizes differences between normoxic and hypoxic proliferation. Fibroblasts were pulsed with [ 3 H]thymidine (0.1 Ci/well) 4 h before the end of the 24 h experimental period with scintillation counting as previously described. To assess proliferation and viability 24 h, experiments were repeated, and fibroblasts were removed from the wells by 0.05% trypsin and then counted using a Fischer hemocytometer/0.4% trypan blue. Immunoblotting. Frozen lung tissue was homogenized on ice using a rotor blender (Fisher) on ice in Tissue protein extraction reagent (T-Per from Sigma). This was supplemented with phosphatase and protease inhibitors (Halt; Sigma). Homogenates were then centrifuged for 15 min at 4 C, and the supernatants were collected and frozen at 80 C until required. The protein concentration was established using a BCA technique (Thermo Scientific), and g of protein were then separated by electrophoresis on a Bis-Tris NuPage gel. Proteins were then transferred to PVDF Immobilon and transfer was confirmed with Ponceau red stain. The blot was blocked at room temperature for 1 2 h in 5% nonfat milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween-20. Membranes were then incubated overnight at 4 C with primary antibody diluted accordingly in 5% milk/ TBS-T. These were subsequently washed using TBS-T and then incubated with secondary antibody for 1 2 h at room temperature. The antibody labeling was visualized using enhanced chemiluminscence (ECL; Amersham) with exposure to autoradiographic film (GE Healthcare). Antibodies and drugs. Antibodies used for the immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry were phospho-p38 MAPK (Cell Signaling), p38 MAPK, p38 MAPK, total p38 MAPK (Cell Signaling), phos- Fig. 2. Increased expression of p38 MAPK -isoform in animal models of PH. A: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using the BCA method. Equal concentrations were then loaded on a gel and blotted for p38 MAPK and -actin for loading control. There are 3 wells for each condition. Immunoblot shown is best representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals with each condition. B: densitometry of immunoblot in A. Values are mean arbitrary values from 3 immunoblots expressed relative to the value for -actin. *P 0.05 by ANOVA. C: lung sections (5 mm) were prepared from normal, CH, and MCT animals. Sections were stained for p38 MAPK using 1:400 dilution. Magnification: 20. Bar represents 150 mm. Arrows identify blood vessels. D: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using BCA method. Equal concentrations were then used in a p38 MAPK activity assay using immunoprecipitation and the phosphorylation of activating transcription factor-2 (ATF-2) as a read out. Immunoblot shown is representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals. E and F: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using BCA method. Equal concentrations were then loaded on a gel and blotted for phosphorylated p38 MAPK and -actin for loading control. Immunoblot shown is representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals with each condition. Densitometry is shown for remaining blots. *P 0.05.
5 L337 pho- and total ATF-2 (Cell Signaling), -actin (Abcam), phospho- STAT3, total STAT3, and -smooth muscle actin (Dako). The p38 MAPK antagonist SB was obtained from Selleck Chemicals and the dose used was 20 mg/kg given intraperitoneally once daily. The p38 MAPK antagonist PHA was used with permission from Pfizer. This was administered intraperitoneally at 3 mg/kg once daily. The difference in kinase activity and specificity between SB and PH is as follows: SB IC 50: 50 nm, K i: 21 nm vs. PH IC 50: 26nM,K i: 3.9 nm. Quantification of pulmonary vascular remodeling. Pulmonary vascular remodeling was quantified by determining the degree of muscularization present in smaller pulmonary arterial vessels with a diameter 80 m. Standard immunohistochemical techniques were used as described below with staining for -smooth muscle actin. In each lung section, pulmonary arteries were characterized as completely muscularized (with complete occlusion or slit-like appearance of lumen), partially muscularized (with incomplete rings of smooth muscle), or nonmuscularized (with no smooth muscle present). The Fig. 3. PH is prevented by administration of SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor. A and B: animals were exposed to a hypobaric hypoxic environment for 2 wk. Some animals received daily injections of SB Hemodynamics (A) and hematocrit (B) were measured after 2 wk. RVSP, right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure. Data represent mean values SE. Total animals n 5 6 per group. C: hearts were isolated from the animals and the RV was dissected out from the left ventricle (LV) and septum. The ventricles were dry blotted and then weighed, and the ratio was calculated. The total RV weight was also plotted. Values are means SD; n 5 per group. **P D: noninvasive systemic blood pressure taken by tail-cuff measurement. E and F: rats were exposed to hypoxia SB The lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained with -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 80 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five random fields per slide were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as completely, partially, or nonmuscularized and are presented as numbers per total number of vessels present in each field. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 5 animals. ***P 0.001, for A C and E.
6 L338 number of vessels in each category was determined by counting the total number in five random fields per slide and using three slides per animal. The vessels were then categorized by degree of muscularization. The individual assessor was blinded to the slides. Immunohistochemistry. IN VIVO MODELS. Immediately after experimentation, the left lung was removed and perfusion fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin. Following fixation the paraffin embedded lungs were sectioned for analysis. These sections were immunohistochemically stained for p38 MAPK or -smooth muscle actin using standard techniques. HUMAN TISSUE. Lung tissue from two female patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) was obtained at the time of lung transplantation centre with local ethics approval REC Reference 11/NE/0291. These patients were in New York Heart Association Functional Class 4 and on optimal background therapy including parenteral prostanoid therapy. Material was fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin by airway perfusion before being prepared for sectioning. Samples were selected from specimens that showed excellent tissue preservation. Control adult lung was obtained from patients who were undergoing routine cardiothoracic intervention, with no echocardiographical evidence of pulmonary hypertension. Sections were immunohistochemically stained for p38 MAPK and phospho-p38 MAPK. Control tissue was obtained from patients undergoing lung resection for solitary lung nodules and had no evidence of pulmonary hypertension on echocardiography. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay/cytokine array. An IL-6 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; R&D Systems) was used to analyze lung homogenates prepared as previously described. The protocol as per manufacturer s instructions was followed. The rat proteome profiler (R&D Systems) was used to analyze 29 cytokines/ chemokines as per manufacturers instructions. This is a qualitative analysis rather than quantitative. SYBR green quantitative PCR. Gene expression of the pulmonary artery fibroblasts was analyzed using SYBR green quantitative PCR. RNA was isolated from the cells using RNAEasy purification kits (Invitrogen), and the purity was quantified using Nanodrop reader. Then these were reverse transcribed and real-time quantitative PCR performed using SYBR Green PCR Mastermix and primers for rat IL-6 (Integrated DNA Technologies) on Applied Biosystems ABI7500 PCR machine. These experiments were done in triplicate. Relative gene expression was quantified by comparison of the Ct method relative to -actin as a housekeeping gene. Data analysis. For normally distributed values, responses were reported as means SE and Students t-test was used. The n value refers to the number of animals involved per experimental procedure. For multiple comparisons of means across different experimental groups, ANOVA was performed with Bonferonni post hoc analysis. Values of P 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant. RESULTS p38 MAPK and the -Isoform Is Important in Both In Vitro And In Vivo Experimental Models of Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling In vitro: hypoxia. Our group and others have shown previously that fibroblasts isolated from chronic hypoxic animals have undergone a phenotypic switch, which results in constitutive activation of p38 MAPK and a proproliferative phenotype. Whether this effect is seen in other models of pulmonary hypertension is unknown. Therefore, we examined the proliferative potential of fibroblasts derived from MCT animals and compared them to that of fibroblasts isolated from both normal and chronic hypoxic animals (Fig. 1A). This clearly showed an increased predisposition to proliferation by the MCT-derived fibroblasts in relation to low dose serum stimulation. The effect was lost at 5% serum stimulation, which may reflect cell contact inhibition. We confirmed that there was increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in both chronic hypoxic and MCT fibroblasts compared with normal fibroblasts (Fig. 1B), suggesting upregulation of this pathway in those fibroblasts derived from experimental models of pulmonary hypertension. This was confirmed on densitometry (data not shown). The addition of conditioned media isolated from chronic hypoxic and MCT fibroblasts to smooth muscle cells resulted in increased proliferation (Fig. 1, C and D). This effect could be prevented when the fibroblasts were incubated with a p38 MAPK inhibitor before collection of the conditioned media. In contrast p38 MAPK inhibition had no direct effect on pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation. This suggests that various mitogens are released from the fibroblast in a p38 MAPK-dependent mechanism, which can promote pulmonary vascular remodeling, and that this is conserved in fibroblasts derived from experimental models of pulmonary hypertension. To investigate this further a cytokine screening array was used (data not shown). Various cytokines were Fig. 4. PH in 2 in vivo animal models is reversed by the administration of SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor. A: animals were exposed to a hypobaric hypoxic environment for 2 wk and then p38 MAPK inhibition was commenced. Hemodynamics and RVSP were measured after 4 wk. Data represent mean values SE. Total animals n 5 6 per group. **P 0.01; ***P 0.001, for normal relative to all other conditions. B: hearts were isolated form the animals and the RV dissected out from the LV and septum. The ventricles were dry blotted and then weighed, and the ratio was calculated. Values are means SE; n 6 7. **P 0.01; ***P C: hematocrit ratio. D: the lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained for -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 80 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as completely, partially, or nonmuscularized. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 6 animals. **P 0.01; ***P E: the lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained for -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 100 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as muscularized or nonmuscularized and the percentage of muscularized vessels calculated. Groups were analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 7 animals. ****P ; P 0.05 for hypoxic drug-treated vs. day 14 hypoxic control. **P 0.01; ***P F and G: animals were injected with MCT and after 2 wk p38 MAPK inhibition was commenced with daily injections. Hemodynamics and RVH were measured after 4 wk. Data represent mean values SE. Total animals n 6 7 per group. *P 0.05; ***P 0.001, for F. *P 0.05; **P 0.01, for G. H: the lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained for -smooth muscle actin, and the vessels 80 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as completely, partially or nonmuscularized. Groups were analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 6 animals. *P 0.05; ***P I: lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained for -smooth muscle actin, and the vessels 100 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as muscularized or nonmuscularized, and the percentage of muscularized vessels was calculated. Groups were analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 6 animals. ****P ; P 0.05 for hypoxic drug-treated vs. day 14 MCT control.
7 identified as being released into the supernatant from hypoxic fibroblasts and perhaps one of the most important with relevance to PVremod is IL-6. Other cytokines/chemokines identified were VEGF-A, CXCL-1, CXCL3, TIMP-1, LIX, and MIP-3. L339 With the addition of p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580, the proinflammatory profile was returned to that of normoxic fibroblasts, suggesting a key role of p38 MAPK in release of proinflammatory mediators. The importance of IL-6 in the conditioned media were demonstrated by abrogation of the
8 L340 proliferative effect when the conditioned media were added in the presence of anti-il-6 antibody (Fig. 1F). Although we identified other chemokines and cytokines, the significance of IL-6 in pulmonary vascular biology has already been shown and therefore seemed an appropriate signal to focus on. In vivo: chronic hypoxia and MCT models. Expression of p38 MAPK was increased in both chronic hypoxic and MCT rat models of pulmonary hypertension after 2 wk (Fig. 2, A and B). Immunohistochemistry showed increased p38 MAPK in the small pulmonary vessels of both chronic hypoxic and MCT animals. This staining was distributed throughout the vessel wall with notable staining in the adventitial and endothelial compartments (Fig. 2C). With the use of a p38 MAPK activity assay, increased activity was demonstrated in whole lung homogenates from chronic hypoxic and MCT animals (Fig. 2D) suggesting because of increased expression there was also increased activity of the p38 MAPK pathway. Furthermore, increased phosphorylated total p38 MAPK was observed in the lungs of those animals with pulmonary hypertension (Fig. 2, E and F). We did not find changes in expression of - or p38 MAPK isoforms (data not shown). Administration of the p38 MAPK Inhibitor SB the Development of Chronic Hypoxic-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension We administered daily p38 MAPK -specific pharmacological inhibitor (SB203580) or vehicle (DMSO) via intraperitoneal injections to animals maintained in a hypoxic environment. After 14 days RV systolic pressure (RVSP) and RVH were significantly increased (P 0.005) in the vehicle-treated animals but remained normal in the animals with the p38 MAPK inhibitor (Fig. 3, A D). There was a significant increase in the percentage of fully muscularized vessels in the vehicle group compared with the normal animals. This increase was significantly less in the drug-treated group indicating prevention of PVremod (Fig. 3, E and F). Knockdown of p38 MAPK activity in the lungs was confirmed by looking at ATF-2 phosphorylation (data not shown). The p38 MAPK Inhibitor SB Reversed Chronic Hypoxic and MCT-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension Chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Animals were exposed to hypoxia for a period of 2 wk and then treated with daily intraperitoneal injections of SB or vehicle for a further 2 wk while remaining in hypoxia. There was a significant reduction in the RVSP in the drug-treated group compared with the vehicle-treated group at 4 wk and control hypoxic animals after 2 wk (Fig. 4A), with almost full reversal to that of normal animals. The degree of RVH was reversed significantly (by 29%) in the drug-treated animals (Fig. 4B). The degree of PVremod was also reduced in the drug-treated animals compared with the control untreated animals (Fig. 4, C and D). The systemic blood pressure (BP) was unchanged between groups although the BP was lower in the 28-day hypoxic group (data not shown). MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension. Two weeks after an injection of MCT, there was an elevated RVSP and increased RVH consistent with the development of pulmonary hypertension in this group of animals. (Fig. 4, E and F). There was no difference between the RVSP rise seen in MCT control animals at 14 or 28 days. After 14 days, these animals were injected daily with vehicle or SB for a further 2 wk. This led to a significant reduction in the RVSP compared with both the 14- and the 28-day time points in MCT controls (Fig. 4E). There was a significant improvement in the degree of RVH observed in the drug-treated animals which almost returned to normal (Fig. 4F). This was mirrored by a reduction in the degree of muscularization in the small vessels in the drug-treated animals (Fig. 4, G and H). There was no difference in the systemic BP between the MCT groups (data not shown). Reversal of Chronic Hypoxic and MCT-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension with a Novel p38 MAPK -Selective Inhibitor (PH ) To examine the hypothesis that the -isoform is important in the pulmonary hypertensive phenotype, we utilized a Fig. 5. PH in a reversal strategy in 2 in vivo animal models by administration of PH , a more selective p38 MAPK inhibitor. A and B: animals were exposed to CH and after 2 wk p38 MAPK inhibition was commenced with daily injections. Hemodynamics and RV hypertrophy (RVH) were measured after 4 wk. Data represent mean values SE. *P 0.05; **P 0.01 for A.**P 0.01; ***P 0.001, for B. C: the lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) were cut. These were stained with -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 80 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as completely, partially, or nonmuscularized. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 10 animals. **P 0.01; P 0.05 for complete muscularized group in drug-treated vs. day 14 hypoxic control. D: lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained with -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 100 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as muscularized or nonmuscularized and the percentage of muscularized vessels calculated. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 10 animals. ****P ; P 0.05 for hypoxic drug-treated vs. day 14 hypoxic control. E and F: animals were injected with MCT and after 2 wk p38 MAPK inhibition was commenced with daily injections. Hemodynamics and RVH were measured after 4 wk. Data represent mean values SE. Total animals n per group. ***P for E.*P 0.05; **P 0.01 for F. G: the lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained with -smooth muscle actin and the vessels 80 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as completely, partially or nonmuscularized. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 10 animals. **P 0.01; P 0.05, for complete muscularized group in drug-treated vs. day 14 hypoxic control. H: lungs were removed after experiment and sections (5 mm) cut. These were stained with -smooth muscle actin, and the vessels 100 mm were analyzed for degree of muscularization. Five to 10 random fields ( 40) were analyzed with 3 slides per animal. The vessels were categorized as muscularized or nonmuscularized, and the percentage of muscularized vessels was calculated. Groups analyzed by ANOVA for overall change with posttest analysis; n 10 animals. ****P ; P 0.05 for drug-treated vs. day 14 MCT control.
9 novel agent with greater specificity for this isoform than SB (3). Chronic hypoxic animals. We adopted a reversal strategy whereby the animals were treated daily intraperitoneal injections of PH after 2 wk of chronic hypoxia. Similar to the study with SB we found a significant reduction in the RVSP in the drug-treated animals after 2 wk of treatment L341 (Fig. 5A) accompanied by a marked reduction in the degree of RVH compared with both 14- and 28-day time points (Fig. 5B), with no change in hematocrit (data not shown). The pulmonary vascular muscularization was reversed in the drug-treated group compared with the 28-day animal untreated group (Fig. 5, C and D). Systemic BP remained unchanged. (data not shown).
10 L342 MCT animals. PH was shown to improve the RVSP in animals with established MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension (Fig. 5E). There was an improvement in the RVH in the drugtreated animals compared with the 14- and 28-day time points (Fig. 5F). Attenuation of progression in the degree of muscularization of the vessels in the drug-treated animals compared with the day 28 untreated animals was identified, and there was a reduction of muscularization in the treated group compared with the day 14 untreated animals, as shown Fig. 5G. Furthermore when the percentage of muscularized vessels was calculated and expressed as percentage of the total number of vessels, this demonstrated that there was a significant reduction in the overall degree of muscularization compared with day 14 MCT (Fig. 5H). Again the systemic BP was unaltered (data not shown).
11 p38 MAPK Inhibition Reduced Hypoxia-Induced Release of IL-6 from Pulmonary Artery Fibroblasts Exposure of RPAF to hypoxia for up to 48 h led to upregulation of IL-6 and release of IL-6 from the cells. Secreted levels of IL-6 were significantly increased at 48 h of exposure. Treatment of cells with SB prevented the release of the IL-6 from hypoxia-exposed fibroblasts (Fig. 6, A and B). This was time dependent with peak mrna effect observed at 12 h after hypoxic exposure (Fig. 6C). This was reduced in the presence of p38 inhibition (data not shown). Further studies showed that pulmonary artery fibroblasts proliferate in response to IL-6, which was not significantly increased in the presence of the soluble IL-6R- subunit (testing transactivation of the IL-6 pathway) but was more pronounced under hypoxic conditions (Fig. 6D). In PASMCs, the addition of IL-6 also proved to be a strong mitogen (Fig. 6E) and incubation with anti-il-6 blocked the PASMC proliferation (Fig. 6F). In addition, the proliferation via IL-6 seemed to be mediated by the classical STAT-3 pathway with increased phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner as shown (Fig. 6, G and H). In vivo p38 MAPK Inhibition Reduces Production of Tissue and Circulating IL-6 and Reverses Proproliferative Phenotype of Fibroblast In the prevention study of the chronic hypoxic-associated pulmonary hypertension we found a reduction in IL-6 levels in the lungs of SB drug-treated animals compared with vehicle-treated hypoxic controls (Fig. 7A). Similarly, in the reversal study with SB203580, IL-6 levels were reduced in the lung and the amount of phospho-stat3 signaling was reduced (Fig. 7, B D). The same findings were observed in the MCT animals with reduced IL-6 levels in the SB drug-treated animals (Fig. 7E). In the reversal studies using PH , serum levels were examined and a significant reduction in serum IL-6 level was seen in the chronic hypoxic and MCT reversal study (Fig. 7, F and G). Other cells such as neutrophils can act as IL-6 reservoirs, and it is likely that the fibroblast is not the only source of IL-6. However, initial experiments have shown no increase in neutrophil activity in our models (data not shown). Of interest is that the fibroblasts isolated from the pulmonary artery of the experimental models following treatment with p38 inhibition, no longer demonstrated the proproliferative phenotype previously observed (Fig. 7H). This suggests that in the experimental pulmonary hypertension fibroblast blockage of the p38 MAPK pathway can restore normal phenotype to the cell in vivo. This may be one of the factors leading to the reversal of PVremod in the drug-treated animals. Increased Expression of phospho-p38 MAPK and p38 MAPK in Vessels from Human IPAH Patients Immunohistochemical staining of sections from the lungs of patients with IPAH who had undergone transplantation showed increased phospho-p38 MAPK expression compared with control lungs (Fig. 8A). This is shown in all layers of the vascular wall (Fig. 8B). There was increased staining for p38 MAPK, which was mainly in a nuclear distribution in the control vessels but involved both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining in the IPAH patients (Fig. 8, C and D). This was again demonstrated in all the layers of the vascular wall (Fig. 8E). With the use of an intensity scoring technique, there was higher expression demonstrated for p38 MAPK in the vessels of patients with IPAH compared with controls (Fig. 8F) (1). In the identified plexiform lesion, there was strong cellular staining for p38 MAPK in cells around the vascular channels in both cytosol and nucleus (Fig. 8G). DISCUSSION L343 This study advances our understanding of the potential role that p38 MAPK plays in the biology of pulmonary vascular remodeling. It demonstrates that p38 MAPK is implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension and administration of selective p38 MAPK inhibitors in vivo demonstrated that the pulmonary hypertensive phenotype cannot only be prevented, but reversed, with improvements in PVremod, acting through inhibition of key inflammatory mediators such as IL-6. Although p38 MAPK has been implicated previously in cytokine biosynthesis and to have a role in MCT-induced pulmonary hypertension, this study is the first to show that the -isoform is specifically implicated and inhibition can lower IL-6 levels and reverse disease. This suggests there may be a novel link between p38 MAPK signaling and inflammation in the development of pulmonary vascular remodeling. Fig. 6. p38 MAPK inhibition reduces interleukin (IL)-6 generation and signaling as a potential mechanism for beneficial effects in PH. A and B: supernatant from normoxic and hypoxic PAF SB was analyzed using a quantitative ELISA to determine actual amounts released. Cells were growth arrested in serum free media for 24 h before hypoxic exposure. The values are mean SE values from triplicate wells for each sample and experiment repeated 3 times using cells from 3 animals. *P 0.05 **P C: PAF were exposed to hypoxia and then RNA isolated after 48 h. The RNA was reverse transcribed into cdna and then analyzed using quantitative (q)rt-pcr. The mrna increased and peaked at 12 h of hypoxia. Values represent ratio of increase of IL-6 gene mrna relative to the housekeeping gene of -actin and calculated using comparative Ct method. Values are representative of triplicate samples from 3 experiments using 3 different animals. D: PAF were exposed to hypoxia in the presence of SB and then RNA isolated after 48 h. The RNA was reverse transcribed into cdna and then analyzed using qrt-pcr. The mrna increased and peaked at 12 h of hypoxia. Values represent ratio of increase of IL-6 gene mrna relative to the housekeeping gene of -actin and calculated using comparative Ct method. Values are representative of triplicate samples from 3 experiments using 3 different animals. **P 0.01; ***P 0.01, for C and D. E: PAF were isolated and incubated with IL-6 (100 ng/ml) soluble IL-6 receptor (sil-6) and then using DNA synthesis as a marker of cell proliferation, the response was observed. Data are mean values SE and are representative of duplicate experiments performed on cells from 3 different animals. *P 0.05; **P 0.005; ***P F: PASMCs were exposed to IL-6 (100 ng/ml) soluble IL-6 receptor (sil-r) and then using DNA synthesis as a marker of cell proliferation, the response was observed. Data are means and are representative of duplicate experiments performed on cells from 3 different animals. ****P G: PASMCs were growth arrested for 24 h and then incubated with serum free media, IL-6 or IL-6 and anti-il-6 antibody. Thymidine assay was used to quantify DNA synthesis, a measure of cell proliferation. Results are plotted as counts per million. Values are means SE and represent mean of 3 experiments on cells from same animal. A total of 3 different animals were used. **P H and I: PASMCs were stimulated with 100 ng/ml IL-6 ( ) or without ( ) and the protein harvested at baseline, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, and 4 h. The cell lysates were immunoblotted for phosphorylated STAT3 and total STAT3. Experiment was repeated 3 times; blots above are representative of those experiments. H shows densitometry from repeat blots. ***P 0.005; ****P 0.001, for I.
12 L344 The fibroblast is an important cell in the pathobiology of pulmonary vascular remodeling and dysregulation of the p38 MAPK pathway in the fibroblast can result in aberrant proliferation. We have previously shown, along with others, that the fibroblast undergoes a proproliferative phenotypic switch when exposed to chronic hypoxia and that p38 MAPK is critically involved. Here we have shown a similar proproliferative transformation with the fibroblasts isolated from MCT animals, again mediated through p38 MAPK. Conditioned media isolated from the hypoxic fibroblast can stimulate smooth muscle cell proliferation and using cytokine arrays, IL-6 was identified as a potential key mediator that was being released by the fibroblast under hypoxic conditions. IL-6 release was blocked by the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB in fibroblasts, implicating p38 MAPK in both proliferation and cytokine biosynthesis in this cell. Similar findings were obtained from conditioned media isolated from fibroblasts derived from experimental animal models of pulmonary hypertension. Therefore, our in vitro fibroblast studies showed that under acute hypoxic conditions there was increased IL-6 production and that IL-6 can, through a STAT-3 pathway, stimulate proliferation of the smooth muscle cell and fibroblast.
13 Increased activity of p38 MAPK in both chronic hypoxic and MCT lung homogenates is in concordance with a previous study showing increased activity of the entire MAPK signaling group in large pulmonary arteries of chronically hypoxic rats (5). However, that study did not specifically demonstrate whether p38 MAPK activity itself was increased or address -isoform expression. Here, we have shown evidence that p38 MAPK and the -isoform are upregulated in the pulmonary vessels of two different in vivo animal models of pulmonary hypertension and has been implicated as a proproliferative and proinflammatory pathway in the pulmonary artery fibroblast. Using the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB we showed that blocking p38 MAPK could prevent the development of pulmonary hypertension as previously described in a MCT study that looked at prevention of the disease only (8). Although prevention studies are critical in outlining early pathogenic mechanisms, studies with established disease are more clinically relevant. In this study after development of established pulmonary hypertension in both hypoxic and MCT models, daily administration of SB reversed the RVSP and RVH and also improved PVremod. The novel and specific p38 MAPK inhibitor PH has been shown to be extremely effective in animal models of rheumatoid arthritis with a 6.9-fold increase in specificity relative to the p38 MAPK -isoform compared with existing inhibitors (3). Furthermore, it has shown tolerability, safety, and efficacy in a clinical trial of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (9). This allowed us to use a drug that has the potential for future development in the treatment of patients with pulmonary hypertension. In addition the targeting of the more specific isoform differentiates the systemic and pulmonary circulation. The p38 MAPK pathway seems to be preferentially upregulated in the pulmonary circulation in pulmonary hypertension and hence provides a rationale for targeting of this pathway. There is support from a study looking at bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. This showed that inhibition of p38 MAPK can prevent the development of RVH, although this was a prevention study in an animal model not representative of true pulmonary arterial disease (18). Although no animal model fully recapitulates disease, the models employed in this study are established and recognized models of pulmonary arterial hypertension. L345 Our data with PH , performed in reversal in vivo studies, produced similar findings to SB with a reduction in the RVSP and RVH and significant attenuation of PVremod in the chronic hypoxic model. There was improvement in the RVSP in the drug-treated MCT group and a significant reversal and attenuation in progression of RVH. The reason that there was a greater observed reduction in the remodeling in the SB treated animals may reflect that the dose used for PH was not optimal for this compound or that the length of administration was not long enough. The dose and length of administration for SB in other animal models have been clearly identified. However, one of the novel aspects of this study is that using a clinically available, specific p38 MAPK inhibitor leads to reversal of pulmonary vascular remodeling in two well-established animal models of pulmonary hypertension. Cytokines and inflammatory responses have been recognized as a driver for PVremod and p38 MAPK has been implicated in inflammatory processes. IL-6 is a known mitogen for vascular smooth muscle cells, and previous transgenic murine studies have implicated IL-6 in the etiology of pulmonary hypertension (2, 10, 16). Moreover, a recent study has identified the upregulation and increased release of IL-6 from pulmonary artery fibroblasts derived from chronic hypoxic calves (7). In addition, serum levels of IL-6 correlate with the prognostic outcome in patients with IPAH (15). Our in vitro studies showed the fibroblast to be a source of IL-6, and in both prevention and reversal studies we found a reduction in the concentration of IL-6 in the lungs and serum of drug-treated animals. Although likely not to be the only source of IL-6, the data presented here suggest the fibroblast can be an important source of this proinflammatory cytokine in the pulmonary vasculature. Studies on human umbilical vascular endothelial cells and alveolar macrophages have also shown that p38 MAPK inhibition can reduce IL-6 release (6, 18). However, our study has shown that inhibition of p38 MAPK resulted in a reversal of the proproliferative phenotype in the fibroblast isolated from in vivo-treated animals, suggesting that in experimental models inhibition can alter the underlying pathological process in the pulmonary vasculature. This study has shown modest reductions in lung IL-6 and serum levels of IL-6. Although not conclusive in Fig. 7. p38 MAPK inhibition in vivo leads to reduced IL-6 in experimental models of PH. A: lungs were isolated from CH animals in the prevention study with SB and homogenized. The protein concentration was normalized by protein concentration as per BCA method. ELISA was used to analyze for IL-6 levels in the lung tissue. Data shown are means SE from triplicate samples from 4/5 animals in each group. B: lungs were isolated from normal and CH animals after treatment in reversal strategy with SB and homogenized. The protein concentration was normalized by protein concentration as per BCA method. ELISA was used to analyze for IL-6 levels in the lung tissue. Drug-treated and normal control animals are at 28 days. Data shown are means SE from triplicate samples from 4/5 animals in each group. *P 0.05 **P C and D: lungs from CH 28-day controls and SB treated hypoxic animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using BCA method. Equal concentrations were then loaded on a gel and blotted for phospho-stat3 and total STAT3. Immunoblot shown is best representative of 3 experiments using lungs from 3 different animals with each condition. Densitometry is shown of other blots. **P E: lungs were isolated from MCT and normal control animals and homogenized. Inhibitor used was SB The protein concentration was normalized by protein concentration as per BCA method. ELISA was used to analyze for IL-6 levels in the lung tissue. Data shown are means SE from triplicate samples from 4/5 animals in each group. *P 0.05; ns is not significant by ANOVA. F: PH reduces serum IL-6 in reversal of CH-induced PH. Serum was collected from animals at the time of cardiac puncture and stored at 80 C until analysis could be performed. ELISA for IL-6 was performed on serum samples. Values shown are means SE. Samples were analyzed in duplicate and total animal number n 11. ***P G: PH reduces serum IL-6 in reversal of MCT-induced PH. Serum was collected from animals at the time of cardiac puncture and stored at 80 C until analysis could be performed. ELISA for IL-6 was performed on serum samples. Values shown are means SE. Samples were analyzed in duplicate and total animal number n 12. *P 0.01; ***P H: fibroblasts undergo phenotypic switch back to normal after p38 MAPK inhibition. PAF were cultured from pulmonary arteries derived from normal, experimental models of PH (CH and MCT) and from animals after treatment with p38 MAPK inhibition PH for 2 wk. Cells were challenged with or without serum to assess proliferation; n 3 4 per group. Experiment repeated 3 times. **P 0.01, ***P
14 L346 Fig. 8. Phospho-p38 MAPK and p38 MAPK expression in explanted lungs from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH). A: sections of 5 mm were taken. Then, normal control lung and IPAH lung are stained for phospho-p38 MAPK at dilution of 1:300. The isotype on IPAH lung is also shown. This dilution was optimally assessed for. Objective: 20. Bar 150 mm. B: high-power microscopy shows that there is strong staining for phospho-p38 MAPK in the intima, media, and the adventitia (arrows). Objective lens: 20 and 40. Bar 50 mm. C: sections of control lung (A) and IPAH lung (B) were stained for p38 MAPK at dilution of 1:300. Objective lens 20. Bar 150 mm. D: staining for p38 MAPKa showed increased cytosolic staining in the IPAH lung (right) compared with control lung (left). E: high-power view ( 40) of staining with isotype and p38 MAPK in a vessel in IPAH lung. This shows staining throughout the vessel layers but especially in adventitia and fibroblast cells (arrow). Bar 50 mm. F: low-power view of a plexiform lesion. Staining for p38 MAPK using 1:300 dilution. Objective lens 20. Bar 150 mm. G: histological scoring shows increased p38 MAPK staining throughout the vascular wall. With the use of a well-validated histological scoring system (Allred), the vascular wall cells were scored for intensity of staining. The intensity multiplied by the number of vessels with that intensity determines the values. Values shown are from 5 random high-power fields from 2 slides. ****P by ANOVA. **P for individual IPAH vs. control columns. these studies, it does raise the interesting possibility that p38 MAPK inhibition reduces local and serum IL-6 levels and that this may underplay a key role in the reversal of pathological remodeling. Of major interest was our finding of increased activity of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and expression of p38 MAPK in the vessels of explanted lungs from patients with IPAH. To our knowledge this is the first time this has been shown in pulmonary arterial hypertension. This was seen in both large and small vessels with increased nuclear and cytosolic distribution, involving endothelial, smooth muscle, and fibroblast cells, including the plexiform lesion, which is pathognomonic of pulmonary vasculopathy. The findings of p38 activation in all layers of the vasculature would suggest that it is unlikely that inhibition of p38 MAPK in the fibroblast alone is producing reversal of the experimental pulmonary hypertension. Indeed our previous work demonstrated that the endothelium in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension is associated with impaired relaxation and reduced nitric oxide production, which could be reversed by inhibition of p38 MAPK (19). However, our data clearly suggest that p38 MAPK is an important pathway throughout the pulmonary vasculature but that the activation of this pathway is critical in the fibroblast, a key cell in the process of PVremod. In summary, the findings presented here suggest a critical role for p38 MAPK and the -isoform in the development and progression of pulmonary hypertension. The fact that increased p38 MAPK activity and expression are observed in both hypoxia and MCT animal models and in human disease suggests a common role in the etiology of many forms of pulmonary hypertension. Furthermore, p38 MAPK signaling through IL-6 provides a novel link between vascular remodeling and inflammation. This provides us with the exciting prospect of a new anti-inflammatory target for the treatment of pulmonary
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Research article. Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Medical College of Georgia, Georgia Health Sciences University, Augusta, Georgia, USA.
 Research article Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension, and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease Wanli Ma, 1 Weihong Han, 1 Peter
Research article Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension, and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease Wanli Ma, 1 Weihong Han, 1 Peter
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
10.00 PBS OVA OVA+isotype antibody 8.00 OVA+anti-HMGB1. PBS Methatroline (mg/ml)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension
 Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent
 Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects.
 Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chen et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807991106 SI Methods Sucrose Gradient Fractionation. Fractionation by sucrose gradient was performed as described by Gasparini et al. [(2001) J Neurosci
Supporting Information Chen et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807991106 SI Methods Sucrose Gradient Fractionation. Fractionation by sucrose gradient was performed as described by Gasparini et al. [(2001) J Neurosci
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit
 Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # P-4059 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone H3K27 Quantification Kit (Colorimetric)
Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats
 Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Comparative Biosciences, Inc. 786 Lucerne Drive Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Telephone: 408.738.9260 www.compbio.com Comparative
Comparative Biosciences Model of Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats Comparative Biosciences, Inc. 786 Lucerne Drive Sunnyvale, CA 94085 Telephone: 408.738.9260 www.compbio.com Comparative
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Potential Role for the Bone Morphogenetic Antagonist Gremlin in Pulmonary Hypertension
 Potential Role for the Bone Morphogenetic Antagonist Gremlin in Pulmonary Hypertension Dr Sean Gaine National Pulmonary Hypertension Unit Mater Misericordiae University Hospital University College Dublin
Potential Role for the Bone Morphogenetic Antagonist Gremlin in Pulmonary Hypertension Dr Sean Gaine National Pulmonary Hypertension Unit Mater Misericordiae University Hospital University College Dublin
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma. patients. Supplemental data. First author: Baojun Wang
 Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Alpha-Tubulin Housekeeping 10,000 tests
 Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
20X Buffer (Tube1) 96-well microplate (12 strips) 1
 PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
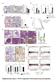 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Cell Lysis Buffer. Catalog number: AR0103
 Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Data Sheet. NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621
 Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
ab Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions.
 ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
2. Langendorff Heart
 2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
2. Langendorff Heart 2.1. Principle Langendorff heart is one type of isolated perfused heart which is widely used for biochemical, physiological, morphological and pharmacological researches. It provides
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Reason for Dissection. Pleomorphic adenoma. Tongue base adenocarcinoma
 Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
Supplementary Table S1 Human Patients Patient Sample No. Gender Age Additional Medication Treatment 1 Reason for Dissection Total Irradiation Dose Estimated Irradiation Dose to SG Gland Time of Resection
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in H5N1 viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors
 Title Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in HN viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors Author(s) Lee, MY; Cheung, CY; Peiris, JSM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2, v. 9 n. Suppl. 4, p. 29-
Title Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in HN viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors Author(s) Lee, MY; Cheung, CY; Peiris, JSM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2, v. 9 n. Suppl. 4, p. 29-
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test
 FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Assay Kit for Measurement of Proteoglycan. (Sulfated Glycosaminoglycan Quantification Kit)
 Assay Kit for Measurement of Proteoglycan. (Sulfated Glycosaminoglycan Quantification Kit) Cat. No. 280560-N INTRODUCTION Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are a major component of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
Assay Kit for Measurement of Proteoglycan. (Sulfated Glycosaminoglycan Quantification Kit) Cat. No. 280560-N INTRODUCTION Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are a major component of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU. PhD THESIS Summary
 ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways
![Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic Agent that May Act through IRS-1, Akt and GSK-3β Pathways](/thumbs/96/128474991.jpg) Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for MedChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Data Synthesis of Substituted 2H-Benzo[e]indazole-9-carboxylate as Potent Antihyperglycemic
Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes
 Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes Manual Version 2.1 / March 2018 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Equipment, Materials and Reagents 3 3. Methods 4 3.1 Coating of tissue culture plates 4 3.2 Thawing Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes
Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes Manual Version 2.1 / March 2018 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Equipment, Materials and Reagents 3 3. Methods 4 3.1 Coating of tissue culture plates 4 3.2 Thawing Pluricyte Cardiomyocytes
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna targets were found in exosomes and absent in free-floating supernatant. Serum exosomes and exosome-free supernatant were separated via ultracentrifugation and lysed to analyze
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences
 Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences Walter Royal, III, MD Professor of Neurology University of Maryland School of Medicine
Cigarette Smoke Exposure and HIV-Related Neurologic Disease Progression Basic Mechanisms and Clinical Consequences Walter Royal, III, MD Professor of Neurology University of Maryland School of Medicine
