Supplemental Figure Legends
|
|
|
- Mervin Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Transcriptional changes are dependent upon Fpn and occur in peritoneal macrophages. A. Mouse bone marrow macrophages were transfected with either WT Fpn-GFP or Fpn(D157G)-GFP. Eighteen h later cells were solubilized, RNA extracted and SOCS3, IL-7 and IL-17R mrna levels were analyzed relative to actin mrna by RT-PCR. B.
2 Thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages from C3H mice were isolated, cultured and incubated in presence or absence of FAC (10 µm Fe) with or without hepcidin (1 µg/ml). Six h later cells were solubilized, RNA extracted and Fpn, SOCS3, IL-7 and IL-17R mrna levels were analyzed by RT-PCR. Supplemental Figure 2. LPS does not induce hepcidin in iron-loaded macrophages. A. Mouse bone marrow macrophages were incubated +/- FAC (10 µm Fe) for 24 h and then incubated for two h +/-LPS (10 ng/ml). Cells were solubilized, RNA extracted and hepcidin and IL-6 mrna were analyzed relative to actin mrna by RT-PCR. B. Mouse bone marrow macrophages incubated as in A were fixed and CHIP performed with either no antibody or with anti-stat3 antibody as described in the methods. The data was quantified by densitometry and normalized to actin. Supplemental Figure 3. Fpn is down-regulated in the duodenum of mice injected with hepcidin. Protein extraction from duodenum of mice injected with or without hepcidin was performed. Fpn levels were analyzed by Western blots using rabbit anti-fpn followed by a peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG. Actin was analyzed as a loading control using goat anti-actin followed by a peroxidase-conjugated donkey anti-goat IgG. Fpn levels were quantified by Bio-Rad QuantOne software. Supplemental Figure 4. Effect of hepcidin injection on rectal temperature and activity of LPS treated mice. A. C57BL/6 mice (five for each group) were treated with or without an intraperitoneal injection of hepcidin (100 µg/mouse). Two h later, mice were injected with PBS or LPS (1 mg/kg) and four h later rectal temperature was measured. B. Mice as in (A) were placed on a Rota-rod that accelerates gradually. The time for the mice to fall from the rod was recorded automatically by digital display (maximum time 300 seconds). Each mouse was given three trials with 15-min intervals between trials. 29
3 Supplemental Figure 5. Effect of a high iron diet on LPS-mediated changes in rectal temperature and activity in wild type and HAMP -/- mice. A. C57BL/6 and HAMP -/- mice were maintained on a normal (350 mg iron/kg mouse chow) or high iron (2 g iron/kg mouse chow) diet. After 48 h mice were sacrificed and sera collected. Hepcidin levels in sera were measured using a radioactive competition assay as described 20. B. C57BL/6 and HAMP -/- mice maintained on a high iron diet (2 g/kg) for 48 h were treated with an intraperitoneal injection of PBS or LPS as in Supplemental figure 3. Rectal temperature was measured four h later. C. Mice as in (B) were placed on top of a Rota-rod that accelerates gradually. The time for the mice to fall from the rod was recorded automatically by digital display (maximum time 300 seconds). Each mouse was given three trials with a 15-min interval between trials. Supplemental Figure 6. HFE -/- mice show LPS-mediated cytokine responses and hepcidin-mediated transcriptional response. A. Age and gender matched C57BL/6 and HFE -/- mice (five for each group) were intraperitonally injected with a sublethal (1 mg/kg) dose of LPS. After four h mice were sacrificed and mrna was extracted from liver. mrna levels for IL-6 and hepcidin were measured relative to actin mrna using RT-PCR. B. Mouse bone marrow macrophages isolated from WT and HFE -/- mice were incubated with FAC (10 µm Fe) for 24 h and then incubated in presence of hepcidin (1 µg/ml). After two h cells were solubilized, RNA extracted and SOCS3, IL-7 and IL-17R mrna levels measured relative to actin mrna using RT-PCR. Supplemental Movie 1 Mice treated as described in Figure 3 were placed in a cage and videotaped for 90 sec. Mice pretreated with hepcidin were marked with an orange tag on the tail. Mice treated with LPS only were marked with a green tag on the tail. 30
4 Supplemental Table 1 Effect of hepcidin on LPS-induced cytokine secretion in macrophages. IL-6 (ng/ml media) TNFα (ng/ml media) -LPS -Hepcidin 1.4± ±1.1 +LPS -Hepcidin 91.2± ±3.14 -LPS +Hepcidin 1.3± ±0.87 +LPS +Hepcidin 21.0± ±4.02 Mouse bone marrow macrophages were incubated with FAC (10 µm Fe) for 24 h and then incubated for two h in the absence or presence of hepcidin (1 µg/ml). After two h -/+ hepcidin LPS was added for an additional four h. Media were collected and levels of IL-6 and TNFα were determined by ELISA. 31
5 Supplemental Table 2 Effect of hepcidin on LPS-induced cytokine secretion in vivo. IL-6 (ng/ml serum) TNFα (ng/ml serum) -LPS -Hepcidin 81± ±2.25 +LPS -Hepcidin 964± ±3.69 -LPS +Hepcidin 79± ±1.24 +LPS +Hepcidin 369± ±4.17 Age and gender matched C57BL/6 mice (five for each group) were treated with an intraperitoneal injection of PBS or hepcidin (100 µg/mouse). After two h a sublethal dose of LPS (1 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally. Sera from these mice were isolated four h post LPS injection and IL-6 (pg/ml serum) and TNFα (pg/ml serum) levels were measured. 32
6 Supplemental Table 3 Effect of a high iron diet on LPS-injected wild type mice. IL-6 (ng/ml serum) TNFα (ng/ml serum) -LPS -Hepcidin 88± ±2.58 +LPS -Hepcidin 869± ±4.12 -LPS +Hepcidin 78± ±3.69 +LPS +Hepcidin 401± ±1.54 Six C57BL/6 mice maintained on a high iron diet for two days were given an intraperitoneal injection of PBS or LPS (1 mg/kg). After four h mice were sacrificed, sera isolated and IL-6 (pg/ml serum) and TNFα (pg/ml serum) levels were measured. 33
7 Supplemental Table 4 Effect of a high iron diet on LPS-injected HAMP -/- mice. IL-6 (ng/ml serum) TNFα (ng/ml serum) -LPS -Hepcidin 132± ±1.34 +LPS -Hepcidin 1782± ±2.46 -LPS +Hepcidin 132±2.1 91±6.70 +LPS +Hepcidin 1841± ±2.48 Six HAMP -/- mice maintained on a high iron diet for two days were given an intraperitoneal injection of PBS or LPS (1 mg/kg). After four h mice were sacrificed, sera isolated and IL-6 (pg/ml serum) and TNFα (pg/ml serum) levels were measured. 34
8 Supplemental Table 5 Primer List Target Forward Reverse Hepcidin agagctgcagcctttgcac gaagatgcagatggggaagt Jak2 tctgtgggagatctgcagtg cacggatgacagctctgaaa Stat3 gacccgccaacaaattaaga tcgtggtaaactggacacca IL-7 gtatttgaccgatgcctgct ctgttttctgggcaaatggt IL-17R tgcctgtggcactgaagtag ttcatggctgcagtgaaaag TNFα agcccccagtctgtatcctt ctccctttgcagaactcagg SOCS3 cctttgacaagcggactctc gccagcataaaaacccttca Actin gacggccaagtcatcatcactattg ccacaggattccatacccaaga 35
9 Supplemental Table 6 Microarray (+Hepcidin 2 hr) Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 4.77 Up BC Mus musculus, Similar to chemokine (C-X3-C) receptor 1, clone MGC:13785 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus small inducible cytokine subfamily, member 2 (Scyb2), 3.08 Up D87747 Mus musculus mrna for murine CXCR-4, complete cds Down BG ectodermal-neural cortex Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte) (Csf3), 2.77 Up AI Mus musculus interleukin 7 receptor (Il7r), 2.71 Up AI interleukin 7 receptor /FL=gb:NM_ gb:m gb:af Up BC Mus musculus chemokine (C-X3-C) receptor 1 (Cx3cr1), 2.69 Down NM_ Mus musculus interleukin 6 (Il6), 2.44 Down NM_ Mus musculus GRO1 oncogene (Gro1), 2.26 Down BB ESTs 2.22 Up NM_ Mus musculus FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (Flt1), 2.16 Down U50712 Mus musculus monocyte chemoattractant protein-5 precursor (MCP-5) mrna, complete cds. Mus musculus CXC chemokine MIP-2gamma precursor, mrna, 2.14 Up AF complete cds. Mus musculus, Similar to interleukin 1 beta, clone MGC:18555 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down BC Down AV expressed sequence AW Mouse mrna for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) Down X Down NM_ Mus musculus lymphotoxin B (Ltb), 1.84 Down BB ESTs 1.8 Down NM_ Mus musculus small inducible cytokine A5 (Scya5), transforming growth factor, beta receptor I /FL=gb:D Up BM gb:nm_ gb:d Down AV bone morphogenetic protein 2 /FL=gb:NM_ Up BG tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 21 /FL=gb:AF gb:ay gb:nm_ gb:bc Down NM_ Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor (Tnf), 1.62 Down AF Mus musculus strain B10.SJ small inducible cytokine A4 (ScyA4) mrna, complete cds Up BC Mus musculus platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide (Pdgfb), 1.58 Up AK Mus musculus adult male tongue cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: c03:interleukin 17 receptor, full insert sequence Up BG Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 21 (Tnfrsf21), 1.56 Up AK Mus musculus interleukin 17 receptor (Il17r), 1.55 Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) (Csf3r), Mus musculus, chemokine (C-C) receptor 1, clone MGC: Up AV IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Up BB kit ligand /FL=gb:U gb:nm_ gb:bc
10 1.51 Up BC gb:m Mus musculus, Similar to platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide, clone IMAGE: , mrna, partial cds. Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) 3.98 Down M36005 Mus musculus selectin, lymphocyte (Sell), 3.17 Down M36005 Mouse lymph node homing receptor mrna, complete cds Up NM_ Mus musculus cadherin 1 (Cdh1), 2.04 Up BB ESTs 1.97 Up NM_ Mus musculus expressed sequence AU (AU016588), 1.89 Up NM_ Mus musculus CD2 antigen (Cd2), 1.78 Up NM_ immunoglobulin superfamily, member 4 /FL=gb:NM_ gb:af gb:ab gb:ab gb:ab gb:af Up NM_ immunoglobulin superfamily, member 4 /FL=gb:NM_ gb:af gb:ab gb:ab gb:ab gb:af Up BG ESTs 1.73 Up NM_ Mus musculus immunoglobulin superfamily, member 4 (Igsf4), 1.73 Down BQ expressed sequence AI Down BB Mus musculus integrin alpha8 mrna, partial cds 1.67 Up AK Mus musculus adult male hippocampus cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: g06:immunoglobulin superfamily, member 4, full insert sequence Down NM_ Mus musculus sialophorin (Spn), 1.62 Up NM_ Mus musculus histocompatibility 2, class II, locus DMa (H2-DMa), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, M (Ptprm), 1.61 Up NM_ Mus musculus histocompatibility 2, class II, locus Mb2 (H2-DMb2), 1.58 Down NM_ Mus musculus, CD86 antigen, clone MGC:18471 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down NM_ RIKEN cdna H11 gene /FL=gb:NM_ Up AU Mus musculus syndecan 2 (Sdc2), 1.55 Up AF Mus musculus claudin-18a2.2 mrna, complete cds, alternatively spliced Up NM_ Mus musculus contactin 1 (Cntn1), 1.51 Down BM chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 2 MAPK signaling pathway 3.04 Down BG ectodermal-neural cortex Down BE expressed sequence AI Up AV RIKEN cdna D10 gene 2.12 Down BC Mus musculus, Similar to interleukin 1 beta, clone MGC:18555 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Up NM_ Mus musculus phospholipase A2, group IIE (Pla2g2e),
11 1.83 Up BQ ESTs 1.82 Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Up NM_ Mus musculus related RAS viral (r-ras) oncogene homolog 2 (Rras2), 1.78 Down NM_ Mus musculus protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 16 (Ptpn16), 1.75 Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_ Up BM transforming growth factor, beta receptor I /FL=gb:D gb:nm_ gb:d Up AK Mus musculus 11 days embryo whole body cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: f24:unclassifiable transcript, full insert sequence Down NM_ Mus musculus fibroblast growth factor 21 (Fgf21), 1.66 Down BB DNA segment, Chr 6, ERATO Doi 213, expressed 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor (Tnf), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.58 Up BC Mus musculus platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide (Pdgfb), 1.56 Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.52 Up BB expressed sequence AW Down AK Mus musculus adult male thymus cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: m24:unclassifiable transcript, full insert sequence Up BB expressed sequence AI Up BC Mus musculus, Similar to platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide, clone IMAGE: , mrna, partial cds. 1.5 Up AV RIKEN cdna D10 gene Focal adhesion 4.3 Up AB Mus musculus mrna for caveolin-1 alfa isoform, complete cds Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.83 Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.72 Up BB integrin beta Down AK Mus musculus 10 day old male pancreas cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: d21:cyclin D2, full insert sequence Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Up NM_ Mus musculus FMS-like tyrosine kinase 1 (Flt1), 2.18 Down BE expressed sequence AI Down NM_ Mus musculus cyclin D2 (Ccnd2), 2.02 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Up BI catenin beta 1.94 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down BQ EST AA Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_ Down BQ expressed sequence AI Up BB expressed sequence AI Up NM_ Mus musculus catenin beta (Catnb), 1.69 Down BB Mus musculus integrin alpha8 mrna, partial cds 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2),
12 1.58 Up BC Mus musculus platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide (Pdgfb), 1.57 Down NM_ RIKEN cdna H11 gene /FL=gb:NM_ Up BI expressed sequence AI Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.55 Up AI expressed sequence AI Down AI thrombospondin 1 /FL=gb:M gb:nm_ Down BF Mus musculus telokin mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF Up BC Mus musculus, Similar to platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide, clone IMAGE: , mrna, partial cds. Regulation of actin cytoskeleton 3.05 Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.83 Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.72 Up BB integrin beta Up AW expressed sequence AI Up NM_ Mus musculus profilin 2 (Pfn2), 2.18 Down BE expressed sequence AI Down BC Mus musculus, Similar to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type 1 beta, clone MGC:5928 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Up NM_ Mus musculus related RAS viral (r-ras) oncogene homolog 2 (Rras2), 1.73 Down BQ expressed sequence AI Down BB Mus musculus integrin alpha8 mrna, partial cds 1.68 Down NM_ Mus musculus fibroblast growth factor 21 (Fgf21), 1.67 Down BB phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, type 1 beta 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.59 Down BQ RIKEN cdna C04 gene 1.59 Up NM_ Mus musculus profilin 2 (Pfn2), 1.58 Up BC Mus musculus platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide (Pdgfb), 1.57 Down NM_ RIKEN cdna H11 gene /FL=gb:NM_ Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.52 Up BB ESTs 1.51 Down BF Mus musculus telokin mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF Up BC Mus musculus, Similar to platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide, clone IMAGE: , mrna, partial cds. Hematopoietic cell lineage 3.56 Up NM_ Mus musculus CD24a antigen (Cd24a), 2.94 Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte) (Csf3), 2.85 Up NM_ CD24a antigen /FL=gb:NM_ gb:m Up AI Mus musculus interleukin 7 receptor (Il7r), 2.71 Up AI interleukin 7 receptor /FL=gb:NM_ gb:m gb:af Down NM_ Mus musculus interleukin 6 (Il6),
13 2.12 Down BC Mus musculus, Similar to interleukin 1 beta, clone MGC:18555 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down BE ESTs 2.03 Down NM_ Mus musculus CD38 antigen (Cd38), 1.99 Down X03019 Mouse mrna for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) Up NM_ Mus musculus CD2 antigen (Cd2), 1.7 Down NM_ Mus musculus decay accelerating factor 1 (Daf1), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor (Tnf), 1.55 Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) (Csf3r), 1.54 Up BB kit ligand /FL=gb:U gb:nm_ gb:bc gb:m Down NM_ decay accelerating factor 1 /FL=gb:NM_ gb:l gb:bc gb:d Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction 7.36 Up NM_ Mus musculus 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2B (Htr2b), 1.95 Down BF expressed sequence AU Down D43775 Mouse mrna for endothelin-1, complete cds Up AW ESTs 1.71 Down AF Mus musculus calcitonin receptor-like receptor mrna, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus complement component 5, receptor 1 (C5r1), 1.68 Up AW ESTs 1.63 Down NM_ Mus musculus formyl peptide receptor, related sequence 2 (Fpr-rs2), 1.59 Down BB ESTs ESTs, Highly similar to BETA-2 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR 1.54 Down AV Up BB Down AV ESTs 1.5 Up AK Calcium signaling pathway (M.musculus) endothelial differentiation sphingolipid G-protein-coupled receptor 1 /FL=gb:NM_ Mus musculus 18 days embryo whole body cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: a16:unclassifiable transcript, full insert sequence Up NM_ Mus musculus 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 2B (Htr2b), 2.03 Down NM_ Mus musculus CD38 antigen (Cd38), 1.95 Down BF expressed sequence AU Up BB Mus musculus strain ILS phospholipase C beta 4 (Plcb4) mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF gb:af Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Up AW ESTs 1.75 Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_
14 1.68 Up AW ESTs 1.57 Up BB expressed sequence AI Down NM_ Mus musculus, ATPase, Ca++ transporting, ubiquitous, clone MGC:28920 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down AV ESTs, Highly similar to BETA-2 ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR (M.musculus) 1.51 Down BF Mus musculus telokin mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF Complement and coagulation cascades 3.2 Down NM_ coagulation factor V /FL=gb:NM_ gb:u Up NM_ Mus musculus serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1), member 1 (Serpine1), 2.43 Down K02782 Mouse complement component C3 mrna, alpha and beta subunits, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus coagulation factor V (F5), 2.11 Down BE ESTs 1.72 Up BB expressed sequence AI Down NM_ Mus musculus decay accelerating factor 1 (Daf1), 1.69 Down NM_ Mus musculus complement component 5, receptor 1 (C5r1), 1.64 Up NM_ Mus musculus complement component 1, q subcomponent, alpha polypeptide (C1qa), 1.6 Up NM_ Mus musculus thrombomodulin (Thbd), 1.6 Up AK Mus musculus adult male testis cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: e17:zinc carboxypeptidase containing protein, full insert sequence Down BB ESTs 1.58 Up NM_ Mus musculus complement component 1, q subcomponent, c polypeptide (C1qc), 1.51 Down NM_ decay accelerating factor 1 /FL=gb:NM_ gb:l gb:bc gb:d Jak-STAT signaling pathway 2.94 Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 (granulocyte) (Csf3), 2.77 Up AI Mus musculus interleukin 7 receptor (Il7r), 2.71 Up AI interleukin 7 receptor /FL=gb:NM_ gb:m gb:af Down NM_ Mus musculus interleukin 6 (Il6), 2.48 Down NM_ Mus musculus signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 (Stat4), 2.32 Down AK Mus musculus 10 day old male pancreas cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: d21:cyclin D2, full insert sequence Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down NM_ Mus musculus cyclin D2 (Ccnd2), 2.02 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down AV expressed sequence AW Mouse mrna for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor 1.99 Down X03019 (GM-CSF).
15 1.94 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down BQ EST AA Up NM_ Mus musculus cytokine inducible SH2-containing protein 3 (Cish3), 1.56 Up NM_ Mus musculus cytokine inducible SH2-containing protein 2 (Cish2), 1.55 Down NM_ Mus musculus colony stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) (Csf3r), Melanogenesis 2.47 Down NM_ Mus musculus wingless-related MMTV integration site 6 (Wnt6), 2.11 Down AV ESTs 1.95 Down BF expressed sequence AU Up BB Mus musculus strain ILS phospholipase C beta 4 (Plcb4) mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF gb:af Up BI catenin beta 1.83 Down D43775 Mouse mrna for endothelin-1, complete cds Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_ Up NM_ Mus musculus catenin beta (Catnb), 1.61 Up BB transcription factor Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.54 Up BB kit ligand /FL=gb:U gb:nm_ gb:bc gb:m Up BB transcription factor 4 Adherens junction 2.88 Up NM_ Mus musculus cadherin 1 (Cdh1), 2.18 Down BE expressed sequence AI Up BI catenin beta 1.74 Up BM transforming growth factor, beta receptor I /FL=gb:D gb:nm_ gb:d Up NM_ Mus musculus catenin beta (Catnb), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor-type, M (Ptprm), 1.61 Up BB transcription factor Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.55 Up AI expressed sequence AI Up BB transcription factor 4 Axon guidance Ratio Direction
16 3.17 Down AV ESTs 3.08 Up D87747 Mus musculus mrna for murine CXCR-4, complete cds Down Z93948 M.musculus mrna for semaphorin Hv (3988 bp) Down BE expressed sequence AI Down BE ESTs, Weakly similar to TRANSFORMING PROTEIN RHOB (M.musculus) 2.04 Down NM_ Mus musculus sema domain, immunoglobulin domain (Ig), short basic domain, secreted, (semaphorin) 3E (Sema3e), 1.68 Down BB ESTs 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.56 Down BQ expressed sequence AI Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.54 Down AI ESTs PPAR signaling pathway 2.8 Up NM_ Mus musculus fatty acid binding protein 3, muscle and heart (Fabp3), 2.5 Up NM_ Mus musculus oxidized low density lipoprotein (lectin-like) receptor 1 (Olr1), 2.45 Down AK Mus musculus 6 days neonate head cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: h20:lipoprotein lipase, full insert sequence Down BC Mus musculus lipoprotein lipase (Lpl), 2.09 Up NM_ Mus musculus fatty acid binding protein 7, brain (Fabp7), 1.78 Down BF glycerol kinase /FL=gb:U gb:nm_ gb:bc Down BF Mus musculus glycerol kinase (Gyk), 1.62 Down AI protective protein for beta-galactosidase 1.6 Up AK Mus musculus adult male testis cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: h15:malic enzyme, supernatant, full insert sequence. 1.6 Down NM_ Mus musculus RIKEN cdna A03 gene ( A03Rik), 1.52 Up BC Mus musculus malic enzyme, supernatant (Mod1), 1.52 Down BQ ESTs Purine metabolism 1.81 Up NM_ Mus musculus adenylosuccinate synthetase 1, muscle (Adss1), 1.74 Down AF Mus musculus fragile histidine triad protein (Fhit) mrna, complete cds Up AF Mus musculus ectonucleotide pyrophosphatasephosphodiesterase 1 allotype b (Enpp1) mrna, Enpp1-b allele, complete cds Down BM phosphodiesterase 4B, camp specific /FL=gb:NM_ gb:af gb:af gb:af Up NM_ Mus musculus adenylate kinase 1 (Ak1), 1.59 Down BG ESTs 1.58 Up AW RIKEN cdna E15 gene 1.56 Up NM_ Mus musculus adenylate kinase 4 (Ak4), RNA polymerase 1-4 (194 kda subunit) /FL=gb:NM_ Down BB gb:af
17 1.51 Up NM_ Mus musculus adenylate kinase 4 (Ak4), 1.5 Down NM_ Mus musculus guanine deaminase (Gda), TGF-beta signaling pathway 1.98 Up AF Mus musculus Smad6 mrna, complete cds Up BM transforming growth factor, beta receptor I /FL=gb:D gb:nm_ gb:d Down AV bone morphogenetic protein 2 /FL=gb:NM_ Up U43884 Mus musculus transcription factor Id1B (Id1B) mrna, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor (Tnf), 1.56 Down NM_ Mus musculus mitogen activated protein kinase 1 (Mapk1), 1.54 Up NM_ Mus musculus inhibitor of DNA binding 3 (Idb3), 1.53 Down AI thrombospondin 1 /FL=gb:M gb:nm_ Wnt signaling pathway 2.47 Down NM_ Mus musculus wingless-related MMTV integration site 6 (Wnt6), 2.32 Down AK Mus musculus 10 day old male pancreas cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: d21:cyclin D2, full insert sequence Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down BE expressed sequence AI Down AV ESTs 2.11 Down NM_ Mus musculus cyclin D2 (Ccnd2), 2.02 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Up BB Mus musculus strain ILS phospholipase C beta 4 (Plcb4) mrna, complete cds /FL=gb:AF gb:af Up BI catenin beta 1.94 Down NM_ cyclin D2 /FL=gb:M gb:m gb:nm_ Down BQ EST AA Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_ Up NM_ Mus musculus catenin beta (Catnb), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.61 Up BB transcription factor Down U34245 Mus musculus fos-related antigen-1 (Fra-1) mrna, complete cds Up BB transcription factor 4 Arachidonic acid metabolism 3.59 Down M94967 Mouse glucocortoid-regulated inflammatory prostaglandin GH synthase (gripghs) mrna, complete cds Up NM_ Mus musculus RIKEN cdna N16 gene ( N16Rik), 2.09 Up NM_ Mus musculus phospholipase A2, group IIE (Pla2g2e),
18 1.71 Up BC Mus musculus, Similar to carbonyl reductase 2, clone MGC:18465 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus prostaglandin E synthase (Ptges), 1.62 Down BB ESTs 1.57 Up NM_ Mus musculus thromboxane A synthase 1, platelet (Tbxas1), 1.55 Up NM_ Mus musculus cytochrome P450, 2b10, phenobarbitol inducible, type b (Cyp2b10), 1.54 Down NM_ Mus musculus, prostaglandin E synthase, clone MGC:35838 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds. ECM-receptor interaction 3.05 Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.83 Up NM_ Mus musculus integrin beta 5 (Itgb5), 2.72 Up BB integrin beta Down BQ expressed sequence AI Up BB expressed sequence AI Down BB Mus musculus integrin alpha8 mrna, partial cds 1.57 Down NM_ RIKEN cdna H11 gene /FL=gb:NM_ Up AU Mus musculus syndecan 2 (Sdc2), 1.53 Down AI thrombospondin 1 /FL=gb:M gb:nm_ Up AK Mus musculus 12 days embryo male wolffian duct includes surrounding region cdna, RIKEN full-length enriched library, clone: f14:hyaluronan mediated motility receptor (RHAMM), full insert sequence Up AF Mus musculus hyaluronan receptor RHAMMV5 mrna, complete cds. Leukocyte transendothelian migration 7.29 Down NM_ Mouse mrna for gelatinase, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus matrix metalloproteinase 9 (Mmp9), 3.08 Up D87747 Mus musculus mrna for murine CXCR-4, complete cds Down BE expressed sequence AI Up AF Mus musculus CXC chemokine MIP-2gamma precursor, mrna, complete cds Up BI catenin beta 1.82 Down X59274 M.musculus mrna brain protein kinase C beta-i Down BF protein kinase C, beta /FL=gb:NM_ Up NM_ Mus musculus catenin beta (Catnb), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus RAS-related C3 botulinum substrate 2 (Rac2), 1.55 Up AF Mus musculus claudin-18a2.2 mrna, complete cds, alternatively spliced. Toll-like receptor interaction 2.69 Down NM_ Mus musculus interleukin 6 (Il6),
19 2.12 Down BC Mus musculus, Similar to interleukin 1 beta, clone MGC:18555 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds. 1.8 Down NM_ Mus musculus small inducible cytokine A5 (Scya5), 1.62 Down NM_ Mus musculus tumor necrosis factor (Tnf), 1.62 Down AF Mus musculus strain B10.SJ small inducible cytokine A4 (ScyA4) mrna, complete cds Down NM_ Mus musculus, CD86 antigen, clone MGC:18471 IMAGE: , mrna, complete cds Up BB expressed sequence AW Up BB expressed sequence AI848108
20
21
22
23
24
25
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
201291_s_at Consensus includes gb:au /FEA=EST /DB_XREF=gi: /DB_XREF=est:AU /CLONE=Y79AA /UG=Hs topoisomerase (DNA)
 201291_s_at Consensus includes gb:au159942 /FEA=EST /DB_XREF=gi:11021463 /DB_XREF=est:AU159942 /CLONE=Y79AA1000724 /UG=Hs.156346 topoisomerase (DNA) II alpha (170kD) /FL=gb:J04088.1 gb:nm_001067.1 201664_at
201291_s_at Consensus includes gb:au159942 /FEA=EST /DB_XREF=gi:11021463 /DB_XREF=est:AU159942 /CLONE=Y79AA1000724 /UG=Hs.156346 topoisomerase (DNA) II alpha (170kD) /FL=gb:J04088.1 gb:nm_001067.1 201664_at
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
 Supplementary Table 1. Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia Pathway Enrichment Score (-log10[p value]) p-value genes Glycosaminoglycan degradation
Supplementary Table 1. Pathways of changes in hypermethylation in F1 offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia Pathway Enrichment Score (-log10[p value]) p-value genes Glycosaminoglycan degradation
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection.
 Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
AVAILABLE BIOMARKER ASSAYS
 AAILABLE BIOMARKER ASSAYS alidation Alpha-2-microglobulin ELISA Anti-CD71/anti-platelet/propidium iodide Anti-KLH IgG ELISA,, Dog, Minipig, Apoptotic, necrotic and dead cells (bone marrow) B (activated
AAILABLE BIOMARKER ASSAYS alidation Alpha-2-microglobulin ELISA Anti-CD71/anti-platelet/propidium iodide Anti-KLH IgG ELISA,, Dog, Minipig, Apoptotic, necrotic and dead cells (bone marrow) B (activated
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
ground and enzymatically digested or mechanically homogenized. The EVs or total vesicles were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of EVs from intestine. (a, b) Intestinal tissues were ground and enzymatically digested or mechanically homogenized. The EVs or total vesicles were isolated by
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of EVs from intestine. (a, b) Intestinal tissues were ground and enzymatically digested or mechanically homogenized. The EVs or total vesicles were isolated by
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
Cell signaling. How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings?
 Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
MCB 4211 Basic Immunology 2nd Exam; 10/26/17 Peoplesoft #:
 For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Information
 Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Innate Immunity II. Integration. Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2
 Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell
 Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. b-galactosidase staining of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
Supplemental Figure Legends
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Antibody array analysis of conditioned media from endothelial cells after treatment with exosomes (*p
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Antibody array analysis of conditioned media from endothelial cells after treatment with exosomes (*p
Thanks to: Signal Transduction. BCB 570 "Signal Transduction" 4/8/08. Drena Dobbs, ISU 1. An Aging Biologist s. One Biologist s Perspective
 BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway
 B Cell Development Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway There is only a 1:3 chance of the join between the V and J region being in frame Vk Jk Ck Non-productive Rearrangement Light chain has a
B Cell Development Ig light chain rearrangement: Rescue pathway There is only a 1:3 chance of the join between the V and J region being in frame Vk Jk Ck Non-productive Rearrangement Light chain has a
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supporting Information. Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered by Oxide Nanoparticles
 Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 1 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6. Supporting Information Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression
Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 1 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6. Supporting Information Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens
 1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
 LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
LECTURE: 07 Title: IMMUNE CELL SURFACE RECEPTORS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: The chemical nature of the cellular surface receptors. Define the location of the
Supplemental Data. NKp46 Identifies an NKT Cell Subset Susceptible to Leukemic Transformation in Mouse and Man
 Supplemental Data NKp46 Identifies an NKT Cell Subset Susceptible to Leukemic Transformation in Mouse and Man Jianhua Yu 1,2*, Takeki Mitsui 1,3*, Min Wei 1, Hsiaoyin Mao 1, Jonathan P Butchar 4, Mithun
Supplemental Data NKp46 Identifies an NKT Cell Subset Susceptible to Leukemic Transformation in Mouse and Man Jianhua Yu 1,2*, Takeki Mitsui 1,3*, Min Wei 1, Hsiaoyin Mao 1, Jonathan P Butchar 4, Mithun
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or
 Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding
 Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding Aleksei Krasnov, Nofima FHFs fiskehelsesamling 1.-2. september 2015 Smoltifiction and breeding suppress immunity in
Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding Aleksei Krasnov, Nofima FHFs fiskehelsesamling 1.-2. september 2015 Smoltifiction and breeding suppress immunity in
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic
 Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
A. Incorrect! It s not correct. Synergism of cytokines refers to two or more cytokines acting together.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses. Skin Biology Lecture Series
 Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles
 Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles The following two tables give the correlation coefficients for the FP profiles and the FN profiles of a single tagging solutions against
Supplementary Material Correlation matrices on FP and FN profiles The following two tables give the correlation coefficients for the FP profiles and the FN profiles of a single tagging solutions against
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
BCR-ABL - LSK BCR-ABL + LKS - (%)
 Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Marker Clone BCR-ABL + LSK (%) BCR-ABL + LKS - (%) BCR-ABL - LSK (%) P value vs. BCR-ABL + LKS - P value vs. BCR-ABL - LSK CD2 RM2-5 12.9 ± 3.6 36.7 ± 6.5 19.3 ± 2.4 0.01 0.10 CD5 53-7.3 13.9 ± 3.2 20.8
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Designer Affinity Reagents. Brian Kay
 Designer Affinity Reagents Brian Kay bkay@uic.edu Types of Affinity Reagents Src SH3 domain Lysozyme Src SH3 domain FN3 monobody Peptide Ligand Antibody Fragment Scaffold M13 Bacteriophage 900 nm x 10
Designer Affinity Reagents Brian Kay bkay@uic.edu Types of Affinity Reagents Src SH3 domain Lysozyme Src SH3 domain FN3 monobody Peptide Ligand Antibody Fragment Scaffold M13 Bacteriophage 900 nm x 10
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Intercellular indirect communication
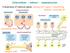 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D )
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D-17-00149) Juan C. López-Rodríguez 1, Guillermo Solís-Fernández 1, Rodrigo
1 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Effects of Ole e 1 allergen on human bronchial epithelial cells cultured at air-liquid interface (No. JIACI-D-17-00149) Juan C. López-Rodríguez 1, Guillermo Solís-Fernández 1, Rodrigo
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler
 Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric
 Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
